引言
在 前一节 中初步尝试使用 colmap + MVS 流程重建了人物的 三维模型, 但是还遗留了 执行时间偏长(几个小时), 结果遗留噪声, 部分区域显得有些粗糙等问题。
前一节直接使用了 openMVS 官方 编译好的 exe 以及程序默认参数,来生成结果。本节试着通过编写程序的方式, 来走一遍 openMVS 的流程, 顺便进一步了解 OpenMVS API, 看看能否按照自己的需求,来调节参数,处理上面遗留的一些问题。
故本节主要梳理 OpenMVS 流程的 API 调用 与 入参的含义。
最终本次实验中, 生成的模型结果如下
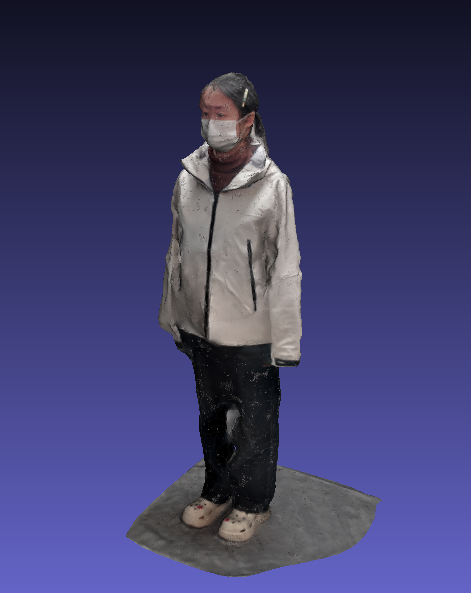
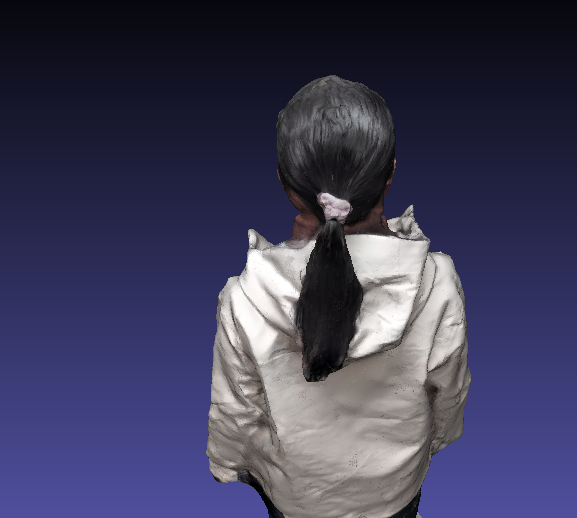


观感上比之前 好了不少

另外, 本次试验中几个主要步骤的耗时如下
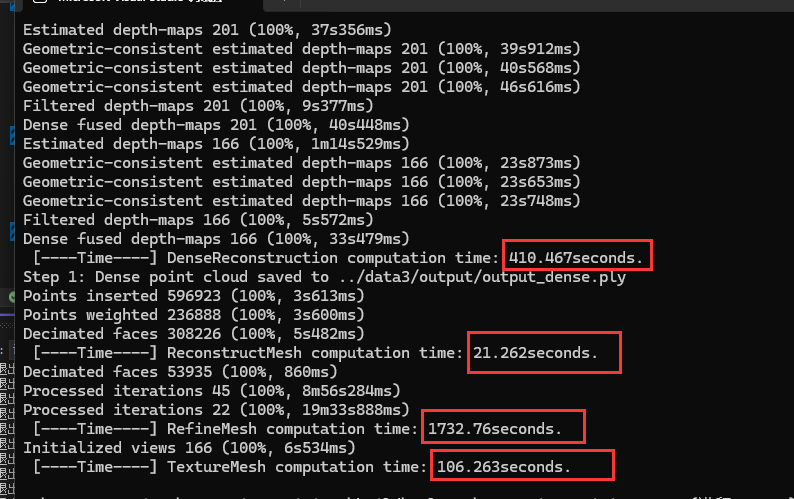 总的流程跑下来大致是 38 分钟 左右(设备: RTX2060, Core i7-10875, 实验时没带充电器,笔记本用电池运行,通电应该能更快一些)。
总的流程跑下来大致是 38 分钟 左右(设备: RTX2060, Core i7-10875, 实验时没带充电器,笔记本用电池运行,通电应该能更快一些)。
此次,最耗时的主要是 refineMesh 那一步, 后续看看是否还能优化。
0.Scene 类与一些基础操作
OpenMVS 流程的几个主要操作都以 Scene 的成员方法的形式进行了封装。
【1】加载 mvs 文件
Scene scene(MAX_THREADS_NUM);
if (scene.Load(INPUT_MVS_FILE) == Scene::SCENE_NA) {
std::cerr << "Failed to load input scene: " << INPUT_MVS_FILE << std::endl;
return LOAD_INPUT_SCENE_FAILED;
}【2】保存 mvs 文件
scene.Save(OUTPUT_SCENE_ROI_TO_MVS);【3】保存 mesh 文件
scene.mesh.Save(OUTPUT_ORIGIN_MESH);1.scene.DenseReconstruction 生成稠密点云
【0】生成稠密点云前,先计算 ROI(Bounding box)范围,然后将 ROI 之外的无用点去除掉,避免其参与计算
scene.EstimateROI(1.0f, -1);// 使用第一个缩放参数可以整体调整生成的 ROI boundingBox 的大小。(无法只沿着某个方向缩小, 不过也够用)
scene.CropToROI(scene.obb);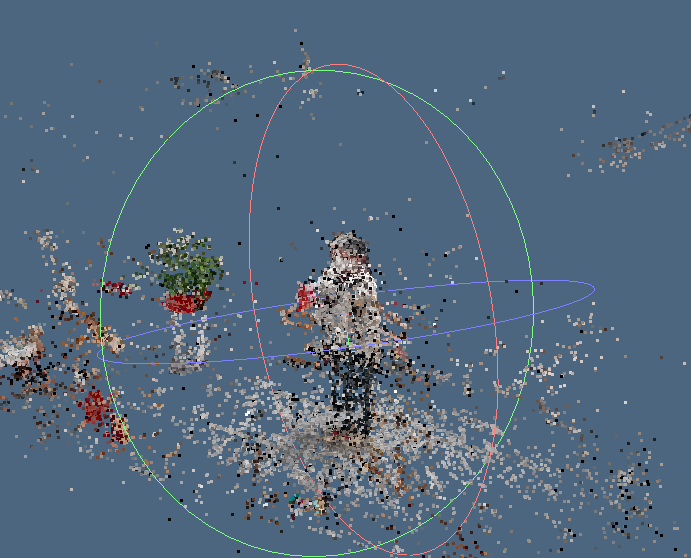
【1】调用函数前需要通过如下方式先进行参数配置
OPTDENSE::init();
MVS::OPTDENSE::update();
OPTDENSE::nResolutionLevel = 1; // How many times to scale down the images before dense reconstruction (0=original,
// 1=half, 2=quarter, etc.).Higher values process faster but produce less detail.
OPTDENSE::nMaxResolution = 2560; // Maximum image resolution in pixels. Images larger than this will be downscaled to
// this resolution.Set to 0 for no limit.
OPTDENSE::nMinResolution = 640; // Minimum image resolution in pixels.Images can not be downscaled to a resolution
// smaller than this.
OPTDENSE::nSubResolutionLevels = 1; // Number of additional lower resolution levels to process for better multi-scale
// depth estimation.0 means only process at the selected resolution level.
OPTDENSE::nNumViews = 4; // Number of neighbor images to use for depth estimation (0 to select valid views).
// More views increase accuracy, but slow down processing.
OPTDENSE::nMinViews = 4; // Minimum number of views in which a point must be visible to be considered during
// neighbor views estimation. Higher values produce more similar neighbor views,
// but may discard some valid points.
OPTDENSE::nMinViewsFuse = 5; // Minimum number of views required to include a depth point in the final fused point
// cloud. Higher values produce cleaner results, but may lose coverage.
//(融合到最终点云中所需的最小视图数量。数值越高,结果越干净,但可能会降低覆盖范围。)
OPTDENSE::nMinViewsTrustPoint = 3; // Minimum number of views for a point to be considered for approximating the
// depth-maps during initialization (<2 - random initialization).
OPTDENSE::nEstimationIters = 5; // Number of iterations for photometric refinement of each depth estimate.More
// iterations improve accuracy, but increase computation time.
OPTDENSE::nEstimationGeometricIters = 3; // Number of iterations for geometric consistency filtering (0 disabled). More
// iterations may produce more accurate results, but increase computation time.
OPTDENSE::nEstimateColors = 2; // Estimate color for each point in the dense cloud based on the source images.
// Disable to skip color computation.
OPTDENSE::nEstimateNormals = 2; // Store estimated normals for each point. Normals are useful for surface
// reconstruction and visualization.
OPTDENSE::nFuseFilter = 2; // Fusion quality level:- Merge only(0): Fast, just merge all points;
// Fuse(1): Standard fusion with outlier removal;
// Dense fuse(2): Slower but produces the densest, highest quality result
OPTDENSE::nOptimize = 4; // flags used to filter the depth-maps after estimation (0 - disabled,
// 1 - remove-speckles, 2 - fill-gaps, 4 - adjust-confidence) 并且这个值是可以叠加的
//(按位运算理解 如果是 5(4 + 1), 即应用了移除噪点(1), 又调整了置信度(4))
OPTDENSE::nIgnoreMaskLabel = -1; // label value to ignore in the image mask, stored in the MVS scene or next to each
// image with '.mask.png' extension (<0 - disabled)
OPTDENSE::fDepthReprojectionErrorThreshold = 0.5f; // dense-fuse maximum distance between measured and depth projected pixel
//(稠密融合(dense-fuse)中,实测像素与深度投影像素之间的最大允许误差距离)
OPTDENSE::bRemoveDmaps = true; // Delete intermediate depth maps after fusion to save disk space. Disable to keep
// depth maps for later inspection or re-fusion.函数声明
bool Scene::DenseReconstruction(int nFusionMode, bool bCrop2ROI, float fBorderROI, float fSampleMeshNeighbors)调用示例
if (!scene.DenseReconstruction(0, true, 0.f, 0.f)) {
std::cerr << "Dense reconstruction failed." << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}生成的稠密点云结果大致如下 (黄线 bounding box 即为 ROI 区域)

2.scene.ReconstructMesh 将稠密点云转为 Mesh
输入参数
struct ReconstructMeshOptions {
float minPointDistance{1.5}; // Increase for smoother, coarser mesh; decrease for finer detail
bool isUseFreeSpaceSupport{false};// 对于室外 或者 复杂的场景, 可以考虑设置为false; 是否使用相机的射线信息来雕刻空白区域以
// 优化表面重建
bool isIntegrateOnly{false}; // 是否只计算 ROI 中的点
float thicknessFactor{1.0}; // 更高的值可以减少噪声, 但可能导致更大的 hole 与 移除 点云分布比较薄的区域
float qualityFactor{1.0};
float decimate{0.2}; // 用于控制三角形面片数 有效 范围 0 - 1
float removeSpurious{20.0}; // Higher value remove more isolated piece
bool removeSpikes{true}; // Automatically detect and remove spike artifacts (sharp, thin protrusions)
// from the mesh. Recommended for cleaner results.
int closeHoleNum{30}; // larger values close bigger holes
int smoothSteps{5}; // More iterations create smoother surfaces, but may lose detail
float edgeLength{0.0}; // Controls mesh resolution and uniformity
};调用示例
if (!scene.ReconstructMesh(
reconstructMeshOptions.minPointDistance,
reconstructMeshOptions.isUseFreeSpaceSupport,
reconstructMeshOptions.isIntegrateOnly,
4,
reconstructMeshOptions.thicknessFactor,
reconstructMeshOptions.qualityFactor)) {
std::cerr << "ReconstructMesh failed." << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}调用 ReconstructMesh 之后 使用 clean 方法清理一下生成的mesh
// 官方示例的 demo 中, ReconstructMesh 之后是这样清理了三次
scene.mesh.Clean(
1.f,
reconstructMeshOptions.removeSpurious,
reconstructMeshOptions.removeSpikes,
reconstructMeshOptions.closeHoleNum,
reconstructMeshOptions.smoothSteps,
reconstructMeshOptions.edgeLength,
false);
scene.mesh.Clean(
reconstructMeshOptions.decimate,
0.f,
reconstructMeshOptions.removeSpikes,
reconstructMeshOptions.closeHoleNum,
0u,
0.f,
false);
scene.mesh.Clean(1.f, 0.f, false, 0u, 0u, 0.f, true);生成的结果
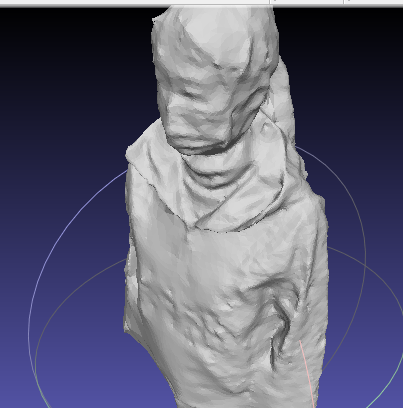
(感觉 这个 Mesh 结果也够用了, 后面也可以权衡一下,是否要花 大量的时间 进行后一步优化)
3.scene.RefineMesh 优化输入的 Mesh
输入参数
struct RefineMeshOptions {
unsigned nResolutionLevel{0}; // Image resolution scale for refinement (0=original, 1=half, etc.).Higher values are
// faster but less detailed. Start with lower resolution for coarse refinement.
unsigned nMinResolution{640}; // Minimum image resolution in pixels.Images can not be downscaled to a resolution
// smaller than this.
unsigned nMaxViews{8}; // Maximum number of view neighbors to use during refinement. More views improve
// accuracy, but increase computation time and memory usage.
float fDecimateMesh{0.3f}; // Simplify the input mesh before refinement (0 = no decimation, 1 = maximum).
// Useful for reducing computation on high-poly meshes.
unsigned nCloseHoles{30}; // Maximum hole size (in edges) to fill before refinement.Closing holes prevents
// artifacts at boundaries (0 - disabled)
unsigned nEnsureEdgeSize{1}; // Subdivide or collapse edges to ensure uniform size (0=no change, 1=moderate,
// 2=aggressive).Helps create more uniform mesh topology.
unsigned nMaxFaceArea{32}; // Maximum face area projected in any pair of images that is not subdivided
// (0 - disabled) (在任何一对图像中,一个面(通常是三维模型中的三角片面)所投影的最大面积,
// 超过这个面积将不会被进一步细分)
unsigned nScales{2}; // Number of multi-scale refinement passes. More scales improve convergence from
// coarse to fine detail.(更多的尺度有助于从粗略结构到精细细节的收敛)
float fScaleStep{0.5}; // Resolution scaling factor between successive refinement scales. Lower values
// create more gradual transitions between scales.
unsigned nAlternatePair{0}; // Which image pairs to use as reference during multi-view refinement:- Both
// references: Use all paired views (most accurate)- Alternate: Switch between left/right
// (balanced)- Left/Right only: Use only one reference (faster, less accurate)
float fRegularityWeight{0.2}; // Weight for mesh regularity term.Higher values produce smoother surfaces, but may lose
// detail.Lower values preserve sharp features, but can be noisy.(低的值会更平滑, 但可能
// 会丢失一些细节。 高的值会保留一些更锐利的细节, 但可能会有更多的噪声)
float fRatioRigidityElasticity{0.90};// Balance between mesh rigidity and elasticity:- 0 = fully elastic (flexible
// deformation)- 1 = fully rigid (minimal deformation)Affects how much the mesh can
// deform. (网格刚性与弹性的平衡: 0 = 完全弹性, 1 完全刚性)
float fGradientStep{45.05}; //(文档里该值的理解拆分为两部分, 整数部分负责控制迭代次数, 小数部分赋值微调)
// opts.gradientStep = iters + gstep*0.1f;
// iters: Number of iterations of gradient descent optimization.
// gstep: Step size for gradient descent optimization.Larger values converge faster,
// but may be unstable.Smaller values are more stable, but slower.
float fThPlanarVertex{0.f}; // Ratio of vertices to treat as planar (constrained to move along their normal).
// Higher values preserve flat surfaces better, but reduce flexibility. (数值越高,
// 越能有效保持平坦表面,但会降低网格的变形灵活性。)
unsigned nReduceMemory{1}; // Memory reduction strategy:- 0 = no reduction (fastest, most memory)-
// 3 = maximum reduction (slowest, least memory)Use higher values for large scenes
// or limited RAM.
};函数调用
if (!scene.RefineMesh(
refineMeshOptions.nResolutionLevel,
refineMeshOptions.nMinResolution,
refineMeshOptions.nMaxViews,
refineMeshOptions.fDecimateMesh,
refineMeshOptions.nCloseHoles,
refineMeshOptions.nEnsureEdgeSize,
refineMeshOptions.nMaxFaceArea,
refineMeshOptions.nScales,
refineMeshOptions.fScaleStep,
refineMeshOptions.nAlternatePair,
refineMeshOptions.fRegularityWeight,
refineMeshOptions.fRatioRigidityElasticity,
refineMeshOptions.fGradientStep,
refineMeshOptions.fThPlanarVertex=0.f,
refineMeshOptions.nReduceMemory=1)) {
std::cerr << "RefineMesh failed." << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}结果如下
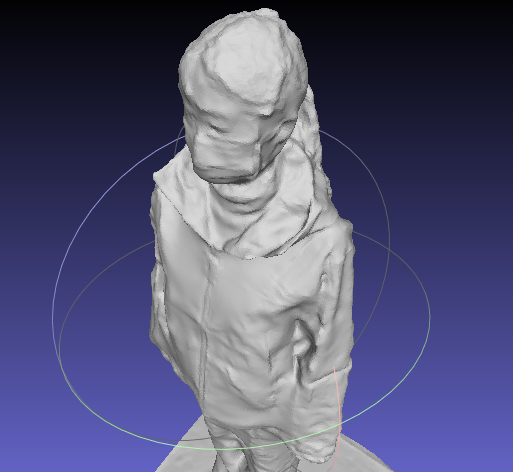
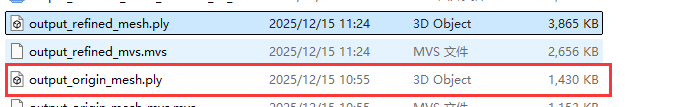
Mesh 文件比优化前 大 1000 多 K, 效果优化前更平滑一些。
4.scene.TextureMesh 为 Mesh 生成贴图
输入参数
struct TextureMeshOptions {
unsigned resolutionLevel{0}; // Image resolution scale for texture extraction (0=original, 1=half, etc.).
// Higher values are faster but produce lower quality textures.
unsigned minResolution{640}; // Minimum image resolution in pixels.Images can not be downscaled to a
// resolution smaller than this.
unsigned minCommonCameras{0}; // Minimum number of cameras that must see a face for it to be textured.
// Higher values ensure better texture quality but may leave some faces
// untextured.
float outlierThreshold{6e-2f}; // Threshold for rejecting outliers during views to face assignment.Higher
// values are more permissive.(用于剔除噪点的阈值。 数值越高, 条件越宽松)
float ratioDataSmoothness{0.6f}; // Balance between data term and smoothness term:0 = prioritize photometric quality
// 1 = prioritize seam smoothness(0 优先保证光度质量 1 优先保证接缝的平滑度)
bool globalSeamLeveling{true}; // Apply global color adjustment to minimize exposure differences between texture
// patches.Recommended for better visual consistency across the entire model.
// (应用全局色彩调整,以最小化纹理块之间的曝光差异。建议启用此选项,以提升整个模型的视觉一致性。)
bool localSeamLeveling{true}; // Apply local color blending along texture seams.Smooths transitions between
// patches.Works well with global seam leveling for best results.
unsigned textureSizeMultiple{0}; // Texture dimensions will be multiples of this value (0 - power of two)
//(纹理尺寸将会是此值的整数倍(0 表示使用 2 的幂次)。)
unsigned rectPackingHeuristic{3};// Algorithm for packing texture patches into atlas:- 0 = MaxRects BSSF (best)-
// 1 = MaxRects BL (fast)- 2 = Skyline BL Higher numbers are faster, but may be less efficient.
uint32_t emptyColor{0x00000000}; // 用于填充没有 texture 覆盖到的区域的颜色
float sharpnessWeight{0.5f}; // Sharpness weight to be applied on the texture (0 - disabled, 0.5 - good value).
int ignoreMaskLabel{-1}; // Label value to ignore in the image mask, stored in the MVS scene or next to each image with
// '.mask.png' extension(-1 - auto estimate mask for lens distortion, -2 - disabled)
int maxTextureSize{8192}; // Maximum texture atlas size in pixels per dimension.Multiple textures are created if needed.
// Larger values allow higher resolution textures, but require more memory (0 - no limit)
};调用示例
if (!scene.TextureMesh(
textureOptions.resolutionLevel,
textureOptions.minResolution,
textureOptions.minCommonCameras,
textureOptions.outlierThreshold,
textureOptions.ratioDataSmoothness,
textureOptions.globalSeamLeveling,
textureOptions.localSeamLeveling,
textureOptions.textureSizeMultiple,
textureOptions.rectPackingHeuristic,
Pixel8U(textureOptions.emptyColor),
textureOptions.sharpnessWeight,
textureOptions.ignoreMaskLabel,
textureOptions.maxTextureSize)) {
std::cerr << "RefineMesh failed." << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}结果如下
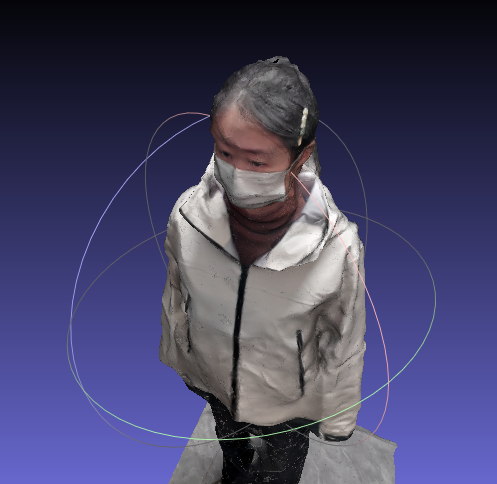

小结
本节进一步调用 API 来进行模型重建, 执行耗时与生成结果上相较于之前都有不少提升。
梳理下来,流程中的 API 可控制的入参有点多,但 openMVS 的API封装用起来也是挺方便的。
后续可以再看看 API 的方法是如何实现的, 还能如何拓展。