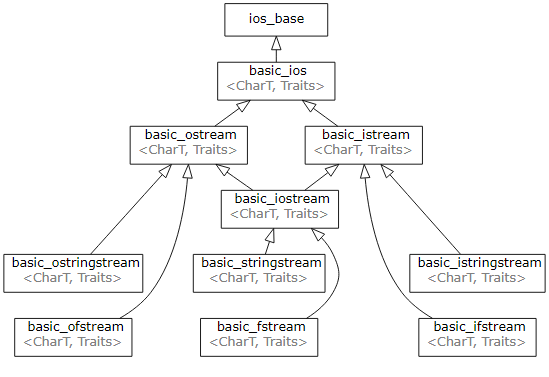
1.I0 库全景图:一张图看懂继承家族与核心组件

bash
ios_base
│
basic_ios<charT>
┌───┴───┐
│ │
basic_istream<charT> basic_ostream<charT>
│ │
└───┬───┘
basic_iostream<charT>
│
┌─────────────────────┼─────────────────────┐
│ │ │
basic_ifstream<charT> basic_istringstream<charT> basic_ofstream<charT>
basic_ofstream<charT> basic_ostringstream<charT> basic_fstream<charT>
basic_fstream<charT> basic_stringstream<charT> basic_stringstream<charT>T 通常是 char / wchar_t;把 basic_ 去掉,就是日常用的类。
箭头含义:纵向 → 公有继承;横向 → 多重继承(iostream 同时继承 istream & ostream)。
核心组件 7 个字
-
缓冲:streambuf* 指针藏在 basic_ios 里,真正读写的地方。
-
格式化:ios_base 存 flags、locale、precision,决定"怎么写"。
-
状态:good()、eof()、fail()、bad() 四个 bool,一行代码判健康。
-
异常:exceptions() 开关,状态位转异常,写库必备。
-
绑定:tie() 让 cin 自动 flush cout,防止"输入前没提示"。
-
移动:C++11 起支持 move,流对象能放容器/返回值,不再祖传引用。
-
模板:一套代码同时支持 char/wchar_t,后缀加 _w 就是宽版本。
2. 继承家族类深度拆解
2.1 ios_base:所有流的"祖师爷"
-
只管理"与字符类型无关"的数据:flags、locale、precision、状态位。
-
所有枚举和常量都挂在这里,例如
std::ios::hexstd::ios::scientificstd::ios::failbit -
典型用法:一行代码关同步,提速 cin/cout
cpp
// 1. 提速神器:关同步 + 解绑
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 关同步,cin/scanf 不再交叉 flush
std::cin.tie(nullptr); // 解绑 cout,输入前不隐式 flush 输出
// 2. 格式化输出:十六进制 + 前缀 0x
std::cout.setf(std::ios::hex | std::ios::showbase);
std::cout << 255; // 输出:0xff
std::cout.unsetf(std::ios::basefield); // 恢复十进制
// 3. 状态机一览
std::cout << std::cout.good(); // 1 (流健康)
std::cout << std::cout.eof(); // 0 (未到文件尾)
std::cout << std::cout.fail(); // 0 (无格式错误)
std::cout << std::cout.bad(); // 0 (无致命错误)- 状态机查询速记表
good()真=一切正常
eof()真=读到文件尾
fail()真=格式错误/磁盘满
bad()真=流已崩,救不回来
2.2 istream / ostream:标准输入输出实战
-
运算符
>>/<<本质是函数重载,返回流引用,所以能链式写。 -
常用操控符(头文件
<iomanip>)cpp// 1. 链式读 + 跳过空格 int a, b; std::cin >> a >> b; // 输入:10 20 std::cout << "a=" << a << " b=" << b << '\n'; // 输出:a=10 b=20 // 2. 行读,保留空格 std::string line; std::getline(std::cin, line); // 输入:hello world std::cout << "echo: " << line << '\n'; // 输出:echo: hello world // 3. 操纵符:宽度 + 填充 std::cout << std::setw(6) << std::setfill('*') << 42 << '\n'; // 输出:***42 // 4. 状态位短路------读到文件尾自动停 double val; while (std::cin >> val) { // 读到 Ctrl+D(Ctrl+Z) 结束 std::cout << "got " << val << '\n'; } // 循环结束后 cin.fail() == 1,cin.eof() == 1
2.3 fstream 家族:文件 IO 的六把钥匙
六把钥匙 = 3 类 × 2 模式(文本/二进制)
| 类 | 默认 mode | 常用组合 |
|---|---|---|
| ifstream | in | binary | in |
| ofstream | out | binary | out | trunc |
| fstream | in | out | binary | in | out |
cpp
// 1. 二进制写浮点数组
std::ofstream fout("data.bin", std::ios::binary);
float arr[] = {1.1f, 2.2f, 3.3f};
fout.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(arr), sizeof(arr)); // 写入 12 字节
fout.close();
// 2. 二进制读回
std::ifstream fin("data.bin", std::ios::binary);
float tmp;
while (fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&tmp), sizeof(tmp)))
std::cout << tmp << ' '; // 输出:1.1 2.2 3.3
fin.close();
// 3. 文本追加写日志
std::ofstream log("run.log", std::ios::app);
log.exceptions(std::ofstream::failbit | std::ofstream::badbit); // 抛异常
log << __TIME__ << " program start\n"; // 输出:14:30:12 program start
// 4. fstream 同时读写
std::fstream fs("rw.txt", std::ios::in | std::ios::out | std::ios::trunc);
fs << "hello\n"; // 写
fs.seekg(0); // 回到开头
std::string s;
std::getline(fs, s);
std::cout << s << '\n'; // 输出:hello2.4 sstream 家族:内存 stringstream 的黑科技
把内存当文件用,省去格式解析的麻烦。
cpp
// 1. 任意类型 → string(安全替代 sprintf)
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << 3.14159 << ',' << 42 << ',' << "C++";
std::string s = oss.str(); // s == "3.14159,42,C++"
std::cout << s << '\n';
// 2. string → 任意类型(自动空格分隔)
std::istringstream iss("100 3.14 hello");
int i; double d; std::string w;
iss >> i >> d >> w; // i=100, d=3.14, w="hello"
std::cout << "i=" << i << " d=" << d << " w=" << w << '\n';
// 3. 循环复用:清空缓冲区 + 重置状态
for (int n : {1, 2, 3}) {
oss.str(""); // 清空缓冲区
oss.clear(); // 重置 failbit/eofbit
oss << "id=" << n;
send_to_log(oss.str()); // 假想的日志函数
}
// 4. 高性能拼接(C++20 移动语义)
auto build_big_string() {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << std::string(1024*1024, 'A'); // 1 MB
return oss.str(); // NRVO + move,零拷贝返回
}
std::cout << "size=" << build_big_string().size() << '\n'; // 输出:size=1048576ios_base 管格式,istream 读 ostream 写;
文件加 file,内存加 string;
状态位短路,异常可控,清空先 str("") 再 clear()。
3.I0 流状态机:good、eof、fail、bad 四大标志位详解
-
I0操作的过程中,可能会发生各种错误,10流对象中给了四种状态标识错误,可以参考下图2-1和2-2进行理解。goodbit表示流没有错误/eofbit表示流到达文件结束/failbit表示IO操作失败了/badbit表示流崩溃了出现了系统级错误。
-
一个常见的lO流错误是cin>>i,i是一个int类型的对象,如果我们在控制台输入一个字符,cin对象的failbit状态位就会被设置,cin就进入错误状态,一个流一旦发生错误,后续的IO操作都会失败,我们可以调用cin.clear()函数来恢复cin的状态为goodbit。
-
badbit表示系统级错误,如不可恢复的读写错误,通常情况下,badbit一旦被设置了,流就无法再使用了。
-
failbit表示一个逻辑错误,如期望读取一个整形,但是却读取到一个字符,failbit被设置了,流是可以恢复的,恢复以后可以继续使用。
-
如果到达文件结束位置eofbit和failbit都会被置位。如果想再次读取当前文件,可以恢复一下流的状态,同时重置一个文件指针位置。
-
goodbit表示流未发生错误。
-
也可以用setstate和rdstate两个函数来控制流状态,eofbit/failbit/badbit/goodbit是ios_base基类中定义的静态成员变量,可以直接使用的,并且是他们是可以组合的位运算值,具体使用细节可以参考文档。


cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << cin.good() << endl;
cout << cin.eof() << endl;
cout << cin.bad() << endl;
cout << cin.fail() << endl << endl;
int i = 0;
// 输⼊⼀个字符或多个字符,cin读取失败,流状态被标记failbit
cin >> i;
cout << i << endl;
cout << cin.good() << endl;
cout << cin.eof() << endl;
cout << cin.bad() << endl; cout << cin.fail() << endl << endl;
if (cin.fail())
{
// clear可以恢复流状态位 goodbit
cin.clear();
// 我们还要把缓冲区中的多个字符都读出来,读到数字停下来,否则再去
//cin >> i还是会失败
char ch = cin.peek();
while (!(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'))
{
ch = cin.get();
cout << ch;
ch = cin.peek();
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << cin.good() << endl;
cout << cin.eof() << endl;
cout << cin.bad() << endl;
cout << cin.fail() << endl << endl;
cin >> i;
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}4.管理输出缓冲区
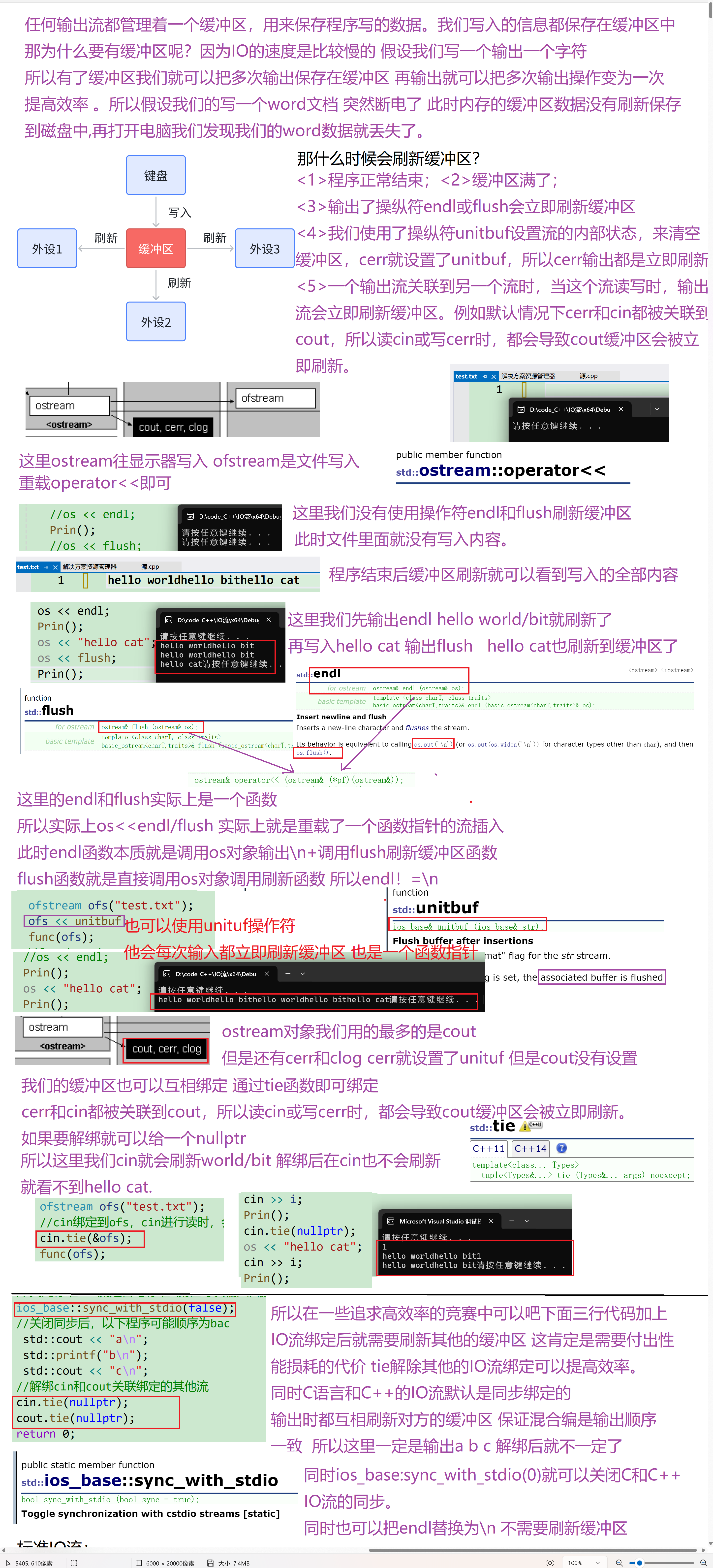
- 任何输出流都管理着一个缓冲区,用来保存程序写的数据。如果我们执行os<<"helloworld";字符串可能立即输出,也可能被操作系统保存在缓冲区中,随后再输出。有了缓冲区机制,操作系统就可能将多个输出操作组合成为一个单一的系统级写操作。因为设备的写操作通常是很耗时的,允许操作系统将多个输出操作组合为单一的设备写操作肯可能带来很大的性能提升。
- 会触发缓冲区刷新,将数据真正的写到输出设备或文件的原因有很多,如:<1>程序正常结束;<2>缓冲区满了;<3>输出了操纵符endl或flush会立即刷新缓冲区<4>我们使用了操纵符unitbuf设置流的内部状态,来清空缓冲区,cerr就设置了unitbuf,所以cerr输出都是立即刷新的。<5>一个输出流关联到另一个流时,当这个流读写时,输出流会立即刷新缓冲区。例如默认情况下cerr和cin都被关联到cout,所以读cin或写cerr时,都会导致cout缓冲区会被立即刷新。
- tie可以支持跟其他流绑定和解绑,具体参考文档
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/tie/
cpp
void Prin()
{
FILE* file;
char buffer[1024]; // 假设每行数据不超过1024个字符
// 打开文件,"r" 表示以只读方式打开
file = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (file == NULL) {
perror("Error opening file");
return ;
}
// 读取并打印文件内容
while (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), file)) {
printf("%s", buffer);
}
// 关闭文件
fclose(file);
}
void func(ostream& os)
{
os << "hello world";
os << "hello bit";
// "hello world"和"hello bit"是否输出不确定
system("pause");
// 遇到endl,"hello world"和"hello bit"⼀定刷新缓冲区输出了
//os << endl;
int i;
cin >> i;
Prin();
cin.tie(nullptr);
os << "hello cat";
cin >> i;
Prin();
//os << flush;
//int i;
//cin >> i;
// "hello cat"是否输出不确定
system("pause");
}
int main()
{
ofstream ofs("test.txt");
//cin绑定到ofs,cin进⾏读时,会刷新ofs的缓冲区
cin.tie(&ofs);
func(ofs);
//func(cout);
//unitbuf设置后,ofs每次写都直接刷新
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//在io需求比较高的地方,如部分大量输入的竞赛题中,加上以下几行代码可以提高C++IO效率
//并且建议用'n'替代endl,因为endl会刷新缓冲区
//关闭标准C++流是否与标准C流在每次输入/输出操作后同步。
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
//关闭同步后,以下程序可能顺序为bac
std::cout << "a\n";
std::printf("b\n");
std::cout << "c\n";
//解绑cin和cout关联绑定的其他流
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
return 0;
}
5.标准IO流
- C++标准IO流前面已经使用得比较多了,C++标准IO流默认是关联到控制台窗口的。cin是istream类型全局对象,cout/cerr/clog是ostream类型的全局对象,内置类型这两个类都直接进行了重载实现,所以可以直接使用,自定义类型就需要我们自己重载<<和>>运算符。
- ostream和istream是不支持拷贝的,只支持移动(外部不能使用,因为是保护成员)。
- istream的cin对象支持转换为bool值,进行条件逻辑判断,一旦被设置了badbit或failbit标志位,
就返回false,如果是goodbit就返回true。 - ostream和istream还有不少其他接口,实践中相对用得比较少,需要时大家查查文档。
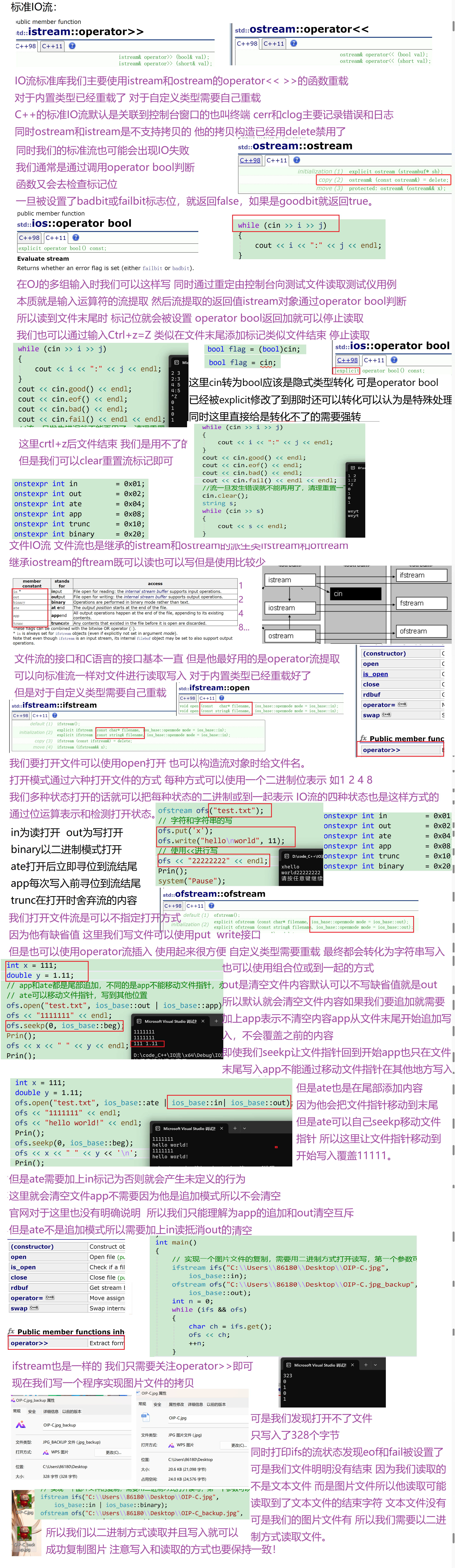
6.文件 IO 流进阶
- ofstream是输出文件流,也就是写文件的流,ofstream是ostream的派生类;ifstream是输入文件流,也就是读文件的流,ifstream是istream的派生类;fstream是ifstream和ofstream的派生类,既可以读也可以写。
- https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/fstream/
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io
- 文件流对象可以在构造时打开文件,也可以调用open函数打开文件,打开文件的mode有5-1图中的几种。in为读打开;out为写打开;binary以二进制模式打开;ate打开后立即寻位到流结尾;app每次写入前寻位到流结尾;trunc在打开时舍弃流的内容;这些值是ios_base中定义的成员变量继承下来的并且他们也是组合的独立二进制位值,需要组合时,可以或到一起。他们之间的区别,具体参考下面的代码演示。
- 文件流打开后如果需要可以主动调用close函数关闭,也可以不关闭,因为流对象析构函数中会关闭。
- 文件流打开文件失败或读写失败,也会使用lO流状态标记,我们调用operator bool或operator!判断即可。
- ifstream文件流的读数据主要可以使用get/read/>>重载,ofstream文件流写数据主要可以使用put/write/<<重载,具体主要参考下面代码的演示。
- 相比c语言文件读写的接口,C++fstream流功能更强大方便,使用<<和>>进行文件读写很方便,尤其是针对自定义类型对象的读写。

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 0, j = 1;
//持续的输入,要结束需要输入Ctrl+Z换行,Ctrl+Z用于告诉程序输入已经完成,
// 类似于在文件末尾添加一个标记。
//istream&operator>>(int i),>>运算符重载的返回值是istream对象,
// istream对象可以调用operator bool转换为bool值
//本质在底层是将cin的eofbit和failbit标志位设置了,
// cin调用operatorbool函数语法逻辑上实现转换为bool值
while (cin >> i >> j)
{
cout << i << ":" << j << endl;
}
cout << cin.good() << endl;
cout << cin.eof() << endl;
cout << cin.bad() << endl;
cout << cin.fail() << endl << endl;
//流一旦发生错误就不能再用了,清理重置一下再能使用
cin.clear();
string s;
while (cin >> s)
{
cout << s << endl;
}
}
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day << endl;
return out;
}
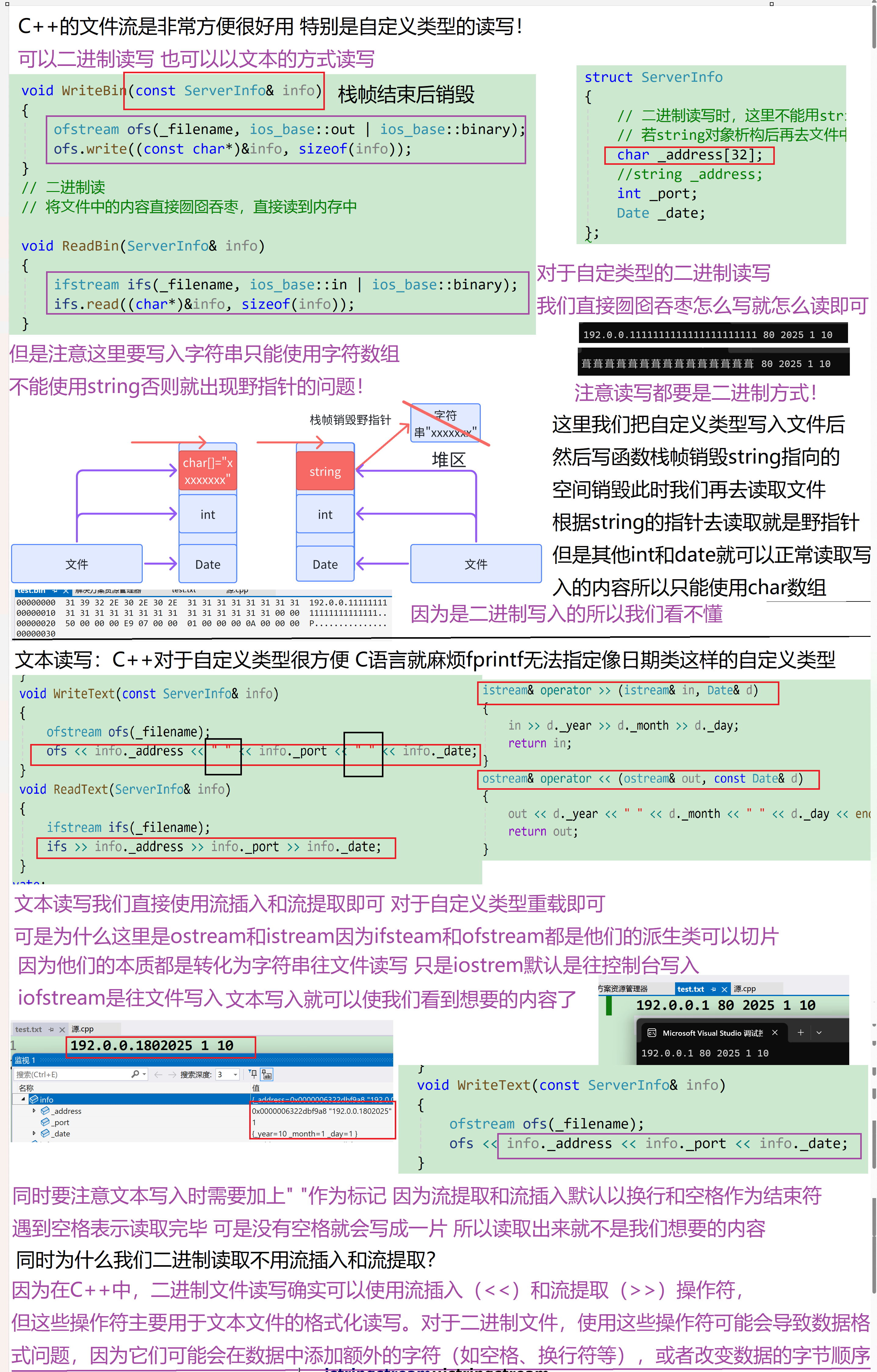
struct ServerInfo
{
// ⼆进制读写时,这⾥不能⽤string,否则写到⽂件中的是string中指向字符数组的指针
// 若string对象析构后再去⽂件中读取string对象,string中读到是⼀个野指针。
char _address[32];
//string _address;
int _port;
Date _date;
};
struct ConfigManager
{
public:
ConfigManager(const char* filename)
:_filename(filename)
{}
// ⼆进制写
// 内存中怎么存,囫囵吞枣,就怎么直接写出去
void WriteBin(const ServerInfo& info)
{
ofstream ofs(_filename, ios_base::out | ios_base::binary);
ofs.write((const char*)&info, sizeof(info));
}
// ⼆进制读
// 将⽂件中的内容直接囫囵吞枣,直接读到内存中
void ReadBin(ServerInfo& info)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename, ios_base::in | ios_base::binary);
ifs.read((char*)&info, sizeof(info));
}
void WriteText(const ServerInfo& info)
{
ofstream ofs(_filename);
ofs << info._address << " " << info._port << " " << info._date;
}
void ReadText(ServerInfo& info)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename);
ifs >> info._address >> info._port >> info._date;
}
private:
string _filename; // 配置⽂件
};
void WriteBin()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "192.0.0.1111111111111111111111", 80, { 2025, 1, 10 }
};
// ⼆进制读写
ConfigManager cf_bin("test.bin");
cf_bin.WriteBin(winfo);
}
void ReadBin()
{
// ⼆进制读写
ConfigManager cf_bin("test.bin");
ServerInfo rbinfo;
cf_bin.ReadBin(rbinfo);
cout << rbinfo._address << " " << rbinfo._port << " " << rbinfo._date <<endl;
}
void WriteText()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "192.0.0.1", 80, { 2025, 1, 10 } };
// ⽂本读写
ConfigManager cf_text("test.txt");
cf_text.WriteText(winfo);
}
void ReadText()
{
ConfigManager cf_text("test.txt");
ServerInfo rtinfo;
cf_text.ReadText(rtinfo);
cout << rtinfo._address << " " << rtinfo._port << " " << rtinfo._date <<endl;
}
int main()
{
WriteBin();
ReadBin();
//WriteText();
//ReadText();
return 0;
}
7.string IO 流技巧
ostringstream 是用于向字符串写入数据的流,它是 ostream 的派生类;istringstream 是用于从字符串读取数据的流,它是 istream 的派生类;stringstream 是 ostringstream 和 istringstream 的派生类,既可以读也可以写。因此,在需要同时进行读写操作时,使用 stringstream 会非常方便。
stringstream 系列底层维护了一个 string 类型的对象,用于保存数据。其使用方法与文件流类似,只是数据的读写交互都是针对底层的 string 对象进行的。stringstream 最常用的方式是通过 << 和 >> 运算符重载,实现数据与 string 之间的转换。
string流使用str函数获取底层的string对象,或者写入底层的string对象,具体细节参考下面代码理解。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//int i = 123;
//Date d = { 2025, 4, 10 };
//stringstream oss;
//oss << i << endl;
//oss << d << endl;
//string s = oss.str();
//cout << s << endl;
//stringstream iss("100 2025 9 9");
////iss.str("100 2025 9 9");
//int j;
Date x;
//iss >> j >> x;
//cout << j << endl;
//cout << x << endl;
int a = 1234;
int b = 5678;
string str;// 将⼀个整形变量转化为字符串,存储到stri类对象中
stringstream ss;
ss << a << b;
ss >> str;
ss.clear();
ss.str("");
double dd = 12.34;
ss << dd;
ss >> str;
cout << str << endl;
//cout << ss.fail() << endl;
//cout << ss.bad() << endl;
// 注意多次转换时,必须使⽤clear将上次转换状态清空掉
// stringstreams在转换结尾时(即最后⼀个转换后),会将其内部状态设置为badbit和failbit
// 因此下⼀次转换是必须调⽤clear()将状态重置为goodbit才可以转换
// 但是clear()不会将stringstreams底层字符串清空掉, str给⼀个空串可以清掉底层的字符串
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream & in, Date & d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream & out, const Date & d)
{
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day << endl;
return out;
}
struct ChatInfo
{
string _name; // 名字
int _id;// id
Date _date; // 时间
string _msg; // 聊天信息
};
int main()
{
//结构信息序列化为字符串
ChatInfo winfo = { "张三", 135246, { 2022, 4, 10 }, "晚上⼀起看电影吧" };
ostringstream oss;
oss << winfo._name << " " << winfo._id << " " << winfo._date << " " <<
winfo._msg;
string str = oss.str();
cout << str << endl << endl;
// 我们通过⽹络这个字符串发送给对象,实际开发中,信息相对更复杂,
// ⼀般会选⽤Json、xml等⽅式进⾏更好的⽀持
// 字符串解析成结构信息
ChatInfo rInfo;
istringstream iss(str);
iss >> rInfo._name >> rInfo._id >> rInfo._date >> rInfo._msg;
cout << "-------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << rInfo._name << "(" << rInfo._id << ") ";
cout << rInfo._date << endl;
cout << rInfo._name << ":>" << rInfo._msg << endl;
cout << "-------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}后言:IO 流学习路线图与常见面试题 Top10
| 阶段 | 目标 | 关键词 | 推荐实验 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 会用 | 能读写控制台、文件、字符串 | cin / cout / ifstream / ostringstream |
把 100 行日志写文件,再读回来 |
| 2. 懂缓冲 | 解释"为什么没打印" | 行缓冲、全缓冲、flush、endl、tie | 写程序去掉 \n 观察现象 |
| 3. 会定位 | 排查格式错误、EOF、badbit | good()/fail()/eof()/clear() |
故意读字母给 int 看状态 |
| 4. 会定制 | 重定向、同步/异步、二进制 | rdbuf()/sync_with_stdio()/read() |
把 cout 重定向到文件 |
| 5. 会扩展 | 自定义 streambuf | overflow()/underflow() |
写 20 行日志缓冲自动落盘 |
-
为什么
cin >> x能当 while 条件?答:返回
cin,转operator bool等价!fail()。 -
读到文件尾还会
fail()吗?答:只置
eofbit不会fail();再读一次才置failbit。 -
如何让
cout立即打印?答:
<< endl/<< flush/cout.flush()。 -
关闭
cin同步有什么副作用?答:
scanf/printf/cin/cout混用结果不确定。 -
ifstream二进制与文本模式区别?答:文本模式把
\n转\r\n,二进制原样写入。 -
ostringstream比sprintf安全在哪?答:自动推类型、无缓冲区溢出、支持
std::string。 -
怎样把
cout重定向到文件?答:
cout.rdbuf(file.rdbuf());恢复再传一遍原rdbuf。 -
自定义
streambuf要实现哪两个关键函数?答:
overflow(int c)写缓冲满,underflow()读空。 -
cerr与cout缓冲策略差异?答:
cerr无缓冲,每条立即出屏;cout行/全缓冲。 -
如何判断上一次读是成功的 EOF?
答:
eof() && !fail()为真。
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << 3.14 << " hello";
std::cout << oss.str() << '\n'; // 3.14 hello
std::ifstream fin("data.txt");
int x;
while(fin >> x) std::cout << x << ' '; // 读到 EOF 自动停
if(fin.eof() && !fin.fail()) std::cout << "\n正常读完\n";
}