目录
[1. 字符串的创建和初始化](#1. 字符串的创建和初始化)
[2. 字符串基本操作](#2. 字符串基本操作)
[2.1 获取字符串信息](#2.1 获取字符串信息)
[2.2 访问和修改字符](#2.2 访问和修改字符)
[3. 字符串修改操作](#3. 字符串修改操作)
[3.1 追加字符串](#3.1 追加字符串)
[3.2 插入字符串](#3.2 插入字符串)
[3.3 删除字串内容](#3.3 删除字串内容)
[3.4 替换字符串](#3.4 替换字符串)
[4. 字符串查找和子字符串](#4. 字符串查找和子字符串)
[4.1 查找操作](#4.1 查找操作)
[4.2 提取子字符串](#4.2 提取子字符串)
[5. 字符串比较](#5. 字符串比较)
[6. 字符串与数值转换](#6. 字符串与数值转换)
[6.1 数值转换为字符串](#6.1 数值转换为字符串)
[6.2 字符串转换为数值](#6.2 字符串转换为数值)
[7. 字符串输入输出](#7. 字符串输入输出)
[7.1 输入输出操作](#7.1 输入输出操作)
[8. 其他有用操作](#8. 其他有用操作)
[8.1 调整字符串大小](#8.1 调整字符串大小)
[8.2 字符串交换](#8.2 字符串交换)
引言
在C++编程中,字符串处理是日常开发中必不可少的一部分。C++标准模板库(STL)中的string类提供了强大而灵活的字符串操作功能,相比传统的C风格字符串(字符数组),string更加安全、易用且功能丰富。本文将详细介绍string类的常用方法,并通过实际示例展示其用法。
1. 字符串的创建和初始化
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 1. 默认构造函数,创建空字符串
std::string str1;
// 2. 使用C风格字符串初始化
std::string str2 = "Hello, World!";
std::string str3("Hello, C++");
// 3. 使用另一个string对象初始化
std::string str4(str3);
std::string str5 = str2;
// 4. 使用部分字符序列初始化
std::string str6("Hello, World!", 5); // 只取前5个字符: "Hello"
// 5. 使用多个相同字符初始化
std::string str7(10, '*'); // "**********"
// 6. 使用迭代器初始化
std::string str8(str2.begin(), str2.begin() + 5); // "Hello"
std::cout << str1 << std::endl;
std::cout << str2 << std::endl;
std::cout << str3 << std::endl;
std::cout << str4 << std::endl;
std::cout << str5 << std::endl;
std::cout << str6 << std::endl;
std::cout << str7 << std::endl;
std::cout << str8 << std::endl;
return 0;
}结果: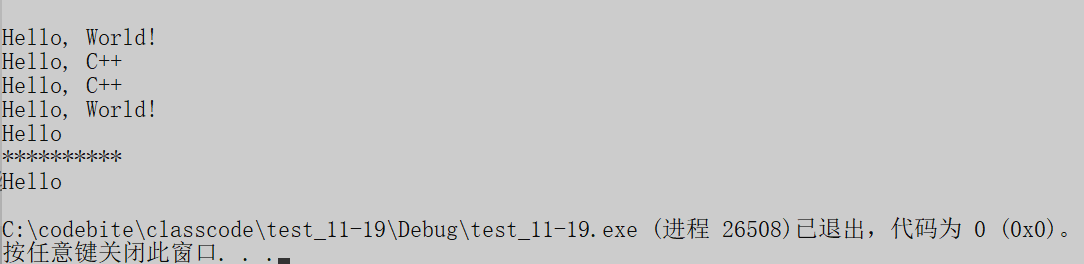
2. 字符串基本操作
2.1 获取字符串信息
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello, C++ STL!......";
// 获取字符串长度
std::cout << "Length: " << str.length() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size: " << str.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Capacity: " << str.capacity() << std::endl;
// 检查字符串是否为空
std::string emptyStr;
std::cout << "Is empty? " << emptyStr.empty() << std::endl; // 1 (true)
std::cout << "Is str empty? " << str.empty() << std::endl; // 0 (false)
// 获取C风格字符串
const char* cstr = str.c_str();
std::cout << "C-string: " << cstr << std::endl;
return 0;
}结果:
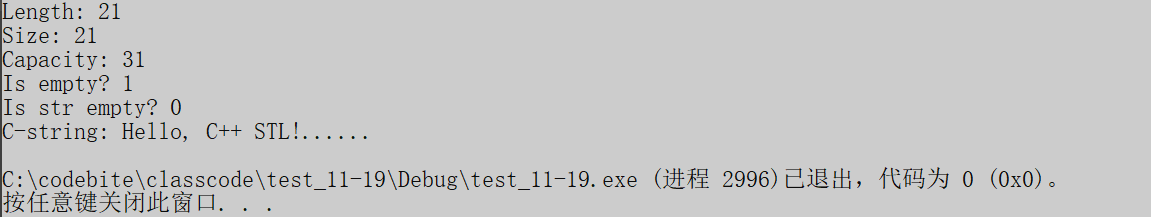
补充:
- size()和length()在功能上完全相同,它们都返回字符串当前包含的字符数。
为什么有两个相同的函数?
string类的诞生是早于STL容器的,早期的string类用length来表示字符数,后来为了与STL容器接口保持一致,所以添加了size()函数,我个人更推荐使用size(),既方便记忆,也更能体现STL容器设计理念的一致性。
- capacity()返回的是当前为字符串分配的内存空间(以字符数为单位),这个空间可以容纳的字符数。这个值通常大于或等于
size()。
当向字符串添加字符时,如果size()小于capacity(),则不需要重新分配内存。只有当size()达到capacity()时,再添加字符就会触发内存重新分配,增加capacity(),以便容纳更多的字符。
为了减少重新分配内存所造成的性能开销,通常扩容的逻辑为按原来容量的1.5倍到2倍进行扩容。
3.c_str()的存在打通了C语言的字符串与C++字符串之间的隔阂,实现了向下兼容,事实上string类的底层就是管理了一个动态数组,c_str()就是返回这个数组的首元素地址。
2.2 访问和修改字符
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello";
// 使用下标访问
std::cout << "str[0] = " << str[0] << std::endl; // 'H'
std::cout << "str[1] = " << str[1] << std::endl; // 'e'
// 使用at()访问(会检查边界)
std::cout << "str.at(2) = " << str.at(2) << std::endl; // 'l'
// 修改字符
str[0] = 'h';
str.at(1) = 'E';
std::cout << "After modification: " << str << std::endl; // "hello"
// 获取第一个和最后一个字符
std::cout << "Front: " << str.front() << std::endl; // 'h'
std::cout << "Back: " << str.back() << std::endl; // 'o'
return 0;
}结果:
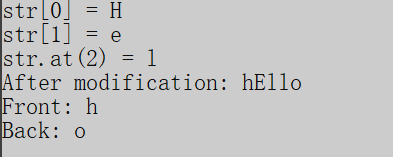
补充:
- at()访问元素和[]访问元素的核心区别总结
| 特性 | operator[] (str[index]) |
at() (str.at(index)) |
|---|---|---|
| 边界检查 | 不进行边界检查 | 进行边界检查 |
| 越界行为 | 未定义行为(可能导致崩溃) | 抛出std::out_of_range异常 |
| 性能 | 更高效(无检查开销) | 稍慢(有检查开销) |
| 适用场景 | 已知索引安全的快速访问 | 需要安全检查的情况 |
| 异常安全 | 不抛出异常 | 抛出异常 |
3. 字符串修改操作
3.1 追加字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello";
// 使用+=运算符
str += ", World";
std::cout << "After +=: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, World"
// 使用append()函数
str.append("!");
std::cout << "After append: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, World!"
str.append(" Welcome to C++", 9); // 只追加前9个字符
std::cout << "After append with length: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, World! Welcome"
// 追加多个相同字符
str.append(3, '!');
std::cout << "After append chars: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, World! Welcome!!!"
return 0;
}结果:

3.2 插入字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello World!";
// 在指定位置插入
str.insert(6, "Beautiful ");
std::cout << "After insert: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello Beautiful World!"
// 插入部分字符串
std::string insertStr = "Amazing and ";
str.insert(6, insertStr, 0, 8); // 从insertStr的第0个位置开始插入8个字符
std::cout << "After partial insert: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello Amazing Beautiful World!"
// 插入多个相同字符
str.insert(0, 3, '*'); // 在开头插入3个*
std::cout << "After inserting chars: " << str << std::endl; // "***Hello Amazing Beautiful World!"
return 0;
}结果:
3.3 删除字串内容
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello, World! This is C++.";
// 删除从位置7开始的5个字符
str.erase(7, 5);
std::cout << "After erase: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, ! This is C++."
// 删除从位置7到末尾的所有字符
std::string str2 = "Hello, World!";
str2.erase(7);
std::cout << "After erase to end: " << str2 << std::endl; // "Hello, "
// 删除最后一个字符
str2.pop_back();
std::cout << "After pop_back: " << str2 << std::endl; // "Hello,"
// 清空整个字符串
str2.clear();
std::cout << "After clear, is empty? " << str2.empty() << std::endl; // 1 (true)
return 0;
}结果:

3.4 替换字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello, World!";
// 替换从位置7开始的5个字符
str.replace(7, 5, "C++");
std::cout << "After replace: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, C++!"
// 使用子字符串替换
std::string newStr = "Amazing cpp";
str.replace(7, 3, newStr, 8, 3); // 用newStr中从8开始的3个字符替换
std::cout << "After replace with substring: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello, cpp!"
return 0;
}结果:

4. 字符串查找和子字符串
4.1 查找操作
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello, World! Hello, C++!";
// 查找子字符串
size_t pos = str.find("Hello");
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "Found 'Hello' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 0
}
// 从指定位置开始查找
pos = str.find("Hello", 1);
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "Found second 'Hello' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 14
}
// 查找字符
pos = str.find('W');
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "Found 'W' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 7
}
// 反向查找
pos = str.rfind("Hello");
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "Found last 'Hello' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 14
}
// 查找字符集中任意字符首次出现的位置
pos = str.find_first_of(" ,!");//字符集就是(" ,!")
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "First of ', !' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 5
}
// 查找不在字符集中的字符首次出现的位置
pos = str.find_first_not_of("Helo");//字符集就是("Helo")
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "First not of 'Helo' at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 4 (,)
}
return 0;
}结果:

补充:
- 上面的这些查找函数,如果找到了目标字符或字符串,则返回字符下标或字符串首元素下标,如果没有找到目标字符或字符串,则返回string::npos表示"没有找到"或"无效位置"。std::string::npos是C++中std::string类的一个静态常量成员。
cpp
// npos的定义
static const size_t npos = -1;尽管它被定义为-1,但由于size_t是无符号整型 ,-1会被转换为该类型的最大值
4.2 提取子字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello, World! Welcome to C++ Programming.";
// 提取子字符串
std::string sub1 = str.substr(7, 5);//返回从下标7开始的5个字符
std::cout << "Substring 1: " << sub1 << std::endl; // "World"
// 从指定位置到末尾
std::string sub2 = str.substr(7);//返回从下标7开始后面所有字符
std::cout << "Substring 2: " << sub2 << std::endl; // "World! Welcome to C++ Programming."
// 结合find使用
size_t commaPos = str.find(',');
if (commaPos != std::string::npos) {
std::string beforeComma = str.substr(0, commaPos);
std::cout << "Before comma: " << beforeComma << std::endl; // "Hello"
}
return 0;
}结果:

5. 字符串比较
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "apple";
std::string str2 = "banana";
std::string str3 = "apple";
// 使用比较运算符
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "str1 == str2: " << (str1 == str2) << std::endl; // false
std::cout << "str1 == str3: " << (str1 == str3) << std::endl; // true
std::cout << "str1 < str2: " << (str1 < str2) << std::endl; // true
std::cout << "str1 > str2: " << (str1 > str2) << std::endl; // false
// 使用compare()函数
int result = str1.compare(str2);
if (result < 0) {
std::cout << "str1 is less than str2" << std::endl;
}
else if (result > 0) {
std::cout << "str1 is greater than str2" << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "str1 is equal to str2" << std::endl;
}
// 比较子字符串
std::string str4 = "Hello, World!";
std::string str5 = "Hello, C++!";
result = str4.compare(0, 5, str5, 0, 5); // 比较前5个字符
std::cout << "Compare first 5 chars: " << result << std::endl; // 0 (相等)
return 0;
}结果:

补充:
-
注意: 比较运算符的返回结果与字符串长度无关,字符串的比较逻辑为,从左到右依次比较每一个字符的ASCII码,>和<比较运算符,当遇到第一个ASCII码不相等的字符时,进行ASCII码比较,然后返回结果,比较结束。
-
compare()函数,例如:a.compare(b), a>b则返回值大于0,a<b则返回值小于0,a==b则返回值等于0.
6. 字符串与数值转换
6.1 数值转换为字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
// C++11之后可以使用to_string函数
int num = 123;
double pi = 3.14159;
std::string str1 = std::to_string(num);
std::string str2 = std::to_string(pi);
std::cout << "Integer to string: " << str1 << std::endl; // "123"
std::cout << "Double to string: " << str2 << std::endl; // "3.141590"
return 0;
}结果:

6.2 字符串转换为数值
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "123";
std::string str2 = "3.14159";
std::string str3 = "100";
// 字符串转整数
int num1 = std::stoi(str1);
std::cout << "String to int: " << num1 << std::endl; // 123
// 字符串转浮点数
double num2 = std::stod(str2);
std::cout << "String to double: " << num2 << std::endl; // 3.14159
// 指定进制转换
int num3 = std::stoi(str3, nullptr, 2); // 二进制
std::cout << "Binary string to int: " << num3 << std::endl; // 4
// 获取转换停止的位置
std::string str4 = "123abc";
size_t pos;
int num4 = std::stoi(str4, &pos);
std::cout << "Number: " << num4 << ", Stopped at position: " << pos << std::endl; // 123, 3
return 0;
}结果:

7. 字符串输入输出
7.1 输入输出操作
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
int main() {
// 从标准输入读取
std::string input;
std::cout << "Enter a string: ";
std::getline(std::cin, input);
std::cout << "You entered: " << input << std::endl;
// 使用stringstream进行字符串分割
std::string data = "Apple Banana Cherry Date";
std::stringstream ss(data);
std::string fruit;
std::cout << "\nFruits:" << std::endl;
while (std::getline(ss, fruit, ' ')) {
std::cout << "- " << fruit << std::endl;
}
// 使用stringstream进行字符串拼接
std::stringstream ss2;
ss2 << "The value is: " << 42 << " and pi is: " << 3.14;
std::cout << "\n" << ss2.str() << std::endl;
return 0;
}结果:

补充:
cin和getline获取字符串的区别
| 特性 | cin >> |
getline() |
|---|---|---|
| 读取方式 | 读取到空白字符(空格、制表符、换行符)停止 | 读取到换行符停止 |
| 处理空白字符 | 跳过前导空白,遇到空白停止读取 | 不跳过空白,读取所有字符直到换行符 |
| 换行符处理 | 留在输入缓冲区中 | 从输入缓冲区读取并丢弃 |
| 读取整行 | 不能直接读取整行(遇到空格会停止) | 专门用于读取整行 |
| 使用场景 | 读取单词、数字等以空白分隔的数据 | 读取包含空格的整行文本 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string input1, input2;
// 示例1: 使用getline读取
std::cout << "\n示例1: 使用getline读取" << std::endl;
std::cout << "请输入一行文本(包含空格): ";
std::cin.ignore(); // 清除上一个输入留下的换行符
std::getline(std::cin, input2); // 用户输入: Hello World
std::cout << "getline读取的内容: \"" << input2 << "\"" << std::endl;
std::cout << "长度: " << input2.length() << std::endl;
// 示例2: 使用cin读取
std::cout << "示例2: 使用cin读取" << std::endl;
std::cout << "请输入一行文本(包含空格): ";
std::cin >> input1; // 用户输入: Hello World
std::cout << "cin读取的内容: \"" << input1 << "\"" << std::endl;
std::cout << "长度: " << input1.length() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
8. 其他有用操作
8.1 调整字符串大小
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello";
std::string str2;
str2.reserve(64);
//如果提前知道要写入的字符串的长度,可以使用reserve()函数,
//提前分配好足够的空间,减少后续重新分配内存造成的性能损失
std::cout <<"str2 Capacity: "<< str2.capacity() << std::endl;
// 调整大小,如果新大小大于当前大小,用指定字符填充
str.resize(10, '!');
std::cout << "After resize to 10: " << str << std::endl; // "Hello!!!!!"
// 调整大小,如果新大小小于当前大小,截断
str.resize(3);
std::cout << "After resize to 3: " << str << std::endl; // "Hel"
// 保留容量
std::string longStr = "This is a long string for testing capacity";
std::cout << "Capacity before: " << longStr.capacity() << std::endl;
longStr.shrink_to_fit(); // 请求减少容量以适应大小,建议性请求,编译器不一定会执行
std::cout << "Capacity after shrink_to_fit: " << longStr.capacity() << std::endl;
return 0;
}结果:
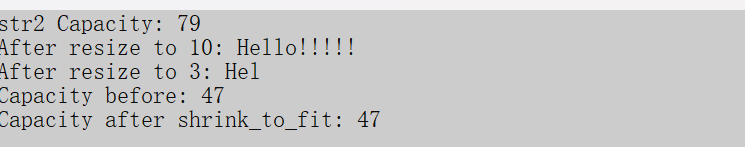
8.2 字符串交换
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "Hello";
std::string str2 = "World";
std::cout << "Before swap:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "str1: " << str1 << std::endl; // "Hello"
std::cout << "str2: " << str2 << std::endl; // "World"
str1.swap(str2);
std::cout << "\nAfter swap:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "str1: " << str1 << std::endl; // "World"
std::cout << "str2: " << str2 << std::endl; // "Hello"
return 0;
}结果:

那么本期的内容就到这里了,觉得有收获的同学们可以给个点赞、评论、关注、收藏哦,谢谢大家。