RINEX文件进行卫星导航解算,包括卫星坐标计算和用户位置解算的完整流程。
整体解算流程
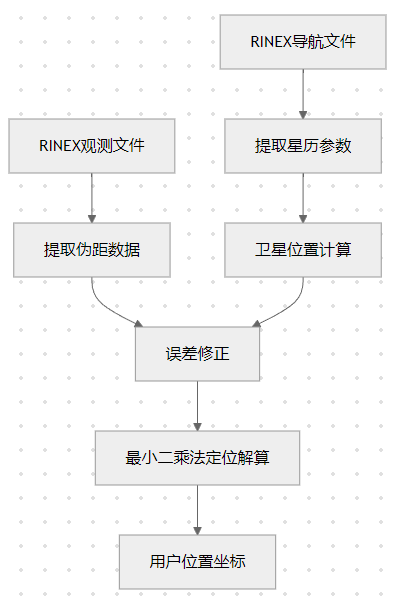
RINEX文件结构解析
观测文件格式
c
3.04 OBSERVATION DATA M: Mixed RINEX VERSION / TYPE
teqc 2019Feb25 NOAA/NOS/NGS/CORS 20240429 06:34:24UTCPGM / RUN BY / DATE
MARKER NAME
MARKER NUMBER
OBSERVER / AGENCY
REC # / TYPE / VERS
ANT # / TYPE
-2162989.6650 -4487349.1120 3838429.4097 APPROX POSITION XYZ
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 ANTENNA: DELTA H/E/N
1 1 WAVELENGTH FACT L1/2
6 C1 L1 L2 P1 P2 S1 TYPES OF OBSERV导航文件格式
c
3.04 NAVIGATION DATA M: Mixed RINEX VERSION / TYPE
teqc 2019Feb25 NOAA/NOS/NGS/CORS 20240429 06:34:24UTCPGM / RUN BY / DATE
END OF HEADER
1 24 4 28 6 34 24.0 0.110304355756D-03 0.000000000000D+00 0.000000000000D+00
0.700000000000D+01 0.206250000000D+02 0.465377655669D-08 0.290441894374D+01
0.115018337965D-05 0.144875647966D-01 0.119209289551D-04 0.515365028381D+04
0.388800000000D+06 0.111758708954D-06 0.000000000000D+00 0.000000000000D+00
0.112000000000D+04 0.000000000000D+00 0.512227416039D-08 0.700000000000D+01
0.214890000000D+06 0.000000000000D+00 0.000000000000D+00 0.000000000000D+00MATLAB实现代码
1. RINEX文件读取
matlab
function [obs_data, header] = read_rinex_obs(filename)
% 读取RINEX观测文件
fid = fopen(filename, 'r');
if fid == -1
error('无法打开文件: %s', filename);
end
% 读取文件头
header = struct();
while ~feof(fid)
line = fgetl(fid);
if contains(line, 'END OF HEADER')
break;
end
% 解析头文件信息...
end
% 读取观测数据
obs_data = struct();
while ~feof(fid)
line = fgetl(fid);
if length(line) < 2
continue;
end
% 解析历元时刻
if line(1) == '>'
% 新历元开始
year = str2double(line(2:5));
month = str2double(line(7:8));
day = str2double(line(10:11));
hour = str2double(line(13:14));
minute = str2double(line(16:17));
second = str2double(line(18:29));
epoch_time = datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second);
obs_data.(datestr(epoch_time, 'yyyymmdd_HHMMSS')) = struct();
current_epoch = datestr(epoch_time, 'yyyymmdd_HHMMSS');
else
% 解析卫星观测数据
sat_id = strtrim(line(1:3));
observations = sscanf(line(4:end), '%f');
% 存储伪距、载波相位等观测值
if length(observations) >= 1
obs_data.(current_epoch).(sat_id).C1 = observations(1); % C/A码伪距
end
end
end
fclose(fid);
end2. 导航文件读取与星历参数提取
matlab
function eph = read_rinex_nav(filename)
% 读取RINEX导航文件并提取星历参数
fid = fopen(filename, 'r');
if fid == -1
error('无法打开文件: %s', filename);
end
% 跳过文件头
while ~feof(fid)
line = fgetl(fid);
if contains(line, 'END OF HEADER')
break;
end
end
eph = struct();
while ~feof(fid)
% 读取星历数据块
line1 = fgetl(fid);
if isempty(line1) || length(line1) < 5
continue;
end
% 解析卫星PRN号和参考时间
prn = str2double(line1(1:2));
year = str2double(line1(4:5)) + 2000;
month = str2double(line1(7:8));
day = str2double(line1(10:11));
hour = str2double(line1(13:14));
minute = str2double(line1(16:17));
second = str2double(line1(18:22));
toc = datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second);
% 读取其他星历参数
line2 = fgetl(fid); line3 = fgetl(fid); line4 = fgetl(fid);
line5 = fgetl(fid); line6 = fgetl(fid); line7 = fgetl(fid); line8 = fgetl(fid);
% 解析关键星历参数
af0 = str2double(line1(23:41));
af1 = str2double(line1(42:60));
af2 = str2double(line1(61:79));
iode = str2double(line2(4:22));
crs = str2double(line2(23:41));
delta_n = str2double(line2(42:60));
m0 = str2double(line2(61:79));
cuc = str2double(line3(4:22));
ecc = str2double(line3(23:41));
cus = str2double(line3(42:60));
sqrt_a = str2double(line3(61:79));
toe = str2double(line4(4:22));
cic = str2double(line4(23:41));
omega0 = str2double(line4(42:60));
cis = str2double(line4(61:79));
i0 = str2double(line5(4:22));
crc = str2double(line5(23:41));
omega = str2double(line5(42:60));
omega_dot = str2double(line5(61:79));
idot = str2double(line6(4:22));
% 存储星历数据
eph(prn).af0 = af0;
eph(prn).af1 = af1;
eph(prn).af2 = af2;
eph(prn).iode = iode;
eph(prn).crs = crs;
eph(prn).delta_n = delta_n;
eph(prn).m0 = m0;
eph(prn).cuc = cuc;
eph(prn).ecc = ecc;
eph(prn).cus = cus;
eph(prn).sqrt_a = sqrt_a;
eph(prn).toe = toe;
eph(prn).cic = cic;
eph(prn).omega0 = omega0;
eph(prn).cis = cis;
eph(prn).i0 = i0;
eph(prn).crc = crc;
eph(prn).omega = omega;
eph(prn).omega_dot = omega_dot;
eph(prn).idot = idot;
eph(prn).toc = toc;
end
fclose(fid);
end3. 卫星位置计算
matlab
function [sat_pos, sat_clock_corr] = calculate_satellite_position(eph, prn, transmit_time)
% 根据星历参数计算卫星在ECEF坐标系中的位置
% 输入:eph - 星历数据,prn - 卫星号,transmit_time - 信号发射时间
% GPS系统常量
GM = 3.986005e14; % 地球引力常数 (m^3/s^2)
omega_e_dot = 7.2921151467e-5; % 地球自转角速度 (rad/s)
% 提取该卫星的星历参数
af0 = eph(prn).af0;
af1 = eph(prn).af1;
af2 = eph(prn).af2;
sqrt_a = eph(prn).sqrt_a;
delta_n = eph(prn).delta_n;
m0 = eph(prn).m0;
ecc = eph(prn).ecc;
omega = eph(prn).omega;
cuc = eph(prn).cuc;
cus = eph(prn).cus;
crc = eph(prn).crc;
crs = eph(prn).crs;
cic = eph(prn).cic;
cis = eph(prn).cis;
i0 = eph(prn).i0;
idot = eph(prn).idot;
omega0 = eph(prn).omega0;
omega_dot = eph(prn).omega_dot;
toe = eph(prn).toe;
% 1. 计算信号传播时间tk (从参考时间toe开始)
tk = transmit_time - toe;
% 2. 卫星时钟修正
sat_clock_corr = af0 + af1 * tk + af2 * tk^2;
% 3. 校正后的发射时间
t = transmit_time - sat_clock_corr;
tk = t - toe;
% 4. 计算平近点角
a = sqrt_a^2; % 轨道长半轴
n0 = sqrt(GM / a^3); % 计算平均角速度
n = n0 + delta_n; % 校正后的平均角速度
mk = m0 + n * tk; % 平近点角
% 5. 解开普勒方程求偏近点角
ek = mk;
for iter = 1:10 % 迭代求解
ek_new = mk + ecc * sin(ek);
if abs(ek_new - ek) < 1e-12
break;
end
ek = ek_new;
end
% 6. 计算真近点角
vk = atan2(sqrt(1 - ecc^2) * sin(ek), cos(ek) - ecc);
% 7. 计算升交距角
phik = vk + omega;
% 8. 计算二阶调和修正
delta_uk = cus * sin(2 * phik) + cuc * cos(2 * phik); % 纬度幅角修正
delta_rk = crs * sin(2 * phik) + crc * cos(2 * phik); % 向径修正
delta_ik = cis * sin(2 * phik) + cic * cos(2 * phik); % 轨道倾角修正
% 9. 计算修正后的轨道参数
uk = phik + delta_uk; % 修正后的纬度幅角
rk = a * (1 - ecc * cos(ek)) + delta_rk; % 修正后的向径
ik = i0 + idot * tk + delta_ik; % 修正后的轨道倾角
% 10. 计算卫星在轨道平面内的位置
xk_orb = rk * cos(uk);
yk_orb = rk * sin(uk);
% 11. 计算升交点经度
omega_k = omega0 + (omega_dot - omega_e_dot) * tk - omega_e_dot * toe;
% 12. 计算地固坐标系中的卫星位置
xk = xk_orb * cos(omega_k) - yk_orb * cos(ik) * sin(omega_k);
yk = xk_orb * sin(omega_k) + yk_orb * cos(ik) * cos(omega_k);
zk = yk_orb * sin(ik);
sat_pos = [xk; yk; zk];
end4. 伪距定位解算
matlab
function [pos, clock_bias, dop, residuals] = pseudorange_positioning(obs_data, eph, epoch_time, initial_pos)
% 使用伪距测量法解算用户位置
% 输入:观测数据,星历数据,历元时间,初始位置估计
% 提取该历元的观测数据
epoch_str = datestr(epoch_time, 'yyyymmdd_HHMMSS');
if ~isfield(obs_data, epoch_str)
error('该历元无观测数据');
end
current_obs = obs_data.(epoch_str);
satellites = fieldnames(current_obs);
% 初始化
num_sats = length(satellites);
if num_sats < 4
error('可见卫星数不足4颗,无法定位');
end
% 光速 (m/s)
c = 299792458;
% 初始估计
x = [initial_pos; 0]; % [X; Y; Z; 接收机钟差]
% 迭代求解
max_iter = 10;
tolerance = 1e-6;
for iter = 1:max_iter
H = zeros(num_sats, 4); % 设计矩阵
w = zeros(num_sats, 1); % 残差向量
predicted_ranges = zeros(num_sats, 1);
for i = 1:num_sats
sat_id = satellites{i};
prn = str2double(sat_id(2:3)); % 提取卫星PRN号
% 获取伪距观测值
if isfield(current_obs.(sat_id), 'C1')
pseudorange = current_obs.(sat_id).C1;
else
continue;
end
% 计算信号发射时间 (考虑卫星钟差和传播时间近似)
transmit_time = epoch_time - pseudorange / c;
% 计算卫星位置和卫星钟差
[sat_pos, sat_clock_corr] = calculate_satellite_position(eph, prn, transmit_time);
% 计算几何距离
geometric_range = norm(sat_pos - x(1:3));
% 预测的伪距 (包含接收机钟差)
predicted_ranges(i) = geometric_range + x(4) * c - sat_clock_corr * c;
% 计算视线向量 (单位向量)
line_of_sight = (sat_pos - x(1:3)) / geometric_range;
% 构建设计矩阵
H(i, 1:3) = -line_of_sight;
H(i, 4) = 1;
% 计算残差
w(i) = pseudorange - predicted_ranges(i);
end
% 最小二乘解
dx = (H' * H) \ (H' * w);
% 更新估计
x = x + dx;
% 检查收敛
if norm(dx) < tolerance
break;
end
end
% 输出结果
pos = x(1:3);
clock_bias = x(4);
% 计算DOP值
Q = inv(H' * H);
dop.gdop = sqrt(trace(Q));
dop.pdop = sqrt(trace(Q(1:3, 1:3)));
dop.hdop = sqrt(Q(1,1) + Q(2,2));
dop.vdop = sqrt(Q(3,3));
dop.tdop = sqrt(Q(4,4));
% 计算残差
residuals = w;
end5. 完整的主程序
matlab
function main_gnss_solver()
% 主程序:GNSS定位解算
% 文件路径
obs_file = 'example.obs'; % RINEX观测文件
nav_file = 'example.nav'; % RINEX导航文件
% 读取RINEX文件
fprintf('读取RINEX文件...\n');
[obs_data, obs_header] = read_rinex_obs(obs_file);
eph = read_rinex_nav(nav_file);
% 从观测文件头获取近似坐标
if isfield(obs_header, 'APPROX_POSITION')
initial_pos = obs_header.APPROX_POSITION;
else
% 如果没有近似坐标,使用地球中心作为初始估计
initial_pos = [0; 0; 0];
end
% 选择要处理的历元
epoch_fields = fieldnames(obs_data);
first_epoch = datetime(epoch_fields{1}, 'InputFormat', 'yyyyMMdd_HHmmss');
fprintf('处理历元: %s\n', datestr(first_epoch));
% 执行定位解算
[pos, clock_bias, dop, residuals] = pseudorange_positioning(...
obs_data, eph, first_epoch, initial_pos);
% 坐标转换 (ECEF到经纬高)
[lat, lon, height] = ecef2llh(pos);
% 显示结果
fprintf('\n=== 定位结果 ===\n');
fprintf('ECEF坐标: X=%.3f m, Y=%.3f m, Z=%.3f m\n', pos);
fprintf('经纬高: 纬度=%.6f°, 经度=%.6f°, 高程=%.3f m\n', ...
lat, lon, height);
fprintf('接收机钟差: %.3f m (%.9f s)\n', clock_bias, clock_bias/299792458);
fprintf('\n=== DOP值 ===\n');
fprintf('GDOP: %.3f\n', dop.gdop);
fprintf('PDOP: %.3f\n', dop.pdop);
fprintf('HDOP: %.3f\n', dop.hdop);
fprintf('VDOP: %.3f\n', dop.vdop);
fprintf('TDOP: %.3f\n', dop.tdop);
% 残差分析
fprintf('\n=== 残差分析 ===\n');
fprintf('RMS残差: %.3f m\n', rms(residuals));
fprintf('最大残差: %.3f m\n', max(abs(residuals)));
end
function [lat, lon, height] = ecef2llh(xyz)
% ECEF坐标转经纬高
x = xyz(1); y = xyz(2); z = xyz(3);
% WGS84椭球参数
a = 6378137.0; % 长半轴
f = 1/298.257223563; % 扁率
e2 = 2*f - f^2; % 第一偏心率平方
% 计算经度
lon = atan2(y, x);
% 迭代计算纬度和高程
p = sqrt(x^2 + y^2);
lat = atan2(z, p * (1 - e2));
for i = 1:10
N = a / sqrt(1 - e2 * sin(lat)^2);
height = p / cos(lat) - N;
lat_new = atan2(z, p * (1 - e2 * N / (N + height)));
if abs(lat_new - lat) < 1e-15
break;
end
lat = lat_new;
end
% 转换为度
lat = rad2deg(lat);
lon = rad2deg(lon);
end参考代码 卫星导航解算 www.3dddown.com/csa/64134.html
关键技术与误差处理
主要误差源及修正
matlab
function corrected_pseudorange = apply_error_corrections(raw_pr, sat_pos, rec_pos, eph, time)
% 应用各种误差修正
% 1. 卫星钟差修正 (已在卫星位置计算中处理)
% 2. 电离层延迟修正 (Klobuchar模型)
iono_delay = klobuchar_correction(rec_pos, sat_pos, time);
% 3. 对流层延迟修正
tropo_delay = hopfield_correction(rec_pos, sat_pos);
% 4. 地球自转修正 (Sagnac效应)
sagnac_corr = sagnac_correction(sat_pos, rec_pos);
corrected_pseudorange = raw_pr - iono_delay - tropo_delay + sagnac_corr;
end
function iono_delay = klobuchar_correction(rec_pos, sat_pos, time)
% Klobuchar电离层模型
% 简化实现 - 实际应用需要电离层参数
elevation = calculate_elevation(rec_pos, sat_pos);
iono_delay = 5.0 / sin(elevation + 0.1); % 简化模型
end
function tropo_delay = hopfield_correction(rec_pos, sat_pos)
% Hopfield对流层模型
elevation = calculate_elevation(rec_pos, sat_pos);
tropo_delay = 2.3 / sin(elevation); % 简化模型
end建议
- 数据质量检查:处理前先检查数据完整性和质量
- 多历元平滑:使用多个历元数据进行平滑提高精度
- 多系统融合:结合GPS、GLONASS、Galileo等多系统数据
- 精密星历:如需更高精度,可使用精密星历替代广播星历