WPF 力导引算法实现图布局
1 经典基础算法
-
Eades 算法 (1984)
-
核心思想:最早引入"弹簧-质点"模型的算法,边模拟为弹簧(吸引力),非邻接节点间模拟为斥力。
-
特点:简单直观,但收敛较慢,易陷入局部最优。
-
-
Fruchterman-Reingold 算法 (1991)
-
核心思想:引入"温度"概念控制位移幅度,迭代中温度逐渐降低(类似模拟退火)。
-
力模型:
-
吸引力:与边长度成正比(
f_a = d^2 / k,d为边长,k为理想边长)。 -
斥力:与节点距离平方成反比(
f_r = -k^2 / d)。
-
-
特点:布局紧凑均匀,适用于中小规模网络。
-
-
Kamada-Kawai 算法 (1989)
-
核心思想 :基于能量最小化,目标是将所有节点对的几何距离逼近其图论最短路径长度。
-
特点:能较好展现全局结构,但计算所有节点对最短路径开销大,适用于数百节点的图。
-
2 高性能优化算法(适合大规模网络)
-
Barnes-Hut 近似算法 (基于四叉树/八叉树)
-
核心思想:将远距离节点群近似为单个质心,将斥力计算复杂度从 O(N²) 降为 O(N log N)。
-
应用:常用于天体物理的N-body问题,被集成到许多力导引布局工具中。
-
-
ForceAtlas2 (2011)
-
核心思想:专为Gephi软件设计的算法,在FR基础上改进:
-
引入度依赖的斥力(高度数节点产生更强斥力,避免中心重叠)。
-
支持边缘权重调整吸引力。
-
采用自适应温度 和防止震荡的阻尼。
-
-
特点:适合复杂真实网络(如社交网络),布局层次清晰。
-
-
LinLog 模型
-
核心思想 :优化能量函数为
U = Σ边的距离 - Σ节点对的log(距离),强调聚类结构。 -
特点:同一簇内节点更紧密,簇间距离更明显。
-
3 代码实现
- 数据模型
cs
/// <summary>
/// 节点
/// </summary>
public class Node
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public double X { get; set; }
public double Y { get; set; }
public double Radius { get; set; }
// 布局计算中使用的临时变量
internal double DX { get; set; } // X轴位移/速度
internal double DY { get; set; } // Y轴位移/速度
internal int Degree { get; set; } // 节点的度(连接数)
public Node(string id, double radius = 5.0)
{
Id = id;
Radius = radius;
}
public override string ToString() => $"Node[{Id}]: ({X:F2}, {Y:F2})";
}
/// <summary>
/// 关系
/// </summary>
public class Relationship
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string SourceId { get; set; }
public string TargetId { get; set; }
public Relationship(string source, string target)
{
SourceId = source;
TargetId = target;
Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
public Relationship(string source, string target, string id)
{
SourceId = source;
TargetId = target;
Id = id;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 图结构
/// </summary>
public class Graph
{
public Dictionary<string, Node> Nodes { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, Relationship> Relationships { get; set; }
public Graph()
{
Nodes = new Dictionary<string, Node>();
Relationships = new Dictionary<string, Relationship>();
}
public void AddNode(Node node)
{
Nodes[node.Id] = node;
}
public void AddRelationship(Relationship relationship)
{
Relationships[relationship.Id] = relationship;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 矩形布局范围
/// </summary>
public struct LayoutBounds
{
public double MinX;
public double MaxX;
public double MinY;
public double MaxY;
public LayoutBounds(double x, double y, double width, double height)
{
MinX = x;
MinY = y;
MaxX = x + width;
MaxY = y + height;
}
public double Width => MaxX - MinX;
public double Height => MaxY - MinY;
public double CenterX => (MinX + MaxX) / 2.0;
public double CenterY => (MinY + MaxY) / 2.0;
}- 核心算法
cs
public class LinLogLayout
{
// 配置参数
private const int Iterations = 100; // 迭代次数
private const double RepulsionForce = 20.0; // 斥力
private const double AttractionForce = 1.0; // 引力
private const double StepSize = 0.8; // 稍微调大初始步长以适应约束
private const double Decay = 0.97; // 衰变系数
private const double GravityStrength = 0.01; // 强度越大,图越紧凑在中央
private const double MinClearance = 0.1; // 斥力计算的最小安全距离(防止除以零,并作为最小非重叠缓冲)
private const double Epsilon = 1e-6; // 防止除以零的微小值 (Epsilon)
private const double MaxMovementPerStep = 2.0; // 限制节点单步最大移动距离。值越小,越稳定,但收敛越慢。在边界小的情况下,此值应适当减小。
/// <summary>
/// 执行布局计算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="nodes">节点列表</param>
/// <param name="relations">关系列表</param>
/// <param name="bounds">矩形限制范围</param>
public void ComputeLayout(List<Node> nodes, List<Relationship> relations, LayoutBounds bounds)
{
if (nodes == null || nodes.Count == 0) return;
// 1. 初始化:将节点随机放置在边界范围内
// 这比在(0,0)附近随机更好,避免一开始就飞出很远
Random rnd = new Random();
foreach (var n in nodes)
{
// 如果节点还没坐标(或是0,0),给一个范围内的随机值
if (Math.Abs(n.X) < 0.001 && Math.Abs(n.Y) < 0.001)
{
n.X = bounds.MinX + rnd.NextDouble() * bounds.Width;
n.Y = bounds.MinY + rnd.NextDouble() * bounds.Height;
}
}
var nodeDict = nodes.ToDictionary(n => n.Id);
// 筛选有效关系
var validRelations = relations
.Where(r => nodeDict.ContainsKey(r.SourceId) && nodeDict.ContainsKey(r.TargetId))
.ToList();
double currentStep = StepSize;
// 2. 迭代循环
for (int i = 0; i < Iterations; i++)
{
// 重置力向量
foreach (var n in nodes) { n.DX = 0; n.DY = 0; }
// --- A. 计算斥力 (Repulsion) 考虑 Radius ---
for (int a = 0; a < nodes.Count; a++)
{
var nodeA = nodes[a];
for (int b = a + 1; b < nodes.Count; b++)
{
var nodeB = nodes[b];
double dx = nodeA.X - nodeB.X;
double dy = nodeA.Y - nodeB.Y;
double distSq = dx * dx + dy * dy;
double dist = Math.Sqrt(distSq); // 节点中心点的实际距离
// NaN 保护机制 1: 检查中心距离是否为零
if (dist < Epsilon)
{
// 节点完全重叠,施加随机扰动以获得方向
dx = rnd.NextDouble() * 2 * Epsilon;
dy = rnd.NextDouble() * 2 * Epsilon;
dist = Math.Sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
// 确保 dist 不会是 NaN 或零
if (dist < Epsilon) dist = Epsilon;
}
// 1. 计算两个节点半径之和
double sumOfRadii = nodeA.Radius + nodeB.Radius;
// 2. 计算节点表面之间的净空距离 (Clearance)
double clearance = dist - sumOfRadii;
// 3. 确定用于斥力计算的有效距离 (Effective Distance)
// 如果节点重叠 (clearance <= 0),将有效距离强制设为 MinClearance (0.1)
// 这将产生巨大的斥力来推开重叠的节点
double effectiveDist = Math.Max(clearance, MinClearance);
// 4. 应用 LinLog 斥力公式: F = K / effectiveDist
// 注意:这里的斥力是基于表面距离的,而不是中心距离。
double force = RepulsionForce / effectiveDist;
// 5. 应用斥力 (方向仍基于中心点连线)
double fx = (dx / dist) * force;
double fy = (dy / dist) * force;
nodeA.DX += fx; nodeA.DY += fy;
nodeB.DX -= fx; nodeB.DY -= fy;
}
}
// --- B. 计算引力 (Attraction) ---
foreach (var rel in validRelations)
{
var u = nodeDict[rel.SourceId];
var v = nodeDict[rel.TargetId];
double dx = v.X - u.X;
double dy = v.Y - u.Y;
double distSq = dx * dx + dy * dy;
double dist = Math.Sqrt(distSq);
// NaN 保护机制 2: 检查中心距离是否为零
if (dist < Epsilon)
{
// 节点重叠,跳过引力计算(让斥力将它们推开)
continue;
}
// LinLog Attraction
double force = AttractionForce;
double fx = (dx / dist) * force;
double fy = (dy / dist) * force;
u.DX += fx;
u.DY += fy;
v.DX -= fx;
v.DY -= fy;
}
// --- C. 计算中心引力 (Central Gravity) ---
double centerX = bounds.CenterX;
double centerY = bounds.CenterY;
foreach (var n in nodes)
{
double dx = n.X - centerX; // 节点指向中心的向量是 -dx
double dy = n.Y - centerY;
double dist = Math.Sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
// NaN 保护机制 3: 检查距离是否为零
if (dist < Epsilon)
{
// 节点在中心点,力为零,跳过计算
continue;
}
double force = GravityStrength * dist;
n.DX -= (dx / dist) * force;
n.DY -= (dy / dist) * force;
}
// --- D. 更新位置并应用边界约束 ---
foreach (var n in nodes)
{
// 1. 计算理论位移
double movementX = n.DX * currentStep;
double movementY = n.DY * currentStep;
double movementDist = Math.Sqrt(movementX * movementX + movementY * movementY);
// 2. 限制最大位移
if (movementDist > MaxMovementPerStep)
{
// 如果超出最大限制,按比例缩小位移向量
double ratio = MaxMovementPerStep / movementDist;
movementX *= ratio;
movementY *= ratio;
}
// 3. 应用位移
n.X += movementX;
n.Y += movementY;
// 4. 矩形边界硬约束
if (n.X < bounds.MinX) n.X = bounds.MinX;
else if (n.X > bounds.MaxX) n.X = bounds.MaxX;
if (n.Y < bounds.MinY) n.Y = bounds.MinY;
else if (n.Y > bounds.MaxY) n.Y = bounds.MaxY;
}
//foreach (var n in nodes)
//{
// // 移动
// n.X += n.DX * currentStep;
// n.Y += n.DY * currentStep;
// // 边界限制 (Clamping)
// if (n.X < bounds.MinX) n.X = bounds.MinX;
// else if (n.X > bounds.MaxX) n.X = bounds.MaxX;
// if (n.Y < bounds.MinY) n.Y = bounds.MinY;
// else if (n.Y > bounds.MaxY) n.Y = bounds.MaxY;
//}
// --- E. 冷却 ---
currentStep *= Decay;
}
}
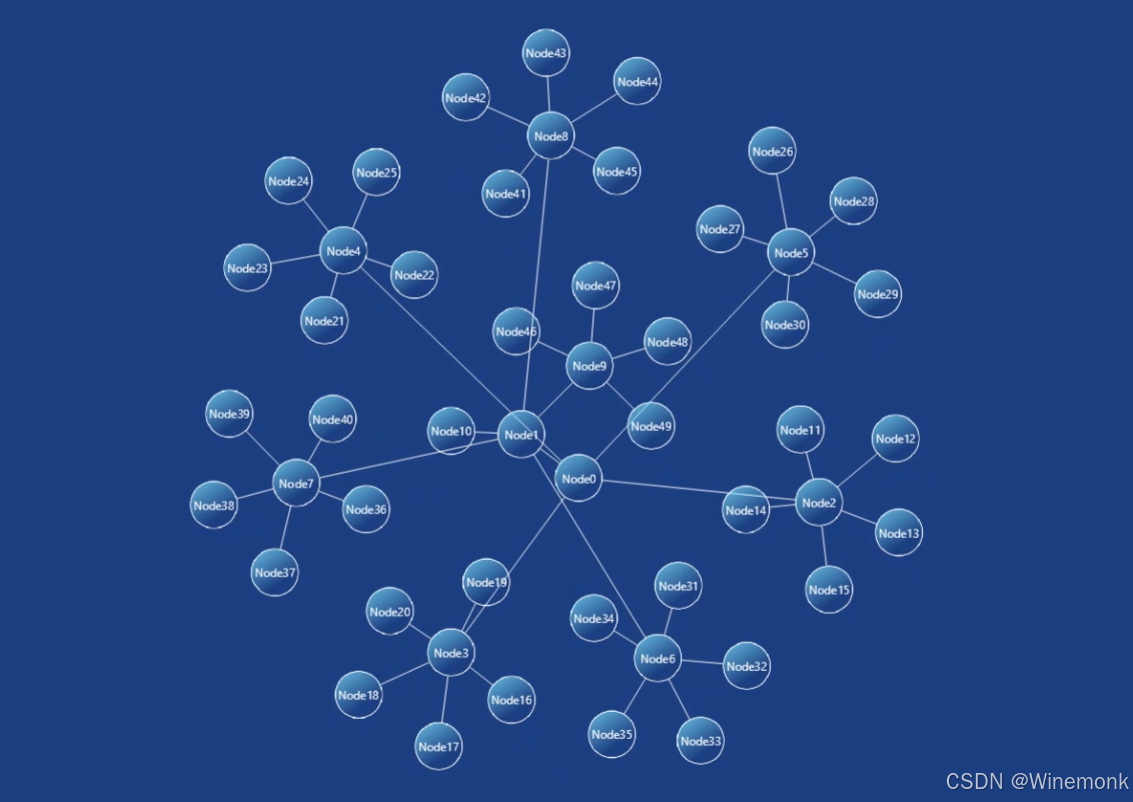
}效果Demo:
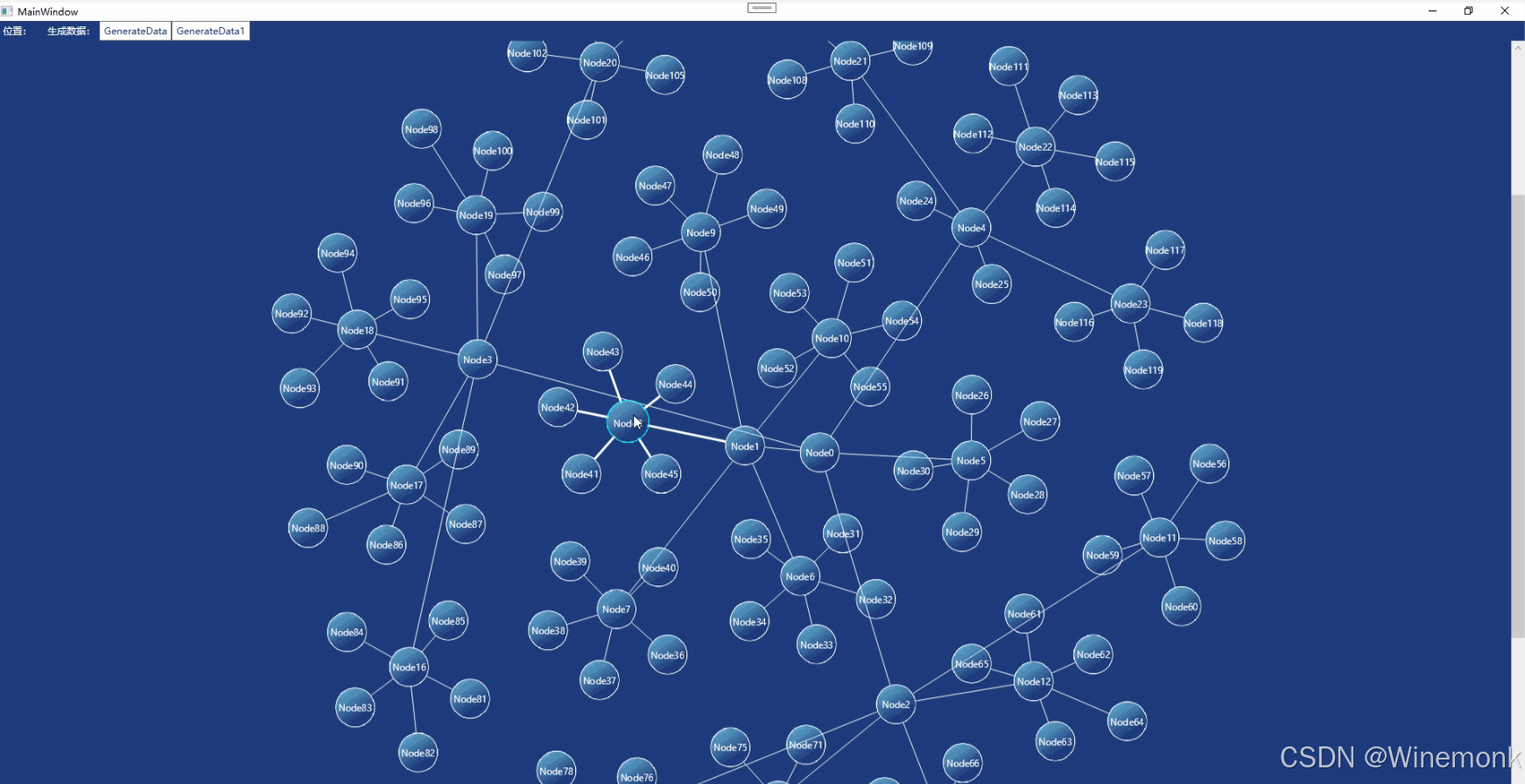

效果视频:

https://live.csdn.net/v/504775
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Winemonk/images/master/blog/post/202512091617226.mp4