序言
之前我们学习过函数,那么一个类中有多少种方法呢?这篇文章我们一起来学习
Instance methods
这是最常见的方法
对象的实例方法可以访问实例变量和this。
dart
import 'dart:math';
class Point {
final double x;
final double y;
// Sets the x and y instance variables
// before the constructor body runs.
Point(this.x, this.y);
double distanceTo(Point other) {
var dx = x - other.x;
var dy = y - other.y;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
}Operators
计算符,他和方法有什么关系呀?
大多数运算符是具有特殊名称的实例方法。Dart允许您定义具有以下名称的运算符
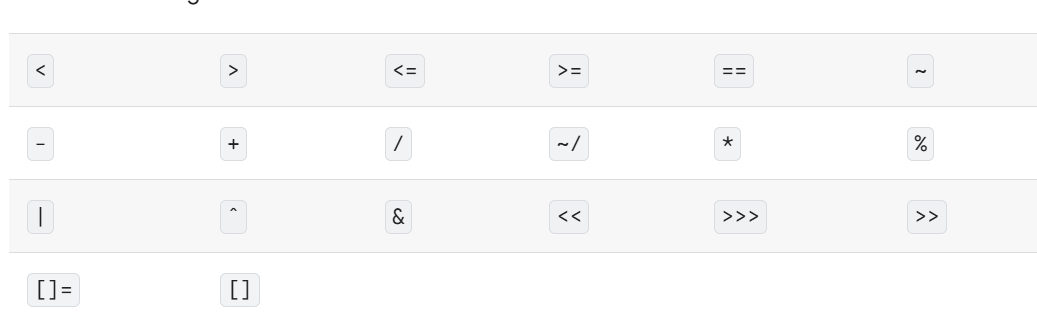
要声明运算符,先使用内置的标识符运算符(operator),再使用正在定义的运算符。下面的例子定义了向量的加法(+)、减法(-)和相等(==):
dart
class Vector {
final int x, y;
Vector(this.x, this.y);
Vector operator +(Vector v) => Vector(x + v.x, y + v.y);
Vector operator -(Vector v) => Vector(x - v.x, y - v.y);
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
other is Vector && x == other.x && y == other.y;
@override
int get hashCode => Object.hash(x, y);
}
void main() {
final v = Vector(2, 3);
final w = Vector(2, 2);
assert(v + w == Vector(4, 5));
assert(v - w == Vector(0, 1));
}下面是num类中对于==的定义

Getters and setters
这个也是我们学习过的内容了
getter和setter是特殊的方法,提供了对对象属性的读写访问。回想一下,每个实例变量都有一个隐式的getter,如果合适的话还会加上一个setter。你可以通过实现getter和setter来创建额外的属性,使用get和set关键字:
dart
/// A rectangle in a screen coordinate system,
/// where the origin `(0, 0)` is in the top-left corner.
class Rectangle {
double left, top, width, height;
Rectangle(this.left, this.top, this.width, this.height);
// Define two calculated properties: right and bottom.
double get right => left + width;
set right(double value) => left = value - width;
double get bottom => top + height;
set bottom(double value) => top = value - height;
}
void main() {
var rect = Rectangle(3, 4, 20, 15);
assert(rect.left == 3);
rect.right = 12;
assert(rect.left == -8);
}运算符如 ++ 需要先获取当前值,然后进行计算和赋值。Dart 规范要求调用 getter 仅一次,以避免副作用。
Abstract methods
实例方法、getter 和 setter 方法都可以是抽象的,它们定义了一个接口,但将具体实现留给其他类。
抽象方法只能存在于抽象类或mixin中。
dart
abstract class Doer {
// Define instance variables and methods...
void doSomething(); // Define an abstract method.
}
class EffectiveDoer extends Doer {
void doSomething() {
// Provide an implementation, so the method is not abstract here...
}
}