仿射变换(Affine Transformation)是一种保持图像平行性 和共线性 的几何变换,核心是通过线性变换(缩放、旋转、剪切)与平移变换的组合,改变图像的位置、姿态和尺寸,但不改变图形的平行关系(如平行线变换后仍平行)。OpenCV 中通过 cv2.warpAffine() 函数实现仿射变换,需先构造仿射变换矩阵,广泛用于图像校正、姿态调整、视角变换等场景。
一、核心原理
1. 仿射变换的数学表达
对于图像中任意像素点 (x, y),仿射变换后映射到新坐标 (x', y'),其数学公式为:
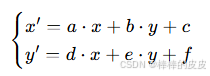
用矩阵形式表示为:
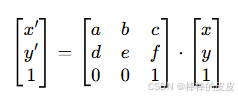
其中:
- 2×3 矩阵
[[a,b,c],[d,e,f]]为仿射变换矩阵 (OpenCV 中需用numpy.ndarray表示, dtype 为np.float32); - 前 2×2 子矩阵
[[a,b],[d,e]]负责线性变换(缩放、旋转、剪切); - 最后一列
[c,f]负责平移变换(x 方向平移c,y 方向平移f)。
2. 仿射变换的三大基础操作
仿射变换可分解为三种基础变换的组合,也可直接通过这三种变换构造矩阵:
| 基础变换 | 作用 | 变换矩阵特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 平移(Translation) | 图像沿 x/y 轴移动 | 前 2×2 为单位矩阵 [[1,0],[0,1]],平移量 [c,f] |
| 旋转(Rotation) | 图像绕原点 / 特定点旋转 | 前 2×2 为旋转矩阵 [[cosθ, -sinθ],[sinθ, cosθ]],可结合平移实现绕任意点旋转 |
| 缩放(Scaling) | 图像沿 x/y 轴缩放 | 前 2×2 为对角矩阵 [[sx,0],[0,sy]](sx/sy 为宽 / 高缩放比例) |
3. 仿射变换矩阵的构造方式
OpenCV 提供两种核心构造方法,无需手动计算矩阵:
- 通过三点映射构造 :已知原图中 3 个非共线点及其变换后的对应点,用
cv2.getAffineTransform(src_pts, dst_pts)自动计算变换矩阵(最常用); - 手动构造:直接根据平移、旋转、缩放的数学公式创建 2×3 矩阵(适合简单变换)。
二、核心函数详解
1. cv2.getAffineTransform():通过三点映射生成变换矩阵
函数原型
python
cv2.getAffineTransform(src_pts, dst_pts)参数说明
| 参数 | 含义 | 要求 |
|---|---|---|
src_pts |
原图中 3 个非共线点的坐标 | 格式为 np.float32([[x1,y1], [x2,y2], [x3,y3]]) |
dst_pts |
变换后对应 3 个点的坐标 | 格式与 src_pts 一致,数量必须为 3 |
返回值
2×3 仿射变换矩阵(np.float32 类型)。
2. cv2.warpAffine():应用仿射变换
函数原型
python
cv2.warpAffine(src, M, dsize, dst=None, flags=None, borderMode=None, borderValue=None)参数说明
| 参数 | 含义 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|
src |
输入图像 | 单通道 / 多通道均可(灰度图 / 彩色图) |
M |
仿射变换矩阵 | 必须是 2×3 的 np.float32 矩阵 |
dsize |
输出图像尺寸 | 格式为 (width, height)(与 OpenCV 图像 shape 相反) |
flags |
插值算法(可选) | 默认 cv2.INTER_LINEAR,缩小用 INTER_AREA,高质量放大用 INTER_CUBIC |
borderMode |
边界填充模式(可选) | 默认 cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT(常数填充),也可设为 BORDER_REPLICATE(复制边界) |
borderValue |
边界填充值(可选) | 仅 borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT 有效,默认黑色(0),彩色图用 (b,g,r) 格式 |
返回值
变换后的输出图像(numpy.ndarray 类型)。
三、完整实现代码(多种场景)
1. 基础场景:通过三点映射实现任意仿射变换
已知原图 3 个点和目标点,自动计算矩阵实现变换(如校正倾斜图像):
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 读取图像
img = cv2.imread("lena.jpg")
if img is None:
print("无法读取图像,请检查路径!")
exit()
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 转为RGB用于matplotlib显示
# 2. 定义原图3个点和变换后对应3个点(非共线)
# 原图中选择3个特征点(如左上角、右上角、左下角)
src_pts = np.float32([[50, 50], [200, 50], [50, 200]])
# 变换后目标点(示例:向右倾斜、向下平移)
dst_pts = np.float32([[50, 50], [250, 80], [30, 220]])
# 3. 计算仿射变换矩阵
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(src_pts, dst_pts)
# 4. 应用仿射变换(输出尺寸与原图一致)
img_affine = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (w, h), flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR, borderValue=(255,255,255))
img_affine_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_affine, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 5. 绘制特征点(可视化对应关系)
for (x, y) in src_pts.astype(int):
cv2.circle(img_rgb, (x, y), 5, (255, 0, 0), -1) # 原图点:蓝色
for (x, y) in dst_pts.astype(int):
cv2.circle(img_affine_rgb, (x, y), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1) # 目标点:绿色
# 6. 显示结果
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.title("Original Image (Blue Points)")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_affine_rgb)
plt.title("Affine Transformation (Green Points)")
plt.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()2. 常用场景:手动构造矩阵实现平移、旋转、缩放
(1)平移变换(沿 x 轴右移 100 像素,y 轴下移 50 像素)
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("lena.jpg")
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 构造平移矩阵:[[1,0,c],[0,1,f]],c=x平移量,f=y平移量
tx, ty = 100, 50 # x右移100,y下移50
M_translate = np.float32([[1, 0, tx], [0, 1, ty]])
# 应用变换(输出尺寸可适当放大,避免图像被截断)
img_translate = cv2.warpAffine(img, M_translate, (w + tx, h + ty), borderValue=(255,255,255))
img_translate_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_translate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 显示
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.title(f"Original ({h}×{w})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_translate_rgb)
plt.title(f"Translated (x+100, y+50) ({img_translate.shape[0]}×{img_translate.shape[1]})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()2)旋转变换(绕图像中心旋转 45°,缩放比例 0.8)
旋转矩阵需结合平移(先将旋转中心移至原点,旋转后再移回原位置),公式如下:
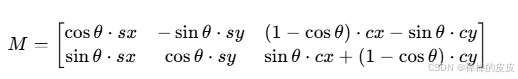
其中:θ 为旋转角度(弧度),sx/sy 为缩放比例,(cx, cy) 为旋转中心。
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("lena.jpg")
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 旋转参数
angle = 45 # 旋转角度(度)
scale = 0.8 # 旋转时的缩放比例
cx, cy = w // 2, h // 2 # 旋转中心(图像中心)
# 计算旋转矩阵(OpenCV内置函数,无需手动计算)
M_rotate = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cx, cy), angle, scale)
# 应用旋转(输出尺寸可按旋转后的边界调整,避免截断)
img_rotate = cv2.warpAffine(img, M_rotate, (w, h), flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC, borderValue=(255,255,255))
img_rotate_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_rotate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 显示
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.title(f"Original ({h}×{w})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_rotate_rgb)
plt.title(f"Rotated {angle}° (scale={scale})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()(3)缩放变换(宽度缩放 1.5 倍,高度缩放 0.8 倍)
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("lena.jpg")
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 构造缩放矩阵:[[sx,0,0],[0,sy,0]],sx=宽度缩放比,sy=高度缩放比
sx, sy = 1.5, 0.8
M_scale = np.float32([[sx, 0, 0], [0, sy, 0]])
# 应用缩放(输出尺寸=原图尺寸×缩放比)
new_w, new_h = int(w * sx), int(h * sy)
img_scale = cv2.warpAffine(img, M_scale, (new_w, new_h), flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
img_scale_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_scale, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 显示
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.title(f"Original ({h}×{w})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_scale_rgb)
plt.title(f"Scaled (sx={sx}, sy={sy}) ({new_h}×{new_w})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()3. 实用场景:图像校正(倾斜文档校正)
通过选择文档的四个角点(先取 3 个计算仿射矩阵),校正倾斜的文档图像:
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def correct_skew_image(img, src_pts, target_size):
"""
校正倾斜图像(仿射变换)
:param img: 输入倾斜图像
:param src_pts: 原图中文档的3个角点(np.float32)
:param target_size: 校正后目标尺寸 (width, height)
:return: 校正后的图像
"""
# 定义校正后目标点(文档的三个角点:左上角、右上角、左下角)
dst_pts = np.float32([[0, 0], [target_size[0]-1, 0], [0, target_size[1]-1]])
# 计算仿射矩阵
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(src_pts, dst_pts)
# 应用变换
corrected_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, target_size, flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC, borderValue=(255,255,255))
return corrected_img
# 1. 读取倾斜文档图像
img_skew = cv2.imread("skew_document.jpg")
if img_skew is None:
print("无法读取倾斜图像,请检查路径!")
exit()
h, w = img_skew.shape[:2]
img_skew_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_skew, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 2. 手动选择原图中3个角点(可通过图像查看工具获取坐标)
src_pts = np.float32([[60, 80], [420, 70], [50, 500]]) # 示例坐标,需根据实际图像调整
# 3. 校正图像(目标尺寸:宽400,高550)
target_size = (400, 550)
img_corrected = correct_skew_image(img_skew, src_pts, target_size)
img_corrected_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_corrected, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 4. 绘制角点可视化
for (x, y) in src_pts.astype(int):
cv2.circle(img_skew_rgb, (x, y), 6, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 5. 显示结果
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_skew_rgb)
plt.title("Skewed Image (Green Corners)")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_corrected_rgb)
plt.title(f"Corrected Image ({target_size[1]}×{target_size[0]})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()四、关键说明与应用场景
1. 仿射变换的核心特点
- 保持平行性:原图中平行线,变换后仍为平行线;
- 保持共线性:原图中共线点,变换后仍共线;
- 灵活性:可组合平移、旋转、缩放、剪切等多种变换;
- 仅需 3 个点:通过 3 个非共线点的映射关系即可唯一确定变换矩阵。
2. 典型应用场景
- 图像校正:倾斜文档、车牌、身份证等图像的水平 / 垂直校正;
- 姿态调整:调整图像的旋转角度、位置,适配特定显示区域;
- 视角变换:模拟不同视角下的图像(如将倾斜的物体转为正面视角);
- 数据增强:深度学习中通过仿射变换(旋转、平移、缩放)扩充样本集,提升模型泛化能力。
3. 与透视变换的区别
仿射变换 vs 透视变换(Perspective Transformation):
| 特性 | 仿射变换 | 透视变换 |
|---|---|---|
| 变换矩阵 | 2×3 矩阵 | 3×3 矩阵 |
| 核心特点 | 保持平行性 | 不保持平行性(可将平行线变为相交线) |
| 点映射需求 | 3 个非共线点 | 4 个非共线点 |
| 适用场景 | 简单姿态调整、校正 | 复杂视角变换(如拍摄的文档转为正射投影) |
五、注意事项
- 坐标格式 :
src_pts和dst_pts必须是np.float32类型,否则会报错; - 输出尺寸 :
dsize格式为(width, height),需与图像shape(height, width)区分,避免尺寸错乱; - 边界填充 :变换后图像可能超出原尺寸,需通过
borderMode和borderValue设置边界填充(如白色填充避免黑边); - 插值算法选择 :
- 缩小图像:用
cv2.INTER_AREA(避免锯齿); - 放大图像 / 保持细节:用
cv2.INTER_CUBIC或cv2.INTER_LINEAR;
- 缩小图像:用
- 旋转中心 :绕非原点旋转时,需先平移到原点、旋转、再平移回原位置,推荐用
cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()自动计算矩阵,避免手动计算错误。
通过 cv2.getAffineTransform() 构造矩阵、cv2.warpAffine() 应用变换,可轻松实现各类仿射变换需求,掌握三点映射和矩阵构造逻辑是核心。