HTTP请求方法全面解析:从基础到面试实战
一、HTTP请求方法深度剖析
1. HTTP请求方法概述
HTTP请求方法是客户端告诉服务器期望执行什么操作的指令。它们在RESTful架构设计中扮演着关键角色,决定了API的行为模式和资源操作方式。
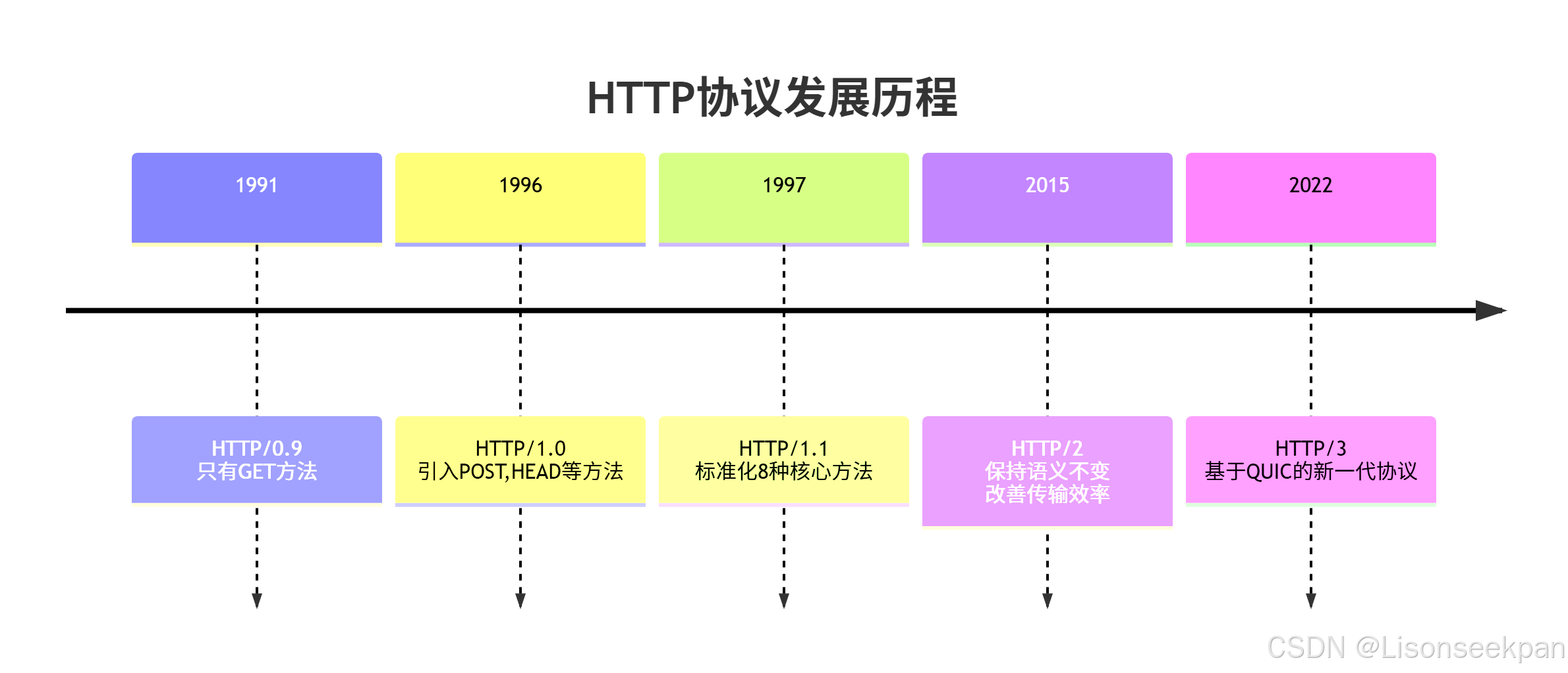
HTTP协议的演进
2. 八大核心HTTP方法详述
① GET - 获取资源
核心特征:
- ✅ 安全的(Safe):不修改服务器状态
- 🔄 幂等的(Idempotent):重复请求效果一致
- 💾 可缓存的(Cacheable)
请求结构:
http
GET /api/products/123 HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Accept: application/json
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0
Cache-Control: no-cacheJava实现示例:
java
public class GetRequestExample {
// 使用HttpURLConnection实现GET请求
public static String httpGet(String urlStr) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
conn.setReadTimeout(10000);
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()))) {
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(line);
}
}
return response.toString();
}
} else {
throw new IOException("HTTP error: " + responseCode);
}
}
// 使用OkHttp实现GET请求
public static String okHttpGet(String urlStr) throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.readTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(urlStr)
.addHeader("Accept", "application/json")
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
{
return response.body().string();
} else {
throw new IOException("HTTP error: " + response.code());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String response = httpGet("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1");
System.out.println("GET Response: " + response);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}② POST - 创建资源
核心特征:
- ❌ 不安全(Non-Safe):会修改服务器状态
- ❌ 非幂等(Non-Idempotent):重复请求可能有不同结果
- ⚠️ 有条件缓存
完整商业级POST实现:
java
public class PostRequestExample {
// 通用的JSON POST请求
public static String sendJsonPost(String urlStr, String jsonPayload) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
conn.setRequestProperty("Accept", "application/json");
conn.setDoOutput(true);
// 写入请求体
try (OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] input = jsonPayload.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
// 读取响应
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode >= 200 && responseCode < 300) {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
String responseLine;
while ((responseLine = br.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(responseLine.trim());
}
return response.toString();
}
} else {
// 处理错误情况
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getErrorStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
{
StringBuilder errorResponse = new StringBuilder();
String errorLine;
while ((errorLine = br.readLine()) != null) {
errorResponse.append(errorLine.trim());
}
throw new IOException("HTTP Error: " + responseCode + ", Message: " + errorResponse);
}
}
}
// 带认证头的POST请求
public static String sendAuthenticatedPost(String urlStr, String payload, String token) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
conn.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
conn.setDoOutput(true);
// 写入请求体
try (OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] input = payload.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
// 读取响应...
return readResponse(conn);
}
// 电商下单接口实战示例
public static String placeOrder(String userId, List<CartItem> items, PaymentInfo paymentInfo) throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
OrderRequest orderRequest = new OrderRequest(userId, items, paymentInfo);
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(orderRequest);
return sendJsonPost("https://api.ecommerce.com/v1/orders", jsonPayload);
}
}
// 订单请求DTO
class OrderRequest {
private String userId;
private List<CartItem> items;
private PaymentInfo paymentInfo;
private String idempotencyKey; // 防止重复下单
public OrderRequest(String userId, List<CartItem> items, PaymentInfo paymentInfo) {
this.userId = userId;
this.items = items;
this.paymentInfo = paymentInfo;
this.idempotencyKey = UUID.randomUUID().toString());
// getters and setters
}③ PUT vs PATCH - 更新操作深度辨析
关键技术差异对比:
| 方面 | PUT | PATCH |
|---|---|---|
| 更新范围 | 整个资源 | 部分字段 |
| 幂等性 | 必须保证 | 推荐保证 |
| 带宽使用 | 较高(传送完整资源) | 较低(只传变更字段) |
| 错误恢复 | 重新发送整个资源 | 只需发送变更字段 |
| 冲突解决 | 乐观锁控制 | 细粒度锁定 |
Java实现对比:
java
public class UpdateOperations {
// PUT - 完全替换用户信息
public static String putUpdateUser(Long userId, User user) throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
URL url = new URL("https://api.example.com/users/" + userId);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("PUT");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
conn.setRequestProperty("If-Match", user.getEtag()); // 乐观锁控制
return sendJsonRequest(conn, jsonPayload);
}
// PATCH - 部分更新用户邮箱
public static String patchUpdateEmail(Long userId, String newEmail) throws IOException throws IOException {
// JSON Patch格式
String jsonPatch = "[{ \"op\": \"replace\", \"path\": \"/email\", \"value\": \"" + newEmail + "\" }]";
URL url = new URL("https://api.example.com/users/" + userId);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("PATCH");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json-patch+json");
return sendJsonRequest(conn, jsonPatch);
}
// 企业级PUT实现
public static String enterprisePut(String urlStr, Object entity, Map<String, String> headers) throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(entity);
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("PUT");
// 设置自定义头
if (headers != null) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : headers.entrySet()) {
{
conn.setRequestProperty(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
conn.setDoOutput(true);
writePayload(conn, jsonPayload);
return handleResponse(conn);
}
// 幂等性保障机制
public static String idempotentPut(String urlStr, Object entity, String idempotencyKey) throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(entity);
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("PUT");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
conn.setRequestProperty("Idempotency-Key", idempotencyKey);
return sendJsonRequest(conn, jsonPayload);
}
}④ DELETE - 资源删除
java
public class DeleteExamples {
// 硬删除 - 直接从数据库中删除
public static String hardDelete(String urlStr) throws IOException throws IOException {
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("DELETE");
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NO_CONTENT) {
return "Successfully deleted";
} else {
throw new IOException("Delete failed: " + responseCode);
}
}
// 软删除 - 标记删除状态
public static String softDelete(String urlStr) throws IOException {
String deletePatch = "[{ \"op\": \"replace\", \"path\": \"/deleted\", \"value\": true }]";
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("PATCH");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json-patch+json");
return sendJsonRequest(conn, deletePatch);
}
// 批量删除
public static String batchDelete(List<Long> ids) throws IOException {
BatchDeleteRequest batchRequest = new BatchDeleteRequest(ids);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(batchRequest);
return sendJsonPost("https://api.example.com/bulk-delete", jsonPayload);
}
}三、HTTP方法特性全方位对比
核心技术指标矩阵
| HTTP方法 | 安全性 | 幂等性 | 缓存性 | 请求体 | 成功状态码 | 典型用例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | ✅ 安全 | ✅ 幂等 | ✅ 可缓存 | ❌ 无 | 200, 304 | 商品浏览、搜索 |
| POST | ❌ 不安全 | ❌ 非幂等 | ⚠️ 有条件 | ✅ 有 | 201, 200 | 用户注册、订单提交 |
| PUT | ❌ 不安全 | ✅ 幂等 | ❌ 不可缓存 | ✅ 有 | 200, 204 | 个人资料全量更新 |
| DELETE | ❌ 不安全 | ✅ 幂等 | ❌ 不可缓存 | ❌ 无 | 204, 200 | 删除订单、注销账号 |
| PATCH | ❌ 不安全 | ⚠️ 应设计为幂等 | ❌ 不可缓存 | ✅ 有 | 200 | 修改邮箱、局部更新 |
真实场景应用指南
java
public class HttpMethodSelectorGuide {
/**
* CRUD操作与方法对应关系
*/
public enum Operation {
CREATE(POST),
READ(GET),
UPDATE_FULL(PUT),
UPDATE_PARTIAL(PATCH),
DELETE(DELETE);
private final String method;
Operation(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
}
/**
* 根据操作意图选择最合适的HTTP方法
*/
public static String selectBestMethod(ActionContext context) {
switch (context.getIntent()) {
case RETRIEVE_INFO:
return "GET";
case CREATE_NEW_RESOURCE:
return "POST";
case REPLACE_COMPLETELY:
return "PUT";
case MODIFY_PARTIALLY:
return "PATCH";
case REMOVE_RESOURCE:
return "DELETE";
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown intent: " + context.getIntent());
}
}
}四、Java高级HTTP客户端实战
1. Spring RestTemplate综合应用
java
@Service
public class ApiClientService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ApiClientService(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
this.restTemplate = builder
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.additionalInterceptors(new LoggingInterceptor()))
.build();
}
// RESTful API完整CRUD操作
public class UserApiClient {
// CREATE - 注册用户
public User register(UserRegistrationDto registrationDto) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headersheaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<UserRegistrationDto> request = new HttpEntity<>(registrationDto, headers);
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(
BASE_URL + "/users", request, User.class);
if (response.getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.CREATED) {
return response.getBody();
} else {
throw new ApiException("Registration failed");
}
}
// READ - 获取用户详情
public User getUserById(Long id) {
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(
BASE_URL + "/users/" + id, User.class);
return response.getBody();
}
// UPDATE FULL - 修改整个用户对象
public User updateUserFull(Long id, User user) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setIfMatch(user.getEtag()); // 乐观锁
HttpEntity<User> request = new HttpEntity<>(user, headers);
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(
BASE_URL + "/users/" + id, HttpMethod.PUT, request, User.class);
return response.getBody();
}
// UPDATE PARTIAL - 只修改密码
public User changePassword(Long id, PasswordChangeDto passwordChange) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.valueOf("application/json-patch+json")));
// JSON Patch格式
JsonPatch patch = JsonPatch.fromJson(objectMapper.readTree(
"["[{ \"op\": \"replace\", \"path\": \"/password\", \"value\": \"" + passwordChange.getNewPassword() + "\" }]"));
HttpEntity<JsonPatch> request = new HttpEntity<>(patch, headers);
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(
BASE_URL + "/users/" + id, HttpMethod.PATCH, request, User.class);
return response.getBody();
}
// DELETE - 注销账户
public void deleteAccount(Long id) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setBasicAuth(getCurrentUsername(), getCurrentPassword()));
restTemplate.delete(BASE_URL + "/users/" + id);
}
}
}2. Apache HttpClient企业级配置
java
@Component
public class EnterpriseHttpClient {
private final CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
public EnterpriseHttpClient() {
// 连接池配置
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager =
new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
connectionManager.setMaxTotal(200); // 总连接数
connectionManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(50); // 每路由连接数
// 请求配置
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(15000)
.setSocketTimeout(60000)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(15000)
.build();
this.httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(connectionManager)
.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig)
.addInterceptorLast(new RetryInterceptor())
.addInterceptorLast(new MetricsInterceptor())
.build();
}
// 带有重试机制的GET请求
public String robustHttpGet(String urlStr, int maxRetries) throws IOException {
int retryCount = 0;
while (retryCount <= maxRetries) {
try {
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(urlStr);
request.setHeader("Accept", "application/json");
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request)) {
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
();
if (statusCode >= 200 && statusCode < 400) {
return EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
} else if (shouldRetry(statusCode)) {
retryCount++;
Thread.sleep(exponentialBackoff(retryCount)); // 指数退避
} else {
{
throw new IOException("HTTP Error: " + statusCode);
}
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException | SocketTimeoutException e) {
retryCount++;
if (retryCount > maxRetries) {
throw e;
}
}
}
// 断路器模式的POST请求
public String circuitBreakerPost(String urlStr, String payload) throws IOException {
CircuitBreaker breaker = circuitBreakerRegistry.circuitBreaker("api-service"));
return breaker.executeSupplier(() -> {
try {
return executePost(urlStr, payload);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
});
}
}
}五、HTTP面试高频真题深度解析
🎯 Part 1:基础概念题
题目1:GET和POST的本质区别是什么?
参考答案:
java
/**
* GET vs POST核心区别深度解析
*/
public class GetVsPostComparison {
/*
* 根本区别:语义层面
* GET: 获取资源(Safe & Idempotent)
* POST: 提交数据处理(Non-Safe & Non-Idempotent)
*/
// 1. 数据传输方式
class TransmissionDifference {
// GET - 参数放在URL中
String getUrl = "https://api.com/search?keyword=mobile&limit=10");
// POST - 参数放在请求体中
String postUrl = "https://api.com/users";
String postBody = "{ \"name\": \"John\", \"age\": 30 }";
}
// 2. 安全性差异
class SafetyConsiderations {
/*
* GET请求:
* - 参数暴露在URL中
* - 可能被浏览器历史记录
* - 可能被服务器日志记录
* => 不适合传输敏感信息
*/
/*
* POST请求:
* - 参数在请求体中
* - 相对安全(但仍需HTTPS加密)
*/
}
// 3. 幂等性影响
class IdempotenceImpact {
/*
* 前端需要考虑的重点:
* - GET请求可以直接刷新页面
* - POST请求刷新时会提示重新提交
*/
}
}加分回答:
java
// 从HTTP协议规范角度深入解释
public class ProtocolLevelDifferences {
/*
* RFC 7231明确规定了各自的语义:
* GET: 安全的、幂等的,不应产生副作用
* POST: 不安全的、非幂等的,允许产生副作用
*/
}题目2:PUT和POST都可以创建资源,它们有什么区别?
标准答案结构:
java
public class PutPostCreationDiff {
// 主要区别体现在客户端对资源标识的控制权上
/**
* 创建资源时的关键决策因素:
* - 谁来决定资源的ID?
* - 是否需要保证幂等性?
*/
enum CreationScenario {
// 当客户端不知道也不关心资源ID时 - 使用POST
CLIENT_CANT_DETERMINE_ID("POST"),
// 当客户端知道要创建的资源的完整标识时 - 使用PUT
RESOURCE_ID_DETERMINED_BY_CLIENT("PUT");
}
// 实例演示
public void demonstrateUsage() {
// POST创建 - ID由服务器生成
createWithPost("/articles", articleDto); // 返回 /articles/123
// PUT创建 - ID由客户端指定
createWithPut("/articles/123", articleDto); // 创建ID为123的文章
}
}🎯 Part 2:进阶应用题
题目3:如何设计一个防重复提交的订单接口?
解决方案:
java
@Component
public class IdempotentOrderService {
private final RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 幂等性保障三重机制:
*/
// 机制1:客户端生成的幂等键
public ResponseEntity<Order> createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request,
@RequestHeader("Idempotency-Key") String idempotencyKey) {
// 第一步:检查幂等键
if (redisTemplate.hasKey(idempotencyKey)) {
// 已经处理过该请求
Order cachedOrder = (Order) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(idempotencyKey)) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(cachedOrder);
}
// 第二步:执行业务逻辑
Order order = processOrderCreation(request);
// 第三步:存储幂等键与结果的映射
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(idempotencyKey, order, Duration.ofHours(24)));
return ResponseEntity.created(URI.create("/orders/" + order.getId())).body(order);
}
// 机制2:数据库唯一约束
@Transactional
public synchronized public synchronized Order createOrderAtomic(OrderRequest request) {
// 依赖数据库的唯一约束来防止重复
}
}
}🎯 Part 3:场景设计题
题目4:如何选择合适的HTTP方法来更新用户的邮件地址?
决策流程图:
java
public class MethodSelectionStrategy {
public String selectUpdateMethod(UpdateContext context) {
if (context.hasFullResource())) {
return "PUT"; // 完全替换
} else if (context.supportPartialUpdates())) {
{
return "PATCH"; // 推荐使用,避免误覆盖其他字段
} else {
{
return "POST"; // 通用更新端点
}
}
}
}六、HTTP最佳实践与反模式
✅ 最佳实践清单
java
public class HttpBestPractices {
// 1. 正确的状态码使用
class StatusCodes {
/*
* 200 OK - 一般成功响应
* 201 Created - 创建资源成功
* 204 No Content - 删除成功
* 400 Bad Request - 客户端错误
* 401 Unauthorized - 身份认证失败
* 403 Forbidden - 权限不足
* 404 Not Found - 资源不存在
* 409 Conflict - 资源冲突
* 422 Unprocessable Entity - 语义错误
*/
}
// 2. 正确的幂等性设计
public class IdempotenceDesignPatterns {
// 模式A:唯一交易号
public Order createOrder(String tradeNo, OrderRequest request) {
// 优先检查tradeNo是否已存在
}
}
}
// 3. 适当的缓存策略
public class CacheStrategies {
// GET请求适当设置缓存头
public ResponseEntity<?> cacheOptimization() {
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.cacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(30, TimeUnit.DAYS)))
.eTag(generateStrongEtag())
.lastModified(lastModifiedTime))
))
.body(result);
}
}
}❌ 常见反模式警告
java
public class AntiPatternWarnings {
// 反模式1:使用GET执行有副作用的操作
@Deprecated
public void wrongApproach() {
// ❌ 错误的做法 - 用GET删除资源
doGet("/delete-user?id=123");
// ✅ 正确的做法 - 用DELETE方法
doDelete("/users/123");
}
}七、性能优化与企业级考虑
高性能HTTP客户端配置
yaml
# application.yml - Spring Boot HTTP客户端配置
spring:
web:
client:
timeout:
connect: 10000
read: 30000
http:
client:
pool:
max-total: 200
default-max-per-route: 20
resilience4j:
circuitbreaker:
instances:
apiclient:
failure-rate-threshold: 50
wait-duration-in-open-state: 60s总结要点
通过对HTTP请求方法的深入学习,我们应该掌握:
- 核心方法论:深刻理解各方法的语义特性和适用范围
- 实用工具箱:熟练运用各类HTTP客户端完成不同的业务需求
- 面试准备:能够从容应对各种深度的HTTP相关问题
- 工程思维:在设计API时合理选择HTTP方法,充分考虑性能和用户体验
这份全面的HTTP请求方法指南不仅涵盖了理论基础,还包含了大量的实战代码和企业级最佳实践,帮助你在日常开发和求职面试中都游刃有余。