简介:
本文汇总 Java IO 核心类及方法,含字节流、字符流、缓冲流、转换流、对象流、随机访问文件及 NIO 的 Buffer、Channel 等。详细列出各类型构造方法与读写、关闭等操作,助开发者快速查阅,提升文件处理效率。
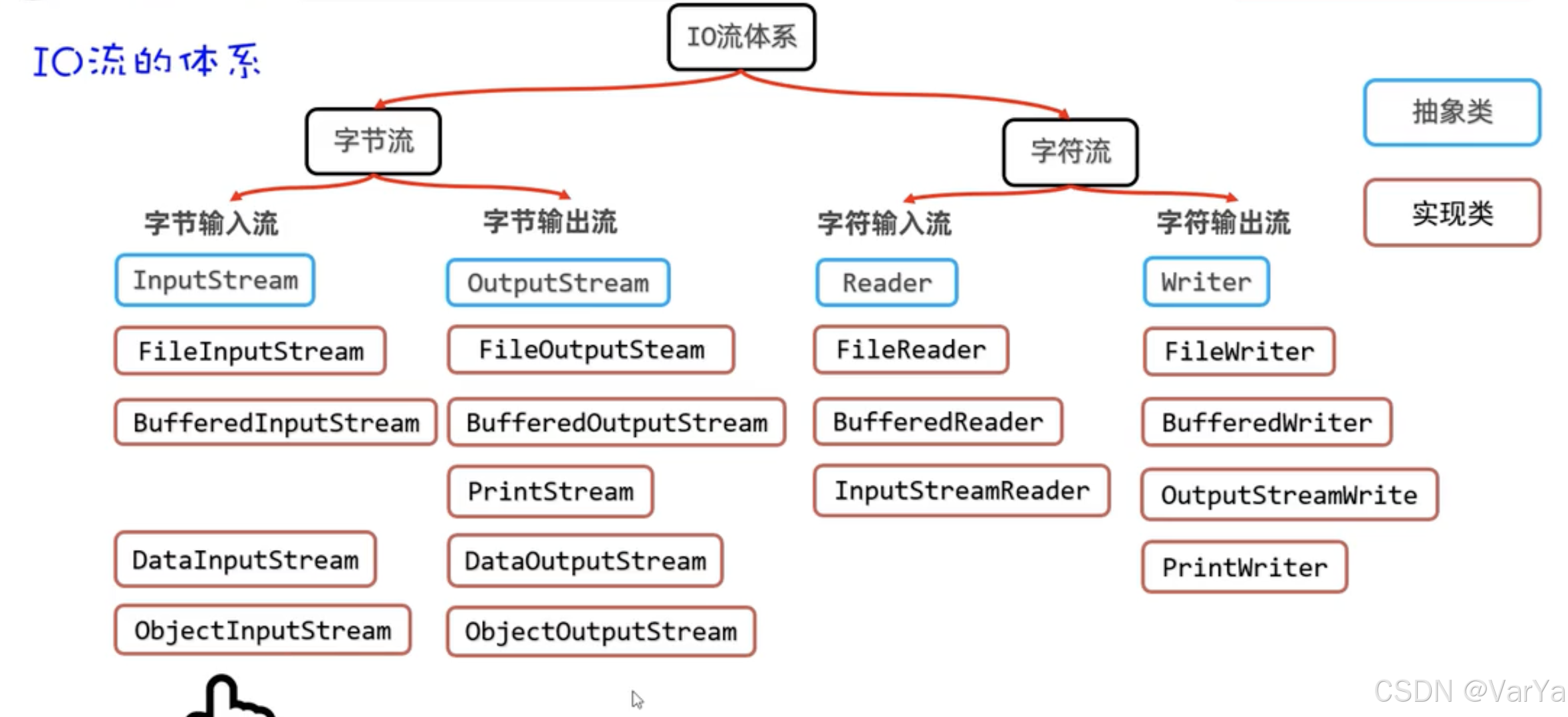
文章目录
InputStream
int read(): 读取单个字节的数据int read(byte[] b): 读取字节到数组中,返回实际读取的字节数int read(byte[] b, int off, int len): 从偏移量off开始读取最多len个字节到数组b中long skip(long n): 跳过并丢弃输入流中的n个字节int available(): 返回可以读取的字节数void close(): 关闭输入流并释放资源void mark(int readlimit): 标记当前位置void reset(): 重置到上次标记的位置boolean markSupported(): 判断是否支持标记操作
FileInputStream
FileInputStream(String name): 通过文件名创建文件输入流FileInputStream(File file): 通过File对象创建文件输入流int read(): 读取单个字节int read(byte[] b): 读取字节到数组long skip(long n): 跳过n个字节int available(): 返回可读取的字节数void close(): 关闭流
OutputStream
void write(int b): 写入单个字节void write(byte[] b): 写入整个字节数组void write(byte[] b, int off, int len): 写入字节数组的一部分void flush(): 刷新输出流,强制写出所有缓冲的数据void close(): 关闭输出流并释放资源
FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream(String name): 通过文件名创建文件输出流FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append): 创建文件输出流,可选择是否追加FileOutputStream(File file): 通过File对象创建文件输出流void write(int b): 写入单个字节void write(byte[] b): 写入字节数组void flush(): 刷新输出流void close(): 关闭流
Reader
int read(): 读取单个字符int read(char[] cbuf): 读取字符到数组中int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len): 读取字符到数组的指定位置long skip(long n): 跳过n个字符boolean ready(): 判断是否准备好读取void close(): 关闭读取器void mark(int readAheadLimit): 标记当前位置void reset(): 重置到上次标记的位置boolean markSupported(): 判断是否支持标记
FileReader
FileReader(String fileName): 通过文件名创建文件读取器FileReader(File file): 通过File对象创建文件读取器int read(): 读取单个字符int read(char[] cbuf): 读取字符到数组long skip(long n): 跳过n个字符boolean ready(): 判断是否准备好读取void close(): 关闭读取器
Writer
void write(int c): 写入单个字符void write(char[] cbuf): 写入字符数组void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len): 写入字符数组的一部分void write(String str): 写入字符串void write(String str, int off, int len): 写入字符串的一部分Writer append(CharSequence csq): 添加字符序列Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end): 添加字符序列的一部分Writer append(char c): 添加单个字符void flush(): 刷新输出void close(): 关闭写入器
FileWriter
FileWriter(String fileName): 通过文件名创建文件写入器FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append): 创建文件写入器,可选择是否追加FileWriter(File file): 通过File对象创建文件写入器void write(int c): 写入单个字符void write(char[] cbuf): 写入字符数组void write(String str): 写入字符串void flush(): 刷新输出void close(): 关闭写入器
BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in): 创建带默认缓冲区大小的缓冲输入流BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size): 创建指定缓冲区大小的缓冲输入流int read(): 读取单个字节int read(byte[] b, int off, int len): 读取字节到数组long skip(long n): 跳过n个字节int available(): 返回可读取的字节数void close(): 关闭流void mark(int readlimit): 标记当前位置void reset(): 重置到上次标记的位置boolean markSupported(): 判断是否支持标记
BufferedOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建带默认缓冲区大小的缓冲输出流BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size): 创建指定缓冲区大小的缓冲输出流void write(int b): 写入单个字节void write(byte[] b, int off, int len): 写入字节数组的一部分void flush(): 刷新输出流void close(): 关闭流
BufferedReader
BufferedReader(Reader in): 创建带默认缓冲区大小的缓冲读取器BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz): 创建指定缓冲区大小的缓冲读取器String readLine(): 读取一行文本int read(): 读取单个字符int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len): 读取字符到数组long skip(long n): 跳过n个字符boolean ready(): 判断是否准备好读取void close(): 关闭读取器void mark(int readAheadLimit): 标记当前位置void reset(): 重置到上次标记的位置
BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter(Writer out): 创建带默认缓冲区大小的缓冲写入器BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz): 创建指定缓冲区大小的缓冲写入器void write(int c): 写入单个字符void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len): 写入字符数组的一部分void write(String s, int off, int len): 写入字符串的一部分void newLine(): 写入行分隔符void flush(): 刷新输出void close(): 关闭写入器
InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in): 创建使用默认字符集的转换输入流InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName): 创建使用指定字符集的转换输入流InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs): 创建使用指定字符集的转换输入流String getEncoding(): 获取当前使用的字符编码int read(): 读取单个字符int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length): 读取字符到数组boolean ready(): 判断是否准备好读取void close(): 关闭读取器long skip(long n): 跳过n个字符
OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out): 创建使用默认字符集的转换输出流OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName): 创建使用指定字符集的转换输出流OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs): 创建使用指定字符集的转换输出流String getEncoding(): 获取当前使用的字符编码void write(int c): 写入单个字符void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len): 写入字符数组的一部分void write(String str, int off, int len): 写入字符串的一部分void flush(): 刷新输出void close(): 关闭写入器boolean ready(): 判断是否准备好写入
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream(InputStream in): 创建对象输入流Object readObject(): 读取对象boolean readBoolean(): 读取布尔值byte readByte(): 读取字节char readChar(): 读取字符short readShort(): 读取短整型int readInt(): 读取整型long readLong(): 读取长整型float readFloat(): 读取浮点型double readDouble(): 读取双精度浮点型void defaultReadObject(): 读取默认序列化的对象void readFields(): 读取对象的持久字段int available(): 返回可读取的字节数void close(): 关闭流
ObjectOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建对象输出流void writeObject(Object obj): 写入对象void writeBoolean(boolean val): 写入布尔值void writeByte(int val): 写入字节void writeChar(int val): 写入字符void writeShort(int val): 写入短整型void writeInt(int val): 写入整型void writeLong(long val): 写入长整型void writeFloat(float val): 写入浮点型void writeDouble(double val): 写入双精度浮点型void defaultWriteObject(): 写入对象的默认序列化数据void writeFields(): 写入对象的持久字段void flush(): 刷新输出流void close(): 关闭流void reset(): 重置对象缓存void writeClassDescriptor(ObjectStreamClass desc): 写入类描述符
RandomAccessFile
RandomAccessFile(String name, String mode): 创建随机访问文件RandomAccessFile(File file, String mode): 通过File对象创建随机访问文件void seek(long pos): 设置文件指针位置long getFilePointer(): 获取当前文件指针位置long length(): 获取文件长度void setLength(long newLength): 设置文件长度int read(): 读取单个字节int read(byte[] b): 读取字节到数组int read(byte[] b, int off, int len): 读取字节到数组的指定位置boolean readBoolean(): 读取布尔值byte readByte(): 读取字节char readChar(): 读取字符short readShort(): 读取短整型int readInt(): 读取整型long readLong(): 读取长整型float readFloat(): 读取浮点型double readDouble(): 读取双精度浮点型String readLine(): 读取一行文本void write(int b): 写入单个字节void write(byte[] b): 写入字节数组void write(byte[] b, int off, int len): 写入字节数组的一部分void writeBoolean(boolean v): 写入布尔值void writeByte(int v): 写入字节void writeChar(int v): 写入字符void writeShort(int v): 写入短整型void writeInt(int v): 写入整型void writeLong(long v): 写入长整型void writeFloat(float v): 写入浮点型void writeDouble(double v): 写入双精度浮点型void writeBytes(String s): 写入字符串的字节序列void writeChars(String s): 写入字符串的字符序列void writeUTF(String str): 以UTF-8编码写入字符串String readUTF(): 读取UTF-8编码的字符串int skipBytes(int n): 跳过n个字节void close(): 关闭文件
Buffer
int capacity(): 返回缓冲区的容量int position(): 返回缓冲区的位置Buffer position(int newPosition): 设置缓冲区的位置int limit(): 返回缓冲区的限制Buffer limit(int newLimit): 设置缓冲区的限制Buffer clear(): 清空缓冲区,准备新的通道读取或相对放置操作Buffer flip(): 反转此缓冲区Buffer rewind(): 重绕此缓冲区int remaining(): 返回当前位置与限制之间的元素数boolean hasRemaining(): 判断当前位置和限制之间是否有元素Buffer mark(): 在此缓冲区的当前位置设置标记Buffer reset(): 重置此缓冲区的位置到标记位置int compareTo(Buffer that): 将此缓冲区与另一个缓冲区进行比较boolean equals(Object ob): 判断此缓冲区是否等于另一个对象int hashCode(): 返回此缓冲区的哈希码
Channel
int read(ByteBuffer dst): 从通道读取数据到缓冲区long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts): 分散读取,从通道读取到多个缓冲区long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length): 从指定偏移量开始分散读取int write(ByteBuffer src): 从缓冲区写入数据到通道long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs): 聚集写入,从多个缓冲区写入到通道long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length): 从指定偏移量开始聚集写入long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count): 从源通道传输数据long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target): 传输数据到目标通道void close(): 关闭通道boolean isOpen(): 判断通道是否打开
Path
Path getFileName(): 返回此路径的文件名组件Path getParent(): 返回此路径的父路径Path getRoot(): 返回此路径的根组件int getNameCount(): 返回此路径中的名称元素数量Path getName(int index): 返回此路径的指定名称元素Path subpath(int beginIndex, int endIndex): 返回此路径的子路径boolean isAbsolute(): 判断此路径是否为绝对路径Path toAbsolutePath(): 返回此路径的绝对路径Path normalize(): 返回此路径的规范化路径Path resolve(Path other): 解析此路径与给定路径Path resolve(String other): 解析此路径与给定路径字符串boolean startsWith(Path other): 判断此路径是否以给定路径开始
Files
static long size(Path path): 返回文件大小static boolean exists(Path path): 判断文件是否存在static boolean isRegularFile(Path path): 判断是否为普通文件static boolean isDirectory(Path path): 判断是否为目录static Path createFile(Path path): 创建文件static Path createDirectory(Path dir): 创建目录static Path createDirectories(Path dir): 创建多级目录static Path delete(Path path): 删除文件static boolean deleteIfExists(Path path): 如果存在则删除文件static Path copy(Path source, Path target): 复制文件static Path move(Path source, Path target): 移动文件static List<String> readAllLines(Path path): 读取文件的所有行static byte[] readAllBytes(Path path): 读取文件的所有字节static Path write(Path path, byte[] bytes): 写入字节到文件static Path write(Path path, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> lines): 写入行到文件