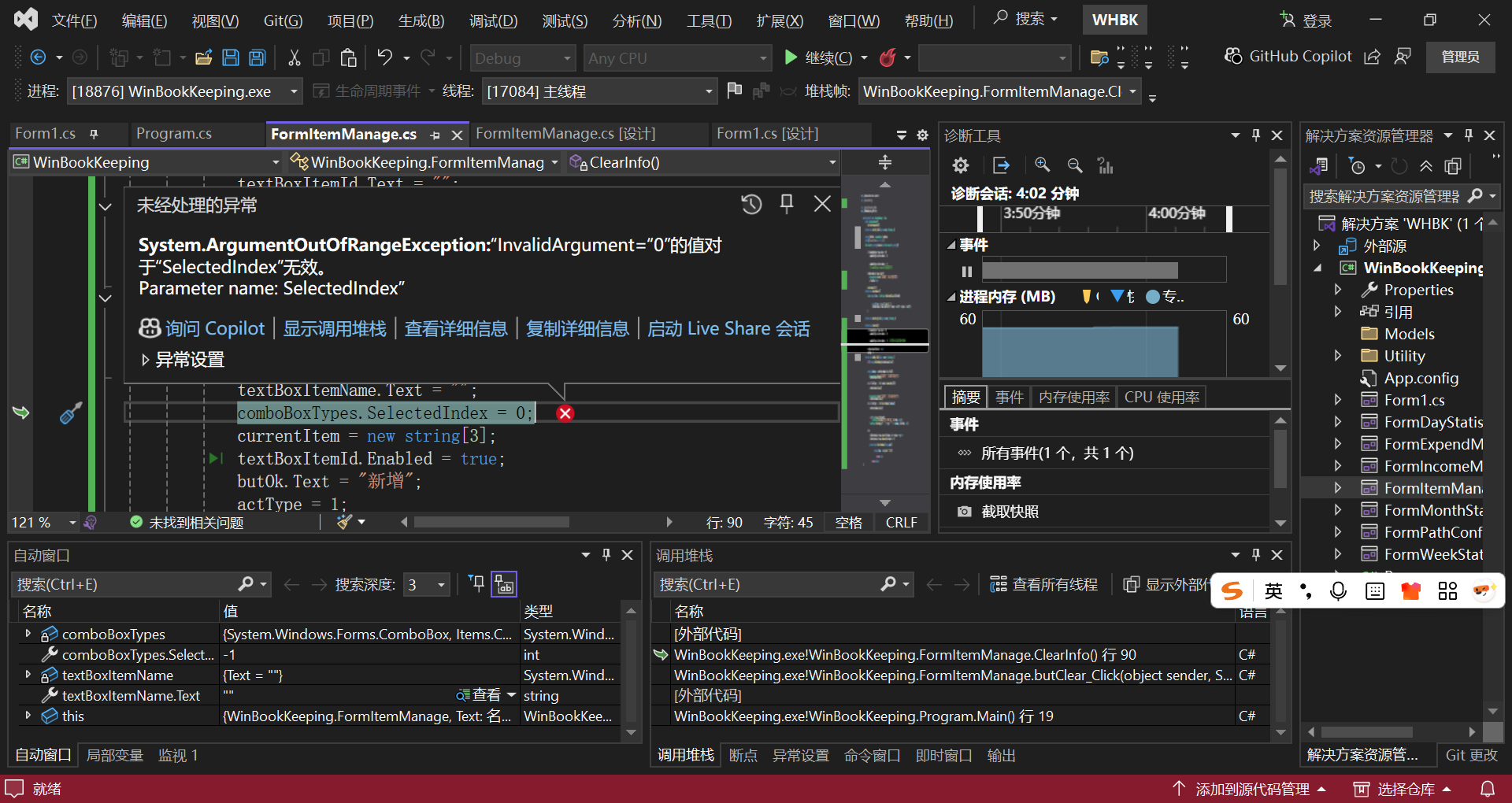
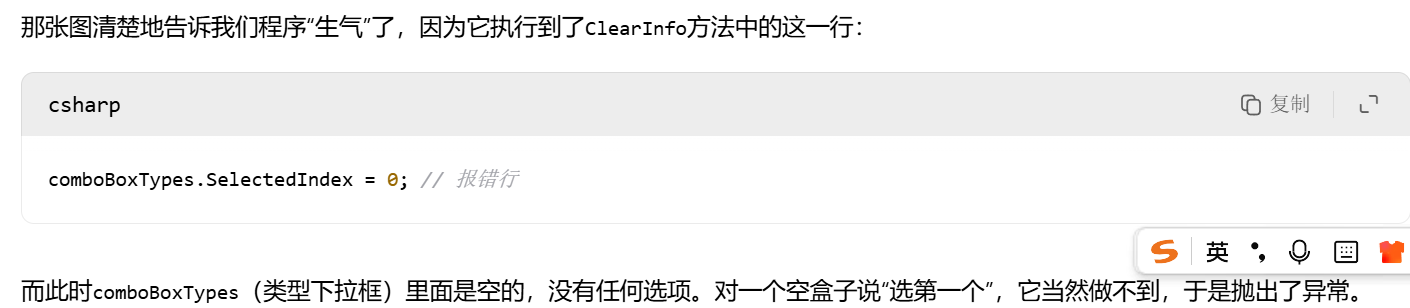
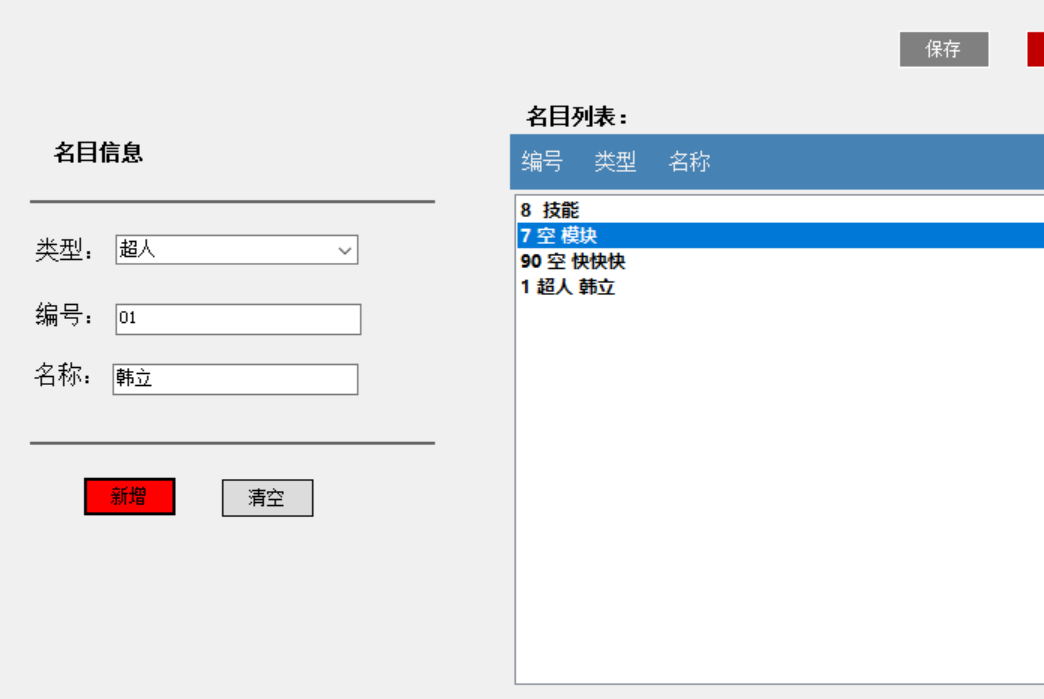
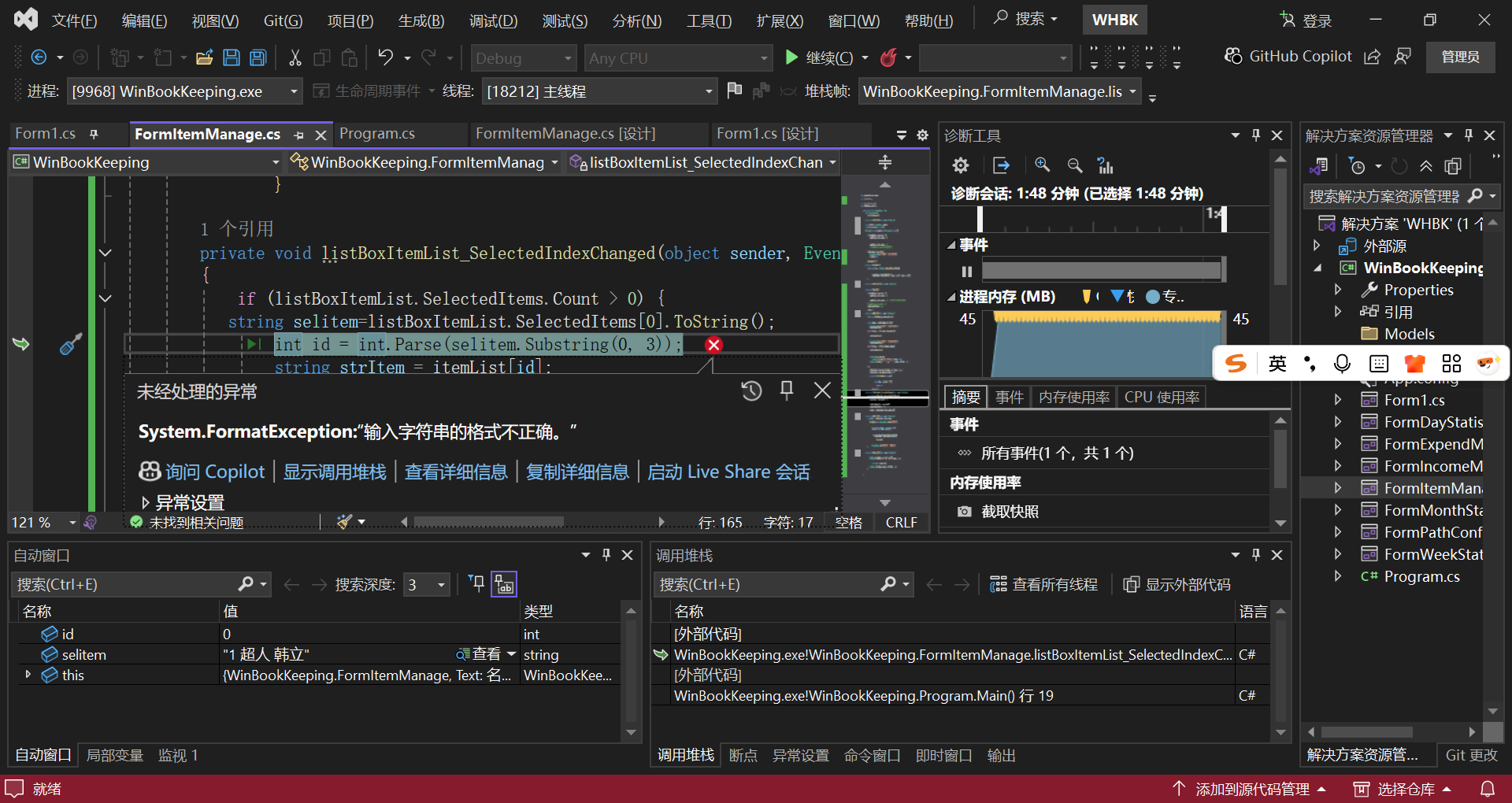
列表中的行无法成功删除
csharp
private void LoadItemList()
{
List<string> lines = TextHelper.ReadTextAllLines(filePath);
if (lines.Count > 1)
{
for (int i = 1; i < lines.Count; i++)
{
string[] arr = lines[i].Split(';');
listBoxItemList.Items.Add(arr[0] + wSpace + arr[1] + wSpace + arr[2]);
itemList.Add(int.Parse(arr[0]), lines[i]);
}
}
}//怎么理解 List<string> lines = TextHelper.ReadTextAllLines(filePath); line作用 我新增相应名目 是保存在filepath中吗



csharp
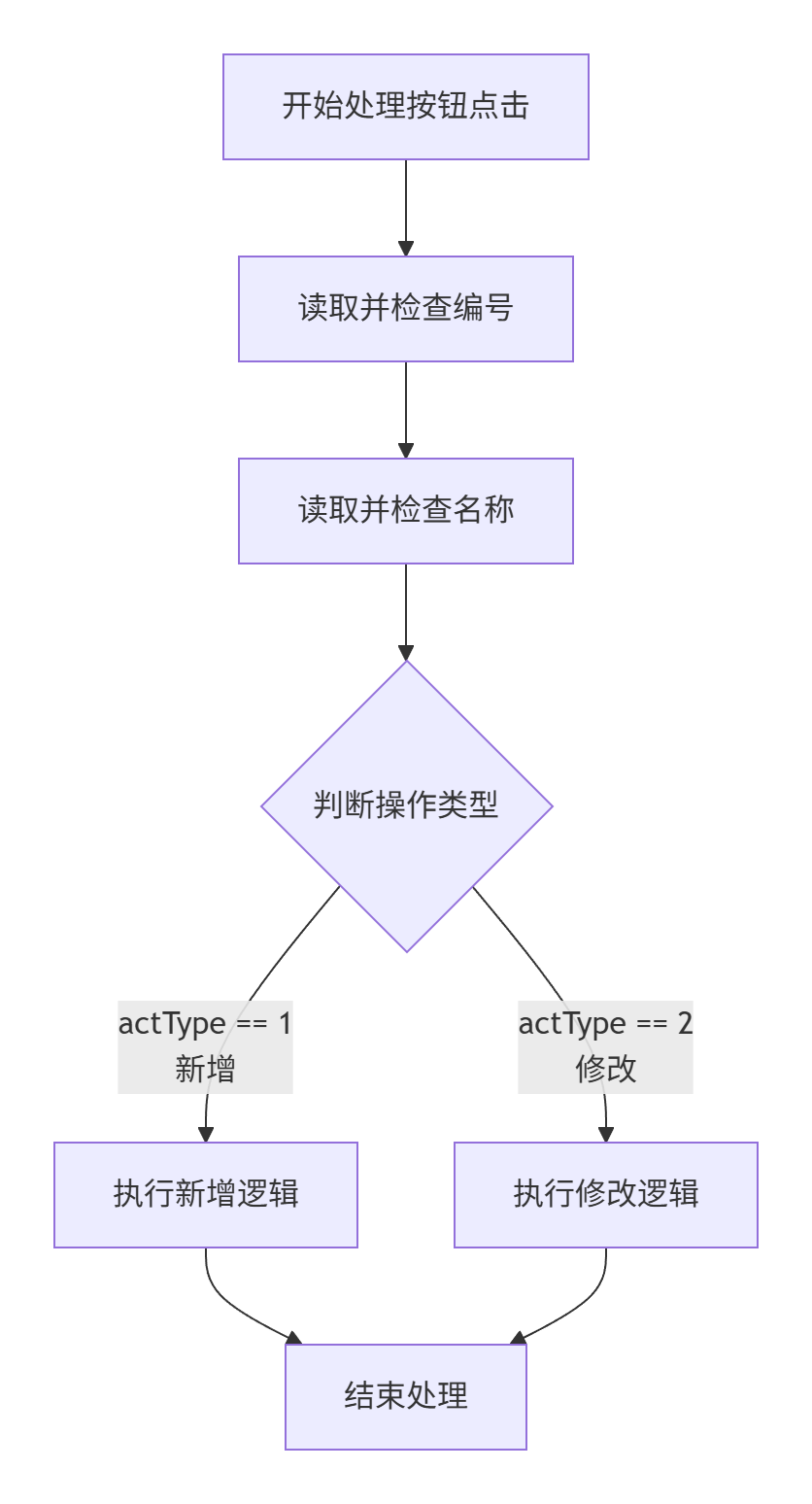
private void butOk_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int id = 0;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(textBoxItemId.Text))
{
id = Convert.ToInt32(textBoxItemId.Text);
}
string type = comboBoxTypes.Text.Trim();
string itemName = textBoxItemName.Text.Trim();
if (id == 0)
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目编号不能为空");
textBoxItemId.Focus();
return;
}
else if (actType == 1 && itemList.ContainsKey(id))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目编号已存在");
textBoxItemId.Focus();
return;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(itemName))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目名称不能为空");
textBoxItemName.Focus();
return;
}
else if (actType == 1 && ExistItemName(itemName))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目名称已存在!");
textBoxItemName.Focus();
return;
}
if (actType == 1)
{
if (!File.Exists(filePath))
{
TextHelper.WriteMsg("编号;类型;名称", filePath, false);
}
TextHelper.WriteMsg(id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName, filePath, true);
listBoxItemList.Items.Add(id + wSpace + type + wSpace + itemName);
itemList.Add(id, id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName);
}
else
{
itemList[id]=id+";"+type+";"+itemName;
listBoxItemList.Items.Insert(selIndex, id + wSpace + type +
wSpace + itemName);
listBoxItemList.Items.RemoveAt(selIndex + 1);
}
}
csharp
if (actType == 1)
{
if (!File.Exists(filePath))
{
TextHelper.WriteMsg("编号;类型;名称", filePath, false);
}
TextHelper.WriteMsg(id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName, filePath, true);
listBoxItemList.Items.Add(id + wSpace + type + wSpace + itemName);
itemList.Add(id, id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName);
}



在 butOk_Click这个方法中,不是已经实现了修改操作吗?为什么还需要listBoxItemList_SelectedIndexChanged这个方法





csharp
private void butOk_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int id = 0;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(textBoxItemId.Text))
{
id = Convert.ToInt32(textBoxItemId.Text);
}
string type = comboBoxTypes.Text.Trim();
string itemName = textBoxItemName.Text.Trim();
if (id == 0)
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目编号不能为空");
textBoxItemId.Focus();
return;
}
else if (actType == 1 && itemList.ContainsKey(id))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目编号已存在");
textBoxItemId.Focus();
return;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(itemName))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目名称不能为空");
textBoxItemName.Focus();
return;
}
else if (actType == 1 && ExistItemName(itemName))
{
MessageHelper.Error("名目提交", "名目名称已存在!");
textBoxItemName.Focus();
return;
}
if (actType == 1)
{
if (!File.Exists(filePath))
{
TextHelper.WriteMsg("编号;类型;名称", filePath, false);
}//这段代码先检查数据文件是否存在。
//如果不存在(比如第一次使用程序),
//就调用TextHelper.WriteMsg方法创建文件。
//这里的第二个参数是false,意味着覆盖写入。所以这行代码会写入标题行编号; 类型; 名称,为后续的数据记录建立格式
TextHelper.WriteMsg(id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName, filePath, true);
//紧接着,将新名目的信息(编号、类型、名称)用分号;
//拼接成一行(例如 "1;支出;早餐"),然后再次调用TextHelper.WriteMsg。
// 注意这里的第二个参数是true,这代表追加模式。新数据会被添加到文件末尾,不会影响已有的内容
listBoxItemList.Items.Add(id + wSpace + type + wSpace + itemName);
//这行代码将新名目以更易读的格式(例如用空格连接:"1 支出 早餐")
//添加到窗体的ListBox控件中
//Items.Add方法会在列表的末尾添加一个新项。
itemList.Add(id, id + ";" + type + ";" + itemName);
//为了程序运行时能快速查询和操作数据,需要在内存中也保存一份名目信息。
//简单来说,当你新增一个名目时,这段代码像一位细心的管家,会同时完成三件事:
// 记入账本:把新项目追加到硬盘上的数据文件里,永久保存。
//更新清单:在窗口的列表里立刻显示出新项目,让你能看到。
//更新备忘录:在程序的内存里也存一份,方便后续快速处理。
}
else
{
itemList[id]=id+";"+type+";"+itemName;//更新内存数据
//itemList是一个在内存中存储所有名目信息的字典(Dictionary)。
//这行代码直接通过名目编号(id)找到对应的条目,
//并将其值更新为修改后的新信息(用分号拼接的字符串)。这确保了内存中的数据是最新的
listBoxItemList.Items.Insert(selIndex, id + wSpace + type +
wSpace + itemName);
//在列表框中插入新项
//selIndex是当前选中项在列表框中的原始位置索引。
//Items.Insert方法用于在列表的指定位置插入一个新项。
//这里是在原位置(selIndex)插入修改后名目的新字符串(用空格连接,便于显示)
listBoxItemList.Items.RemoveAt(selIndex + 1);
//从列表框中移除旧项
//由于上一步操作是在原位置插入了一项,原来选中的那个旧项并没有被删除,而是被挤到了下一位(位置变成了 selIndex + 1)。
//因此,这行代码的作用就是移除这个已经过时的旧项。通过 Items.RemoveAt方法,根据索引精确删除指定项
}
//这种"先插入,后删除"的操作方式,其核心目的是为了保持修改后的名目在列表中的位置不变。如果直接修改原位置的项内容,在某些控件中可能不够直接或会触发不必要的刷新问题。
//而先插入新内容再删除旧内容,是一种常见且可靠的实现原地更新效果的方法。
}
private bool ExistItemName(string name) {
foreach (int key in itemList.Keys)
{
string val = itemList[key];
string iName = val.Split(';')[2];
if (iName == name)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void listBoxItemList_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{//事件处理方法。它的作用就像一个小助手,每当你在列表里点击选择一个不同的名目时,
//这个小助手就会自动跳出来工作
if (listBoxItemList.SelectedItems.Count > 0)
{//小助手首先会确认你是不是真的点中了一个名目。
//这是为了防止在列表为空时发生错误。
string selitem=listBoxItemList.SelectedItems[0].ToString();
//接着,它把你选中的那一行文字(比如 "1 支出 买菜")整个拿出来
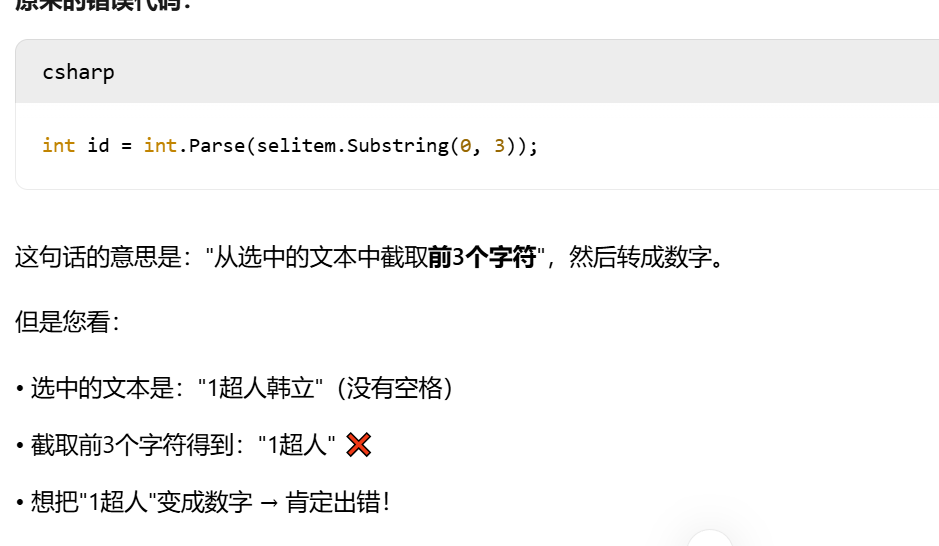
//int id = int.Parse(selitem.Substring(0, 3));
string[] parts = selitem.Split(' ');
if (parts.Length > 0 && int.TryParse(parts[0], out int id))
{//然后,它把这串文字用空格分开,并尝试把第一个部分(就是编号)转换成数字。
//这一步很关键,因为编号是找到对应名目详细资料的"钥匙"
if (itemList.ContainsKey(id))
{//拿到"钥匙"(编号)后,小助手会去一个叫 itemList的大资料库(字典)里,
//找出这个名目最详细的原始记录(是用分号分隔的完整字符串,如 "1;支出;买菜")
string strItem = itemList[id];
//if (itemList.ContainsKey(id)) { }
//int id = int.Parse(parts[0]);
//string strItem = itemList[id];
currentItem = strItem.Split(';');
textBoxItemId.Text = currentItem[0];
textBoxItemName.Text = currentItem[2];
comboBoxTypes.Text = currentItem[1];
//找到后,它就把这条详细记录拆开,分别填到右边的各个输入框里:
// 编号填到 textBoxItemId
//名称填到 textBoxItemName
//类型填到 comboBoxTypes
textBoxItemId.Enabled = false;
//把编号输入框锁住 (textBoxItemId.Enabled = false),防止你误修改关键的编号。
actType = 2;
//把 actType变量设置为 2,告诉程序:"现在是修改模式哦!"
butOk.Text = "修改";
//
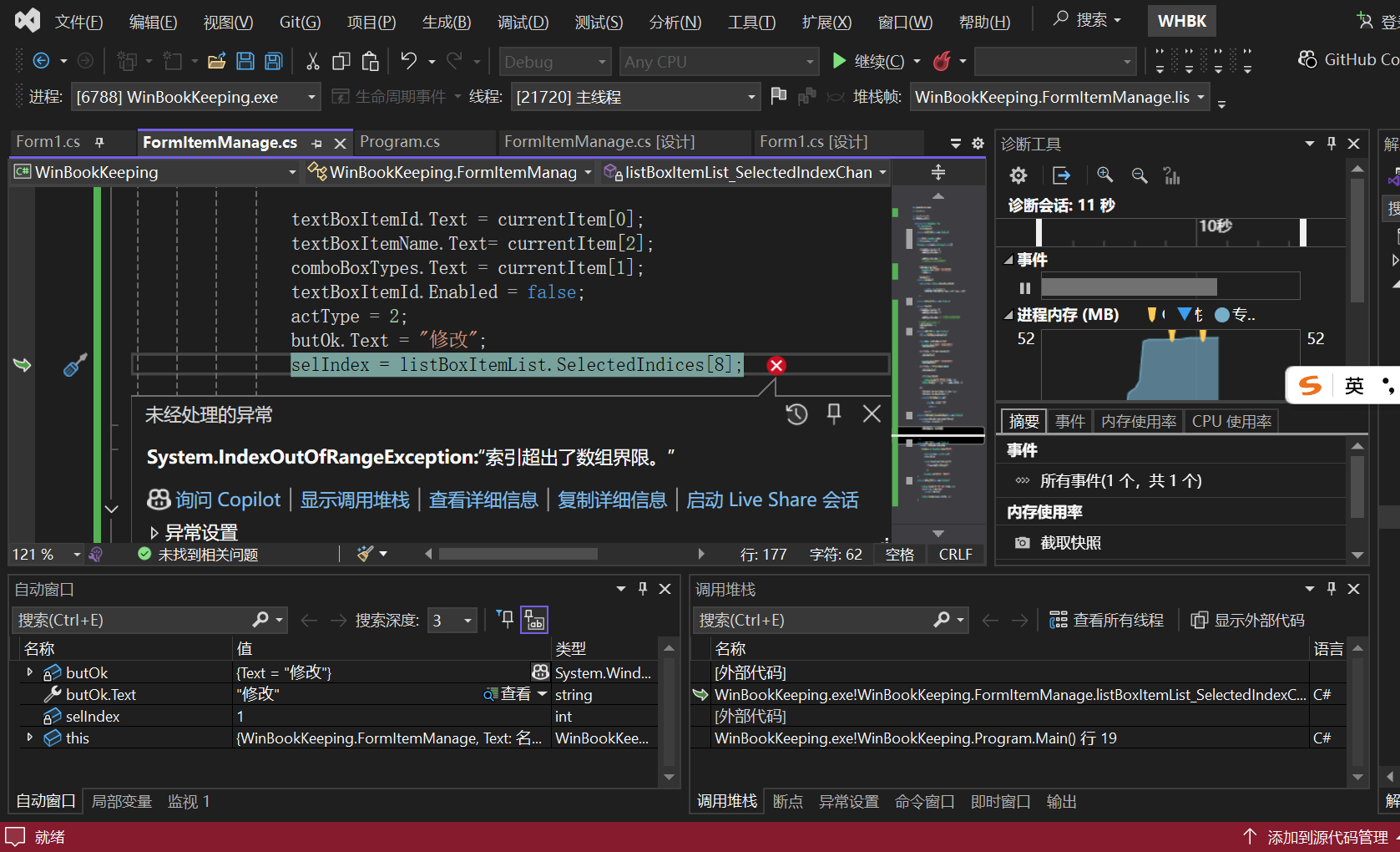
selIndex = listBoxItemList.SelectedIndex;
//把"新增"按钮的文字改成"修改"(butOk.Text = "修改"),让你清楚接下来要做什么操作。
//记录下当前选中的是列表中的第几项(selIndex),方便之后修改时准确定位。
}
}//,这个方法的核心逻辑是:通过界面选中的显示文本解析出唯一标识(ID),
//再利用此ID从数据源中获取完整信息,最后用这些信息更新编辑表单
// 实现交互:让用户能够通过简单的点击操作来选择和查看现有名目的详细信息。
//准备编辑:在填充表单的同时,将整个界面的状态从"准备新增"切换到"准备修改",为后续的保存操作做好准备。
//保持一致性:确保界面显示(listBoxItemList)、内存中的数据模型(itemList) 和编辑表单上的信息是同步的。
else
{
MessageHelper.Error("错误", "无法解析编号");
}
}
}
// 它的核心价值在于,它让程序能够即时响应你的选择动作 。想象一下,如果你点击一个名目后,右边的输入框没有任何变化,那这个程序用起来就会非常不方便。
// 而这个事件处理程序正是实现了这种"点击即显示"的流畅交互体验。
//listBoxItemList_SelectedIndexChanged 是 响应选择,负责 "开始编辑" ,它的工作是准备。
//butOk_Click 是 响应点击,负责 "确认更改" ,它的工作是执行。
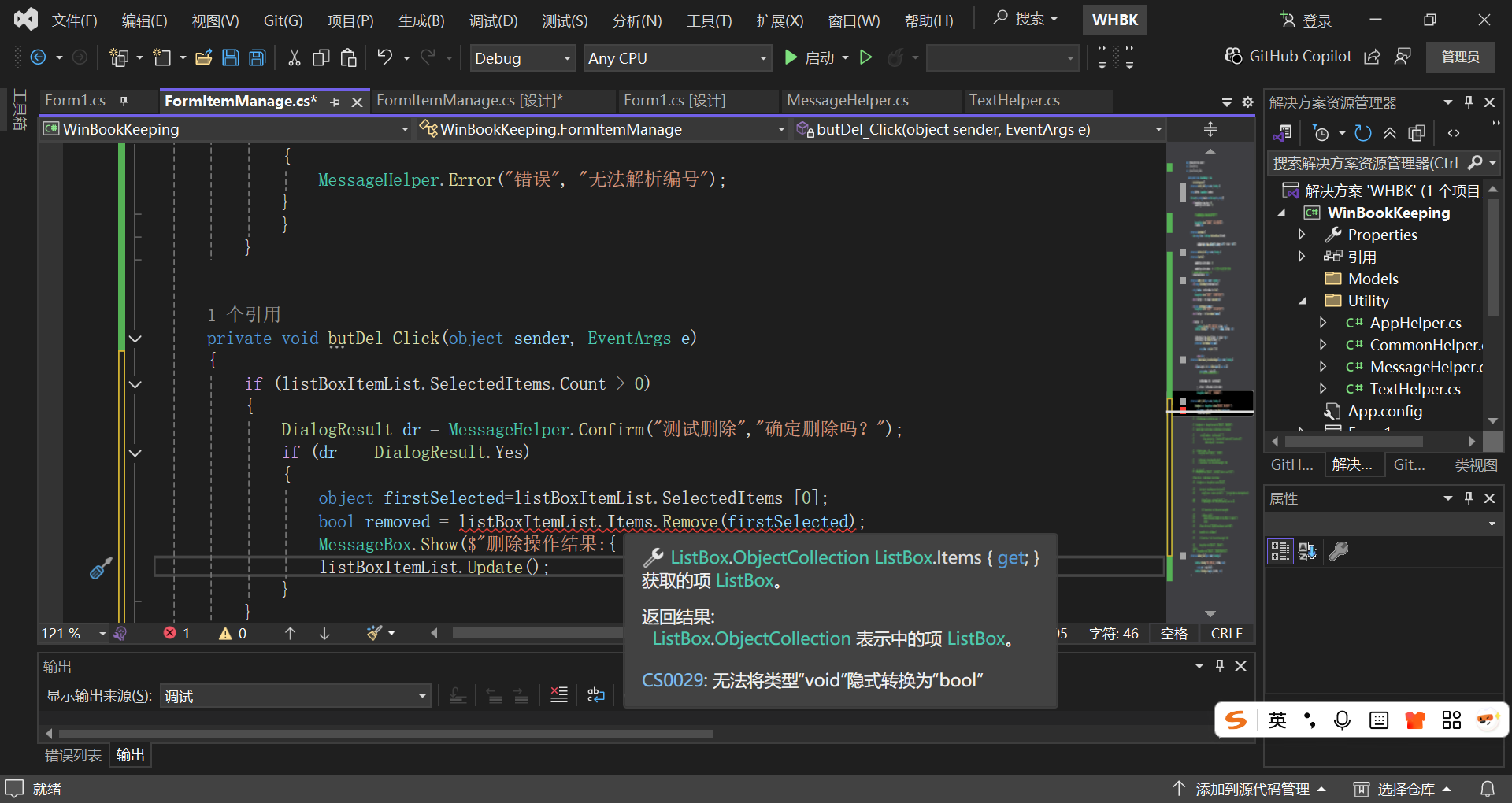
private void butDel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 超级详细的调试版本
if (listBoxIt