1.链表的分类
链表的分类
① 单向或者双向
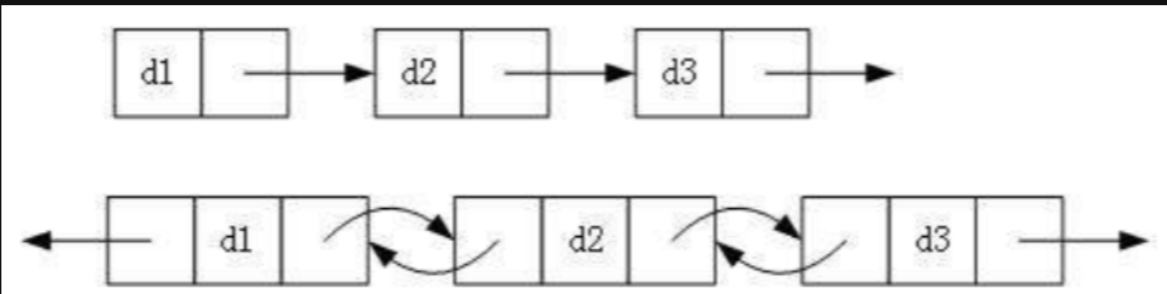
② 带头或者不带头

③ 循环或者非循环
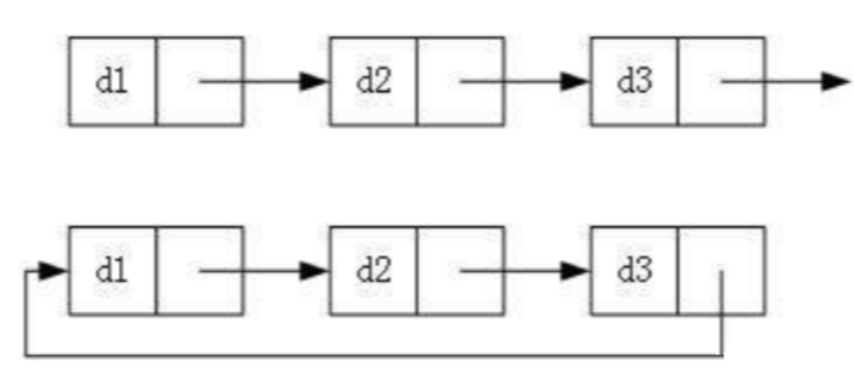
常用的链表:
根据上面的分类我们可以细分出8种不同类型的链表,这么多链表我们一个个讲解这并没有意义。我们实际中最常用的链表是 "无头单向非循环链表 " 和 "带头双向循环链表" ,至于 "无头单项非循环链表" 我们在前面已经讲述过了,我们下面将讲解其反面: "带头双向循环列表" !
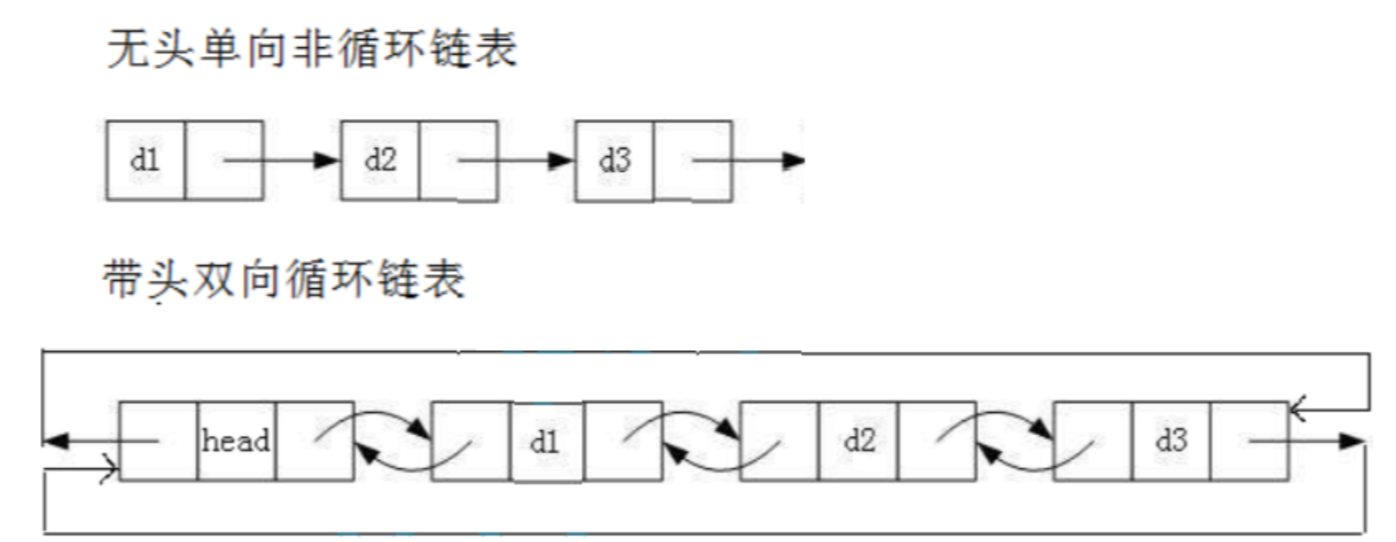
解读:
① 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存储数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等。此外,在笔试中单链表的出现频率较多。
② 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,但是实现反而简单。一般用来单独存储数据**,实际中使用的链表数据结构都是带头双向循环链表**。另外,这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现后会发现结构会带来很多优势。双向链表严格来说只需要快速的实现两个接口,insert 和 earse,头尾的插入和删除就可以搞定了,这就是结构的优势!链表的接口函数
2.双向链表分步实现:
(List.h)
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DLNodeDataType;
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
DLNodeDataType data;
struct DoubleListNode* next; // 指向后继节点的指针
struct DoubleListNode* prev; // 指向前驱节点的指针
}DLNode;
DLNode* DListInit();
void DListPushBack(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListPrint(DLNode* pHead);
void DListPopBack(DLNode* pHead);
void DListPushFront(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListPopFront(DLNode* pHead);
DLNode* DListFind(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListInsert(DLNode* pos, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListEarse(DLNode* pos);DListInit初始化函数:
cpp
DLNode* DListInit()
{
DLNode* pHead = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
if (pHead == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pHead->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = pHead;
return pHead;
//这里我们使用 malloc 函数开辟一块空间作为 "哨兵位" pHead ,
//最后将其进行一个初始化。最后再将 pHead 作为结果返回回去,外面就可以接收到了。
//这就是返回值的方法,当然这里也可以采用二级指针的方法来完成。
}CreateNewNode创建新节点函数:
cpp
DLNode* CreateNewNode(DLNodeDataType x)
{
DLNode* newNode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return newNode;
}DListPushBack尾插函数:
哨兵位头节点的好处:不用分情况处理
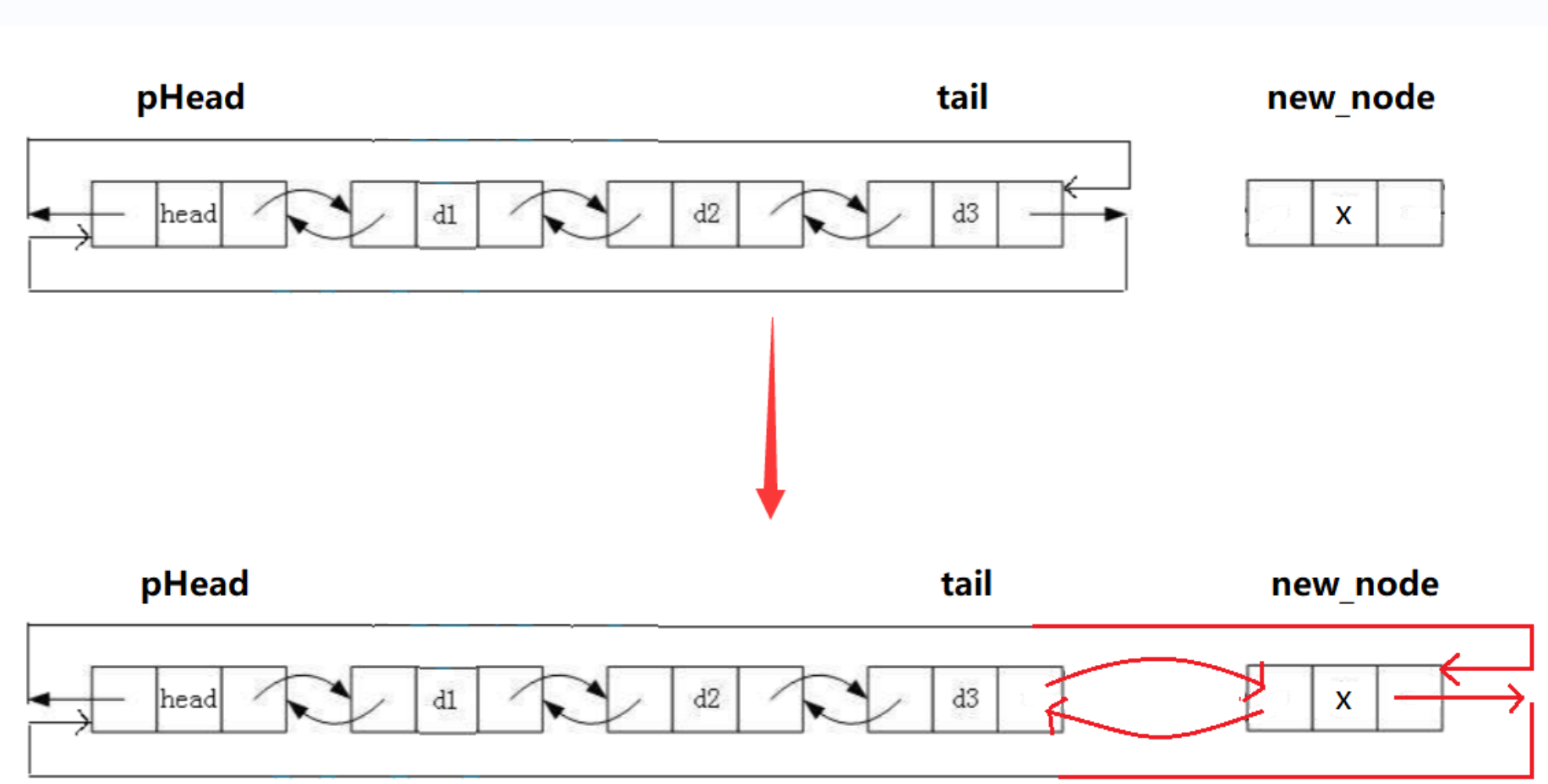
cpp
//因为不用改变 pList,所以不需要使用二级指针
void DListPushBack(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* tail = pHead->prev;
DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
tail->next = newNode;//原尾指向新尾
newNode->prev = tail;//新尾指回原尾
pHead->prev = newNode;//哨兵指到新尾
newNode->next = pHead;//新尾指回哨兵
}DListPrint打印函数:
cpp
void DListPrint(DLNode* pHead)
{
//用结构体指针 pHead 接收, 这里的 pHead 表示哨兵位。
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历链表就需要从 pHead->next 开始(即第一个有效数据节点)
//当 cur 等于 pHead 就相当于全部走了一遍了,这时就结束。
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}DListPopBack尾删函数:
cpp
void DListPopBack(DLNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
DLNode* tali = pHead->prev;//记录原尾等下释放
pHead->prev = pHead->prev->prev;//头链接到新尾
pHead->prev->next = pHead;//新尾链接到头
free(tali);
tali = NULL;//不置空也行
}测试1
cpp
void TestList1()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushBack(pList, 1);
DListPushBack(pList, 2);
DListPushBack(pList, 3);
DListPushBack(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DListPopBack(pList);
DListPopBack(pList);
DListPrint(pList);
}
DListPushFront头插函数:
cpp
void DListPushFront(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
pHead->next->prev = newNode;//原一指回新一
newNode->next = pHead->next;//新一指向原一
pHead->next = newNode;//哨兵指向新一
newNode->prev = pHead;//新一指回哨兵
//只有哨兵位头结点也能头插
}DListPopFront头删函数:
cpp
void DListPopFront(DLNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
DLNode* head = pHead->next;//记录原一等下释放
pHead->next = head->next;//哨兵头指向原二
head->prev = pHead;//原二指回哨兵头
free(head);
head = NULL;//不置空也行
}测试2
cpp
void TestList2()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushFront(pList, 1);
DListPushFront(pList, 2);
DListPushFront(pList, 3);
DListPushFront(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DListPopFront(pList);
DListPopFront(pList);
DListPrint(pList);
}
DListFind查找函数:
cpp
DLNode* DListFind(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历链表就需要从 pHead->next 开始(即第一个有效数据节点)(和打印一样)
//当 cur 等于 pHead 就相当于全部走了一遍了,这时就结束。
while (cur != pHead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}DListInsert指定位置之前插入函数:
cpp
void DListInsert(DLNode* pos, DLNodeDataType x)//在pos之前插入
{
assert(pos != NULL);
DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
DLNode* posPrev = pos->prev;//记录pos前节点
posPrev->next = newNode;//pos前节点指向新节点
newNode->prev = posPrev;//新节点指回pos前节点
newNode->next = pos;//新节点指向pos
pos->prev = newNode;//pos指回新节点
}DListEarse删除指定位置函数:
cpp
void DListEarse(DLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos != NULL);
assert(pos->next != pos);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
DLNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
DLNode* posNext = pos->next;
posPrev->next = posNext;//pos前节点指向pos后节点
posNext->prev = posPrev;//pos后节点指回pos前节点
free(pos);
}DListDestory销毁链表函数:
cpp
void DListDestory(DLNode* pHead)//保持接口函数的一致性就不传二级了,让使用者自己置空
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
DLNode* curNext = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = curNext;
}
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;//不能使外面置空,让使用者自己置空
}测试3
cpp
void TestList3()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushBack(pList, 1);
DListPushBack(pList, 2);
DListPushBack(pList, 3);
DListPushBack(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DLNode* pos = DListFind(pList, 1);
DListInsert(pos, 60);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 4);
DListInsert(pos, 70);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 2);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 4);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 60);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
DListDestory(pList);
pList = NULL;
}
所以,双向链表严格来说只需要快速地实现 insert 和 earse 这两个接口就可以搞定了。
为什么会这么简单?就是结构的优势!
如果以后让你快速实现一个双向链表,你把 "pos位置之前插入" 和 "删除pos位置" 这两个接口写好,
头尾的插入和删除直接复用就可以搞定了**。复用的代码直接放在下面的完整代码了。**
3.双向链表完整实现代码:
List.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DLNodeDataType;
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
DLNodeDataType data;
struct DoubleListNode* next; // 指向后继节点的指针
struct DoubleListNode* prev; // 指向前驱节点的指针
}DLNode;
DLNode* DListInit();
void DListPushBack(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListPrint(DLNode* pHead);
void DListPopBack(DLNode* pHead);
void DListPushFront(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListPopFront(DLNode* pHead);
DLNode* DListFind(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListInsert(DLNode* pos, DLNodeDataType x);
void DListEarse(DLNode* pos);
void DListDestory(DLNode* pHead);//保持接口函数的一致性就不传二级了,让使用者自己置空List.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "List.h"
DLNode* DListInit()
{
DLNode* pHead = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
if (pHead == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pHead->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = pHead;
return pHead;
//这里我们使用 malloc 函数开辟一块空间作为 "哨兵位" pHead ,
//最后将其进行一个初始化。最后再将 pHead 作为结果返回回去,外面就可以接收到了。
//这就是返回值的方法,当然这里也可以采用二级指针的方法来完成。
}
DLNode* CreateNewNode(DLNodeDataType x)
{
//动态内存开辟一块 DLNode 大小的空间给 newNode
DLNode* newNode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//放置数据
newNode->data = x;
//初始化
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
//返回
return newNode;
}
void DListPushBack(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
//DLNode* tail = pHead->prev;
//DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
//tail->next = newNode;//原尾指向新尾
//newNode->prev = tail;//新尾指回原尾
//pHead->prev = newNode;//哨兵指到新尾
//newNode->next = pHead;//新尾指回哨兵
DListInsert(pHead, x);//在pHead的前一个插入就是尾插
}
void DListPrint(DLNode* pHead)
{
//用结构体指针 pHead 接收, 这里的 pHead 表示哨兵位。
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历链表就需要从 pHead->next 开始(即第一个有效数据节点)
//当 cur 等于 pHead 就相当于全部走了一遍了,这时就结束。
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void DListPopBack(DLNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
//DLNode* tali = pHead->prev;//记录原尾等下释放
//pHead->prev = pHead->prev->prev;//头链接到新尾
//pHead->prev->next = pHead;//新尾链接到头
//free(tali);
DListEarse(pHead->prev);
}
void DListPushFront(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
//DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
//pHead->next->prev = newNode;//原一指回新一
//newNode->next = pHead->next;//新一指向原一
//pHead->next = newNode;//哨兵指向新一
//newNode->prev = pHead;//新一指回哨兵
//空链表也能头插
DListInsert(pHead->next, x);//在pHead的前一个就是插入就是头删
}
void DListPopFront(DLNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
//DLNode* head = pHead->next;//记录原一等下释放
//pHead->next = head->next;//哨兵头指向原二
//head->prev = pHead;//原二指回哨兵头
//free(head);
//head = NULL;//不置空也行
DListEarse(pHead->next);
}
DLNode* DListFind(DLNode* pHead, DLNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历链表就需要从 pHead->next 开始(即第一个有效数据节点)(和打印一样)
//当 cur 等于 pHead 就相当于全部走了一遍了,这时就结束。
while (cur != pHead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void DListInsert(DLNode* pos, DLNodeDataType x)//在pos之前插入
{
assert(pos != NULL);
DLNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
DLNode* posPrev = pos->prev;//记录pos前节点
posPrev->next = newNode;//pos前节点指向新节点
newNode->prev = posPrev;//新节点指回pos前节点
newNode->next = pos;//新节点指向pos
pos->prev = newNode;//pos指回新节点
}
void DListEarse(DLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos != NULL);
assert(pos->next != pos);//防止删掉哨兵位头节点
DLNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
DLNode* posNext = pos->next;
posPrev->next = posNext;//pos前节点指向pos后节点
posNext->prev = posPrev;//pos后节点指回pos前节点
free(pos);
pos = NULL;//不置空也行
}
void DListDestory(DLNode* pHead)//保持接口函数的一致性就不传二级了,让使用者自己置空
{
assert(pHead != NULL);
DLNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
DLNode* curNext = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = curNext;
}
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;//不能使外面置空,让使用者自己置空
}Test.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "List.h"
void TestList1()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushBack(pList, 1);
DListPushBack(pList, 2);
DListPushBack(pList, 3);
DListPushBack(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DListPopBack(pList);
DListPopBack(pList);
DListPrint(pList);
}
void TestList2()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushFront(pList, 1);
DListPushFront(pList, 2);
DListPushFront(pList, 3);
DListPushFront(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DListPopFront(pList);
DListPopFront(pList);
DListPrint(pList);
}
void TestList3()
{
DLNode* pList = DListInit();
DListPushBack(pList, 1);
DListPushBack(pList, 2);
DListPushBack(pList, 3);
DListPushBack(pList, 4);
DListPrint(pList);
DLNode* pos = DListFind(pList, 1);
DListInsert(pos, 60);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 4);
DListInsert(pos, 70);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 2);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 4);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
pos = DListFind(pList, 60);
DListEarse(pos);
DListPrint(pList);
DListDestory(pList);
pList = NULL;
}
int main()
{
//TestList1();
//TestList2();
TestList3();
return 0;
}4.温习顺序表和链表的优缺点:
前面讲单链表前就总结过顺序表和链表的优缺点

新增的红色的内容是一些底层,也不是很重要,想了解可以点下面大佬文章的链接
与程序员相关的CPU缓存知识 | 酷 壳 - CoolShell
本章完。
下一章:栈和队列