
🎬 个人主页 :艾莉丝努力练剑
❄专栏传送门 :《C语言》《数据结构与算法》《C/C++干货分享&学习过程记录》
《Linux操作系统编程详解》《笔试/面试常见算法:从基础到进阶》《Python干货分享》
⭐️为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平
🎬 艾莉丝的简介:

🎬 艾莉丝的Linux专栏简介:

文章目录
- [5 ~> Linux中的第一个系统程序:进度条](#5 ~> Linux中的第一个系统程序:进度条)
-
- [5.1 两个储备知识:回车换行 / 缓冲区](#5.1 两个储备知识:回车换行 / 缓冲区)
-
- [5.1.1 回车和换行是一码事吗?](#5.1.1 回车和换行是一码事吗?)
- [5.1.2 缓冲区](#5.1.2 缓冲区)
- [5.2 观察:行缓冲区](#5.2 观察:行缓冲区)
- [5.3 练练手:demo:光标快速回退,完成倒计时功能](#5.3 练练手:demo:光标快速回退,完成倒计时功能)
-
- [5.3.1 代码演示](#5.3.1 代码演示)
- [5.3.2 最终效果呈现](#5.3.2 最终效果呈现)
- [5.4 进度条(两种方式,这里只演示后一种)](#5.4 进度条(两种方式,这里只演示后一种))
-
- [5.4.1 Makefile](#5.4.1 Makefile)
-
- [5.4.2 Process.h](#5.4.2 Process.h)
- [5.4.3 Process.c](#5.4.3 Process.c)
- [5.4.4 main.c](#5.4.4 main.c)
- [5.5 数据流动示意图](#5.5 数据流动示意图)
- [5.6 效果演示](#5.6 效果演示)
-
- [5.6.1 静态效果](#5.6.1 静态效果)
- [5.6.2 动态效果](#5.6.2 动态效果)
- 结尾

5 ~> Linux中的第一个系统程序:进度条
5.1 两个储备知识:回车换行 / 缓冲区
5.1.1 回车和换行是一码事吗?
回车和换行不是一码事。
这是一张普通的作文纸,每次我们写完一行,都要从下一行开头开始继续往下写,写完一段,都要新起一行------

如下图,键盘、打字机上面都有回车键------


为什么说回车和换行不是一回事呢?
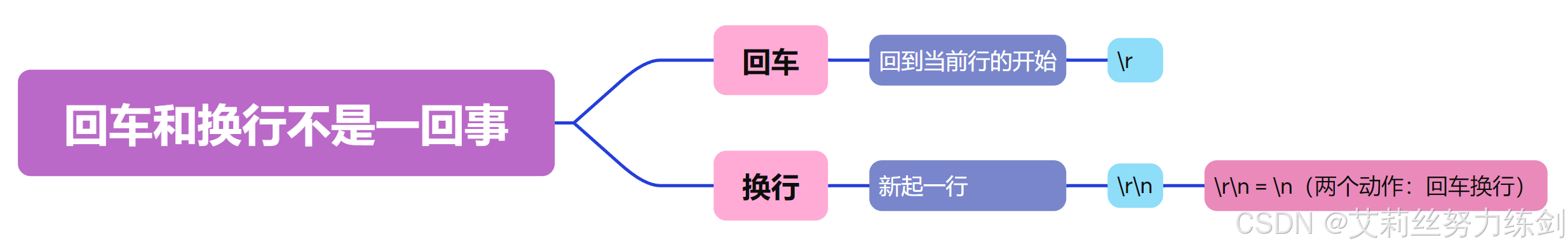
是的,回车换行是两个动作,\r是回车,\n是换行(和\r\n是一样的),在C/C++里面\n(C)、std::endl(C++)是把两个动作(回车和换行)合写成一个一个了。
5.1.2 缓冲区
bash
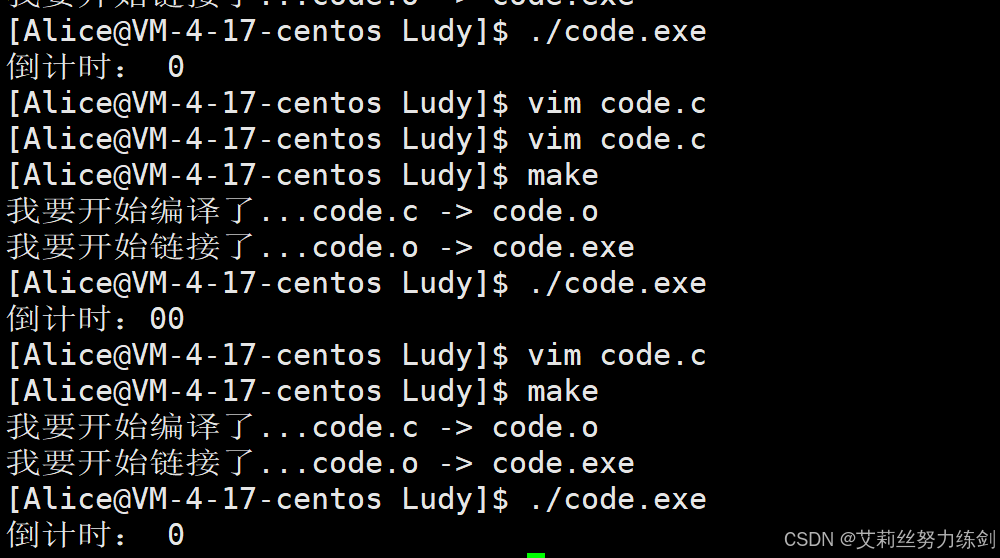
[Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$ vim code.c
[Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$ make
我要开始编译了...code.c -> code.o
我要开始链接了...code.o -> code.exe
[Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$ ./code.exe
hello world![Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$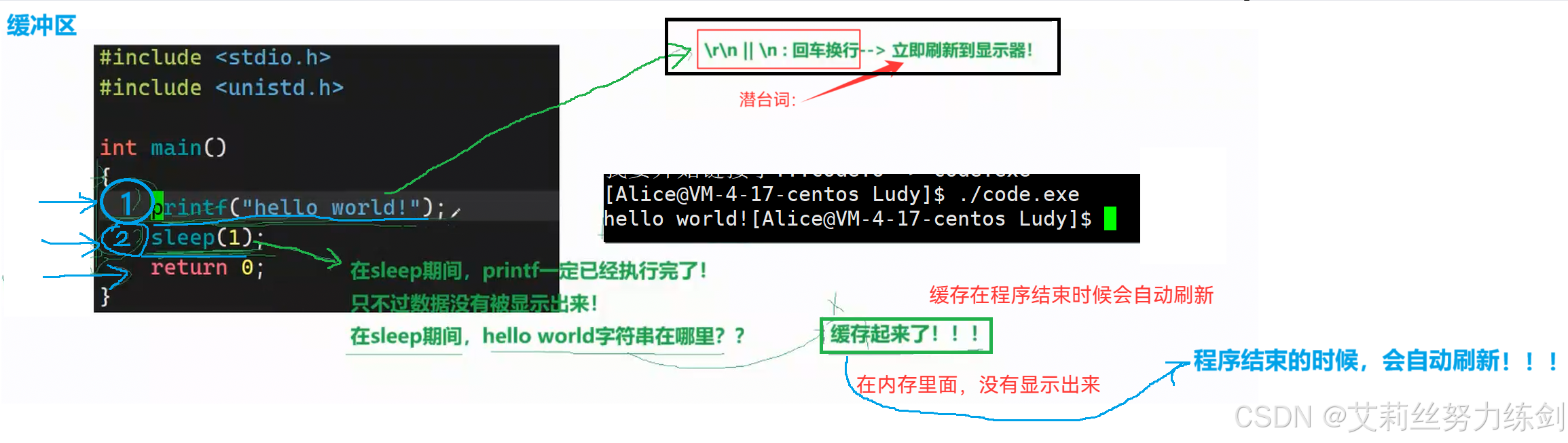
这里就是字符位数不够,右对齐了------
bash
fflush(stdout); # 强制刷新缓冲区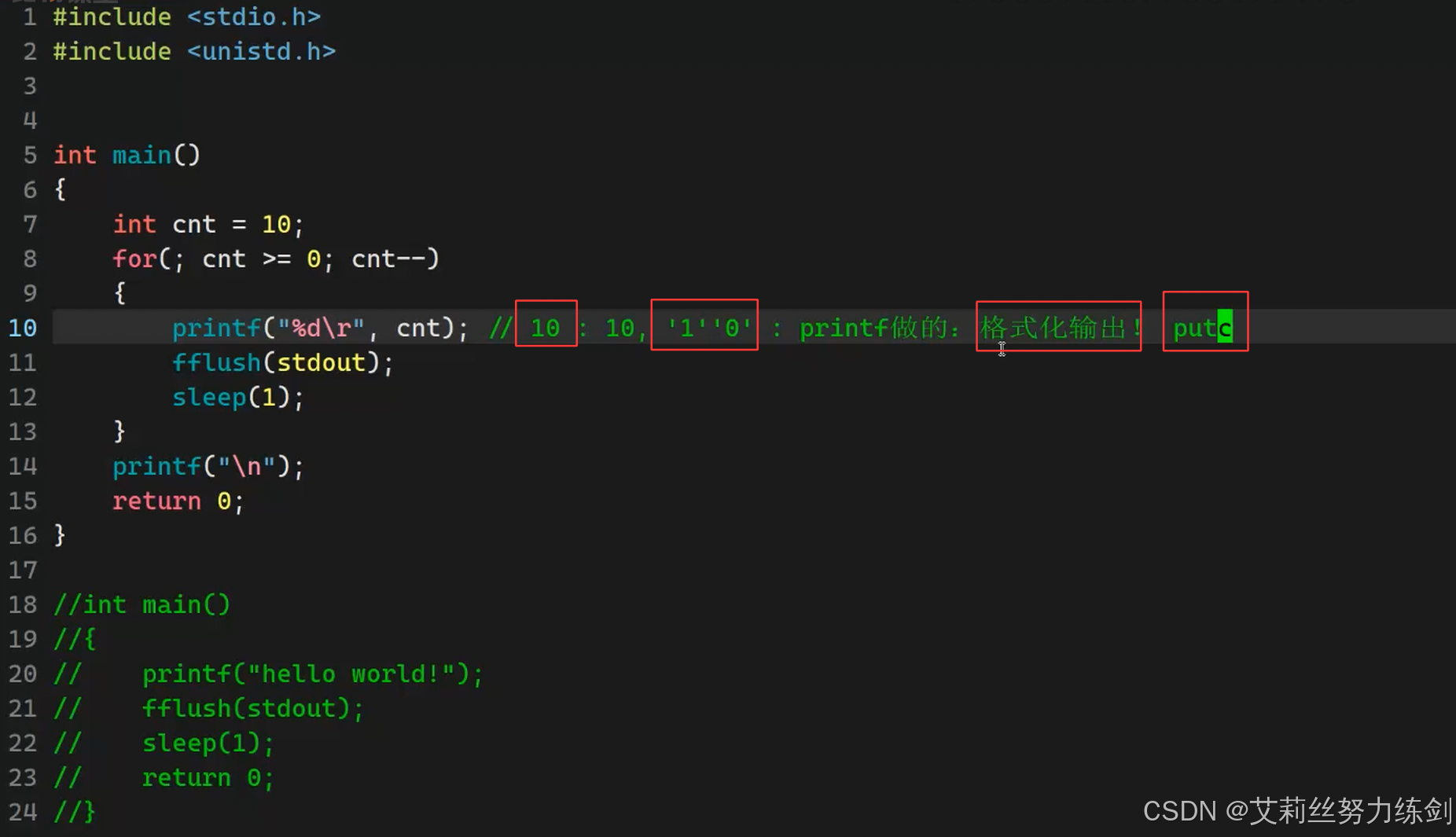
5.2 观察:行缓冲区
下面的代码会有哪些现象?
bash
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello Alice!\n");
sleep(3);
return 0;
}
bash
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello Alice!");
sleep(3);
return 0;
}
bash
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello Alice!");
fflush(stdout);
sleep(3);
return 0;
}5.3 练练手:demo:光标快速回退,完成倒计时功能
5.3.1 代码演示
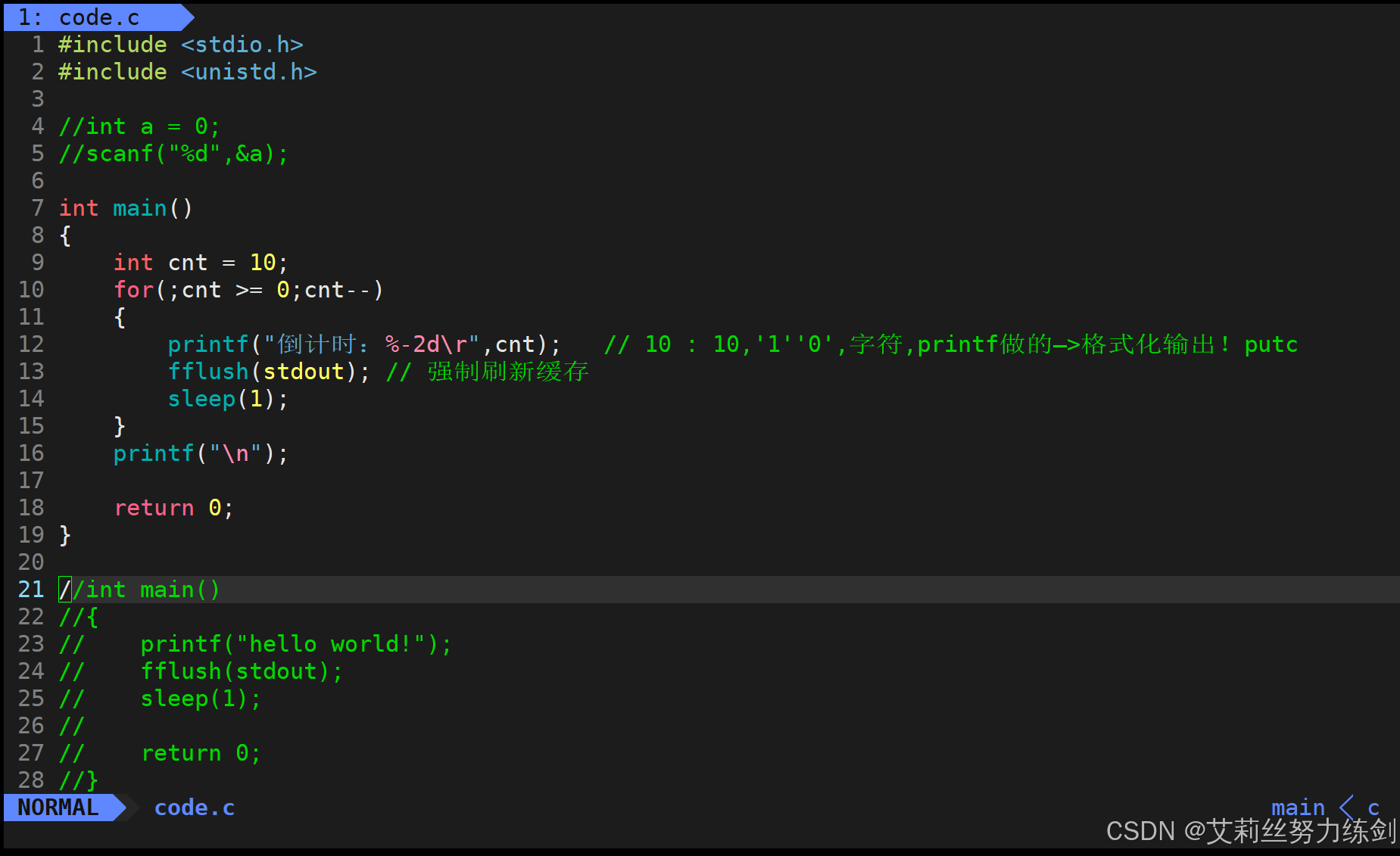
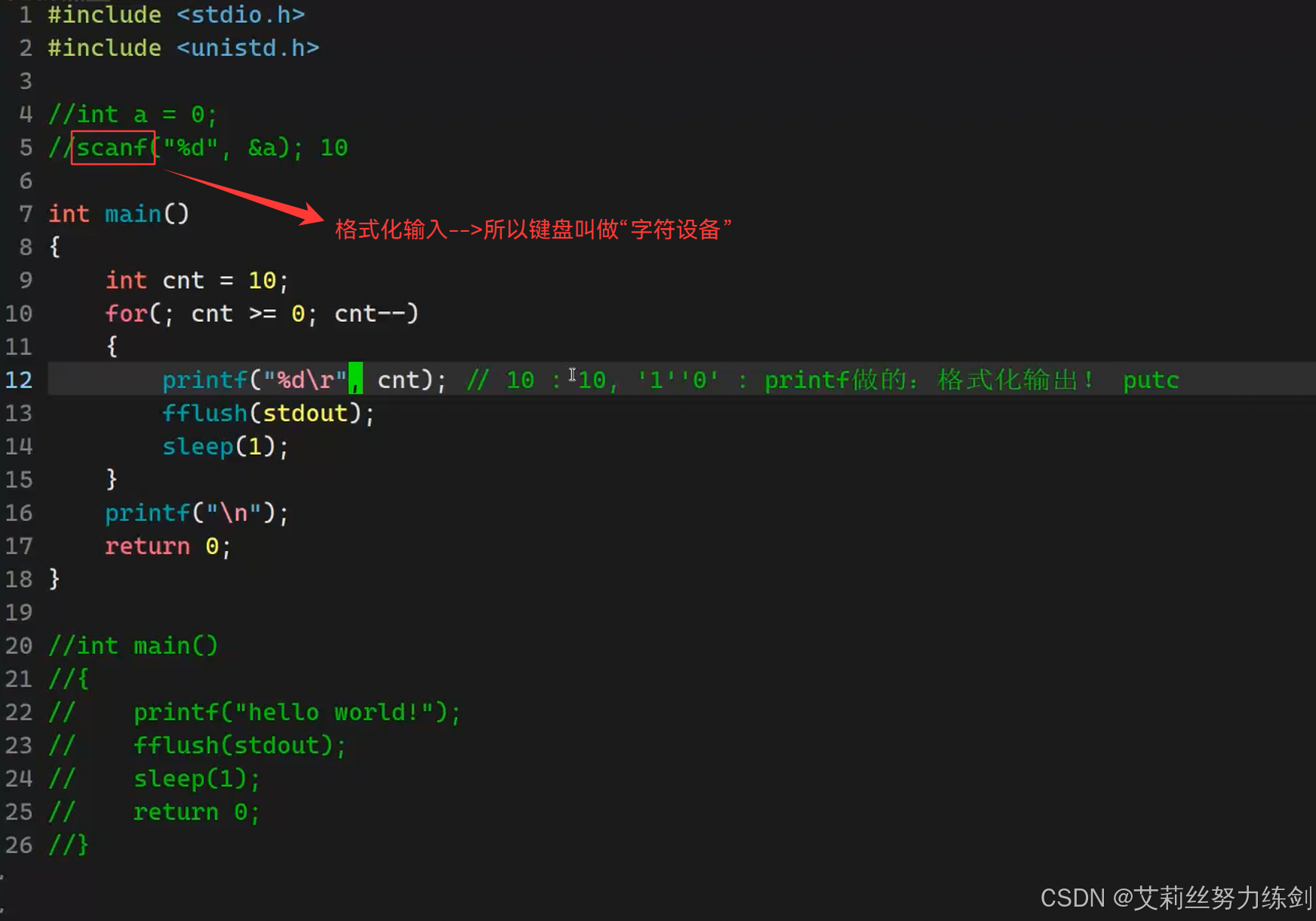
bash
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 //int a = 0;
5 //scanf("%d",&a);
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 int cnt = 10;
10 for(;cnt >= 0;cnt--)
11 {
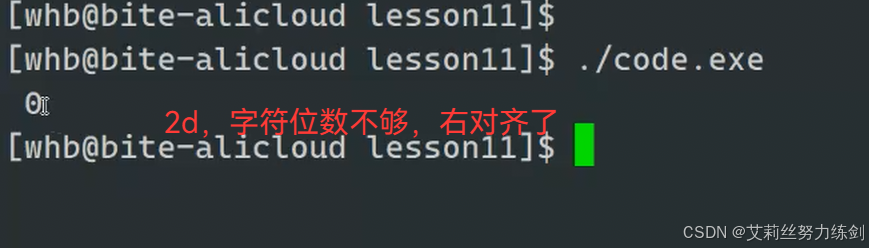
12 printf("倒计时:%-2d\r",cnt); // 10 : 10,'1''0',字符,printf做的--->格式化输出!putc
13 fflush(stdout); // 强制刷新缓存
14 sleep(1);
15 }
16 printf("\n");
17
18 return 0;
19 }
20
21 //int main()
22 //{
23 // printf("hello world!");
24 // fflush(stdout);
25 // sleep(1);
26 //
27 // return 0;
28 //} 5.3.2 最终效果呈现
bash
[Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$ make
我要开始编译了...code.c -> code.o
我要开始链接了...code.o -> code.exe
[Alice@VM-4-17-centos Ludy]$ ./code.exe
倒计时:0 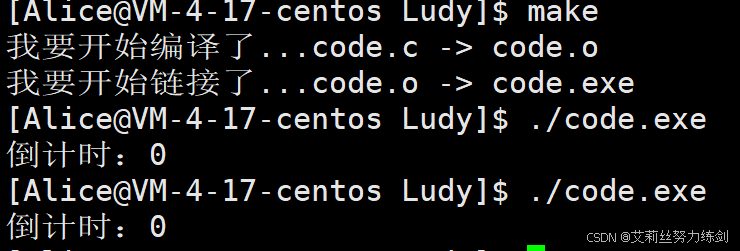
5.4 进度条(两种方式,这里只演示后一种)
进度条是用户界面中常见的元素,用于直观展示任务的完成进度。接下来,艾莉丝会介绍如何使用C语言在Linux操作系统中(centos版本)实现一个功能完整的进度条------也是我们介绍的Linux中的第一个系统程序。
5.4.1 Makefile
bash
1 Bin=process_bar
2 Cc=gcc
3 Src=$(wildcard *.c)
4 Obj=$(Src:.c=.o)
5
6 # @:不回显
7
8 $(Bin):$(Obj)
9 @echo "$^ link to $@"
10 @$(Cc) -o $@ $^
11 %.o:%.c
12 @echo "compling $< to $@"
13 @$(Cc) -c $<
14
15 .PHONY:clean
16 clean:
17 @echo "Clean Project...Done"
18 @rm -f $(Obj) $(Bin)
19
20 .PHONY:Print
21 Print:
22 @echo $(Bin)
23 @echo $(Cc)
24 @echo $(Src)
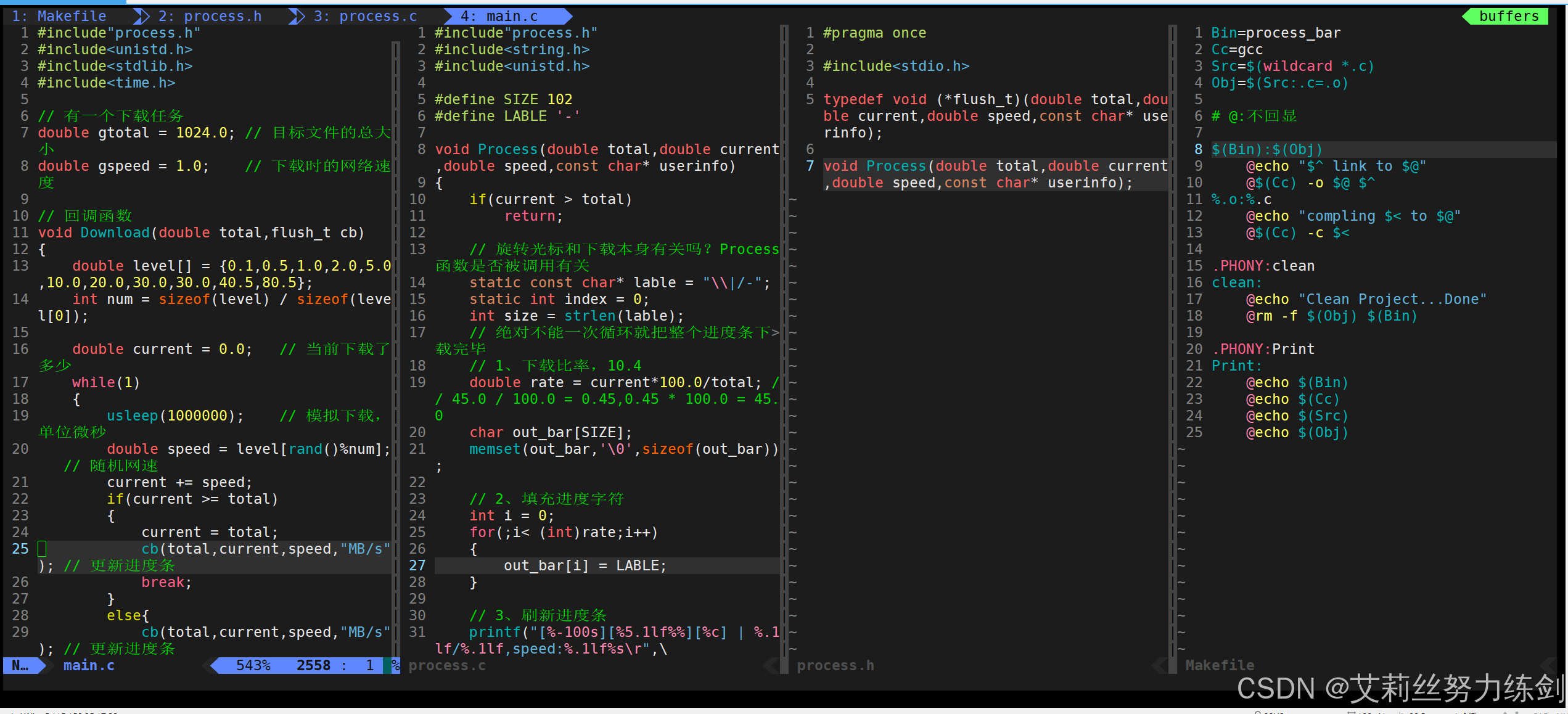
25 @echo $(Obj)5.4.2 Process.h
定义函数指针类型
flush_t,支持回调机制。声明进度条显示函数接口。
total - 总任务量:表示需要完成的全部工作量;
current - 当前完成量:表示已经完成的工作量;
speed - 当前速度:表示单位时间内完成的工作量;
userinfo - 用户信息:这里表示速度单位:"MB/s"
bash
1 //#ifndef PROCESS_H
2 //#define PROCESS_H
3 //
4 //#include<stdio.h>
5 //
6 //// ANSI 颜色代码
7 //#define COLOR_RED "\033[31m"
8 //#define COLOR_GREEN "\033[32m"
9 //#define COLOR_YELLOW "\033[33m"
10 //#define COLOR_BLUE "\033[34m"
11 //#define COLOR_MAGENTA "\033[35m"
12 //#define COLOR_CYAN "\033[36m"
13 //#define COLOR_RESET "\033[0m"
14 //
15 //typedef void (*flush_t)(double total,double current,double speed,const char* userinfo);
16 //
17 //void Process(double total,double current,double speed,const char* userinfo);
18 //
19 //#endif
20
21 #ifndef PROCESS_H
22 #define PROCESS_H
23
24 // ANSI 颜色代码
25 #define COLOR_RED "\033[31m"
26 #define COLOR_GREEN "\033[32m"
27 #define COLOR_YELLOW "\033[33m"
28 #define COLOR_BLUE "\033[34m"
29 #define COLOR_MAGENTA "\033[35m"
30 #define COLOR_CYAN "\033[36m"
31 #define COLOR_RESET "\033[0m"
32
33 typedef void (*flush_t)(double total,double current,double speed,const char* userinfo);
34
35 void Process(double total,double current,double speed,const char* userinfo);
36
37 #endif 5.4.3 Process.c
1、 百分比计算: current * 100.0 / total
2、 进度条填充: 使用循环填充 - 字符
3、 旋转光标: 通过字符序列|\\-/实现动画效果
4、 实时刷新: 使用\r回车符和fflush(stdout)实现原地更新
bash
1 #include "process.h"
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5
6 // 如果头文件中没有定义颜色,则在这里定义
7 #ifndef COLOR_RED
8 #define COLOR_RED "\033[31m"
9 #define COLOR_GREEN "\033[32m"
10 #define COLOR_YELLOW "\033[33m"
11 #define COLOR_BLUE "\033[34m"
12 #define COLOR_MAGENTA "\033[35m"
13 #define COLOR_CYAN "\033[36m"
14 #define COLOR_RESET "\033[0m"
15 #endif
16
17 #define SIZE 102
18 #define LABEL '='
19
20 void Process(double total, double current, double speed, const char* userinfo)
21 {
22 if(current > total)
23 return;
24
25 // 旋转光标
26 static const char* lable = "|/-\\";
27 static int index = 0;
28 int size = strlen(lable);
29
30 // 下载比率
31 double rate = current * 100.0 / total;
32 char out_bar[SIZE];
33 memset(out_bar, '\0', sizeof(out_bar));
34
35 // 填充进度字符
36 int i = 0;
37 int bar_length = (int)rate;
38 if(bar_length > 100) bar_length = 100;
39 for(; i < bar_length; i++)
40 {
41 out_bar[i] = LABEL;
42 }
43
44 // 选择颜色基于进度
45 const char* color;
46 if(rate < 30.0)
47 color = COLOR_RED;
48 else if(rate < 70.0)
49 color = COLOR_YELLOW;
50 else
51 color = COLOR_GREEN;
52
53 // 修复:在 printf 开头添加颜色变量
54 // 刷新进度条 - 使用 \r 确保不换行
55 printf("\r[%-100s] %5.1f%% [%c] %.1f/%.1f speed:%.1f %s",
56 out_bar, rate, lable[index], current, total, speed, userinfo);
57 fflush(stdout);
58
59 index++;
60 index %= size;
61
62 // 进度条完成,记得换行
63 if(current >= total)
64 {
65 printf("\n");
66 }
67 }
68
69 //#include"process.h"
70 //#include<stdlib.h>
71 //#include<string.h>
72 //#include<stdio.h>
73 //#include<unistd.h>
74 //
75 //#define SIZE 103
76 //#define LABLE '='
77 //
78 //void Process(double total,double current,double speed,const char* userinfo)
79 //{
80 // if(current > total)
81 // return;
82 //
83 // // 旋转光标和下载本身有关吗?Process函数是否被调用有关
84 // static const char* lable = "|/-\\";
85 // static int index = 0;
86 // int size = strlen(lable);
87 // // 绝对不能一次循环就把整个进度条下载完毕
88 // // 1、下载比率,10.4
89 // double rate = current*100.0/total; // 45.0 / 100.0 = 0.45,0.45 * 100.0 = 45.0
90 // char out_bar[SIZE];
91 // memset(out_bar,'\0',sizeof(out_bar));
92 //
93 // // 2、填充进度字符
94 // int i = 0;
95 // int bar_length = (int)rate;
96 // if(bar_length > 100) bar_length = 100;
97 // for(; i < bar_length; i++)
98 //
99 // out_bar[i] = LABLE;
100 // }
101 //
102 // // 选择颜色基于进度
103 // const char* color;
104 // if(rate < 30.0)
105 // color = COLOR_RED;
106 // else if(rate < 70.0)
107 // color = COLOR_YELLOW;
108 // else
109 // color = COLOR_GREEN;
110 //
111 // // 3、刷新进度条
112 // printf("[%-100s][%5.1lf%%][%c] | %.1lf/%.1lf,speed:%.1lf%s\r",\
113 // color, out_bar,rate,lable[index],current,total,speed,userinfo,COLOR_RESET);
114 //
115 // fflush(stdout);
116 // index++;
117 // index %= size;
118 //
119 // // 4、进度条完成,记得换行
120 // if(current >= total)
121 // printf("\r\n");
122 // //printf("\n");
123 //}
124
125 //// 进度条的版本一-->version1版本
126 //void Processversion1()
127 //{
128 // const char* lable = "\\|/-";
129 // int len = strlen(lable);
130 // char out_bar[SIZE];
131 // memset(out_bar,'\0',sizeof(out_bar));
132 // while(cnt <= 100)
133 // {
134 // printf("[%-100s][%3d%%][%c]\r",out_bar,cnt,lable[cnt % len]);
135 // fflush(stdout);
136 // out_bar[cnt] = LABLE;
137 // cnt++;
138 //
139 // usleep(30000);
140 // }
141 //
142 // printf("\r\n");
143 //}
144
145 //void Process()
146 //{
147 // const char* lable[] = {
148 // "loading.",
149 // "loading..",
150 // "loading...",
151 // };
152 //
153 // int size = sizeof(lable) / sizeof(lable[0]);
154 // int cnt = 0;
155 // char out_bar[SIZE];
156 // memset(out_bar,'\0',sizeof(out_bar));
157 // while(cnt <= 100)
158 // {
159 // printf("[%-100s][%3d%%][%-7s]\r",out_bar,cnt,lable[cnt%size]);
160 // fflush(stdout);
161 // out_bar[cnt] = LABLE;
162 // cnt++;
163 //
164 // usleep(1000000);
165 // }
166 // printf("\r\n");
167 //}5.4.4 main.c
bash
1 #include"process.h"
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<time.h>
5 #include<stdio.h>
6
7 // 有一个下载任务
8 double gtotal = 1024.0; // 目标文件的总大小
9 double gspeed = 1.0; // 下载时的网络速度
10
11 // 回调函数
12 void Download(double total,flush_t cb)
13 {
14 double level[] = {0.5,1.0,2.0,5.0,10.0,20.0,30.0,30.0,40.5,80.5};
15 int num = sizeof(level) / sizeof(level[0]);
16
17 double current = 0.0; // 当前下载了多少
18 while(1)
19 {
20 usleep(100000); // 模拟下载,单位微秒
21 double speed = level[rand()%num]; // 随机网速
22 current += speed;
23 if(current >= total)
24 {
25 current = total;
26 cb(total,current,speed,"MB/s"); // 更新进度条
27 break;
28 }
29 else{
30 cb(total,current,speed,"MB/s"); // 更新进度条
31 }
32 }
33 }
34
35 // 添加进度条色块
36
37 int main()
38 {
39 //// version
40 // Process(); // 进度条程序
41
42 srand(time(NULL));
43 // 多个不同大小程序的下载
44 printf("download:\n");
45 Download(gtotal,Process);
46
47 printf("download:\n");
48 Download(120.0,Process);
49
50 printf("download:\n");
51 Download(11.8,Process);
52
53 printf("download:\n");
54 Download(78.9,Process);
55
56 printf("download:\n");
57 Download(900.0,Process);
58
59
60 return 0;
61 }5.5 数据流动示意图
bash
初始化阶段
↓
total = 1024.0 (总任务量)
↓
循环更新阶段
↓
current = 0 → 逐渐增加 → total (当前进度)
speed = 随机值 (实时速度)
userinfo = "MB/s" (单位信息)
↓
显示阶段
↓
[----------] [45.5%] [\] | 465.9/1024.0, speed:25.3MB/s5.6 效果演示
5.6.1 静态效果

5.6.2 动态效果
到博客创作玩之前,艾莉丝只写了无色的进度条的版本
进度条(无色)
结尾
uu们,本文的内容到这里就全部结束了,艾莉丝再次感谢您的阅读!
结语:希望对学习Linux相关内容的uu有所帮助,不要忘记给博主"一键四连"哦!
往期回顾:
【Linux基础开发工具 (五)】详解自动化构建:make / Makefile
🗡博主在这里放了一只小狗,大家看完了摸摸小狗放松一下吧!🗡 ૮₍ ˶ ˊ ᴥ ˋ˶₎ა
