uip之TCP服务器是基于ENC28J60实现TCP服务器的功能,主要文件有ENC28J60芯片驱动程序,uip程序和uip APP程序。
本文基于ENC28J60以太网控制器实现了一个TCP服务器系统,主要包括以下内容:
- 系统架构
- 硬件平台:STM32F10x + ENC28J60
- 软件组件:uIP协议栈、TCP服务器应用、驱动程序
- 核心功能实现
- TCP服务器监听5000端口
- 支持8个并发TCP连接
- 实现数据收发和状态管理
- 提供连接建立、数据传输、超时处理等回调函数
- 关键技术点
- 网络初始化配置(IP、MAC、子网掩码等)
- uIP协议栈移植和优化
- 数据缓冲区管理
- ARP协议处理
- 定时器管理(500ms轮询)
- 性能特点
- 支持最大1518字节以太网帧
- TCP窗口大小动态调整
- 连接状态监控和日志记录
- 异常处理和重传机制
该系统实现了完整的TCP服务器功能,能够稳定处理客户端连接和数据传输,为嵌入式网络应用提供了可靠的基础平台。
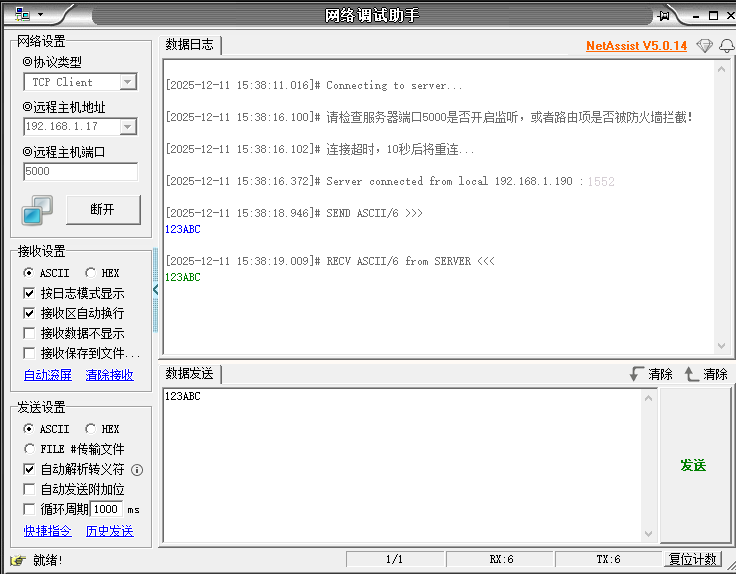
移植后,如下图:
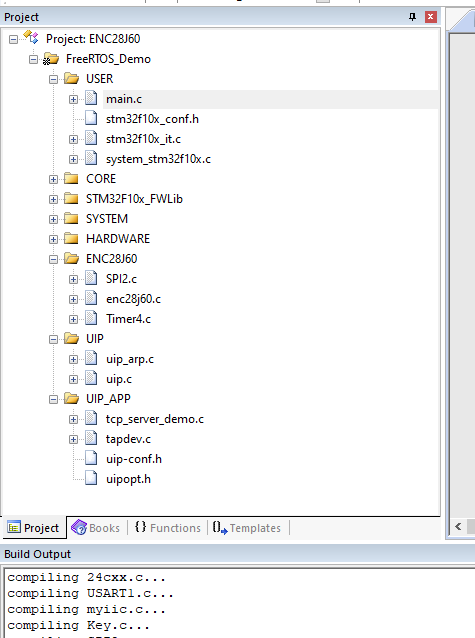
在上图中,uipopt.h用来配置支持监听客户端数量,tcp_server_demo.c是TCP服务器的APP程序。
1、tcp_server_demo.c
这是在别人基础上,改写得到的。改写的原因,主要是表达不够清晰。
#include "tcp_server_demo.h"
#include "string.h" //使能strcpy(),strlen(),memset()
#include "stdio.h" //getchar(),putchar(),scanf(),printf(),puts(),gets(),sprintf()
#include "uip_arp.h"
#include "tapdev.h"
u8 tcp_server_databuf[200]; //发送数据缓存
u8 tcp_server_sta; //服务端状态
//[7]:0,无连接;1,已经连接;
//[6]:0,无数据;1,收到客户端数据
//[5]:0,无数据;1,有数据需要发送
//这是一个TCP 服务器应用回调函数。
//该函数通过tcp_demo_appcall调用,实现Web Server的功能.
//当uip事件发生时,tcp_demo_appcall函数会被调用,根据所属端口,确定是否执行该函数。
//例如 : 当一个TCP连接被创建时、有新的数据到达、数据已经被应答、数据需要重发等事件
void tcp_server_demo_appcall(void)
{
if(uip_aborted())tcp_server_aborted(); //连接终止
if(uip_timedout())tcp_server_timedout(); //连接超时
if(uip_closed())tcp_server_closed(); //连接关闭
if(uip_connected()) tcp_server_connected(); //连接成功
if(uip_acked())
{
tcp_server_acked(); //发送的数据成功送达
uip_flags = uip_flags & (~UIP_ACKDATA);
}
//接收到一个新的TCP数据包
if ( uip_newdata() )//收到新数据
{
if( (tcp_server_sta&(1<<6))==0 )//还未收到数据
{
if(uip_len>199)//保存到uip_buf[]中的数据长度为uip_len;
{
((u8*)uip_appdata)[199]=0;
}
strcpy((char*)tcp_server_databuf,uip_appdata);
//将接收到的数据拷贝到tcp_server_databuf[]
printf("tcp_server_databuf[]=%s\r\n",tcp_server_databuf);
tcp_server_sta|=1<<6;//表示收到客户端数据
tcp_server_sta|=1<<5;//要求将接收到的数据回传
}
}
//当需要重发、新数据到达、数据包送达、连接建立时,通知uip发送数据
if(uip_rexmit()||uip_newdata()||uip_acked()||uip_connected()||uip_poll())
{//uip_poll()读"轮询标志",若建立,则查应用程序是否有要发送的数据。
tcp_server_senddata();
}
}
//终止连接
void tcp_server_aborted(void)
{
tcp_server_sta&=~(1<<7); //标志没有连接
uip_log("tcp_server aborted!\r\n");//打印log
}
//连接超时
void tcp_server_timedout(void)
{
tcp_server_sta&=~(1<<7); //标志没有连接
uip_log("tcp_server timeout!\r\n");//打印log
}
//连接关闭
void tcp_server_closed(void)
{
tcp_server_sta&=~(1<<7); //标志没有连接
uip_log("tcp_server closed!\r\n");//打印log
}
//连接建立
void tcp_server_connected(void)
{
tcp_server_sta|=1<<7; //标志连接成功
uip_log("tcp_server connected!\r\n");//打印log
}
//发送的数据成功送达
void tcp_server_acked(void)
{
uip_log("tcp_server acked!\r\n");//表示成功发送
}
//装载"发送数据",待发送用户数据的长度为uip_slen,目的是准备给客户端发送数据
void tcp_server_senddata(void)
{
struct tcp_demo_appstate *s = (struct tcp_demo_appstate *)&uipConnectPointer->appstate;
if( tcp_server_sta&(1<<5) )//有数据需要发送
{
s->textptr=tcp_server_databuf;//s->textptr指向"待发送的用户数据的首地址tcp_server_databuf"
s->textlen=strlen((const char*)tcp_server_databuf);
if(s->textlen>0)
{
uip_send(s->textptr, s->textlen);//发送TCP数据包
//将s->textptr[]中前s->textlen个字节拷贝到首地址为uip_sappdata的缓冲区
//待发送用户数据的长度为uip_slen=s->textlen
//在TCP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[54];
//在UDP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[42];
s->textlen=0;
}
tcp_server_sta&=~(1<<5);//清除标记
tcp_server_sta&=~(1<<6);//清除标记
}
}
void TCP_Server_Init(void)
{
u8 i;
struct uipConnectType *p_uipConnect;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_CONNS; ++i)
{
p_uipConnect=&uipConnectTable[i];
p_uipConnect->appstate.textlen=0;
p_uipConnect->appstate.textptr=NULL;
}
}
//TCP应用接口函数tcp_demo_appcall()
//完成TCP服务(包括server和client)和HTTP服务
void tcp_demo_appcall(void)
{
tcp_server_demo_appcall();
}
//打印日志用
void uip_log(char *m)
{
printf("uIP log:%s\r\n",m);
}2、tcp_server_demo.h
#include "stm32f10x.h"//使能uint8_t,uint16_t,uint32_t,uint64_t,int8_t,int16_t,int32_t,int64_t
extern u8 tcp_server_sta; //服务端状态
void tcp_server_demo_appcall(void);
void tcp_server_aborted(void);
void tcp_server_timedout(void);
void tcp_server_closed(void);
void tcp_server_connected(void);
void tcp_server_newdata(void);
void tcp_server_acked(void);
void tcp_server_senddata(void);
void tcp_demo_appcall(void);
void TCP_Server_Init(void);3、tapdev.c
这个文件改动较大,直接贴出来分享。
#include "tapdev.h"
#include "stdio.h" //getchar(),putchar(),scanf(),printf(),puts(),gets(),sprintf()
#include "string.h" //使能strcpy(),strlen(),memset()
#include "uip.h"
#include "uip_arp.h"
//#include "httpd.h"
#include "enc28j60.h"
#include "24cxx.h"
//#include "httpd-fsdata.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "Timer4.h"
#include "relay.h"
struct strTimer uIP_PeriodicTimer;
struct strTimer ARP_Timer;
uint8_t Local_IP[4];//本地IP地址
u16 Local_Port;//本机端口
//配置网卡硬件,并设置MAC地址
//返回值:0,正常;1,失败;
u8 Network_Init(void)
{
NetworkInformation net_info;
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
u8 i,res=0;
uip_init();
//My_uip_listenports[]初始化为0,uipConnectTable[]初始化为0,设置TCP客户端默认端口为1024
TCP_Server_Init();
printf("\nWelcome to use Net-Relay\n");
Local_Port=5000;//本机端口为5000
uip_listen(HTONS(Local_Port));
//监听5000端口,用于TCP Server
//小端存储方式将5000的高8位值和低8位值交换
//从EEPROM读取本地IP地址,如:"192.168.1.17"
Local_IP[0] = 192;
Local_IP[1] = 168;
Local_IP[2] = 1;
Local_IP[3] = 17;
uip_ipaddr(ipaddr,Local_IP[0],Local_IP[1],Local_IP[2],Local_IP[3]);
//将Local_IP[]中的前4个字节构造成一个IP地址,保存道ipaddr[]中
//u16型数组ipaddr[2]用来存放IP地址
uip_sethostaddr(ipaddr);//设置此主机的IP地址。
printf("IP:%d.%d.%d.%d\n",Local_IP[0],Local_IP[1],Local_IP[2],Local_IP[3]);
//从EEPROM读取本地子网掩码: 255.255.255.0
net_info.sn[0] = 255;
net_info.sn[1] = 255;
net_info.sn[2] = 255;
net_info.sn[3] = 0;
uip_ipaddr(ipaddr,net_info.sn[0],net_info.sn[1],net_info.sn[2],net_info.sn[3]);
//将net_info.sn[]中的前4个字节构造成一个IP地址,保存道ipaddr[]中
//u16型数组ipaddr[2]用来存放子网掩码
uip_setnetmask(ipaddr);//设置子网掩码
printf("Mask:%d.%d.%d.%d\n",net_info.sn[0],net_info.sn[1],net_info.sn[2],net_info.sn[3]);
//从EEPROM读取本地网关:192.168.1.1
net_info.gw[0] = 192;
net_info.gw[1] = 168;
net_info.gw[2] = 1;
net_info.gw[3] = 1;
uip_ipaddr(ipaddr,net_info.gw[0],net_info.gw[1],net_info.gw[2],net_info.gw[3]);
//将net_info.gw[]中的前4个字节构造成一个IP地址,保存道ipaddr[]中
//u16型数组ipaddr[2]用来存放网关地址
uip_setdraddr(ipaddr);
//设置网关地址(其实就是你路由器的IP地址)
printf("Gate:%d.%d.%d.%d\n",net_info.gw[0],net_info.gw[1],net_info.gw[2],net_info.gw[3]);
//从EEPROM读取本地MAC地址:0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02
net_info.mac[0] = 0;
net_info.mac[1] = 8;
net_info.mac[2] = 0xDC;
net_info.mac[3] = 0x11;
net_info.mac[4] = 0x11;
net_info.mac[5] = 0x02;
printf("Mac:%02x-%02x-%02x-%02x-%02x-%02x\n",\
net_info.mac[0],net_info.mac[1],net_info.mac[2],net_info.mac[3],net_info.mac[4],net_info.mac[5]);
res=ENC28J60_Init((u8*)net_info.mac);//初始化ENC28J60
//把MAC地址写入缓存区
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
uip_ethaddr.addr[i]=net_info.mac[i];//记录ENC28J60的MAC地址
}
ENC28J60_PHY_Write(PHLCON,0x0476);
//PHLCON:PHY模块LED控制寄存器
//指示灯状态:0x476 is PHLCON LEDA(绿)=links status, LEDB(红)=receive/transmit
timer_set(&uIP_PeriodicTimer,50);//50*10=500毫秒
timer_set(&ARP_Timer,1000);//1000*10=10000毫秒=10秒
return res;
}
//函数功能:打印一条报文;
void Print_Send_Package(unsigned char* buf,u16 len)
{
u16 i;
u8 temp;
printf("\r\nSend_Len=%u\r\n",len); //将"\r\nW5500:"发送到调试串口,由PC显示;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
temp=0;
if( ( (buf[i]==0x0D)||(buf[i]==0x0A) ) )
{
printf("%c",buf[i]);
temp=1;
}
if(temp==0)
{
if( ( (buf[i]>0x20)&&(buf[i]<='~') ) ) printf("%c",buf[i]);
else
{
printf(" 0x%02X",buf[i]);
printf(" ");
}
}
}
printf("\r\n");//将"\r\n"发送到调试串口,由PC显示;
}
//函数功能:打印一条报文;
void Print_Receive_Package(unsigned char* buf,u16 len)
{
u16 i;
u8 temp;
if(len)
printf("\r\nReceive_Len=%u\r\n",len); //将"\r\nW5500:"发送到调试串口,由PC显示;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
temp=0;
if( ( (buf[i]==0x0D)||(buf[i]==0x0A) ) )
{
printf("%c",buf[i]);
temp=1;
}
if(temp==0)
{
if( ( (buf[i]>0x20)&&(buf[i]<='~') ) ) printf("%c",buf[i]);
else
{
printf(" 0x%02X",buf[i]);
printf(" ");
}
}
}
if(len) printf("\r\n");//将"\r\n"发送到调试串口,由PC显示;
}
/*
arp_table[0].ip=192:168:1:190 arp_table[0].mac=B4:2E:99:59:EC:1E arp_table[0].time=188
arp_table[1].ip=192:168:1:1 arp_table[1].mac=60:DA:83:44:76:21 arp_table[1].time=203
arp_table[2].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[2].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[2].time=0
arp_table[3].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[3].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[3].time=0
arp_table[4].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[4].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[4].time=0
arp_table[5].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[5].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[5].time=0
arp_table[6].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[6].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[6].time=0
arp_table[7].ip=0:0:0:0 arp_table[7].mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 arp_table[7].time=0
*/
void Print_ARP_Table(void)
{
u8_t i;
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
printf("\r\n");
for(i=0;i<UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE;i++)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
printf("arp_table[%u].ip=%u:%u:%u:%u ",
i,(u8)tabptr->ipaddr[0],(u8)(tabptr->ipaddr[0]>>8),
(u8)tabptr->ipaddr[1],(u8)(tabptr->ipaddr[1]>>8)
);
printf("arp_table[%u].mac=%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X ",
i,tabptr->ethaddr.addr[0],tabptr->ethaddr.addr[1],
tabptr->ethaddr.addr[2],tabptr->ethaddr.addr[3],
tabptr->ethaddr.addr[4],tabptr->ethaddr.addr[5]
);
printf("arp_table[%u].time=%u\r\n",i,tabptr->time);
}
}
void Print_uipConnection(void)
{
u8_t i;
struct uipConnectType *p;
printf("\r\n");
for(i=0;i<UIP_CONNS;i++)
{
p = &uipConnectTable[i];
printf("uipConnectTable[%u], lport=%u, rport=%u, %u:%u:%u:%u\r\n",
i,p->lport,p->rport,
(u8)p->ripaddr[0],(u8)(p->ripaddr[0]>>8),
(u8)p->ripaddr[1],(u8)(p->ripaddr[1]>>8)
);
}
}
#define ARPPointer ( (struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0] )
#define TCPPointer ( (struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0] )
//读取一包数据,保存到uip_buf[],并返回数据长度;
//MAX_FRAMELEN定义为1518
uint16_t tapdev_read(void)
{
u8 ch;
u32 len;
len=ENC28J60_Packet_Receive(MAX_FRAMELEN,uip_buf);
ch=0;
if( (u8)ARPPointer->ethhdr.type==(u8)(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP>>8) )ch=1;
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->ethhdr.type>>8)==(u8)UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)ARPPointer->sipaddr[0]==192 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->sipaddr[0]>>8)==168) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)ARPPointer->sipaddr[1]==1) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->sipaddr[1]>>8)==190 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if(ch==0x20) Print_Receive_Package(uip_buf,len);
else ch=0;
if(ch==0 && (u8)TCPPointer->ethhdr.type==(u8)(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP>>8) )ch=1;
if((u8)(TCPPointer->ethhdr.type>>8)==(u8)UIP_ETHTYPE_IP )ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)TCPPointer->srcipaddr[0]==192 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(TCPPointer->srcipaddr[0]>>8)==168) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)TCPPointer->srcipaddr[1]==1) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(TCPPointer->srcipaddr[1]>>8)==190 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if(ch==0x20) Print_Receive_Package(uip_buf,len);
return len;
}
//发送一包数据
void tapdev_send(void)
{
u8 ch;
ch=0;
if( (u8)ARPPointer->ethhdr.type==(u8)(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP>>8) )ch=1;
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->ethhdr.type>>8)==(u8)UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)ARPPointer->dipaddr[0]==192 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->dipaddr[0]>>8)==168) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)ARPPointer->dipaddr[1]==1) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(ARPPointer->dipaddr[1]>>8)==190 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if(ch==0x20) Print_Send_Package(uip_buf,uip_len);
else ch=0;
if(ch==0 && (u8)TCPPointer->ethhdr.type==(u8)(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP>>8) )ch=1;
if((u8)(TCPPointer->ethhdr.type>>8)==(u8)UIP_ETHTYPE_IP )ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)TCPPointer->destipaddr[0]==192 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(TCPPointer->destipaddr[0]>>8)==168) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)TCPPointer->destipaddr[1]==1) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if( (u8)(TCPPointer->destipaddr[1]>>8)==190 ) ch=(u8)(ch<<1);
if(ch==0x20) Print_Send_Package(uip_buf,uip_len);
ENC28J60_Packet_Send(uip_len,uip_buf);
printf("\r\nTX=%u\r\n",uip_len);
delay_us(uip_len);
uip_len=0;
}
//函数功能:如果发现ENC28J60复位了,则重新初始化ENC28J60
void If_ENC28J60Reset_Do_Resart(void)
{
u8 i;
u8 tmpMAC[6];
tmpMAC[0]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR5);
tmpMAC[1]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR4);
tmpMAC[2]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR3);
tmpMAC[3]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR2);
tmpMAC[4]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR1);
tmpMAC[5]=ENC28J60_Read(MAADR0);
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
if(tmpMAC[i]!=uip_ethaddr.addr[i])//发现ENC28J60复位了
{
ENC28J60_Init(uip_ethaddr.addr);
i=6;
}
}
}
//uip轮询事件处理函数
//必须将该函数插入用户主循环,循环调用.
void uIP_Periodic_Work(void)
{
u8 i;
if(timer_expired(&uIP_PeriodicTimer)) //0.5秒定时器超时
{
timer_reset(&uIP_PeriodicTimer); //复位0.5秒定时器
//轮流处理每个TCP连接, UIP_CONNS缺省是40个
for(i=0;i<UIP_CONNS;i++)
{
uip_periodic(i);
//处理TCP通信事件,相当于执行"uip_conn = &uipConnectTable[i];uip_process(UIP_TIMER);"
if(uip_len>0)//保存到uip_buf[]中的数据长度为uip_len;
{
uip_arp_out();
//uip_buf[]中是IPV4数据包,才会执行
//1、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",则在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找是否有这个IP地址;
//1)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中没有这个IP地址,发送ARP请求;
//2)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中有这个IP地址,设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,发送TCP数据;
//2、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",则设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址",
//设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,然后发送TCP数据
}
}
#if UIP_UDP //UIP_UDP
//轮流处理每个UDP连接, UIP_UDP_CONNS缺省是10个
for(i=0;i<UIP_UDP_CONNS;i++)
{
uip_udp_periodic(i); //处理UDP通信事件
//当上面的函数执行后,如果需要发送数据,则全局变量uip_len>0
//需要发送的数据在uip_buf, 长度是uip_len (这是2个全局变量)
if(uip_len > 0)//保存到uip_buf[]中的数据长度为uip_len;
{
uip_arp_out();
//uip_buf[]中是IPV4数据包,才会执行
//1、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",则在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找是否有这个IP地址;
//1)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中没有这个IP地址,发送ARP请求;
//2)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中有这个IP地址,设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,发送TCP数据;
//2、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",则设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址",
//设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,然后发送TCP数据
}
}
#endif
}
}
#define EthernetHeaderPointer ( (struct uip_eth_hdr *)&uip_buf[0] )
//uip_eth_hdr型结构:以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
//EthernetHeaderPointer为uip_eth_hdr型结构指针
//uip_buf[0]~uip_buf[5]为目的MAC地址
//uip_buf[6]~uip_buf[11]为源MAC地址
//uip_buf[12]~uip_buf[13]为报文类型
void HTTP_Work(void)
{
uip_len=tapdev_read();
if(uip_len)
{
uip_arp_arpin();
//uip_buf[]中是ARP数据包,才会执行
//处理接收到的ARP数据包:
//如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包;
//如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP应答,则更新ARP表;
uip_input();//uip_buf[]中是IPV4数据包,才会执行
if(uip_len>0)//保存到uip_buf[]中的数据长度为uip_len;
{
uip_arp_out();
//uip_buf[]中是IPV4数据包,才会执行
//1、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",则在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找是否有这个IP地址;
//1)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中没有这个IP地址,发送ARP请求;
//2)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中有这个IP地址,设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,发送TCP数据;
//2、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",则设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址",
//设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,然后发送TCP数据
}
}
else
{
uIP_Periodic_Work();//处理uip事件,必须插入到用户程序的循环体中
}
if(timer_expired(&ARP_Timer))
{
timer_reset(&ARP_Timer);
uip_arp_timer();
//10秒执行一次,如果"远程设备IP地址不为0,且建立时间超过20分钟",则将其IP地址设置为0
}
}4、tapdev.h
#include <stdint.h>
#include "sys.h"
typedef struct NetworkInformation_t
{
uint8_t mac[6]; ///< Source Mac Address
uint8_t ip[4]; ///< Source IP Address
uint8_t sn[4]; ///< Subnet Mask
uint8_t gw[4]; ///< Gateway IP Address
}NetworkInformation;
extern uint8_t Local_IP[4];//本地IP地址
extern u16 Local_Port;//本机端口
u8 Network_Init(void); //修改为带返回值的函数
uint16_t tapdev_read(void);
void tapdev_send(void);
void If_ENC28J60Reset_Do_Resart(void);
void Print_ARP_Table(void);
void Print_uipConnection(void);
void HTTP_Work(void);5、uipopt.h
#ifndef __UIP_CONF_H__
#define __UIP_CONF_H__
#include <inttypes.h>
typedef uint8_t u8_t;
typedef uint16_t u16_t;
typedef unsigned short uip_stats_t;
//CPU大小端模式,STM32是小端模式的
#define UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN //STM32在KEIL编译器中是小端存储模式
#define UIP_CONF_MAX_CONNECTIONS 8 //允许同时打开8个TCP连接数量
#define UIP_CONF_MAX_LISTENPORTS 8 //允许同时监听的端口数量
#define UIP_CONF_ARPTAB_SIZE 8 //ARP表的大小
#define UIP_CONF_BUFFER_SIZE 1500 //uIP缓存大小
/*
由于以太网EthernetII最大的数据帧是1518Bytes;
去掉以太网帧的帧头14Bytes和帧尾CRC校验部分4Bytes,
那么剩下承载上层协议的地方也就是Data域最大就只能有1500Bytes,这个值我们就把它称之为链路层MTU。
目前大多数的路由设备的MTU都为1500。Internet上的标准MTU值为576字节。
UDP 包的大小就应该是 1500 - IP头(20) - UDP头(8) = 1472(Bytes)
TCP 包的大小就应该是 1500 - IP头(20) - TCP头(20) = 1460 (Bytes)
如果我们定义的TCP和UDP包没有超过范围,那么我们的包在IP层就不用分包了,这样传输过程中就避免了在IP层组包发生的错误;
如果超过范围,即"IP数据包"大于1500字节,发送方IP层就需要将数据包分成若干片,而接收方IP层就需要进行数据报的重组。
更严重的是,如果IP层组包发生错误,那么包就会被丢弃。接收方无法重组数据包,将导致丢弃整个IP数据报。
因此,UDP是不可靠传输;
但是TCP发生组包错误时,该包会被重传,目的是保证可靠传输。
*/
#define UIP_CONF_LOGGING 1 //日志开关
#define UIP_CONF_UDP 0 //UDP支持开关
#define UIP_CONF_UDP_CHECKSUMS 0 //UDP校验和开关
//是否使用UDP校验和.
//注意:
//对UDP校验和的支持目前并不包含于uIP,故此项无用.
//uIP统计开关
#define UIP_CONF_STATISTICS 1
#define My_REPLACEMENT 0 //PT协程不用替换
#endif 6、uipopt.h
这是uip自带的配置,不用修改。
#ifndef __UIPOPT_H__
#define __UIPOPT_H__
//#include "uipopt.h"
//定义UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN=3412
#ifndef UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN
#define UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN 3412
#endif /* UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN */
//定义UIP_BIG_ENDIAN=1234
#ifndef UIP_BIG_ENDIAN
#define UIP_BIG_ENDIAN 1234
#endif /* UIP_BIG_ENDIAN */
#include "uip-conf.h"
#define UIP_FIXEDADDR 0
#ifdef UIP_CONF_PINGADDRCONF
#define UIP_PINGADDRCONF UIP_CONF_PINGADDRCONF
#else /* UIP_CONF_PINGADDRCONF */
#define UIP_PINGADDRCONF 0
#endif /* UIP_CONF_PINGADDRCONF */
#define UIP_FIXEDETHADDR 0
#define UIP_TTL 64 //uip发送的IP包的生存时间(TTL),通常此项不应更改.
#define UIP_REASSEMBLY 0
#define UIP_REASS_MAXAGE 40
#ifdef UIP_CONF_UDP
#define UIP_UDP UIP_CONF_UDP
#else /* UIP_CONF_UDP */
#define UIP_UDP 0
#endif /* UIP_CONF_UDP */
#ifdef UIP_CONF_UDP_CHECKSUMS
#define UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS UIP_CONF_UDP_CHECKSUMS
//是否使用UDP校验和.
//注意:
//对UDP校验和的支持目前并不包含于uIP,故此项无用.
#else
#define UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS 0
#endif
#ifdef UIP_CONF_UDP_CONNS
#define UIP_UDP_CONNS UIP_CONF_UDP_CONNS
#else /* UIP_CONF_UDP_CONNS */
#define UIP_UDP_CONNS 10
#endif /* UIP_CONF_UDP_CONNS */
//#define UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN 1 //允许主动连接功能。
#define UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN 0 //禁用主动连接功能,仅支持被动监听连接。
#ifndef UIP_CONF_MAX_CONNECTIONS
#define UIP_CONNS 10 //最大同时打开的TCP连接数.
#else /* UIP_CONF_MAX_CONNECTIONS */
#define UIP_CONNS UIP_CONF_MAX_CONNECTIONS //最大同时打开的TCP连接数.
#endif /* UIP_CONF_MAX_CONNECTIONS */
#ifndef UIP_CONF_MAX_LISTENPORTS
#define UIP_LISTENPORTS 20
#else /* UIP_CONF_MAX_LISTENPORTS */
#define UIP_LISTENPORTS UIP_CONF_MAX_LISTENPORTS
#endif /* UIP_CONF_MAX_LISTENPORTS */
#define UIP_URGDATA 0
#define UIP_RTO 3
#define UIP_MAXRTX 8 //一段数据最大重传多少次才取消连接.
#define UIP_MAXSYNRTX 5 //一段SYN数据要最大得传多少次,才认定连接请求失败.
#define UIP_TCP_MSS (UIP_BUFSIZE - UIP_LLH_LEN - UIP_TCPIP_HLEN)
//TCP最大段大小:1500-14-40
#ifndef UIP_CONF_RECEIVE_WINDOW
#define UIP_RECEIVE_WINDOW UIP_TCP_MSS
#else
#define UIP_RECEIVE_WINDOW UIP_CONF_RECEIVE_WINDOW
#endif
#define UIP_TIME_WAIT_TIMEOUT 120 //一个连接处于TIME_WAIT状态的最大时间
#ifdef UIP_CONF_ARPTAB_SIZE
#define UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE UIP_CONF_ARPTAB_SIZE //ARP表的大小
#else
#define UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE 8 //ARP表的大小
#endif
#define UIP_ARP_MAXAGE 120
//timer_set(&ARP_Timer,1000);//1000*10=10000毫秒
//以10s为单位的ARP表项的最大年龄.120代表的是20分钟(BSD中的默认值).
#ifndef UIP_CONF_BUFFER_SIZE
#define UIP_BUFSIZE 400
#else /* UIP_CONF_BUFFER_SIZE */
#define UIP_BUFSIZE UIP_CONF_BUFFER_SIZE //不小于60字节,不大于1500字节.这个值越小,TCP的吞吐量就越小,相反越大.
#endif /* UIP_CONF_BUFFER_SIZE */
#ifndef UIP_CONF_STATISTICS
#define UIP_STATISTICS 0
#else /* UIP_CONF_STATISTICS */
#define UIP_STATISTICS UIP_CONF_STATISTICS //uIP统计开关被设置1
#endif /* UIP_CONF_STATISTICS */
#ifndef UIP_CONF_LOGGING
#define UIP_LOGGING 0
#else /* UIP_CONF_LOGGING */
#define UIP_LOGGING UIP_CONF_LOGGING
#endif /* UIP_CONF_LOGGING */
#ifndef UIP_CONF_BROADCAST
#define UIP_BROADCAST 0 //支持广播,此标志用于配置广播的支持,仅在开启UDP时才有意义.
#else /* UIP_CONF_BROADCAST */
#define UIP_BROADCAST UIP_CONF_BROADCAST
#endif /* UIP_CONF_BROADCAST */
void uip_log(char *msg);
#ifdef UIP_CONF_LLH_LEN
#define UIP_LLH_LEN UIP_CONF_LLH_LEN
#else /* UIP_CONF_LLH_LEN */
#define UIP_LLH_LEN 14
#endif /* UIP_CONF_LLH_LEN */
//CPU大小端模式,STM32是小端模式的
//在"uip-conf.h"定义过UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER=UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN=3412
//在"uipopt.h"定义UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN=3412
#ifdef UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER
#define UIP_BYTE_ORDER UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER
#else /* UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER */
#define UIP_BYTE_ORDER UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN
#endif /* UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER */
#endif /* __UIPOPT_H__ */7、uip_arp.c
这个文件,被我修改了,因为不方便阅读。
#include "uip_arp.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "tapdev.h"
struct arp_entry arp_table[UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE];
//ARP表保存的是远程设备的IP地址,MAC地址和建立的时间
static u8_t ARPTimeCounter; //声明字节静态变量ARPTimeCounter
//函数功能:将ARP表中的IP地址设置为0
void uip_arp_init(void)
{
u8_t i;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
memset( arp_table[i].ipaddr, 0, 4 );
//将首地址为arp_table[i].ipaddr的缓存的前4个字节设置为0
}
}
//函数功能:
//如果ARP表中的某个"IP地址和MAC地址"的建立时间在20分钟内,没有更新,则将这个IP地址设置为0
//注意:uip_arp_timer()每10秒执行一次
void uip_arp_timer(void)
{
u8_t i;
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
u8_t deltValue;
++ARPTimeCounter;//10秒计数器加1
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];//获取首地址
if( ARPTimeCounter >= tabptr->time )
deltValue=ARPTimeCounter - tabptr->time;//"IP地址和MAC地址"建立多长时间
else
{
deltValue=256 - tabptr->time;
deltValue=deltValue + ARPTimeCounter;
}
//发现ARP表中有一个"IP地址和MAC地址"建立时间,长期没有更新,因此将这个IP地址设置为0
if( (tabptr->ipaddr[0] | tabptr->ipaddr[1]) != 0 && deltValue >= UIP_ARP_MAXAGE)
{//远程设备IP地址不为0,且建立时间超过120*10=1200秒=20分钟
memset(tabptr->ipaddr, 0, 4);
//将首地址为tabptr->ipaddr的缓存的前4个字节设置为0
}
}
}
//函数功能:更新ARP表
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
//ipaddr是接收到的"发送方的4字节ip地址",ethaddr是接收到的"发送方的6字节mac地址"
static void uip_arp_update(u16_t *ipaddr, struct uip_eth_addr *ethaddr)
{
u8_t i;
u8_t tmpage;
register struct arp_entry *tabptr;
//register请求编译器将局部变量tabptr存储在寄存器中,以提高访问速度。
/* Walk through the ARP mapping table and try to find an entry to
update. If none is found, the IP -> MAC address mapping is
inserted in the ARP table. */
u8_t find;
u8_t deltValue;
//在ARP表里发现有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",则更新MAC地址后,返回
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
/* Only check those entries that are actually in use. */
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] != 0 && tabptr->ipaddr[1] != 0)
{
//检查传入数据包的源IP地址是否与ARP表项中的IP地址匹配。
/* Check if the source IP address of the incoming packet matches the IP address in this ARP table entry. */
if(ipaddr[0] == tabptr->ipaddr[0] && ipaddr[1] == tabptr->ipaddr[1])
{//在ARP表里发现这个IP地址
/* An old entry found, update this and return. */
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6);//更新MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
return;
}
}
}
//在ARP表里没有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",则查找"IP地址为0"的存储位置
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(tabptr->ipaddr[0] == 0 && tabptr->ipaddr[1] == 0)
{//在arp_table[]中,发现IP地址为0,则将在这个位置保存新的"IP地址和MAC地址"
memcpy(tabptr->ipaddr, ipaddr, 4); //保存新的IP地址
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6); //保存新的MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
break;
}
}
//在ARP表里没有"ipaddr所指向的IP地址",也没有找到"IP地址为0"的存储位置
//则查找"IP地址和MAC地址"建立最久的条目,用来保存新的"IP地址和MAC地址"
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE)//没有发现IP地址为0
{
tmpage = 0;find = 0;
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{//查找建立时间最长的"IP地址和MAC地址"
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
if(ARPTimeCounter >= tabptr->time)
deltValue=ARPTimeCounter - tabptr->time;//"IP地址和MAC地址"建立多长时间
else
{
deltValue=256 - tabptr->time;
deltValue=deltValue + ARPTimeCounter;
}
//如果ARPTimeCounter<tabptr->time,deltValue<0;
if( deltValue > tmpage)
{
tmpage = deltValue;
find = i;//记录,然后再循环查找
}
}
i = find;//记录修改位置
tabptr = &arp_table[find];
memcpy(tabptr->ipaddr, ipaddr, 4); //保存新的IP地址
memcpy(tabptr->ethaddr.addr, ethaddr->addr, 6); //保存新的MAC地址
tabptr->time = ARPTimeCounter;
}
}
/*
计算机发送ARP请求,60个字节
以太网头部数据:0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0x08 0x06
ARP头部数据:0x00 0x01 0x08 0x00 0x06 0x04 0x00 0x01 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0x11
填充数据:0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
ENC28J60发送ARP应答,42个字节
以太网头部数据:0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02 0x08 0x06
ARP头部数据:0x00 0x01 0x08 0x00 0x06 0x04 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0x11 0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE
*/
//函数功能:处理接收到的ARP数据包:如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包;如果"接收到的操作码"是ARP应答,则更新ARP表;
//分析uip_buf[]中的"ARP数据包"
//1.由于外部设备发送了"ARP请求数据包",如果pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包;
//目的是让对方知道自己的MAC地址;
//2.在发送TCP数据时,由于uip_arp_out()执行后发现ARP表中没有"接收方的IP地址",因此,它生成了"ARP请求数据包";
//对方收到后,就会发送ARP应答包;如果pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP应答,则更新ARP表中的
//"IP地址,MAC地址和建立时间";
void uip_arp_arpin(void)
{
struct arp_hdr *pARPHeader;
pARPHeader=(struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
if( uip_len < sizeof(struct arp_hdr) )
{
uip_len = 0;
return;
}
if( pARPHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP) )//uip_buf[]中不是ARP数据包,则退出
return;
//pARPHeader->opcode的操作码是ARP请求,则ENC28J60准备ARP应答数据包
//pARPHeader->opcodee的操作码是ARP应答,则更新ARP表
uip_len = 0;
//pARPHeader->opcode是ARP消息的类型,ARP请求是1,ARP回复是2,RARP请求是3,RARP回复是4
switch(pARPHeader->opcode)
{
case HTONS(ARP_REQUEST)://ENC28J60收到"ARP请求"
//ARP请求。如果它询问我们的地址,我们会发送回复。
/* ARP request. If it asked for our address, we send out a reply. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(pARPHeader->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr))
{//接收到的目的IP地址和ENC28J60的IP地址相同,表示这个数据是我的
/* First, we register the one who made the request in our ARP
table, since it is likely that we will do more communication
with this host in the future. */
uip_arp_update(pARPHeader->sipaddr, &pARPHeader->shwaddr);
//sipaddr是接收到的"发送方的4字节ip地址",shwaddr是接收到的"发送方的6字节mac地址"
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
/* The reply opcode is 2. */
pARPHeader->opcode = HTONS(2);
//设置操作码:ARP回复是2
memcpy(pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"接收方MAC地址"
memcpy(pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"发送方MAC地址"为ENC28J60的MAC地址
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址"为ENC28J60的MAC地址
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"目的MAC地址"
pARPHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
//设置太网帧的类型为0x0806,表示后面跟着的是ARP数据包;
pARPHeader->dipaddr[0] = pARPHeader->sipaddr[0];pARPHeader->dipaddr[1] = pARPHeader->sipaddr[1];
//设置"接收方ip地址"
pARPHeader->sipaddr[0] = uip_hostaddr[0];pARPHeader->sipaddr[1] = uip_hostaddr[1];
//设置"发送方ip地址"
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送ARP应答数据包
}
break;
case HTONS(ARP_REPLY)://ENC28J60收到"ARP回复"
//ARP回复。如果ARP表是为我们准备的,我们会插入或更新该表。
/* ARP reply. We insert or update the ARP table if it was meant for us. */
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(pARPHeader->dipaddr, uip_hostaddr))
{//接收到的目的IP地址和ENC28J60的IP地址相同,表示这个数据是我的
uip_arp_update(pARPHeader->sipaddr, &pARPHeader->shwaddr);
//pARPHeader->sipaddr是发送方的4字节ip地址
//pARPHeader->shwaddr为"发送方的6字节mac地址"
//先在ARP表里发现这个IP地址,则更新MAC地址;如果没有发现这个IP地址,则在ARP表里查找IP地址为0的条目;
//若发现IP地址为0,则保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。如果ARP表里没有IP地址为0的条目,则根据通讯时间去查找条目,
//然后保存远程IP地址和MAC地址。
}
break;
}
return;
}
//函数功能:
//1、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",则在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找是否有这个IP地址;
//1)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中没有这个IP地址,发送ARP请求;
//2)、如果"ARP表arp_table[]"中有这个IP地址,设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,发送TCP数据;
//2、如果收到的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",则设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址",设置发送方MAC地址是本地的MAC地址,IP地址为本地的IP地址,然后发送TCP数据
//分析uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"
//1.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",且ARP表里也没有这个IP地址,则准备ARP请求数据包;
//2.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址",且ARP表里也有这个IP地址,
//则使用"ARP表中的对应的MAC地址"作为目的地址,修改以太网头部中的"目的地址",然后设置以太网头部中的"源地址"为本地的MAC地址;
//最后设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据;
//3.如果uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址",
//则设置以太网头部中的"目的地址"为"广播MAC地址",然后设置以太网头部中的"源地址"为本地的MAC地址,
//最后设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据;
void uip_arp_out(void)
{
static u16_t TmpIpAddress[2];//保存的是"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"或是"ENC28J60的IP地址"
struct arp_entry *tabptr;
unsigned char ch1,ch2,ch3;
u8_t i;
struct ethip_hdr *pEthernetHeader;
struct arp_hdr *pARPHeader;
pEthernetHeader=(struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
if( pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP) )//uip_buf[]中不是IPV4数据包,则退出
return;
ch1=0;
if(pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0]==0xFFFF) ch1=1;
if(pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1]==0xFFFF) ch1=(unsigned char)(ch1<<1);
if( ch1!=2 )//uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"不是"广播IP地址"
{
ch2=0;
if( (pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) == (uip_hostaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) ) ch2=1;
if( (pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) == (uip_hostaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) )
ch2=(unsigned char)(ch2<<1);
//uip_hostaddr为"ENC28J60的IP地址"
//uip_netmask为"ENC28J60的子网掩码"
//IP地址前3个字节相同,只是最后一个字节不同,通常它们位于"同一网络(子网)"内
if(ch2!=0x02)//不位于"同一网络(子网)"内
{
TmpIpAddress[0] = uip_draddr[0];//uip_draddr为"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"
TmpIpAddress[1] = uip_draddr[1];//uip_draddr为"ENC28J60的网关IP地址"
//将"网关地址"拷贝到TmpIpAddress[]中
}
else//位于"同一网络(子网)"内
{
TmpIpAddress[0] = pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[0];//pEthernetHeader->destipaddr为"接收方IP地址"
TmpIpAddress[1] = pEthernetHeader->destipaddr[1];//pEthernetHeader->destipaddr为"接收方IP地址"
//将"接收方IP地址"拷贝到TmpIpAddress[]中
}
for(i = 0; i < UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE; ++i)
{//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中查找TmpIpAddress的IP地址
tabptr = &arp_table[i];
ch3=0;
if(TmpIpAddress[0] == tabptr->ipaddr[0]) ch3=1;
if(TmpIpAddress[1] == tabptr->ipaddr[1]) ch3=(unsigned char)(ch3<<1);
if(ch3==2)//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中,找到了TmpIpAddress的IP地址
{
memcpy(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, tabptr->ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"目的MAC地址",准备发送TCP数据
break;
}
}
if(i == UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE)//在"ARP表arp_table[]"中,没有找到TmpIpAddress的IP地址
{
pARPHeader=(struct arp_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
memset(pARPHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr, 0xff, 6);
//设置"目的mac地址"为"0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF"
memcpy(pARPHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址"为"ENC28J60的MAC地址"
pARPHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP);
//设置"以太网帧的类型"为"ARP请求包类型"
pARPHeader->hwtype = HTONS(ARP_HWTYPE_ETH);//设置"硬件类型",若是以太网,值是0x0001
pARPHeader->protocol = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);//设置"协议类型",若是ipv4,值是0x0800
pARPHeader->hwlen = 6;//设置"硬件长度",定义物理地址(MAC地址)的长度,若是mac地址就是6
pARPHeader->protolen = 4;//设置"协议长度",定义逻辑地址(IP地址)的长度,若是ip地址就是4
pARPHeader->opcode = HTONS(ARP_REQUEST);
//设置"操作码":为ARP请求,是1
memcpy(pARPHeader->shwaddr.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"发送方的6字节mac地址"为"ENC28J60的MAC地址"
uip_ipaddr_copy(pARPHeader->sipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
//设置"发送方的4字节ip地址"为"ENC28J60的IP地址"
memset(pARPHeader->dhwaddr.addr, 0x00, 6);
//设置"接收方的6字节mac地址"为"0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00"
uip_ipaddr_copy(pARPHeader->dipaddr, TmpIpAddress);
//设置"接收方的4字节ip地址"
uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN];
//UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=40,UIP_LLH_LEN=14
uip_len = sizeof(struct arp_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送ARP请求
return;
}
}
else//uip_buf[]中的"IP数据包部分"的"接收方IP地址"是"广播IP地址"
{
//设置"目的MAC地址"为"广播的MAC地址":"0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF,0xFF",准备发送TCP数据
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[0]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[1]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[2]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[3]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[4]=0xFF;
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.dest.addr[5]=0xFF;
}
memcpy(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.src.addr, uip_ethaddr.addr, 6);
//设置"源MAC地址",准备发送TCP数据
//uip_ethaddr.addr[]保存的是ENC28J60的MAC地址
pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type = HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP);
//设置"以太网帧的类型"为"IPV4数据包类型",准备发送TCP数据
uip_len += sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
tapdev_send();//发送TCP数据
}
//函数功能:若IP数据包中有"新的IP地址和MAC地址",则更新ARP表
void uip_arp_ipin(void)
{
struct ethip_hdr *pEthernetHeader;
pEthernetHeader=(struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
// uip_len -= sizeof(struct uip_eth_hdr);
if( (pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]) != (uip_hostaddr[0] & uip_netmask[0]))
{
return;
}
if((pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]) != (uip_hostaddr[1] & uip_netmask[1]))
{
return;
}
uip_arp_update(pEthernetHeader->srcipaddr, &(pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.src));
return;
}8、uip_arp.h
#include "uip.h"
//uip_eth_hdr型结构:以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
struct uip_eth_hdr {
struct uip_eth_addr dest; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放目的MAC地址
struct uip_eth_addr src; //uip_eth_addr结构成员是字节型数组addr[6],存放源MAC地址
u16_t type;
//太网帧的类型
//0x0800表示后面跟着的是IPV4数据包;
//0x0806表示后面跟着的是ARP数据包;
//0x86dd表示后面跟着的是IPV6数据包;
};
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP 0x0806 //ARP请求包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP 0x0800 //IPV4数据包类型
#define UIP_ETHTYPE_IP6 0x86dd //IPv6包类型
//ARP结构
struct arp_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;
//以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
u16_t hwtype; //硬件类型,若是以太网,值是0x0001
u16_t protocol; //协议类型,若是ipv4,值是0x0800
u8_t hwlen; //硬件长度,定义物理地址(MAC地址)的长度,若是mac地址就是6
u8_t protolen; //协议长度,定义逻辑地址(IP地址)的长度,若是ip地址就是4
u16_t opcode; //操作码:定义ARP分组是请求还是应答。ARP请求是1,ARP回复是2,RARP请求是3,RARP回复是4
struct uip_eth_addr shwaddr; //发送方的6字节mac地址
u16_t sipaddr[2]; //发送方的4字节ip地址
struct uip_eth_addr dhwaddr; //接收方的6字节mac地址
u16_t dipaddr[2]; //接收方的4字节ip地址
};
//以太网结构
struct ethip_hdr
{
struct uip_eth_hdr ethhdr;
//以太网首部有14字节:接收方MAC地址(占6个字节),发送方MAC地址(占6个字节),以太网帧的类型(占2个字节)。
//IP头部(IP header),占20给字节
u8_t vhl;//版本与首部长度
u8_t tos;//服务类型
u8_t len[2];//IP报文总长度2个字节
u8_t ipid[2];//标识,2字节,用于分片重组
u8_t ipoffset[2];//标志与片偏移,2字节,包含DF/MF标志和偏移量
u8_t ttl;//生存时间
u8_t proto;//协议:1字节,如6表示TCP,17表示UDP
u16_t ipchksum;//检验和
u16_t srcipaddr[2];//发送方IP地址,4字节
u16_t destipaddr[2];//接收方IP地址,4字节
};
#define ARP_REQUEST 1 //ARP请求
#define ARP_REPLY 2 //ARP回复
#define ARP_HWTYPE_ETH 1 //设置"硬件类型",若是以太网,值是0x0001
struct arp_entry
{
u16_t ipaddr[2]; //远程设备的IP地址
struct uip_eth_addr ethaddr; //远程设备的MAC地址
u8_t time; //"IP地址和MAC地址"建立的时间
};
extern struct arp_entry arp_table[UIP_ARPTAB_SIZE];
void uip_arp_init(void);
void uip_arp_timer(void);
void uip_arp_arpin(void);
void uip_arp_out(void);
void uip_arp_ipin(void);
//使用eaddr,修改本地的MAC地址
#define uip_setethaddr(eaddr) do {uip_ethaddr.addr[0] = eaddr.addr[0]; \
uip_ethaddr.addr[1] = eaddr.addr[1];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[2] = eaddr.addr[2];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[3] = eaddr.addr[3];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[4] = eaddr.addr[4];\
uip_ethaddr.addr[5] = eaddr.addr[5];} while(0)9、uip.c
这个文件,修改了变量的名字。凡是妨碍阅读的地方,我做了修改。
#include "uip.h"
#include "uip_arp.h"
#define DEBUG_PRINTF(...) /*printf(__VA_ARGS__)*/
//__VA_ARGS__ 宏是用来表示可变参数宏的可变参数的内容。
//简单的说就是将可变参数宏中的 ... 的内容原样传递给右边 __VA_ARGS__ 所在的位置。
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
#include "uip-neighbor.h"
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
#include <string.h>
#if UIP_FIXEDADDR > 0
const uip_ipaddr_t uip_hostaddr =
{HTONS((UIP_IPADDR0 << 8) | UIP_IPADDR1),
HTONS((UIP_IPADDR2 << 8) | UIP_IPADDR3)};
const uip_ipaddr_t uip_draddr =
{HTONS((UIP_DRIPADDR0 << 8) | UIP_DRIPADDR1),
HTONS((UIP_DRIPADDR2 << 8) | UIP_DRIPADDR3)};
const uip_ipaddr_t uip_netmask =
{HTONS((UIP_NETMASK0 << 8) | UIP_NETMASK1),
HTONS((UIP_NETMASK2 << 8) | UIP_NETMASK3)};
#else
uip_ipaddr_t uip_hostaddr;//用来存放ENC28J60的IP地址
uip_ipaddr_t uip_netmask; //用来存放ENC28J60的子网掩码
uip_ipaddr_t uip_draddr; //用来存放ENC28J60的网关地址
#endif /* UIP_FIXEDADDR */
//static const uip_ipaddr_t all_ones_addr =
//#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
// {0xffff,0xffff,0xffff,0xffff,0xffff,0xffff,0xffff,0xffff};
//#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
// {0xffff,0xffff};
//#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
static const uip_ipaddr_t all_zeroes_addr =
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
{0x0000,0x0000,0x0000,0x0000,0x0000,0x0000,0x0000,0x0000};
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
{0x0000,0x0000};
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
#if UIP_FIXEDETHADDR
const struct uip_eth_addr uip_ethaddr = {{UIP_ETHADDR0,
UIP_ETHADDR1,
UIP_ETHADDR2,
UIP_ETHADDR3,
UIP_ETHADDR4,
UIP_ETHADDR5}};
#else
struct uip_eth_addr uip_ethaddr = {{0,0,0,0,0,0}};//记录ENC28J60的MAC地址
#endif
#ifndef UIP_CONF_EXTERNAL_BUFFER
u8_t uip_buf[UIP_BUFSIZE + 2];//ENC28JI60接收和发送数据的缓存
/* The packet buffer that contains incoming packets. */
#endif /* UIP_CONF_EXTERNAL_BUFFER */
u16_t uip_len;//记录uip_buf[]中的数据长度为uip_len;
/* The uip_len is either 8 or 16 bits,depending on the maximum packet size. */
u16_t uip_slen;
void *uip_appdata;
/* The uip_appdata pointer points to application data. */
void *uip_sappdata;
/* The uip_appdata pointer points to the application data which is to be sent. */
#if UIP_URGDATA > 0
void *uip_urgdata; /* The uip_urgdata pointer points to
urgent data (out-of-band data), if
present. */
u16_t uip_urglen, uip_surglen;
#endif /* UIP_URGDATA > 0 */
u8_t uip_flags;
/* The uip_flags variable is used for communication between the TCP/IP stack and the application program. */
struct uipConnectType uipConnectTable[UIP_CONNS];
/* The uipConnectTable array holds all TCP connections. */
struct uipConnectType *uipConnectPointer;
/* uipConnectPointer always points to the current connection. */
u16_t My_uip_listenports[UIP_LISTENPORTS];
/* The uip_listenports list all currently listning ports. */
#if UIP_UDP
struct uip_udp_conn *uip_udp_conn;
struct uip_udp_conn uip_udp_conns[UIP_UDP_CONNS];
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
static u16_t ipid;
/* Ths ipid variable is an increasing number that is used for the IP ID field. */
void uip_setipid(u16_t id) { ipid = id; }
static u8_t iss[4];
/* TCP发送的序列号,The iss variable is used for the TCP initial sequence number. */
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
static u16_t lastport; /* Keeps track of the last port used for
a new connection. */
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
/* Temporary variables. */
u8_t uip_acc32[4];//uip_acc32[]是以"大端存储方式"工作的
static u8_t c, opt;
static u16_t tmp16;
/* Structures and definitions. */
//uip_tcpip_hdr结构中的标志位flags定义如下:
#define TCP_FIN 0x01 //标志位中的FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
#define TCP_SYN 0x02 //标志位中的SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
#define TCP_RST 0x04 //标志位中的RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
#define TCP_PSH 0x08 //标志位中的PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
#define TCP_ACK 0x10 //标志位中的ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
#define TCP_URG 0x20 //标志位中的URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
#define TCP_CTL 0x3f
#define TCP_OPT_END 0 /*TCP 选项列表的结尾,End of TCP options list */
#define TCP_OPT_NOOP 1 /*不执行操作",TCP选项,"No-operation" TCP option */
#define TCP_OPT_MSS 2 /*最大段大小的字节总数为2,Maximum segment size TCP option */
#define TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN 4 /*TCP选项中MSS选项的长度。 Length of TCP MSS option. */
#define ICMP_ECHO_REPLY 0 //ICMP报文类型:应答类型
#define ICMP_ECHO 8 //ICMP报文类型:请求类型填
#define ICMP6_ECHO_REPLY 129
#define ICMP6_ECHO 128
#define ICMP6_NEIGHBOR_SOLICITATION 135
#define ICMP6_NEIGHBOR_ADVERTISEMENT 136
#define ICMP6_FLAG_S (1 << 6)
#define ICMP6_OPTION_SOURCE_LINK_ADDRESS 1
#define ICMP6_OPTION_TARGET_LINK_ADDRESS 2
/* Macros. */
#define BUF ((struct uip_tcpip_hdr *)&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN])
#define FBUF ((struct uip_tcpip_hdr *)&uip_reassbuf[0])
#define ICMPBUF ((struct uip_icmpip_hdr *)&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN])
#define UDPBUF ((struct uip_udpip_hdr *)&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN])
#if UIP_STATISTICS == 1 //程序已经将uIP统计开关设置1
struct uip_stats_type uip_stats;
#define UIP_STAT(s) s
#else
#define UIP_STAT(s)
#endif /* UIP_STATISTICS == 1 */
#if UIP_LOGGING == 1
#include <stdio.h>
void uip_log(char *msg);
#define UIP_LOG(m) uip_log(m)
#else
#define UIP_LOG(m)
#endif /* UIP_LOGGING == 1 */
#if ! UIP_ARCH_ADD32
//函数功能:op32[]"大端存储方式"的数据和op16"小端存储方式"的数据,相加,结果保存在uip_acc32[]
//uip_acc32[]是以"大端存储方式"工作的
//op32[]是以"大端存储方式"工作的
//op16是以"小端存储方式"工作的
void uip_add32(u8_t *op32, u16_t op16)
{
uip_acc32[3] = op32[3] + (op16 & 0xff);
uip_acc32[2] = op32[2] + (op16 >> 8);
uip_acc32[1] = op32[1];
uip_acc32[0] = op32[0];
if( uip_acc32[2] < (op16 >> 8) )//有进位
{
++uip_acc32[1];
if(uip_acc32[1] == 0)//有进位
{
++uip_acc32[0];
}
}
if( uip_acc32[3] < (op16 & 0xff) )//有进位
{
++uip_acc32[2];
if(uip_acc32[2] == 0)//有进位
{
++uip_acc32[1];
if(uip_acc32[1] == 0)//有进位
{
++uip_acc32[0];
}
}
}
}
#endif /* UIP_ARCH_ADD32 */
#if ! UIP_ARCH_CHKSUM
//函数功能:将"大端存储方式"的data[]中的前len个字节按照"双字节进行累加和校验"
//data为"待校验数据缓存"的起始地址
//len为待校验数据的字节总数
static u16_t chksum(u16_t sum, const u8_t *data, u16_t len)
{
u16_t t;
const u8_t *dataptr;
const u8_t *last_byte;
dataptr = data; //指向"待校验数据缓存"的起始地址
last_byte = data + len - 1; //指向"待校验数据缓存"的结束地址
while(dataptr < last_byte)//至少有两个字节才能执行此while循环
{
t = (dataptr[0] << 8) + dataptr[1];//生成"大端存储方式"的16位整型数据
sum += t;//计算"累加和"
if(sum < t)//sum越过0x0000,发生进位
{
sum++;//若有进位,则加1
}
dataptr += 2;//修改指针,为下次计算"累加和"做准备
}
if(dataptr == last_byte)//剩余一个字节
{
t = (dataptr[0] << 8) + 0;//生成"大端存储方式"的16位整型数据
sum += t;//计算"累加和"
if(sum < t)//sum越过0x0000,发生进位
{
sum++;//若有进位,则加1
}
}
return sum;//按照"大端存储方式"返回sum
}
//函数功能:将data[]中的前len个字节按照双字节进行累加和校验
u16_t uip_chksum(u16_t *data, u16_t len)
{
u16_t sum;
sum=chksum(0, (u8_t *)data, len);
//将"大端存储方式"的data[]中的前len个字节按照"双字节进行累加和校验"
return htons(sum);
//将sum转换为"小端端存储方式"返回,因为KEIL使用的是小端存储方式
}
#ifndef UIP_ARCH_IPCHKSUM
//函数功能:将"大端存储方式"的首地址为&uip_buf[14]的缓存中的前20个字节按照"双字节进行累加和校验";
//IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节
//计算"IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header)"20个字节的校验和
u16_t uip_ipchksum(u16_t x)
{
u16_t sum;
u8_t *tmpIPDataPointer;
tmpIPDataPointer=&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN];
sum = chksum(0, tmpIPDataPointer, UIP_IPH_LEN);
//将"大端存储方式"的tmpIPDataPointer[]中的前20个字节按照"双字节进行累加和校验"
//定义UIP_LLH_LEN=14,IP头的大小为UIP_IPH_LEN=20,IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节
DEBUG_PRINTF("uip_ip_chksum%u: sum 0x%04x\n",x,sum);
return (sum == 0) ? 0xffff : htons(sum);
//htons()将累加和sum按照小端存储方式返回
}
#endif
//计算"上层长度,IP协议,发送方IP和接收方IP,TCP头和数据"的校验和
//proto=UIP_PROTO_TCP 6 //TCP协议
//proto=UIP_PROTO_UDP 17 //UDP协议编
//proto=UIP_PROTO_ICMP6 58 //ICMP6协议
static u16_t upper_layer_chksum(u8_t proto)
{
u16_t upper_layer_len;
u16_t sum;
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
upper_layer_len = (((u16_t)(BUF->len[0]) << 8) + BUF->len[1]);
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
upper_layer_len = (((u16_t)(BUF->len[0]) << 8) + BUF->len[1]) - UIP_IPH_LEN;
//上层长度upper_layer_len = IP报文总长度 - IP头的大小
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
sum = upper_layer_len + proto;
/*累加"上层长度和IP协议"时,无需考虑进位。
IP protocol and length fields. This addition cannot carry. */
sum = chksum(sum, (u8_t *)&BUF->srcipaddr[0], 2 * sizeof(uip_ipaddr_t));
/* 发送方IP和接收方IP需要考虑累加时考虑进位。Sum IP source and destination addresses. */
sum = chksum(sum, &uip_buf[UIP_IPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN],upper_layer_len);
//&uip_buf[UIP_IPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN]为TCP头部在uip_buf[]中的首地址
/*累加"TCP头和数据"时需要考虑加法进位。 Sum TCP header and data. */
return (sum == 0) ? 0xffff : htons(sum);
}
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
u16_t
uip_icmp6chksum(void)
{
return upper_layer_chksum(UIP_PROTO_ICMP6);
}
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
//计算TCP头部的校验和
u16_t uip_tcpchksum(void)
{
return upper_layer_chksum(UIP_PROTO_TCP);
//按照"TCP协议头"计算校验和
}
#if UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS
u16_t
uip_udpchksum(void)
{
return upper_layer_chksum(UIP_PROTO_UDP);
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS */
#endif /* UIP_ARCH_CHKSUM */
//函数功能:My_uip_listenports[]初始化为0,uipConnectTable[]初始化为0
void uip_init(void)
{
//TCP端口监听数最多有8个
for(c = 0; c < UIP_LISTENPORTS; ++c)
{
My_uip_listenports[c] = 0;
}
//TCP连接最多有8个设备
for(c = 0; c < UIP_CONNS; ++c)
{
uipConnectTable[c].tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;
}
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
lastport = 1024; //设置TCP客户端默认端口为1024
//动态端口的范围是从1024到65535。
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
#if UIP_UDP
for(c = 0; c < UIP_UDP_CONNS; ++c)
{
uip_udp_conns[c].lport = 0;
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
/* IPv4 initialization. */
#if UIP_FIXEDADDR == 0
/* uip_hostaddr[0] = uip_hostaddr[1] = 0;*/
#endif /* UIP_FIXEDADDR */
uipConnectPointer = &uipConnectTable[0];//初始化指针
}
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
struct uipConnectType *
uip_connect(uip_ipaddr_t *ripaddr, u16_t rport)
{
register struct uipConnectType *conn, *cconn;
/* Find an unused local port. */
again:
++lastport;
if(lastport >= 32000)
{
lastport = 4096;
}
/* Check if this port is already in use, and if so try to find
another one. */
for(c = 0; c < UIP_CONNS; ++c)
{
conn = &uipConnectTable[c];
if(conn->tcpstateflags != UIP_CLOSED &&
conn->lport == htons(lastport))
{
goto again;
}
}
conn = 0;
for(c = 0; c < UIP_CONNS; ++c)
{
cconn = &uipConnectTable[c];
if(cconn->tcpstateflags == UIP_CLOSED)
{
conn = cconn;
break;
}
if(cconn->tcpstateflags == UIP_TIME_WAIT)
{
if(conn == 0 ||
cconn->timer > conn->timer)
{
conn = cconn;
}
}
}
if(conn == 0)
{
return 0;
}
conn->tcpstateflags = UIP_SYN_SENT;
conn->snd_nxt[0] = iss[0];
conn->snd_nxt[1] = iss[1];
conn->snd_nxt[2] = iss[2];
conn->snd_nxt[3] = iss[3];
conn->initialmss = conn->mss = UIP_TCP_MSS;
conn->len = 1; /* TCP length of the SYN is one. */
conn->nrtx = 0;
conn->timer = 1; /* Send the SYN next time around. */
conn->rto = UIP_RTO;
conn->sa = 0;
conn->sv = 16; /* Initial value of the RTT variance. */
conn->lport = htons(lastport);
conn->rport = rport;
uip_ipaddr_copy(&conn->ripaddr, ripaddr);
return conn;
}
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if UIP_UDP
struct uip_udp_conn *
uip_udp_new(uip_ipaddr_t *ripaddr, u16_t rport)
{
register struct uip_udp_conn *conn;
/* Find an unused local port. */
again:
++lastport;
if(lastport >= 32000)
{
lastport = 4096;
}
for(c = 0; c < UIP_UDP_CONNS; ++c)
{
if(uip_udp_conns[c].lport == htons(lastport))
{
goto again;
}
}
conn = 0;
for(c = 0; c < UIP_UDP_CONNS; ++c)
{
if(uip_udp_conns[c].lport == 0)
{
conn = &uip_udp_conns[c];
break;
}
}
if(conn == 0)
{
return 0;
}
conn->lport = HTONS(lastport);
conn->rport = rport;
if(ripaddr == NULL)
{
memset(conn->ripaddr, 0, sizeof(uip_ipaddr_t));
}
else
{
uip_ipaddr_copy(&conn->ripaddr, ripaddr);
}
conn->ttl = UIP_TTL;
return conn;
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
//函数功能:将My_uip_listenports[]全部设置为0
void uip_unlisten(u16_t port)
{
for(c = 0; c < UIP_LISTENPORTS; ++c)
{
if(My_uip_listenports[c] == port)
{
My_uip_listenports[c] = 0;
return;
}
}
}
//函数功能:将My_uip_listenports[]全部设置为port
void uip_listen(u16_t port)
{
for(c = 0; c < UIP_LISTENPORTS; ++c)
{
if(My_uip_listenports[c] == 0)
{
My_uip_listenports[c] = port;
return;
}
}
}
/* XXX: IP fragment reassembly: not well-tested. */
#if UIP_REASSEMBLY && !UIP_CONF_IPV6
#define UIP_REASS_BUFSIZE (UIP_BUFSIZE - UIP_LLH_LEN)
static u8_t uip_reassbuf[UIP_REASS_BUFSIZE];
static u8_t uip_reassbitmap[UIP_REASS_BUFSIZE / (8 * 8)];
static const u8_t bitmap_bits[8] = {0xff, 0x7f, 0x3f, 0x1f,
0x0f, 0x07, 0x03, 0x01};
static u16_t uip_reasslen;
static u8_t uip_reassflags;
#define UIP_REASS_FLAG_LASTFRAG 0x01
static u8_t uip_reasstmr;
#define IP_MF 0x20
static u8_t
uip_reass(void)
{
u16_t offset, len;
u16_t i;
/* If ip_reasstmr is zero, no packet is present in the buffer, so we
write the IP header of the fragment into the reassembly
buffer. The timer is updated with the maximum age. */
if(uip_reasstmr == 0) {
memcpy(uip_reassbuf, &BUF->vhl, UIP_IPH_LEN);
uip_reasstmr = UIP_REASS_MAXAGE;
uip_reassflags = 0;
/* Clear the bitmap. */
memset(uip_reassbitmap, 0, sizeof(uip_reassbitmap));
}
/* Check if the incoming fragment matches the one currently present
in the reasembly buffer. If so, we proceed with copying the
fragment into the buffer. */
if(BUF->srcipaddr[0] == FBUF->srcipaddr[0] &&
BUF->srcipaddr[1] == FBUF->srcipaddr[1] &&
BUF->destipaddr[0] == FBUF->destipaddr[0] &&
BUF->destipaddr[1] == FBUF->destipaddr[1] &&
BUF->ipid[0] == FBUF->ipid[0] &&
BUF->ipid[1] == FBUF->ipid[1]) {
len = (BUF->len[0] << 8) + BUF->len[1] - (BUF->vhl & 0x0f) * 4;
offset = (((BUF->ipoffset[0] & 0x3f) << 8) + BUF->ipoffset[1]) * 8;
/* If the offset or the offset + fragment length overflows the
reassembly buffer, we discard the entire packet. */
if(offset > UIP_REASS_BUFSIZE ||
offset + len > UIP_REASS_BUFSIZE) {
uip_reasstmr = 0;
goto nullreturn;
}
/* Copy the fragment into the reassembly buffer, at the right
offset. */
memcpy(&uip_reassbuf[UIP_IPH_LEN + offset],
(char *)BUF + (int)((BUF->vhl & 0x0f) * 4),
len);
/* Update the bitmap. */
if(offset / (8 * 8) == (offset + len) / (8 * 8)) {
/* If the two endpoints are in the same byte, we only update
that byte. */
uip_reassbitmap[offset / (8 * 8)] |=
bitmap_bits[(offset / 8 ) & 7] &
~bitmap_bits[((offset + len) / 8 ) & 7];
} else {
/* If the two endpoints are in different bytes, we update the
bytes in the endpoints and fill the stuff inbetween with
0xff. */
uip_reassbitmap[offset / (8 * 8)] |=
bitmap_bits[(offset / 8 ) & 7];
for(i = 1 + offset / (8 * 8); i < (offset + len) / (8 * 8); ++i) {
uip_reassbitmap[i] = 0xff;
}
uip_reassbitmap[(offset + len) / (8 * 8)] |=
~bitmap_bits[((offset + len) / 8 ) & 7];
}
/* If this fragment has the More Fragments flag set to zero, we
know that this is the last fragment, so we can calculate the
size of the entire packet. We also set the
IP_REASS_FLAG_LASTFRAG flag to indicate that we have received
the final fragment. */
if((BUF->ipoffset[0] & IP_MF) == 0) {
uip_reassflags |= UIP_REASS_FLAG_LASTFRAG;
uip_reasslen = offset + len;
}
/* Finally, we check if we have a full packet in the buffer. We do
this by checking if we have the last fragment and if all bits
in the bitmap are set. */
if(uip_reassflags & UIP_REASS_FLAG_LASTFRAG) {
/* Check all bytes up to and including all but the last byte in
the bitmap. */
for(i = 0; i < uip_reasslen / (8 * 8) - 1; ++i) {
if(uip_reassbitmap[i] != 0xff) {
goto nullreturn;
}
}
/* Check the last byte in the bitmap. It should contain just the
right amount of bits. */
if(uip_reassbitmap[uip_reasslen / (8 * 8)] !=
(u8_t)~bitmap_bits[uip_reasslen / 8 & 7]) {
goto nullreturn;
}
/* If we have come this far, we have a full packet in the
buffer, so we allocate a pbuf and copy the packet into it. We
also reset the timer. */
uip_reasstmr = 0;
memcpy(BUF, FBUF, uip_reasslen);
/* Pretend to be a "normal" (i.e., not fragmented) IP packet
from now on. */
BUF->ipoffset[0] = BUF->ipoffset[1] = 0;
BUF->len[0] = uip_reasslen >> 8;
BUF->len[1] = uip_reasslen & 0xff;
BUF->ipchksum = 0;
BUF->ipchksum = ~(uip_ipchksum(1));
return uip_reasslen;
}
}
nullreturn:
return 0;
}
#endif /* UIP_REASSEMBLY */
//函数功能:接收端下一个期望接收的序列号
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和n"小端存储方式"的数据,相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
static void uip_add_rcv_nxt(u16_t n)
{
uip_add32(uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt, n);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和n"小端存储方式"的数据,相加,结果保存在uip_acc32[]
uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[0] = uip_acc32[0];//更新uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[0]
uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[1] = uip_acc32[1];//更新uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[1]
uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[2] = uip_acc32[2];//更新uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[2]
uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[3] = uip_acc32[3];//更新uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[3]
}
void uip_process(u8_t flag)
{
register struct uipConnectType *pConnect = uipConnectPointer;
//修改pConnect,就是等同于修改uipConnectPointer
struct ethip_hdr *pEthernetHeader;
u16_t tmp;
pEthernetHeader=(struct ethip_hdr *)&uip_buf[0];
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
if( pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP6) )
//uip_buf[]中不是IPV6数据包,则退出
return;
#else
if( pEthernetHeader->ethhdr.type!=htons(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP) )
//uip_buf[]中不是IPV4数据包,则退出
return;
#endif
#if UIP_UDP
if(flag == UIP_UDP_SEND_CONN) {
goto udp_send;
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
uip_sappdata = uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_IPTCPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN];
//这里的uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[54];uip_appdata=&uip_buf[54];
/* Check if we were invoked because of a poll request for a
particular connection. */
if(flag == UIP_POLL_REQUEST)
{
if( (pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_TS_MASK) == UIP_ESTABLISHED && !uip_outstanding(pConnect) )
{
uip_flags = UIP_POLL;
tcp_demo_appcall();//执行tcp_demo_appcall()实际是执行tcp_demo_appcall()
goto appsend;
}
goto drop;
/* Check if we were invoked because of the perodic timer fireing. */
}
else if(flag == UIP_TIMER)
{
#if UIP_REASSEMBLY
if(uip_reasstmr != 0) {
--uip_reasstmr;
}
#endif /* UIP_REASSEMBLY */
/*增加"TCP发送的序列号",大端存储方式。Increase the initial sequence number. */
if(++iss[3] == 0)//最低8位加1,产生进位
{
if(++iss[2] == 0)//次低8位加1,产生进位
{
if(++iss[1] == 0)//次高8位加1,产生进位
{ ++iss[0];}//最高8位加1
}
}
uip_len = 0; /* Reset the length variables. */
uip_slen = 0; /* Reset the length variables. */
/*检查连接是否处于仅等待超时的状态。
若情况如此,我们将延长连接的超时时间,若超时则断开连接。
Check if the connection is in a state in which we simply wait for the connection to time out.
If so, we increase the connection's timer and remove the connection if it times out. */
//检测"TCP状态"
if(pConnect->tcpstateflags == UIP_TIME_WAIT || pConnect->tcpstateflags == UIP_FIN_WAIT_2)
{
++(pConnect->timer);
if(pConnect->timer == UIP_TIME_WAIT_TIMEOUT)//超时
{ pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED; }
}
else if(pConnect->tcpstateflags != UIP_CLOSED)
{
//若连接存在未处理数据,我们将延长连接计时器,若达到重传超时时间(RTO),则重新发送数据。
/* If the connection has outstanding data,we increase the connection's timer and see if it has reached the RTO value in which case we retransmit. */
if(uip_outstanding(pConnect))
{//uip_outstanding(pConnect)和"pConnect.len"等价
if(pConnect->timer-- == 0)
{
if(pConnect->nrtx == UIP_MAXRTX || ((pConnect->tcpstateflags == UIP_SYN_SENT || pConnect->tcpstateflags == UIP_SYN_RCVD) && pConnect->nrtx == UIP_MAXSYNRTX))
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;//修改"TCP状态"
/* We call tcp_demo_appcall() with uip_flags set to UIP_TIMEDOUT to inform the application that the connection has timed out. */
uip_flags = UIP_TIMEDOUT;
tcp_demo_appcall();
/* We also send a reset packet to the remote host. */
BUF->flags = TCP_RST | TCP_ACK;
goto tcp_send_nodata;
}
/* Exponential backoff. */
pConnect->timer = UIP_RTO << ( pConnect->nrtx > 4 ? 4:pConnect->nrtx );
++(pConnect->nrtx);
/* Ok, so we need to retransmit. We do this differently depending on which state we are in. In ESTABLISHED, we call upon the application so that it may prepare the data for the retransmit.
In SYN_RCVD, we resend the SYNACK that we sent earlier and in LAST_ACK we have to retransmit our FINACK. */
//因此我们需要重传数据。具体操作方式会根据系统状态的不同而有所变化。
//在已建立连接的状态下,我们会调用应用程序来准备重传所需的数据。
//在SYN_RCVD阶段,我们重新发送先前发送的SYNACK;而在LAST_ACK阶段,则需要重新传输我们的FINACK 。
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.rexmit);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.tcp.rexmit"
switch(pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_TS_MASK)
{//"TCP状态"
case UIP_SYN_RCVD:
/* In the SYN_RCVD state, we should retransmit our SYNACK. */
goto tcp_send_synack;
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
case UIP_SYN_SENT:
/* In the SYN_SENT state, we retransmit out SYN. */
BUF->flags = 0;
goto tcp_send_syn;
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
case UIP_ESTABLISHED:
//在已建立的连接状态下,我们调用应用程序执行实际重传操作,随后跳转至发送数据包的代码段(apprexmit标签)。
/* In the ESTABLISHED state, we call upon the application to do the actual retransmit after which we jump into the code for sending out the packet (the apprexmit label). */
uip_flags = UIP_REXMIT;//重新传输上次发送的数据。
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto apprexmit;
case UIP_FIN_WAIT_1:
case UIP_CLOSING:
case UIP_LAST_ACK:
/* In all these states we should retransmit a FINACK. */
goto tcp_send_finack;
}
}
}
else if((pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_TS_MASK) == UIP_ESTABLISHED)
{
/* 如果不需要重传,我们会轮询应用程序以获取新数据。
If there was no need for a retransmission, we poll the application for new data. */
uip_flags = UIP_POLL;
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto appsend;
}
}
goto drop;
}
#if UIP_UDP
if(flag == UIP_UDP_TIMER)
{
if(uip_udp_conn->lport != 0) {
uipConnectPointer = NULL;
uip_sappdata = uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN + UIP_IPUDPH_LEN];
//在UDP中这里的uip_appdata=&uip_buf[42];
uip_len = uip_slen = 0;
uip_flags = UIP_POLL;
UIP_UDP_APPCALL();
goto udp_send;
} else {
goto drop;
}
}
#endif
/* This is where the input processing starts. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.recv);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.recv"
/* Start of IP input header processing code. */
//////////检查"IP版本和IP头部长度"是否正确///////////////
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* Check validity of the IP header. */
if((BUF->vtc & 0xf0) != 0x60) { /* IP version and header length. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.vhlerr);
UIP_LOG("ipv6: invalid version.");
goto drop;
}
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/* 检查IP头的有效性。Check validity of the IP header. */
//BUF->vhl为"IP版本和IP头部长度":
//版本:"0x45的高4位"为0x04表示IPv4版本;头部长度:"0x45的低4位"为0x05,表示IPv4头部长度,单位为32位字
//即IP头部/IPV4头部为:5 * 4 = 20 字节。
if(BUF->vhl != 0x45)//ip版本和首部长度不是0x45
{ /* IP version and header length. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.drop"
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.vhlerr);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.vhlerr"
// UIP_LOG("ip: invalid version or header length.");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
//////////如果"IP版本和IP头部长度"正确,则执行下面语句///////////////
//////////检查"IP报文总长度"是否正确///////////////
/*
检查数据包的大小。
如果uip_len比"IP报头中报告的大小"要小,那么我们认为数据包在传输过程中被损坏。
如果uip_len大于"IP包头中报告的大小",则该包已经被填充,我们需要将uip_len设置为正确的值
Check the size of the packet.
If the size reported to us in uip_len is smaller the size reported in the IP header, we assume that the packet has been corrupted in transit.
If the size of uip_len is larger than the size reported in the IP packet header,the packet has been padded and we set uip_len to the correct value..
*/
//BUF->len[]表示"IP报文总长度",占2个字节,它是"IP头,TCP头部和TCP数据的长度"
tmp=BUF->len[0];tmp=(u16_t)(tmp << 8);tmp=tmp + BUF->len[1];//计算"IP报文总长度"
if( tmp <= uip_len )//该数据包已经被填充
{
uip_len = tmp;//将uip_len设置为正确的"IP报文总长度"
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
uip_len += 40; /* The length reported in the IPv6 header is the
length of the payload that follows the
header. However, uIP uses the uip_len variable
for holding the size of the entire packet,
including the IP header. For IPv4 this is not a
problem as the length field in the IPv4 header
contains the length of the entire packet. But
for IPv6 we need to add the size of the IPv6
header (40 bytes). */
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
}
else//数据包在传输过程中被损坏
{
// UIP_LOG("ip: packet shorter than reported in IP header.");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
//////////如果"IP报文总长度"正确,则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查数据包是否被"分成多个包"///////////////
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* 检查"标志字段和片偏移字段"。 Check the fragment flag. */
//标志字段第1位(保留位,bit15)始终为0;
//标志字段第2位(DF位,bit14),DF=1禁止对该数据包分片;DF=0允许分片;
//标志字段第3位(MF位,bit13),MF=1表示后续还有分片;MF=0表示当前是最后一个分片;
//片偏移字段占13位,bit12:0,表示"当前分片"在原始数据包中的起始位置。
//计算方式:偏移值 = 起始字节数 / 8。如果偏移值为5,则表示分片在原始数据包中,是从第5*8=40字节开始。
//0x40 0x00, 禁止对该数据包分片。
//DF=0允许分片,但MF=0表示当前是最后一个分片,也就是没有分片。
tmp=BUF->ipoffset[0];tmp=(u16_t)(tmp << 8);tmp=tmp + BUF->ipoffset[1];
//计算"标志字段和片偏移字段"
// if( (BUF->ipoffset[0] & 0x3f) != 0 || BUF->ipoffset[1] != 0 )
if( (tmp & 0x3FFF) != 0 )//发现该数据包被"分成多个包",uip不支持分包
{
#if UIP_REASSEMBLY
uip_len = uip_reass();
if(uip_len == 0) {
goto drop;
}
#else /* UIP_REASSEMBLY */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop); //相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.drop"
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.fragerr); //相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.fragerr"
UIP_LOG("ip: fragment dropped.");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
#endif /* UIP_REASSEMBLY */
}
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
//////////如果数据包没有被"分成多个包",则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查"本地IP地址"是否为0,"接收到目的IP地址"与"本地IP地址"是否相同///////////////
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(uip_hostaddr, all_zeroes_addr))
{//如果本地IP为0,则返回1
/* If we are configured to use ping IP address configuration and
hasn't been assigned an IP address yet, we accept all ICMP
packets. */
#if UIP_PINGADDRCONF && !UIP_CONF_IPV6
if(BUF->proto == UIP_PROTO_ICMP) {
UIP_LOG("ip: possible ping config packet received.");
goto icmp_input;
} else {
UIP_LOG("ip: packet dropped since no address assigned.");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
#endif /* UIP_PINGADDRCONF */
}
else//如果本地IP不为0
{
//如果配置了IP广播支持,则会检查是否存在可能发往我们的广播UDP数据包。
/* If IP broadcast support is configured, we check for a broadcast UDP packet, which may be destined to us. */
#if UIP_BROADCAST
DEBUG_PRINTF("UDP IP checksum 0x%04x\n", uip_ipchksum(2));
if(BUF->proto == UIP_PROTO_UDP &&
uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->destipaddr, all_ones_addr)
/*&&
uip_ipchksum(3) == 0xffff*/) {
goto udp_input;
}
#endif
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
if(!uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->destipaddr, uip_hostaddr))//接收到目的IP地址与本地IP地址相同,则返回1
{
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.ip.drop"
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
#else
/* For IPv6, packet reception is a little trickier as we need to
make sure that we listen to certain multicast addresses (all
hosts multicast address, and the solicited-node multicast
address) as well. However, we will cheat here and accept all
multicast packets that are sent to the ff02::/16 addresses. */
if(!uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->destipaddr, uip_hostaddr) &&
BUF->destipaddr[0] != HTONS(0xff02)) {
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);
goto drop;
}
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
}
//////////如果"本地IP地址"为0或者"接收到目的IP地址"与"本地IP地址"不同,则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查"IP头部校验和"是否为0xFFFF///////////////
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
//计算"IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header)"20个字节的校验和
if(uip_ipchksum(4) != 0xffff)//"IP头部校验和"错误
{ /* Compute and check the IP header checksum. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.chkerr);
UIP_LOG("ip: bad checksum.");
goto drop;//"IP头部校验和"错误,跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
//////////如果"IP头部校验和"正确,则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查数据包是否是"TCP数据"///////////////
if(BUF->proto == UIP_PROTO_TCP)//检查TCP数据包。如果是,请继续进行TCP输入处理。
{ //如果BUF->proto=6表示是"TCP数据"
/* Check for TCP packet. If so,proceed with TCP input processing. */
goto tcp_input;//是TCP数据,则跳转至tcp_input标号处执行
}
//////////如果数据包不是"TCP数据",则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查数据包是否是"UDP数据"///////////////
#if UIP_UDP
if(BUF->proto == UIP_PROTO_UDP)
{//如果BUF->proto=17表示是"UDP数据"
goto udp_input;//是UDP数据,则跳转至udp_input标号处执行
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
//////////如果数据包不是"TCP数据",也不是"UDP数据",则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查数据包是否是"ICMP数据"///////////////
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* ICMPv4 processing code follows. */
if(BUF->proto != UIP_PROTO_ICMP)
{ //如果BUF->proto=1表示是"ICMP数据"
/* We only allow ICMP packets from here. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.protoerr);
UIP_LOG("ip: neither tcp nor icmp.");
goto drop;//该数据包不是ICMP数据,跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
//////////如果接收到的数据包是"ICMP数据",则执行下面的语句///////////////
//////////检查数据包是否是"ICMP请求数据包"///////////////
#if UIP_PINGADDRCONF
icmp_input:
#endif /* UIP_PINGADDRCONF */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.recv);
/* ICMP echo (i.e., ping) processing. This is simple, we only change
the ICMP type from ECHO to ECHO_REPLY and adjust the ICMP
checksum before we return the packet. */
if(ICMPBUF->type != ICMP_ECHO)//不是"ICMP请求数据包"
{//ICMP_ECHO是请求类型
//ICMP报文类型,请求类型填ICMP_ECHO=8,应答类型填ICMP_ECHO_REPLY=0;
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.typeerr);
UIP_LOG("icmp: not icmp echo.");
goto drop;//该数据包不是"ICMP请求数据包",跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
//////////如果数据包是"ICMP请求数据包",则执行下面的语句///////////////
/* If we are configured to use ping IP address assignment, we use
the destination IP address of this ping packet and assign it to
ourself. */
#if UIP_PINGADDRCONF
if((uip_hostaddr[0] | uip_hostaddr[1]) == 0) {
uip_hostaddr[0] = BUF->destipaddr[0];
uip_hostaddr[1] = BUF->destipaddr[1];
}
#endif /* UIP_PINGADDRCONF */
ICMPBUF->type = ICMP_ECHO_REPLY;
//设置"ICMP报文类型"为"应答类型",填ICMP_ECHO_REPLY=0;
if(ICMPBUF->icmpchksum >= HTONS(0xffff - (ICMP_ECHO << 8)))
{//设置"ICMP应答数据的校验和"
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum += HTONS(ICMP_ECHO << 8) + 1;
}
else
{//设置"ICMP应答数据的校验和"
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum += HTONS(ICMP_ECHO << 8);
}
/*交换双方的IP地址,Swap IP addresses. */
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->destipaddr, BUF->srcipaddr);//设置"接收方IP地址"
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);//设置"发送方IP地址"
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.sent);
goto send;//跳转至send标号处执行
/* IPv4输入报头处理代码的结束。End of IPv4 input header processing code. */
#else /* 开始IPv6输入报头处理代码。!UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/* This is IPv6 ICMPv6 processing code. */
DEBUG_PRINTF("icmp6_input: length %d\n", uip_len);
if(BUF->proto != UIP_PROTO_ICMP6) { /* We only allow ICMPv6 packets from
here. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.protoerr);
UIP_LOG("ip: neither tcp nor icmp6.");
goto drop;//该数据包不是"ICMP6请求数据包",跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.recv);
/* If we get a neighbor solicitation for our address we should send
a neighbor advertisement message back. */
if(ICMPBUF->type == ICMP6_NEIGHBOR_SOLICITATION) {
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(ICMPBUF->icmp6data, uip_hostaddr))
{
if(ICMPBUF->options[0] == ICMP6_OPTION_SOURCE_LINK_ADDRESS) {
/* Save the sender's address in our neighbor list. */
uip_neighbor_add(ICMPBUF->srcipaddr, &(ICMPBUF->options[2]));
}
/* We should now send a neighbor advertisement back to where the
neighbor solicication came from. */
ICMPBUF->type = ICMP6_NEIGHBOR_ADVERTISEMENT;
ICMPBUF->flags = ICMP6_FLAG_S; /* Solicited flag. */
ICMPBUF->reserved1 = ICMPBUF->reserved2 = ICMPBUF->reserved3 = 0;
uip_ipaddr_copy(ICMPBUF->destipaddr, ICMPBUF->srcipaddr);
uip_ipaddr_copy(ICMPBUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
ICMPBUF->options[0] = ICMP6_OPTION_TARGET_LINK_ADDRESS;
ICMPBUF->options[1] = 1; /* Options length, 1 = 8 bytes. */
memcpy(&(ICMPBUF->options[2]), &uip_ethaddr, sizeof(uip_ethaddr));
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum = 0;
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum = ~uip_icmp6chksum();
goto send;
}
goto drop;
} else if(ICMPBUF->type == ICMP6_ECHO) {
/* ICMP echo (i.e., ping) processing. This is simple, we only
change the ICMP type from ECHO to ECHO_REPLY and update the
ICMP checksum before we return the packet. */
ICMPBUF->type = ICMP6_ECHO_REPLY;
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->destipaddr, BUF->srcipaddr);
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum = 0;
ICMPBUF->icmpchksum = ~uip_icmp6chksum();
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.sent);
goto send;
} else {
DEBUG_PRINTF("Unknown icmp6 message type %d\n", ICMPBUF->type);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.icmp.typeerr);
UIP_LOG("icmp: unknown ICMP message.");
goto drop;
}
/* End of IPv6 ICMP processing. */
#endif /*IPv6输入报头处理代码结束。 !UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
#if UIP_UDP
///////如果数据包是"UDP数据",则执行下面的语句///////////
/* UDP input processing. */
udp_input:
/* UDP processing is really just a hack. We don't do anything to the
UDP/IP headers, but let the UDP application do all the hard
work. If the application sets uip_slen, it has a packet to
send. */
#if UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS
uip_len = uip_len - UIP_IPUDPH_LEN;
uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN + UIP_IPUDPH_LEN];
//在UDP中这里的uip_appdata=&uip_buf[42];
if(UDPBUF->udpchksum != 0 && uip_udpchksum() != 0xffff) {
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.udp.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.udp.chkerr);
UIP_LOG("udp: bad checksum.");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
#else /* UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS */
uip_len = uip_len - UIP_IPUDPH_LEN;
#endif /* UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS */
/* Demultiplex this UDP packet between the UDP "connections". */
for(uip_udp_conn = &uip_udp_conns[0];
uip_udp_conn < &uip_udp_conns[UIP_UDP_CONNS];
++uip_udp_conn) {
/* If the local UDP port is non-zero, the connection is considered
to be used. If so, the local port number is checked against the
destination port number in the received packet. If the two port
numbers match, the remote port number is checked if the
connection is bound to a remote port. Finally, if the
connection is bound to a remote IP address, the source IP
address of the packet is checked. */
if(uip_udp_conn->lport != 0 &&
UDPBUF->destport == uip_udp_conn->lport &&
(uip_udp_conn->rport == 0 ||
UDPBUF->srcport == uip_udp_conn->rport) &&
(uip_ipaddr_cmp(uip_udp_conn->ripaddr, all_zeroes_addr) ||
uip_ipaddr_cmp(uip_udp_conn->ripaddr, all_ones_addr) ||
uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_udp_conn->ripaddr))) {
goto udp_found;
}
}
UIP_LOG("udp: no matching connection found");
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
udp_found:
uipConnectPointer = NULL;
uip_flags = UIP_NEWDATA;
uip_sappdata = uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN + UIP_IPUDPH_LEN];
//在UDP中这里的uip_appdata=&uip_buf[42];
uip_slen = 0;
UIP_UDP_APPCALL();
udp_send:
if(uip_slen == 0) {
goto drop;//跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
uip_len = uip_slen + UIP_IPUDPH_LEN;
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* For IPv6, the IP length field does not include the IPv6 IP header
length. */
BUF->len[0] = ((uip_len - UIP_IPH_LEN) >> 8);
BUF->len[1] = ((uip_len - UIP_IPH_LEN) & 0xff);
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
BUF->len[0] = (uip_len >> 8);
BUF->len[1] = (uip_len & 0xff);
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
BUF->ttl = uip_udp_conn->ttl;
BUF->proto = UIP_PROTO_UDP;
UDPBUF->udplen = HTONS(uip_slen + UIP_UDPH_LEN);
UDPBUF->udpchksum = 0;
BUF->srcport = uip_udp_conn->lport;
BUF->destport = uip_udp_conn->rport;
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->destipaddr, uip_udp_conn->ripaddr);
uip_appdata = &uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN + UIP_IPTCPH_LEN];
//在UDP中这里的uip_appdata=&uip_buf[42];
#if UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS
/* Calculate UDP checksum. */
UDPBUF->udpchksum = ~(uip_udpchksum());
if(UDPBUF->udpchksum == 0) {
UDPBUF->udpchksum = 0xffff;
}
#endif /* UIP_UDP_CHECKSUMS */
goto ip_send_nolen;
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
///////如果数据包是"TCP数据",则执行下面的语句///////////
////////////检查"TCP头部的校验和"是否正确/////////
/* TCP输入处理。TCP input processing. */
tcp_input:
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.recv);//相当于执行"++uip_stats.tcp.recv"
/* Start of TCP input header processing code. */
//计算TCP头部的校验和
if(uip_tcpchksum() != 0xffff)//如果"TCP头部的校验和"错误,则执行
{ /* Compute and check the TCP checksum. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.drop);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.chkerr);
UIP_LOG("tcp: bad checksum.");
goto drop;//"TCP头部的校验和"错误,跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
////////////如果"TCP头部的校验和"正确,则执行下面的语句/////////
////////////检查"uipConnectTable[]"里是否有接收到到的远程IP地址和端口,目的端口是否是我的/////////
/* Demultiplex this segment. */
/* First check any active connections. */
//在uipConnectTable[]中查找"TCP状态和标志"不是UIP_CLOSED,
//"接收到的目的端口"是本地端口,且"发送方端口"是表里的远程端口
//"发送方的IP地址"是表里的远程IP地址,以上条件满足,则表示这个连接是正确的
for(pConnect = &uipConnectTable[0]; pConnect <= &uipConnectTable[UIP_CONNS - 1];++pConnect)
{//在uipConnectTable[]查找
if( pConnect->tcpstateflags != UIP_CLOSED
&& BUF->destport == pConnect->lport
&& BUF->srcport == pConnect->rport
&& uip_ipaddr_cmp(BUF->srcipaddr, pConnect->ripaddr))
{
goto TCP_found;//"TCP数据包"连接参数正确,则跳转至TCP_found标号处执行
}
}
////////////如果"uipConnectTable[]"里没有接收到到的远程IP地址和端口,或目的端口不是否是我的/////////
/* If we didn't find and active connection that expected the packet,
either this packet is an old duplicate, or this is a SYN packet
destined for a connection in LISTEN. If the SYN flag isn't set,
it is an old packet and we send a RST. */
if((BUF->flags & TCP_CTL) != TCP_SYN)
{//如果bit1=0同步标志,则不用"建立连接并设置初始序列号"
//标志位
//URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
//PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
//RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
//FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
goto reset;
}
tmp16 = BUF->destport;//读"接收方端口"
/* Next, check listening connections. */
for(c = 0; c < UIP_LISTENPORTS; ++c)
{
if(tmp16 == My_uip_listenports[c])//查找这个端口是否存在
goto found_listen;
}
/* No matching connection found, so we send a RST packet. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.synrst);
reset:
/* We do not send resets in response to resets. */
if(BUF->flags & TCP_RST)
{//如果bit2=1,则重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//标志位
//URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
//PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
//RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
//FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
goto drop;
}
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.rst);
BUF->flags = TCP_RST | TCP_ACK;//bit2=1重置连接,bit4=1确认应答
//标志位
//URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
//PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
//RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
//FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
uip_len = UIP_IPTCPH_LEN;
//UIP_IPTCPH_LEN=40="IP头的大小" + "TCP头的大小"
BUF->tcpoffset = 5 << 4;//数据偏移
/*翻转TCP报头中的seqno和ackno字段。 Flip the seqno and ackno fields in the TCP header. */
//将"我的序列号和应答序列号"交换位置保存
//交换后,BUF->ackno[]保存的是"我的序列号",BUF->seqno[]保存的是"应答序列号"
c = BUF->seqno[3];BUF->seqno[3] = BUF->ackno[3];BUF->ackno[3] = c;
c = BUF->seqno[2];BUF->seqno[2] = BUF->ackno[2];BUF->ackno[2] = c;
c = BUF->seqno[1];BUF->seqno[1] = BUF->ackno[1];BUF->ackno[1] = c;
c = BUF->seqno[0];BUF->seqno[0] = BUF->ackno[0];BUF->ackno[0] = c;
/* We also have to increase the sequence number we are
acknowledging. If the least significant byte overflowed, we need
to propagate the carry to the other bytes as well. */
//将"我的序列号"加1
if(++BUF->ackno[3] == 0)
{//BUF->ackno[]保存的是"我的序列号""我的序列号"的最低8位加1,产生进位
if(++BUF->ackno[2] == 0)
{
if(++BUF->ackno[1] == 0)
{
++BUF->ackno[0];
}
}
}
/*交换发送方端口和接收方端口,Swap port numbers. */
tmp16 = BUF->srcport; BUF->srcport = BUF->destport; BUF->destport = tmp16;
/* Swap IP addresses. */
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->destipaddr, BUF->srcipaddr);//设置接收方IP地址
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);//设置发送方IP地址为本地IP地址
/* And send out the RST packet! */
goto tcp_send_noconn;
/* This label will be jumped to if we matched the incoming packet
with a connection in LISTEN. In that case, we should create a new
connection and send a SYNACK in return. */
found_listen:
/* First we check if there are any connections avaliable. Unused
connections are kept in the same table as used connections, but
unused ones have the tcpstate set to CLOSED. Also, connections in
TIME_WAIT are kept track of and we'll use the oldest one if no
CLOSED connections are found. Thanks to Eddie C. Dost for a very
nice algorithm for the TIME_WAIT search. */
//下面这段是读取pConnect的值
pConnect = 0;
for(c = 0; c < UIP_CONNS; ++c)
{
if(uipConnectTable[c].tcpstateflags == UIP_CLOSED)
{
pConnect = &uipConnectTable[c];
break;
}
if(uipConnectTable[c].tcpstateflags == UIP_TIME_WAIT)
{
if(pConnect == 0 || uipConnectTable[c].timer > pConnect->timer)
{
pConnect = &uipConnectTable[c];
}
}
}
if(pConnect == 0)
{
/* All connections are used already, we drop packet and hope that
the remote end will retransmit the packet at a time when we
have more spare connections. */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.syndrop);
UIP_LOG("tcp: found no unused connections.");
goto drop;
}
uipConnectPointer = pConnect;
/* Fill in the necessary fields for the new connection. */
pConnect->rto = pConnect->timer = UIP_RTO;
pConnect->sa = 0;
pConnect->sv = 4;
pConnect->nrtx = 0;
pConnect->lport = BUF->destport;//设置本地本地端口
pConnect->rport = BUF->srcport;//将"发送方端口"保存到"远程端口"
uip_ipaddr_copy(pConnect->ripaddr, BUF->srcipaddr);
//将"发送方IP地址"拷贝到"远程IP地址"
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_SYN_RCVD;//设置"TCP状态"
//更新"发送的序列号"
pConnect->snd_nxt[0] = iss[0];
pConnect->snd_nxt[1] = iss[1];
pConnect->snd_nxt[2] = iss[2];
pConnect->snd_nxt[3] = iss[3];
pConnect->len = 1;
/* rcv_nxt should be the seqno from the incoming packet + 1. */
//此处的BUF->seqno[]保存的是"应答序列号"
pConnect->rcv_nxt[3] = BUF->seqno[3];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[2] = BUF->seqno[2];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[1] = BUF->seqno[1];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[0] = BUF->seqno[0];
uip_add_rcv_nxt(1);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和1相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
/* Parse the TCP MSS option, if present. */
if( (BUF->tcpoffset & 0xf0) > 0x50 )//TCP头部的长度大于20个字节
{//BUF->tcpoffset的高4位表示TCP头部的长度,即(0x70>>4)*4=28;
for(c = 0; c < ((BUF->tcpoffset >> 4) - 5) << 2 ;)
{
opt = uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + c];
//UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=40,UIP_LLH_LEN=14
if(opt == TCP_OPT_END)//TCP选项列表的结尾
{/* End of options. */
break;
}
else if(opt == TCP_OPT_NOOP)
{
++c;
/* NOP option. */
}
else if(opt == TCP_OPT_MSS && uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c] == TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN)
{//TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN=4,表示TCP选项中MSS选项的长度
/* An MSS option with the right option length. */
tmp16 = ((u16_t)uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 2 + c] << 8) | (u16_t)uip_buf[UIP_IPTCPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 3 + c];
pConnect->initialmss = pConnect->mss = tmp16 > UIP_TCP_MSS ? UIP_TCP_MSS: tmp16;
//UIP_TCP_MSS为TCP最大段大小:1500-14-40
/* And we are done processing options. */
break;
}
else
{
/* All other options have a length field, so that we easily can skip past them. */
if(uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c] == 0)
{
/* If the length field is zero, the options are malformed and we don't process them further. */
break;
}
c += uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c];
}
}
}
/* Our response will be a SYNACK. */
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
tcp_send_synack:
BUF->flags = TCP_ACK;
tcp_send_syn:
BUF->flags |= TCP_SYN;
#else /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
tcp_send_synack:
BUF->flags = TCP_SYN | TCP_ACK;
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
/* We send out the TCP Maximum Segment Size option with our SYNACK. */
BUF->optdata[0] = TCP_OPT_MSS;//最大段字节总数为2
BUF->optdata[1] = TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN;//TCP选项中MSS选项的长度
BUF->optdata[2] = (UIP_TCP_MSS) / 256;//最大段高8数值,TCP最大段大小为(1500-14-40)
BUF->optdata[3] = (UIP_TCP_MSS) & 255;//最大段低8数值,TCP最大段大小为(1500-14-40)
uip_len = UIP_IPTCPH_LEN + TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN;
//UIP_IPTCPH_LEN="IP头的大小20" + "TCP头的大小20"
//得到uip_len=44
BUF->tcpoffset = ((UIP_TCPH_LEN + TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN) / 4) << 4;
//数据偏移:[(TCP头的大小20+4)/4]<<4
goto tcp_send;
/* This label will be jumped to if we found an active connection. */
///////////TCP数据包正确/////////
TCP_found:
uipConnectPointer = pConnect;//TCP数据包正确,更新uip连接指针
uip_flags = 0;
/* We do a very naive form of TCP reset processing; we just accept
any RST and kill our connection. We should in fact check if the
sequence number of this reset is wihtin our advertised window
before we accept the reset. */
if(BUF->flags & TCP_RST)
{//bit2=1重置连接,强制断开异常连接
//标志位
//URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
//PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
//RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
//FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;
UIP_LOG("tcp: got reset, aborting connection.");
uip_flags = UIP_ABORT;
//远程主机已中止该连接,因此该连接已消失。或者应用程序表示它想要中止连接。
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto drop;//中止该连接,跳转至标号drop处,令"uip_len = 0;uip_flags = 0;",然会退出该函数
}
/* Calculated the length of the data, if the application has sent any data to us. */
c = (BUF->tcpoffset >> 4) << 2;
//计算"TCP头部的长度",比如(0x70>>4)*4=28;
/* uip_len will contain the length of the actual TCP data. This is
calculated by subtracing the length of the TCP header (in
c) and the length of the IP header (20 bytes). */
uip_len = uip_len - c - UIP_IPH_LEN;//计算剩余长度
/* UIP_IPH_LEN为IP头的大小,IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节*/
/* First, check if the sequence number of the incoming packet is
what we're expecting next. If not, we send out an ACK with the
correct numbers in. */
if( !( ((pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_TS_MASK) == UIP_SYN_SENT) &&
((BUF->flags & TCP_CTL) == (TCP_SYN | TCP_ACK)) ) )
{
if( ( uip_len > 0 || ( (BUF->flags & (TCP_SYN | TCP_FIN)) != 0 ) ) &&
( BUF->seqno[0] != pConnect->rcv_nxt[0] || BUF->seqno[1] != pConnect->rcv_nxt[1] ||
BUF->seqno[2] != pConnect->rcv_nxt[2] || BUF->seqno[3] != pConnect->rcv_nxt[3]))
{
goto tcp_send_ack;
}
}
/* Next, check if the incoming segment acknowledges any outstanding
data. If so, we update the sequence number, reset the length of
the outstanding data, calculate RTT estimations, and reset the
retransmission timer. */
if((BUF->flags & TCP_ACK) && uip_outstanding(pConnect))
{
uip_add32(pConnect->snd_nxt, pConnect->len);
//pConnect->snd_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和pConnect->len"小端存储方式"的数据,相加,结果保存在uip_acc32[]
if(BUF->ackno[0] == uip_acc32[0] &&
BUF->ackno[1] == uip_acc32[1] &&
BUF->ackno[2] == uip_acc32[2] &&
BUF->ackno[3] == uip_acc32[3])
{
/* Update sequence number. */
pConnect->snd_nxt[0] = uip_acc32[0];
pConnect->snd_nxt[1] = uip_acc32[1];
pConnect->snd_nxt[2] = uip_acc32[2];
pConnect->snd_nxt[3] = uip_acc32[3];
/* Do RTT estimation, unless we have done retransmissions. */
if(pConnect->nrtx == 0)
{
signed char m;
m = pConnect->rto - pConnect->timer;
/* This is taken directly from VJs original code in his paper */
m = m - (pConnect->sa >> 3);
pConnect->sa += m;
if(m < 0) { m = -m; }
m = m - (pConnect->sv >> 2);
pConnect->sv += m;
pConnect->rto = (pConnect->sa >> 3) + pConnect->sv;
}
uip_flags = UIP_ACKDATA;//设置接收到TCP应答标志,Set the acknowledged flag.
/* Reset the retransmission timer. */
pConnect->timer = pConnect->rto;
/* Reset length of outstanding data. */
pConnect->len = 0;
}
}
/* Do different things depending on in what state the connection is. */
switch(pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_TS_MASK)
{
/* CLOSED and LISTEN are not handled here. CLOSE_WAIT is not
implemented, since we force the application to close when the
peer sends a FIN (hence the application goes directly from
ESTABLISHED to LAST_ACK). */
case UIP_SYN_RCVD:
/* In SYN_RCVD we have sent out a SYNACK in response to a SYN, and
we are waiting for an ACK that acknowledges the data we sent
out the last time. Therefore, we want to have the UIP_ACKDATA
flag set. If so, we enter the ESTABLISHED state. */
if(uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA) {
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_ESTABLISHED;
uip_flags = UIP_CONNECTED;
pConnect->len = 0;
if(uip_len > 0) {
uip_flags |= UIP_NEWDATA;
uip_add_rcv_nxt(uip_len);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和uip_len相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
}
uip_slen = 0;
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto appsend;
}
goto drop;
#if UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN
case UIP_SYN_SENT:
/* In SYN_SENT, we wait for a SYNACK that is sent in response to
our SYN. The rcv_nxt is set to sequence number in the SYNACK
plus one, and we send an ACK. We move into the ESTABLISHED
state. */
if((uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA) &&
(BUF->flags & TCP_CTL) == (TCP_SYN | TCP_ACK)) {
/* Parse the TCP MSS option, if present. */
if((BUF->tcpoffset & 0xf0) > 0x50) {
for(c = 0; c < ((BUF->tcpoffset >> 4) - 5) << 2 ;) {
opt = uip_buf[UIP_IPTCPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + c];
if(opt == TCP_OPT_END) {
/* End of options. */
break;
} else if(opt == TCP_OPT_NOOP) {
++c;
/* NOP option. */
} else if(opt == TCP_OPT_MSS &&
uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c] == TCP_OPT_MSS_LEN) {
/* An MSS option with the right option length. */
tmp16 = (uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 2 + c] << 8) |
uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 3 + c];
pConnect->initialmss =
pConnect->mss = tmp16 > UIP_TCP_MSS? UIP_TCP_MSS: tmp16;
/* And we are done processing options. */
break;
} else {
/* All other options have a length field, so that we easily
can skip past them. */
if(uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c] == 0) {
/* If the length field is zero, the options are malformed
and we don't process them further. */
break;
}
c += uip_buf[UIP_TCPIP_HLEN + UIP_LLH_LEN + 1 + c];
}
}
}
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_ESTABLISHED;
pConnect->rcv_nxt[0] = BUF->seqno[0];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[1] = BUF->seqno[1];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[2] = BUF->seqno[2];
pConnect->rcv_nxt[3] = BUF->seqno[3];
uip_add_rcv_nxt(1);
uip_flags = UIP_CONNECTED | UIP_NEWDATA;
pConnect->len = 0;
uip_len = 0;
uip_slen = 0;
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto appsend;
}
/* Inform the application that the connection failed */
uip_flags = UIP_ABORT;
tcp_demo_appcall();
/* The connection is closed after we send the RST */
uipConnectPointer->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;
goto reset;
#endif /* UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN */
case UIP_ESTABLISHED:
/* In the ESTABLISHED state, we call upon the application to feed
data into the uip_buf. If the UIP_ACKDATA flag is set, the
application should put new data into the buffer, otherwise we are
retransmitting an old segment, and the application should put that
data into the buffer.
If the incoming packet is a FIN, we should close the connection on
this side as well, and we send out a FIN and enter the LAST_ACK
state. We require that there is no outstanding data; otherwise the
sequence numbers will be screwed up. */
if(BUF->flags & TCP_FIN && !(pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_STOPPED))
{
if(uip_outstanding(pConnect))
{
goto drop;
}
uip_add_rcv_nxt(1 + uip_len);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和uip_len+1相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
uip_flags |= UIP_CLOSE;
if(uip_len > 0)
{
uip_flags |= UIP_NEWDATA;
}
tcp_demo_appcall();
pConnect->len = 1;
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_LAST_ACK;
pConnect->nrtx = 0;
tcp_send_finack:
BUF->flags = TCP_FIN | TCP_ACK;
goto tcp_send_nodata;
}
/* Check the URG flag. If this is set, the segment carries urgent
data that we must pass to the application. */
if((BUF->flags & TCP_URG) != 0)
{//标志位中的URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//本程序中的紧急指针的值时钟为0x0000
#if UIP_URGDATA > 0
uip_urglen = (BUF->urgp[0] << 8) | BUF->urgp[1];
if(uip_urglen > uip_len) {
/* There is more urgent data in the next segment to come. */
uip_urglen = uip_len;
}
uip_add_rcv_nxt(uip_urglen);
uip_len -= uip_urglen;
uip_urgdata = uip_appdata;
uip_appdata += uip_urglen;
} else {
uip_urglen = 0;
#else
uip_appdata = ((char *)uip_appdata) + ((BUF->urgp[0] << 8) | BUF->urgp[1]);
//((BUF->urgp[0] << 8) | BUF->urgp[1])为紧急指针的值
//在TCP中uip_appdata=&uip_buf[54],加上"紧急指针的值",就指向接收到的用户数据
uip_len -= (BUF->urgp[0] << 8) | BUF->urgp[1];
#endif /* UIP_URGDATA > 0 */
}
/* If uip_len > 0 we have TCP data in the packet, and we flag this
by setting the UIP_NEWDATA flag and update the sequence number
we acknowledge. If the application has stopped the dataflow
using uip_stop(), we must not accept any data packets from the
remote host. */
if(uip_len > 0 && !(pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_STOPPED)) {
uip_flags |= UIP_NEWDATA;
uip_add_rcv_nxt(uip_len);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和uip_len相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
}
/* Check if the available buffer space advertised by the other end
is smaller than the initial MSS for this connection. If so, we
set the current MSS to the window size to ensure that the
application does not send more data than the other end can
handle.
If the remote host advertises a zero window, we set the MSS to
the initial MSS so that the application will send an entire MSS
of data. This data will not be acknowledged by the receiver,
and the application will retransmit it. This is called the
"persistent timer" and uses the retransmission mechanim.
*/
tmp16 = ((u16_t)BUF->wnd[0] << 8) + (u16_t)BUF->wnd[1];
//当前"计算机接收的缓冲区"的大小
if(tmp16 > pConnect->initialmss || tmp16 == 0)
{
tmp16 = pConnect->initialmss;//ENC28J60的"最大段大小"
}
pConnect->mss = tmp16;
/* If this packet constitutes an ACK for outstanding data (flagged
by the UIP_ACKDATA flag, we should call the application since it
might want to send more data. If the incoming packet had data
from the peer (as flagged by the UIP_NEWDATA flag), the
application must also be notified.
When the application is called, the global variable uip_len
contains the length of the incoming data. The application can
access the incoming data through the global pointer
uip_appdata, which usually points UIP_IPTCPH_LEN + UIP_LLH_LEN
bytes into the uip_buf array.
If the application wishes to send any data, this data should be
put into the uip_appdata and the length of the data should be
put into uip_len. If the application don't have any data to
send, uip_len must be set to 0. */
if(uip_flags & (UIP_NEWDATA | UIP_ACKDATA))
{
uip_slen = 0;
tcp_demo_appcall();
appsend:
if(uip_flags & UIP_ABORT)
{
uip_slen = 0;
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;
BUF->flags = TCP_RST | TCP_ACK;
goto tcp_send_nodata;
}
if(uip_flags & UIP_CLOSE)
{
uip_slen = 0;
pConnect->len = 1;
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_FIN_WAIT_1;
pConnect->nrtx = 0;
BUF->flags = TCP_FIN | TCP_ACK;
goto tcp_send_nodata;
}
/* If uip_slen > 0, the application has data to be sent. */
if(uip_slen > 0)
{
/* If the connection has acknowledged data, the contents of the ->len variable should be discarded. */
if((uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA) != 0){ pConnect->len = 0;}
/* If the ->len variable is non-zero the connection has already data in transit and cannot send anymore right now. */
if(pConnect->len == 0)
{
/* The application cannot send more than what is allowed by the mss (the minumum of the MSS and the available window). */
if(uip_slen > pConnect->mss) { uip_slen = pConnect->mss; }
/* Remember how much data we send out now so that we know when everything has been acknowledged. */
pConnect->len = uip_slen;
}
else
{
/* If the application already had unacknowledged data, we make sure that the application does not send (i.e.,retransmit) out more than it previously sent out. */
uip_slen = pConnect->len;
}
}
pConnect->nrtx = 0;
apprexmit://重新传输上次发送的数据。
uip_appdata = uip_sappdata;
//在TCP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[54];
//在UDP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[42];
/* If the application has data to be sent, or if the incoming
packet had new data in it, we must send out a packet. */
if(uip_slen > 0 && pConnect->len > 0)
{
/* Add the length of the IP and TCP headers. */
uip_len = pConnect->len + UIP_TCPIP_HLEN;
//UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=UIP_IPTCPH_LEN=40="IP头的大小" + "TCP头的大小"
/* We always set the ACK flag in response packets. */
BUF->flags = TCP_ACK | TCP_PSH;
/* Send the packet. */
goto tcp_send_noopts;
}
/* If there is no data to send, just send out a pure ACK if there is newdata. */
if(uip_flags & UIP_NEWDATA)
{
uip_len = UIP_TCPIP_HLEN;
//UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=UIP_IPTCPH_LEN=40="IP头的大小" + "TCP头的大小"
BUF->flags = TCP_ACK;
goto tcp_send_noopts;
}
}
goto drop;
case UIP_LAST_ACK:
/* We can close this connection if the peer has acknowledged our
FIN. This is indicated by the UIP_ACKDATA flag. */
if(uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA)
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSED;
uip_flags = UIP_CLOSE;
tcp_demo_appcall();
}
break;
case UIP_FIN_WAIT_1:
/* The application has closed the connection, but the remote host
hasn't closed its end yet. Thus we do nothing but wait for a
FIN from the other side. */
if(uip_len > 0)
{
uip_add_rcv_nxt(uip_len);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和uip_len相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
}
if(BUF->flags & TCP_FIN)
{
if(uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA)
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_TIME_WAIT;
pConnect->timer = 0;
pConnect->len = 0;
}
else
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_CLOSING;
}
uip_add_rcv_nxt(1);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和1相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
uip_flags = UIP_CLOSE;
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto tcp_send_ack;
}
else if(uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA)
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_FIN_WAIT_2;
pConnect->len = 0;
goto drop;
}
if(uip_len > 0)
{
goto tcp_send_ack;
}
goto drop;
case UIP_FIN_WAIT_2:
if(uip_len > 0)
{
uip_add_rcv_nxt(uip_len);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和uip_len相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
}
if(BUF->flags & TCP_FIN)
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_TIME_WAIT;
pConnect->timer = 0;
uip_add_rcv_nxt(1);
//uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]"大端存储方式"的数据和1相加,结果保存在uipConnectPointer->rcv_nxt[]
uip_flags = UIP_CLOSE;
tcp_demo_appcall();
goto tcp_send_ack;
}
if(uip_len > 0)
{
goto tcp_send_ack;
}
goto drop;
case UIP_TIME_WAIT:
goto tcp_send_ack;
case UIP_CLOSING:
if(uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA)
{
pConnect->tcpstateflags = UIP_TIME_WAIT;
pConnect->timer = 0;
}
}
goto drop;
/* We jump here when we are ready to send the packet, and just want
to set the appropriate TCP sequence numbers in the TCP header. */
tcp_send_ack:
BUF->flags = TCP_ACK;
tcp_send_nodata:
uip_len = UIP_IPTCPH_LEN;
//UIP_IPTCPH_LEN=40="IP头的大小" + "TCP头的大小"
tcp_send_noopts:
BUF->tcpoffset = (UIP_TCPH_LEN / 4) << 4;
tcp_send:
/* We're done with the input processing. We are now ready to send a
reply. Our job is to fill in all the fields of the TCP and IP
headers before calculating the checksum and finally send the
packet. */
//修改"TCP头部中的确认号"
BUF->ackno[0] = pConnect->rcv_nxt[0];
BUF->ackno[1] = pConnect->rcv_nxt[1];
BUF->ackno[2] = pConnect->rcv_nxt[2];
BUF->ackno[3] = pConnect->rcv_nxt[3];
//修改"TCP头部中的序列号"
BUF->seqno[0] = pConnect->snd_nxt[0];
BUF->seqno[1] = pConnect->snd_nxt[1];
BUF->seqno[2] = pConnect->snd_nxt[2];
BUF->seqno[3] = pConnect->snd_nxt[3];
BUF->proto = UIP_PROTO_TCP;//修改"IP头部中的协议"
BUF->srcport = pConnect->lport;//修改"TCP头部中的发送方端口"
BUF->destport = pConnect->rport;//修改"TCP头部中的接收方端口"
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->srcipaddr, uip_hostaddr);//修改"IP头部中的发送方IP地址"
uip_ipaddr_copy(BUF->destipaddr, pConnect->ripaddr);//修改"IP头部中的接收方IP地址"
if(pConnect->tcpstateflags & UIP_STOPPED)
{
/* If the connection has issued uip_stop(), we advertise a zero
window so that the remote host will stop sending data. */
BUF->wnd[0] = BUF->wnd[1] = 0;//修改"TCP头部中的窗口大小"
}
else
{
BUF->wnd[0] = ((UIP_RECEIVE_WINDOW) >> 8);//修改"TCP头部中的窗口大小"
BUF->wnd[1] = ((UIP_RECEIVE_WINDOW) & 0xff);//修改"TCP头部中的窗口大小"
}
tcp_send_noconn:
BUF->ttl = UIP_TTL;//修改IP头部中的"生存时间值"
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* For IPv6, the IP length field does not include the IPv6 IP header
length. */
BUF->len[0] = ((uip_len - UIP_IPH_LEN) >> 8);
BUF->len[1] = ((uip_len - UIP_IPH_LEN) & 0xff);
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
BUF->len[0] = (uip_len >> 8);BUF->len[1] = (uip_len & 0xff);//修改IP头部中的"IP报文总长度"
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
BUF->urgp[0] = BUF->urgp[1] = 0;//修改TCP头部中的"紧急指针"
BUF->tcpchksum = 0;BUF->tcpchksum = ~(uip_tcpchksum());//计算TCP头部的校验和
#if UIP_UDP
ip_send_nolen:
#endif
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
BUF->vtc = 0x60;
BUF->tcflow = 0x00;
BUF->flow = 0x00;
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*修改"IP头部"*/
BUF->vhl = 0x45;//设置"IP版本和头部长度"
BUF->tos = 0;//设置"//服务类型"
BUF->ipoffset[0] = BUF->ipoffset[1] = 0;//设置"片偏移"
++ipid;BUF->ipid[0] = ipid >> 8;BUF->ipid[1] = ipid & 0xff;//设置"标识"
BUF->ipchksum = 0;BUF->ipchksum = ~(uip_ipchksum(5));//设置"检验和"
DEBUG_PRINTF("uip ip_send_nolen: chkecum 0x%04x\n", uip_ipchksum(6));
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.tcp.sent);
send:
DEBUG_PRINTF("Sending packet with length %d (%d)\n", uip_len,
(BUF->len[0] << 8) | BUF->len[1]);
UIP_STAT(++uip_stats.ip.sent);
/* Return and let the caller do the actual transmission. */
uip_flags = 0;
return;
drop:
uip_len = 0;
uip_flags = 0;
return;
}
//函数类型:如果是小端存储方式,则将val的高8位值和低8位值交换
u16_t htons(u16_t val)
{
return HTONS(val);
}
//函数功能:将data[]中前len个字节拷贝到首地址为uip_sappdata的缓冲区
//在TCP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[54];
//在UDP中uip_sappdata = &uip_buf[42];
void uip_send(const void *data, int len)
{
if(len > 0)
{
uip_slen = len;
if(data != uip_sappdata)
{
memcpy(uip_sappdata, (data), uip_slen);
}
}
}10、uip.h
这个文件主要是删除了不该包含的头文件。
#ifndef __UIP_H__
#define __UIP_H__
#include "uipopt.h" //必须包含,因为要用到"UIP_UDP宏,UIP_URGDATA宏和UIP_FIXEDADDR宏"
#include "tcp_server_demo.h"
/* IP地址的重新表示; Repressentation of an IP address. */
//"声明变量"的语句前加typedef会让该变量成为一种新的数据类型;
typedef u16_t uip_ip4addr_t[2];
//uip_ip4addr_t[]数组有2个元素,每个元素都是u16_t型。
//使用typedef修饰后,uip_ip4addr_t就变成了数据类型,可以用来声明u16型数组,且数组元素数量为2个
typedef u16_t uip_ip6addr_t[8];
//uip_ip6addr_t[]数组有8个元素,每个元素都是u16_t型。
//使用typedef修饰后,uip_ip6addr_t就变成了数据类型,可以用来声明u16型数组,且数组元素数量为8个
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
typedef uip_ip6addr_t uip_ipaddr_t; //起别名:将uip_ip6addr_t重命名为uip_ipaddr_t
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
typedef uip_ip4addr_t uip_ipaddr_t;
//起别名:将uip_ip4addr_t重命名为uip_ipaddr_t
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* First, the functions that should be called from the
* system. Initialization, the periodic timer and incoming packets are
* handled by the following three functions.
*/
/**
* \defgroup uipconffunc uIP configuration functions
* @{
*
* The uIP configuration functions are used for setting run-time
* parameters in uIP such as IP addresses.
*/
/*设置此主机的IP地址。
* Set the IP address of this host.
*
* The IP address is represented as a 4-byte array where the first
* octet of the IP address is put in the first member of the 4-byte
* array.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t addr;
uip_ipaddr(&addr, 192,168,1,2);
uip_sethostaddr(&addr);
\endcode
* \param addr A pointer to an IP address of type uip_ipaddr_t;
*
* \sa uip_ipaddr()
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_sethostaddr(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy(uip_hostaddr, (addr))
//保存ENC28J60的IP地址
/**
* Get the IP address of this host.
*
* The IP address is represented as a 4-byte array where the first
* octet of the IP address is put in the first member of the 4-byte
* array.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t hostaddr;
uip_gethostaddr(&hostaddr);
\endcode
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable that will be
* filled in with the currently configured IP address.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_gethostaddr(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy((addr), uip_hostaddr)
/**
* Set the default router's IP address.
*
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable containing the IP
* address of the default router.
*
* \sa uip_ipaddr()
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_setdraddr(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy(uip_draddr, (addr)) //保存ENC28J60的网关地址
/*设置网络掩码
* Set the netmask.
*
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable containing the IP
* address of the netmask.
*
* \sa uip_ipaddr()
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_setnetmask(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy(uip_netmask, (addr))
//保存ENC28J60的子网掩码
/**
* Get the default router's IP address.
*
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable that will be
* filled in with the IP address of the default router.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_getdraddr(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy((addr), uip_draddr)
/**
* Get the netmask.
*
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable that will be
* filled in with the value of the netmask.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_getnetmask(addr) uip_ipaddr_copy((addr), uip_netmask)
/** @} */
/**
* \defgroup uipinit uIP initialization functions
* @{
*
* The uIP initialization functions are used for booting uIP.
*/
/**
* uIP initialization function.
*
* This function should be called at boot up to initilize the uIP
* TCP/IP stack.
*/
void uip_init(void);
/**
* uIP initialization function.
*
* This function may be used at boot time to set the initial ip_id.
*/
void uip_setipid(u16_t id);
/** @} */
/**
* \defgroup uipdevfunc uIP device driver functions
* @{
*
* These functions are used by a network device driver for interacting
* with uIP.
*/
/**
* Process an incoming packet.
*
* This function should be called when the device driver has received
* a packet from the network. The packet from the device driver must
* be present in the uip_buf buffer, and the length of the packet
* should be placed in the uip_len variable.
*
* When the function returns, there may be an outbound packet placed
* in the uip_buf packet buffer. If so, the uip_len variable is set to
* the length of the packet. If no packet is to be sent out, the
* uip_len variable is set to 0.
*
* The usual way of calling the function is presented by the source
* code below.
\code
uip_len = devicedriver_poll();
if(uip_len > 0) {
uip_input();
if(uip_len > 0) {
devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \note If you are writing a uIP device driver that needs ARP
* (Address Resolution Protocol), e.g., when running uIP over
* Ethernet, you will need to call the uIP ARP code before calling
* this function:
\code
#define BUF ((struct uip_eth_hdr *)&uip_buf[0])
uip_len = ethernet_devicedrver_poll();
if(uip_len > 0) {
if(BUF->type == HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_IP)) {
uip_arp_ipin();
uip_input();
if(uip_len > 0) {
uip_arp_out();
ethernet_devicedriver_send();
}
} else if(BUF->type == HTONS(UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP)) {
uip_arp_arpin();
if(uip_len > 0) {
ethernet_devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_input() uip_process(UIP_DATA)
/**
* Periodic processing for a connection identified by its number.
*
* This function does the necessary periodic processing (timers,
* polling) for a uIP TCP conneciton, and should be called when the
* periodic uIP timer goes off. It should be called for every
* connection, regardless of whether they are open of closed.
*
* When the function returns, it may have an outbound packet waiting
* for service in the uIP packet buffer, and if so the uip_len
* variable is set to a value larger than zero. The device driver
* should be called to send out the packet.
*
* The ususal way of calling the function is through a for() loop like
* this:
\code
for(i = 0; i < UIP_CONNS; ++i) {
uip_periodic(i);
if(uip_len > 0) {
devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \note If you are writing a uIP device driver that needs ARP
* (Address Resolution Protocol), e.g., when running uIP over
* Ethernet, you will need to call the uip_arp_out() function before
* calling the device driver:
\code
for(i = 0; i < UIP_CONNS; ++i) {
uip_periodic(i);
if(uip_len > 0) {
uip_arp_out();
ethernet_devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \param conn The number of the connection which is to be periodically polled.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_periodic(conn) do { uipConnectPointer = &uipConnectTable[conn]; \
uip_process(UIP_TIMER); } while (0)
/**
*
*
*/
#define uip_conn_active(conn) (uipConnectTable[conn].tcpstateflags != UIP_CLOSED)
/**
* Perform periodic processing for a connection identified by a pointer
* to its structure.
*
* Same as uip_periodic() but takes a pointer to the actual uipConnectPointer
* struct instead of an integer as its argument. This function can be
* used to force periodic processing of a specific connection.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uipConnectPointer struct for the connection to
* be processed.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_periodic_conn(conn) do { uipConnectPointer = conn; \
uip_process(UIP_TIMER); } while (0)
/**
* Reuqest that a particular connection should be polled.
*
* Similar to uip_periodic_conn() but does not perform any timer
* processing. The application is polled for new data.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uip_conn struct for the connection to
* be processed.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_poll_conn(conn) do { uipConnectPointer = conn; \
uip_process(UIP_POLL_REQUEST); } while (0)
#if UIP_UDP
/**
* Periodic processing for a UDP connection identified by its number.
*
* This function is essentially the same as uip_periodic(), but for
* UDP connections. It is called in a similar fashion as the
* uip_periodic() function:
\code
for(i = 0; i < UIP_UDP_CONNS; i++) {
uip_udp_periodic(i);
if(uip_len > 0) {
devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \note As for the uip_periodic() function, special care has to be
* taken when using uIP together with ARP and Ethernet:
\code
for(i = 0; i < UIP_UDP_CONNS; i++) {
uip_udp_periodic(i);
if(uip_len > 0) {
uip_arp_out();
ethernet_devicedriver_send();
}
}
\endcode
*
* \param conn The number of the UDP connection to be processed.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_udp_periodic(conn) do { uip_udp_conn = &uip_udp_conns[conn]; \
uip_process(UIP_UDP_TIMER); } while (0)
/**
* Periodic processing for a UDP connection identified by a pointer to
* its structure.
*
* Same as uip_udp_periodic() but takes a pointer to the actual
* uip_conn struct instead of an integer as its argument. This
* function can be used to force periodic processing of a specific
* connection.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uip_udp_conn struct for the connection
* to be processed.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_udp_periodic_conn(conn) do { uip_udp_conn = conn; \
uip_process(UIP_UDP_TIMER); } while (0)
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
/**
* The uIP packet buffer.
*
* The uip_buf array is used to hold incoming and outgoing
* packets. The device driver should place incoming data into this
* buffer. When sending data, the device driver should read the link
* level headers and the TCP/IP headers from this buffer. The size of
* the link level headers is configured by the UIP_LLH_LEN define.
*
* \note The application data need not be placed in this buffer, so
* the device driver must read it from the place pointed to by the
* uip_appdata pointer as illustrated by the following example:
\code
void
devicedriver_send(void)
{
hwsend(&uip_buf[0], UIP_LLH_LEN);
if(uip_len <= UIP_LLH_LEN + UIP_TCPIP_HLEN) {
hwsend(&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN], uip_len - UIP_LLH_LEN);
} else {
hwsend(&uip_buf[UIP_LLH_LEN], UIP_TCPIP_HLEN);
hwsend(uip_appdata, uip_len - UIP_TCPIP_HLEN - UIP_LLH_LEN);
}
}
\endcode
*/
extern u8_t uip_buf[UIP_BUFSIZE+2];
/** @} */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Functions that are used by the uIP application program. Opening and
* closing connections, sending and receiving data, etc. is all
* handled by the functions below.
*/
/**
* \defgroup uipappfunc uIP application functions
* @{
*
* Functions used by an application running of top of uIP.
*/
/**
* Start listening to the specified port.
*
* \note Since this function expects the port number in network byte
* order, a conversion using HTONS() or htons() is necessary.
*
\code
uip_listen(HTONS(80));
\endcode
*
* \param port A 16-bit port number in network byte order.
*/
void uip_listen(u16_t port);
/**
* Stop listening to the specified port.
*
* \note Since this function expects the port number in network byte
* order, a conversion using HTONS() or htons() is necessary.
*
\code
uip_unlisten(HTONS(80));
\endcode
*
* \param port A 16-bit port number in network byte order.
*/
void uip_unlisten(u16_t port);
/**
* Connect to a remote host using TCP.
*
* This function is used to start a new connection to the specified
* port on the specied host. It allocates a new connection identifier,
* sets the connection to the SYN_SENT state and sets the
* retransmission timer to 0. This will cause a TCP SYN segment to be
* sent out the next time this connection is periodically processed,
* which usually is done within 0.5 seconds after the call to
* uip_connect().
*
* \note This function is avaliable only if support for active open
* has been configured by defining UIP_ACTIVE_OPEN to 1 in uipopt.h.
*
* \note Since this function requires the port number to be in network
* byte order, a conversion using HTONS() or htons() is necessary.
*
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 192,168,1,2);
uip_connect(&ipaddr, HTONS(80));
\endcode
*
* \param ripaddr The IP address of the remote hot.
*
* \param port A 16-bit port number in network byte order.
*
* \return A pointer to the uIP connection identifier for the new connection,
* or NULL if no connection could be allocated.
*
*/
struct uipConnectType *uip_connect(uip_ipaddr_t *ripaddr, u16_t port);
/**
* \internal
*
* Check if a connection has outstanding (i.e., unacknowledged) data.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uip_conn structure for the connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_outstanding(conn) ((conn)->len)
/**
* Send data on the current connection.
*
* This function is used to send out a single segment of TCP
* data. Only applications that have been invoked by uIP for event
* processing can send data.
*
* The amount of data that actually is sent out after a call to this
* funcion is determined by the maximum amount of data TCP allows. uIP
* will automatically crop the data so that only the appropriate
* amount of data is sent. The function uip_mss() can be used to query
* uIP for the amount of data that actually will be sent.
*
* \note This function does not guarantee that the sent data will
* arrive at the destination. If the data is lost in the network, the
* application will be invoked with the uip_rexmit() event being
* set. The application will then have to resend the data using this
* function.
*
* \param data A pointer to the data which is to be sent.
*
* \param len The maximum amount of data bytes to be sent.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
void uip_send(const void *data, int len);
/**
* The length of any incoming data that is currently avaliable (if avaliable)
* in the uip_appdata buffer.
*
* The test function uip_data() must first be used to check if there
* is any data available at all.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
/*void uip_datalen(void);*/
#define uip_datalen() uip_len
/**
* The length of any out-of-band data (urgent data) that has arrived
* on the connection.
*
* \note The configuration parameter UIP_URGDATA must be set for this
* function to be enabled.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_urgdatalen() uip_urglen
/**
* Close the current connection.
*
* This function will close the current connection in a nice way.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_close() (uip_flags = UIP_CLOSE)
/**
* Abort the current connection.
*
* This function will abort (reset) the current connection, and is
* usually used when an error has occured that prevents using the
* uip_close() function.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_abort() (uip_flags = UIP_ABORT)
//建立"中止连接标志"。
/**
* Tell the sending host to stop sending data.
*
* This function will close our receiver's window so that we stop
* receiving data for the current connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_stop() (uipConnectPointer->tcpstateflags |= UIP_STOPPED)
/**
* Find out if the current connection has been previously stopped with
* uip_stop().
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_stopped(conn) ((conn)->tcpstateflags & UIP_STOPPED)
/**
* Restart the current connection, if is has previously been stopped
* with uip_stop().
*
* This function will open the receiver's window again so that we
* start receiving data for the current connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_restart() do { uip_flags |= UIP_NEWDATA; \
uipConnectPointer->tcpstateflags &= ~UIP_STOPPED; \
} while(0)
/* uIP tests that can be made to determine in what state the current
connection is, and what the application function should do. */
/**
* Is the current connection a UDP connection?
*
* This function checks whether the current connection is a UDP connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*
*/
#define uip_udpconnection() (uipConnectPointer == NULL)
/**
* Is new incoming data available?
*
* Will reduce to non-zero if there is new data for the application
* present at the uip_appdata pointer. The size of the data is
* avaliable through the uip_len variable.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_newdata() (uip_flags & UIP_NEWDATA)
//表示已经向我们发送了新数据
/**
* Has previously sent data been acknowledged?
*
* Will reduce to non-zero if the previously sent data has been
* acknowledged by the remote host. This means that the application
* can send new data.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_acked() (uip_flags & UIP_ACKDATA)
//读接收到的TCP应答标志
/**
* Has the connection just been connected?
*
* Reduces to non-zero if the current connection has been connected to
* a remote host. This will happen both if the connection has been
* actively opened (with uip_connect()) or passively opened (with
* uip_listen()).
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_connected() (uip_flags & UIP_CONNECTED)
/**
* Has the connection been closed by the other end?
*
* Is non-zero if the connection has been closed by the remote
* host. The application may then do the necessary clean-ups.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_closed() (uip_flags & UIP_CLOSE)
/**
* Has the connection been aborted by the other end?
*
* Non-zero if the current connection has been aborted (reset) by the
* remote host.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_aborted() (uip_flags & UIP_ABORT)
/**
* Has the connection timed out?
*
* Non-zero if the current connection has been aborted due to too many
* retransmissions.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_timedout() (uip_flags & UIP_TIMEDOUT)
/**
* Do we need to retransmit previously data?
*
* Reduces to non-zero if the previously sent data has been lost in
* the network, and the application should retransmit it. The
* application should send the exact same data as it did the last
* time, using the uip_send() function.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_rexmit() (uip_flags & UIP_REXMIT) //重传
/**
* Is the connection being polled by uIP?
*
* Is non-zero if the reason the application is invoked is that the
* current connection has been idle for a while and should be
* polled.
*
* The polling event can be used for sending data without having to
* wait for the remote host to send data.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_poll() (uip_flags & UIP_POLL)
//读"轮询标志",若建立,则查应用程序是否有要发送的数据。
/**
* Get the initial maxium segment size (MSS) of the current
* connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_initialmss() (uipConnectPointer->initialmss)
//uipConnectPointer->initialmss用来记录ENC28J60的"最大段大小",也就是发送缓存的大小
/**
* Get the current maxium segment size that can be sent on the current
* connection.
*
* The current maxiumum segment size that can be sent on the
* connection is computed from the receiver's window and the MSS of
* the connection (which also is available by calling
* uip_initialmss()).
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_mss() (uipConnectPointer->mss)
//当前最大段大小
/**
* Set up a new UDP connection.
*
* This function sets up a new UDP connection. The function will
* automatically allocate an unused local port for the new
* connection. However, another port can be chosen by using the
* uip_udp_bind() call, after the uip_udp_new() function has been
* called.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t addr;
struct uip_udp_conn *c;
uip_ipaddr(&addr, 192,168,2,1);
c = uip_udp_new(&addr, HTONS(12345));
if(c != NULL) {
uip_udp_bind(c, HTONS(12344));
}
\endcode
* \param ripaddr The IP address of the remote host.
*
* \param rport The remote port number in network byte order.
*
* \return The uip_udp_conn structure for the new connection or NULL
* if no connection could be allocated.
*/
struct uip_udp_conn *uip_udp_new(uip_ipaddr_t *ripaddr, u16_t rport);
/**
* Removed a UDP connection.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uip_udp_conn structure for the connection.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_udp_remove(conn) (conn)->lport = 0
/**
* Bind a UDP connection to a local port.
*
* \param conn A pointer to the uip_udp_conn structure for the
* connection.
*
* \param port The local port number, in network byte order.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_udp_bind(conn, port) (conn)->lport = port
/**
* Send a UDP datagram of length len on the current connection.
*
* This function can only be called in response to a UDP event (poll
* or newdata). The data must be present in the uip_buf buffer, at the
* place pointed to by the uip_appdata pointer.
*
* \param len The length of the data in the uip_buf buffer.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_udp_send(len) uip_send((char *)uip_appdata, len)
/** @} */
/* uIP convenience and converting functions. */
/**
* \defgroup uipconvfunc uIP conversion functions
* @{
*
* These functions can be used for converting between different data
* formats used by uIP.
*/
/*将"addr0,addr1,addr2和addr3"四个字节构造成一个IP地址addr
* Construct an IP address from four bytes.
*
* This function constructs an IP address of the type that uIP handles
* internally from four bytes. The function is handy for specifying IP
* addresses to use with e.g. the uip_connect() function.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
struct uipConnectType *c;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 192,168,1,2);
c = uip_connect(&ipaddr, HTONS(80));
\endcode
*
* \param addr A pointer to a uip_ipaddr_t variable that will be
* filled in with the IP address.
*
* \param addr0 The first octet of the IP address.
* \param addr1 The second octet of the IP address.
* \param addr2 The third octet of the IP address.
* \param addr3 The forth octet of the IP address.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr(addr, addr0,addr1,addr2,addr3) do { \
((u16_t *)(addr))[0] = HTONS(((addr0) << 8) | (addr1)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[1] = HTONS(((addr2) << 8) | (addr3)); \
} while(0)
/**
* Construct an IPv6 address from eight 16-bit words.
*
* This function constructs an IPv6 address.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ip6addr(addr, addr0,addr1,addr2,addr3,addr4,addr5,addr6,addr7) do { \
((u16_t *)(addr))[0] = HTONS((addr0)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[1] = HTONS((addr1)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[2] = HTONS((addr2)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[3] = HTONS((addr3)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[4] = HTONS((addr4)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[5] = HTONS((addr5)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[6] = HTONS((addr6)); \
((u16_t *)(addr))[7] = HTONS((addr7)); \
} while(0)
/**
* Copy an IP address to another IP address.
*
* Copies an IP address from one place to another.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr1, ipaddr2;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr1, 192,16,1,2);
uip_ipaddr_copy(&ipaddr2, &ipaddr1);
\endcode
*
* \param dest The destination for the copy.
* \param src The source from where to copy.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
#define uip_ipaddr_copy(dest, src) do { \
((u16_t *)dest)[0] = ((u16_t *)src)[0]; \
((u16_t *)dest)[1] = ((u16_t *)src)[1]; \
} while(0)
#else /* !UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
#define uip_ipaddr_copy(dest, src) memcpy(dest, src, sizeof(uip_ip6addr_t))
#endif /* !UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/**
* Compare two IP addresses
*
* Compares two IP addresses.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr1, ipaddr2;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr1, 192,16,1,2);
if(uip_ipaddr_cmp(&ipaddr2, &ipaddr1)) {
printf("They are the same");
}
\endcode
*
* \param addr1 The first IP address.
* \param addr2 The second IP address.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6 //IPV4
#define uip_ipaddr_cmp(addr1, addr2) ( ((u16_t *)addr1)[0] == ((u16_t *)addr2)[0] && ((u16_t *)addr1)[1] == ((u16_t *)addr2)[1] )
//如果addr1[]和addr2[]相同,则返回1
#else //IPV6
#define uip_ipaddr_cmp(addr1, addr2) (memcmp(addr1, addr2, sizeof(uip_ip6addr_t)) == 0)
#endif
/**
* Compare two IP addresses with netmasks
*
* Compares two IP addresses with netmasks. The masks are used to mask
* out the bits that are to be compared.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr1, ipaddr2, mask;
uip_ipaddr(&mask, 255,255,255,0);
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr1, 192,16,1,2);
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr2, 192,16,1,3);
if(uip_ipaddr_maskcmp(&ipaddr1, &ipaddr2, &mask)) {
printf("They are the same");
}
\endcode
*
* \param addr1 The first IP address.
* \param addr2 The second IP address.
* \param mask The netmask.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr_maskcmp(addr1, addr2, mask) \
( ( ( ((u16_t *)addr1)[0] & ((u16_t *)mask)[0] ) == (((u16_t *)addr2)[0] & ((u16_t *)mask)[0]) ) && \
( (((u16_t *)addr1)[1] & ((u16_t *)mask)[1]) == (((u16_t *)addr2)[1] & ((u16_t *)mask)[1]) ) )
//如果"IP地址addr1和IP地址addr2相同"则返回1
/**
* Mask out the network part of an IP address.
*
* Masks out the network part of an IP address, given the address and
* the netmask.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr1, ipaddr2, netmask;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr1, 192,16,1,2);
uip_ipaddr(&netmask, 255,255,255,0);
uip_ipaddr_mask(&ipaddr2, &ipaddr1, &netmask);
\endcode
*
* In the example above, the variable "ipaddr2" will contain the IP
* address 192.168.1.0.
*
* \param dest Where the result is to be placed.
* \param src The IP address.
* \param mask The netmask.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr_mask(dest, src, mask) do { \
((u16_t *)dest)[0] = ((u16_t *)src)[0] & ((u16_t *)mask)[0]; \
((u16_t *)dest)[1] = ((u16_t *)src)[1] & ((u16_t *)mask)[1]; \
} while(0)
/**
* Pick the first octet of an IP address.
*
* Picks out the first octet of an IP address.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
u8_t octet;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 1,2,3,4);
octet = uip_ipaddr1(&ipaddr);
\endcode
*
* In the example above, the variable "octet" will contain the value 1.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr1(addr) (htons(((u16_t *)(addr))[0]) >> 8)
/**
* Pick the second octet of an IP address.
*
* Picks out the second octet of an IP address.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
u8_t octet;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 1,2,3,4);
octet = uip_ipaddr2(&ipaddr);
\endcode
*
* In the example above, the variable "octet" will contain the value 2.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr2(addr) (htons(((u16_t *)(addr))[0]) & 0xff)
/**
* Pick the third octet of an IP address.
*
* Picks out the third octet of an IP address.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
u8_t octet;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 1,2,3,4);
octet = uip_ipaddr3(&ipaddr);
\endcode
*
* In the example above, the variable "octet" will contain the value 3.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr3(addr) (htons(((u16_t *)(addr))[1]) >> 8)
/**
* Pick the fourth octet of an IP address.
*
* Picks out the fourth octet of an IP address.
*
* Example:
\code
uip_ipaddr_t ipaddr;
u8_t octet;
uip_ipaddr(&ipaddr, 1,2,3,4);
octet = uip_ipaddr4(&ipaddr);
\endcode
*
* In the example above, the variable "octet" will contain the value 4.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define uip_ipaddr4(addr) (htons(((u16_t *)(addr))[1]) & 0xff)
/**
* Convert 16-bit quantity from host byte order to network byte order.
*
* This macro is primarily used for converting constants from host
* byte order to network byte order. For converting variables to
* network byte order, use the htons() function instead.
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#ifndef HTONS
//在"uip-conf.h"定义过UIP_CONF_BYTE_ORDER=UIP_LITTLE_ENDIAN=3412
//在"uipopt.h"定义UIP_BIG_ENDIAN=1234
#if UIP_BYTE_ORDER == UIP_BIG_ENDIAN
#define HTONS(n) (n)
#else /* UIP_BYTE_ORDER == UIP_BIG_ENDIAN */
#define HTONS(n) (u16_t)((((u16_t) (n)) << 8) | (((u16_t) (n)) >> 8))
//小端存储方式将val的高8位值和低8位值交换
#endif /* UIP_BYTE_ORDER == UIP_BIG_ENDIAN */
#else
#error "HTONS already defined!"
#endif /* HTONS */
/**
* Convert 16-bit quantity from host byte order to network byte order.
*
* This function is primarily used for converting variables from host
* byte order to network byte order. For converting constants to
* network byte order, use the HTONS() macro instead.
*/
#ifndef htons
u16_t htons(u16_t val);
#endif /* htons */
#ifndef ntohs
#define ntohs htons
#endif
/** @} */
/**
* Pointer to the application data in the packet buffer.
*
* This pointer points to the application data when the application is
* called. If the application wishes to send data, the application may
* use this space to write the data into before calling uip_send().
*/
extern void *uip_appdata;
#if UIP_URGDATA > 0
/* u8_t *uip_urgdata:
*
* This pointer points to any urgent data that has been received. Only
* present if compiled with support for urgent data (UIP_URGDATA).
*/
extern void *uip_urgdata;
#endif /* UIP_URGDATA > 0 */
/**
* \defgroup uipdrivervars Variables used in uIP device drivers
* @{
*
* uIP has a few global variables that are used in device drivers for
* uIP.
*/
/**
* The length of the packet in the uip_buf buffer.
*
* The global variable uip_len holds the length of the packet in the
* uip_buf buffer.
*
* When the network device driver calls the uIP input function,
* uip_len should be set to the length of the packet in the uip_buf
* buffer.
*
* When sending packets, the device driver should use the contents of
* the uip_len variable to determine the length of the outgoing
* packet.
*
*/
extern u16_t uip_len;
/** @} */
#if UIP_URGDATA > 0
extern u16_t uip_urglen, uip_surglen;
#endif /* UIP_URGDATA > 0 */
struct tcp_demo_appstate
{
u8_t *textptr;//指向"待发送的用户数据的首地址"
int textlen; //"待发送的用户数据的字节总数"
};
typedef struct tcp_demo_appstate uip_tcp_appstate_t;
/**
* Representation of a uIP TCP connection.
*
* The uip_conn structure is used for identifying a connection. All
* but one field in the structure are to be considered read-only by an
* application. The only exception is the appstate field whos purpose
* is to let the application store application-specific state (e.g.,
* file pointers) for the connection. The type of this field is
* configured in the "uipopt.h" header file.
*/
struct uipConnectType {
uip_ipaddr_t ripaddr;//远程IP地址
u16_t lport; //本地TCP端口,采用网络字节顺序(大端存储方式)
u16_t rport; //远程TCP端口,采用网络字节顺序(大端存储方式)
u8_t rcv_nxt[4]; //我们预计接下来将收到的序列号
u8_t snd_nxt[4]; //我们上次发送的序列号
u16_t len; //先前发送的数据的长度
u16_t mss; //连接的当前最大段大小
u16_t initialmss; //连接的初始最大段大小
u8_t sa; //重传超时计算状态变量
u8_t sv; //重传超时计算状态变量
u8_t rto; //重传超时
u8_t tcpstateflags; //TCP状态和标志。TCP state and flags
u8_t timer; //重传计时器。The retransmission timer
u8_t nrtx; //上次发送的段的重传次数
uip_tcp_appstate_t appstate;//工作在TCP模式时使用
// struct httpd_state appstate; //工作在HTTP服务器时使用
};
/**
* Pointer to the current TCP connection.
*
* The uipConnectPointer pointer can be used to access the current TCP
* connection.
*/
extern struct uipConnectType *uipConnectPointer;
/* The array containing all uIP connections. */
extern struct uipConnectType uipConnectTable[UIP_CONNS];
/**
* \addtogroup uiparch
* @{
*/
/**
* 4-byte array used for the 32-bit sequence number calculations.
*/
extern u8_t uip_acc32[4];
/** @} */
#if UIP_UDP
/**
* Representation of a uIP UDP connection.
*/
struct uip_udp_conn {
uip_ipaddr_t ripaddr; /**< The IP address of the remote peer. */
u16_t lport; /**< The local port number in network byte order. */
u16_t rport; /**< The remote port number in network byte order. */
u8_t ttl; /**< Default time-to-live. */
/** The application state. */
uip_udp_appstate_t appstate;
};
/**
* The current UDP connection.
*/
extern struct uip_udp_conn *uip_udp_conn;
extern struct uip_udp_conn uip_udp_conns[UIP_UDP_CONNS];
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
/**
* The structure holding the TCP/IP statistics that are gathered if UIP_STATISTICS is set to 1.
*
*/
struct uip_stats_type {
struct {
uip_stats_t drop; /**< IP层上丢弃的数据包数。Number of dropped packets at the IP layer. */
uip_stats_t recv; /**< IP层上接收的数据包数。Number of received packets at the IP layer. */
uip_stats_t sent; /**< IP层发送的数据包数。Number of sent packets at the IP layer. */
uip_stats_t vhlerr; /**< 由于错误的IP版本或报头长度而丢弃的数据包数。Number of packets dropped due to wrong IP version or header length. */
uip_stats_t hblenerr; /**< 由于IP长度错误、字节过高而丢弃的数据包数。Number of packets dropped due to wrong IP length, high byte. */
uip_stats_t lblenerr; /**< 由于IP长度错误、字节过低而丢弃的数据包数。Number of packets dropped due to wrong IP length, low byte. */
uip_stats_t fragerr; /**< 自这些数据包成为IP片段以来被丢弃的次数。Number of packets dropped since they were IP fragments. */
uip_stats_t chkerr; /**< 由于IP校验和错误而丢弃的数据包数。Number of packets dropped due to IP checksum errors. */
uip_stats_t protoerr; /**< 自这些数据包既不是ICMP、UDP也不是TCP数据包以来被丢弃的数据包数。Number of packets dropped since they were neither ICMP, UDP nor TCP. */
} ip; /**< IP statistics. */
struct {
uip_stats_t drop; /**< 丢弃的ICMP数据包数。Number of dropped ICMP packets. */
uip_stats_t recv; /**< 收到的ICMP数据包数。Number of received ICMP packets. */
uip_stats_t sent; /**< 发送的ICMP数据包数。Number of sent ICMP packets. */
uip_stats_t typeerr; /**< 具有错误类型的ICMP数据包数。Number of ICMP packets with a wrong type. */
} icmp; /**< ICMP statistics. */
struct {
uip_stats_t drop; /**< 已丢弃的TCP段数。Number of dropped TCP segments. */
uip_stats_t recv; /**< 接收的TCP段数。Number of recived TCP segments. */
uip_stats_t sent; /**< 发送的TCP段数。Number of sent TCP segments. */
uip_stats_t chkerr; /**< 具有错误校验和的TCP段数。Number of TCP segments with a bad checksum. */
uip_stats_t ackerr; /**< 具有错误ACK编号的TCP段数。Number of TCP segments with a bad ACK number. */
uip_stats_t rst; /**< 接收的TCP RST(重置)段数。Number of recevied TCP RST (reset) segments. */
uip_stats_t rexmit; /**< 重传的TCP段数。Number of retransmitted TCP segments. */
uip_stats_t syndrop; /**< 由于连接数太少,导致SYN被删除的数量是可用的。Number of dropped SYNs due to too few connections was avaliable. */
uip_stats_t synrst; /**< 关闭端口的SYN数量,触发RST。Number of SYNs for closed ports,triggering a RST. */
} tcp; /**< TCP statistics. */
#if UIP_UDP
struct {
uip_stats_t drop; /**< Number of dropped UDP segments. */
uip_stats_t recv; /**< Number of recived UDP segments. */
uip_stats_t sent; /**< Number of sent UDP segments. */
uip_stats_t chkerr; /**< Number of UDP segments with a bad
checksum. */
} udp; /**< UDP statistics. */
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
};
/**
* The uIP TCP/IP statistics.
*
* This is the variable in which the uIP TCP/IP statistics are gathered.
*/
extern struct uip_stats_type uip_stats;
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* All the stuff below this point is internal to uIP and should not be
* used directly by an application or by a device driver.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* u8_t uip_flags:
*
* When the application is called, uip_flags will contain the flags
* that are defined in this file. Please read below for more
* infomation.
*/
extern u8_t uip_flags;
/* The following flags may be set in the global variable uip_flags
before calling the application callback. The UIP_ACKDATA,
UIP_NEWDATA, and UIP_CLOSE flags may both be set at the same time,
whereas the others are mutualy exclusive. Note that these flags
should *NOT* be accessed directly, but only through the uIP
functions/macros. */
#define UIP_ACKDATA 1
/*接收到应答标志
Signifies that the outstanding data was acked and the application should send out new data instead of retransmitting the last data. */
#define UIP_NEWDATA 2
/*表示已经向我们发送了新数据
Flags the fact that the peer has sent us new data. */
#define UIP_REXMIT 4
/* 告诉应用程序重新传输上次发送的数据。
Tells the application to retransmit the data that was last sent. */
#define UIP_POLL 8
/*用于轮询应用程序,以检查应用程序是否有要发送的数据。
Used for polling the application, to check if the application has data that it wants to send. */
#define UIP_CLOSE 16 /* The remote host has closed the
connection, thus the connection has
gone away. Or the application signals
that it wants to close the
connection. */
#define UIP_ABORT 32
/*远程主机已中止该连接,因此该连接已消失。或者应用程序表示它想要中止连接。
The remote host has aborted the connection, thus the connection has gone away.
Or the application signals that it wants to abort the connection. */
#define UIP_CONNECTED 64 /* We have got a connection from a remote
host and have set up a new connection
for it, or an active connection has
been successfully established. */
#define UIP_TIMEDOUT 128 /* The connection has been aborted due to
too many retransmissions. */
/* uip_process(flag):
*
* The actual uIP function which does all the work.
*/
void uip_process(u8_t flag);
/* The following flags are passed as an argument to the uip_process()
function. They are used to distinguish between the two cases where
uip_process() is called. It can be called either because we have
incoming data that should be processed, or because the periodic
timer has fired. These values are never used directly, but only in
the macrose defined in this file. */
#define UIP_DATA 1 /* Tells uIP that there is incoming
data in the uip_buf buffer. The
length of the data is stored in the
global variable uip_len. */
#define UIP_TIMER 2 /* Tells uIP that the periodic timer
has fired. */
#define UIP_POLL_REQUEST 3 /* Tells uIP that a connection should
be polled. */
#define UIP_UDP_SEND_CONN 4 /* Tells uIP that a UDP datagram
should be constructed in the
uip_buf buffer. */
#if UIP_UDP
#define UIP_UDP_TIMER 5
#endif /* UIP_UDP */
/*TCP状态是uipConnectTable[c].tcpstateflags的值
The TCP states used in the uipConnectPointer->tcpstateflags. */
#define UIP_CLOSED 0
#define UIP_SYN_RCVD 1
#define UIP_SYN_SENT 2
#define UIP_ESTABLISHED 3
#define UIP_FIN_WAIT_1 4
#define UIP_FIN_WAIT_2 5
#define UIP_CLOSING 6
#define UIP_TIME_WAIT 7
#define UIP_LAST_ACK 8
#define UIP_TS_MASK 15
#define UIP_STOPPED 16
//协议:
#define UIP_PROTO_ICMP 1 //ICMP协议编号定义为1
#define UIP_PROTO_TCP 6 //TCP协议编号定义为6
#define UIP_PROTO_UDP 17 //TCP协议编号定义为17
#define UIP_PROTO_ICMP6 58 //ICMP6协议编号定义为58
/* The TCP and IP headers. */
struct uip_tcpip_hdr {
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* IPv6 header. */
u8_t vtc,
tcflow;
u16_t flow;
u8_t len[2];
u8_t proto, ttl;
uip_ip6addr_t srcipaddr, destipaddr;
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节*/
u8_t vhl;
//IP版本和IP头部长度:
//版本(Version):0x45 的高4位为0x04表示IPv4版本
//头部长度(Header Length):低4位为0x05,表示IPv4头部长度,单位为32位字
//即IP头部/IPV4头部为:5 * 4 = 20 字节。
u8_t tos; //服务类型
u8_t len[2]; //IP报文总长度2个字节,它是"IP头,TCP头部和TCP数据的长度"
u8_t ipid[2];
//标识,2字节,表示数据包唯一ID,分片时,所有分片段使用相同ID,表示属于同一包数据。
//是"发送方"采用"ID计数器"得到的数值
u8_t ipoffset[2]; //标志字段和片偏移字段
//标志字段第1位(保留位,bit15)始终为0;
//标志字段第2位(DF位,bit14),DF=1禁止对该数据包分片;DF=0允许分片;
//标志字段第3位(MF位,bit13),MF=1表示后续还有分片;MF=0表示当前是最后一个分片;
//片偏移字段占13位,bit12:0,表示"当前分片"在原始数据包中的起始位置。
//计算方式:偏移值 = 起始字节数 / 8。如果偏移值为5,则表示分片在原始数据包中,是从第5*8=40字节开始。
//0x40 0x00, 禁止对该数据包分片。
//DF=0允许分片,但MF=0表示当前是最后一个分片,也就是没有分片。
u8_t ttl; //生存时间
u8_t proto; //协议:1字节,如6表示TCP,17表示UDP
u16_t ipchksum; //检验和
u16_t srcipaddr[2];//发送方IP地址,4字节
u16_t destipaddr[2];//接收方IP地址,4字节
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
//TCP头部(TCP header)总共为20字节。
//但是,在某些场合,特别是在处理选项(Options)时,TCP头部的长度为24字节。
u16_t srcport; //发送方端口,0x0A 0x1F,表示发送方端口为2591
u16_t destport; //接收方端口,0x00 0x50,表示接收方端口为80
u8_t seqno[4]; //序列号,比如:0x4B 0xF8 0x27 0x37
u8_t ackno[4]; //确认号,比如:0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
u8_t tcpoffset;//表示TCP头部的长度,即(0x70>>4)*4=28;
u8_t flags;
//标志位
//URG:bit5紧急指针有效,表示数据需立即处理 。
//ACK:bit4确认应答,用于确认数据已接收 。
//PSH:bit3推送数据,要求接收方立即传递给应用层 。
//RST:bit2重置连接,强制断开异常连接 。
//SYN:bit1同步标志,用于建立连接并设置初始序列号
//FIN:bit0结束标志,表示发送方完成数据传输
u8_t wnd[2]; //窗口大小, 告诉接收方,当前"发送方接收的缓冲区"的大小
u16_t tcpchksum; //校验和
u8_t urgp[2]; //紧急指针
u8_t optdata[4];
//最大段字节数1个字节,MSS选项的长度占1个字节,最大段高8数值,最大段低8数值
};
/*
下面是ENC28J60发送给计算机的TCP数据
0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E 0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02 0x08 0x00 0x45
0x00 0x00 0x49 0x00 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x40 0x06 0xF6 0x66 0xC0 0xA8 0x01
0x11 0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE 0x00 0x50 0x15 0xE1 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x77 0x4C
0xFC 0x96 0x03 0x50 0x18 0x05 0xA6 0xBB 0x3D 0x00 0x00
<html><body><div 0x20 align=center><br><h2>Hello</h2></div></body></html>
以太网首部的接收方MAC地址:0xB4 0x2E 0x99 0x59 0xEC 0x1E
以太网首部的发送方MAC地址:0x00 0x08 0xDC 0x11 0x11 0x02
以太网首部的IPV4数据包类型:0x08 0x00
IPV4头部的IP版本和头部长度vhl:0x45
IPV4头部的服务类型tos:0x00
IPV4头部的IP报文总长度len[2]:0x00 0x49
IPV4头部的标识ipid[2]:0x00 0x06
IPV4头部的标志与片偏移ipoffset[2]:0x00 0x00
IPV4头部的生存时间ttl:0x40
IPV4头部的TCP协议:0x06
IPV4头部的检验和ipchksum:0xF6 0x66
IPV4头部的发送方IP地址:0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0x11
IPV4头部的接收方IP地址:0xC0 0xA8 0x01 0xBE
TCP头部的源端口:0x00 0x50
TCP头部的目的端口:0x15 0xE1
TCP头部的序列号:0x00 0x00 0x00 0x77
TCP头部的确认号:0x4C 0xFC 0x96 0x03
TCP头部的数据偏移:0x50
TCP头部的标志位:0x18
TCP头部的窗口大小:0x05 0xA6
TCP头部的校验和tcpchksum:0xBB 0x3D
TCP头部的紧急指针:0x00 0x00
用户数据:<html><body><div 0x20 align=center><br><h2>Hello</h2></div></body></html>
*/
/* The ICMP and IP headers. */
struct uip_icmpip_hdr {
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* IPv6 header. */
u8_t vtc,
tcf;
u16_t flow;
u8_t len[2];
u8_t proto, ttl;
uip_ip6addr_t srcipaddr, destipaddr;
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节*/
u8_t vhl;//IP版本和头部长度
u8_t tos;//服务类型
u8_t len[2];//IP报文总长度2个字节
u8_t ipid[2];//标识,2字节,用于分片重组
u8_t ipoffset[2];//片偏移,2字节,包含DF/MF标志和偏移量
u8_t ttl;//生存时间
u8_t proto;//协议:1字节,如6表示TCP,17表示UDP
u16_t ipchksum;//检验和
u16_t srcipaddr[2];//发送方IP地址,4字节
u16_t destipaddr[2];//接收方IP地址,4字节
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/* ICMP (echo) header. */
u8_t type; //ICMP报文类型,请求类型填ICMP_ECHO=8,应答类型填ICMP_ECHO_REPLY=0;
u8_t icode; //这里填0即可
u16_t icmpchksum; //包括数据在内的整个ICMP数据包的校验和
#if !UIP_CONF_IPV6
u16_t id;
u16_t seqno;
#else /* !UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
u8_t flags;
u8_t reserved1;
u8_t reserved2;
u8_t reserved3;
u8_t icmp6data[16];
u8_t options[1];
#endif /* !UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
};
/* The UDP and IP headers. */
struct uip_udpip_hdr {
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
/* IPv6 header. */
u8_t vtc;
u8_t tcf;
u16_t flow;
u8_t len[2];
u8_t proto, ttl;
uip_ip6addr_t srcipaddr, destipaddr;
#else /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节*/
u8_t vhl; //IP版本和头部长度
u8_t tos; //服务类型
u8_t len[2]; //IP报文总长度2个字节
u8_t ipid[2]; //标识,2字节,用于分片重组
u8_t ipoffset[2]; //片偏移,2字节
u8_t ttl; //生存时间
u8_t proto; //协议:1字节,如6表示TCP,17表示UDP
u16_t ipchksum; //检验和
u16_t srcipaddr[2]; //发送方IP地址,4字节
u16_t destipaddr[2]; //接收方IP地址,4字节
#endif /* UIP_CONF_IPV6 */
/*UDP头部(UDP header)长度的字节数是8*/
u16_t srcport; //发送方端口,2字节
u16_t destport; //接收方端口,2字节
u16_t udplen; //UDP数据报总长度
u16_t udpchksum; //UDP校验和
};
/**
* The buffer size available for user data in the \ref uip_buf buffer.
*
* This macro holds the available size for user data in the \ref
* uip_buf buffer. The macro is intended to be used for checking
* bounds of available user data.
*
* Example:
\code
snprintf(uip_appdata, UIP_APPDATA_SIZE, "%u\n", i);
\endcode
*
* \hideinitializer
*/
#define UIP_APPDATA_SIZE (UIP_BUFSIZE - UIP_LLH_LEN - UIP_TCPIP_HLEN)
//APP数据长度: UIP_APPDATA_SIZE=1500-14-40=1456
/* Header sizes. */
#if UIP_CONF_IPV6
#define UIP_IPH_LEN 40
#else //IPV4的IP头的大小
#define UIP_IPH_LEN 20
/* IP头的大小。Size of IP header
IP头部/IPV4头部(IPv4 header),占20个字节
*/
#endif
#define UIP_UDPH_LEN 8 /*UDP头部(UDP header)长度的字节数是8,Size of UDP header */
#define UIP_TCPH_LEN 20
/* TCP头的大小。Size of TCP header
TCP头部(TCP header)总共为20字节。
但是,在某些场合,特别是在处理选项(Options)时,TCP头部的长度为24字节。 */
#define UIP_IPUDPH_LEN (UIP_UDPH_LEN + UIP_IPH_LEN)
/*UIP_IPUDPH_LEN=28 Size of IP + UDP header */
#define UIP_IPTCPH_LEN (UIP_TCPH_LEN + UIP_IPH_LEN)
/*UIP_IPTCPH_LEN=40 "IP头的大小" + "TCP头的大小", Size of IP + TCP header */
#define UIP_TCPIP_HLEN UIP_IPTCPH_LEN //UIP_TCPIP_HLEN=40
#if UIP_FIXEDADDR
extern const uip_ipaddr_t uip_hostaddr, uip_netmask, uip_draddr;
#else /* UIP_FIXEDADDR */
extern uip_ipaddr_t uip_hostaddr, uip_netmask, uip_draddr;
extern struct uip_eth_addr uip_ethaddr;//记录ENC28J60的MAC地址
#endif /* UIP_FIXEDADDR */
/* addr[6]表示6个字节的以太网地址。Representation of a 48-bit Ethernet address. */
struct uip_eth_addr {
u8_t addr[6];
};
/**
* Calculate the Internet checksum over a buffer.
*
* The Internet checksum is the one's complement of the one's
* complement sum of all 16-bit words in the buffer.
*
* See RFC1071.
*
* \param buf A pointer to the buffer over which the checksum is to be
* computed.
*
* \param len The length of the buffer over which the checksum is to
* be computed.
*
* \return The Internet checksum of the buffer.
*/
u16_t uip_chksum(u16_t *buf, u16_t len);
/**
* Calculate the IP header checksum of the packet header in uip_buf.
*
* The IP header checksum is the Internet checksum of the 20 bytes of
* the IP header.
*
* \return The IP header checksum of the IP header in the uip_buf
* buffer.
*/
u16_t uip_ipchksum(u16_t x);
/**
* Calculate the TCP checksum of the packet in uip_buf and uip_appdata.
*
* The TCP checksum is the Internet checksum of data contents of the
* TCP segment, and a pseudo-header as defined in RFC793.
*
* \return The TCP checksum of the TCP segment in uip_buf and pointed
* to by uip_appdata.
*/
u16_t uip_tcpchksum(void);
/**
* Calculate the UDP checksum of the packet in uip_buf and uip_appdata.
*
* The UDP checksum is the Internet checksum of data contents of the
* UDP segment, and a pseudo-header as defined in RFC768.
*
* \return The UDP checksum of the UDP segment in uip_buf and pointed
* to by uip_appdata.
*/
u16_t uip_udpchksum(void);
#endif /* __UIP_H__ */
/** @} */11、Timer4.c
这是我增加的时间计数器文件,因为uip的time实在太啰嗦了。
#include "Timer4.h"
u32 My_uipTimer=0;//uip计时器,每10ms增加1.
void TIM4_Interrupt_Initializtion(u16 arr,u16 psc);//函数声明
//My_uipTimer每10ms增加1
clock_time_t clock_time(void)
{
return My_uipTimer; /* 10ms 单位 */
}
//令t->interval=interval,令t->start=My_uipTimer,My_uipTimer每10ms增加1
void timer_set(struct strTimer *t, clock_time_t interval)
{
t->interval = interval;
t->start = clock_time();
//令t->start=My_uipTimer
//My_uipTimer每10ms增加1
}
void timer_reset(struct strTimer *t)
{
t->start += t->interval;
}
void timer_restart(struct strTimer *t)
{
t->start = clock_time();
}
int timer_expired(struct strTimer *t)
{
return (clock_time_t)(clock_time() - t->start) >= (clock_time_t)t->interval;
}
//通用定时器2中断初始化
//APB1时钟为72MHz
//arr:自动重装值。
//psc:时钟预分频数
//TIM_CKD_DIV1:定时器时钟 = 输入频率
//TIM_CKD_DIV2:定时器时钟 = 输入频率/2
//TIM_CKD_DIV4:定时器时钟 = 输入频率/4
//TIM4_Interrupt_Initializtion(1000,72);//当arr=1000,psc=72时,则为1ms,误差为1us;
void TIM4_Interrupt_Initializtion(u16 arr,u16 psc)
{
TIM_TimeBaseInitTypeDef TIM_TimeBaseStructure;
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
// u8 ch;
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_TIM4, ENABLE); //使能定时器TIM4的APB1外设时钟
//定时器TIM4初始化
TIM_TimeBaseStructure.TIM_Period = arr-1; //设置在下一个更新事件装入活动的自动重装载寄存器周期的值
TIM_TimeBaseStructure.TIM_Prescaler =psc-1; //设置用来作为TIMx时钟频率除数的预分频值
TIM_TimeBaseStructure.TIM_ClockDivision = TIM_CKD_DIV1; //设置时钟分割:TDTS = Tck_tim
//计算公式:arr*psc/72000000/1,当arr=1000,psc=72时,则为1ms,误差为1us;
TIM_TimeBaseStructure.TIM_CounterMode = TIM_CounterMode_Up; //TIM向上计数模式
TIM_TimeBaseStructure.TIM_RepetitionCounter=0;//TIM4~TIM7不用设置也可以
TIM_TimeBaseInit(TIM4, &TIM_TimeBaseStructure); //根据指定的参数初始化TIMx的时间基数单位
TIM_SetCounter(TIM4,0); //设置TIM4的计数器值为0;
TIM_ClearFlag(TIM4, TIM_FLAG_Update); //清除TIM4溢出的待处理标志位
TIM_ClearITPendingBit(TIM4, TIM_IT_Update ); //清除TIM4中断的待处理位
TIM_ITConfig(TIM4,TIM_IT_Update,ENABLE ); //允许TIM4溢出产生中断
//中断优先级NVIC设置
//NVIC_PriorityGroup_4设置NVIC中断分组4:表示抢占优先级为4位,取值为0~15,没有响应优先级,取值为0
//NVIC_PriorityGroup_3设置NVIC中断分组3:表示抢占优先级为3位,取值为0~7,响应优先级只有1位,取值为0~1
//NVIC_PriorityGroup_2设置NVIC中断分组3:表示抢占优先级为2位,取值为0~3,响应优先级只有2位,取值为0~3
//NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_4);//设置系统中断优先级分组4
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = TIM4_IRQn; //TIM4中断
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 11; //设置抢占优先级为11
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 0; //设置响应优先级为0
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE; //IRQ通道被使能
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure); //根据NVIC_InitStruct中指定的参数初始化NVIC嵌套向量中断控制寄存器
TIM_Cmd(TIM4, ENABLE);//使能TIM4外设
}
//函数功能:TIM4每10ms中断一次
void TIM4_IRQHandler()
{
if (TIM_GetITStatus(TIM4,TIM_IT_Update) != RESET) //TIM4计数器溢出产生中断
{
My_uipTimer++;//uip计时器增加1
TIM_ClearITPendingBit(TIM4,TIM_IT_Update); //清除TIM4计数器的溢出中断标志;
}
}12、Timer4.h
#ifndef __Timer4_H
#define __Timer4_H
#include "stm32f10x.h" //使能uint8_t,uint16_t,uint32_t,uint64_t,int8_t,int16_t,int32_t,int64_t
typedef int clock_time_t;
struct strTimer
{
clock_time_t start; //start为int型
clock_time_t interval; //interval为int型
};
clock_time_t clock_time(void);
extern u32 My_uipTimer;//uip 计时器,每10ms增加1.
void timer_set(struct strTimer *t, clock_time_t interval);
void timer_reset(struct strTimer *t);
void timer_restart(struct strTimer *t);
int timer_expired(struct strTimer *t);
extern void TIM4_Interrupt_Initializtion(u16 arr,u16 psc);
#endif13、enc28j60.c
这个在网上较多,函数名基本都一样。
#include "enc28j60.h"
#include "SPI2.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "Timer4.h"
static u8 ENC28J60BANK;
static u32 NextPacketPtr; //接收缓冲器读指针
//读取ENC28J60寄存器(带操作码)
//op:操作码
//addr:寄存器地址/参数
//返回值:读到的数据
u8 ENC28J60_Read_Op(u8 op,u8 addr)
{
u8 dat=0;
ENC28J60_CS=0;
dat=op|(addr&ADDR_MASK);
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(dat);
dat=SPI2_ReadWriteByte(0xFF);
//如果是读取MAC/MII寄存器,则第二次读到的数据才是正确的,见手册29页
if(addr&0x80)dat=SPI2_ReadWriteByte(0xFF);
ENC28J60_CS=1;
return dat;
}
//读取ENC28J60寄存器(带操作码)
//op:操作码
//addr:寄存器地址
//data:参数
void ENC28J60_Write_Op(u8 op,u8 addr,u8 data)
{
u8 dat = 0;
ENC28J60_CS=0;
dat=op|(addr&ADDR_MASK);
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(dat);
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(data);
ENC28J60_CS=1;
}
//读取ENC28J60接收缓存数据
//len:要读取的数据长度
//data:输出数据缓存区(末尾自动添加结束符)
void ENC28J60_Read_Buf(u32 len,u8* data)
{
ENC28J60_CS=0;
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM);
while(len)
{
len--;
*data=(u8)SPI2_ReadWriteByte(0);
data++;
}
*data='\0';
ENC28J60_CS=1;
}
//向ENC28J60写发送缓存数据
//len:要写入的数据长度
//data:数据缓存区
void ENC28J60_Write_Buf(u32 len,u8* data)
{
ENC28J60_CS=0;
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(ENC28J60_WRITE_BUF_MEM);
while(len)
{
len--;
SPI2_ReadWriteByte(*data);
data++;
}
ENC28J60_CS=1;
}
//设置ENC28J60寄存器Bank
//ban:要设置的bank
void ENC28J60_Set_Bank(u8 bank)
{
if((bank&BANK_MASK)!=ENC28J60BANK)//和当前bank不一致的时候,才设置
{
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_CLR,ECON1,(ECON1_BSEL1|ECON1_BSEL0));
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,ECON1,(bank&BANK_MASK)>>5);
ENC28J60BANK=(bank&BANK_MASK);
}
}
//读取ENC28J60指定寄存器
//addr:寄存器地址
//返回值:读到的数据
u8 ENC28J60_Read(u8 addr)
{
ENC28J60_Set_Bank(addr);//设置BANK
return ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_CTRL_REG,addr);
}
//向ENC28J60指定寄存器写数据
//addr:寄存器地址
//data:要写入的数据
void ENC28J60_Write(u8 addr,u8 data)
{
ENC28J60_Set_Bank(addr);
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_WRITE_CTRL_REG,addr,data);
}
//向ENC28J60的PHY寄存器写入数据
//addr:寄存器地址
//data:要写入的数据
void ENC28J60_PHY_Write(u8 addr,u32 data)
{
u16 retry=0;
ENC28J60_Write(MIREGADR,addr); //设置PHY寄存器地址
ENC28J60_Write(MIWRL,data); //写入数据
ENC28J60_Write(MIWRH,data>>8);
while((ENC28J60_Read(MISTAT)&MISTAT_BUSY)&&retry<0XFFF)retry++;//等待写入PHY结束
}
//函数功能:初始化ENC28J60
//macaddr:MAC地址
//返回值:0,初始化成功;
// 1,初始化失败;
u8 ENC28J60_Init(u8* macaddr)
{
u16 retry=0;
ENC28J60_Reset();//初始化SPI2,然后使用RESET引脚复位ENC28J60
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_SOFT_RESET,0,ENC28J60_SOFT_RESET);//软件复位
while(!(ENC28J60_Read(ESTAT)&ESTAT_CLKRDY)&&retry<500)//等待时钟稳定
{
retry++;
delay_ms(1);
};
if(retry>=500)return 1;//ENC28J60初始化失败
TIM4_Interrupt_Initializtion(10000,72);//当arr=10000,psc=72时,则为10ms,误差为1us;
retry=ENC28J60_Get_EREVID();
printf("ENC28J60 ID=0x%02X\r\n",retry);
/*
接收缓冲器由一个硬件管理的循环FIFO缓冲器构成。
将"寄存器对ERXSTH:ERXSTL"和"寄存器对ERXNDH:ERXNDL"作为指针,定义缓冲器的容量和其在存储器中的位置。ERXST和ERXND指向的字节均包含在FIFO缓冲器内。
当从以太网接口接收数据字节时,这些字节被顺序写入接收缓冲器。 但是当写入由ERXND 指向的存储单元后,
硬件会自动将接收的下一字节写入由ERXST指向的存储单元。 因此接收硬件将不会写入FIFO以外的单元。
*/
NextPacketPtr=RXSTART_INIT;//设置"接收缓冲器读指针"为0
ENC28J60_Write(ERXSTL,RXSTART_INIT&0xFF);ENC28J60_Write(ERXSTH,RXSTART_INIT>>8);
//设置"ENC28J60接收缓冲器写指针"起始值
/*
"寄存器对ERXWRPTH:ERXWRPTL"定义硬件向FIFO中的哪个位置写入其接收到的字节。 指针是只读的,
在成功接收到一个数据包后,硬件会自动更新指针。指针可用于判断FIFO 内剩余空间的大小8K-1500。
*/
ENC28J60_Write(ERXRDPTL,RXSTART_INIT&0xFF);ENC28J60_Write(ERXRDPTH,RXSTART_INIT>>8);
//设置"ENC28J60接收缓冲器起始指针"的值
ENC28J60_Write(ERXNDL,RXSTOP_INIT&0xFF);ENC28J60_Write(ERXNDH,RXSTOP_INIT>>8);
//设置"ENC28J60接收缓冲器结束指针"的值
ENC28J60_Write(ETXSTL,TXSTART_INIT&0xFF);ENC28J60_Write(ETXSTH,TXSTART_INIT>>8);
//设置"ENC28J60发送缓冲器起始指针"的值
ENC28J60_Write(ETXNDL,TXSTOP_INIT&0xFF);ENC28J60_Write(ETXNDH,TXSTOP_INIT>>8);
//设置"ENC28J60发送缓冲器结束指针"的值
// do bank 1 stuff,packet filter:
// For broadcast packets we allow only ARP packtets
// All other packets should be unicast only for our mac (MAADR)
//
// The pattern to match on is therefore
// Type ETH.DST
// ARP BROADCAST
// 06 08 -- ff ff ff ff ff ff -> ip checksum for theses bytes=f7f9
// in binary these poitions are:11 0000 0011 1111
// This is hex 303F->EPMM0=0x3f,EPMM1=0x30
//接收过滤器
//UCEN:单播过滤器使能位
//当ANDOR = 1 时:
//1 = 目标地址与本地MAC 地址不匹配的数据包将被丢弃
//0 = 禁止过滤器
//当ANDOR = 0 时:
//1 = 目标地址与本地MAC 地址匹配的数据包会被接受
//0 = 禁止过滤器
//CRCEN:后过滤器CRC 校验使能位
//1 = 所有CRC 无效的数据包都将被丢弃
//0 = 不考虑CRC 是否有效
//PMEN:格式匹配过滤器使能位
//当ANDOR = 1 时:
//1 = 数据包必须符合格式匹配条件,否则将被丢弃
//0 = 禁止过滤器
//当ANDOR = 0 时:
//1 = 符合格式匹配条件的数据包将被接受
//0 = 禁止过滤器
ENC28J60_Write(ERXFCON,ERXFCON_UCEN|ERXFCON_CRCEN|ERXFCON_PMEN);
ENC28J60_Write(EPMM0,0x3f);
ENC28J60_Write(EPMM1,0x30);
ENC28J60_Write(EPMCSL,0xf9);
ENC28J60_Write(EPMCSH,0xf7);
// do bank 2 stuff
// enable MAC receive
//bit 0 MARXEN:MAC 接收使能位
//1 = 允许MAC 接收数据包
//0 = 禁止数据包接收
//bit 3 TXPAUS:暂停控制帧发送使能位
//1 = 允许MAC 发送暂停控制帧(用于全双工模式下的流量控制)
//0 = 禁止暂停帧发送
//bit 2 RXPAUS:暂停控制帧接收使能位
//1 = 当接收到暂停控制帧时,禁止发送(正常操作)
//0 = 忽略接收到的暂停控制帧
ENC28J60_Write(MACON1,MACON1_MARXEN|MACON1_TXPAUS|MACON1_RXPAUS);
// bring MAC out of reset
//将MACON2 中的MARST 位清零,使MAC 退出复位状态。
ENC28J60_Write(MACON2,0x00);
// enable automatic padding to 60bytes and CRC operations
//bit 7-5 PADCFG2:PACDFG0:自动填充和CRC 配置位
//111 = 用0 填充所有短帧至64 字节长,并追加一个有效的CRC
//110 = 不自动填充短帧
//101 = MAC 自动检测具有8100h 类型字段的VLAN 协议帧,并自动填充到64 字节长。如果不
//是VLAN 帧,则填充至60 字节长。填充后还要追加一个有效的CRC
//100 = 不自动填充短帧
//011 = 用0 填充所有短帧至64 字节长,并追加一个有效的CRC
//010 = 不自动填充短帧
//001 = 用0 填充所有短帧至60 字节长,并追加一个有效的CRC
//000 = 不自动填充短帧
//bit 4 TXCRCEN:发送CRC 使能位
//1 = 不管PADCFG如何,MAC都会在发送帧的末尾追加一个有效的CRC。 如果PADCFG规定要
//追加有效的CRC,则必须将TXCRCEN 置1。
//0 = MAC不会追加CRC。 检查最后4 个字节,如果不是有效的CRC 则报告给发送状态向量。
//bit 0 FULDPX:MAC 全双工使能位
//1 = MAC工作在全双工模式下。 PHCON1.PDPXMD 位必须置1。
//0 = MAC工作在半双工模式下。 PHCON1.PDPXMD 位必须清零。
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,MACON3,MACON3_PADCFG0|MACON3_TXCRCEN|MACON3_FRMLNEN|MACON3_FULDPX);
// set inter-frame gap (non-back-to-back)
//配置非背对背包间间隔寄存器的低字节
//MAIPGL。 大多数应用使用12h 编程该寄存器。
//如果使用半双工模式,应编程非背对背包间间隔
//寄存器的高字节MAIPGH。 大多数应用使用0Ch
//编程该寄存器。
ENC28J60_Write(MAIPGL,0x12);
ENC28J60_Write(MAIPGH,0x0C);
// set inter-frame gap (back-to-back)
//配置背对背包间间隔寄存器MABBIPG。当使用
//全双工模式时,大多数应用使用15h 编程该寄存
//器,而使用半双工模式时则使用12h 进行编程。
ENC28J60_Write(MABBIPG,0x15);
// Set the maximum packet size which the controller will accept
// Do not send packets longer than MAX_FRAMELEN:
// 最大帧长度 1500
ENC28J60_Write(MAMXFLL,MAX_FRAMELEN&0xFF);
ENC28J60_Write(MAMXFLH,MAX_FRAMELEN>>8);
// do bank 3 stuff
// write MAC address
// NOTE: MAC address in ENC28J60 is byte-backward
//设置MAC地址
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR5,macaddr[0]);
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR4,macaddr[1]);
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR3,macaddr[2]);
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR2,macaddr[3]);
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR1,macaddr[4]);
ENC28J60_Write(MAADR0,macaddr[5]);
//配置PHY为全双工 LEDB为拉电流
ENC28J60_PHY_Write(PHCON1,PHCON1_PDPXMD);
// no loopback of transmitted frames 禁止环回
//HDLDIS:PHY 半双工环回禁止位
//当PHCON1.PDPXMD = 1 或PHCON1.PLOOPBK = 1 时:
//此位可被忽略。
//当PHCON1.PDPXMD = 0 且PHCON1.PLOOPBK = 0 时:
//1 = 要发送的数据仅通过双绞线接口发出
//0 = 要发送的数据会环回到MAC 并通过双绞线接口发出
ENC28J60_PHY_Write(PHCON2,PHCON2_HDLDIS);
// switch to bank 0
//ECON1 寄存器
//寄存器3-1 所示为ECON1 寄存器,它用于控制
//ENC28J60 的主要功能。 ECON1 中包含接收使能、发
//送请求、DMA 控制和存储区选择位。
ENC28J60_Set_Bank(ECON1);
// enable interrutps
//EIE: 以太网中断允许寄存器
//bit 7 INTIE: 全局INT 中断允许位
//1 = 允许中断事件驱动INT 引脚
//0 = 禁止所有INT 引脚的活动(引脚始终被驱动为高电平)
//bit 6 PKTIE: 接收数据包待处理中断允许位
//1 = 允许接收数据包待处理中断
//0 = 禁止接收数据包待处理中断
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,EIE,EIE_INTIE|EIE_PKTIE);
// enable packet reception
//bit 2 RXEN:接收使能位
//1 = 通过当前过滤器的数据包将被写入接收缓冲器
//0 = 忽略所有接收的数据包
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,ECON1,ECON1_RXEN);
if(ENC28J60_Read(MAADR5)== macaddr[0])return 0;//初始化成功
else return 1;
}
//读取EREVID
u8 ENC28J60_Get_EREVID(void)
{
//在EREVID 内也存储了版本信息。 EREVID 是一个只读控
//制寄存器,包含一个5 位标识符,用来标识器件特定硅片
//的版本号
return ENC28J60_Read(EREVID);
}
//#include "uip.h"
//通过ENC28J60发送数据包到网络
//len:数据包大小
//packet:数据包
void ENC28J60_Packet_Send(u32 len,u8* packet)
{
//设置发送缓冲区地址写指针入口
ENC28J60_Write(EWRPTL,TXSTART_INIT&0xFF);
ENC28J60_Write(EWRPTH,TXSTART_INIT>>8);
//设置TXND指针,以对应给定的数据包大小
ENC28J60_Write(ETXNDL,(TXSTART_INIT+len)&0xFF);
ENC28J60_Write(ETXNDH,(TXSTART_INIT+len)>>8);
//写每包控制字节(0x00表示使用macon3的设置)
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_WRITE_BUF_MEM,0,0x00);
//复制数据包到发送缓冲区
//printf("len:%d\r\n",len); //监视发送数据长度
ENC28J60_Write_Buf(len,packet);
//发送数据到网络
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,ECON1,ECON1_TXRTS);
//复位发送逻辑的问题。参见Rev. B4 Silicon Errata point 12.
if((ENC28J60_Read(EIR)&EIR_TXERIF))ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_CLR,ECON1,ECON1_TXRTS);
}
//函数功能:读"接收缓冲区的接收量大小寄存器",直到ENC28J60接收完成
uint16_t ENC28J60_Read_RX_Length(void)
{
u32 tmpNextPacketPtr; //接收缓冲器读指针
uint16_t val=0,val1=0;
u32 len;
if( ENC28J60_Read(EPKTCNT)==0 )//如果没有收到数据包,则返回0
return 0; //是否收到数据包?
tmpNextPacketPtr=NextPacketPtr;
do
{
ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTL,(tmpNextPacketPtr));ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTH,(tmpNextPacketPtr)>>8);
//设置接收缓冲器读指针
val1=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0);len|=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0)<<8;
//读包的长度
if (val1 != 0)
{
delay_us(1);//延时1us
ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTL,(tmpNextPacketPtr));ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTH,(tmpNextPacketPtr)>>8);
//设置接收缓冲器读指针
val=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0);len|=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0)<<8;
//读包的长度
if(val != val1)
printf("\r\n\r\n\r\nRX_len1=%u RX_len2=%u\r\n",val1,val);
}
}while (val != val1);
//若前后所读"接收缓冲区的接收量大小寄存器"不等,则表示ENC28J60正在接收数据
return val;
}
//函数功能:从网络获取一个数据包内容
//maxlen:数据包最大允许接收长度,读到的最大数据长度为(maxlen-1)
//packet:数据包缓存区
//返回值:收到的数据包长度(字节)
u32 ENC28J60_Packet_Receive(u32 maxlen,u8* packet)
{
u32 rxstat;
u32 len;
if( ENC28J60_Read(EPKTCNT)==0 )//如果没有收到数据包,则返回0
return 0; //是否收到数据包?
ENC28J60_Read_RX_Length();
ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTL,(NextPacketPtr));ENC28J60_Write(ERDPTH,(NextPacketPtr)>>8);
//设置接收缓冲器读指针
NextPacketPtr=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0);NextPacketPtr|=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0)<<8;
//读下一个包的指针
len=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0);len|=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0)<<8;
//读包的长度
len-=4; //去掉CRC计数
rxstat=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0);rxstat|=ENC28J60_Read_Op(ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM,0)<<8;
//读取接收状态
if (len>maxlen-1)len=maxlen-1;//限制接收长度
//检查CRC和符号错误
// ERXFCON.CRCEN为默认设置,一般我们不需要检查.
if((rxstat&0x80)==0)len=0;//无效
else ENC28J60_Read_Buf(len,packet);//从接收缓冲器中复制数据包
ENC28J60_Write(ERXRDPTL,(NextPacketPtr));ENC28J60_Write(ERXRDPTH,(NextPacketPtr)>>8);
//RX读指针移动到下一个接收到的数据包的开始位置,并释放我们刚才读出过的内存
ENC28J60_Write_Op(ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET,ECON2,ECON2_PKTDEC);
//递减数据包计数器标志我们已经得到了这个包
return(len);
}14、enc28j60.h
#include "sys.h"
#define ADDR_MASK 0x1F
#define BANK_MASK 0x60
#define SPRD_MASK 0x80
// All-bank registers
#define EIE 0x1B
#define EIR 0x1C
#define ESTAT 0x1D
#define ECON2 0x1E
#define ECON1 0x1F
// Bank 0 registers
#define ERDPTL (0x00|0x00)
#define ERDPTH (0x01|0x00)
#define EWRPTL (0x02|0x00)
#define EWRPTH (0x03|0x00)
#define ETXSTL (0x04|0x00)
#define ETXSTH (0x05|0x00)
#define ETXNDL (0x06|0x00)
#define ETXNDH (0x07|0x00)
#define ERXSTL (0x08|0x00)
#define ERXSTH (0x09|0x00)
#define ERXNDL (0x0A|0x00)
#define ERXNDH (0x0B|0x00)
//ERXWRPTH:ERXWRPTL 寄存器定义硬件向FIFO 中
//的哪个位置写入其接收到的字节。 指针是只读的,在成
//功接收到一个数据包后,硬件会自动更新指针。 指针可
//用于判断FIFO 内剩余空间的大小。
#define ERXRDPTL (0x0C|0x00)
#define ERXRDPTH (0x0D|0x00)
#define ERXWRPTL (0x0E|0x00)
#define ERXWRPTH (0x0F|0x00)
#define EDMASTL (0x10|0x00)
#define EDMASTH (0x11|0x00)
#define EDMANDL (0x12|0x00)
#define EDMANDH (0x13|0x00)
#define EDMADSTL (0x14|0x00)
#define EDMADSTH (0x15|0x00)
#define EDMACSL (0x16|0x00)
#define EDMACSH (0x17|0x00)
// Bank 1 registers
#define EHT0 (0x00|0x20)
#define EHT1 (0x01|0x20)
#define EHT2 (0x02|0x20)
#define EHT3 (0x03|0x20)
#define EHT4 (0x04|0x20)
#define EHT5 (0x05|0x20)
#define EHT6 (0x06|0x20)
#define EHT7 (0x07|0x20)
#define EPMM0 (0x08|0x20)
#define EPMM1 (0x09|0x20)
#define EPMM2 (0x0A|0x20)
#define EPMM3 (0x0B|0x20)
#define EPMM4 (0x0C|0x20)
#define EPMM5 (0x0D|0x20)
#define EPMM6 (0x0E|0x20)
#define EPMM7 (0x0F|0x20)
#define EPMCSL (0x10|0x20)
#define EPMCSH (0x11|0x20)
#define EPMOL (0x14|0x20)
#define EPMOH (0x15|0x20)
#define EWOLIE (0x16|0x20)
#define EWOLIR (0x17|0x20)
#define ERXFCON (0x18|0x20)
#define EPKTCNT (0x19|0x20)
// Bank 2 registers
#define MACON1 (0x00|0x40|0x80)
#define MACON2 (0x01|0x40|0x80)
#define MACON3 (0x02|0x40|0x80)
#define MACON4 (0x03|0x40|0x80)
#define MABBIPG (0x04|0x40|0x80)
#define MAIPGL (0x06|0x40|0x80)
#define MAIPGH (0x07|0x40|0x80)
#define MACLCON1 (0x08|0x40|0x80)
#define MACLCON2 (0x09|0x40|0x80)
#define MAMXFLL (0x0A|0x40|0x80)
#define MAMXFLH (0x0B|0x40|0x80)
#define MAPHSUP (0x0D|0x40|0x80)
#define MICON (0x11|0x40|0x80)
#define MICMD (0x12|0x40|0x80)
#define MIREGADR (0x14|0x40|0x80)
#define MIWRL (0x16|0x40|0x80)
#define MIWRH (0x17|0x40|0x80)
#define MIRDL (0x18|0x40|0x80)
#define MIRDH (0x19|0x40|0x80)
// Bank 3 registers
#define MAADR1 (0x00|0x60|0x80)
#define MAADR0 (0x01|0x60|0x80)
#define MAADR3 (0x02|0x60|0x80)
#define MAADR2 (0x03|0x60|0x80)
#define MAADR5 (0x04|0x60|0x80)
#define MAADR4 (0x05|0x60|0x80)
#define EBSTSD (0x06|0x60)
#define EBSTCON (0x07|0x60)
#define EBSTCSL (0x08|0x60)
#define EBSTCSH (0x09|0x60)
#define MISTAT (0x0A|0x60|0x80)
#define EREVID (0x12|0x60)
#define ECOCON (0x15|0x60)
#define EFLOCON (0x17|0x60)
#define EPAUSL (0x18|0x60)
#define EPAUSH (0x19|0x60)
// PHY registers
#define PHCON1 0x00
#define PHSTAT1 0x01
#define PHHID1 0x02
#define PHHID2 0x03
#define PHCON2 0x10
#define PHSTAT2 0x11
#define PHIE 0x12
#define PHIR 0x13
#define PHLCON 0x14
// ENC28J60 ERXFCON Register Bit Definitions
#define ERXFCON_UCEN 0x80
#define ERXFCON_ANDOR 0x40
#define ERXFCON_CRCEN 0x20
#define ERXFCON_PMEN 0x10
#define ERXFCON_MPEN 0x08
#define ERXFCON_HTEN 0x04
#define ERXFCON_MCEN 0x02
#define ERXFCON_BCEN 0x01
// ENC28J60 EIE Register Bit Definitions
#define EIE_INTIE 0x80
#define EIE_PKTIE 0x40
#define EIE_DMAIE 0x20
#define EIE_LINKIE 0x10
#define EIE_TXIE 0x08
#define EIE_WOLIE 0x04
#define EIE_TXERIE 0x02
#define EIE_RXERIE 0x01
// ENC28J60 EIR Register Bit Definitions
#define EIR_PKTIF 0x40
#define EIR_DMAIF 0x20
#define EIR_LINKIF 0x10
#define EIR_TXIF 0x08
#define EIR_WOLIF 0x04
#define EIR_TXERIF 0x02
#define EIR_RXERIF 0x01
// ENC28J60 ESTAT Register Bit Definitions
#define ESTAT_INT 0x80
#define ESTAT_LATECOL 0x10
#define ESTAT_RXBUSY 0x04
#define ESTAT_TXABRT 0x02
#define ESTAT_CLKRDY 0x01
// ENC28J60 ECON2 Register Bit Definitions
#define ECON2_AUTOINC 0x80
#define ECON2_PKTDEC 0x40
#define ECON2_PWRSV 0x20
#define ECON2_VRPS 0x08
// ENC28J60 ECON1 Register Bit Definitions
#define ECON1_TXRST 0x80
#define ECON1_RXRST 0x40
#define ECON1_DMAST 0x20
#define ECON1_CSUMEN 0x10
#define ECON1_TXRTS 0x08
#define ECON1_RXEN 0x04
#define ECON1_BSEL1 0x02
#define ECON1_BSEL0 0x01
// ENC28J60 MACON1 Register Bit Definitions
#define MACON1_LOOPBK 0x10
#define MACON1_TXPAUS 0x08
#define MACON1_RXPAUS 0x04
#define MACON1_PASSALL 0x02
#define MACON1_MARXEN 0x01
// ENC28J60 MACON2 Register Bit Definitions
#define MACON2_MARST 0x80
#define MACON2_RNDRST 0x40
#define MACON2_MARXRST 0x08
#define MACON2_RFUNRST 0x04
#define MACON2_MATXRST 0x02
#define MACON2_TFUNRST 0x01
// ENC28J60 MACON3 Register Bit Definitions
#define MACON3_PADCFG2 0x80
#define MACON3_PADCFG1 0x40
#define MACON3_PADCFG0 0x20
#define MACON3_TXCRCEN 0x10
#define MACON3_PHDRLEN 0x08
#define MACON3_HFRMLEN 0x04
#define MACON3_FRMLNEN 0x02
#define MACON3_FULDPX 0x01
// ENC28J60 MICMD Register Bit Definitions
#define MICMD_MIISCAN 0x02
#define MICMD_MIIRD 0x01
// ENC28J60 MISTAT Register Bit Definitions
#define MISTAT_NVALID 0x04
#define MISTAT_SCAN 0x02
#define MISTAT_BUSY 0x01
// ENC28J60 PHY PHCON1 Register Bit Definitions
#define PHCON1_PRST 0x8000
#define PHCON1_PLOOPBK 0x4000
#define PHCON1_PPWRSV 0x0800
#define PHCON1_PDPXMD 0x0100
// ENC28J60 PHY PHSTAT1 Register Bit Definitions
#define PHSTAT1_PFDPX 0x1000
#define PHSTAT1_PHDPX 0x0800
#define PHSTAT1_LLSTAT 0x0004
#define PHSTAT1_JBSTAT 0x0002
// ENC28J60 PHY PHCON2 Register Bit Definitions
#define PHCON2_FRCLINK 0x4000
#define PHCON2_TXDIS 0x2000
#define PHCON2_JABBER 0x0400
#define PHCON2_HDLDIS 0x0100
// ENC28J60 Packet Control Byte Bit Definitions
#define PKTCTRL_PHUGEEN 0x08
#define PKTCTRL_PPADEN 0x04
#define PKTCTRL_PCRCEN 0x02
#define PKTCTRL_POVERRIDE 0x01
// SPI operation codes
#define ENC28J60_READ_CTRL_REG 0x00
#define ENC28J60_READ_BUF_MEM 0x3A
#define ENC28J60_WRITE_CTRL_REG 0x40
#define ENC28J60_WRITE_BUF_MEM 0x7A
#define ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_SET 0x80
#define ENC28J60_BIT_FIELD_CLR 0xA0
#define ENC28J60_SOFT_RESET 0xFF
// The RXSTART_INIT should be zero. See Rev. B4 Silicon Errata
// buffer boundaries applied to internal 8K ram
// the entire available packet buffer space is allocated
//
// start with recbuf at 0/
#define RXSTART_INIT 0x0
// receive buffer end
#define RXSTOP_INIT (0x1FFF-1518-1)
// start TX buffer at 0x1FFF-0x0600, pace for one full ethernet frame (0~1518 bytes)
#define TXSTART_INIT (0x1FFF-1518)
// stp TX buffer at end of mem
#define TXSTOP_INIT 0x1FFF
// max frame length which the conroller will accept:
#define MAX_FRAMELEN 1518
// (note: maximum ethernet frame length would be 1518)
//最大以太网帧长度为1518
//////////////////////////////
//SPI1初始化
void ENC28J60_Reset(void);
u8 ENC28J60_Read_Op(u8 op,u8 addr);
void ENC28J60_Write_Op(u8 op,u8 addr,u8 data);
void ENC28J60_Read_Buf(u32 len,u8* data);
void ENC28J60_Write_Buf(u32 len,u8* data);
void ENC28J60_Set_Bank(u8 bank);
u8 ENC28J60_Read(u8 addr);
void ENC28J60_Write(u8 addr,u8 data);
void ENC28J60_PHY_Write(u8 addr,u32 data);
u8 ENC28J60_Init(u8* macaddr);
u8 ENC28J60_Get_EREVID(void);
void ENC28J60_Packet_Send(u32 len,u8* packet);
u32 ENC28J60_Packet_Receive(u32 maxlen,u8* packet); 14、SPI2.c
#include "SPI2.h"
#include "sys.h"
#include "delay.h"
void SPI1_Init(void)
{
SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
/*使能SPI1和GPIOA的时钟*/
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_SPI1|RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
/*SPI1 接口信号配置*/
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_5 | GPIO_Pin_6 | GPIO_Pin_7;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
/*分配给ENC28J60芯片的SPI1_NSS信号配置*/
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_4;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_4); //置高分配给ENC28J60的 SPI1_NSS信号
/* SPI1接口模式参数配置 */
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_2Lines_FullDuplex;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_Low;//时钟极性
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_1Edge;//时钟相位
//CPHA=0,表示第1个边沿:
//对于CPOL=0,空闲时,钟引脚输出低电平,数据采样时刻发生在第1个边沿,就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
//对于CPOL=1,空闲时,钟引脚输出高电平,数据采样时刻发生在第1个边沿,就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
//CPHA=1,表示第2个边沿:
//对于CPOL=0,空闲时,钟引脚输出低电平,数据采样时刻发生在第2个边沿,就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
//对于CPOL=1,空闲时,钟引脚输出高电平,数据采样时刻发生在第2个边沿,就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_8;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CRCPolynomial = 7;
SPI_Init(SPI1, &SPI_InitStructure);
/*使能SPI1接口*/
SPI_Cmd(SPI1, ENABLE);
}
//SPI1读写一字节数据
unsigned char SPI1_ReadWrite(unsigned char writedat)
{
/* Loop while DR register in not emplty */
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1,SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
/* Send byte through the SPI1 peripheral */
SPI_I2S_SendData(SPI1, writedat);
/* Wait to receive a byte */
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET);
/* Return the byte read from the SPI bus */
return SPI_I2S_ReceiveData(SPI1);
}
//函数功能:SPI2接口的IO口配置
static void SPI2_GPIO_Config(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB, ENABLE); //使能GPIOB的外设时钟
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_SPI2, ENABLE); //使能SPI2的外设时钟
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_13; //选择PIN13,是SPI2的SCL
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP; //选择引脚为复用推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz; //设置引脚的最高工作速率为10MHz
//GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed =GPIO_Speed_10MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure); //根据GPIO_InitStructure结构指针所指向的参数配置PB13引脚
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_14; //选择PIN14,是SPI2的MISO
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP; //选择引脚为复用推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz; //设置引脚的最高工作速率为10MHz
//GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed =GPIO_Speed_10MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure); //根据GPIO_InitStructure结构指针所指向的参数配置PB14引脚
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_15; //选择PIN15,是SPI2的MOSI
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP; //选择引脚为复用推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz; //设置引脚的最高工作速率为10MHz
//GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed =GPIO_Speed_10MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure); //根据GPIO_InitStructure结构指针所指向的参数配置PB15引脚
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9; //选择PIN9,是片选脚CS
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP; //选择引脚为推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz; //设置引脚的最高工作速率为50MHz
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure); //根据GPIO_InitStructure结构指针所指向的参数配置PB9引脚
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_12; //选择PIN12,是片选脚RESET
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP; //选择引脚为推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_10MHz; //设置引脚的最高工作速率为50MHz
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure); //根据GPIO_InitStructure结构指针所指向的参数配置PB12引脚
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOB, GPIO_Pin_9); //命令PB9输出高电平,片选脚CS
}
//函数功能:设置SPI2的工作模式
static void SPI2_Mode_Config(void)
{
SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_2Lines_FullDuplex;
//SPI设置为双线双向全双工
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master; //设置为主SPI
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b; //设置SPI发送接收为8位帧结构
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_Low;//时钟极性
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_1Edge;//时钟相位
//CPHA=0,表示第1个边沿:
//对于CPOL=0,空闲时,钟引脚输出低电平,数据采样时刻发生在第1个边沿,就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
//对于CPOL=1,空闲时,钟引脚输出高电平,数据采样时刻发生在第1个边沿,就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
//CPHA=1,表示第2个边沿:
//对于CPOL=0,空闲时,钟引脚输出低电平,数据采样时刻发生在第2个边沿,就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
//对于CPOL=1,空闲时,钟引脚输出高电平,数据采样时刻发生在第2个边沿,就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft; //设置NSS输出由SSI位控制
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_8;
//设置波特率预分频值为256
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB; //设置数据传输先从MSB位开始
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CRCPolynomial = 7; //使用CRC7校验
SPI_Init(SPI2, &SPI_InitStructure);
SPI_Cmd(SPI2, ENABLE); //使能SPI外设
}
//函数功能:SPI2总线读写一个字节
u8 SPI2_ReadWriteByte(u8 TxData)
{
u8 delay=0;
u8 RxData = 0;
while ( SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI2, SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET ){ if(delay++>200) return 0; }
//检查指定的SPI标志位设置与否:发送缓存空标志位
delay=0;
// printf("TxData=0x%02X ",TxData);
SPI_I2S_SendData(SPI2, TxData); //通过外设SPIx发送一个数据,写SPI2_DR
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI2, SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET){ if(delay++>200)return 0; }
//检查指定的SPI标志位设置与否:接受缓存非空标志位
RxData=SPI_I2S_ReceiveData(SPI2); //返回通过SPIx最近接收的数据,写读PI1_DR
// printf("RxData=0x%02X\r\n",RxData);
return RxData;
}
//函数功能:SPI2速度设置
//SpeedSet=0,SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_2 2分频 (SPI 36M@sys 72M)
//SpeedSet=1,SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_8 8分频 (SPI 9M@sys 72M)
//SpeedSet=2,SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_16 16分频 (SPI 4.5M@sys 72M)
//SpeedSet=7,SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_256 256分频 (SPI 281.25K@sys 72M)
//SpeedSet:0~7
//SPI速度=fAPB1/2^(SpeedSet+1)
//APB1时钟一般为36Mhz
void SPI2_SetSpeed(u8 SpeedSet)
{
SpeedSet&=0X07; //限制范围
SPI2->CR1&=0XFFC7;
SPI2->CR1|=SpeedSet<<3; //设置SPI2速度
SPI2->CR1|=1<<6; //SPI设备使能
}
void SPI2_Init(void)
{
SPI2_GPIO_Config();
SPI2_Mode_Config();
}
//函数功能:初始化SPI2,然后使用RESET引脚复位ENC28J60
//包括SPI初始化/IO初始化等
void ENC28J60_Reset(void)
{
SPI2_Init(); //初始化SPI2
SPI2_SetSpeed(SPI_SPEED_4); //SPI2 SCK频率为36M/4=9Mhz
ENC28J60_RST=0; //复位ENC28J60
delay_ms(10);
ENC28J60_RST=1; //复位结束
delay_ms(10);
}15、SPI2.h
#ifndef __SPI2_H
#define __SPI2_H
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "sys.h"
#define ENC28J60_CS PBout(9) //ENC28J60片选信号
#define ENC28J60_RST PBout(12) //ENC28J60复位信号
// SPI总线速度设置
#define SPI_SPEED_2 0
#define SPI_SPEED_4 1
#define SPI_SPEED_8 2
#define SPI_SPEED_16 3
#define SPI_SPEED_32 4
#define SPI_SPEED_64 5
#define SPI_SPEED_128 6
#define SPI_SPEED_256 7
void SPI2_Init(void);
void SPI2_SetSpeed(u8 SpeedSet);
u8 SPI2_ReadWriteByte(u8 TxData);
void ENC28J60_Reset(void);
#endif /*结束 __SPI2_H的if定义*/16、main.c
#include "stm32f10x.h"//使能uint8_t,uint16_t,uint32_t,uint64_t,int8_t,int16_t,int32_t,int64_t
#include "stdio.h" //getchar(),putchar(),scanf(),printf(),puts(),gets(),sprintf()
#include "delay.h"
#include "USART1.h"
#include "IWDG.h"
#include "enc28j60.h"
#include "uip.h"
#include "uip_arp.h"
#include "tapdev.h"
#include "rtc.h"
//TCP服务器的IP地址为192.168.1.17,本地端口为5000,保存到Local_Port中
u8 Main_cnt;
const char CPU_Reset_REG[]="\r\nCPU reset!\r\n";
int main(void)
{
HSE_SetSysClock(RCC_PLLMul_6); // 设置系统时钟为12MHz * 6 = 72MHz
// SystemInit();//在使用IAP时,该语句需要屏蔽
NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_4);//设置系统中断优先级分组4
USART1_Serial_Interface_Enable(115200);
SysRstSrcRecord();//系统复位记录
delay_ms(1000);
Set_Default_Network_Parameter();
if(RTC_Init())
{
printf("RTC Init Error\n");
delay_ms(1000);
}
else
{
delay_ms(1000);
Time_Display();//2021年测试
}
while(Network_Init()) //初始化ENC28J60错误
{
printf("ENC28J60 Init Error\n");
delay_ms(1000);
}
while(1)
{
If_ENC28J60Reset_Do_Resart();
HTTP_Work();
if(str_RTC_Data.Second_Flag )
{
Time_Display();//2021年测试
str_RTC_Data.Second_Flag=FALSE;
Main_cnt++;
if(Main_cnt%10==0)
{
Print_ARP_Table();
Print_uipConnection();
}
}
}
}