本文介绍了一个经过修改的ARP协议实现文件uip_arp.c,主要功能包括:
- 初始化ARP表(uip_arp_init)
- 定时维护ARP表,清理超时条目(uip_arp_timer)
- 处理接收到的ARP请求和应答(uip_arp_arpin)
- 处理IP数据包发送时的ARP查询(uip_arp_out)
- 从IP数据包中更新ARP表(uip_arp_ipin)
该实现包含ARP表管理、请求/应答处理、超时机制等功能,支持以太网和IPv4协议,使用静态ARP表存储IP-MAC映射关系。通过定时器定期清理超时条目,并实现了完整的ARP请求/应答流程,包括本地IP地址匹配、MAC地址更新等核心功能。
"uip_arp.c"我做了点修改,原因是源文件太难懂了。
uip_arp.c文件如下:
#include "uip_arp.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "tapdev.h"
struct arp_entry arp_table[UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE];
//ARP表保存的是远程设备的IP地址,MAC地址和建立的时间
static u8_t ARPTimeCounter; //声明字节静态变量ARPTimeCounter
//函数功能:将ARP表中的IP地址设置为0
void uip_arp_init(void)
{
u8_t i;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
memset( arp_table[i].ipaddr, 0, 4 );
//将首地址为arp_table[i].ipaddr的缓存的前4个字节设置为0
}
}
//函数功能:
//如果ARP表中的某个"IP地址和MAC地址"的建立时间在20分钟内,没有更新,则将这个IP地址设置为0
//注意:uip_arp_timer()每10秒执行一次
void uip_arp_timer(void)
{
u8_t i;
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
u8_t deltValue;
++ARPTimeCounter;//10秒计数器加1
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];//获取首地址
if( ARPTimeCounter >= tabptr->time )
deltValue=ARPTimeCounter - tabptr->time;//"IP地址和MAC地址"建立多长时间
else
{
deltValue=256 - tabptr->time;
deltValue=deltValue + ARPTimeCounter;
}
//发现ARP表中有一个"IP地址和MAC地址"建立时间,长期没有更新,因此将这个IP地址设置为0
if( (tabptr->ipaddr[0] | tabptr->ipaddr[1]) != 0 && deltValue >= UIP_ARP_MAXAGE)
{//远程设备IP地址不为0,且建立时间超过120*10=1200秒=20分钟
memset(tabptr->ipaddr, 0, 4);
//将首地址为tabptr->ipaddr的缓存的前4个字节设置为0
}
}
}
//函数功能:更新ARP表
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
//ipaddr是接收到的"发送方的4字节ip地址",ethaddr是接收到的"发送方的6字节mac地址"
static void uip_arp_update(u16_t *ipaddr, struct uip_eth_addr *ethaddr)
{
u8_t i;
u8_t tmpage;
register struct arp_entry *tabptr;
//register请求编译器将局部变量tabptr存储在寄存器中,以提高访问速度。
/* Walk through the ARP mapping table and try to find an entry to
update. If none is found, the IP -> MAC address mapping is
inserted in the ARP table. */
u8_t find;
u8_t deltValue;
//在ARP表里发现有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",则更新MAC地址后,返回
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
/* Only check those entries that are actually in use. */
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] != 0 && tabptr->ipaddr[1] != 0)
{
//检查传入数据包的源IP地址是否与ARP表项中的IP地址匹配。
/* Check if the source IP address of the incoming packet matches the IP address in this ARP table entry. */
if(ipaddr[0] == tabptr->ipaddr[0] && ipaddr[1] == tabptr->ipaddr[1])
{//在ARP表里发现这个IP地址
/* An old entry found, update this and return. */
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6);//更新MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
return;
}
}
}
//在ARP表里没有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",则查找"IP地址为0"的存储位置
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] == 0 && tabptr->ipaddr[1] == 0)
{//在arp_table[]中,发现IP地址为0,则将在这个位置保存新的"IP地址和MAC地址"
memcpy(tabptr->ipaddr, ipaddr, 4); //保存新的IP地址
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6); //保存新的MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
break;
}
}
//在ARP表里没有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",也没有找到"IP地址为0"的存储位置
//则查找"IP地址和MAC地址"建立最久的条目,用来保存新的"IP地址和MAC地址"
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE)//没有发现IP地址为0
{
tmpage = 0;find = 0;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{//查找建立时间最长的"IP地址和MAC地址"
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(ARPTimeCounter >= tabptr->time)
deltValue=ARPTimeCounter - tabptr->time;//"IP地址和MAC地址"建立多长时间
else
{
deltValue=256 - tabptr->time;
deltValue=deltValue + ARPTimeCounter;
}
//如果ARPTimeCounter<tabptr->time,deltValue < 0;
if( deltValue > tmpage)
{
tmpage = deltValue;
find = i;//记录,然后再循环查找
}
}
i = find;//记录修改位置
tabptr = &arp_table[find];
memcpy(tabptr->ipaddr, ipaddr, 4); //保存新的IP地址
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6); //保存新的MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
}
}
/*
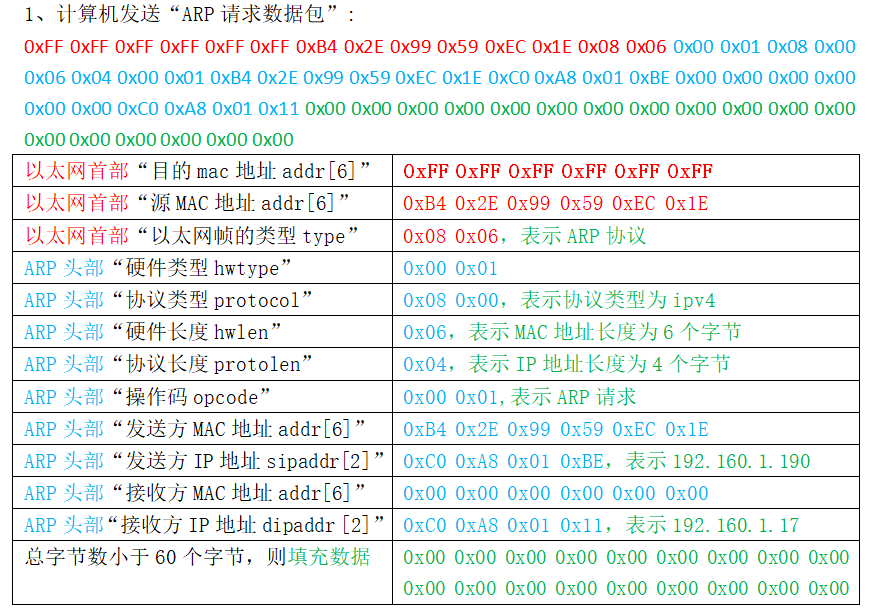
计算机发送ARP请求,60个字节
以太网头部数据:0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0x08 0x06
ARP头部数据:0x00 0x01 0x08 0x00 0x06 0x04 0x00 0x01 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0x11
填充数据:0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
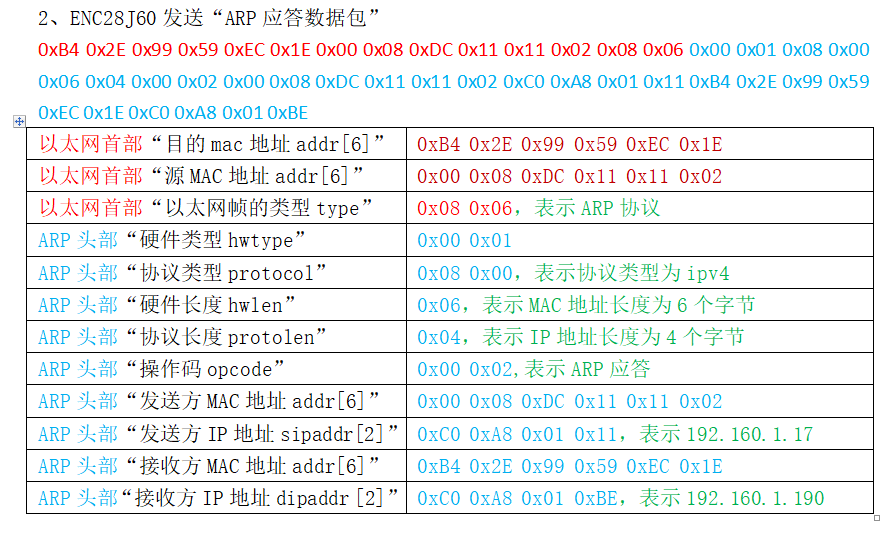
ENC28J60发送ARP应答,42个字节
以太网头部数据:0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02 0x08 0x06
ARP头部数据:0x00 0x01 0x08 0x00 0x06 0x04 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0x11 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE
*/
//函数功能:处理接收到的ARP数据包:如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包;如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP应答,则更新ARP表;
//分析uip_buf[]中的"ARP数据包"
//1.由于外部设备发送了"ARP请求数据包",如果pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包;
//目的是让对方知道自己的MAC地址;
//2.在发送TCP数据时,由于uip_arp_out()执行后发现ARP表中没有"接收方的IP地址",因此,它生成了"ARP请求数据包";
//对方收到后,就会发送ARP应答包;如果pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP应答,则更新ARP表中的
//"IP地址,MAC地址和建立时间";
void uip_arp_arpin(void)
{
struct arp_hdr *pARPHeader;
pARPHeader=(struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
if( uip_len < sizeof(struct arp_hdr) )
{
uip_len = 0;
return;
}
if( pARPHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP) )//uip_buf[]中不是ARP数据包,则退出
return;
//pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包
//pARPHeader->opcodee的操作码是ARP应答,则更新ARP表
uip_len = 0;
//pARPHeader->opcode是ARP消息的类型,ARP请求是1,ARP回复是2,RARP请求是3,RARP回复是4
switch(pARPHeader->opcode)
{
case HTONS(ARP_REQUEST)://ENC28J60收到"ARP请求"
//ARP请求。如果它询问我们的地址,我们会发送回复。
/* ARP request. If it asked for our address, we send out a reply. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(pARPHeader->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr))
{//接收到的目的IP地址和ENC28J60的IP地址相同,表示这个数据是我的
/* First, we register the one who made the request in our ARP
table, since it is likely that we will do more communication
with this host in the future. */
uip_arp_update(pARPHeader->sipaddr, &pARPHeader->shwaddr);
//sipaddr是接收到的"发送方的4字节ip地址",shwaddr是接收到的"发送方的6字节mac地址"
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
/* The reply opcode is 2. */
pARPHeader->opcode = HTONS(2);
//设置操作码:ARP回复是2
memcpy(pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"接收方MAC地址"
memcpy(pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"发送方MAC地址"为ENC28J60的MAC地址
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址"为ENC28J60的MAC地址
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"目的MAC地址"
pARPHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
//设置太网帧的类型为0x0806,表示后面跟着的是ARP数据包;
pARPHeader->dipaddr[0] = pARPHeader->sipaddr[0];pARPHeader->dipaddr[1] = pARPHeader->sipaddr[1];
//设置"接收方ip地址"
pARPHeader->sipaddr[0] = uip_hostaddr[0];pARPHeader->sipaddr[1] = uip_hostaddr[1];
//设置"发送方ip地址"
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送ARP应答数据包
}
break;
case HTONS(ARP_REPLY)://ENC28J60收到"ARP回复"
//ARP回复。如果ARP表是为我们准备的,我们会插入或更新该表。
/* ARP reply. We insert or update the ARP table if it was meant for us. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(pARPHeader->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr))
{//接收到的目的IP地址和ENC28J60的IP地址相同,表示这个数据是我的
uip_arp_update(pARPHeader->sipaddr, &pARPHeader->shwaddr);
//pARPHeader->sipaddr是发送方的4字节ip地址
//pARPHeader->shwaddr为"发送方的6字节mac地址"
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
}
break;
}
return;
}
//函数功能:
//1、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",则在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找是否有这个IP地址;
//1)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中没有这个IP地址,发送ARP请求;
//2)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中有这个IP地址,设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,发送TCP数据;
//2、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",则设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址",设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,然后发送TCP数据
//分析uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"
//1.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",且ARP表里也没有这个IP地址,则准备ARP请求数据包;
//2.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",且ARP表里也有这个IP地址,
//则使用"ARP表中的对应的MAC地址"作为目的地址,修改以太网头部中的"目的地址",然后设置以太网头部中的"源地址"为本地的MAC地址;
//最后设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据;
//3.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",
//则设置以太网头部中的"目的地址"为"广播MAC地址",然后设置以太网头部中的"源地址"为本地的MAC地址,
//最后设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据;
void uip_arp_out(void)
{
static u16_t TmpIpAddress[2];//保存的是"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"或是"ENC28J60的IP地址"
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
unsigned char ch1,ch2,ch3;
u8_t i;
struct ethip_hdr *pEthernetHeader;
struct arp_hdr *pARPHeader;
pEthernetHeader=(struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
if( pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP) )//uip_buf[]中不是IPV4数据包,则退出
return;
ch1=0;
if(pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0]==0xFFFF) ch1=1;
if(pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1]==0xFFFF) ch1=(unsigned char)(ch1<<1);
if( ch1!=2 )//uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址"
{
ch2=0;
if( (pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) == (uip_hostaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) ) ch2=1;
if( (pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) == (uip_hostaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) )
ch2=(unsigned char)(ch2<<1);
//uip_hostaddr为"ENC28J60的IP地址"
//uip_netmask为"ENC28J60的子网掩码"
//IP地址前3个字节相同,只是最后一个字节不同,通常它们位于"同一网络(子网)"内
if(ch2!=0x02)//不位于"同一网络(子网)"内
{
TmpIpAddress[0] = uip_draddr[0];//uip_draddr为"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"
TmpIpAddress[1] = uip_draddr[1];//uip_draddr为"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"
//将"网关地址"拷贝到TmpIpAddress[]中
}
else//位于"同一网络(子网)"内
{
TmpIpAddress[0] = pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0];//pEthernetHeader->destipaddr为"接收方IP地址"
TmpIpAddress[1] = pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1];//pEthernetHeader->destipaddr为"接收方IP地址"
}
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找TmpIpAddress的IP地址
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
ch3=0;
if(TmpIpAddress[0] == tabptr->ipaddr[0]) ch3=1;
if(TmpIpAddress[1] == tabptr->ipaddr[1]) ch3=(unsigned char)(ch3<<1);
if(ch3==2)//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中,找到了TmpIpAddress的IP地址
{
memcpy(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, tabptr->ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"目的MAC地址",准备发送TCP数据
break;
}
}
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE)//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中,没有找到TmpIpAddress的IP地址
{
pARPHeader=(struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
memset(pARPHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, 0xff, 6);
//设置"目的mac地址"为"0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF"
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址"为"ENC28J60的MAC地址"
pARPHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
//设置"以太网帧的类型"为"ARP请求包类型"
pARPHeader->hwtype = HTONS(ARP_HWTYPE_ETH);//设置"硬件类型",若是以太网,值是0x0001
pARPHeader->protocol = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);//设置"协议类型",若是ipv4,值是0x0800
pARPHeader->hwlen = 6;//设置"硬件长度",定义物理地址(MAC地址)的长度,若是mac地址就是6
pARPHeader->protolen = 4;//设置"协议长度",定义逻辑地址(IP地址)的长度,若是ip地址就是4
pARPHeader->opcode = HTONS(ARP_REQUEST);
//设置"操作码":为ARP请求,是1
memcpy(pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"发送方的6字节mac地址"为"ENC28J60的MAC地址"
uip_ipaddr_copy(pARPHeader->sipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
//设置"发送方的4字节ip地址"为"ENC28J60的IP地址"
memset(pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, 0x00, 6);
//设置"接收方的6字节mac地址"为"0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00"
uip_ipaddr_copy(pARPHeader->dipaddr, TmpIpAddress);
//设置"接收方的4字节ip地址"
uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN];
//UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=40,UIP_LLH_LEN=14
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送ARP请求
return;
}
}
else//uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址"
{
//设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址":"0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF",准备发送TCP数据
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[0]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[1]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[2]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[3]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[4]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[5]=0xFF;
}
memcpy(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址",准备发送TCP数据
//uip_ethaddr.addr[]保存的是ENC28J60的MAC地址
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);
//设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据
uip_len += sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送TCP数据
}
//函数功能:若IP数据包中有"新的IP地址和MAC地址",则更新ARP表
void uip_arp_ipin(void)
{
struct ethip_hdr *pEthernetHeader;
pEthernetHeader=(struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
// uip_len -= sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
if( (pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) != (uip_hostaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]))
{
return;
}
if((pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) != (uip_hostaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]))
{
return;
}
uip_arp_update(pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr, &(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.src));
return;
}
uip_arp.h文件
#include "uip.h"
//uip_eth_hdr型结构:以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
struct uip_eth_hdr {
struct uip_eth_addr dest; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放目的MAC地址
struct uip_eth_addr src; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放源MAC地址
u16_t type;
//太网帧的类型
//0x0800表示后面跟着的是IPV4数据包;
//0x0806表示后面跟着的是ARP数据包;
//0x86dd表示后面跟着的是IPV6数据包;
};
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP 0x0806 //ARP请求包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP 0x0800 //IPV4数据包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP6 0x86dd //IPv6包类型
//ARP结构
struct arp_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;
//以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
u16_t hwtype; //硬件类型,若是以太网,值是0x0001
u16_t protocol; //协议类型,若是ipv4,值是0x0800
u8_t hwlen; //硬件长度,定义物理地址(MAC地址)的长度,若是mac地址就是6
u8_t protolen; //协议长度,定义逻辑地址(IP地址)的长度,若是ip地址就是4
u16_t opcode; //操作码:定义ARP分组是请求还是应答。ARP请求是1,ARP回复是2,RARP请求是3,RARP回复是4
struct uip_eth_addr shwaddr; //发送方的6字节mac地址
u16_t sipaddr[2]; //发送方的4字节ip地址
struct uip_eth_addr dhwaddr; //接收方的6字节mac地址
u16_t dipaddr[2]; //接收方的4字节ip地址
};
//以太网结构
struct ethip_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;
//以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
//IP头部(IP header),占20给字节
u8_t vhl;//版本与首部长度
u8_t tos;//服务类型
u8_t len[2];//IP报文总长度2个字节
u8_t ipid[2];//标识,2字节,用于分片重组
u8_t ipoffset[2];//标志与片偏移,2字节,包含DF/MF标志和偏移量
u8_t ttl;//生存时间
u8_t proto;//协议:1字节,如6表示TCP,17表示UDP
u16_t ipchksum;//检验和
u16_t srcipaddr[2];//发送方IP地址,4字节
u16_t destipaddr[2];//接收方IP地址,4字节
};
#define ARP_REQUEST 1 //ARP请求
#define ARP_REPLY 2 //ARP回复
#define ARP_HWTYPE_ETH 1 //设置"硬件类型",若是以太网,值是0x0001
struct arp_entry
{
u16_t ipaddr[2]; //远程设备的IP地址
struct uip_eth_addr ethaddr; //远程设备的MAC地址
u8_t time; //"IP地址和MAC地址"建立的时间
};
extern struct arp_entry arp_table[UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE];
void uip_arp_init(void);
void uip_arp_timer(void);
void uip_arp_arpin(void);
void uip_arp_out(void);
void uip_arp_ipin(void);
//使用eaddr,修改本地的MAC地址
#define uip_setethaddr(eaddr) do {uip_ethaddr.addr[0] = eaddr.addr[0]; \
uip_ethaddr.addr[1] = eaddr.addr[1];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[2] = eaddr.addr[2];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[3] = eaddr.addr[3];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[4] = eaddr.addr[4];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[5] = eaddr.addr[5];} while(0)附上uip中的uip_arp..c原文件:
#include "uip_arp.h"
#include "string.h"
struct arp_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;//uip_eth_hdr型结构:目的地址占6个字节,源地址占6个字节,报文类型占1个字节
u16_t hwtype;
u16_t protocol;
u8_t hwlen;
u8_t protolen;
u16_t opcode;
struct uip_eth_addr shwaddr;
u16_t sipaddr[2];
struct uip_eth_addr dhwaddr;
u16_t dipaddr[2];
};
struct ethip_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;//uip_eth_hdr型结构:目的地址占6个字节,源地址占6个字节,报文类型占1个字节
/* IP header. */
u8_t vhl,
tos,
len[2],
ipid[2],
ipoffset[2],
ttl,
proto;
u16_t ipchksum;
u16_t srcipaddr[2],
destipaddr[2];
};
#define ARP_REQUEST 1
#define ARP_REPLY 2
#define ARP_HWTYPE_ETH 1
//uip_eth_addr结构成员为字节型数组addr[6]
static const struct uip_eth_addr broadcast_ethaddr ={
{ 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff}
};
static const u16_t broadcast_ipaddr[2] = {0xffff,0xffff};
struct arp_entry
{
u16_t ipaddr[2];
struct uip_eth_addr ethaddr; //uip_eth_addr结构成员为字节型数组addr[6]
u8_t time;
};
static struct arp_entry arp_table[UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE];
//宏定义UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE=8
static u16_t ipaddr[2];
static u8_t i, c;
static u8_t arptime; //声明字节静态变量arptime
static u8_t tmpage; //声明字节静态变量tmpage
#define BUF ((struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0])
#define IPBUF ((struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0])
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* Initialize the ARP module.
*
*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
uip_arp_init(void)
{
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
memset(arp_table[i].ipaddr, 0, 4);
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* Periodic ARP processing function.
*
* This function performs periodic timer processing in the ARP module
* and should be called at regular intervals. The recommended interval
* is 10 seconds between the calls.
*
*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void uip_arp_timer(void)
{
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
++arptime;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{//宏定义UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE=8
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if((tabptr->ipaddr[0] | tabptr->ipaddr[1]) != 0 &&
arptime - tabptr->time >= UIP_ARP_MAXAGE) {
memset(tabptr->ipaddr, 0, 4);
}
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static void
uip_arp_update(u16_t *ipaddr, struct uip_eth_addr *ethaddr)
{
register struct arp_entry *tabptr;
/* Walk through the ARP mapping table and try to find an entry to
update. If none is found, the IP -> MAC address mapping is
inserted in the ARP table. */
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i) {
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
/* Only check those entries that are actually in use. */
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] != 0 &&
tabptr->ipaddr[1] != 0) {
/* Check if the source IP address of the incoming packet matches
the IP address in this ARP table entry. */
if(ipaddr[0] == tabptr->ipaddr[0] &&
ipaddr[1] == tabptr->ipaddr[1]) {
/* An old entry found, update this and return. */
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6);
tabptr->time = arptime;
return;
}
}
}
/* If we get here, no existing ARP table entry was found, so we
create one. */
/* First, we try to find an unused entry in the ARP table. */
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i) {
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] == 0 &&
tabptr->ipaddr[1] == 0) {
break;
}
}
/* If no unused entry is found, we try to find the oldest entry and
throw it away. */
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE) {
tmpage = 0;
c = 0;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i) {
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(arptime - tabptr->time > tmpage) {
tmpage = arptime - tabptr->time;
c = i;
}
}
i = c;
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
}
/* Now, i is the ARP table entry which we will fill with the new
information. */
memcpy(tabptr->ipaddr, ipaddr, 4);
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6);
tabptr->time = arptime;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* ARP processing for incoming IP packets
*
* This function should be called by the device driver when an IP
* packet has been received. The function will check if the address is
* in the ARP cache, and if so the ARP cache entry will be
* refreshed. If no ARP cache entry was found, a new one is created.
*
* This function expects an IP packet with a prepended Ethernet header
* in the uip_buf[] buffer, and the length of the packet in the global
* variable uip_len.
*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if 0
void
uip_arp_ipin(void)
{
uip_len -= sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
/* Only insert/update an entry if the source IP address of the
incoming IP packet comes from a host on the local network. */
if((IPBUF->srcipaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) !=
(uip_hostaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0])) {
return;
}
if((IPBUF->srcipaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) !=
(uip_hostaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1])) {
return;
}
uip_arp_update(IPBUF->srcipaddr, &(IPBUF->ethhdr.src));
return;
}
#endif /* 0 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* ARP processing for incoming ARP packets.
*
* This function should be called by the device driver when an ARP
* packet has been received. The function will act differently
* depending on the ARP packet type: if it is a reply for a request
* that we previously sent out, the ARP cache will be filled in with
* the values from the ARP reply. If the incoming ARP packet is an ARP
* request for our IP address, an ARP reply packet is created and put
* into the uip_buf[] buffer.
*
* When the function returns, the value of the global variable uip_len
* indicates whether the device driver should send out a packet or
* not. If uip_len is zero, no packet should be sent. If uip_len is
* non-zero, it contains the length of the outbound packet that is
* present in the uip_buf[] buffer.
*
* This function expects an ARP packet with a prepended Ethernet
* header in the uip_buf[] buffer, and the length of the packet in the
* global variable uip_len.
*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void uip_arp_arpin(void)
{
if( uip_len < sizeof(struct arp_hdr) )
{
uip_len = 0;
return;
}
uip_len = 0;
switch(BUF->opcode) {
case HTONS(ARP_REQUEST):
/* ARP request. If it asked for our address, we send out a
reply. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr)) {
/* First, we register the one who made the request in our ARP
table, since it is likely that we will do more communication
with this host in the future. */
uip_arp_update(BUF->sipaddr, &BUF->shwaddr);
/* The reply opcode is 2. */
BUF->opcode = HTONS(2);
memcpy(BUF->dhwaddr.addr, BUF->shwaddr.addr, 6);
memcpy(BUF->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
memcpy(BUF->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
memcpy(BUF->ethhdr.dest.addr, BUF->dhwaddr.addr, 6);
BUF->dipaddr[0] = BUF->sipaddr[0];
BUF->dipaddr[1] = BUF->sipaddr[1];
BUF->sipaddr[0] = uip_hostaddr[0];
BUF->sipaddr[1] = uip_hostaddr[1];
BUF->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
}
break;
case HTONS(ARP_REPLY):
/* ARP reply. We insert or update the ARP table if it was meant
for us. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr)) {
uip_arp_update(BUF->sipaddr, &BUF->shwaddr);
}
break;
}
return;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* Prepend Ethernet header to an outbound IP packet and see if we need
* to send out an ARP request.
*
* This function should be called before sending out an IP packet. The
* function checks the destination IP address of the IP packet to see
* what Ethernet MAC address that should be used as a destination MAC
* address on the Ethernet.
*
* If the destination IP address is in the local network (determined
* by logical ANDing of netmask and our IP address), the function
* checks the ARP cache to see if an entry for the destination IP
* address is found. If so, an Ethernet header is prepended and the
* function returns. If no ARP cache entry is found for the
* destination IP address, the packet in the uip_buf[] is replaced by
* an ARP request packet for the IP address. The IP packet is dropped
* and it is assumed that they higher level protocols (e.g., TCP)
* eventually will retransmit the dropped packet.
*
* If the destination IP address is not on the local network, the IP
* address of the default router is used instead.
*
* When the function returns, a packet is present in the uip_buf[]
* buffer, and the length of the packet is in the global variable
* uip_len.
*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void uip_arp_out(void)
{
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
/* Find the destination IP address in the ARP table and construct
the Ethernet header. If the destination IP addres isn't on the
local network, we use the default router's IP address instead.
If not ARP table entry is found, we overwrite the original IP
packet with an ARP request for the IP address. */
/* First check if destination is a local broadcast. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(IPBUF->destipaddr, broadcast_ipaddr))
{
memcpy(IPBUF->ethhdr.dest.addr, broadcast_ethaddr.addr, 6);
}
else
{
/* Check if the destination address is on the local network. */
if(!uip_ipaddr_maskcmp(IPBUF->destipaddr, uip_hostaddr, uip_netmask))
{
/* Destination address was not on the local network, so we need to
use the default router's IP address instead of the destination
address when determining the MAC address. */
uip_ipaddr_copy(ipaddr, uip_draddr);
}
else
{
/* Else, we use the destination IP address. */
uip_ipaddr_copy(ipaddr, IPBUF->destipaddr);
}
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(ipaddr, tabptr->ipaddr))
{
break;
}
}
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE)
{
/* The destination address was not in our ARP table, so we
overwrite the IP packet with an ARP request. */
memset(BUF->ethhdr.dest.addr, 0xff, 6);
memset(BUF->dhwaddr.addr, 0x00, 6);
memcpy(BUF->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
memcpy(BUF->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->dipaddr, ipaddr);
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->sipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
BUF->opcode = HTONS(ARP_REQUEST); /* ARP request. */
BUF->hwtype = HTONS(ARP_HWTYPE_ETH);
BUF->protocol = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);
BUF->hwlen = 6;
BUF->protolen = 4;
BUF->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN];
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
return;
}
/* Build an ethernet header. */
memcpy(IPBUF->ethhdr.dest.addr, tabptr->ethaddr.addr, 6);
}
memcpy(IPBUF->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
IPBUF->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);
uip_len += sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/** @} */
/** @} */附上uip中的uip_arp..h原文件:
#include "uip.h"
extern struct uip_eth_addr uip_ethaddr;
//uip_eth_hdr型结构:目的地址占6个字节,源地址占6个字节,报文类型占1个字节
struct uip_eth_hdr {
struct uip_eth_addr dest; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放目的MAC地址
struct uip_eth_addr src; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放源MAC地址
u16_t type;
//报文类型
//0x0800表示后面跟着的是IPV4数据包;
//0x0806表示后面跟着的是ARP数据包;
//0x86dd表示后面跟着的是IPV6数据包;
};
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP 0x0806 //ARP请求包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP 0x0800 //IPV4数据包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP6 0x86dd //IPv6包类型
void uip_arp_init(void);
#define uip_arp_ipin()
void uip_arp_arpin(void);
void uip_arp_out(void);
void uip_arp_timer(void);
#define uip_setethaddr(eaddr) do {uip_ethaddr.addr[0] = eaddr.addr[0]; \
uip_ethaddr.addr[1] = eaddr.addr[1];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[2] = eaddr.addr[2];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[3] = eaddr.addr[3];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[4] = eaddr.addr[4];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[5] = eaddr.addr[5];} while(0)看看它的源文件写的,我们发现"生成数据和发送数据"分家了。
测试结果:
为了更加清晰了解ARP数据包,附上测试结果。