

package Day01;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMap1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//建一个HashMap对象
HashMap<Student,String> map = new HashMap<>();
//创建三个学生对象
Student student1 = new Student("张三",20);
Student student2 = new Student("李四",21);
Student student3 = new Student("王五",22);
Student student4 = new Student("李四",21);
//向HashMap中添加对象元素和籍贯
map.put(student1,"广东省");
map.put(student2,"云南省");
map.put(student3,"河北省");
map.put(student4,"河南省");
//对元素遍历
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Student,String> entry:entries){
Student key = entry.getKey();
String name = key.getName();
int age = key.getAge();
System.out.println(name+","+age+"="+entry.getValue());
}
}
}核心点:如果HashMap的键位置存储的是自定义对象,需要重写equals和hashcode
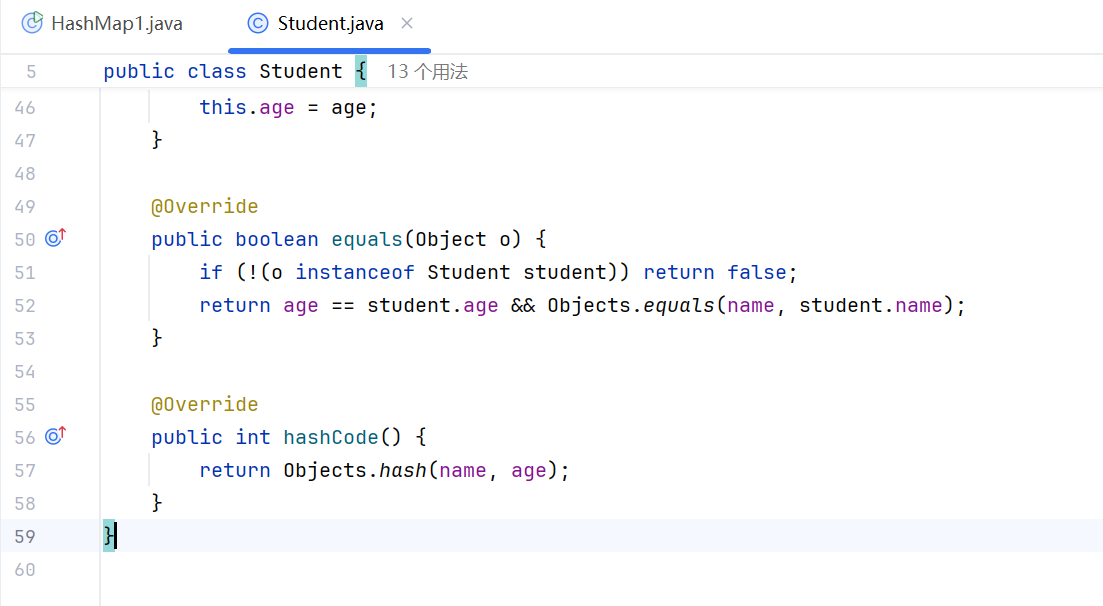

package Day01;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//统计ABCD景点想去的人数
//创建HashMap集合
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "B", "C", "D","A","B","C","A","A","B","C","A","B");
//遍历集合
//生成对象的单列数组
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
if(map.containsKey(list.get(i))){
int i1 = map.get(list.get(i)) + 1;
map.put(list.get(i),i1);
}else {
map.put(list.get(i),1);
}
}
//计算集合中最大值
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
int MaxValue = 0;
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:entries){
if(entry.getValue()>MaxValue){
MaxValue = entry.getValue();
}
}
//因为可能存在两个键值相同的情况
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:entries){
if(entry.getValue()==MaxValue){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}