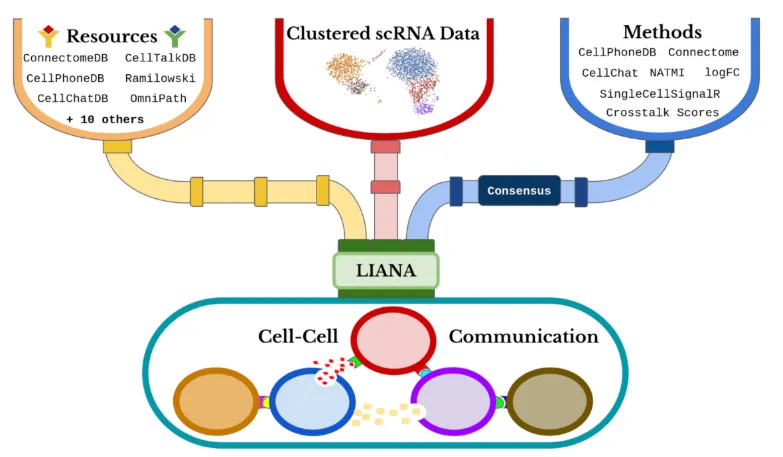
单细胞RNA测序的快速发展激发了人们对细胞间通讯机制的研究兴趣。近年来,已有多种用于研究细胞---细胞通讯(CCC)的工具和数据库被相继开发。然而,这些方法通常是固定绑定的------每种分析工具往往只能与特定的资源配套使用------尽管从原理上讲,任何计算方法都可以与任意配体--受体数据库组合使用。为了解决这一限制,研究团队开发了liana框架,旨在将分析方法与资源解耦,从而实现灵活组合与扩展。
分析流程
1.导入
rm(list=ls())
library(tidyverse)
library(magrittr)
library(SeuratData)
library(liana)2.数据来源和方法
# CCC资源
# Resource currently included in OmniPathR (and hence `liana`) include:
show_resources()
# [1] "Default" "Consensus" "Baccin2019" "CellCall"
# [5] "CellChatDB" "Cellinker" "CellPhoneDB" "CellTalkDB"
# [9] "connectomeDB2020" "EMBRACE" "Guide2Pharma" "HPMR"
# [13] "ICELLNET" "iTALK" "Kirouac2010" "LRdb"
# [17] "Ramilowski2015" "OmniPath" "MouseConsensus"
# CCC方法
# Resource currently included in OmniPathR (and hence `liana`) include:
show_methods()
# [1] "connectome" "logfc" "natmi" "sca"
# [5] "cellphonedb" "cytotalk" "call_squidpy" "call_cellchat"
# [9] "call_connectome" "call_sca" "call_italk" "call_natmi"3.准备数据
liana_path <- system.file(package = "liana")
testdata <-
readRDS(file.path(liana_path , "testdata", "input", "testdata.rds"))
testdata %>% dplyr::glimpse()
# ormal class 'Seurat' [package "SeuratObject"] with 13 slots
# ..@ assays :List of 1
# .. ..$ RNA:Formal class 'Assay' [package "Seurat"] with 8 slots
# ..@ meta.data :'data.frame': 90 obs. of 4 variables:
# .. ..$ orig.ident : Factor w/ 1 level "pbmc3k": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
# .. ..$ nCount_RNA : num [1:90] 4903 3914 4973 3281 2641 ...
# .. ..$ nFeature_RNA : int [1:90] 1352 1112 1445 1015 928 937 899 1713 960 888 ...
# .. ..$ seurat_annotations: Factor w/ 3 levels "B","CD8 T","NK": 1 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 ...
# ..@ active.assay: chr "RNA"
# ..@ active.ident: Factor w/ 3 levels "B","CD8 T","NK": 1 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 ...
# .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:90] "AAACATTGAGCTAC" "AAACTTGAAAAACG" "AAAGGCCTGTCTAG" "AAAGTTTGGGGTGA" ...
# ..@ graphs : list()
# ..@ neighbors : list()
# ..@ reductions : list()
# ..@ images : list()
# ..@ project.name: chr "SeuratProject"
# ..@ misc : list()
# ..@ version :Classes 'package_version', 'numeric_version' hidden list of 1
# .. ..$ : int [1:3] 3 2 3
# ..@ commands :List of 2
# .. ..$ FindVariableFeatures.RNA:Formal class 'SeuratCommand' [package "Seurat"] with 5 slots
# .. ..$ NormalizeData.RNA :Formal class 'SeuratCommand' [package "SeuratObject"] with 5 slots
# ..@ tools : list()4.运行liana
liana_test <- liana_wrap(testdata)
# Liana 会返回一个结果列表,其中的每个元素都对应一种分析方法。
liana_test %>% dplyr::glimpse()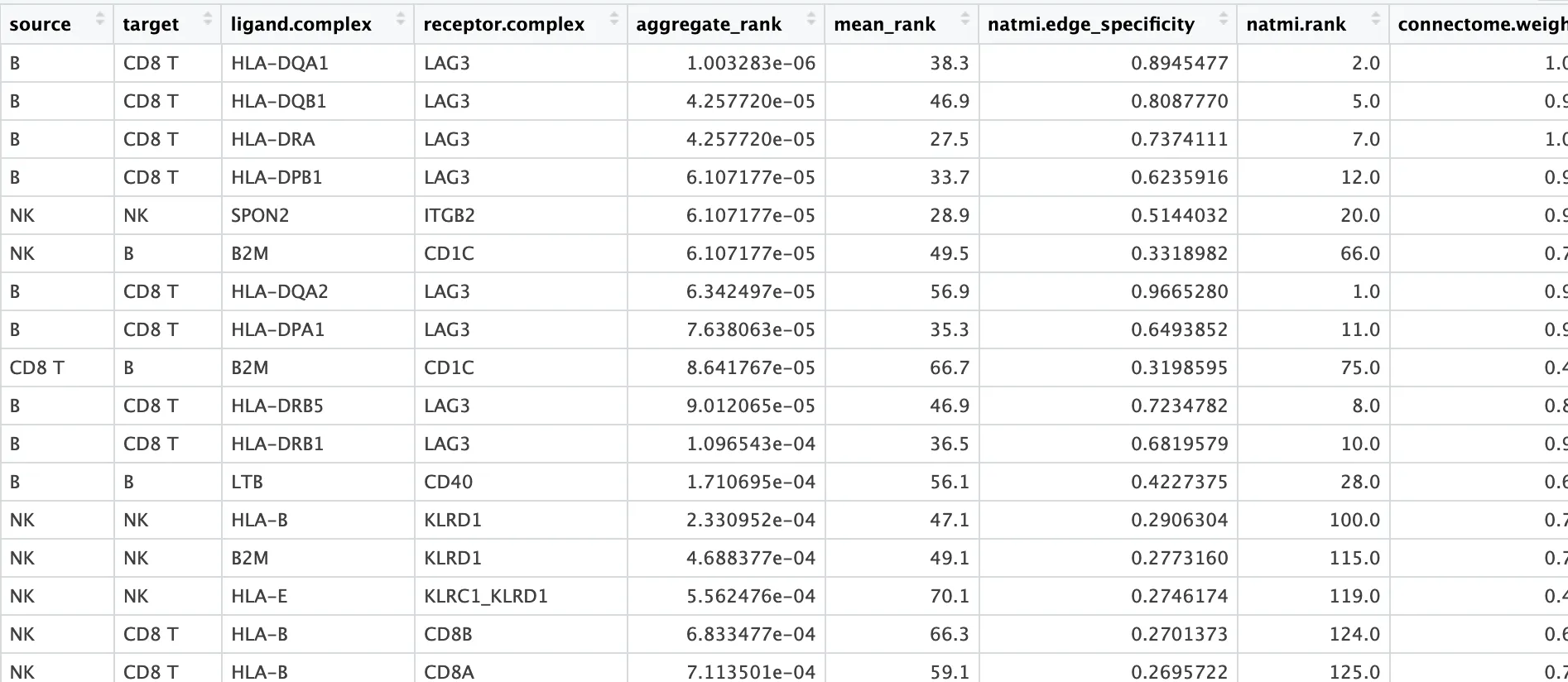
5.聚合并获取共识排序
# 将这些结果聚合为一个包含共识排序的tibble表
liana_test <- liana_test %>%
liana_aggregate()
dplyr::glimpse(liana_test)
# Rows: 735
# Columns: 16
# $ source <chr> "B", "B", "B", "B", "NK", "NK", "B", "B", "CD8 T", "B", "B", "B", ...
# $ target <chr> "CD8 T", "CD8 T", "CD8 T", "CD8 T", "NK", "B", "CD8 T", "CD8 T", "...
# $ ligand.complex <chr> "HLA-DQA1", "HLA-DQB1", "HLA-DRA", "HLA-DPB1", "SPON2", "B2M", "HL...
# $ receptor.complex <chr> "LAG3", "LAG3", "LAG3", "LAG3", "ITGB2", "CD1C", "LAG3", "LAG3", "...
# $ aggregate_rank <dbl> 1.003283e-06, 4.257720e-05, 4.257720e-05, 6.107177e-05, 6.107177e-...
# $ mean_rank <dbl> 38.3, 46.9, 27.5, 33.7, 28.9, 49.5, 56.9, 35.3, 66.7, 46.9, 36.5, ...
# $ natmi.edge_specificity <dbl> 0.8945477, 0.8087770, 0.7374111, 0.6235916, 0.5144032, 0.3318982, ...
# $ natmi.rank <dbl> 2, 5, 7, 12, 20, 66, 1, 11, 75, 8, 10, 28, 100, 115, 119, 124, 125...
# $ connectome.weight_sc <dbl> 1.0054344, 0.9026001, 1.0097786, 0.9181296, 0.9000847, 0.7056198, ...
# $ connectome.rank <dbl> 2, 7, 1, 5, 8, 19, 6, 4, 64, 9, 3, 21, 13, 14, 52, 24, 18, 20, 16,...
# $ logfc.logfc_comb <dbl> 2.4495727, 2.2335507, 2.7106868, 2.1918963, 2.2886801, 1.0668249, ...
# $ logfc.rank <dbl> 2, 4, 1, 6, 3, 52, 8, 5, 82, 9, 7, 61, 23, 25, 44, 57, 48, 51, 43,...
# $ sca.LRscore <dbl> 0.8693937, 0.8561886, 0.8985606, 0.8892920, 0.9046142, 0.9062742, ...
# $ sca.rank <dbl> 109, 142, 52, 69, 37, 34, 193, 80, 36, 132, 86, 94, 23, 15, 59, 50...
# $ cellphonedb.pvalue <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, ...
# $ cellphonedb.rank <dbl> 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, 76.5, ...6.简单绘图可视化
6.1. 气泡图
liana_test %>%
liana_dotplot(source_groups = c("B"),
target_groups = c("NK", "CD8 T", "B"),
ntop = 20)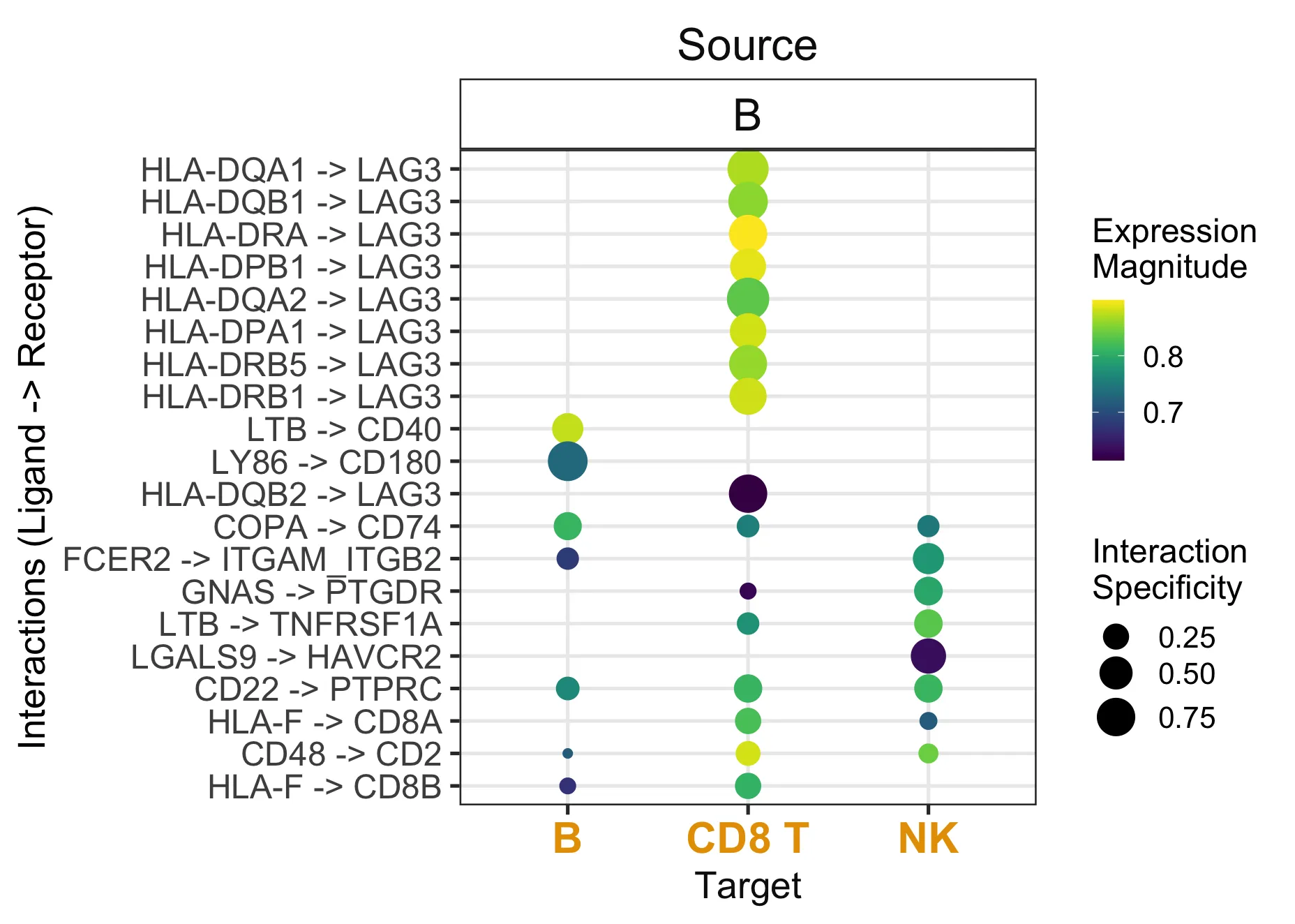
6.2. 频率热图
liana_trunc <- liana_test %>%
# 仅保留在不同方法之间结果一致的相互作用。
filter(aggregate_rank <= 0.01)
heat_freq(liana_trunc)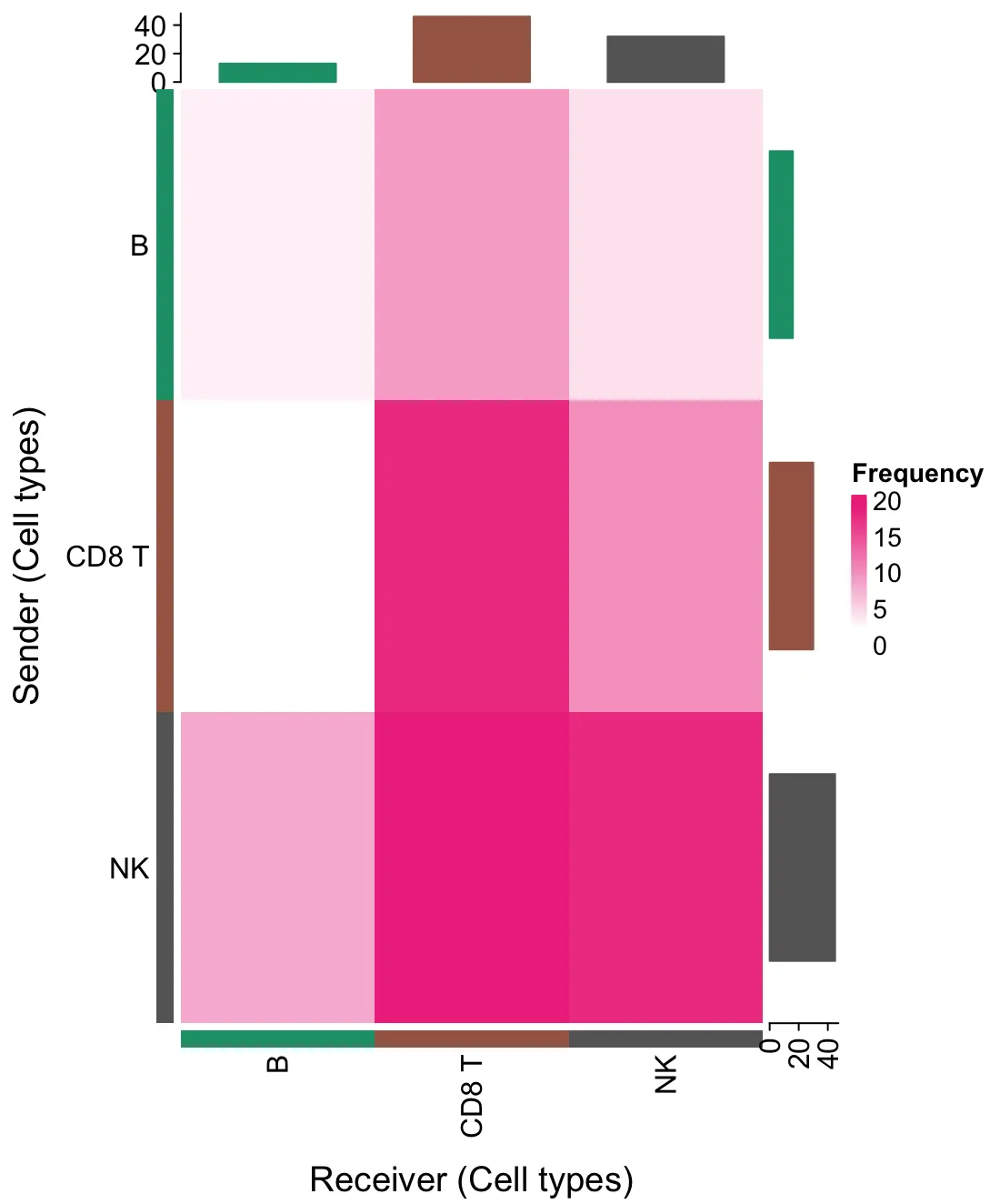
6.3. 频率弦图
# if(!require("circlize")){
# install.packages("circlize", quiet = TRUE,
# repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
p <- chord_freq(liana_trunc,
source_groups = c("CD8 T", "NK", "B"),
target_groups = c("CD8 T", "NK", "B"))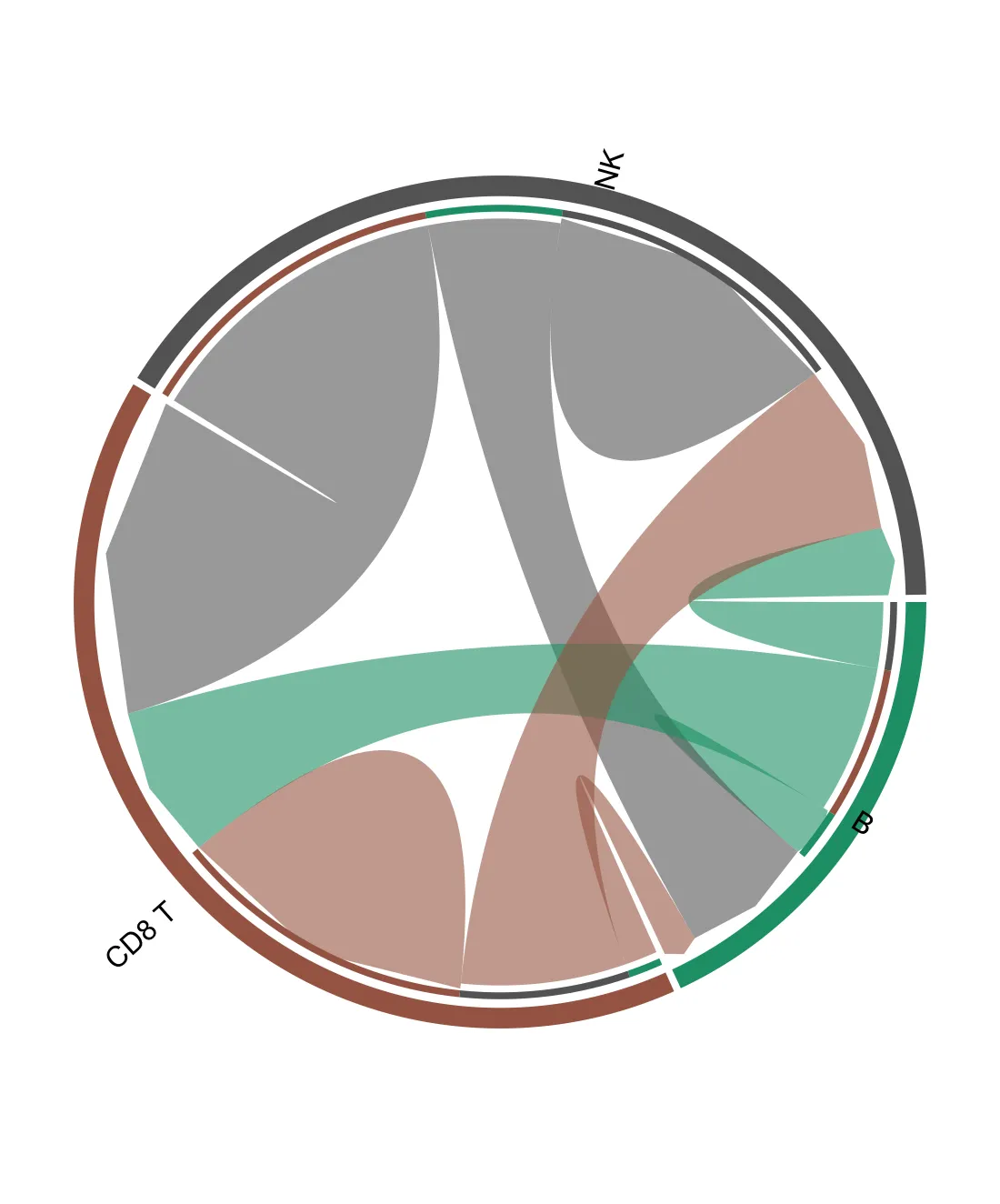
7.选择特定的分析方法
现在只运行 CellPhoneDB的基于置换的算法。同时,为了节省计算时间,会减少置换次数。需要注意的是,LIANA 中实现的 CPDB算法也可以并行化运行。
sce <- readRDS(file.path(liana_path , "testdata", "input", "testsce.rds"))
# RUN CPDB alone
cpdb_test <- liana_wrap(sce,
method = 'cellphonedb',
resource = c('CellPhoneDB'),
permutation.params = list(nperms=100,
parallelize=FALSE,
workers=4),
expr_prop=0.05)
# 识别感兴趣的相互作用
cpdb_int <- cpdb_test %>%
# 仅保留 p 值 ≤ 0.1 的相互作用
filter(pvalue <= 0.1) %>% # 反映了相互作用的"特异性"
# 根据"强度"(在此例中为 lr_mean)进行排序
rank_method(method_name = "cellphonedb",
mode = "magnitude") %>%
# 保留前 20 个相互作用(不区分细胞类型)
distinct_at(c("ligand.complex", "receptor.complex")) %>%
head(20)
# 结果可视化
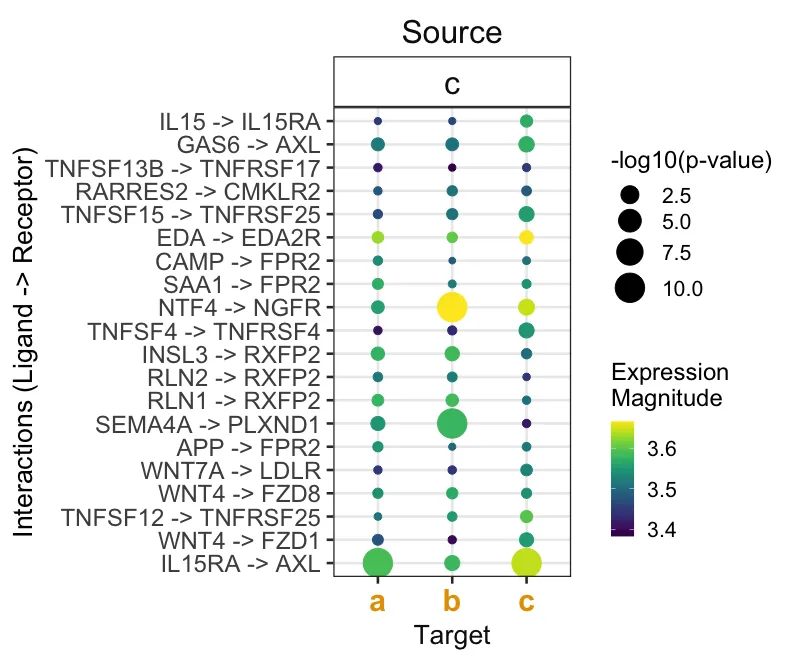
cpdb_test %>%
# 仅保留感兴趣的相互作用
inner_join(cpdb_int,
by = c("ligand.complex", "receptor.complex")) %>%
# 反转点的大小(p 值低 / 特异性高 = 点更大)
# + 对0值添加一个小数值以避免出现无穷大
mutate(pvalue = -log10(pvalue + 1e-10)) %>%
liana_dotplot(source_groups = c("c"),
target_groups = c("c", "a", "b"),
specificity = "pvalue",
magnitude = "lr.mean",
show_complex = TRUE,
size.label = "-log10(p-value)")