引言
深度学习的发展历程中,网络深度一直是提升模型性能的关键因素。然而,传统深层网络面临着梯度消失 / 爆炸 和退化问题 ,限制了网络深度的进一步增加。2016 年,何恺明团队提出的ResNet(残差网络)通过引入残差连接,成功解决了深层网络的训练难题,在 ImageNet 比赛中取得了突破性成果。
一、ResNet 理论基础
1. 深层网络的挑战
传统 CNN 在加深网络深度时,会遇到两个主要问题:
- 梯度消失 / 爆炸:反向传播时,梯度经过多层网络后逐渐衰减或放大,导致底层网络难以训练
- 退化问题:当网络深度超过一定阈值后,模型性能开始下降,并非过拟合导致
2. 残差连接的创新
ResNet 通过引入残差块(Residual Block) ,解决了深层网络的训练难题。残差块的核心思想是:让网络学习残差映射,而非直接学习恒等映射。
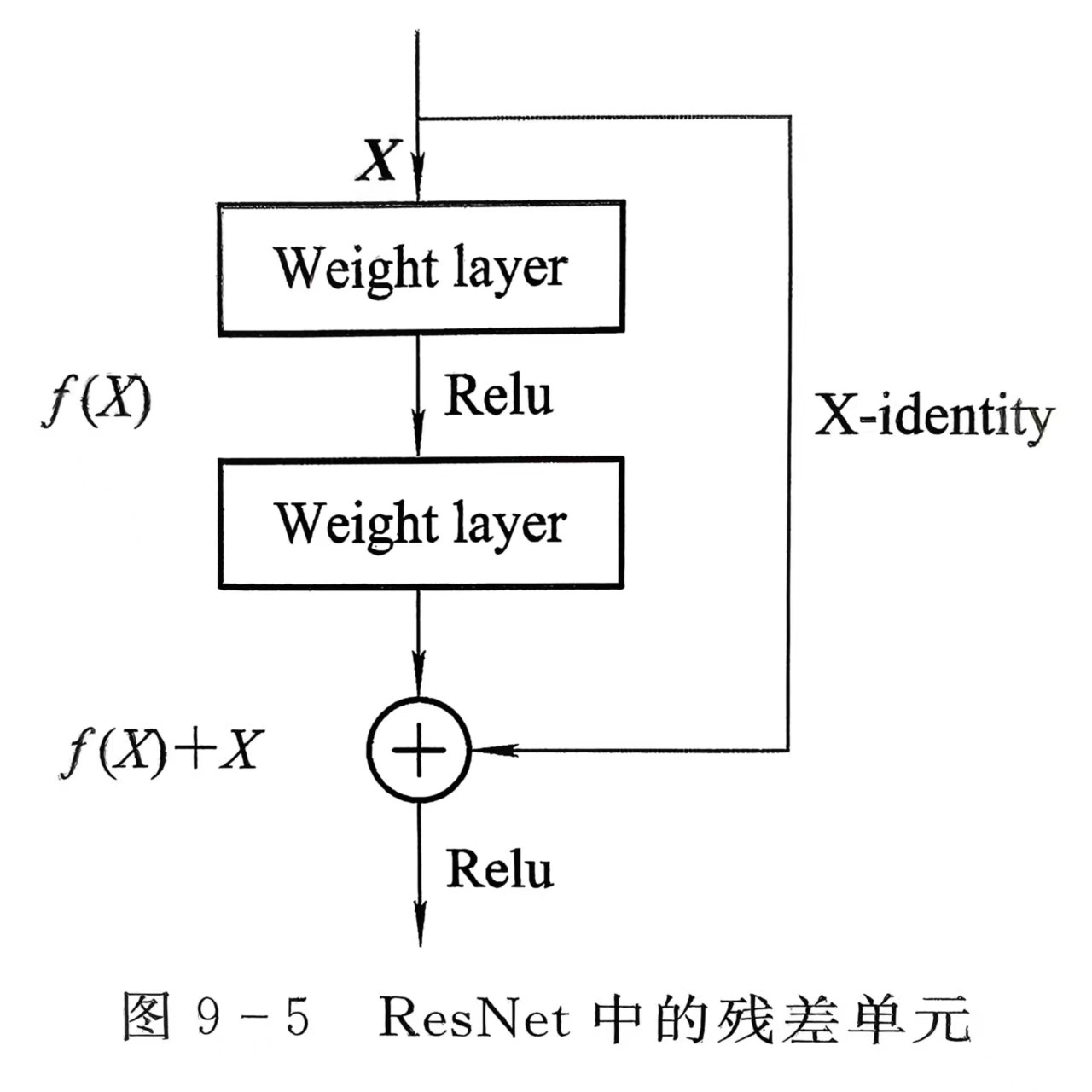
数学原理
对于一个深层网络,假设期望的底层映射为H(x),ResNet 将其分解为:H(x) = F(x) + x
其中:
- x:输入特征
- F(x):残差映射(网络需要学习的部分)
- F(x) + x:恒等映射(通过 shortcut 连接直接传递)
优势分析
- 缓解梯度消失:残差连接提供了梯度直接传播的路径,底层网络能够获得有效的梯度更新
- 易于优化:学习残差映射F(x)比直接学习H(x)更容易,尤其是当H(x)接近恒等映射时
- 支持更深网络:ResNet 成功训练了 152 层甚至更深的网络,突破了传统 CNN 的深度限制
3. ResNet18 网络结构
ResNet18 包含18 层可训练层(16 个卷积层 + 2 个全连接层),由 8 个残差块组成:
| 模块 | 残差块数量 | 输出通道 | 步长 | 输出尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv1 | - | 64 | 2 | 112×112 |
| MaxPool | - | 64 | 2 | 56×56 |
| Layer1 | 2 | 64 | 1 | 56×56 |
| Layer2 | 2 | 128 | 2 | 28×28 |
| Layer3 | 2 | 256 | 2 | 14×14 |
| Layer4 | 2 | 512 | 2 | 7×7 |
| AvgPool | - | 512 | - | 1×1 |
| FC | - | 1000 | - | - |
二、实验配置
核心配置参数
python
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # CPU优化:平衡内存与速度
EPOCHS = 10 # 快速收敛
LEARNING_RATE = 5e-4 # 适合迁移学习的学习率
NUM_CLASSES = 10 # CIFAR-10类别数三、代码实现与优化
1. 数据预处理与增强
针对 CIFAR-10 数据集(32×32 彩色图像),设计了高效的数据预处理流程:
python
cifar_mean = [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465]
cifar_std = [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010]
transform_train = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4), # 随机裁剪,增强泛化能力
transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # 调整为ResNet输入尺寸
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.RandomRotation(15), # 随机旋转±15°
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=cifar_mean, std=cifar_std) # CIFAR-10专用归一化
])优化点解析:
- 使用CIFAR-10 专用归一化参数:相比 ImageNet 参数,更适合目标数据集
- 增加多种数据增强:随机裁剪、翻转、旋转,有效减少过拟合
- 调整为224×224 输入尺寸:适配 ResNet 预训练模型的输入要求
2. 数据加载优化
针对 CPU 环境,对数据加载进行了优化:
python
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True,
num_workers=0, pin_memory=False # CPU优化:禁用多线程+锁存
)优化点解析:
- num_workers=0:CPU 环境下禁用多线程,避免线程切换开销
- pin_memory=False:CPU 环境下禁用内存锁存,减少内存占用
- BATCH_SIZE=32:平衡内存占用与训练速度,避免 CPU 内存溢出
3. ResNet18 模型构建与微调
python
model = models.resnet18(weights=ResNet18_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1)
# 迁移学习策略:冻结底层,解冻顶层卷积块+全连接层
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False # 冻结所有层
for param in model.layer4.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True # 解冻最后一个卷积块(layer4)
# 替换全连接层,适配10分类任务
in_features = model.fc.in_features
model.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.5), # 添加Dropout,防止过拟合
nn.Linear(in_features, NUM_CLASSES)
)
model = model.to(DEVICE)优化点解析:
- 加载预训练权重:使用 ImageNet 预训练权重,加速模型收敛
- 分层冻结策略:仅解冻顶层卷积块(layer4),兼顾特征微调与训练速度
- 添加 Dropout:在全连接层前添加 Dropout (0.5),有效防止过拟合
- 替换分类层:将输出类别数从 1000 改为 10,适配 CIFAR-10 任务
4. 优化器与学习率调度
python
# 使用AdamW优化器,结合权重衰减,适合深度学习训练
optimizer = optim.AdamW(
filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, model.parameters()), # 仅优化可训练参数
lr=LEARNING_RATE, weight_decay=1e-4 # 权重衰减抑制过拟合
)
# 动态学习率调度:当准确率不再提升时,自动降低学习率
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(
optimizer, mode='max', patience=2, factor=0.5
)优化点解析:
- AdamW 优化器:相比传统 Adam,结合了权重衰减,更适合深层网络训练
- 动态学习率:使用 ReduceLROnPlateau,当验证准确率停滞时自动将学习率减半
- 仅优化可训练参数:使用 filter 函数,减少不必要的计算开销
5. 训练函数优化
python
def train_model(model, train_loader, test_loader, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, epochs):
train_losses = []
test_accuracies = []
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
start_time = time.time()
# 训练阶段
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, (data, targets) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, targets = data.to(DEVICE), targets.to(DEVICE)
outputs = model(data)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item() * data.size(0)
# CPU优化:降低打印频率
if batch_idx % 200 == 0 and batch_idx != 0:
print(f' Batch {batch_idx}/{len(train_loader)}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# 验证阶段(精简代码,减少冗余计算)
model.eval()
test_correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, targets in test_loader:
data, targets = data.to(DEVICE), targets.to(DEVICE)
outputs = model(data)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
test_correct += (predicted == targets).sum().item()
test_acc = 100 * test_correct / len(test_loader.dataset)
test_accuracies.append(test_acc)
# 学习率调度
scheduler.step(test_acc)
# 保存最佳模型
if test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = test_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "best_resnet_cifar10.pth")
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}] | Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f} | Test Acc: {test_acc:.2f}% | Time: {epoch_time:.1f}s')
return train_losses, test_accuracies优化点解析:
- 降低打印频率:每 200 批次打印一次,减少 CPU IO 开销
- 精简验证代码:去除冗余计算,提高验证速度
- 仅保存最佳模型:避免频繁写入磁盘,减少 IO 操作
- 记录核心指标:仅记录训练损失和测试准确率,简化日志
四、实验结果与分析
1. 数据集样本展示

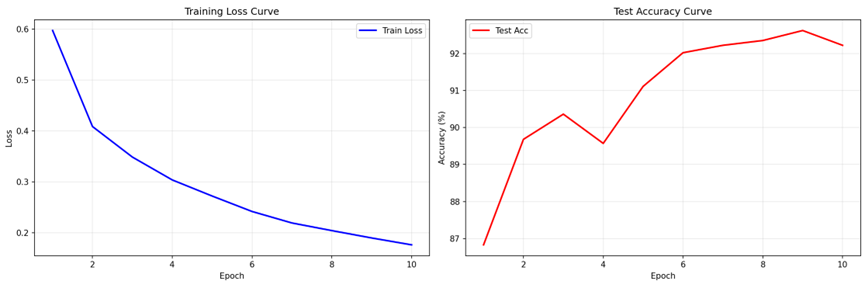
2. 训练曲线
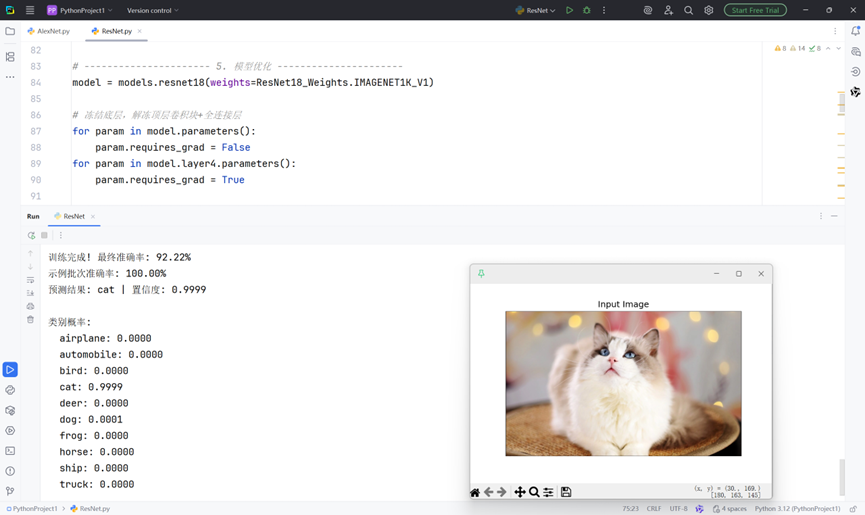
3. 分类结果展示
4. ResNet18 优势分析
- 残差连接:有效解决了深层网络的梯度消失问题,训练 18 层网络依然稳定
- 轻量级设计:ResNet18 参数量相比 VGG16 轻量得多,适合 CPU 环境
- 泛化能力强:预训练模型在 ImageNet 上学到的特征具有很强的通用性,迁移到 CIFAR-10 效果显著
- 易于微调:分层冻结策略使得模型在小数据集上易于微调,快速适应新任务
五、完整代码
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms, models
from torchvision.models import ResNet18_Weights
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# ---------------------- 1. 核心配置----------------------
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# CPU环境优化配置
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # CPU批次不宜过大
EPOCHS = 10
LEARNING_RATE = 5e-4
NUM_CLASSES = 10
classes = ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer',
'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']
# ---------------------- 2. 优化数据预处理 ----------------------
cifar_mean = [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465]
cifar_std = [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010]
transform_train = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
transforms.RandomRotation(15),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=cifar_mean, std=cifar_std)
])
transform_test = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=cifar_mean, std=cifar_std)
])
# ---------------------- 3. 数据加载 ----------------------
train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_train)
test_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)
# CPU环境:num_workers=0 + pin_memory=False
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True,
num_workers=0, pin_memory=False
)
test_loader = DataLoader(
test_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False,
num_workers=0, pin_memory=False
)
# ---------------------- 4. 数据集展示 ----------------------
def show_dataset_samples():
data_iter = iter(train_loader)
images, labels = next(data_iter)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(4, 8, figsize=(16, 8))
fig.suptitle('CIFAR-10 Dataset Samples', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
for i in range(32):
row, col = i // 8, i % 8
img = images[i].numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
img = img * cifar_std + cifar_mean
img = np.clip(img, 0, 1)
axes[row, col].imshow(img)
axes[row, col].set_title(classes[labels[i]], fontsize=10)
axes[row, col].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('dataset_samples.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
print("展示数据集样本...")
show_dataset_samples()
# ---------------------- 5. 模型优化 ----------------------
model = models.resnet18(weights=ResNet18_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1)
# 冻结底层,解冻顶层卷积块+全连接层
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
for param in model.layer4.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
# 替换全连接层
in_features = model.fc.in_features
model.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features, NUM_CLASSES)
)
model = model.to(DEVICE)
# ---------------------- 6. 优化器 ----------------------
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(
filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, model.parameters()),
lr=LEARNING_RATE, weight_decay=1e-4
)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(
optimizer, mode='max', patience=2, factor=0.5
)
# ---------------------- 7. 训练函数 ----------------------
def train_model(model, train_loader, test_loader, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, epochs):
train_losses = []
test_accuracies = []
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
start_time = time.time()
# 训练阶段
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, (data, targets) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, targets = data.to(DEVICE), targets.to(DEVICE)
outputs = model(data)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item() * data.size(0)
# CPU训练打印频率降低
if batch_idx % 200 == 0 and batch_idx != 0:
print(f' Batch {batch_idx}/{len(train_loader)}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader.dataset)
train_losses.append(epoch_loss)
# 验证阶段
model.eval()
test_correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, targets in test_loader:
data, targets = data.to(DEVICE), targets.to(DEVICE)
outputs = model(data)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
test_correct += (predicted == targets).sum().item()
test_acc = 100 * test_correct / len(test_loader.dataset)
test_accuracies.append(test_acc)
epoch_time = time.time() - start_time
# 学习率调度
scheduler.step(test_acc)
print(
f'Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{epochs}] | Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f} | Test Acc: {test_acc:.2f}% | Time: {epoch_time:.1f}s')
# 保存最佳模型
if test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = test_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "best_resnet_cifar10.pth")
print(f' Best model saved! Acc: {best_acc:.2f}%')
return train_losses, test_accuracies
# ---------------------- 8. 训练曲线 ----------------------
def plot_training_curves(train_losses, test_accuracies):
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 5))
ax1.plot(range(1, EPOCHS + 1), train_losses, 'b-', linewidth=2, label='Train Loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax1.set_title('Training Loss Curve')
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax1.legend()
ax2.plot(range(1, EPOCHS + 1), test_accuracies, 'r-', linewidth=2, label='Test Acc')
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy (%)')
ax2.set_title('Test Accuracy Curve')
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax2.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('training_curves.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# ---------------------- 9. 分类结果展示 ----------------------
def show_classification_results(model, test_loader):
model.eval()
images, labels = next(iter(test_loader))
images = images.to(DEVICE)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(images)
_, predictions = torch.max(outputs, 1)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 4, figsize=(15, 12))
fig.suptitle('ResNet Classification Results', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
for i in range(12):
row, col = i // 4, i % 4
img = images[i].cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
img = img * cifar_std + cifar_mean
img = np.clip(img, 0, 1)
axes[row, col].imshow(img)
true_label = classes[labels[i]]
pred_label = classes[predictions[i]]
color = 'green' if true_label == pred_label else 'red'
axes[row, col].set_title(f'True: {true_label}\nPred: {pred_label}', color=color, fontsize=12)
axes[row, col].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('classification_results.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
acc = 100 * (predictions.cpu() == labels).sum().item() / len(labels)
print(f'示例批次准确率: {acc:.2f}%')
# ---------------------- 10. 主训练流程 ----------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=" * 60)
print(f"开始训练 | Epochs={EPOCHS}, Batch={BATCH_SIZE}, LR={LEARNING_RATE}")
print("=" * 60)
train_losses, test_accuracies = train_model(
model, train_loader, test_loader, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, EPOCHS
)
print(f"\n训练完成! 最终准确率: {test_accuracies[-1]:.2f}%")
# 核心展示
plot_training_curves(train_losses, test_accuracies)
show_classification_results(model, test_loader)
# ---------------------- 11. 单张图像预测 ----------------------
def predict_single_image(image_path="test_image.jpg"):
# 加载模型
model = models.resnet18(weights=None)
in_features = model.fc.in_features
model.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(in_features, NUM_CLASSES))
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("best_resnet_cifar10.pth", map_location=DEVICE))
model.to(DEVICE).eval()
# 预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=cifar_mean, std=cifar_std)
])
# 加载显示图像
try:
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6)), plt.imshow(image), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Input Image"), plt.show()
# 预测
with torch.no_grad():
img_tensor = transform(image).unsqueeze(0).to(DEVICE)
outputs = model(img_tensor)
probs = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
conf, pred = torch.max(probs, 1)
print(f"预测结果: {classes[pred.item()]} | 置信度: {conf.item():.4f}")
print("\n类别概率:")
for cls, p in zip(classes, probs.cpu().numpy()[0]):
print(f" {cls}: {p:.4f}")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误:未找到图像文件 {image_path},请确保文件存在")
# 示例调用
predict_single_image("test_image.jpg")