📅 背景:迈向"智能体互联网" (IoA)
时间 :2025 年 4 月 9 日
事件 :Google DeepMind 与 Cloud 团队联合发布 A2A (Agent-to-Agent) 协议 。
愿景 :打破 AI 孤岛,建立一个去中心化、标准化的 "Internet of Agents"。
在 ChatGPT 和 Claude 普及的时代,我们习惯了 人与 AI (User-to-Agent) 的对话。但在 Google 描绘的未来中,真正的爆发在于 AI 与 AI (Agent-to-Agent) 的协作。当你的"日程助理 Agent"能够自动找到"天气 Agent"查询数据,并与"订场 Agent"沟通预定篮球场时,生产力将发生质变。
本文将带你通过 Python + FastAPI ,亲手实现 Google A2A 协议的核心机制,构建两个协作的智能体:WeatherAgent(服务方) 和 BasketBallAgent(消费方)。
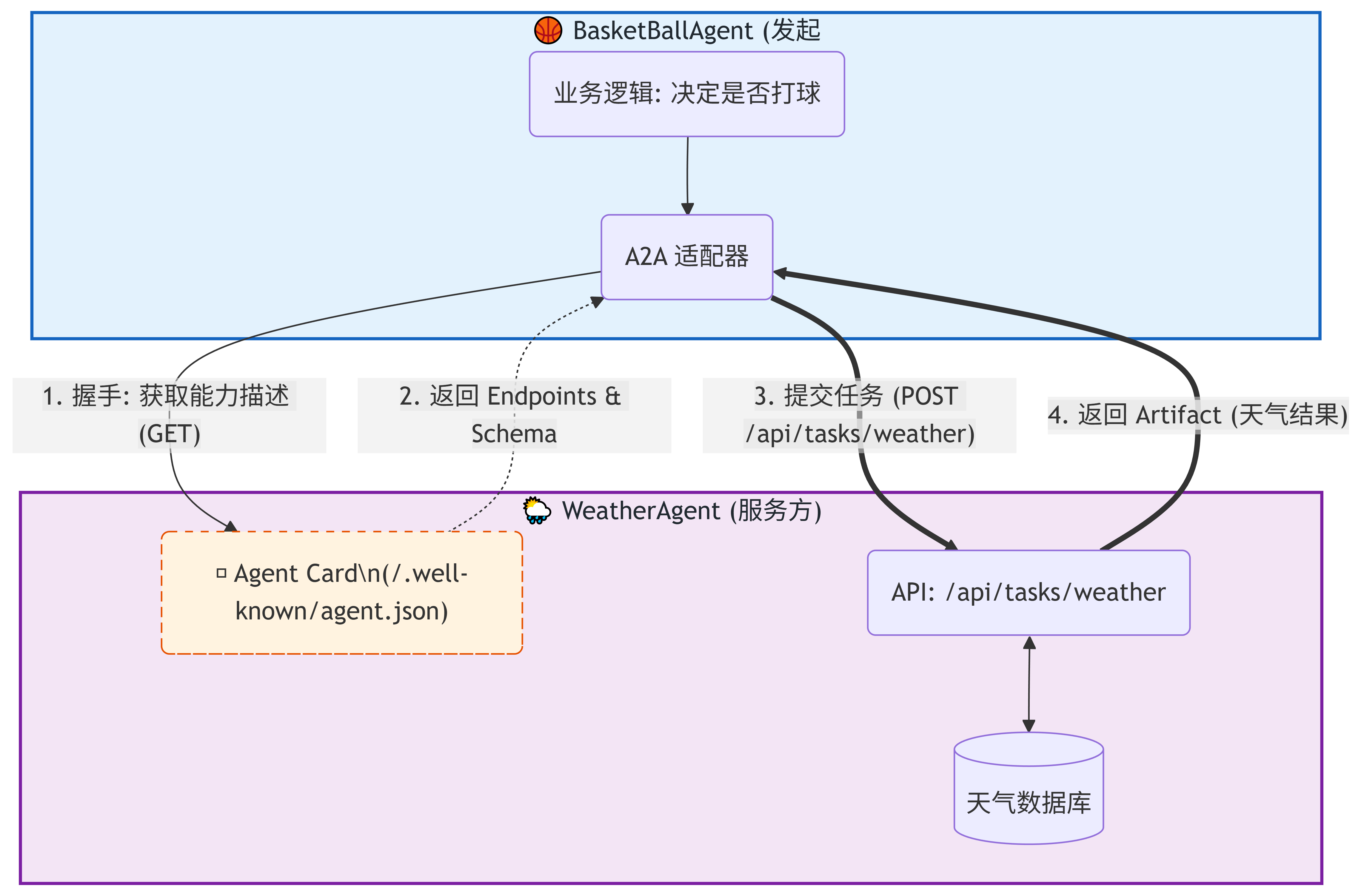
🏗️ A2A 协议架构图解
A2A 协议的核心哲学是 "自描述 (Self-Describing)" 和 "动态发现 (Dynamic Discovery)"。
不同于传统的微服务(硬编码 API 路径),A2A 要求每个 Agent 在固定位置(/.well-known/agent.json)暴露一张 Agent Card(智能体名片)。调用方先看名片,再决定如何交互。
💻 代码实战
我们将实现两个独立的文件:服务端提供天气能力,客户端负责调用决策。
1. 服务端:WeatherAgent.py
这个 Agent 的核心是提供标准化的 /.well-known/agent.json,告诉外界:我是谁,我有什能力,怎么调用我。
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from datetime import date
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
# ----------------------------------------------------
# 1. Agent Card 声明 (A2A 协议的核心)
# ----------------------------------------------------
# 这相当于 AI 界的 "OpenAPI/Swagger",但更面向机器理解
WEATHER_AGENT_CARD = {
"name": "WeatherAgent",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "提供指定日期的天气数据查询",
# 【关键】动态端点:调用者不需要死记硬背 API 路径,而是从这里读取
"endpoints": {
"task_submit": "/api/tasks/weather",
"sse_subscribe": "/api/tasks/updates"
},
# 【关键】输入契约:告诉调用者必须传什么参数
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"date": {"type": "string", "format": "date"},
"location": {"type": "string", "enum": ["北京"]}
},
"required": ["date"]
},
"authentication": {"methods": ["API_Key"]}
}
# 任务请求模型
class WeatherTaskRequest(BaseModel):
task_id: str
params: dict
# 模拟天气数据存储
weather_db = {
"2025-11-08": {"temperature": "25℃", "condition": "雷阵雨"},
"2025-11-09": {"temperature": "18℃", "condition": "小雨转晴"},
"2025-11-10": {"temperature": "22℃", "condition": "多云转晴"}
}
# 暴露协议元数据
@app.get("/.well-known/agent.json")
async def get_agent_card():
return WEATHER_AGENT_CARD
# 具体的业务执行接口
@app.post("/api/tasks/weather")
async def handle_weather_task(request: WeatherTaskRequest):
"""处理天气查询任务"""
target_date = request.params.get("date")
# 简单的参数验证
if not target_date or target_date not in weather_db:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="无效日期参数或无数据")
return {
"task_id": request.task_id,
"status": "completed",
"artifact": {
"date": target_date,
"weather": weather_db[target_date]
}
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("🚀 WeatherAgent 正在启动 (Port: 8000)...")
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)2. 客户端:BasketBallAgent.py
这个 Agent 展示了 A2A 的消费模式。注意看 check_weather 方法,它没有硬编码任务提交的 URL,而是先去查"名片"。
python
import requests
import uuid
class BasketBallAgent:
def __init__(self):
# 在实际 A2A 网络中,这里可能是服务发现中心的地址
self.weather_agent_url = "http://localhost:8000"
self.api_key = "SECRET_KEY" # 模拟鉴权
def _create_task(self, target_date: str) -> dict:
"""创建符合 A2A 标准的任务对象"""
return {
"task_id": str(uuid.uuid4()), # 唯一的任务追踪 ID
"params": {
"date": target_date,
"location": "北京"
}
}
def check_weather(self, target_date: str) -> dict:
"""
【核心逻辑】通过 A2A 协议动态发现并调用
"""
try:
# 1. 发现阶段 (Discovery)
# 哪怕服务端把接口从 /api/tasks/weather 改成了 /v2/query,
# 只要 agent.json 更新了,客户端代码无需修改即可自适应。
print(f"[*] 正在握手: 获取 {self.weather_agent_url} 的 Agent Card...")
agent_card = requests.get(
f"{self.weather_agent_url}/.well-known/agent.json"
).json()
submit_url = agent_card['endpoints']['task_submit']
print(f"[*] 发现任务接口: {submit_url}")
# 2. 执行阶段 (Execution)
task = self._create_task(target_date)
response = requests.post(
f"{self.weather_agent_url}{submit_url}",
json=task,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}"}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()["artifact"]
else:
raise Exception(f"天气查询失败: {response.text}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[!] A2A 通信错误: {e}")
raise
def schedule_meeting(self, date: str):
"""综合决策逻辑"""
print(f"\n--- 开始决策: {date} 是否去打球? ---")
try:
result = self.check_weather(date)
condition = result["weather"]["condition"]
temp = result["weather"]["temperature"]
print(f"[*] 天气反馈: {temp}, {condition}")
# 简单的业务规则
if "雨" not in condition and "雪" not in condition:
return {"decision": "✅ 去打球", "reason": f"天气不错 ({condition})"}
else:
return {"decision": "❌ 取消", "reason": f"天气恶劣 ({condition})"}
except Exception as e:
return {"status": "error", "detail": str(e)}
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
meeting_agent = BasketBallAgent()
# 测试 Case 1: 2025-11-08 (雷阵雨)
res1 = meeting_agent.schedule_meeting("2025-11-08")
print(f"最终结果: {res1}\n")
# 测试 Case 2: 2025-11-10 (多云转晴)
res2 = meeting_agent.schedule_meeting("2025-11-10")
print(f"最终结果: {res2}")🔍 原理深度解析
为什么 Google A2A 要这么设计?相比直接写死 API 调用,这种模式带来了三大变革:
1. 解耦与进化 (Decoupling)
在上面的代码中,BasketBallAgent 并不假设 WeatherAgent 的 API 路径是 /api/tasks/weather。它是通过读取 endpoints 字典动态获取的。
这意味着,服务方可以随意重构后端路由,甚至升级版本,只要更新 agent.json,所有的调用方(Clients)都不需要重新部署代码。
2. 语义标准化 (Semantic Standardization)
input_schema 使用了标准的 JSON Schema。
在未来,BasketBallAgent 可能不仅仅是一个 Python 脚本,而是一个 LLM(大模型) 。LLM 可以阅读 agent.json 中的 description 和 schema,自动理解:"哦,调用这个工具需要传一个 date 格式的字符串",从而实现 Zero-Shot Tool Use(零样本工具调用)。
3. 互操作性 (Interoperability)
A2A 协议旨在成为 AI 界的 HTTP。无论你的 Agent 是基于 LangChain、AutoGPT 还是 CrewAI 开发的,只要大家都遵守 /.well-known/agent.json 的规范,就能无缝连接,形成真正的"智能体互联网"。
🏃♂️ 运行步骤
-
安装依赖:
bashpip install fastapi uvicorn requests pydantic -
启动服务端 :
打开终端窗口 A,运行:
bashpython WeatherAgent.py输出:Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8000
-
运行客户端 :
打开终端窗口 B,运行:
bashpython BasketBallAgent.py -
观察输出 :

🔮 总结
Google A2A 协议的出现,标志着 AI 应用开发从 Prompt Engineering(提示词工程) 转向 Agent Choreography(智能体编排)。
通过本文的实战,我们构建了一个最基础的 A2A 单元。虽然代码简单,但它展示了未来 AI 社会的基本协作单元------每个 Agent 都是一个独立的 Web 服务,通过通用的协议相互连接,共同完成人类无法独立完成的复杂任务。
觉得有帮助?欢迎点赞、收藏、关注,获取更多 AI 前沿实战干货! 🌟