一.栈
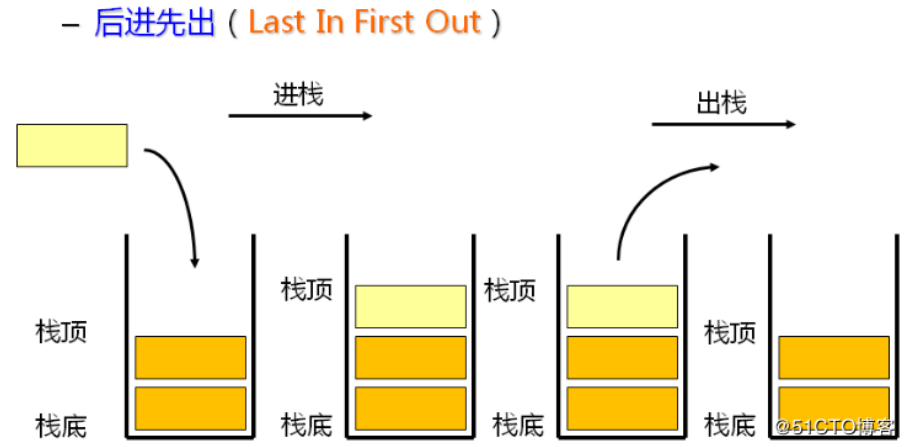
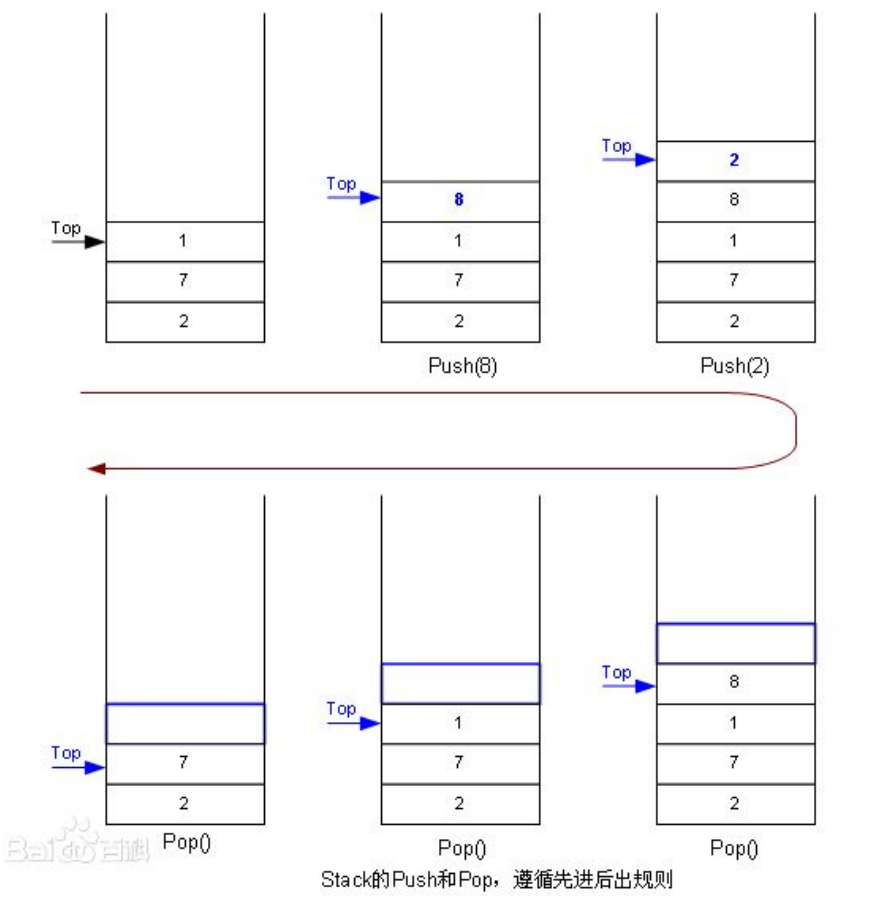
1.栈的概念及结构

2.栈的实现
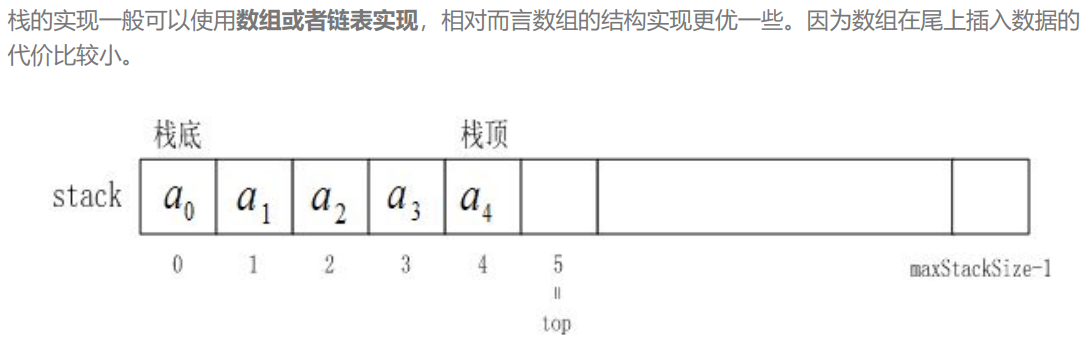
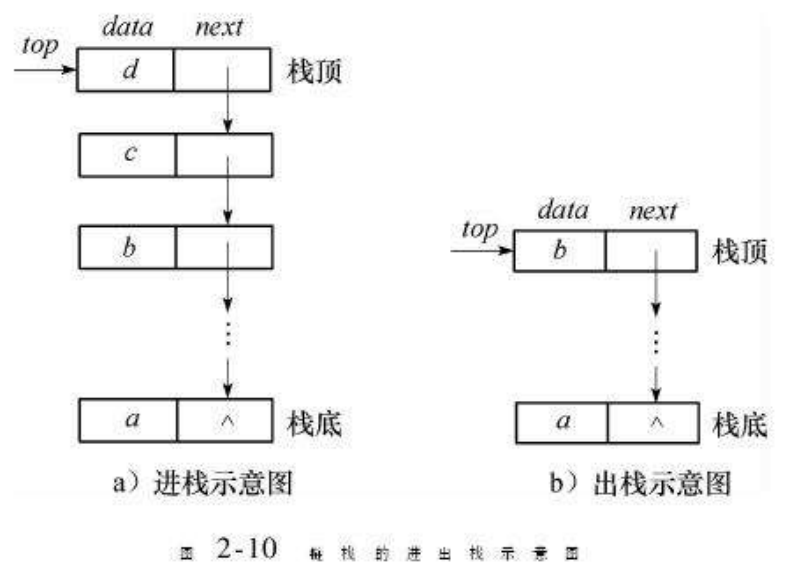
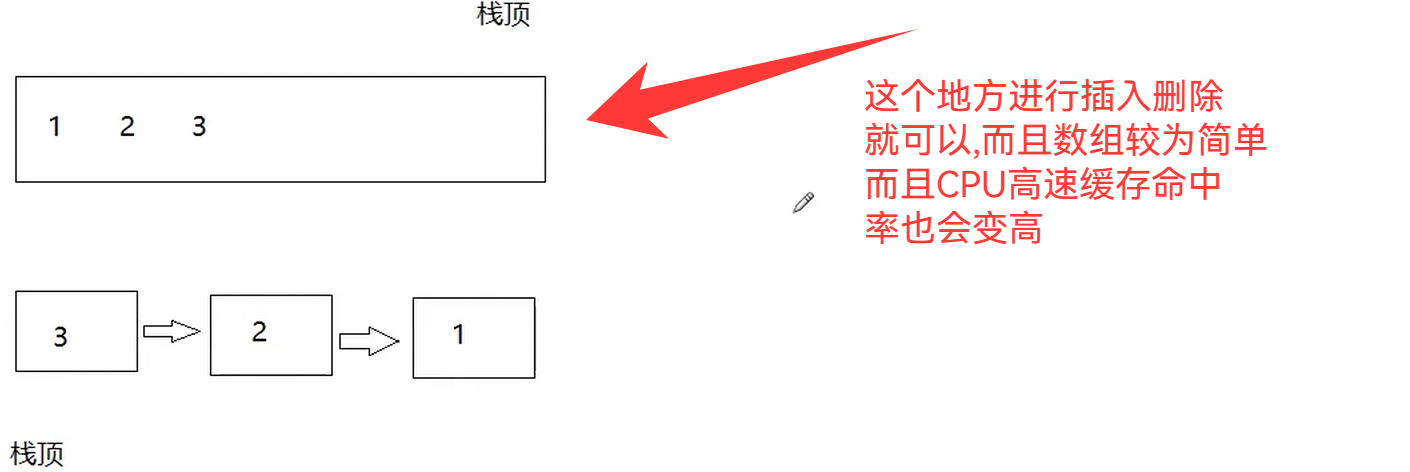
这里我们使用数组作为我们的底层存储
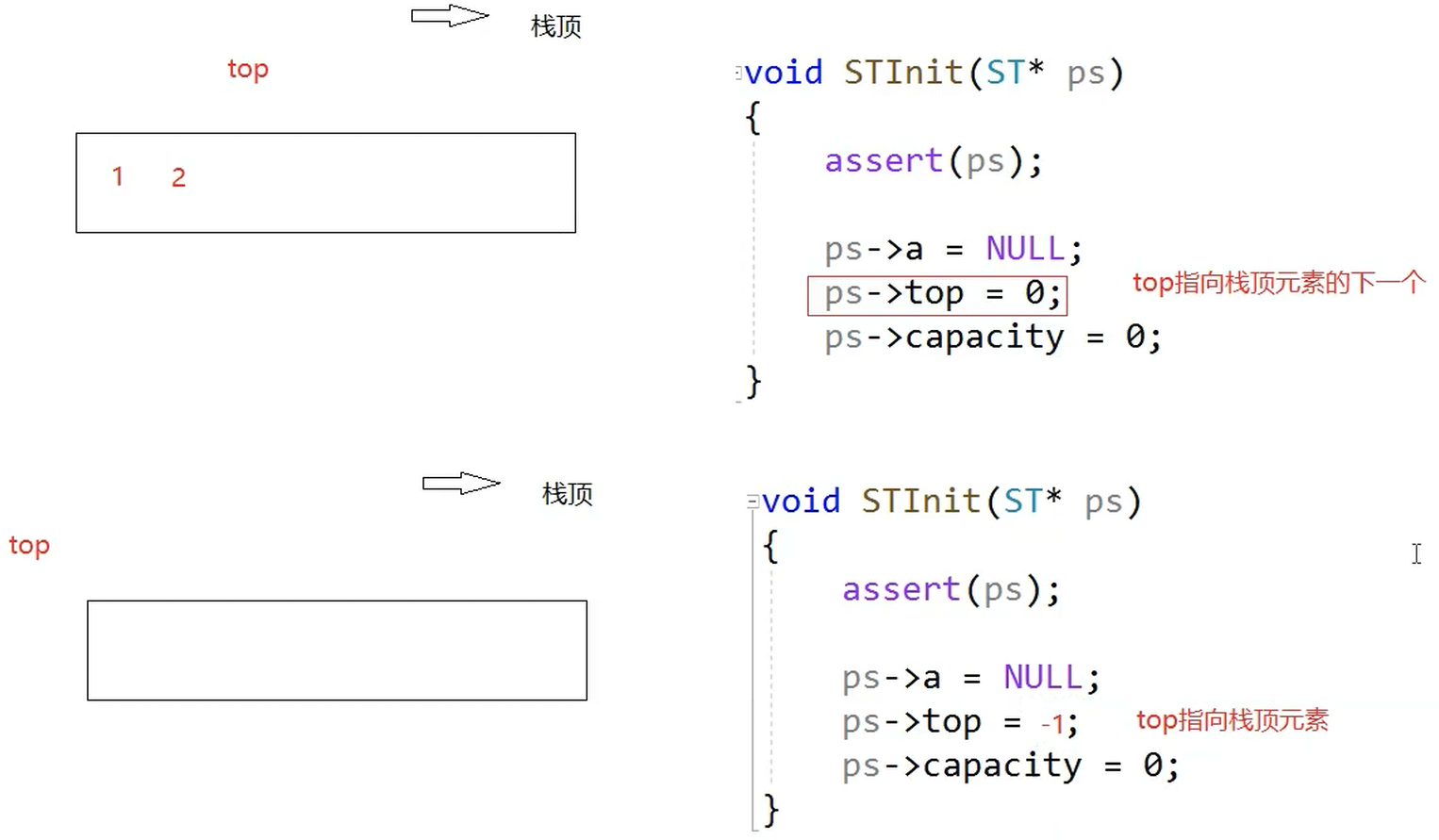
a.Stack.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
int STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);b.Stack.c
cpp
#include"Stack.h"
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
// ջ
// 11:55
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
// ˣ
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}c.test.c
cpp
#include"Stack.h"
int main()
{
ST s;
STInit(&s);
STPush(&s, 1);
STPush(&s, 2);
STPush(&s, 3);
int top = STTop(&s);
printf("%d ", top);
STPop(&s);
top = STTop(&s);
printf("%d ", top);
STPop(&s);
STPush(&s, 4);
STPush(&s, 5);
while (!STEmpty(&s))
{
int top = STTop(&s);
printf("%d ", top);
STPop(&s);
}
STDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}3.概念选择题

B

C
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/

cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '{')
st.push(i);
else {
if (st.empty())
return false;
if (s[i] == ')' && s[st.top()] != '(')
return false;
if (s[i] == '}' && s[st.top()] != '{')
return false;
if (s[i] == ']' && s[st.top()] != '[')
return false;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
};
二.队列
1.队列的概念及结构
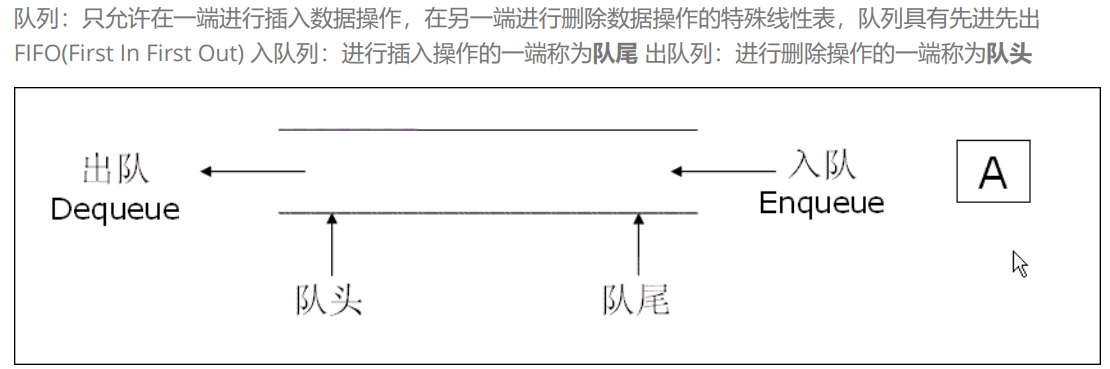
2.队列的实现
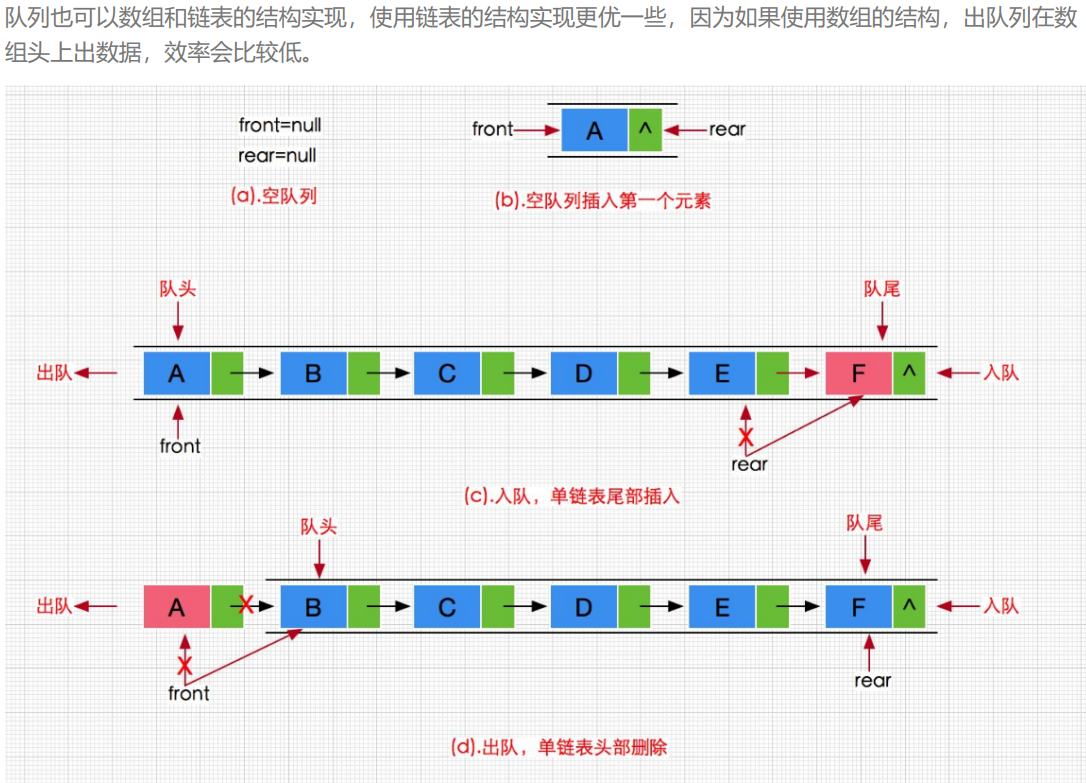
所以,我们实现队列,采用单项不循环单链表(哨兵位,可要可不要)
a.Queue.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
int val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
//// 入队列
//void QueuePush(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail);
//
//// 出队列
//void QueuePop(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail);
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
// 入队列
void QueuePush(Queue *pq, QDataType x);
// 出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);b.Queue.c
cpp
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail)
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
// 0个节点
// 温柔检查
//if (pq->phead == NULL)
// return;
// 暴力检查
assert(pq->phead != NULL);
// 一个节点
// 多个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
// 暴力检查
assert(pq->phead != NULL);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
// 暴力检查
assert(pq->ptail != NULL);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}c.test.c
cpp
#include"Queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return 0;
}三.刷题(我们直接使用对应的C++中的已经实现好的栈和队列)
1.用队列实现栈
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/

cpp
class MyStack {
public:
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
q_push.push(x);
while(q_pop.size())
{
q_push.push(q_pop.front());
q_pop.pop();
}
swap(q_push,q_pop);
}
int pop() {
int ans = q_pop.front();
q_pop.pop();
return ans;
}
int top() {
return q_pop.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q_pop.size() == 0;
}
queue<int> q_pop;
queue<int> q_push;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/2.用栈实现队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/
cpp
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> popst,pushst;
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
pushst.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(popst.empty())
{
while(pushst.size())
{
popst.push(pushst.top());
pushst.pop();
}
}
int x = popst.top();
popst.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if(popst.size())
{
return popst.top();
}
while(pushst.size())
{
popst.push(pushst.top());
pushst.pop();
}
return popst.top();
}
bool empty() {
if(popst.empty() &&pushst.empty())
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/3.设计循环队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/

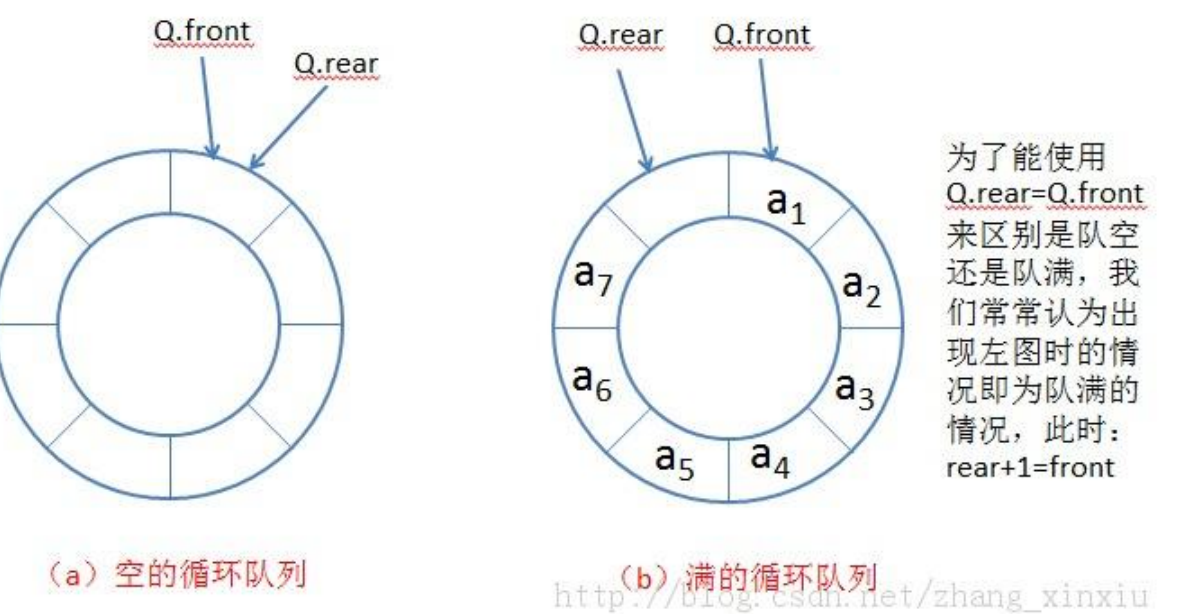
cpp
class MyCircularQueue {
private:
int front;
int end;
int capacity;
vector<int> elements;
public:
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
capacity = k + 1;
elements = vector<int>(k + 1);
front = end = 0;
}
bool enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elements[end] = value;
end = (end + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
bool deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[front];
}
int Rear() {
if(isEmpty())
{
return -1;
}
return elements[(end - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
bool isEmpty() {
return end == front;
}
bool isFull() {
return (end + 1) % capacity == front;
}
};
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue* obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* bool param_1 = obj->enQueue(value);
* bool param_2 = obj->deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj->Front();
* int param_4 = obj->Rear();
* bool param_5 = obj->isEmpty();
* bool param_6 = obj->isFull();
*/