代码仓库:https://github.com/google/adk-go
使用教程:https://google.github.io/adk-docs/
中文文档:https://adk.wiki/get-started/go/
本教程示例代码:<github.com/raoxiaoya/learn-adk>
其他参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1976206965152690702
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dLQrprIK8e7QE47OFy3FjA
从原理到实践:万字长文深入浅出教你优雅开发复杂AI Agent 写的很好
开发环境
bash
go get google.golang.org/adkImportant Links: Docs & Samples & Python ADK & Java ADK & ADK Web.
bash
Go >= 1.24.4
Adk-v0.2Google AI Studio 与 Google Cloud Vertex AI 的区别
| 特性 | Google AI Studio | Vertex AI |
|---|---|---|
| 定位 | 快速原型与实验(开发者友好) | 企业级生产部署(全生命周期 MLOps) |
| 目标用户 | 开发者、研究人员、初学者 | 数据科学家、ML 工程师、企业团队 |
| 是否需要 GCP 项目 | ❌ 不强制(可用 Gmail 登录) | ✅ 必须绑定 Google Cloud 项目 |
| 计费方式 | 使用免费配额或 Google AI API 配额(按调用量计费) | 通过 Google Cloud 账单 计费(更细粒度控制) |
| 是否属于 Google Cloud | 否(独立 Web 工具) | 是(Google Cloud 的核心 AI 服务) |
目前Go版本只能使用Gemini模型,Python版本可以自定义模型。里面提到的类似于LiteLlm这种集成只适用于python这种弱类型编程语言,如果想使用Go+千问这种组合,暂时还实现不了。python版本提供了多种集成能力,但是Go版本没有同步提供。
Using Different Models with ADK
Agent Development Kit (ADK) 对接阿里百炼平台 python版本
通过 Google AI Studio 获取 API KEY:https://aistudio.google.com/app/api-keys
简单的 llmAgent
go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"learn-adk/config"
"log"
"os"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/cmd/launcher"
"google.golang.org/adk/cmd/launcher/full"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool/geminitool"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
RunAgent()
}
func RunAgent() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, "gemini-2.5-pro", &genai.ClientConfig{
APIKey: config.APIKey,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
timeAgent, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "hello_time_agent",
Model: model,
Description: "Tells the current time in a specified city.",
Instruction: "You are a helpful assistant that tells the current time in a city.",
Tools: []tool.Tool{
geminitool.GoogleSearch{},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
config := &launcher.Config{
AgentLoader: agent.NewSingleLoader(timeAgent),
}
l := full.NewLauncher()
if err = l.Execute(ctx, config, os.Args[1:]); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Run failed: %v\n\n%s", err, l.CommandLineSyntax())
}
}说明
name(必填): 每个智能体都需要一个唯一的字符串标识符。这个name对内部操作至关重要,尤其是在多智能体系统中,智能体需要相互引用或委派任务。选择一个能反映智能体功能的描述性名称(例如,customer_support_router,billing_inquiry_agent)。避免使用像user这样的保留名称。description(可选,多智能体推荐): 提供一个简洁的智能体能力摘要。这个描述主要由其他 LLM 智能体用来确定是否应该将任务路由到这个智能体。使其足够具体以区分它与其他智能体(例如,"处理关于当前账单明细的查询",而不仅仅是"账单智能体")。model(必填): 指定将为此智能体的推理提供支持的底层 LLM。这是一个字符串标识符,如"gemini-2.0-flash"。模型的选择会影响智能体的能力、成本和性能。查看模型页面了解可用选项和考虑因素。
instruction指令
- 其核心任务或目标。
- 其个性或角色(例如,"你是一个乐于助人的助手","你是一个机智的海盗")。
- 对其行为的约束(例如,"只回答关于 X 的问题","永远不要透露 Y")。
- 如何以及何时使用其
tools。你应该解释每个工具的用途以及应该在什么情况下调用它,补充工具本身的任何描述。 - 其输出的期望格式(例如,"以 JSON 形式回应","提供一个项目符号列表")。
有效指令的技巧:
- 清晰明确: 避免含糊不清。清楚地说明期望的行动和结果。
- 使用 Markdown: 使用标题、列表等提高复杂指令的可读性。
- 提供示例(少样本): 对于复杂任务或特定输出格式,直接在指令中包含示例。
- 指导工具使用: 不仅仅是列出工具;解释智能体何时 和为什么应该使用它们。
IncludeContents :是否包含对话的上下文,默认值是 default,也就是包含,你也可以设置为 none,也就是不包含。
可能的报错
bash
AGENT_ERROR: doRequest: error sending request: Post "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-pro-preview:streamGenerateContent?alt=sse": EOF
---- 网络问题
AGENT_ERROR: doRequest: error sending request: Post "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-pro-preview:streamGenerateContent?alt=sse": dial tcp
142.250.69.170:443: i/o timeout
---- 网络问题
AGENT_ERROR: Error 429, Message: You exceeded your current quota, please check your plan and billing details.
---- 当前模型需要付费或额度用完,比如 gemini-3-pro 和 gemini-3-pro-preview 应该是付费的。
AGENT_ERROR: Error 404, Message: models/gemini-3 is not found for API version v1beta, or is not supported for generateContent. Call ListModels to see the list of available
models and their supported methods., Status: NOT_FOUND, Details: []
----不支持的模型名称最终选择gemini-2.5-pro模型才能运行成功。
bash
> go run agent.go
User -> what can you do?
Agent -> I can tell you the current time in any city.
User -> what time it is in London?
Agent -> The current time in London is 2:57 AM. The time zone in London is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
User -> what time it is in new york?
Agent -> The current time in New York is 9:59 PM. The time zone is Eastern Standard Time (EST).与手机上的世界时间基本一致,说明它的确调用了 Google Search。
默认情况下,智能体就是流式输出的,不用刻意设置。
Gemini API (就是 genai包 )文档:https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs?hl=zh-cn
那这个API KEY能支持调用哪些模型呢
go
func ListModels() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, &genai.ClientConfig{
APIKey: "AIzaSyBXW7R7Hg8rPqQkazSBbLnfH9HSimMvQ8c",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create client: %v", err)
}
models := client.Models.All(ctx)
for m, e := range models {
if e != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v\n", e)
continue
}
log.Printf("Model: %s\n", m.Name)
}
}
bash
Model: models/embedding-gecko-001
Model: models/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-03-25
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash
Model: models/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06
Model: models/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-06-05
Model: models/gemini-2.5-pro
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-exp
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-001
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-exp-image-generation
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-lite-001
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-lite
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-lite-preview-02-05
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-lite-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.0-pro-exp
Model: models/gemini-2.0-pro-exp-02-05
Model: models/gemini-exp-1206
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-thinking-exp-01-21
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-thinking-exp
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-thinking-exp-1219
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-tts
Model: models/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-tts
Model: models/learnlm-2.0-flash-experimental
Model: models/gemma-3-1b-it
Model: models/gemma-3-4b-it
Model: models/gemma-3-12b-it
Model: models/gemma-3-27b-it
Model: models/gemma-3n-e4b-it
Model: models/gemma-3n-e2b-it
Model: models/gemini-flash-latest
Model: models/gemini-flash-lite-latest
Model: models/gemini-pro-latest
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-lite
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-image
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-09-2025
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-lite-preview-09-2025
Model: models/gemini-3-pro-preview
Model: models/gemini-3-pro-image-preview
Model: models/nano-banana-pro-preview
Model: models/gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.5-computer-use-preview-10-2025
Model: models/embedding-001
Model: models/text-embedding-004
Model: models/gemini-embedding-exp-03-07
Model: models/gemini-embedding-exp
Model: models/gemini-embedding-001
Model: models/aqa
Model: models/imagen-4.0-generate-preview-06-06
Model: models/imagen-4.0-ultra-generate-preview-06-06
Model: models/imagen-4.0-generate-001
Model: models/imagen-4.0-ultra-generate-001
Model: models/imagen-4.0-fast-generate-001
Model: models/veo-2.0-generate-001
Model: models/veo-3.0-generate-001
Model: models/veo-3.0-fast-generate-001
Model: models/veo-3.1-generate-preview
Model: models/veo-3.1-fast-generate-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.0-flash-live-001
Model: models/gemini-live-2.5-flash-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-live-preview
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-native-audio-latest
Model: models/gemini-2.5-flash-native-audio-preview-09-2025即便是这些列出的模型,也不是所以的功能都能免费用,具体可以看价格,比如 Gemini-2.5-pro
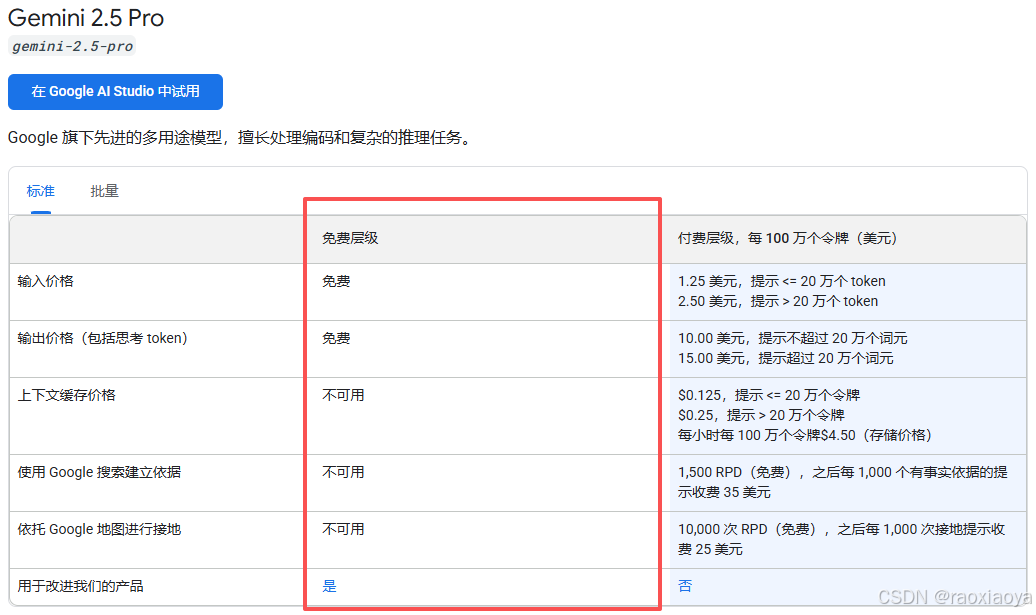
另外,免费调用API还有频率的限制
RPM 每分钟请求数;TPM 每分钟 token 数(输入);RPD 每日请求数
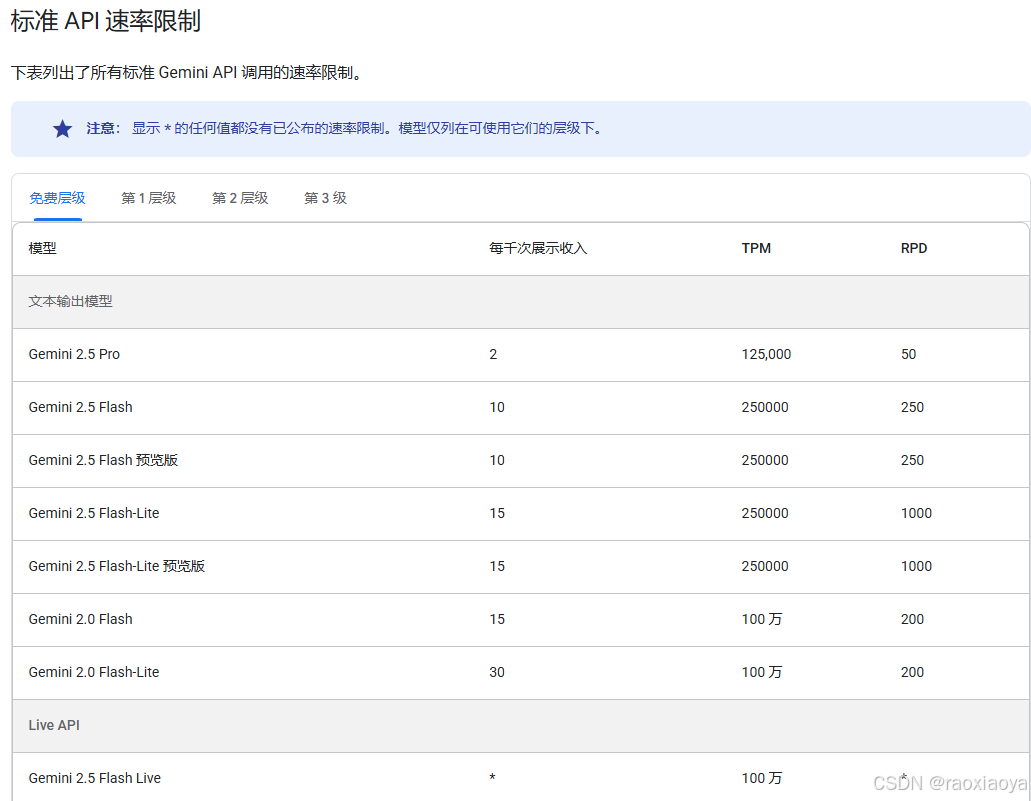
genai.Client.Models 提供的能力
go
func (m Models) All(ctx context.Context) iter.Seq2[*Model, error]
func (m Models) ComputeTokens(ctx context.Context, model string, contents []*Content, config *ComputeTokensConfig) (*ComputeTokensResponse, error)
func (m Models) CountTokens(ctx context.Context, model string, contents []*Content, config *CountTokensConfig) (*CountTokensResponse, error)
func (m Models) Delete(ctx context.Context, model string, config *DeleteModelConfig) (*DeleteModelResponse, error)
func (m Models) EditImage(ctx context.Context, model string, prompt string, referenceImages []ReferenceImage, config *EditImageConfig) (*EditImageResponse, error)
func (m Models) EmbedContent(ctx context.Context, model string, contents []*Content, config *EmbedContentConfig) (*EmbedContentResponse, error)
func (m Models) GenerateContent(ctx context.Context, model string, contents []*Content, config *GenerateContentConfig) (*GenerateContentResponse, error)
func (m Models) GenerateContentStream(ctx context.Context, model string, contents []*Content, config *GenerateContentConfig) iter.Seq2[*GenerateContentResponse, error]
func (m Models) GenerateImages(ctx context.Context, model string, prompt string, config *GenerateImagesConfig) (*GenerateImagesResponse, error)
func (m Models) GenerateVideos(ctx context.Context, model string, prompt string, image *Image, config *GenerateVideosConfig) (*GenerateVideosOperation, error)
func (m Models) GenerateVideosFromSource(ctx context.Context, model string, source *GenerateVideosSource, config *GenerateVideosConfig) (*GenerateVideosOperation, error)
func (m Models) Get(ctx context.Context, model string, config *GetModelConfig) (*Model, error)
func (m Models) List(ctx context.Context, config *ListModelsConfig) (Page[Model], error)
func (m Models) RecontextImage(ctx context.Context, model string, source *RecontextImageSource, config *RecontextImageConfig) (*RecontextImageResponse, error)
func (m Models) SegmentImage(ctx context.Context, model string, source *SegmentImageSource, config *SegmentImageConfig) (*SegmentImageResponse, error)
func (m Models) Update(ctx context.Context, model string, config *UpdateModelConfig) (*Model, error)
func (m Models) UpscaleImage(ctx context.Context, model string, image *Image, upscaleFactor string, config *UpscaleImageConfig) (*UpscaleImageResponse, error)Google Search 工具
https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/google-search?hl=zh-cn
"使用 Google 搜索建立依据"功能可将 Gemini 模型与实时网络内容相关联,并支持所有可用语言。这样一来,Gemini 就可以提供更准确的回答,并引用知识截止日期之后的可验证来源。
接地可帮助您构建能够执行以下操作的应用:
- 提高事实准确性:以真实世界的信息为依据生成回答,从而减少模型幻觉。
- 获取实时信息:回答有关近期活动和主题的问题。
- 提供引用:通过显示模型声明的来源来建立用户信任。
启用 google_search 工具后,模型会自动处理搜索、处理和引用信息的整个工作流程。
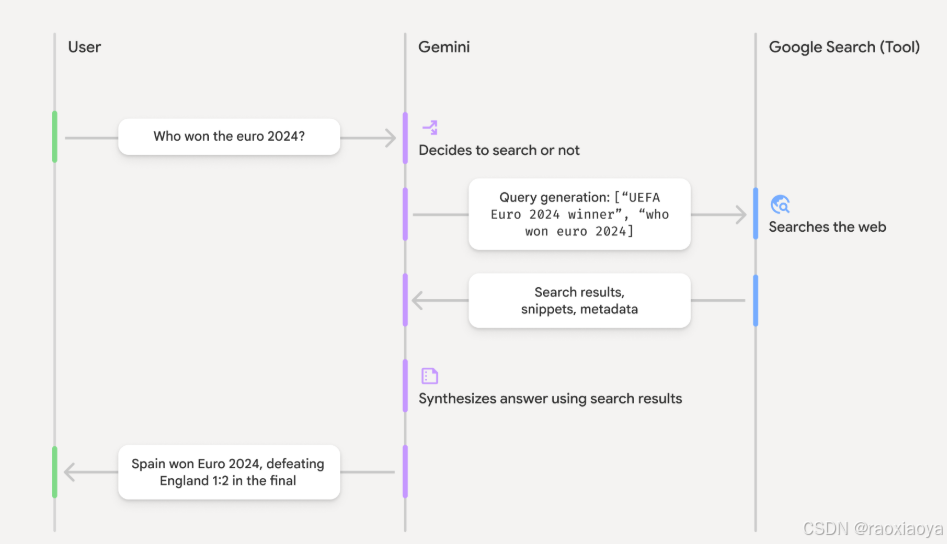
- 用户提示 :您的应用在启用
google_search工具的情况下,将用户提示发送到 Gemini API。 - 提示分析:模型分析提示,确定 Google 搜索是否可以改进回答。
- Google 搜索:如果需要,模型会自动生成一个或多个搜索查询并执行这些查询。
- 搜索结果处理:模型处理搜索结果,整合信息并生成回答。
- 以搜索结果为依据的回答 :API 会返回以搜索结果为依据的最终且用户友好的回答。此响应包含模型的文本回答以及
groundingMetadata,其中包含搜索查询、网页结果和引用。
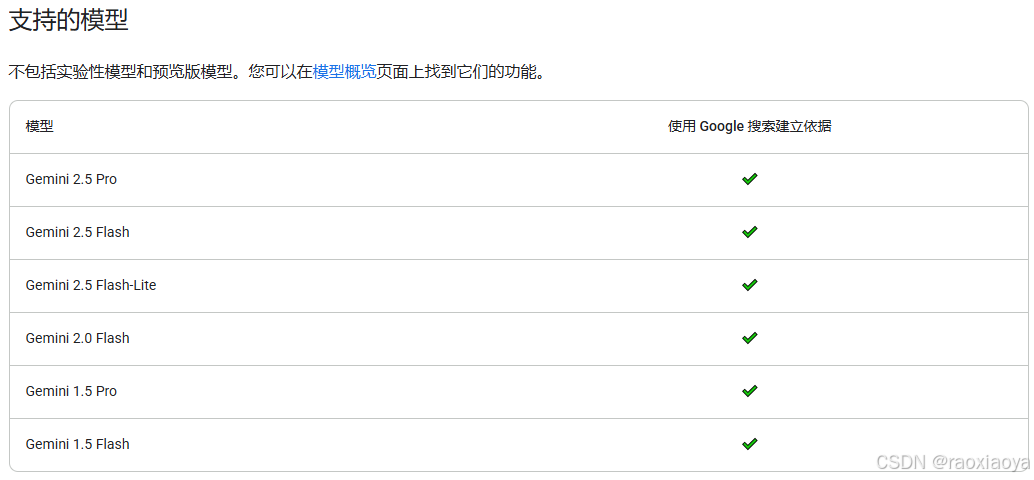
Google Search只支持部分模型
Google Search 并不一定是免费的,按照 Gemini-2.5-pro 的费用表来看,免费层级并不支持 Google Search,但是按照我的测试却是能有的,所以 Gemini 这个定价规则实在够乱的。
Google Map
https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/maps-grounding?hl=zh-cn
...
运行webui
bash
> go run agent.go web api webui
Web servers starts on http://localhost:8080
api: you can access API using http://localhost:8080/api
api: for instance: http://localhost:8080/api/list-apps
webui: you can access API using http://localhost:8080/ui/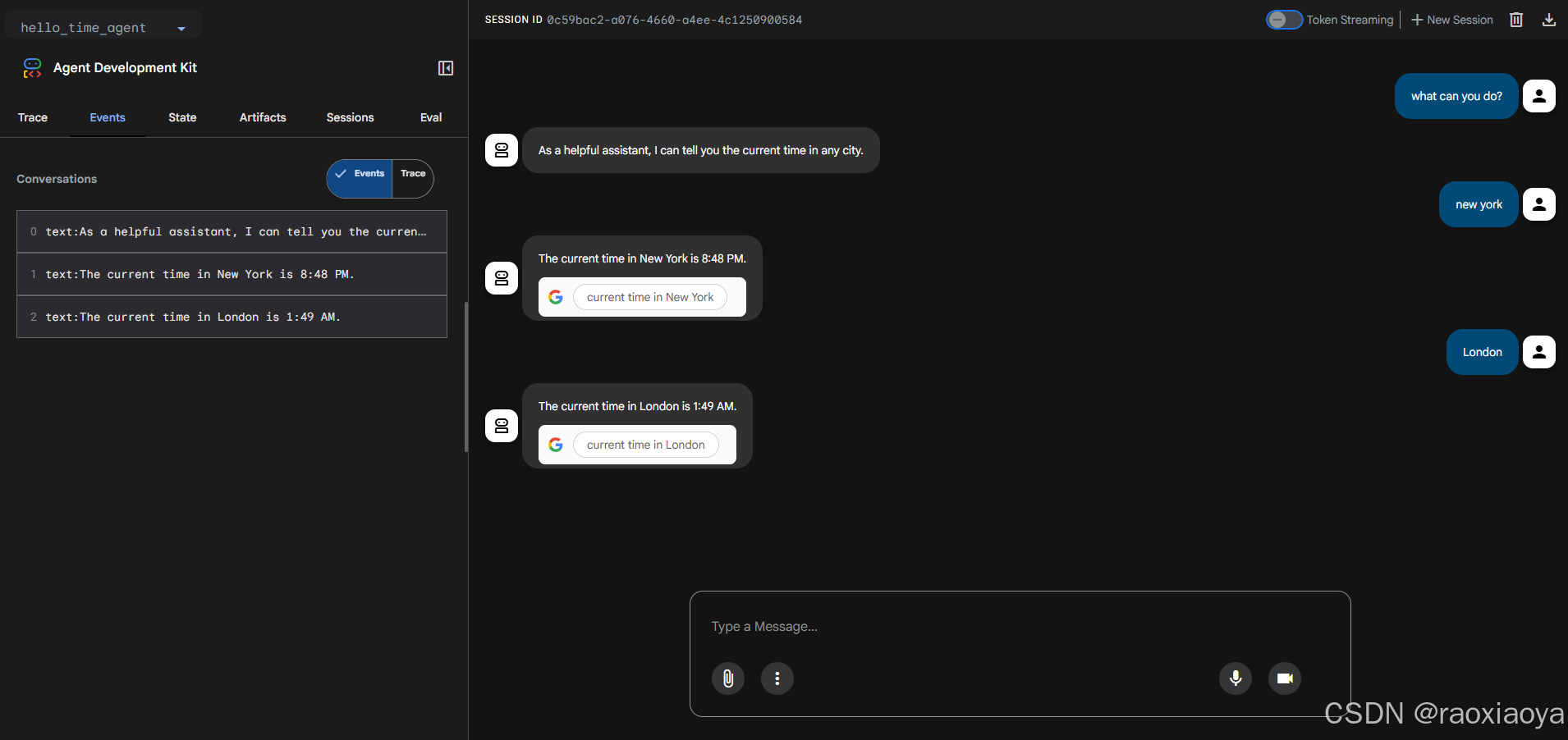
我们可以使用 Google Search 做更多的事情,比如 weather_time_agent
go
a, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "weather_time_agent",
Model: model,
Description: "Agent to answer questions about the time and weather in a city.",
Instruction: "Your SOLE purpose is to answer questions about the current time and weather in a specific city. You MUST refuse to answer any questions unrelated to time or weather.",
Tools: []tool.Tool{
geminitool.GoogleSearch{},
},
})
bash
User -> what can you do?
Agent -> I can tell you the current time and weather in a specific city.
User -> what time it is now in London?
Agent -> The current time in London, United Kingdom, is 07:46 AM. London observes Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
User -> what weather it is now in London?
Agent -> In London, United Kingdom, it is currently partly cloudy with a temperature of 39 °F (4 °C). It feels like 36 °F (2 °C). The humidity is around 96%.说到 tool,在 adk 中有两种,一种是 genai.Tool,比如上面说的Google Search和Google Map,它们是由genai来决定是否调用的;另一种是 adk 这边用户自定义的 functionTool,它们是由agent来调用的。
在一个agent下创建多个functionTool
go
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/cmd/launcher"
"google.golang.org/adk/cmd/launcher/full"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool/functiontool"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// 多工具智能体
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, "gemini-2.5-flash", &genai.ClientConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
weatherTool, err := GetWeather()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create weather tool: %v", err)
}
timeTool, err := GetCurrentTime()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create time tool: %v", err)
}
a, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "weather_time_agent",
Model: model,
Description: "Agent to answer questions about the time and weather in a city.",
Instruction: "You are a helpful agent who can answer user questions about the time and weather in a city.",
Tools: []tool.Tool{
weatherTool,
timeTool,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
config := &launcher.Config{
AgentLoader: agent.NewSingleLoader(a),
}
l := full.NewLauncher()
if err = l.Execute(ctx, config, os.Args[1:]); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Run failed: %v\n\n%s", err, l.CommandLineSyntax())
}
}
type Input struct {
City string `json:"city"`
}
type Output struct {
Status string `json:"status"`
Report string `json:"report"`
}
func GetWeather() (tool.Tool, error) {
handler := func(ctx tool.Context, input Input) (Output, error) {
if strings.ToLower(input.City) == "new york" {
return Output{
Status: "success",
Report: "The weather in New York is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees, Celsius (77 degrees Fahrenheit).",
}, nil
} else {
return Output{
Status: "error",
Report: "The weather information for " + input.City + " is not available.",
}, nil
}
}
weatherTool, err := functiontool.New(functiontool.Config{
Name: "GetWeather",
Description: "Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.",
}, handler)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
} else {
return weatherTool, nil
}
}
func GetCurrentTime() (tool.Tool, error) {
handler := func(ctx tool.Context, input Input) (Output, error) {
if strings.ToLower(input.City) == "new york" {
return Output{
Status: "success",
Report: "The current time in New York is " + time.Now().Format(time.DateTime),
}, nil
} else {
return Output{
Status: "error",
Report: "Sorry, I don't have timezone information for " + input.City + ".",
}, nil
}
}
timeTool, err := functiontool.New(functiontool.Config{
Name: "GetCurrentTime",
Description: "Returns the current time in a specified city.",
}, handler)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
} else {
return timeTool, nil
}
}
bash
User -> what can you do?
Agent -> I can tell you the current time and weather in a city.
User -> what weather it is now in London?
Agent -> I am sorry, I cannot get the weather for London.
User -> what weather it is now in new york?
Agent -> The weather in New York is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius (77 degrees Fahrenheit).
User -> what time it is now in London?
Agent -> Sorry, I don't have timezone information for London.
User -> what time it is now in New York?
Agent -> The current time in New York is 2025-12-03 17:36:37.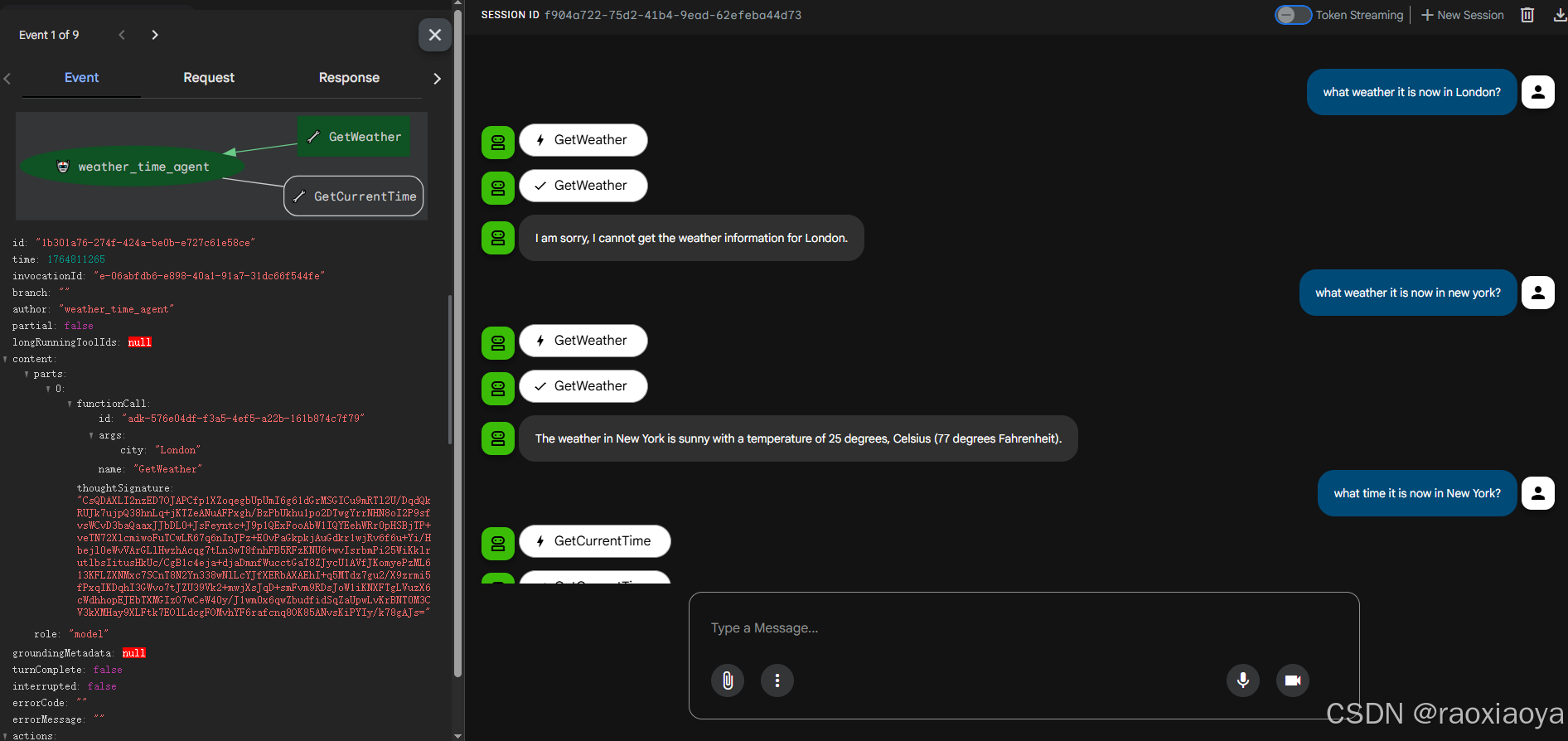
Planner
规划能力,思考能力,adk-go 暂不支持,
workflow Agent 工作流智能体
分为三种:
SequentialAgent顺序智能体:它按照列表中指定的顺序执行其子智能体。LoopAgent循环智能体:它循环(即迭代)执行其子智能体。它**_重复运行_一系列智能体**,执行指定次数的迭代或直到满足终止条件。ParallelAgent并行智能体:它并发执行其子智能体。这极大地加速了可以独立执行任务的工作流。
工作流的特点就是通过语义化的说明来知道agent去做特定的事情,这里面就存在好几个不确定性,首先是你表达的不确定性,其次是agent理解的不确定性,最后是agent执行的不确定性,这就导致了工作流的执行过程和执行结果并不是那么确定性,流程越长不确定性越高。
SequentialAgent
当调用 SequentialAgent 的 run_async() 方法时,它执行以下操作:
- 迭代: 它按照提供的顺序遍历
sub_agents列表。 - 子智能体执行: 对于列表中的每个子智能体,它调用该子智能体的
run_async()方法。
SequentialAgent 将相同的 InvocationContext 传递给其每个子智能体。这意味着它们都共享相同的会话状态,包括临时(temp:)命名空间,使得在单个轮次内的步骤之间传递数据变得容易。
每个子智能体的输出先存储在 state 中的 OutputKey,然后下一步的智能体从 OutputKey 读取。
示例:Code Development Pipeline
- 代码编写智能体: 一个基于规范生成初始代码的
LlmAgent。 - 代码审查智能体: 一个检查生成代码中的错误、风格问题和是否遵守最佳实践的
LlmAgent。它接收代码编写智能体的输出。 - 代码重构智能体: 一个接收已审查的代码(和审查者的评论)并重构它以提高质量和解决问题的
LlmAgent。
提问之后,它有三次输出,第一次是 codeWriterAgent 的输出,第二次是 codeReviewerAgent 的评价;第三次是最终的输出。当然也可以要求前两次不用输出。
从稳定性来看,cli 比 webui 稳定一些。
LoogAgent
示例:你想构建一个可以生成食物图像的智能体,但有时当你想生成特定数量的物品(例如 5 个香蕉)时,它生成的图像中包含了不同数量的物品(例如一张有 7 个香蕉的图像)。你有两个工具:generate_image、count_food_items。因为你想不断生成图像,直到它正确生成指定数量的物品,或者达到一定的迭代次数,所以你应该使用 LoopAgent 构建你的智能体。
当调用 LoopAgent 的 run_async() 方法时,它执行以下操作:
-
子智能体执行: 它_按顺序_遍历
sub_agents列表。对于_每个_子智能体,它调用该智能体的run_async()方法。 -
终止检查:
至关重要的是 ,
LoopAgent本身_不_固有地决定何时停止循环。你_必须_实现一个终止机制以防止无限循环。常见的策略包括:max_iterations:在LoopAgent中设置最大迭代次数。循环将在达到该迭代次数后终止。- 来自子智能体的信号:设计一个或多个子智能体来评估条件(例如,"文档质量是否足够好?","是否已达成共识?")。如果满足条件,子智能体可以发出终止信号(例如,通过触发自定义事件、在共享上下文中设置标志,或返回特定值)。
示例:迭代文档改进
- 编写智能体: 一个生成或改进主题草稿的
LlmAgent。 - 评论智能体: 一个对草稿进行评论,识别需要改进的领域的
LlmAgent。
ParallelAgent
当调用 ParallelAgent 的 run_async() 方法时:
- 并发执行: 它并发 地启动
sub_agents列表中每个 子智能体的run_async()方法。这意味着所有智能体(几乎)同时开始运行。 - 独立分支: 每个子智能体在自己的执行分支中运行。在执行过程中,这些分支之间没有*自动共享*对话历史或状态。
- 结果收集:
ParallelAgent管理并行执行,并通常提供一种方式在所有子智能体完成后访问它们的结果(例如,通过结果或事件列表)。结果的顺序可能不是确定性的。
独立执行和状态管理
理解 ParallelAgent 中的子智能体独立运行是至关重要的 。如果你需要这些智能体之间的通信或数据共享,你必须明确实现它。可能的方法包括:
- 共享
InvocationContext: 你可以向每个子智能体传递一个共享的InvocationContext对象。这个对象可以作为共享数据存储。但是,你需要小心管理对这个共享上下文的并发访问(例如,使用锁)以避免竞态条件。 - 外部状态管理: 使用外部数据库、消息队列或其他机制来管理共享状态并促进智能体之间的通信。
- 后处理: 收集每个分支的结果,然后实现逻辑来协调数据。
完整示例:并行网络研究
想象同时研究多个主题:
- 研究智能体 1: 一个研究"可再生能源"的
LlmAgent。 - 研究智能体 2: 一个研究"电动汽车技术"的
LlmAgent。 - 研究智能体 3: 一个研究"碳捕获方法"的
LlmAgent。
用户最典型 Agent
上面提到的智能体,比如 llmAgent, SequentialAgent, LoogAgent, ParallelAgent 都是 Adk 提供的,