一、官方文档阅读
原文链接:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/vm/gctuning/g1_gc.html
The Garbage-First (G1) garbage collector is a server-style garbage collector, targeted for multiprocessor machines with large memories. It attempts to meet garbage collection (GC) pause time goals with high probability while achieving high throughput. Whole-heap operations, such as global marking, are performed concurrently with the application threads. This prevents interruptions proportional to heap or live-data size.
Garbage-First (G1) 垃圾收集器是一种面向服务器端的垃圾收集器,主要针对配备大容量内存的多处理器机器。其设计目标是在实现高吞吐量的同时,以高概率满足用户设定的垃圾收集 (GC) 停顿时间目标。诸如全局标记等全堆操作会与应用程序线程并发执行,从而避免了因堆大小或存活数据量增加而导致停顿时间成比例增长的问题。
The G1 collector achieves high performance and pause time goals through several techniques.
G1 收集器通过多种技术实现高性能与可控的停顿时间目标。
The heap is partitioned into a set of equally sized heap regions, each a contiguous range of virtual memory. G1 performs a concurrent global marking phase to determine the liveness of objects throughout the heap. After the marking phase completes, G1 knows which regions are mostly empty. It collects these regions first, which often yields a large amount of free space. This is why this method of garbage collection is called Garbage-First. As the name suggests, G1 concentrates its collection and compaction activity on the areas of the heap that are likely to be full of reclaimable objects, that is, garbage. G1 uses a pause prediction model to meet a user-defined pause time target and selects the number of regions to collect based on the specified pause time target.
堆被划分为一组大小相等的堆区域 (Heap Region),每个区域是一段连续的虚拟内存地址空间。G1 会执行一个并发的全局标记阶段,以确定整个堆中对象的存活状态。标记阶段完成后,G1 能够识别出哪些区域基本为空。它会优先回收这些区域,通常能快速释放大量空闲空间。这正是该垃圾收集方法得名 "Garbage-First" 的原因。顾名思义,G1 将其回收与整理 (Compaction) 活动的重点放在那些很可能充满可回收对象(即垃圾)的堆区域上。G1 使用一个停顿预测模型来满足用户自定义的停顿时间目标,并根据指定的停顿时间目标选择要回收的区域数量。
G1 copies objects from one or more regions of the heap to a single region on the heap, and in the process both compacts and frees up memory. This evacuation is performed in parallel on multiprocessors to decrease pause times and increase throughput. Thus, with each garbage collection, G1 continuously works to reduce fragmentation. This is beyond the capability of both of the previous methods. CMS (Concurrent Mark Sweep) garbage collection does not do compaction. Parallel compaction performs only whole-heap compaction, which results in considerable pause times.
G1 通过将对象从一个或多个堆区域复制(疏散)到堆上的单个区域,在此过程中同时完成内存整理与释放。该疏散过程在多处理器上并行执行,旨在降低停顿时间并提高吞吐量。因此,每次垃圾收集时,G1 都在持续工作以减少内存碎片。这是之前两种方法(CMS 和 Parallel Compaction)所不具备的能力:CMS (Concurrent Mark Sweep) 垃圾收集不进行内存整理;而 Parallel Compaction 仅执行全堆整理,这会导致相当长的停顿时间。
It is important to note that G1 is not a real-time collector. It meets the set pause time target with high probability but not absolute certainty. Based on data from previous collections, G1 estimates how many regions can be collected within the target time. Thus, the collector has a reasonably accurate model of the cost of collecting the regions, and it uses this model to determine which and how many regions to collect while staying within the pause time target.
需要重点指出的是,G1 不是 实时收集器。它能以高概率满足设定的停顿时间目标,但无法提供绝对确定性保证。G1 基于以往收集周期的数据,估算在目标时间内可以回收多少区域。因此,收集器拥有一个相对准确的、关于回收区域成本的模型,并利用此模型在满足停顿时间目标的前提下,决定回收哪些区域以及回收多少区域。
The first focus of G1 is to provide a solution for users running applications that require large heaps with limited GC latency. This means heap sizes of around 6 GB or larger, and a stable and predictable pause time below 0.5 seconds.
G1 的首要定位是为需要大堆内存同时又对 GC 延迟敏感的应用场景提供解决方案。这通常意味着堆大小约为 6GB 或更大,且要求稳定、可预测的停顿时间低于 0.5 秒。
Applications running today with either the CMS or the with parallel compaction would benefit from switching to G1 if the application has one or more of the following traits.More than 50% of the Java heap is occupied with live data.The rate of object allocation rate or promotion varies significantly.The application is experiencing undesired long garbage collection or compaction pauses (longer than 0.5 to 1 second).
对于当前正在使用 CMS 或 Parallel Compaction 的应用,如果具备以下一个或多个特征,切换至 G1 可能会带来收益:
- 超过 50% 的 Java 堆被存活数据占用。
- 对象分配速率或晋升(Promotion)速率波动显著。
- 应用正经历不期望的长时间垃圾收集或整理停顿(超过 0.5 到 1 秒)。
G1 is planned as the long-term replacement for the Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector (CMS). Comparing G1 with CMS reveals differences that make G1 a better solution. One difference is that G1 is a compacting collector. Also, G1 offers more predictable garbage collection pauses than the CMS collector, and allows users to specify desired pause targets.
G1 被规划为 CMS 收集器的长期替代方案。与 CMS 相比,G1 的优势在于:首先,G1 是一个整理收集器;其次,G1 能提供比 CMS 更可预测的垃圾收集停顿,并允许用户指定期望的停顿目标。
As with CMS, G1 is designed for applications that require shorter GC pauses.
与 CMS 一样,G1 专为需要较短 GC 停顿的应用而设计。
G1 divides the heap into fixed-sized regions (the gray boxes) as in Figure 9-1, "Heap Division by G1".
G1 将堆划分为固定大小的区域(即灰色方块所示区域),如图所示。
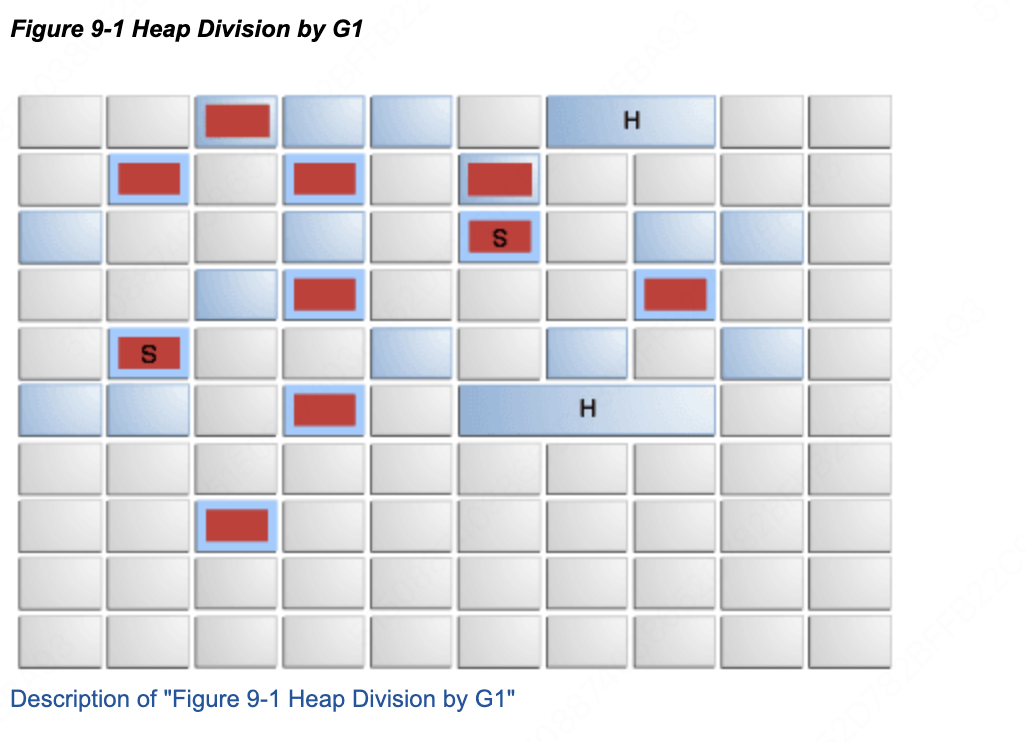 G1 is generational in a logical sense. A set of empty regions is designated as the logical young generation. In the figure, the young generation is light blue. Allocations are done out of that logical young generation, and when the young generation is full, that set of regions is garbage collected (a young collection). In some cases, regions outside the set of young regions (old regions in dark blue) can be garbage collected at the same time. This is referred to as a mixed collection. In the figure, the regions being collected are marked by red boxes. The figure illustrates a mixed collection because both young regions and old regions are being collected. The garbage collection is a compacting collection that copies live objects to selected, initially empty regions. Based on the age of a surviving object, the object can be copied to a survivor region (marked by "S") or to an old region (not specifically shown). The regions marked by "H" contain humongous objects that are larger than half a region and are treated specially; see the section Humongous Objects and Humongous Allocations in Garbage-First Garbage Collector.
G1 is generational in a logical sense. A set of empty regions is designated as the logical young generation. In the figure, the young generation is light blue. Allocations are done out of that logical young generation, and when the young generation is full, that set of regions is garbage collected (a young collection). In some cases, regions outside the set of young regions (old regions in dark blue) can be garbage collected at the same time. This is referred to as a mixed collection. In the figure, the regions being collected are marked by red boxes. The figure illustrates a mixed collection because both young regions and old regions are being collected. The garbage collection is a compacting collection that copies live objects to selected, initially empty regions. Based on the age of a surviving object, the object can be copied to a survivor region (marked by "S") or to an old region (not specifically shown). The regions marked by "H" contain humongous objects that are larger than half a region and are treated specially; see the section Humongous Objects and Humongous Allocations in Garbage-First Garbage Collector.
G1 在逻辑意义上是分代的。一组空区域被指定为逻辑上的年轻代(图中为浅蓝色区域)。对象分配在此逻辑年轻代中进行,当年轻代填满时,会触发针对这组区域的垃圾收集(即 Young Collection,年轻代收集)。在某些情况下,年轻代区域之外的区域(老年代区域,图中为深蓝色)也可能与年轻代一同被回收,这被称为 Mixed Collection(混合收集)。图中,正在被收集的区域用红色方框标出。该图展示的即为一次混合收集,因为同时回收了年轻代和老年代区域。垃圾收集过程是一个整理式收集,会将存活对象复制到预先选定的、初始为空的区域。根据存活对象的年龄,对象可能被复制到幸存者区域(标记为"S")或老年代区域(图中未专门标出)。标记为"H"的区域包含 Humongous Objects(巨型对象),这些对象大小超过半个区域,会被特殊处理(详见《Garbage-First 垃圾收集器》章节中关于 Humongous Objects 和 Humongous Allocations 的部分)。
1.1 Allocation (Evacuation) Failure - 分配(疏散)失败「发生该场景时非常危险,通常这时应用服务会产生不可用的情况」
As with CMS, the G1 collector runs parts of its collection while the application continues to run and there is a risk that the application will allocate objects faster than the garbage collector can recover free space. See the section Concurrent Mode Failure in Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Collector for the analogous CMS behavior. In G1, the failure (exhaustion of the Java heap) occurs while G1 is copying live data out of one region (evacuating) into another region. The copying is done to compact the live data. If a free (empty) region cannot be found during the evacuation of a region being garbage collected, then an allocation failure occurs (because there is no space to allocate the live objects from the region being evacuated) and a stop-the-world (STW) full collection is done.
与 CMS 类似,G1 收集器在应用持续运行的同时执行部分收集工作,因此存在应用分配对象的速度快于垃圾收集器回收空闲空间速度的风险。在 G1 中,当 G1 将存活数据从一个区域复制(疏散)到另一个区域以进行内存整理时,如果无法为待疏散区域中的存活对象找到空闲(空)区域进行安置,就会发生分配失败,进而触发一次 Stop-The-World (STW) 的全堆收集。
1.2 Floating Garbage
Objects can die during a G1 collection and not be collected. G1 uses a technique called snapshot-at-the-beginning (SATB) to guarantee that all live objects are found by the garbage collector. SATB states that any object that is live at the start of the concurrent marking (a marking over the entire heap) is considered live for the purpose of the collection. SATB allows floating garbage in a way analogous to that of a CMS incremental update.
对象可能在一次 G1 收集周期内死亡但未被回收。G1 使用一种称为 Snapshot-At-The-Beginning (SATB) 的技术来确保垃圾收集器能找到所有存活对象。SATB 机制规定,在并发标记(对整个堆的标记)开始时存活的任何对象「写前屏障会将并发标记时被切断引用的对象,重新标记为存活,这些可能是浮动垃圾,待后续 Mixed GC 回收」,在该次收集中都将被视为存活。SATB 允许存在浮动垃圾,其原理与 CMS 的增量更新 (Incremental Update) 机制类似。
1.3 Pauses
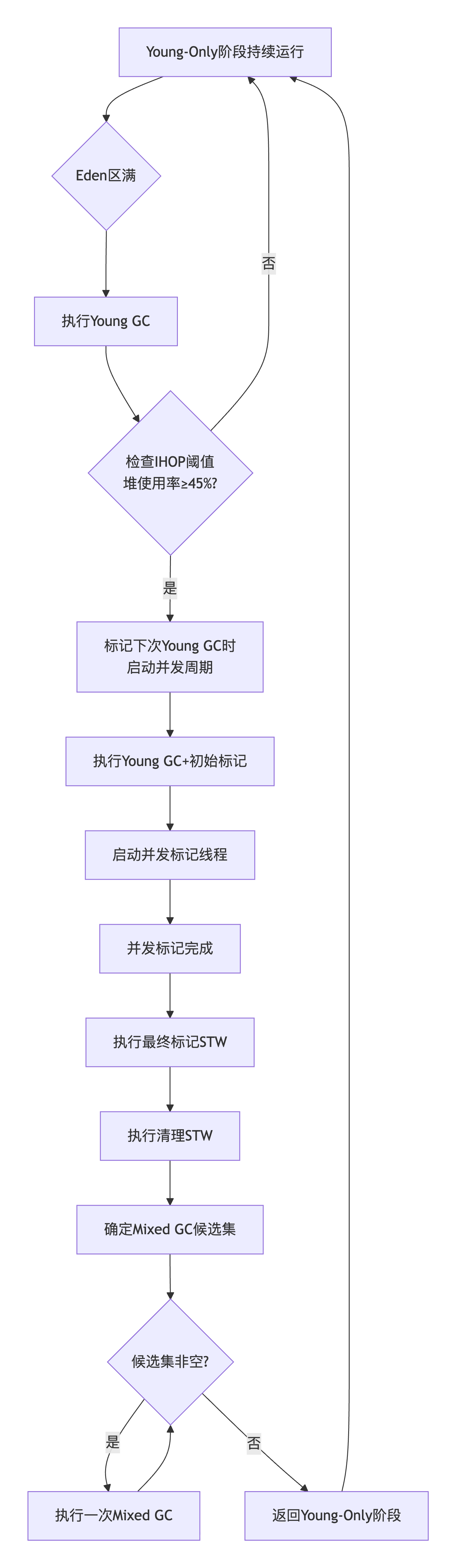
G1 pauses the application to copy live objects to new regions. These pauses can either be young collection pauses where only young regions are collected or mixed collection pauses where young and old regions are evacuated. As with CMS there is a final marking or remark pause to complete the marking while the application is stopped. Whereas CMS also had an initial marking pause, G1 does the initial marking work as part of an evacuation pause. G1 has a cleanup phase at the end of a collection which is partly STW and partly concurrent. The STW part of the cleanup phase identifies empty regions and determines old regions that are candidates for the next collection.
G1 会暂停应用以将存活对象复制到新区域。这些停顿可以是年轻代收集停顿(仅收集年轻代区域),也可以是混合收集停顿(同时疏散年轻代和老年代区域)。与 CMS 一样,存在一个最终标记(或重标记)停顿,在应用停止时完成标记。CMS 有一个初始标记停顿,而 G1 将初始标记工作作为一次疏散停顿的一部分来完成。G1 在收集结束时有一个清理阶段,该阶段部分是 STW 的,部分是并发的。清理阶段的 STW 部分负责识别空区域,并确定可作为下一次收集候选的老年代区域。
1.4 Card Tables and Concurrent Phases - 卡表与并发阶段
If a garbage collector does not collect the entire heap (an incremental collection), the garbage collector needs to know where there are pointers from the uncollected part of the heap into the part of the heap that is being collected. This is typically for a generational garbage collector in which the uncollected part of the heap is usually the old generation, and the collected part of the heap is the young generation. The data structure for keeping this information (old generation pointers to young generation objects), is a remembered set. A card table is a particular type of remembered set. Java HotSpot VM uses an array of bytes as a card table. Each byte is referred to as a card. A card corresponds to a range of addresses in the heap. Dirtying a card means changing the value of the byte to a dirty value; a dirty value might contain a new pointer from the old generation to the young generation in the address range covered by the card.
如果垃圾收集器不收集整个堆(即增量收集),它需要知道堆中未被收集部分(通常是老年代)有哪些指针指向正在被收集的部分(通常是年轻代)。用于保存此类信息(老年代指向年轻代对象的指针)的数据结构称为 记忆集。卡表 是一种特殊类型的记忆集。Java HotSpot VM 使用一个字节数组作为卡表,每个字节称为一张卡。一张卡对应堆中的一段地址范围。弄脏一张卡意味着将该字节的值改为一个"脏"值;一个脏值可能表示在该卡覆盖的地址范围内存在一个从老年代指向年轻代的新指针。
Processing a card means looking at the card to see if there is an old generation to young generation pointer and perhaps doing something with that information such as transferring it to another data structure.
处理一张卡意味着检查该卡以判断是否存在老年代到年轻代的指针,并可能据此信息执行某些操作,例如将其转移到另一个数据结构。
G1 has concurrent marking phase which marks live objects found from the application. The concurrent marking extends from the end of a evacuation pause (where the initial marking work is done) to the remark. The concurrent cleanup phase adds regions emptied by the collection to the list of free regions and clears the remembered sets of those regions. In addition, a concurrent refinement thread runs as needed to process card table entries that have been dirtied by application writes and which may have cross region references.
G1 有一个并发标记阶段,负责标记从应用中发现的存活对象。该并发标记阶段从一次疏散停顿(初始标记工作在此完成)结束开始,持续到重标记停顿之前。并发清理阶段 将收集后清空的区域添加到空闲区域列表,并清除这些区域的记忆集。此外,一个并发 refinement 线程会根据需要运行,以处理被应用写操作弄脏的、可能含有跨区域引用的卡表条目。
1.5 Starting a Concurrent Collection Cycle - 启动并发收集周期
As mentioned previously, both young and old regions are garbage collected in a mixed collection. To collect old regions, G1 does a complete marking of the live objects in the heap. Such a marking is done by a concurrent marking phase. A concurrent marking phase is started when the occupancy of the entire Java heap reaches the value of the parameter InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent. Set the value of this parameter with the command-line option -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=. The default value of InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent is 45.
如前所述,老年代和年轻代区域在混合收集中一同被回收。为收集老年代区域,G1 需要对堆中的存活对象进行一次完整的标记。此类标记由并发标记阶段完成。当整个 Java 堆的使用率达到参数 InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent 的值时,将启动一个并发标记周期。可使用命令行选项 -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent= 设置此参数的值,其默认值为 45。
1.6 Pause Time Goal - 停顿时间目标
Set a pause time goal for G1 with the flag MaxGCPauseMillis. G1 uses a prediction model to decide how much garbage collection work can be done within that target pause time. At the end of a collection, G1 chooses the regions to be collected in the next collection (the collection set). The collection set will contain young regions (the sum of whose sizes determines the size of the logical young generation). It is partly through the selection of the number of young regions in the collection set that G1 exerts control over the length of the GC pauses. You can specify the size of the young generation on the command line as with the other garbage collectors, but doing so may hamper the ability of G1 to attain the target pause time. In addition to the pause time goal, you can specify the length of the time period during which the pause can occur. You can specify the minimum mutator usage with this time span (GCPauseIntervalMillis) along with the pause time goal. The default value for MaxGCPauseMillis is 200 milliseconds. The default value for GCPauseIntervalMillis (0) is the equivalent of no requirement on the time span.
使用 -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis 标志为 G1 设置停顿时间目标。G1 使用预测模型来决定在目标停顿时间内可以完成多少垃圾收集工作。在一次收集结束时,G1 会选择下一次收集要回收的区域(收集集)。收集集将包含年轻代区域(其大小总和决定了逻辑年轻代的尺寸)。G1 部分通过控制收集集中年轻代区域的数量来调控 GC 停顿的长度。虽然可以像其他垃圾收集器一样在命令行指定年轻代的大小,但这样做可能会妨碍 G1 实现目标停顿时间的能力。除了停顿时间目标,您还可以指定停顿发生的时间窗口。您可以使用 -XX:GCPauseIntervalMillis 参数(与此时间跨度一同)以及停顿时间目标,来指定在此时间间隔内应用线程(Mutator)的最小使用率。MaxGCPauseMillis 的默认值是 200 毫秒。GCPauseIntervalMillis 的默认值是 0,这相当于不对时间窗口做要求。
二、G1 垃圾收集周期整理
2.1 垃圾回收流程图
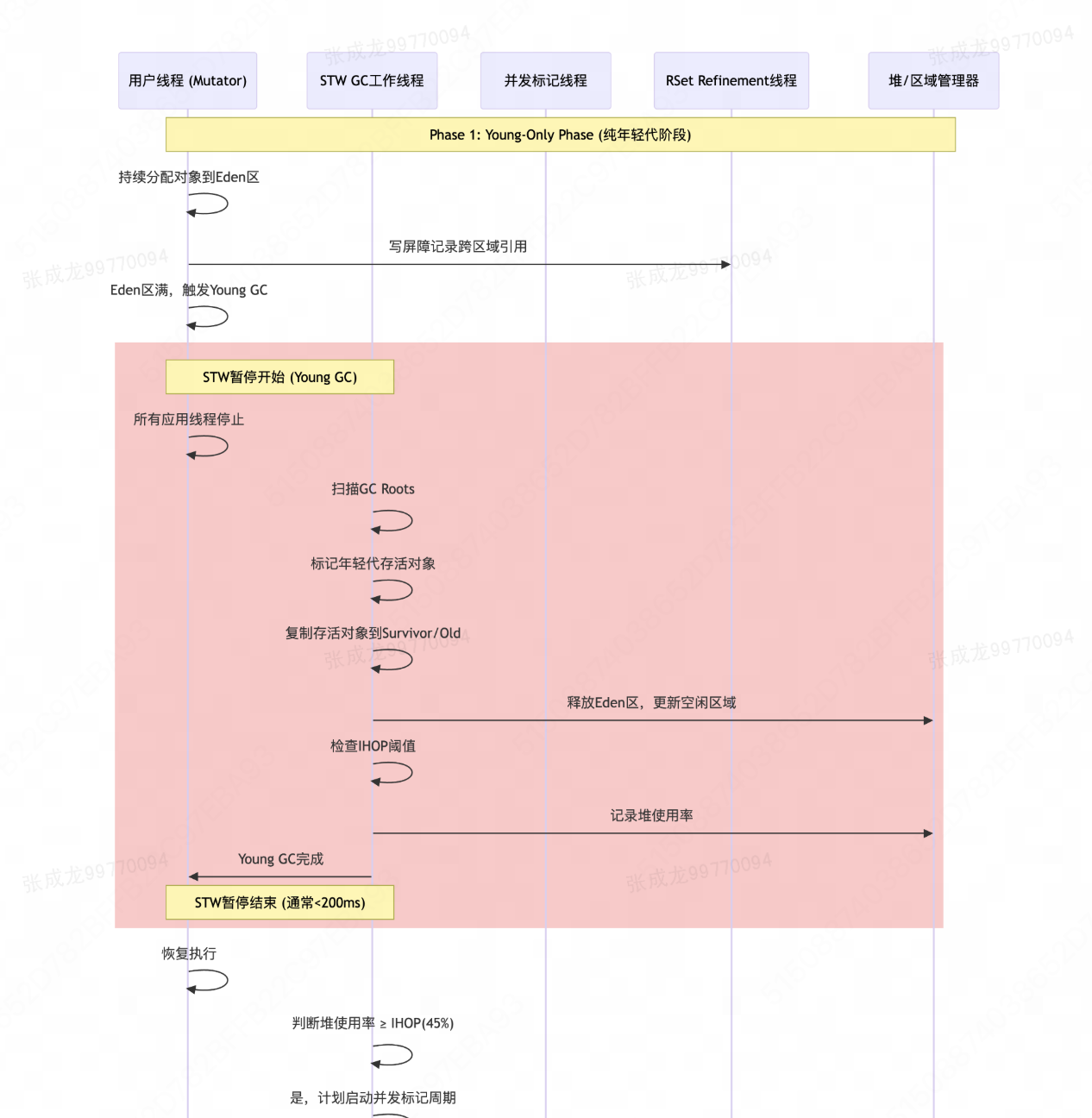

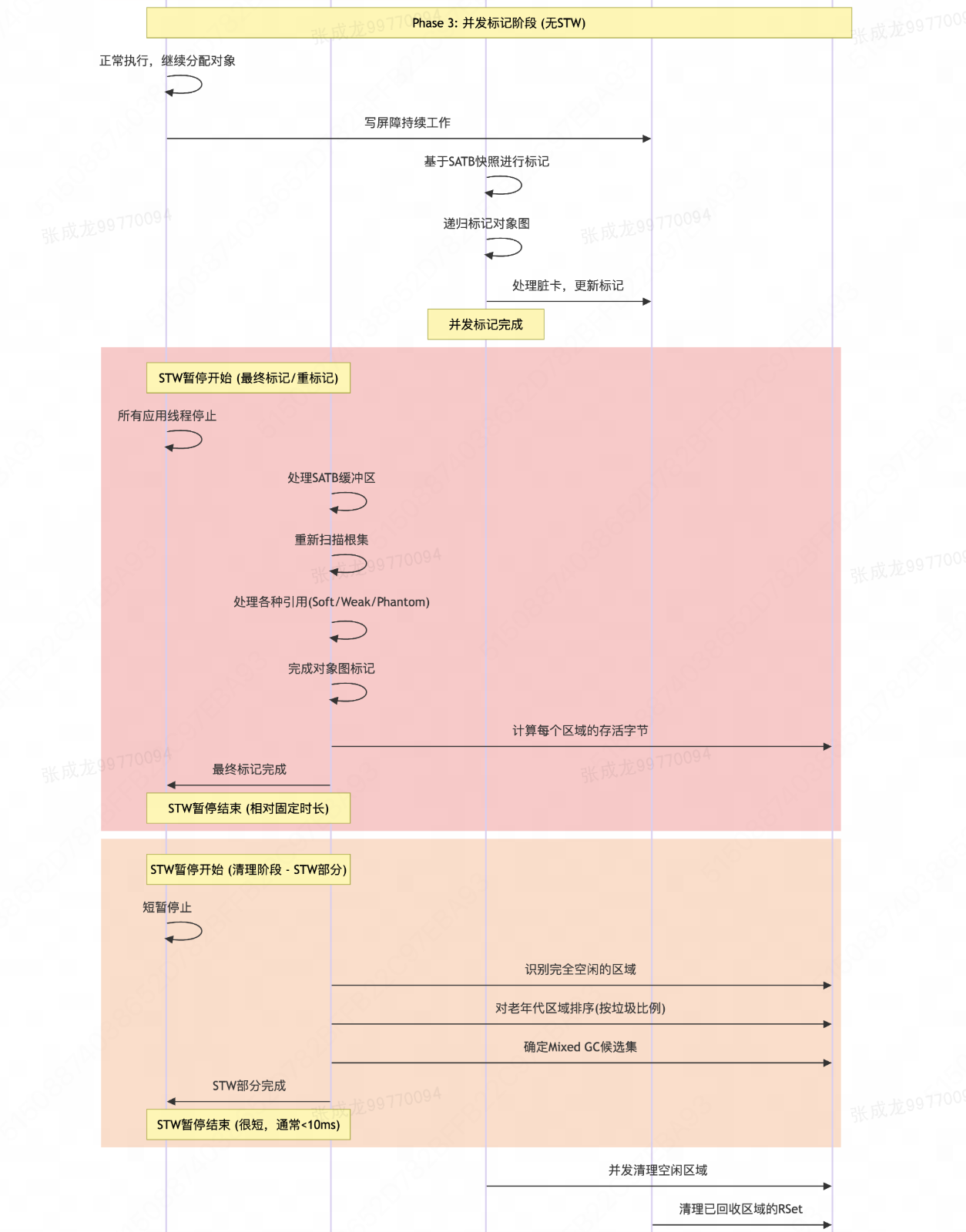
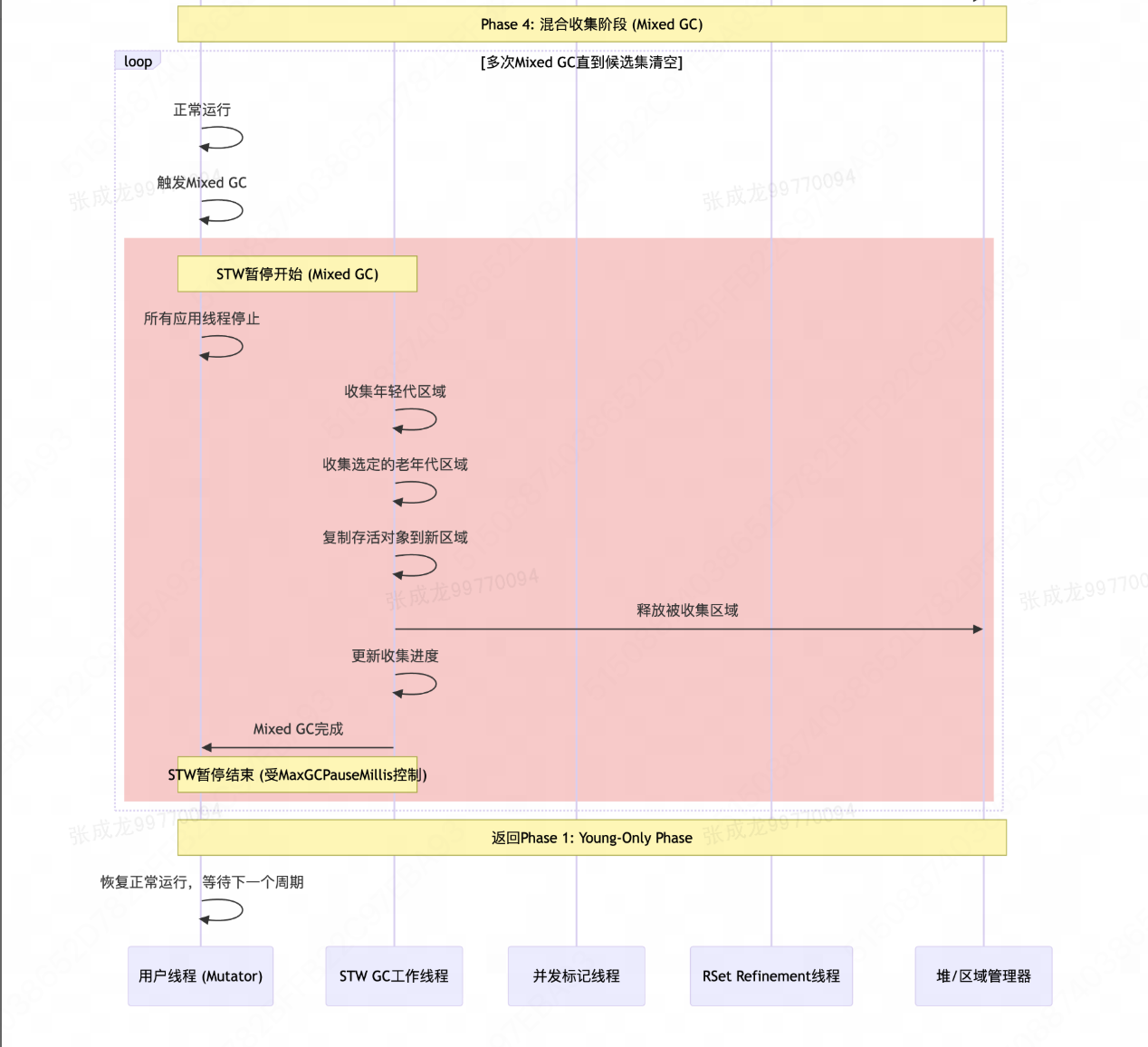
2.2 垃圾回收分阶段交互图
2.3 Card Table & Remembered Set
2.3.1 Card Table和Remembered Set是G1实现高效部分回收的核心
Card Table是"探测器":
- 粗粒度标记哪些地方"可能"有跨区域引用
- 写屏障开销小,快速标记
- 为Refinement线程提供工作线索
Remembered Set是"精确记录":
- 每个Region都有,记录谁引用了自己
- 细粒度,精确到具体位置
- 使GC可以精确扫描,避免全堆遍历
它们共同解决了分代/分区GC的核心难题:如何高效追踪跨区域引用。 Card Table提供快速探测,RSet提供精确记录,Refinement线程在中间桥接。这个三层架构让G1在保持高吞吐量的同时,实现了精确的部分回收和可控的停顿时间。
2.4 RSet refinement 线程介绍
Refinement线程(并发Refinement Thread)是G1中处理跨区域引用的核心维护线程,专门负责"精炼"卡表(Card Table),保持记忆集(RSet)的准确性和时效性。
在G1中,每个区域都有自己的记忆集(RSet),记录其他区域指向本区域的指针。例如:Region A(老年代)中的对象引用Region B(年轻代)中的对象。这种引用关系需要被准确记录,以便在收集Region B时知道要从Region A扫描哪些对象
Refinement线程是G1实现高效跨区域引用追踪的关键组件:
- 做什么:异步处理脏卡,精确识别跨区域引用,更新目标区域的RSet
- 为什么:避免在应用线程中同步更新RSet,减少写屏障开销
- 何时工作:持续在后台运行,也在GC停顿期间辅助处理
核心价值: - 写操作几乎无开销:应用线程只标记脏卡
- 精确RSet:实现精确的跨区域引用追踪
- 减少GC扫描范围:在收集区域时只扫描相关部分
- 自适应:根据负载动态调整工作强度(白/绿/黄/红)
简单来说,Refinement线程让G1在保持RSet准确性的同时,避免了写屏障对应用性能的影响,是实现高吞吐量和低停顿平衡的关键技术之一。

三、G1 垃圾回收日志介绍
bash
2025-12-05T11:45:52.802+0800: 1282286.147: [GC pause (G1 Evacuation Pause) (young) (initial-mark) (to-space exhausted), 69.9688781 secs]
[Parallel Time: 56494.8 ms, GC Workers: 8]
[GC Worker Start (ms): Min: 1282286147.9, Avg: 1282286148.0, Max: 1282286148.0, Diff: 0.1]
[Ext Root Scanning (ms): Min: 1.2, Avg: 2.1, Max: 4.0, Diff: 2.8, Sum: 16.9]
[Update RS (ms): Min: 2127.1, Avg: 2127.4, Max: 2127.8, Diff: 0.7, Sum: 17018.8]
[Processed Buffers: Min: 2751, Avg: 2937.5, Max: 3290, Diff: 539, Sum: 23500]
[Scan RS (ms): Min: 20.1, Avg: 20.6, Max: 21.2, Diff: 1.1, Sum: 164.9]
[Code Root Scanning (ms): Min: 0.0, Avg: 0.0, Max: 0.0, Diff: 0.0, Sum: 0.0]
[Object Copy (ms): Min: 53994.6, Avg: 54001.8, Max: 54040.0, Diff: 45.5, Sum: 432014.6]
[Termination (ms): Min: 2.6, Avg: 40.8, Max: 46.3, Diff: 43.7, Sum: 326.7]
[Termination Attempts: Min: 1, Avg: 1.0, Max: 1, Diff: 0, Sum: 8]
[GC Worker Other (ms): Min: 301.8, Avg: 301.8, Max: 301.9, Diff: 0.1, Sum: 2414.8]
[GC Worker Total (ms): Min: 56494.5, Avg: 56494.6, Max: 56494.6, Diff: 0.1, Sum: 451956.6]
[GC Worker End (ms): Min: 1282342642.5, Avg: 1282342642.5, Max: 1282342642.5, Diff: 0.0]
[Code Root Fixup: 26.0 ms]
[Code Root Purge: 0.0 ms]
[Clear CT: 3.0 ms]
[Other: 13445.0 ms]
[Evacuation Failure: 11416.9 ms]
[Choose CSet: 0.0 ms]
[Ref Proc: 9.1 ms]
[Ref Enq: 53.2 ms]
[Redirty Cards: 1782.0 ms]
[Humongous Register: 0.1 ms]
[Humongous Reclaim: 0.0 ms]
[Free CSet: 19.5 ms]
[Eden: 3752.0M(3752.0M)->0.0B(3824.0M) Survivors: 544.0M->472.0M Heap: 13.3G(14.0G)->13.9G(14.0G)]
Heap after GC invocations=35479 (full 0):
garbage-first heap total 14680064K, used 14546406K [0x0000000440000000, 0x0000000440803800, 0x00000007c0000000)
region size 8192K, 59 young (483328K), 59 survivors (483328K)
Metaspace used 89729K, capacity 92576K, committed 98432K, reserved 1136640K
class space used 9844K, capacity 10432K, committed 11136K, reserved 1048576K
}
[Times: user=75.36 sys=21.78, real=69.97 secs]这是一段非常严重的GC日志,GC停顿接近70秒!
由日志可知此阶段出于 YoungGC 阶段,同时启动对象疏散,但失败了(当前机器无可分配的内存空间),因此触发了G1的降级机制(STW 全堆垃圾回收),导致性能急剧下降。
3.1 各阶段耗时分析
3.1.1 并行阶段
8个GC工作线程并行工作,但仍耗时56.5秒,说明堆非常大或问题严重。
关键子阶段:
- Ext Root Scanning (2.1ms):扫描根对象,正常
- Update RS (2127.4ms = 2.1秒!):更新RSet时间异常长
- Processed Buffers: 23500:处理了23500个缓冲区,说明RSet非常大
- Scan RS (20.6ms):扫描RSet,相对正常
- Object Copy (54001.8ms = 54秒!):对象复制耗时占绝大部分
这是疏散的核心操作,耗时54秒说明:
- 存活对象极多
- 堆碎片化严重
- 可能触发了退化行为
3.1.2 其他阶段
bash
[Evacuation Failure: 11416.9 ms] # 疏散失败处理
[Redirty Cards: 1782.0 ms] # 重新标记卡表
[Free CSet: 19.5 ms] # 释放回收集