3. Function calling
OpenAI 文档参考:https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling
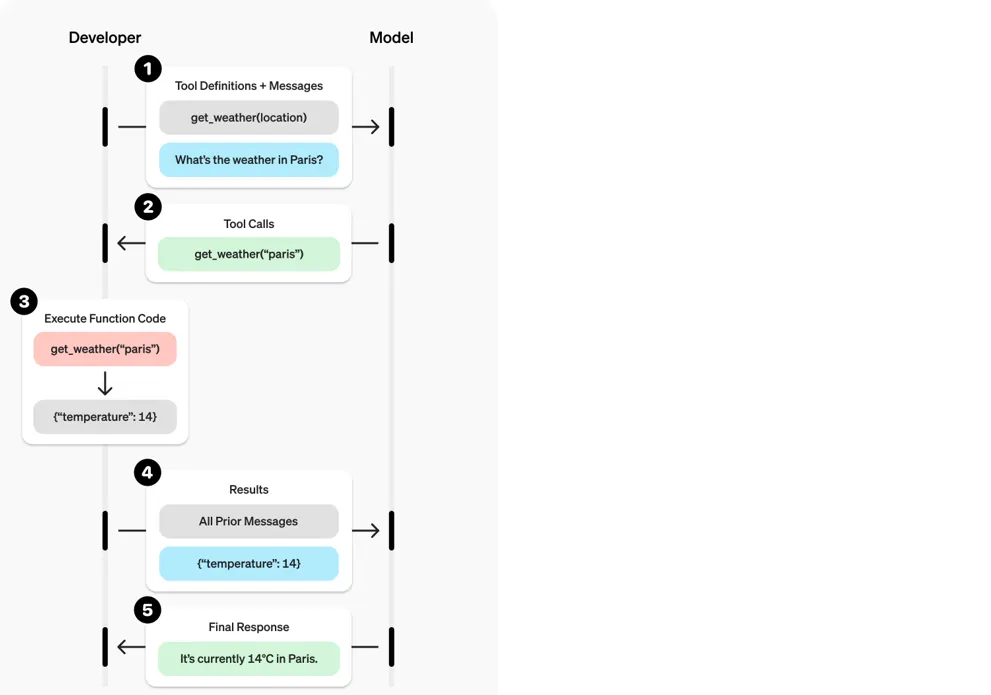
3.1 什么是 Function Calling
在大模型里,Function Calling 是指让模型在回答用户问题时,不直接返回文本答案,而是识别问题意图,并按照约定好的结构化格式(通常是 JSON)"调用"某个函数,再由外部程序执行该函数,最后把执行结果再交给模型或者直接返回给用户。
简单来说,它是 "大模型理解 → 生成结构化调用 → 外部函数执行 → 返回结果" 的闭环。
举个例子:
用户问:
明天下午北京的天气怎么样?模型不会直接生成一句话,而是输出一个函数调用请求:
{
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": {
"location": "北京",
"date": "2025-08-27 14:00"
}
}然后外部程序就会去调用 get_weather(location, date) 这个函数,把真实数据查出来再返回。
3.2 Function Calling 的原理
核心原理有三个环节:
- 意图解析(Natural Language → Structured Data)
- 大模型擅长理解自然语言
- 在提示词(prompt)中告诉模型有哪些可用的函数(包括函数名、参数及说明)
- 模型会把用户的自然语言请求转化成调用哪个函数、传什么参数的结构化数据(JSON 格式)
- 函数调度(外部程序执行)
- 由开发者写的后端逻辑接收模型输出的 JSON
- 根据
name找到对应函数,执行逻辑,得到结果(比如天气 API 查询)
- 结果交互(返回用户 or 再交给模型处理)
- 把结果返回给用户
- 或者再次交给模型,让模型基于结果生成自然语言回答
3.3 实现过程
(以 OpenAI / LangChain 为例)
- 定义可调用函数(函数描述)
你需要提前定义哪些函数可被调用,告诉模型参数含义:
functions = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取指定地点和时间的天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "地点,例如 北京"},
"date": {"type": "string", "description": "时间,例如 2025-08-27 14:00"}
},
"required": ["location", "date"]
}
}
]-
向模型发起请求
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "明天下午北京的天气怎么样?"}],
functions=functions,
function_call="auto"
) -
模型返回函数调用请求
{
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": {
"location": "北京",
"date": "2025-08-27 14:00"
}
} -
执行函数
def get_weather(location, date):
return "北京明天下午14:00 多云,最高温度30°C"result = get_weather(**response.choices[0].message.function_call.arguments)
-
把结果交给模型(可选)
你可以把执行结果再丢给模型,让它生成自然语言回答:
messages.append({
"role": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"content": result
})最终用户得到:
明天下午北京多云,最高气温30°C。四、应用场景
- 数据查询:天气、股票、航班、数据库等
- 执行操作:发邮件、写入日程、控制 IoT 设备
- 多步骤任务:通过多次函数调用,完成复杂的 workflow
- 知识增强:调用内部知识库,补充模型不知道的事实
五、总结
- 是什么:让大模型把自然语言转化为结构化的函数调用
- 原理:LLM 负责理解 → 输出 JSON → 外部程序执行 → 返回结果
- 实现过程:定义函数 → 传给模型 → 模型生成调用 → 外部执行 → 返回结果
这样,模型就从 "纯文本对话" 升级成了一个 "可调度外部工具的智能代理"。
3.3 代码实例
示例1:计算数字
# 示例1:计算数字,函数中也可定义链接数据库进行数据运算
import json
from openai import OpenAI
# 定义求和函数
def sum_number(numbers):
# 参数是列表,需要转换成元算
total = 0
for number in numbers:
total += number
print("逐项相加:", numbers)
print("总和 = " + str(total))
return total
# return sum(numbers)
# 初始化客户端
client = OpenAI()
# 获取大模型回复
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0,
max_tokens=1824,
tools=[
{
# 用 JSON 描述函数,可以定义多个,由大模型决定是否调用
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "sum_number",
"description": "计算一组数的和",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"numbers": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "number"
}
}
},
"required": ["numbers"]
}
}
}
]
)
return response.choices[0].message
# ===== 示例 Prompt =====
# prompt = "我今年18岁,我的父亲今年38岁,我的爷爷今年72岁,我们一共多少岁了?"
# prompt = "中国首都是哪里?"
# prompt = "18减去38等于多少?"
# prompt = "13的平方等于多少?"
prompt = "新中国成立时,小明3岁,请问小明今年多大了?"
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家,你可以计算任何算式。"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
response = get_completion(messages) # 必须将上下文传入
messages.append(response)
print("===== GPT 第一次回答 =====")
print(response)
# ===== 解析函数调用 =====
if response.tool_calls is not None:
for tool_call in response.tool_calls: # 遍历所有函数调用
if tool_call.function.name == "sum_number":
# 调用本地函数
args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
result = sum_number(args["numbers"])
print("===== 本地函数返回结果 =====")
print(result)
# 将工具调用结果再传回给大模型
messages.append({
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识工具调用的 ID
"role": "tool",
"name": "sum_number",
"content": str(result) # 必须转成字符串
})
# 所有工具调用都完成后,再次请求大模型
print("===== GPT 最终回答 =====")
final_response = get_completion(messages)
print(final_response.content)示例2:获取天气
import requests
import json
from openai import OpenAI
# ====== 配置部分 ======
AMAP_API_KEY = "16e14c748bfe7df5a4d58fe74ef3deab"
client = OpenAI()
# ====== 本地函数:获取天气 ======
def get_city_weather(city: str):
"""
输入城市名(中文或英文),返回实况天气信息
"""
# 先通过高德地理编码 API 获取城市 adcode
geo_url = f"<https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/geo?address={city}&key={AMAP_API_KEY}>"
geo_resp = requests.get(geo_url).json()
if geo_resp.get("status") == "1" and geo_resp.get("geocodes"):
adcode = geo_resp["geocodes"][0]["adcode"]
else:
return f"无法获取城市 {city} 的编码"
# 再通过天气 API 获取天气
url = f"<https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?key={AMAP_API_KEY}&city={adcode}&extensions=base&output=JSON>"
response = requests.get(url).json()
print("response:", response)
if response.get("status") == "1" and response.get("lives"):
live = response["lives"][0]
return f"{live['province']}{live['city']} 天气:{live['weather']},气温 {live['temperature']}℃,{live['winddirection']}风 {live['windpower']}级,湿度 {live['humidity']}%(更新时间 {live['reporttime']})"
else:
return f"对不起,无法获取到 {city} 的天气信息。"
# ====== 定义工具(函数调用声明) ======
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_city_weather",
"description": "获取给定城市的实时天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "需要查询天气的城市(可以是中文或英文,例如 北京 或 Beijing)"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
}
]
# ====== 初始 Prompt ======
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "济南今天的天气怎么样?"}
]
# ====== 第一次调用 GPT,可能触发工具调用 ======
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)
response_message = response.choices[0].message
print("response_message:", response_message)
tool_calls = response_message.tool_calls
print("tool_calls:", tool_calls)
# ====== 如果 GPT 要调用工具,就执行本地函数 ======
if tool_calls:
messages.append(response_message) # 先把 assistant 的 tool_call 消息加进去
available_functions = {
"get_city_weather": get_city_weather
}
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
function_response = function_to_call(city=function_args.get("city"))
# 把工具执行结果返回给 GPT
messages.append({
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": str(function_response)
})
# ====== 再次调用 GPT,让它生成自然语言答案 ======
second_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=messages,
)
print("最终回答:", second_response.choices[0].message.content)示例3:爬虫+大模型
参考项目:https://github.com/ScrapeGraphAI/Scrapegraph-ai
12306车票信息爬取+大模型
示例4:简历筛选