前言
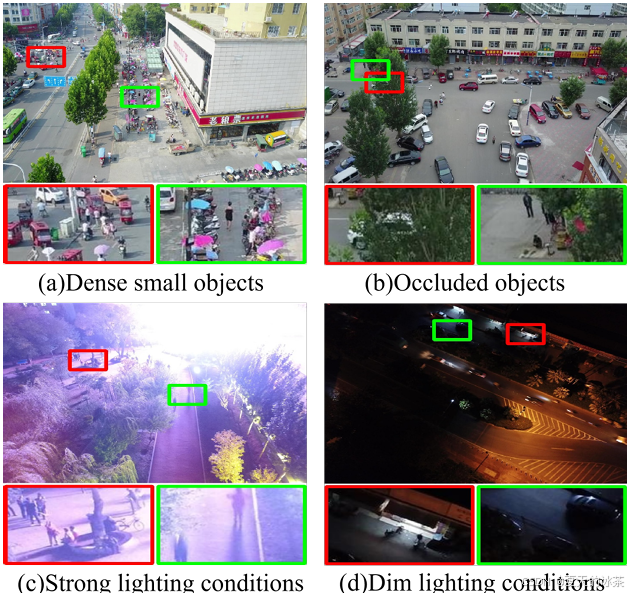
无人机高空俯拍视角下,目标物体(如行人、车辆等)在图像中呈现极高的空间密度和显著的重叠现象。特别是在小目标聚集区域,边界框之间的遮挡与重叠严重干扰了特征提取的准确性。飞行过程中遭遇的光照强度变化以及运动模糊会显著降低图像质量。因此提出了一种专为无人机设计的LAM-YOLO。提出了光遮挡注意力机制,用于增强不同光照条件下的小目标可见能力,集成了Involution模块以改善特征层之间的交互。其次,采用改进的SIB-IoU作为回归损失函数,以加速模型收敛并提高定位精度。最后,实现了一种新颖的检测策略,通过引入两个辅助检测头来识别更小规模的目标。

论文地址:2411.00485
注:此论文未开源代码,文中的代码均为复现。
我创建了一个用于存储小目标检测的复现仓库,欢迎start:Auorui/tiny-target-detection
网络整体结构
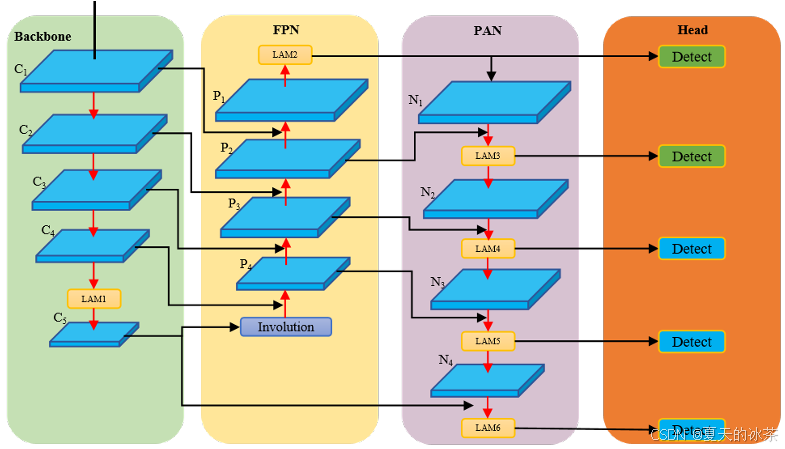
整体的结构还是按照YOLOv8改进的,光照-遮挡注意力模块(LAM)被分别插入到骨干网络的末端以及Neck部分的瓶颈层之后,该模块结合了通道注意力和自注意力机制,以增强模块的光照认知能力。
受Involution卷积机制的启发,在骨干网络和颈部之间加入了卷积块,以增强和共享通道信息,减少特征金字塔网络(FPN)初始阶段的信息损失。最后,引入了两个辅助检测头,分辨率为160×160和320×320,以提高对小目标的检测能力。
我觉得这里面唯一的问题就是检测头太多了,按理来说要增加小目标的准确性,加P2而不用P1,因为P1会导致模型参数量显著增加,计算复杂度急剧上升,同时容易引入过多噪声和背景干扰,反而降低检测性能。P2特征图具有适中的分辨率和语义信息,既能保留足够的细节用于小目标检测,又避免了P1层过高的空间冗余。
但还是考虑到实验的实际性,这里我们按照原文复现。
光照遮挡注意力模块LAM
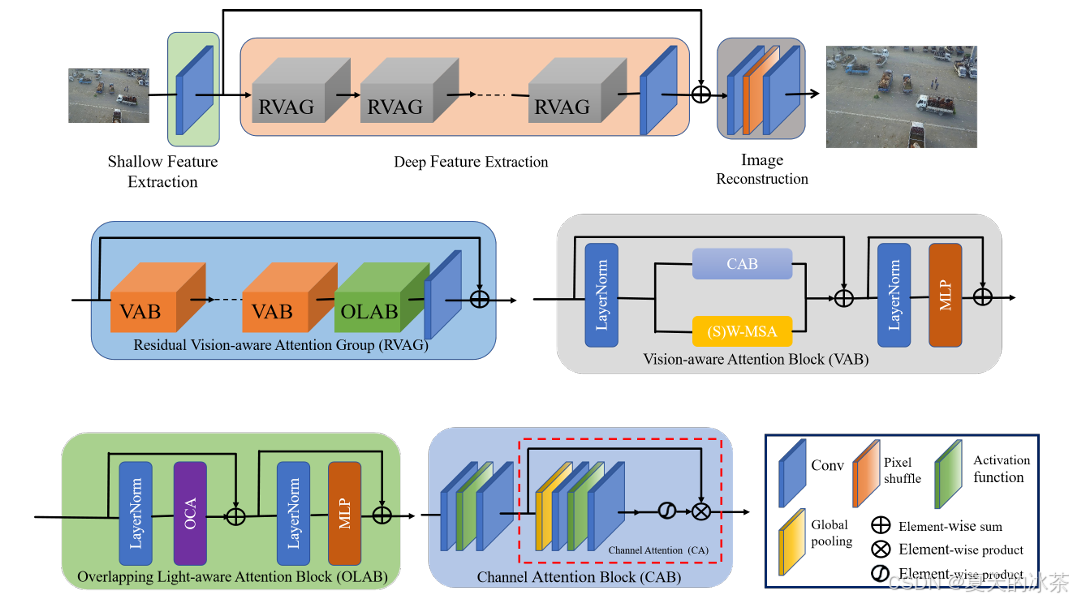
LAM的整体架构由三部分组成:浅层特征提取、深层特征提取和图像重建。
输入低分辨率特征,通过卷积层提取浅层特征,然后再使用一系列残差混合注意力组合RHAG与3×3卷积层Hconv(·)进行深层特征提取,最后通过重建模块重构高分辨率结果。
如上图所示,每个RHAG包含多个混合注意力块(HAB)、重叠交叉注意力块(OCAB)以及带残差连接的3×3卷积层。对于重建模块,采用像素打乱方法对融合特征进行上采样。
这篇文章写作有很大的问题,图文匹配不上对应的,还有很多的简称没用写,我猜测这个是预印本的问题,这里我还是按照图示一个一个来构建。
视觉感知注意力模块VAB
CAB就是本身就是一个通道注意力机制,这个简直是司空见惯了,它这里在通道注意力前面还有一个卷积+激活函数+卷积的一个组合,注意力机制里面是带有两个卷积层的,所以与ultralytics里面实现的有所不同,具体实现如下所示:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from ultralytics.nn.modules.conv import ChannelAttention
class CAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super(CAB, self).__init__()
self.conv_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, bias=True),
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, bias=True),
)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.ca = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim // 8, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(dim // 8, dim, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_block(x)
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.ca(y)
return x * y
if __name__ == "__main__":
dim = 64
batch_size = 4
height, width = 32, 32
input_tensor = torch.randn(batch_size, dim, height, width)
cab = CAB(dim=dim)
print(f"输入形状: {input_tensor.shape}")
output_tensor = cab(input_tensor)
print(f"输出形状: {output_tensor.shape}")(S)W-MSA这个模块没有在原文和图注中出现过,我猜测应该是Shifted Window Attention,不过一般应该简称是SW-MSA的才对,这个部分我们就直接采用官方的代替,但这里面有完全没用提到是如何去进行分为两分支的,写到这里我已经想放弃了。。。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from ultralytics.nn.modules import LayerNorm2d, ChannelAttention
from torchvision.models.swin_transformer import ShiftedWindowAttention, ShiftedWindowAttentionV2
class VAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, window_size=7, shift_size=0, num_heads=8, mlp_ratio=4.0):
super(VAB, self).__init__()
if isinstance(window_size, int):
window_size = [window_size, window_size]
if isinstance(shift_size, int):
shift_size = [shift_size, shift_size]
self.layer_norm1 = LayerNorm2d(dim)
self.layer_norm2 = LayerNorm2d(dim)
self.cab = CAB(dim)
self.sw_msa = ShiftedWindowAttention(
dim=dim,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=shift_size,
num_heads=num_heads
) # or use ShiftedWindowAttentionV2
hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, hidden_dim, 1),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, dim, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
x_norm = self.layer_norm1(x)
print(x_norm.shape)
# 左侧分支:SW-MSA(需要(B, H, W, C)格式)
# 从(B, C, H, W)转换为(B, H, W, C)
x_for_sw_msa = x_norm.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # (B, H, W, C)
x_left = self.sw_msa(x_for_sw_msa) # (B, H, W, C)
x_left = x_left.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# 右侧分支:CAB
x_right = self.cab(x)
x_out = x_left + x_right + identity
identity2 = x_out
x = self.layer_norm2(x_out)
x_out = self.mlp(x) + identity2
return x我从这篇文章里面看到了关于这里面的图:即插即用系列 | 2024 SOTA LAM-YOLO : 无人机小目标检测模型_lam-yolo: drones-based small object detection on l-CSDN博客
它左右的分支应该就是相加才对。
这里面的OLAB模块有面有一个OCA注意力,我找了一下,这个应该指的是Overlapping Cross Attention,然后大家猜猜我找到了什么东西,如下图这是SwinIR的工作图:
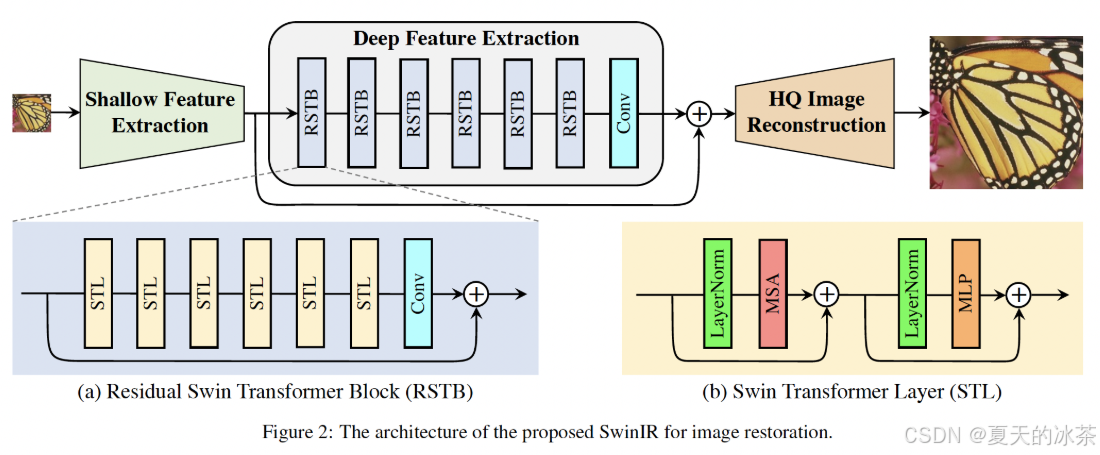
下面是关于HAT的工作图,但却是延续了SwinIR的基本结构,将RSTB升级成RHAG,内部的STL也对应升级成HAB,并且在每个Block中加入了一个OCAB。
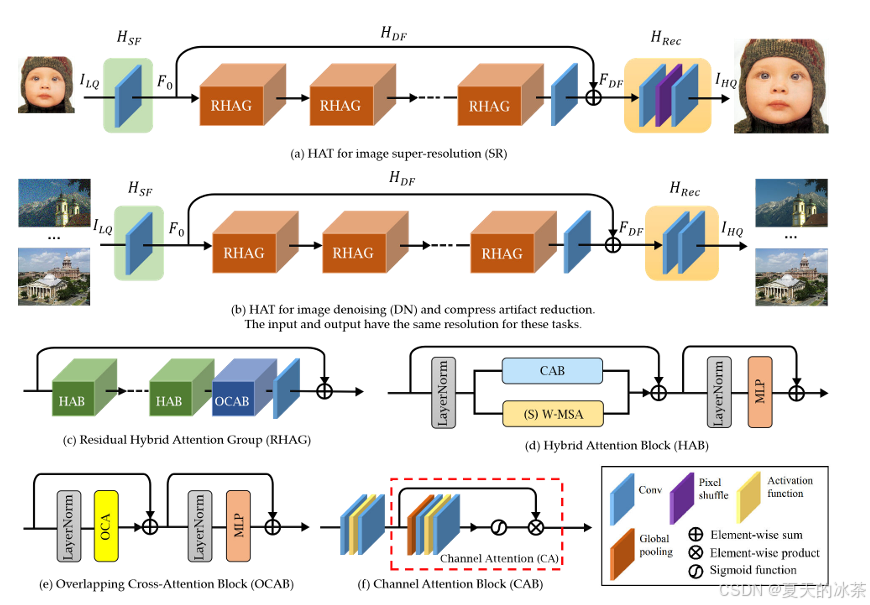
我的天呐,只能说还是太权威了,CVPR2023年的一篇文章图像复原的文章,我改吧改吧弄到目标检测里面整个四区,完全没毛病啊。这篇文章的仓库是:HAT/hat/archs/hat_arch.py at main · XPixelGroup/HAT
现在我也明白了为什么会出现论文名字和模块名不相符的问题,原来是搬过来还没改啊。
好,上面的我也不动就留着,我们现在从这篇CVPR的文章里面去找线索,首先是关于CAB模块:
python
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
"""Channel attention used in RCAN.
Args:
num_feat (int): Channel number of intermediate features.
squeeze_factor (int): Channel squeeze factor. Default: 16.
"""
def __init__(self, num_feat, squeeze_factor=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.attention = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat // squeeze_factor, 1, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat // squeeze_factor, num_feat, 1, padding=0),
nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, x):
y = self.attention(x)
return x * y
class CAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_feat, compress_ratio=3, squeeze_factor=30):
super(CAB, self).__init__()
self.cab = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat // compress_ratio, 3, 1, 1),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat // compress_ratio, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),
ChannelAttention(num_feat, squeeze_factor)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cab(x)基本与我的想法一致,只是因为我想到是采用ultralytics,或许用的是SiLU激活函数。
原本的HAB->VAB:
python
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.checkpoint as checkpoint
from einops import rearrange
from ultralytics.nn.extra_modules import to_2tuple
from timm.layers import trunc_normal_
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
From: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/layers/drop.py
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0], ) + (1, ) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
From: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/layers/drop.py
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
"""Channel attention used in RCAN.
Args:
num_feat (int): Channel number of intermediate features.
squeeze_factor (int): Channel squeeze factor. Default: 16.
"""
def __init__(self, num_feat, squeeze_factor=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.attention = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat // squeeze_factor, 1, padding=0),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat // squeeze_factor, num_feat, 1, padding=0),
nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, x):
y = self.attention(x)
return x * y
class CAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_feat, compress_ratio=3, squeeze_factor=30):
super(CAB, self).__init__()
self.cab = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat // compress_ratio, 3, 1, 1),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Conv2d(num_feat // compress_ratio, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),
ChannelAttention(num_feat, squeeze_factor)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cab(x)
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
def window_partition(x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (b, h, w, c)
window_size (int): window size
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*b, window_size, window_size, c)
"""
b, h, w, c = x.shape
x = x.view(b, h // window_size, window_size, w // window_size, window_size, c)
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, c)
return windows
def window_reverse(windows, window_size, h, w):
"""
Args:
windows: (num_windows*b, window_size, window_size, c)
window_size (int): Window size
h (int): Height of image
w (int): Width of image
Returns:
x: (b, h, w, c)
"""
b = int(windows.shape[0] / (h * w / window_size / window_size))
x = windows.view(b, h // window_size, w // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(b, h, w, -1)
return x
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim**-0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, rpi, mask=None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*b, n, c)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
b_, n, c = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(b_, n, 3, self.num_heads, c // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[rpi.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
nw = mask.shape[0]
attn = attn.view(b_ // nw, nw, self.num_heads, n, n) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, n, n)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(b_, n, c)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class HAB(nn.Module):
r""" Hybrid Attention Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self,
dim,
input_resolution,
num_heads,
window_size=7,
shift_size=0,
compress_ratio=3,
squeeze_factor=30,
conv_scale=0.01,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
drop=0.,
attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size:
# if window size is larger than input resolution, we don't partition windows
self.shift_size = 0
self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution)
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, 'shift_size must in 0-window_size'
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim,
window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size),
num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
proj_drop=drop)
self.conv_scale = conv_scale
self.conv_block = CAB(num_feat=dim, compress_ratio=compress_ratio, squeeze_factor=squeeze_factor)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x, x_size, rpi_sa, attn_mask):
h, w = x_size
b, _, c = x.shape
# assert seq_len == h * w, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(b, h, w, c)
# Conv_X
conv_x = self.conv_block(x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2))
conv_x = conv_x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(b, h * w, c)
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
attn_mask = attn_mask
else:
shifted_x = x
attn_mask = None
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nw*b, window_size, window_size, c
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, c) # nw*b, window_size*window_size, c
# W-MSA/SW-MSA (to be compatible for testing on images whose shapes are the multiple of window size
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, rpi=rpi_sa, mask=attn_mask)
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, c)
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, h, w) # b h' w' c
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
attn_x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
attn_x = shifted_x
attn_x = attn_x.view(b, h * w, c)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(attn_x) + conv_x * self.conv_scale
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x与我本身的实现也差不多是一致的,只是我为了图方便从torchvision里面导入的。
这里稍微简化一下其结构:
python
class LAM(HAT):
def __init__(self, embed_dim):
super(LAM, self).__init__(
embed_dim=embed_dim,
in_chans=embed_dim,
depths=(2, ),
num_heads=(4, )
)Involution卷积模块
出自这一篇文章:arxiv.org/pdf/2103.06255
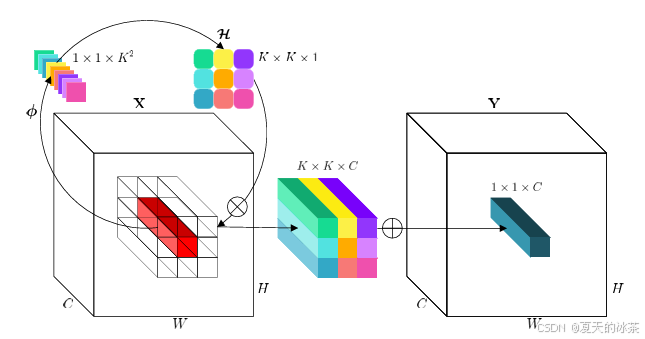
此为原图图示,是一篇CVPR2021年的一篇文章,lam-yolo里面绘制的和这个差不多,我想作者应该不会就这样投出去,大概率是在图上面重修修改了一下,我这里也不纠结了,只希望下次找一篇好的文章来看。
python
class involution(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
channels,
kernel_size,
stride):
super(involution, self).__init__()
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.stride = stride
self.channels = channels
reduction_ratio = 4
self.group_channels = 16
self.groups = self.channels // self.group_channels
self.conv1 = ConvNormAct(
in_channels=channels,
out_channels=channels // reduction_ratio,
kernel_size=1)
self.conv2 = ConvNormAct(
in_channels=channels // reduction_ratio,
out_channels=kernel_size**2 * self.groups,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1)
if stride > 1:
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(stride, stride)
self.unfold = nn.Unfold(kernel_size, 1, (kernel_size-1)//2, stride)
def forward(self, x):
weight = self.conv2(self.conv1(x if self.stride == 1 else self.avgpool(x)))
b, c, h, w = weight.shape
weight = weight.view(b, self.groups, self.kernel_size**2, h, w).unsqueeze(2)
out = self.unfold(x).view(b, self.groups, self.group_channels, self.kernel_size**2, h, w)
out = (weight * out).sum(dim=3).view(b, self.channels, h, w)
return out消融实验
关于它这里的损失函数就不研究,以后有空闲再专门研究一下这些损失函数。
配置文件如下所示:
python
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
# Ultralytics YOLOv8 object detection model with P3/8 - P5/32 outputs
# Model docs: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8
# Task docs: https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 129 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPS
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 129 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPS
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 169 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPS
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 209 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPS
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 209 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPS
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# input -> 640×640×3
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2 C1 320×320×64
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4 160×160×128
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]] # C2 160×160×128
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8 80×80×256
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]] # C3 80×80×256
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16 40×40×512
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]] # C4 40×40×512
- [-1, 1, LAM, [512]] # 7 LAM 1 between C4 and C5 (使用默认参数)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 8-P5/32 20×20×1024
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]] # 20×20×1024
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 10 C5 20×20×1024
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
# FPN 路径(自顶向下)
- [-1, 1, involution, [1024, 7, 1]] # 11
# 上采样 P5 -> P4
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] # 40×40×1024
# 连接 P4 和上采样后的 P5
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4 (注意索引还是为6,不是与LAM层相拼接)
# 融合特征
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 14 40×40×512
# 上采样 P4 -> P3
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] # 15 80×80×512
# 连接 P3 和上采样后的 P4
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # 16 cat backbone P3
# 融合特征 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 17 (P3/8-small) 80×80×256
# 上采样 P3 -> P2
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] # 18 160×160×256
# 连接 P2 和上采样后的 P3
- [[-1, 2], 1, Concat, [1]] # 19 cat backbone P3
# 融合特征 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128]] # 20 (P3/8-small) 160×160×128
# 上采样 P2 -> P1
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] # 21 320×320×128
# 连接 P2 和上采样后的 P3
- [[-1, 0], 1, Concat, [1]] # 22 cat backbone P3
# 融合特征 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 3, C2f, [64]] # 23 (P3/8-small) 320×320×64
- [-1, 1, LAM, [64]] # 24 LAM 2 after FPN
# PAN 路径(自底向上)
# 下采样 P1 -> P2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 20], 1, Concat, [1]]
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128]]
- [-1, 1, LAM, [128]] # 28 LAM after P2 downsampling
# 下采样 P2 -> P3
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 17], 1, Concat, [1]]
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]]
- [-1, 1, LAM, [256]] # 32 LAM after P3 downsampling
# 下采样 P3 -> P4
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]]
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]]
- [-1, 1, LAM, [512]] # 36 LAM after P4 downsampling
# 下采样 P4 -> P5
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # with C5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]]
- [-1, 1, LAM, [1024]] # 40 LAM after P5 downsampling
# 检测头
- [[24, 28, 32, 36, 40], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P1, P3, P4, P5)精度 (P): 0.717
召回率 (R): 0.108
mAP50 (IoU=0.5时的平均精度): 0.126
mAP50-95 (IoU=0.5到0.95的平均精度): 0.0559