效果展示
实现步骤:
word类
头文件
cpp
#pragma once
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
class word
{
public:
word(string s); //构造函数,用来初始化单词(完整传入,不拆分)
string getWord()const; //获得当前对象存储的字符串,加const表示只读操作
bool operator<(const word& a)const; //作用是完成内部排序,相同字符串相邻方便后续统计个数
bool operator==(string s); //辅助统计(相同单词数量)和去重(避免重复打印)
private:
string s;
};源文件
cpp
#include "word.h"
// 构造函数:类名::构造函数名(构造函数名=类名)
word::word(string s) {
this->s = s;
}
//getWord是只读成员函数,返回字符串中存储的完整内容
string word::getWord()const {
return s;
}
//第一个const约束函数的对象a不被修改,第二个约数参数对象不被修改
bool word::operator<(const word& a)const {
return s < a.getWord();
}
bool word::operator==(string s) {
return this->s == s;
}WordSet类
头文件
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"word.h"
using namespace std;
#include<set> //用set:自动排序和去重(用来管理有哪些单词)
class WordSet
{
private:
set<word> set_1;
public:
bool wordset_add(string s);
void show();
};源文件
cpp
#include "WordSet.h"
bool WordSet::wordset_add(string s) {
set_1.insert(word(s)); //将s完整插入到set_1中
return 1;
}
void WordSet::show() {
for (set<word>::iterator it = set_1.begin(); it != set_1.end(); it++) { //或auto it
//cout << it->getWord() << " "; 整体打印出来
cout << (*it).getWord() << " ";
}
}WordMap类
头文件
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"word.h"
#include<map> //用map的键值对来存储单词出现次数
class WordMap
{
private:
map<word,int> map_1;
public:
bool wordmap_add(string s);
void show();
};源文件
cpp
#include "WordMap.h"
bool WordMap::wordmap_add(string s) {
map<word, int>::iterator it = map_1.find(s); //整体
//核对的内容并非单个词,而是一整行字符串
if (it == map_1.end()) { //迭代到最后说明没找到
pair<word, int> p(word(s), 1); //没找到就'包装'成次数为1的word类对象添入map_1里
map_1.insert(p);
} //后面会进行空格及符号处理使其统计单个词的出现次数
else {
it->second++; //若迭代器没到最后,说明找到了相同数据,直接让表示次数的数据++
}
return 1;
}
void WordMap::show() {
for (auto it = map_1.begin(); it != map_1.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first.getWord() << ":出现" << it->second << "次" << endl;
}
}功能调用
头文件
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#include"word.h"
#include"WordMap.h"
#include"WordSet.h"
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>
#include<iterator>
void dataProcessing(); //处理空格和符号
void showData();源文件
cpp
#include"myFunc.h"
//建立集合和映射的实例对象
WordSet set_111;
WordMap map_111;
void showData() {
cout << endl;
cout << "单词集合为:" << endl;
set_111.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "单词集合及出现次数为:" << endl;
map_111.show();
cout << endl;
}
void dataProcessing() {
//打开文件,读取文本
int pos = 0;
string s = " ";
string delimet = ",.?";
ifstream in1("file.txt");
char c = 0;
//提前检查下一个元素是否为结束符(后面是否还有元素)
while (in1.peek() != EOF) { //后面有元素就读取当前元素并输出
in1.read(&c, 1); //最后一个元素会在peek遇到EOF之前read
cout << c; //整个while就是在展示in1写入的所有字符,方便与下面去空格和字符的结果对比
}
in1.close();
ifstream in("file.txt");
while (!in.eof()) {
getline(in, s);
if (s == " ") {
continue;
}
pos = 0;
//npos表不存在的位置(没找到目标内容)
//发现的第一个符号的位置不是不存在的(找到了符号)
while ((pos = s.find_first_of(delimet, pos) != string::npos)){
s.replace(pos, 1, " "); //替换该符号为空字符(相当于删除)
}
//把处理后的行转为字符串流(可逐个读取单词)
string word;
istringstream istream(s);
while (istream >> word) { //从流里逐个读取单词直到结束
if (word.empty()) { //跳过空单词
continue;
}
set_111.wordset_add(word); //自动去重
map_111.wordmap_add(word); //加到映射里统计次数
}
}
in.close();
}文件内容:

编译结果:
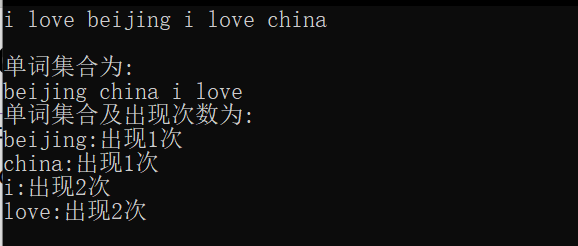
小插曲
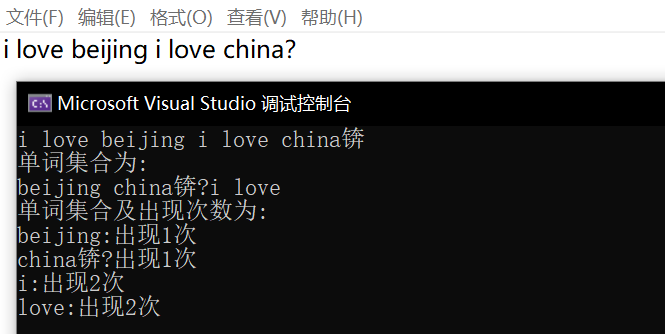
虽然文件处理部分对符号进行了处理,但加入符号后产生了乱码。
下期见~