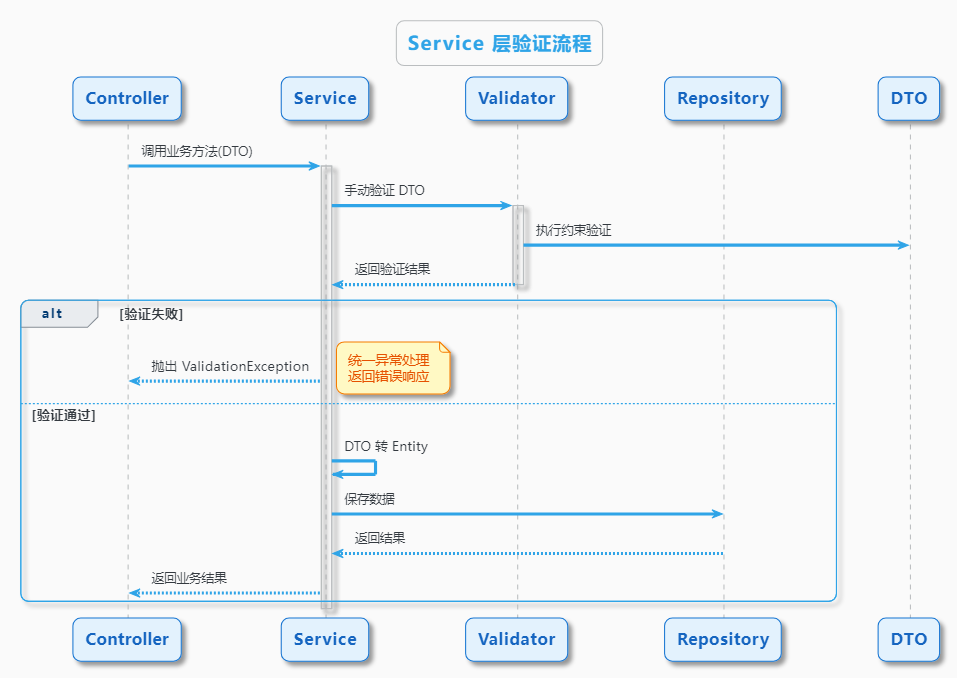
1 Service 层验证架构
2 使用 @Validated 注解(方法级验证)
java
// Service 接口
public interface OrderService {
Order createOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO);
Order updateOrder(Long id, OrderDTO orderDTO);
}
// Service 实现类
@Service
@Validated // ⚠️ 类级别注解:开启方法参数验证
@Slf4j
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
/**
* 创建订单 - 使用 @Valid 自动验证
*/
@Override
public Order createOrder(@Valid OrderDTO orderDTO) {
log.info("创建订单: {}", orderDTO);
// 验证通过后执行业务逻辑
// 1. 检查商品库存
for (OrderItemDTO item : orderDTO.getItems()) {
if (!productService.checkStock(item.getProductId(), item.getQuantity())) {
throw new BusinessException("商品库存不足");
}
}
// 2. 计算总价
BigDecimal totalAmount = calculateTotal(orderDTO);
// 3. 创建订单
Order order = new Order();
order.setCustomerId(orderDTO.getCustomerId());
order.setTotalAmount(totalAmount);
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.PENDING);
// 4. 保存订单
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
/**
* 更新订单 - 使用分组验证
*/
@Override
public Order updateOrder(@PathVariable Long id,
@Validated(ValidationGroups.Update.class) OrderDTO orderDTO) {
Order order = orderRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new BusinessException("订单不存在"));
// 只允许更新特定状态的订单
if (order.getStatus() != OrderStatus.PENDING) {
throw new BusinessException("订单状态不允许修改");
}
// 更新订单信息
order.setRemark(orderDTO.getRemark());
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
private BigDecimal calculateTotal(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
return orderDTO.getItems().stream()
.map(item -> {
Product product = productService.getById(item.getProductId());
return product.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(item.getQuantity()));
})
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
}
}
// DTO 定义
@Data
public class OrderDTO {
@NotNull(groups = ValidationGroups.Update.class, message = "订单ID不能为空")
private Long id;
@NotNull(message = "客户ID不能为空")
private Long customerId;
@Valid
@NotEmpty(message = "订单项不能为空")
@Size(max = 100, message = "订单项不能超过100个")
private List<OrderItemDTO> items;
@Size(max = 500, message = "备注长度不能超过500字符")
private String remark;
@NotNull(message = "收货地址不能为空")
@Valid
private AddressDTO address;
}
@Data
public class OrderItemDTO {
@NotNull(message = "商品ID不能为空")
private Long productId;
@NotNull(message = "数量不能为空")
@Min(value = 1, message = "数量至少为1")
@Max(value = 999, message = "数量不能超过999")
private Integer quantity;
}3 手动调用 Validator(编程式验证)
java
// Service 实现类 - 手动验证方式
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private Validator validator; // ⚠️ 注入 javax.validation.Validator
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
/**
* 批量导入商品 - 逐个验证
*/
public BatchImportResult batchImport(List<ProductDTO> productDTOs) {
List<Product> successProducts = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> errors = new ArrayList<>();
// 逐个验证
for (int i = 0; i < productDTOs.size(); i++) {
ProductDTO dto = productDTOs.get(i);
// 手动验证
Set<ConstraintViolation<ProductDTO>> violations = validator.validate(dto);
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
// 收集错误信息
String errorMsg = String.format("第%d行: %s", i + 1,
violations.stream()
.map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", ")));
errors.add(errorMsg);
log.error("商品验证失败: {}", errorMsg);
} else {
// 验证通过,转换为实体
Product product = convertToEntity(dto);
successProducts.add(product);
}
}
// 如果有错误,返回批量导入结果
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
log.warn("批量导入完成,成功: {}, 失败: {}", successProducts.size(), errors.size());
return BatchImportResult.builder()
.successCount(successProducts.size())
.failCount(errors.size())
.errors(errors)
.build();
}
// 保存所有商品
productRepository.saveAll(successProducts);
return BatchImportResult.success(successProducts.size());
}
/**
* 条件验证 - 根据不同条件使用不同验证组
*/
public Product createOrUpdate(ProductDTO dto, boolean isUpdate) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<ProductDTO>> violations;
if (isUpdate) {
// 更新时验证(需要ID)
violations = validator.validate(dto, ValidationGroups.Update.class);
} else {
// 创建时验证(不需要ID)
violations = validator.validate(dto, ValidationGroups.Create.class);
}
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
String errorMsg = violations.stream()
.map(v -> v.getPropertyPath() + ": " + v.getMessage())
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
throw new ValidationException(errorMsg);
}
// 执行业务逻辑
return isUpdate ? updateProduct(dto) : createProduct(dto);
}
/**
* 验证单个属性
*/
public void validateAndUpdatePrice(Long productId, BigDecimal newPrice) {
ProductDTO dto = new ProductDTO();
dto.setPrice(newPrice);
// 只验证 price 属性
Set<ConstraintViolation<ProductDTO>> violations =
validator.validateProperty(dto, "price");
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
throw new ValidationException(
violations.iterator().next().getMessage()
);
}
// 更新价格
Product product = productRepository.findById(productId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new BusinessException("商品不存在"));
product.setPrice(newPrice);
productRepository.save(product);
}
/**
* 验证属性值(无需创建对象实例)
*/
public boolean isValidProductName(String name) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<ProductDTO>> violations =
validator.validateValue(ProductDTO.class, "name", name);
return violations.isEmpty();
}
private Product convertToEntity(ProductDTO dto) {
Product product = new Product();
product.setName(dto.getName());
product.setPrice(dto.getPrice());
product.setStock(dto.getStock());
return product;
}
private Product createProduct(ProductDTO dto) {
// 创建逻辑
return null;
}
private Product updateProduct(ProductDTO dto) {
// 更新逻辑
return null;
}
}
@Data
@Builder
class BatchImportResult {
private int successCount;
private int failCount;
private List<String> errors;
public static BatchImportResult success(int count) {
return BatchImportResult.builder()
.successCount(count)
.failCount(0)
.errors(Collections.emptyList())
.build();
}
}4 封装验证工具类
java
/**
* 验证工具类 - 简化验证操作
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ValidationHelper {
@Autowired
private Validator validator;
/**
* 验证对象,失败抛出异常
*/
public <T> void validateOrThrow(T object, Class<?>... groups) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> violations = validator.validate(object, groups);
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
String errorMsg = formatViolations(violations);
log.error("验证失败: {}", errorMsg);
throw new ValidationException(errorMsg);
}
}
/**
* 验证对象,返回结果
*/
public <T> ValidationResult validate(T object, Class<?>... groups) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> violations = validator.validate(object, groups);
return new ValidationResult(violations);
}
/**
* 验证属性,失败抛出异常
*/
public <T> void validatePropertyOrThrow(T object, String property, Class<?>... groups) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> violations =
validator.validateProperty(object, property, groups);
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
throw new ValidationException(
property + ": " + violations.iterator().next().getMessage()
);
}
}
/**
* 验证值(无需对象实例)
*/
public <T> boolean isValidValue(Class<T> beanType, String property, Object value, Class<?>... groups) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> violations =
validator.validateValue(beanType, property, value, groups);
return violations.isEmpty();
}
/**
* 批量验证集合
*/
public <T> List<ValidationResult> validateList(List<T> list, Class<?>... groups) {
return list.stream()
.map(item -> validate(item, groups))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 格式化验证错误
*/
private <T> String formatViolations(Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> violations) {
return violations.stream()
.map(v -> v.getPropertyPath() + ": " + v.getMessage())
.collect(Collectors.joining("; "));
}
/**
* 验证结果封装类
*/
@Getter
public static class ValidationResult {
private final boolean valid;
private final Map<String, String> errors;
private final List<String> errorMessages;
public ValidationResult(Set<? extends ConstraintViolation<?>> violations) {
this.valid = violations.isEmpty();
this.errors = violations.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
v -> v.getPropertyPath().toString(),
ConstraintViolation::getMessage,
(v1, v2) -> v1 + "; " + v2,
LinkedHashMap::new
));
this.errorMessages = new ArrayList<>(errors.values());
}
public void throwIfInvalid() {
if (!valid) {
throw new ValidationException(String.join("; ", errorMessages));
}
}
public String getFirstError() {
return errorMessages.isEmpty() ? null : errorMessages.get(0);
}
}
}
// 使用工具类
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private ValidationHelper validationHelper;
public void createUser(UserDTO userDTO) {
// 方式1:验证失败抛出异常
validationHelper.validateOrThrow(userDTO);
// 方式2:获取验证结果
ValidationHelper.ValidationResult result = validationHelper.validate(userDTO);
if (!result.isValid()) {
log.error("用户数据验证失败: {}", result.getErrors());
throw new ValidationException(result.getFirstError());
}
// 业务逻辑
}
}5 Service 层验证注意事项
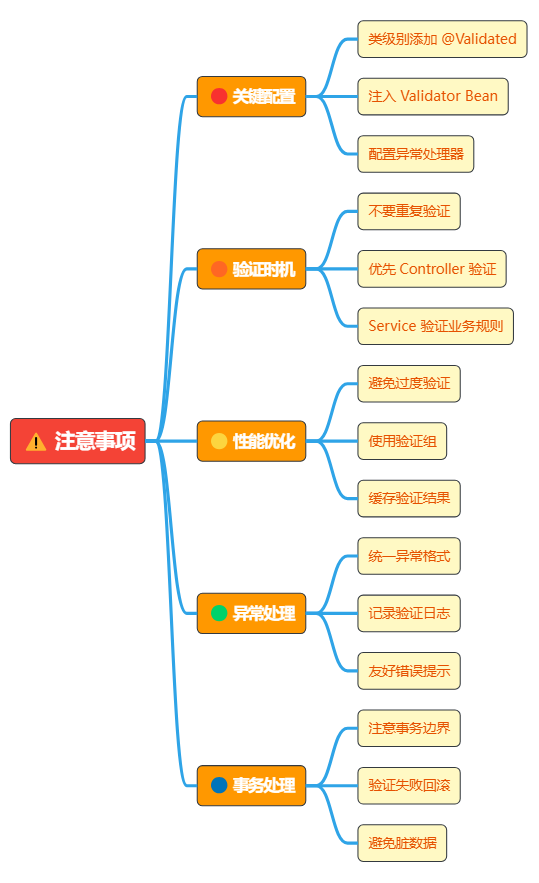
详细说明:
- 🔴** 关键配置**
java
// ✅ 正确:类级别添加 @Validated
@Service
@Validated
public class UserService {
public void create(@Valid UserDTO dto) { }
}
// ❌ 错误:忘记类级别注解
@Service // 缺少 @Validated
public class UserService {
public void create(@Valid UserDTO dto) { } // 不会触发验证
}- 🟠** 验证时机**
java
// ✅ 推荐:Controller 验证格式,Service 验证业务
@RestController
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<?> create(@Valid @RequestBody UserDTO dto) {
// 格式验证已完成
return ResponseEntity.ok(userService.create(dto));
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
public User create(UserDTO dto) {
// 只需验证业务规则
if (userRepository.existsByUsername(dto.getUsername())) {
throw new BusinessException("用户名已存在");
}
return userRepository.save(convert(dto));
}
}- 🟡** 性能优化**
java
// ✅ 使用验证组按需验证
@Service
@Validated
public class ProductService {
// 快速验证:只验证基本字段
public void quickUpdate(@Validated(BasicValidation.class) ProductDTO dto) {
productRepository.updatePrice(dto.getId(), dto.getPrice());
}
// 完整验证:验证所有字段
public void fullUpdate(@Validated(FullValidation.class) ProductDTO dto) {
// 完整更新逻辑
}
}- 🟢** 异常处理**
java
// ✅ Service 层统一处理验证异常
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleConstraintViolation(ConstraintViolationException ex) {
Map<String, String> errors = ex.getConstraintViolations().stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
v -> v.getPropertyPath().toString(),
ConstraintViolation::getMessage
));
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(errors);
}
}- 🔵** 事务处理**
java
// ⚠️ 注意:验证应在事务外进行
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private Validator validator;
@Transactional
public Order createOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
// ❌ 错误:在事务内验证(验证失败导致无用事务)
validator.validate(orderDTO);
return orderRepository.save(convert(orderDTO));
}
// ✅ 正确:验证在事务外
public Order createOrderCorrect(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
// 先验证
Set<ConstraintViolation<OrderDTO>> violations = validator.validate(orderDTO);
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
throw new ValidationException("验证失败");
}
// 再开启事务保存
return saveOrder(orderDTO);
}
@Transactional
private Order saveOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
return orderRepository.save(convert(orderDTO));
}
}6 Service 层验证对比总结
| 特性 | @Validated 注解 | 手动 Validator | 推荐场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 使用方式 | 声明式(注解) | 编程式(代码) | - |
| 灵活性 | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 手动更灵活 |
| 代码量 | 少 | 较多 | 简单用注解 |
| 验证时机 | 方法调用时 | 手动控制 | 复杂用手动 |
| 分组支持 | ✅ | ✅ | 都支持 |
| 条件验证 | ❌ | ✅ | 手动 |
| 批量验证 | ❌ | ✅ | 手动 |
| 适用场景 | 标准业务方法 | 批量、条件、复杂验证 | 按需选择 |
💡** 最佳实践建议**:
- Controller 层 :使用
@Valid验证请求参数格式 - Service 层 :使用
@Validated或手动Validator验证业务规则 - 优先使用 @Validated:代码简洁,适合大多数场景
- 复杂场景用手动验证:批量导入、条件验证、部分属性验证
- 封装工具类:简化手动验证操作,提高代码复用性
7 @Validated/@Valid 不生效的常见情况
- 缺少 @Validated 注解
- Service 层方法参数使用 @Valid/@Validated,但类上未加 @Validated,Spring 不会自动触发方法参数校验。
- 方法不是 public 或未被 Spring 管理
- 只有 public 方法且被 Spring 容器管理的 Bean 才会触发 AOP 校验,private/protected 方法或 new 出来的对象不会生效。
- 参数未加 @Valid/@Validated
- 方法参数未加 @Valid/@Validated 注解时,不会自动校验。
- DTO 未加约束注解
- DTO 字段未加 @NotNull、@Size 等约束注解,校验不会生效。
- 嵌套对象未加 @Valid
- DTO 中嵌套对象未加 @Valid 注解,嵌套校验不会生效。
- 未配置异常处理器
- 校验异常未被捕获,导致异常未能正确返回前端。
- 直接调用本类方法(this.xxx)
- Spring 的 AOP 只对代理对象生效,直接调用本类方法不会触发校验。
- 未使用 SpringMVC 参数绑定
- Controller 层未用 @RequestBody/@ModelAttribute 等参数绑定,@Valid 不会自动生效。
示例:本类方法调用不生效
java
@Service
@Validated
public class UserService {
public void create(@Valid UserDTO dto) { ... }
public void batchCreate(List<UserDTO> list) {
// ❌ 直接调用本类方法,不会触发参数校验
list.forEach(this::create);
}
}解决方法:通过代理调用
java
@Autowired
private UserService userServiceProxy;
public void batchCreate(List<UserDTO> list) {
// ✅ 通过代理对象调用,触发参数校验
list.forEach(userServiceProxy::create);
}