106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
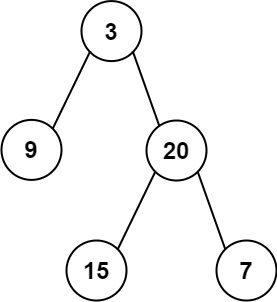
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
输出:[-1]提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder和postorder都由 不同 的值组成postorder中每一个值都在inorder中inorder保证是树的中序遍历postorder保证是树的后序遍历
首先,该题给出了中序遍历和后序遍历,中序遍历的的顺序是 左 中 右 ,后序遍历的顺序是 左 右 中,所以后续遍历的倒数第一个数即为当前树的根节点,先找到当前树的根节点,再在中序遍历中找到当前根节点的位置,其左边就是左子树的中序遍历的结果,其右侧就是右子树的中序遍历结果。如当前例子数组中序遍历为【9,3,15,20,7】 后序遍历为【9,15,7,20,3】。 当前总树的根节点为后序遍历的最后一个数即为3,在中序遍历中找到3的位置,其左侧为【9】即为左子树的中序遍历结果,右侧为【15,20,7】即为右子树的中序遍历结果。要记得后序遍历的顺序是左 右 中,则可以看出当前数组除去最后一个数字为根节点的值,左右子树的值都已给出,则只需要将数量对应即可,也就是左子树的后序遍历结果的数量和左子树的中序遍历数量相同,即为【9】,右子树的后序遍历结果为【15,7,20】。接着进行分冶逐步构建二叉树
java
public static void main(String[] args) { // 测试用
int[] mid = {2,3,1}; // 左 中 右
int[] last = {3,2,1}; // 左 右 中
System.out.println(buildTree(mid, last));
}
public static TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder){
TreeNode res = helper(inorder, postorder);
return res;
}
public static TreeNode helper(int[] inorder, int[] postorder){
if (inorder.length == 0 || postorder.length == 0){
return null;
}
if (inorder.length == 1){
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[0]);
return root;
}
int back1 = postorder.length - 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[back1]);
int mid = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == postorder[back1]){
mid = i;
break;
}
}
int[] leftmid = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, mid); // 左子树的中序遍历
int[] leftlast = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, 0, mid); // 左子树的后序遍历
int[] rightmid = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, mid + 1, inorder.length); // 右子树的中序遍历
int[] rightlast = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, mid, postorder.length - 1); // 右子树的后序遍历
root.left = helper(leftmid, leftlast);
root.right = helper(rightmid, rightlast);
return root;
}以上为记录分享用,代码较差请见谅。