鸿蒙学习实战之路-多端交互最佳实践
多端交互是 HarmonyOS 应用开发中的重要特性,本文将介绍如何在鸿蒙应用中实现多端设备之间的高效交互,包括跨设备通信、数据共享、协同操作等内容。
关于本文
自己学习并使用 HarmonyOS 多端交互的记录,旨在帮助小伙伴们少走弯路
华为开发者联盟-多端交互文档永远是你的好伙伴,请收藏!
- 本文并不能代替官方文档,所有的内容也都是基于官方文档+自己尝试的记录。
- 基本所有章节基本都会附上对应的文档链接,强烈建议你点看看看
- 所有结合代码操作的部分,建议自己动手尝试一下
代码测试环境
| 环境/工具 | 版本/说明 |
|---|---|
| DevEco Studio | 5.0.3.400 |
| HarmonyOS SDK | API Version 12 |
| Node.js | 18.19.0 |
| 测试设备 | HarmonyOS 4.0+ 模拟器 |
1. 概述
在 HarmonyOS 分布式系统中,多端交互是实现设备协同的核心技术。通过多端交互,用户可以在不同设备之间无缝切换任务、共享数据和协同操作,极大提升了用户体验。
1.1 多端交互基本概念
在 HarmonyOS 中,多端交互支持多种输入设备,如图 1 所示:
图1输入设备
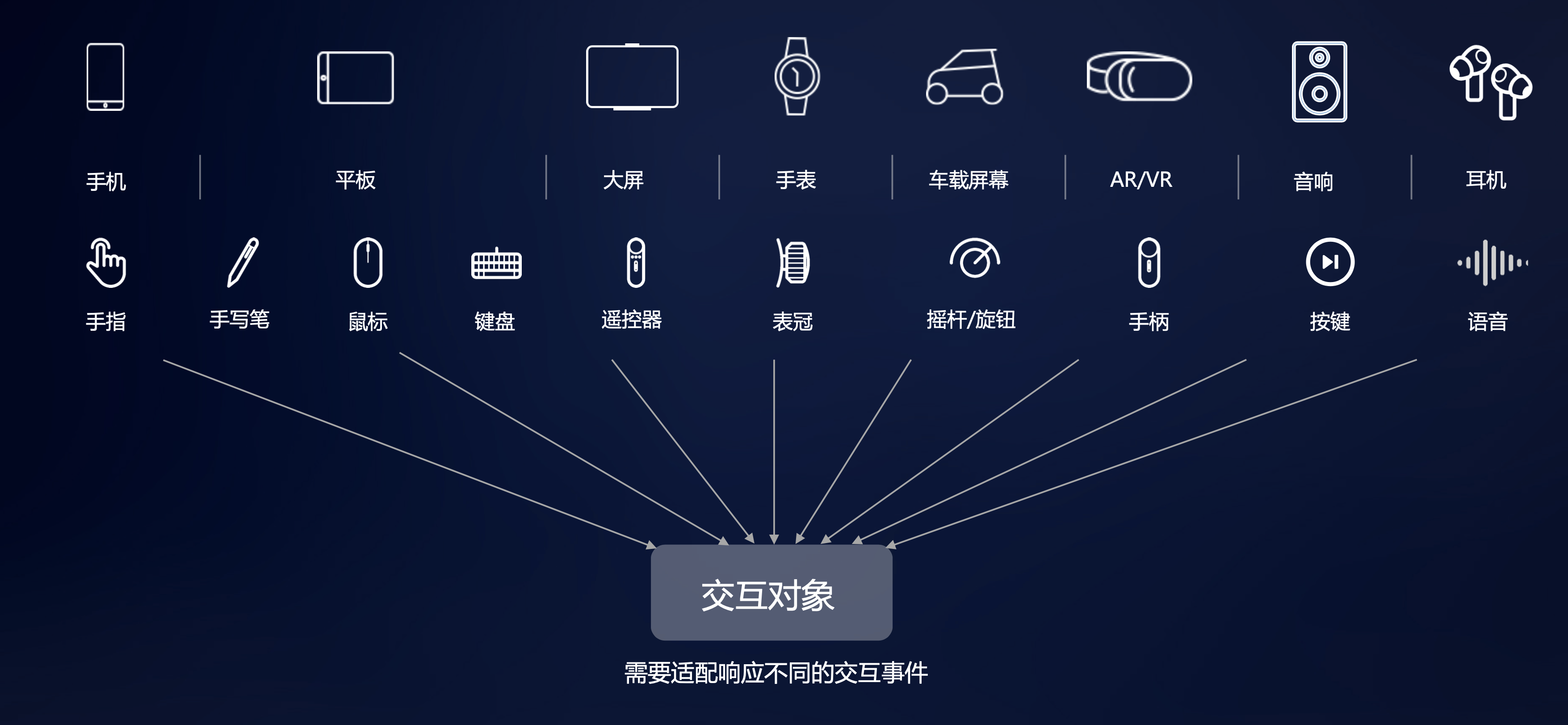
多端交互是指在 HarmonyOS 分布式系统中,不同设备之间通过分布式能力框架进行通信和协作的技术。
1.2 多端交互的应用场景
- 跨设备任务迁移:用户可以在手机上开始编辑文档,然后无缝切换到平板继续编辑
- 多屏协同:手机与平板、电脑等设备协同工作,扩展显示和操作空间
- 数据共享:照片、文档等数据在不同设备之间实时共享
- 设备联动:智能家居设备之间的联动控制,如手机控制智能电视、智能音箱等
2. 分布式能力框架
HarmonyOS 提供了完整的分布式能力框架,用于支持多端设备之间的交互。
2.1 分布式能力框架概述
分布式能力框架包含以下核心组件:
- 分布式软总线:提供设备发现、连接和通信能力
- 分布式数据管理:提供跨设备数据共享和同步能力
- 分布式任务调度:提供跨设备任务分发和迁移能力
- 分布式安全:提供跨设备安全认证和数据加密能力
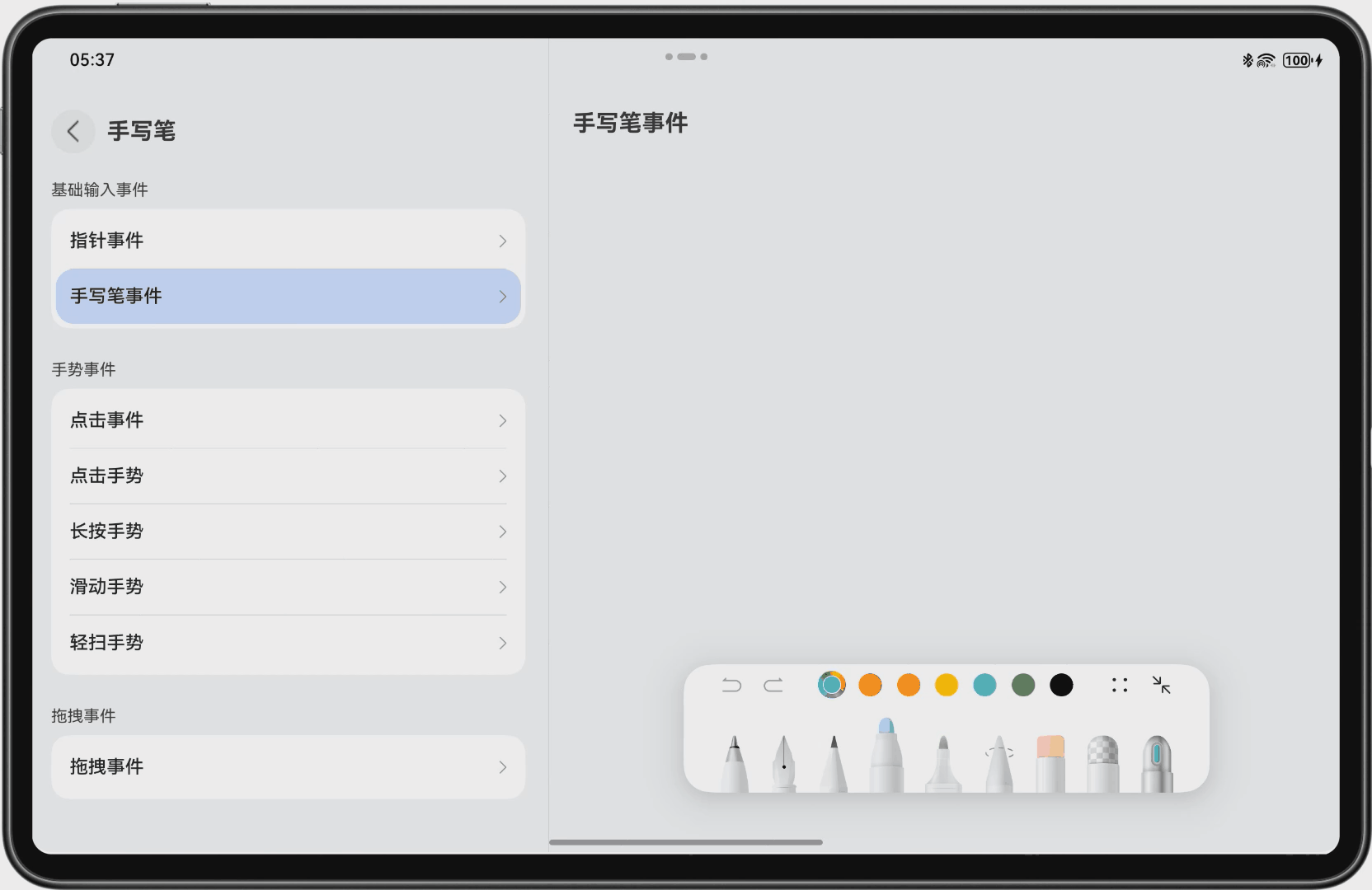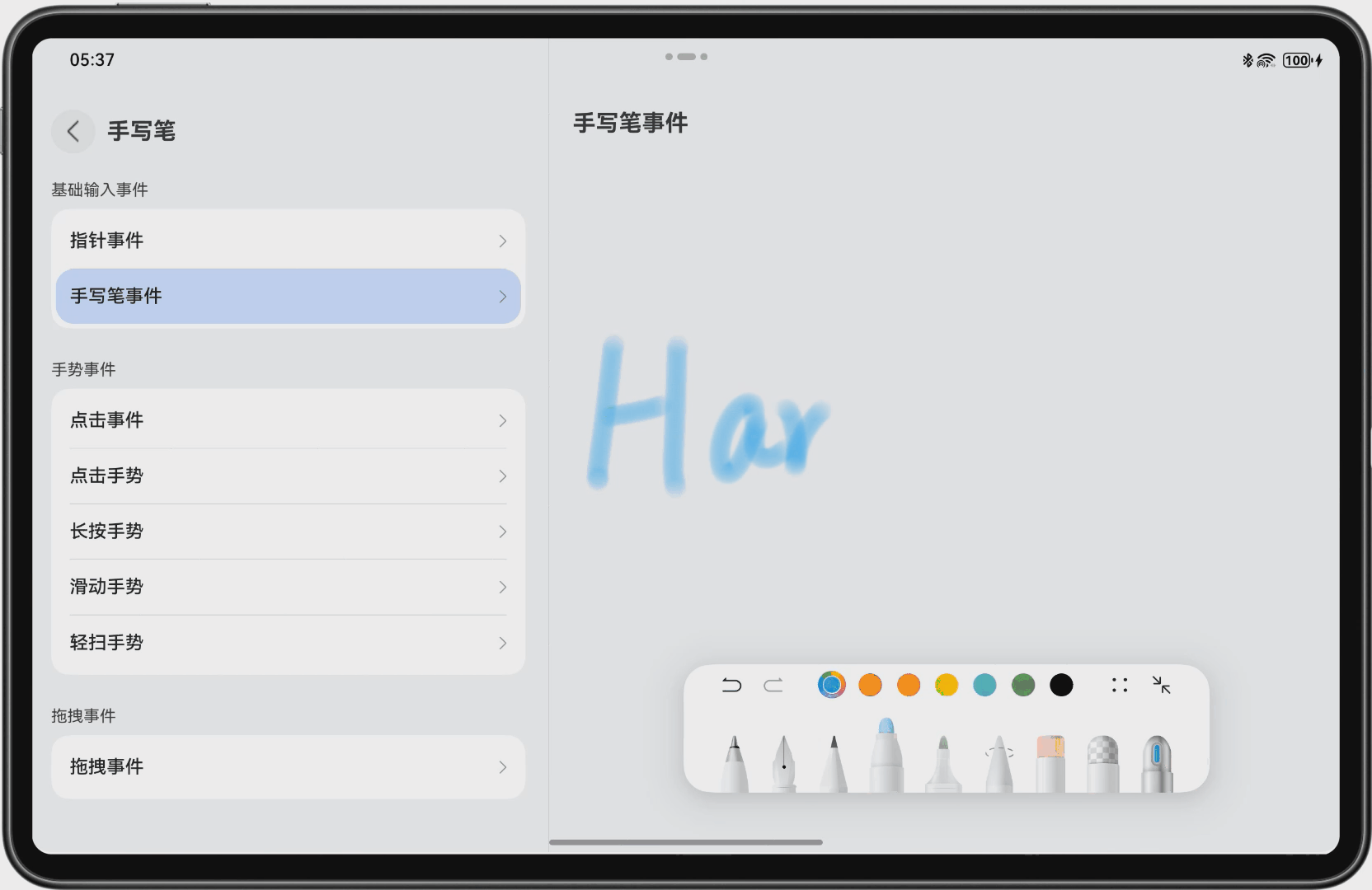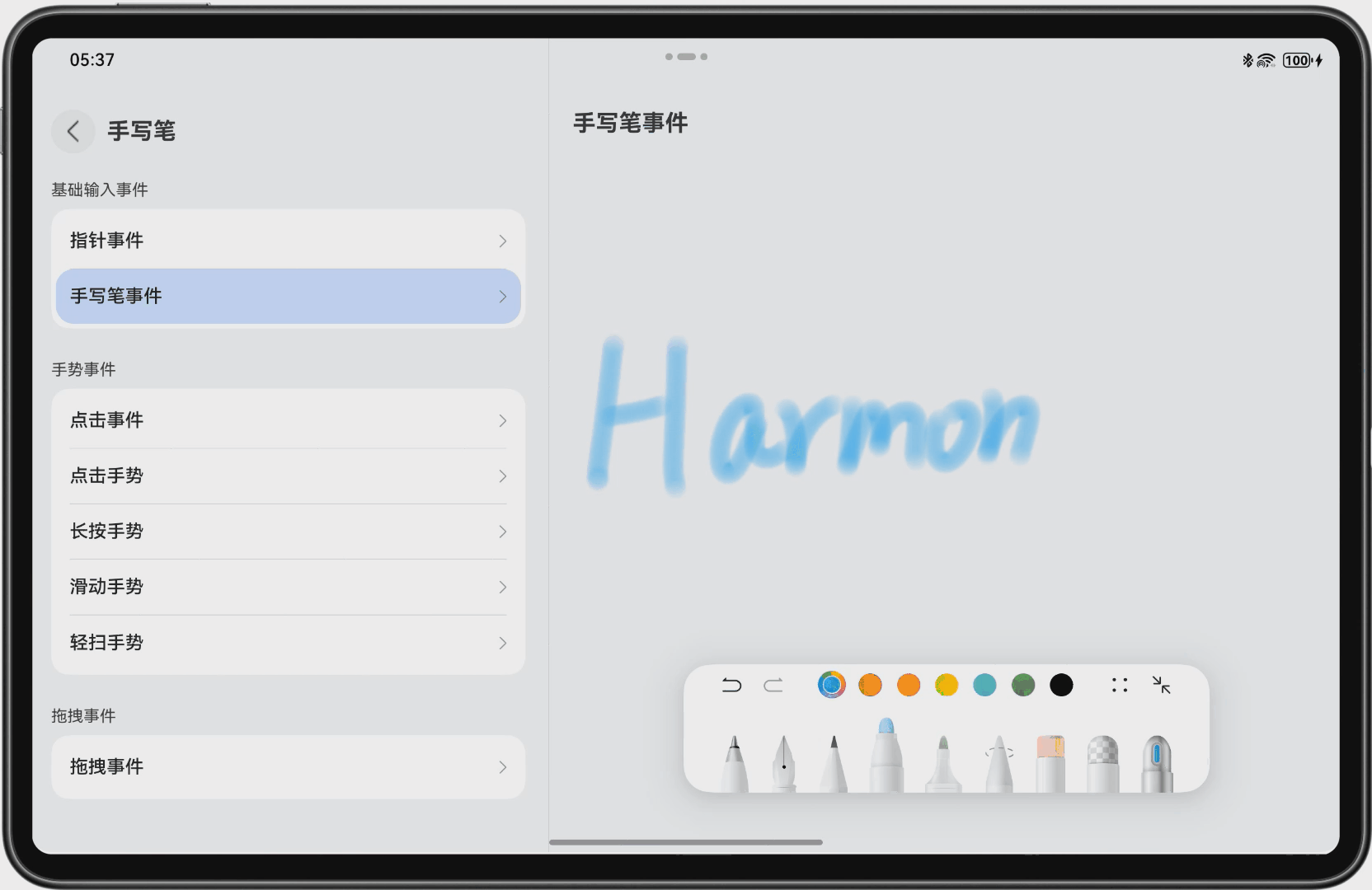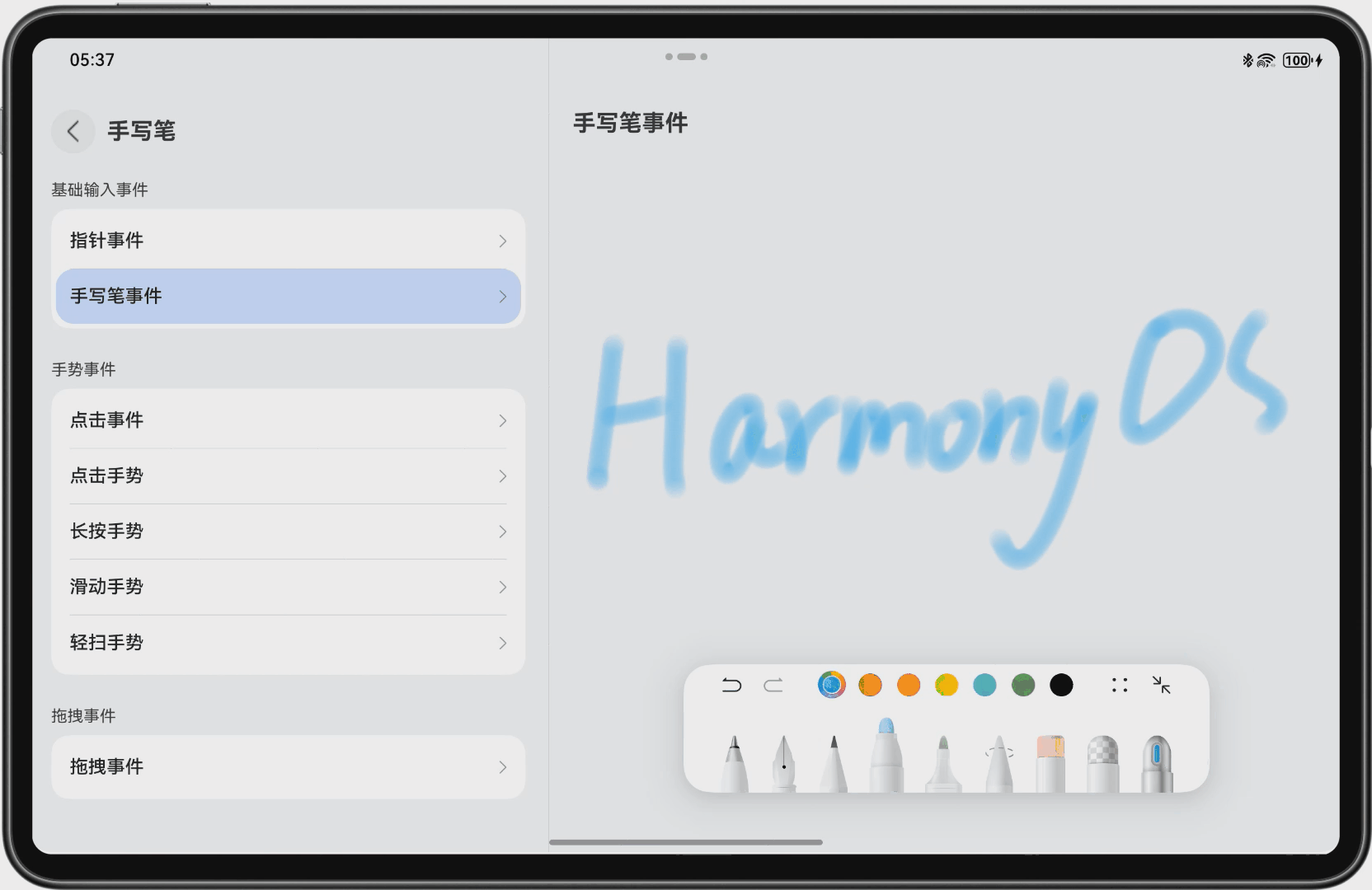
为了更好地理解多端交互,我们可以看一个手写笔套件的示例,如图 2 所示:
图2手写笔套件示例
2.2 配置分布式能力
在项目的module.json5文件中添加分布式能力相关配置:
json5
{
module: {
// ...其他配置
abilities: [
{
// ...其他配置
skills: [
{
// ...其他配置
},
],
},
],
requestPermissions: [
{
name: "ohos.permission.DISTRIBUTED_DATASYNC",
},
{
name: "ohos.permission.GET_DISTRIBUTED_DEVICE_INFO",
},
],
},
}3. 设备发现与连接
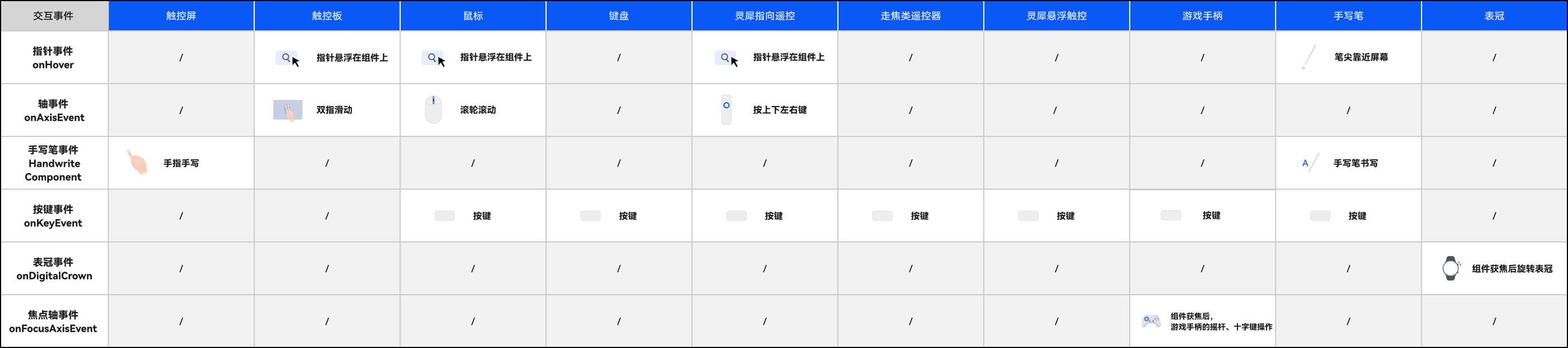
在多端交互中,了解不同输入设备的基础输入事件触发方式非常重要,如图 3 所示:
图3输入设备基础输入事件触发方式一览表
3.1 设备发现
使用分布式软总线 API 发现附近的设备:
typescript
import { businessError } from "@kit.BasicServicesKits";
import { distributedDeviceManager } from "@kit.DeviceManagerKit";
// 获取分布式设备管理器
let deviceManager = distributedDeviceManager.getDistributedDeviceManager();
// 发现设备
if (deviceManager) {
deviceManager.startDeviceDiscovery(
(
discoveryMode: number,
filterOptions: string,
callback: (
deviceId: string,
deviceInfo: distributedDeviceManager.DeviceInfo
) => void,
onFailure: (code: number, error: businessError.BusinessError) => void
) => {
console.log("设备发现开始");
}
);
// 监听设备发现事件
deviceManager.on(
"deviceStateChange",
(data: {
action: number;
deviceId: string;
deviceInfo: distributedDeviceManager.DeviceInfo;
}) => {
console.log(`设备状态变化: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`);
if (
data.action ===
distributedDeviceManager.DeviceStateChangeAction.DEVICE_FOUND
) {
console.log(`发现设备: ${data.deviceInfo.deviceName}`);
}
}
);
}3.2 设备连接
与发现的设备建立连接:
typescript
// 连接设备
if (deviceManager) {
deviceManager.connectDevice(
deviceId,
(code: number, data: distributedDeviceManager.ConnectResult) => {
if (code === 0) {
console.log("设备连接成功");
} else {
console.error(`设备连接失败: ${code}`);
}
}
);
}4. 跨设备数据共享
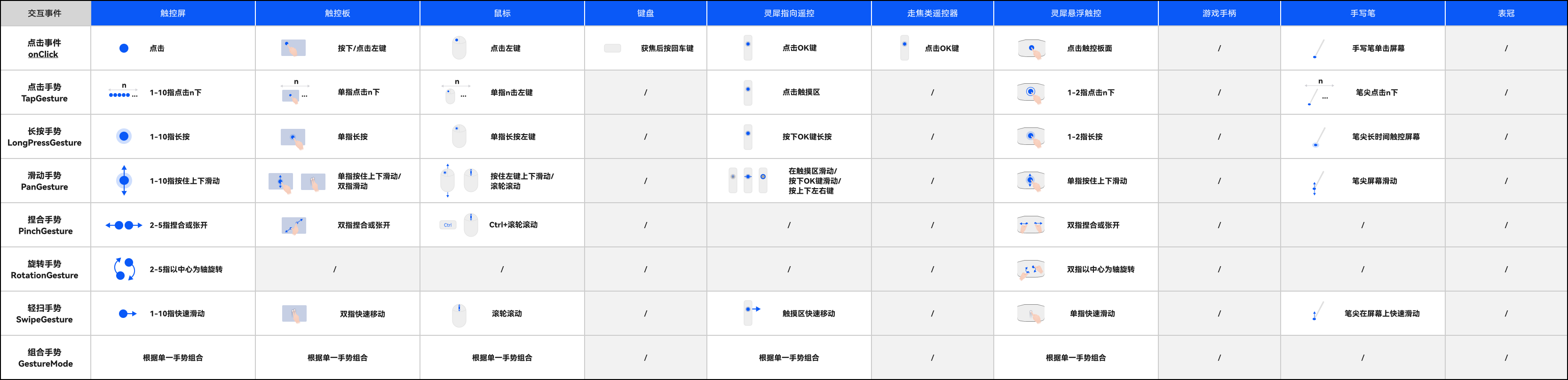
在多端交互中,手势事件是重要的交互方式之一。下图为常见手势事件在不同输入设备上的触发方式,如图 4 所示:
图4输入设备手势事件触发方式一览表
4.1 分布式数据对象
使用分布式数据对象实现跨设备数据共享:
typescript
import { distributedData } from "@kit.DistributedDataKit";
// 创建分布式数据对象
let distributedObject = distributedData.createDistributedObject({
message: "Hello HarmonyOS",
count: 0,
});
// 监听数据变化
distributedObject.on(
"change",
(data: { changedKeys: Array<string>; deviceId: string }) => {
console.log(`数据变化: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`);
}
);
// 更新数据
distributedObject.set("message", "Hello Distributed World");
distributedObject.set("count", distributedObject.get("count") + 1);4.2 分布式文件系统
使用分布式文件系统实现跨设备文件共享:
typescript
import { distributedFS } from "@kit.DistributedFileKit";
// 获取分布式文件路径
let distributedPath = distributedFS.getDistributedDir(globalThis.context);
console.log(`分布式文件路径: ${distributedPath}`);
// 在分布式路径下创建文件
let filePath = distributedPath + "/test.txt";
let fileContent = "这是一个分布式文件示例";
distributedFS.writeFile(filePath, fileContent, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`文件写入失败: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
} else {
console.log("文件写入成功");
}
});5. 跨设备任务调度
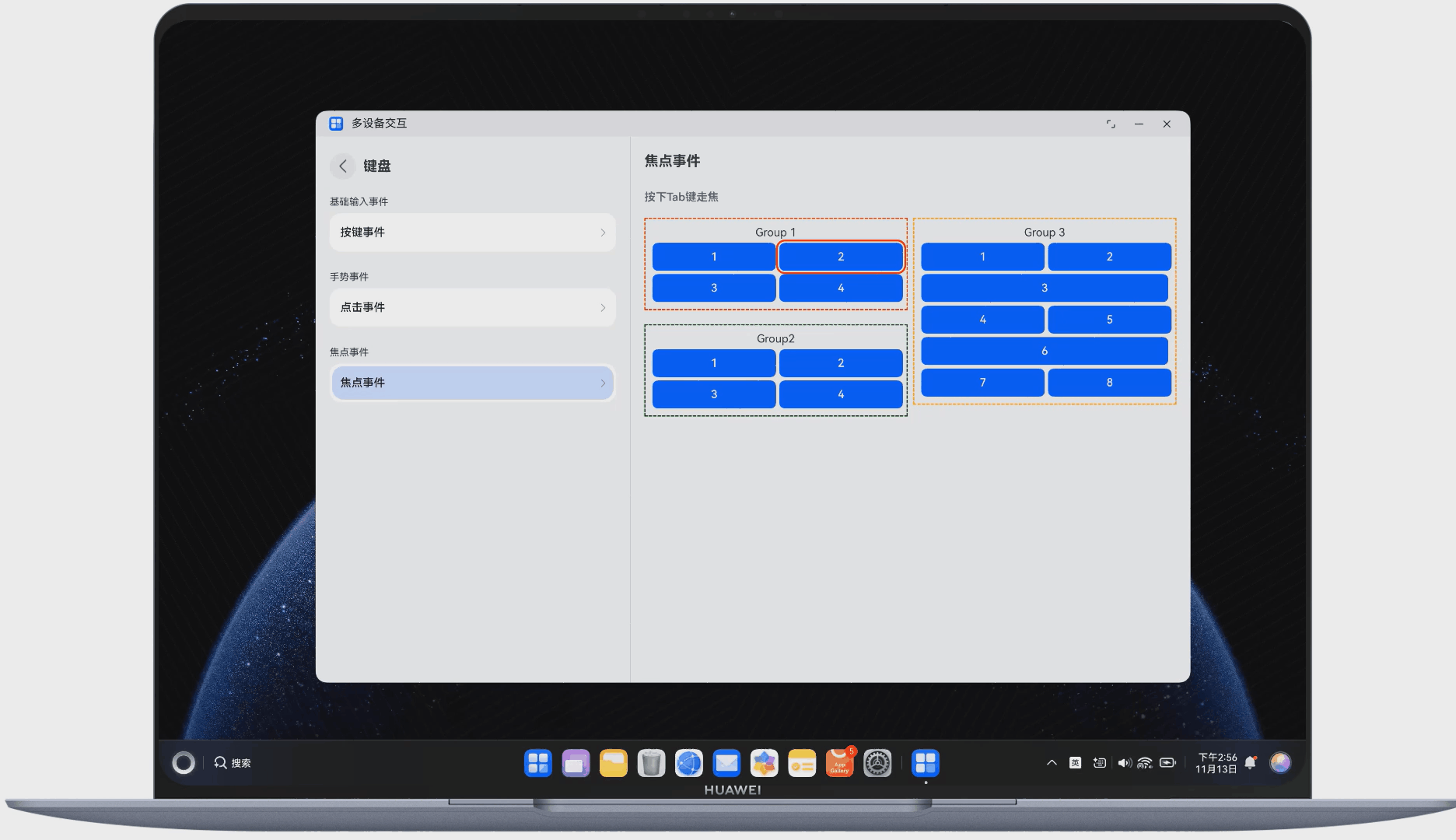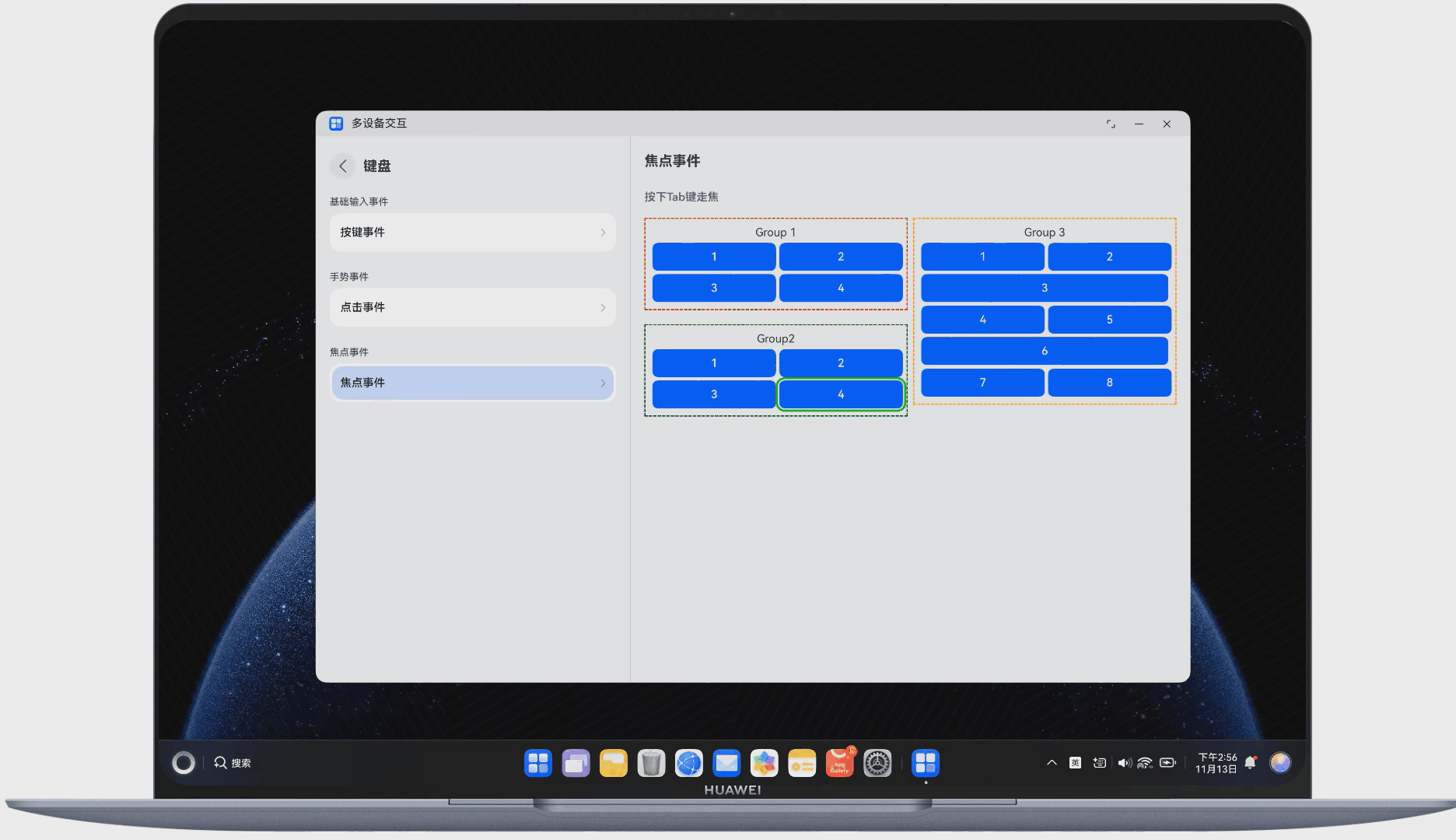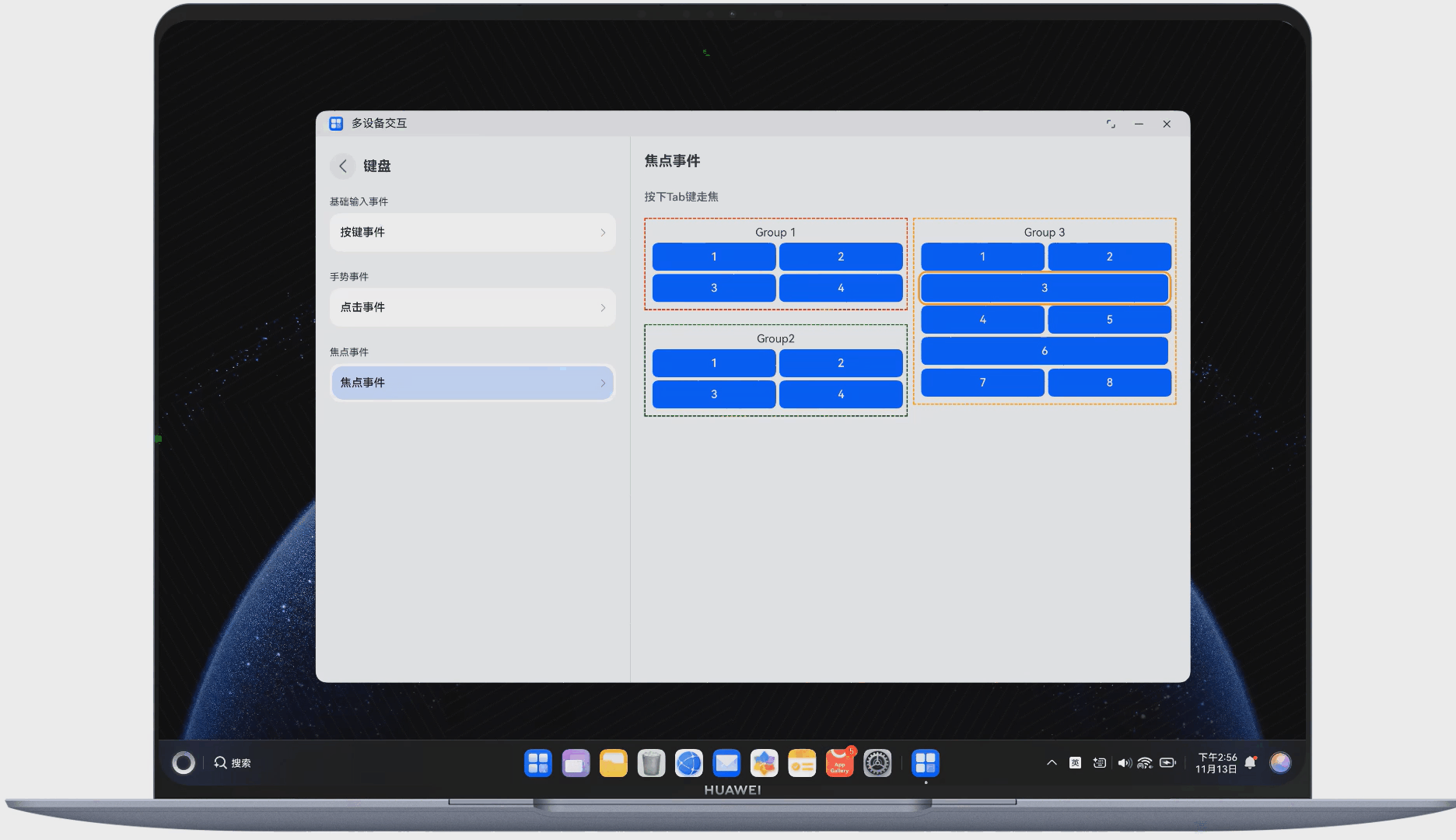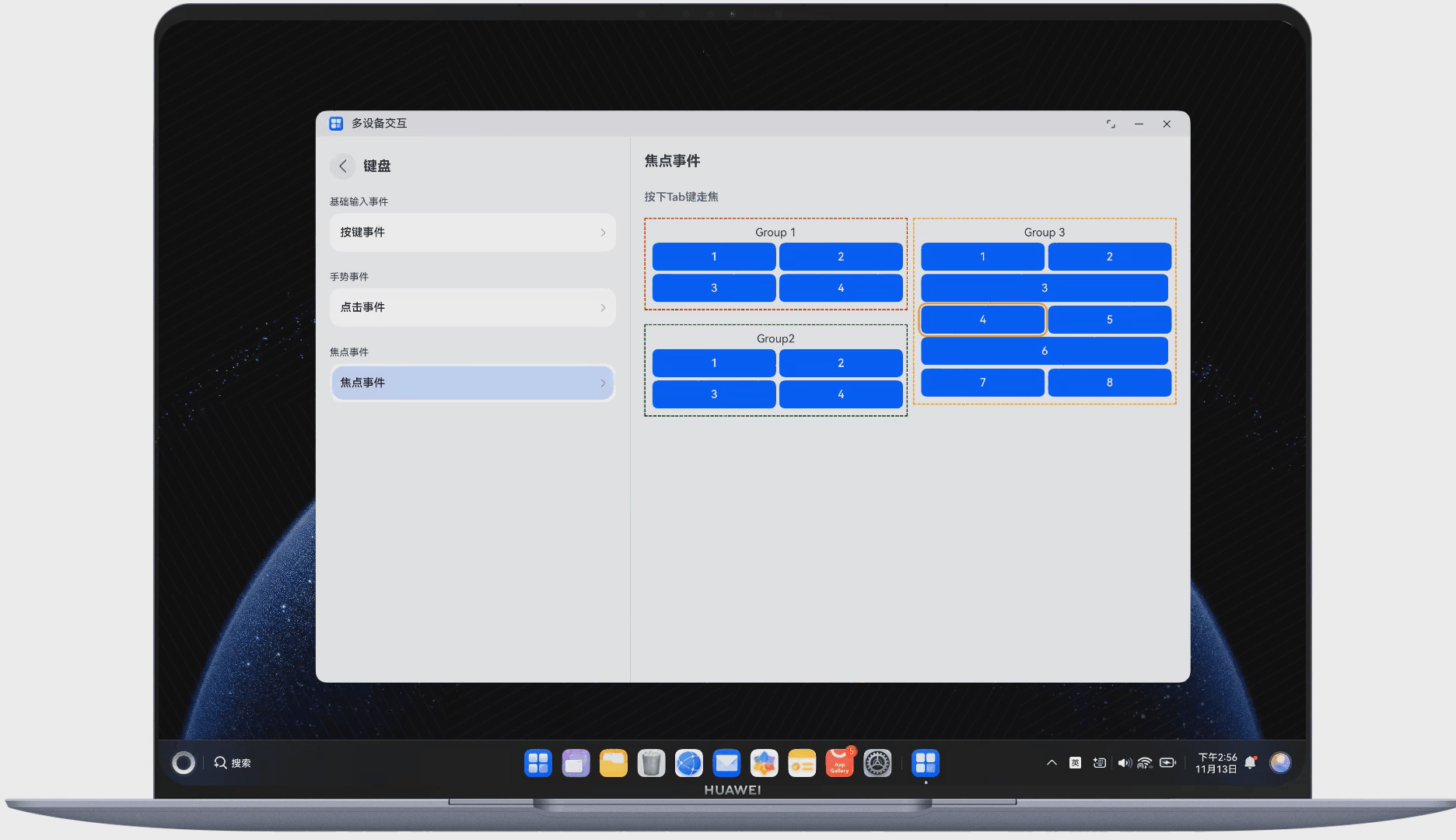
在多端交互中,键盘交互也是重要的组成部分。下面展示了使用键盘走焦的示例,如图 5 所示:
图5使用键盘走焦
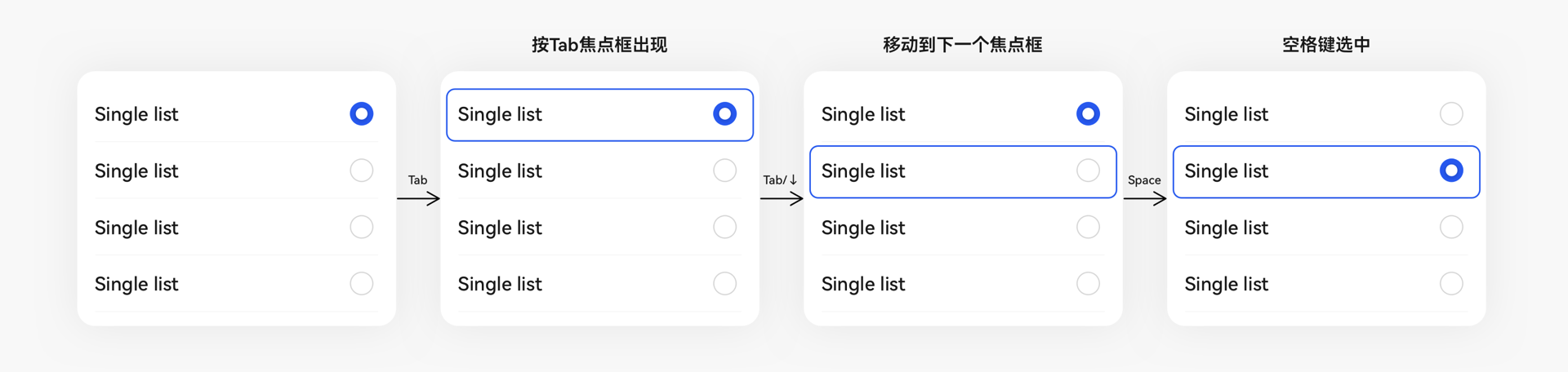
同时,良好的走焦样式指引对于提升用户体验非常重要,如图 6 所示:
图6走焦样式指引案例
5.1 任务迁移
将任务从当前设备迁移到目标设备:
typescript
import { distributedTask } from "@kit.DistributedTaskKit";
// 迁移任务
let taskInfo = {
bundleName: "com.example.myapplication",
abilityName: "EntryAbility",
parameters: {
key1: "value1",
key2: "value2",
},
};
distributedTask.migrateTaskToDevice(deviceId, taskInfo, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`任务迁移失败: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
} else {
console.log("任务迁移成功");
}
});5.2 远程调用
调用目标设备上的能力:
typescript
import { remote } from "@kit.RemoteDeviceKit";
// 创建远程调用会话
let session = remote.createRemoteSession(deviceId);
// 调用远程方法
session.callRemoteMethod("remoteMethod", { param: "test" }, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`远程调用失败: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
} else {
console.log(`远程调用结果: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
// 关闭会话
session.close();
});6. 多端交互最佳实践
6.1 场景一:跨设备文档编辑
实现思路:
- 使用分布式数据对象同步文档内容
- 使用分布式任务调度实现编辑任务迁移
- 使用分布式安全确保文档内容安全
typescript
// 文档编辑示例
import { distributedData } from '@kit.DistributedDataKit';
@Component
export struct DistributedDocumentEditor {
// 创建分布式文档对象
private docObject = distributedData.createDistributedObject({
content: '',
cursorPosition: 0,
lastEditTime: 0
});
@State localContent: string = '';
build() {
Column() {
TextInput({
text: this.localContent,
placeholder: '开始编辑文档...'
})
.width('100%')
.height(300)
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.localContent = value;
// 同步到分布式数据对象
this.docObject.set('content', value);
this.docObject.set('lastEditTime', Date.now());
})
Button('同步到其他设备')
.onClick(() => {
console.log('文档已同步');
})
}
.padding(20)
}
aboutToAppear() {
// 监听分布式数据变化
this.docObject.on('change', (data) => {
if (data.changedKeys.includes('content')) {
this.localContent = this.docObject.get('content') as string;
}
});
}
}6.2 场景二:多设备协同游戏
实现思路:
- 使用分布式软总线实现设备间实时通信
- 使用分布式数据管理同步游戏状态
- 使用分布式任务调度协调游戏流程
typescript
// 多设备协同游戏示例
import { distributedData } from '@kit.DistributedDataKit';
import { distributedDeviceManager } from '@kit.DeviceManagerKit';
@Component
export struct DistributedGame {
// 游戏状态
private gameState = distributedData.createDistributedObject({
players: [] as Array<{ deviceId: string; name: string; score: number }>,
currentTurn: '',
gameStatus: 'waiting' // waiting, playing, finished
});
@State localPlayerName: string = '玩家1';
@State connectedDevices: Array<distributedDeviceManager.DeviceInfo> = [];
build() {
Column() {
Text('多设备协同游戏')
.fontSize(24)
.margin(20)
TextInput({
text: this.localPlayerName,
placeholder: '输入你的昵称'
})
.width('80%')
.margin(20)
Button('加入游戏')
.onClick(() => {
this.joinGame();
})
Text('已连接设备:')
.fontSize(18)
.margin(20)
ForEach(this.connectedDevices, (device) => {
Text(device.deviceName)
.padding(10)
})
Button('开始游戏')
.onClick(() => {
this.startGame();
})
.margin(20)
}
}
joinGame() {
// 获取设备管理器
let deviceManager = distributedDeviceManager.getDistributedDeviceManager();
if (deviceManager) {
// 获取本地设备信息
let localDeviceInfo = deviceManager.getLocalDeviceInfo();
// 添加玩家到游戏状态
let players = this.gameState.get('players') as Array<{ deviceId: string; name: string; score: number }>;
players.push({
deviceId: localDeviceInfo.deviceId,
name: this.localPlayerName,
score: 0
});
this.gameState.set('players', players);
this.gameState.set('gameStatus', 'waiting');
console.log(`${this.localPlayerName} 加入了游戏`);
}
}
startGame() {
// 设置游戏状态为开始
this.gameState.set('gameStatus', 'playing');
// 设置当前回合
let players = this.gameState.get('players') as Array<{ deviceId: string; name: string; score: number }>;
if (players.length > 0) {
this.gameState.set('currentTurn', players[0].deviceId);
}
console.log('游戏开始');
}
aboutToAppear() {
// 监听设备连接状态
let deviceManager = distributedDeviceManager.getDistributedDeviceManager();
if (deviceManager) {
deviceManager.on('deviceStateChange', (data) => {
if (data.action === distributedDeviceManager.DeviceStateChangeAction.DEVICE_ONLINE) {
this.connectedDevices.push(data.deviceInfo);
} else if (data.action === distributedDeviceManager.DeviceStateChangeAction.DEVICE_OFFLINE) {
this.connectedDevices = this.connectedDevices.filter(device => device.deviceId !== data.deviceId);
}
});
}
}
}7. 多端交互性能优化
7.1 减少数据传输量
- 只传输必要的数据字段
- 使用压缩算法减少数据大小
- 批量传输数据,减少通信次数
7.2 优化设备发现机制
- 使用合适的发现模式(主动/被动)
- 设置合理的发现超时时间
- 避免频繁扫描设备
7.3 合理使用缓存
- 在本地缓存常用数据
- 减少跨设备数据查询次数
- 使用增量同步减少数据传输
8. 总结
多端交互是 HarmonyOS 分布式能力的核心特性,通过本文的介绍,我们了解了:
- HarmonyOS 分布式能力框架的基本组成
- 设备发现与连接的实现方法
- 跨设备数据共享的技术方案
- 跨设备任务调度的使用场景
- 多端交互的最佳实践案例
- 性能优化的关键策略
通过合理应用这些技术,开发者可以构建出更加智能、高效的多端协同应用,为用户提供无缝的跨设备体验。