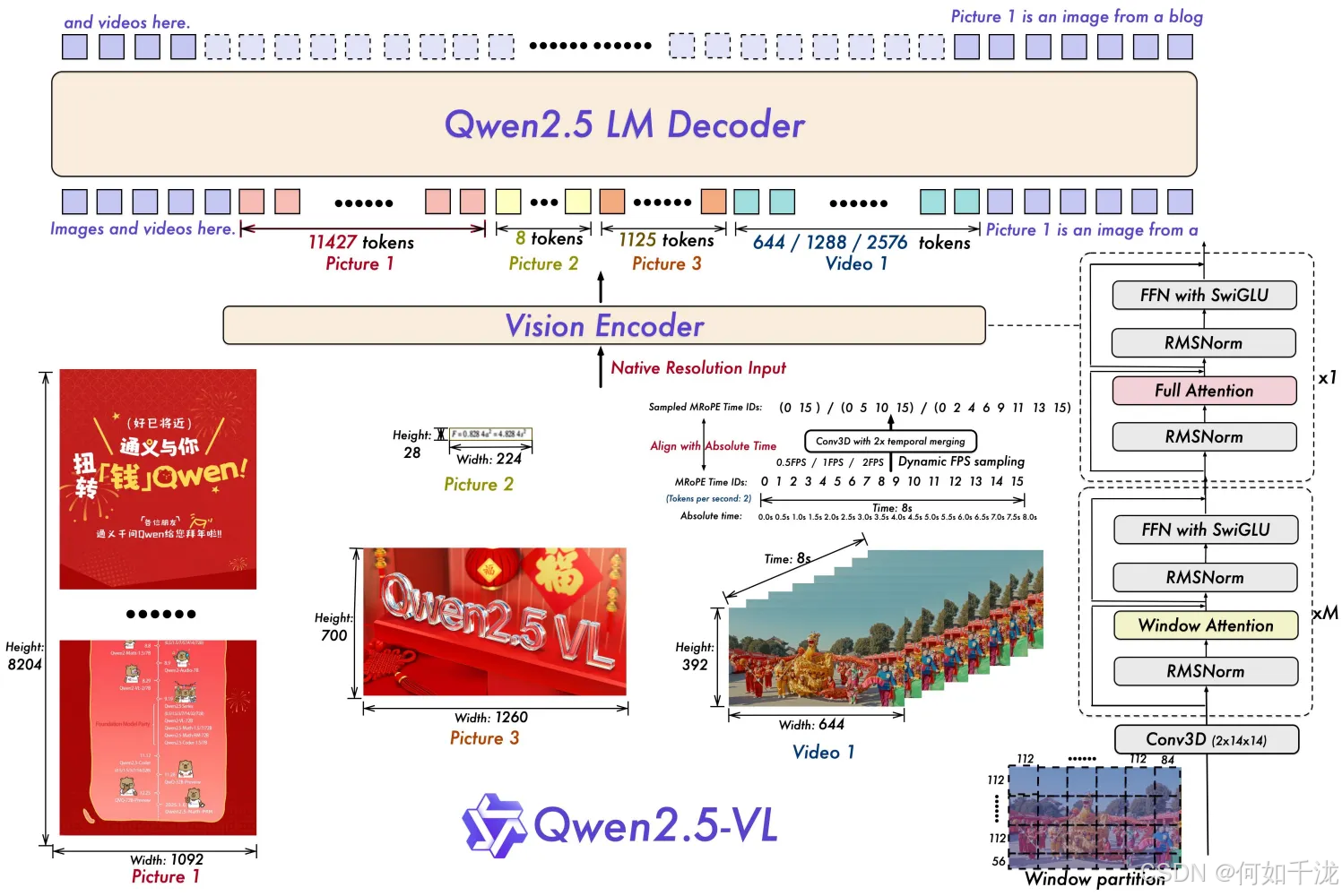
输入数据:
json
{
"messages":
[
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "<image><image><image><image><image><image>甲状腺左叶中部背侧见低回声,大小约1.3×1.0×0.9cm,形态不规则,边界不清,内见点状强回声,CDFI:未见明确血流信号。"
}
],
"images":
[
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.5.20250113.85943.515.jpg",
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.1.20230410.92234.187.jpg",
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.3.20230410.92248.500.jpg",
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.4.20230410.92302.281.jpg",
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.6.20250113.85952.125.jpg",
"./data_filtered/1.2.840.113663.1500.1.341662655.3.7.20250113.90010.921.jpg",
]
}Qwen2.5-VL 中swift/llm/template/template/qwen.py用于将文本和图像/视频输入联合编码 (tokenize + 媒体预处理)的 _encode 方法实现。其主要目标是:
- 将文本中的
<image>或<video>占位符替换为适当数量的媒体 token; - 同时对实际的图像或视频数据进行预处理,生成模型可接受的张量;
- 保持 labels 和 loss_scale(用于控制 loss 权重的掩码)与 input_ids 对齐。
python
def _encode(self, inputs: StdTemplateInputs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# step1:将文本和<image>进行tokenizer
encoded = super()._encode(inputs)
processor = self.processor
input_ids = encoded['input_ids']
labels = encoded['labels']
loss_scale = encoded.get('loss_scale', None)
for media_type in ['images', 'videos']:
mm_data = getattr(inputs, media_type)
if mm_data:
if media_type == 'images':
media_token = self.image_token_id
# step2: 对图像进行处理
media_inputs = processor.image_processor(images=mm_data, return_tensors='pt', do_resize=False)
media_grid_thw = media_inputs['image_grid_thw']
else:
kwargs = {}
if hasattr(processor, 'video_processor'):
processor_func = processor.video_processor
else:
processor_func = processor.image_processor
kwargs['images'] = None
media_inputs = processor_func(videos=mm_data, return_tensors='pt', do_resize=False, **kwargs)
media_grid_thw = media_inputs['video_grid_thw']
media_token = self.video_token_id
if self.version == 'v2_5':
fps = inputs.mm_processor_kwargs['fps']
media_inputs['second_per_grid_ts'] = [
processor.image_processor.temporal_patch_size / tmp for tmp in fps
]
idx_list = findall(input_ids, media_token)
merge_length = processor.image_processor.merge_size**2
def _get_new_tokens(i):
# Qwen2.5-VL将2*2个patch合并为一个token
token_len = (media_grid_thw[i].prod() // merge_length)
return [media_token] * token_len
# step3: 将图像token进行替换
input_ids, labels, loss_scale = self._extend_tokens(input_ids, labels, loss_scale, idx_list,
_get_new_tokens)
encoded.update(media_inputs)
encoded['input_ids'] = input_ids
encoded['labels'] = labels
encoded['loss_scale'] = loss_scale
return encodedStep 1:调用父类编码文本
python
encoded = super()._encode(inputs)- 父类
_encode通常只处理纯文本输入,比如将文本(含<image>、<video>等占位符)用 tokenizer 转为input_ids,并生成对应的labels(用于语言建模)和可选的loss_scale(控制哪些 token 参与 loss 计算)。 - 此时,
<image>或<video>会被替换成一个特定的 token ID。
生成的结果如下所示:
python
['<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>', '甲状腺左叶中部背侧见低回声,大小约1.3×1.0×0.9cm,形态不规则,边界不清,内见点状强回声,CDFI:未见明确血流信号。', [151645]]
python
{'input_ids': [151652, 151655, 151653, 151652, 151655, 151653, 151652, 151655, 151653, 151652, 151655, 151653, 151652, 151655, 151653, 151652, 151655, 151653, 115293, ...], 'labels': [-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, 115293, ...], 'loss_scale': None}input_ids:输入数据labels:标签,其中 -100表示不计算损失。
Step 2:处理多模态数据(图像或视频)
循环处理 images 和 videos:
图像处理分支(media_type == 'images')
python
media_inputs = processor.image_processor(images=mm_data, return_tensors='pt', do_resize=False)
media_grid_thw = media_inputs['image_grid_thw']Qwen2.5-VL 模态视觉-语言模型中 图像预处理器(image processor) 的transformers/models/qwen2_vl/image_processing_qwen2_vl_fast.py核心函数 _preprocess,负责将一批原始图像张量(torch.Tensor)转换为模型可接受的 扁平化视觉 token(patches) ,并记录每个图像在 token 空间中的 时空网格结构 (image_grid_thw)
python
def _preprocess(
self,
images: list["torch.Tensor"],
do_resize: bool,
size: SizeDict,
interpolation: Optional["F.InterpolationMode"],
do_rescale: bool,
rescale_factor: float,
do_normalize: bool,
image_mean: Optional[Union[float, list[float]]],
image_std: Optional[Union[float, list[float]]],
patch_size: int,
temporal_patch_size: int,
merge_size: int,
disable_grouping: Optional[bool],
return_tensors: Optional[Union[str, TensorType]],
**kwargs,
):
# Group images by size for batched resizing
# grouped_images: [6, 3, 616, 840]
# grouped_images_index: [(616, 840), index(0-5)]
grouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(images, disable_grouping=disable_grouping)
resized_images_grouped = {}
for shape, stacked_images in grouped_images.items():
height, width = stacked_images.shape[-2:]
if do_resize:
resized_height, resized_width = smart_resize(
height,
width,
factor=patch_size * merge_size,
min_pixels=size["shortest_edge"],
max_pixels=size["longest_edge"],
)
stacked_images = self.resize(
image=stacked_images,
size=SizeDict(height=resized_height, width=resized_width),
interpolation=interpolation,
)
resized_images_grouped[shape] = stacked_images
# resized_images: list [3, 616, 840] * 6
resized_images = reorder_images(resized_images_grouped, grouped_images_index)
# Group images by size for further processing
# Needed in case do_resize is False, or resize returns images with different sizes
grouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(resized_images, disable_grouping=disable_grouping)
processed_images_grouped = {}
processed_grids = {}
for shape, stacked_images in grouped_images.items():
resized_height, resized_width = stacked_images.shape[-2:]
# Fused rescale and normalize
patches = self.rescale_and_normalize(
stacked_images, do_rescale, rescale_factor, do_normalize, image_mean, image_std
)
if patches.ndim == 4:
# add a temporal dimension if we have images
patches = patches.unsqueeze(1)
if patches.shape[1] % temporal_patch_size != 0:
# 对于图像,重复temporal_patch_size(2)次
repeats = patches[:, -1:].repeat(1, temporal_patch_size - 1, 1, 1, 1)
patches = torch.cat([patches, repeats], dim=1)
batch_size, grid_t, channel = patches.shape[:3]
grid_t = grid_t // temporal_patch_size
grid_h, grid_w = resized_height // patch_size, resized_width // patch_size
# 将merge_size(2)*merge_size(2)个patch作为一个整体
patches = patches.view(
batch_size,
grid_t,
temporal_patch_size,
channel,
grid_h // merge_size,
merge_size,
patch_size,
grid_w // merge_size,
merge_size,
patch_size,
)
# Reorder dimensions to group grid and patch information for subsequent flattening.
# (batch, grid_t, grid_h, grid_w, merge_h, merge_w, channel, temp_patch_size, patch_h, patch_w)
patches = patches.permute(0, 1, 4, 7, 5, 8, 3, 2, 6, 9)
flatten_patches = patches.reshape(
batch_size,
grid_t * grid_h * grid_w,
channel * temporal_patch_size * patch_size * patch_size,
)
processed_images_grouped[shape] = flatten_patches
processed_grids[shape] = [[grid_t, grid_h, grid_w]] * batch_size
processed_images = reorder_images(processed_images_grouped, grouped_images_index)
processed_grids = reorder_images(processed_grids, grouped_images_index)
# 将所有图像concat
pixel_values = torch.cat(processed_images, dim=0)
image_grid_thw = torch.tensor(processed_grids)
return BatchFeature(
data={"pixel_values": pixel_values, "image_grid_thw": image_grid_thw}, tensor_type=return_tensors
)-
按图像尺寸分组(用于批处理加速)
pythongrouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(images, disable_grouping=disable_grouping)- 目的 :相同尺寸的图像可以堆叠成一个 batch(
[N, C, H, W]),避免逐张处理,提高 GPU 利用率。 - 输出 :
grouped_images: dict,key 为(H, W),value 是torch.Tensor(stacked images),shape为[N, C, H, W]grouped_images_index: 记录原始图像顺序,用于后续还原。具体为(shape, index)
- 目的 :相同尺寸的图像可以堆叠成一个 batch(
-
可选 Resize:智能缩放(smart resize)
pythonif do_resize: resized_height, resized_width = smart_resize( height, width, factor=patch_size * merge_size, min_pixels=size["shortest_edge"], max_pixels=size["longest_edge"], ) stacked_images = self.resize(...)smart_resize保证:- 缩放后的
H和W都是patch_size * merge_size的整数倍(例如 14×2=28); - 总像素数在
[min_pixels, max_pixels]范围内(避免过大/过小); - 保持原始宽高比(通常通过 padding 或缩放+裁剪实现)。
- 缩放后的
- 这是为了后续能 整除地划分为 patch 和合并单元
-
还原图像顺序
pythonresized_images = reorder_images(resized_images_grouped, grouped_images_index)- 将分组处理后的图像按原始输入顺序排列,确保
resized_images[i]对应images[i]。
- 将分组处理后的图像按原始输入顺序排列,确保
-
再次分组(因 resize 后尺寸可能变化)
pythongrouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(resized_images, ...) -
核心:Patch 提取与 Token Merging
对每一组同尺寸图像
stacked_images(shape:[B, C, H, W]):-
增加时序维度(为兼容视频)
pythonif patches.ndim == 4: patches = patches.unsqueeze(1) # [B, 1, C, H, W]图像视为 单帧视频(T=1)
-
补齐时序维度(满足
temporal_patch_size整除)pythonif patches.shape[1] % temporal_patch_size != 0: repeats = patches[:, -1:].repeat(1, temporal_patch_size - 1, ...) patches = torch.cat([patches, repeats], dim=1)- 对图像(T=1),若
temporal_patch_size=2,则复制最后一帧,变成 T=2; - 为了后续能按
temporal_patch_size切分时序 patch。
- 对图像(T=1),若
-
计算网格维度
pythongrid_t = T // temporal_patch_size grid_h = H // patch_size grid_w = W // patch_size- 例如:H=616, patch_size=14 → grid_h = 44;
- merge_size=2 → 合并后 token 网格为
grid_h // 2 = 22。
-
关键:View + Permute 实现 Token Merging
pythonpatches = patches.view( batch_size, grid_t, temporal_patch_size, channel, grid_h // merge_size, # merged grid height merge_size, # patches within one merged unit (height) patch_size, grid_w // merge_size, # merged grid width merge_size, # patches within one merged unit (width) patch_size, ) patches = patches.permute(0, 1, 4, 7, 5, 8, 3, 2, 6, 9) # -> [B, grid_t, grid_h_m, grid_w_m, merge_h, merge_w, C, T_patch, P_h, P_w] flatten_patches = patches.reshape( batch_size, grid_t * grid_h * grid_w, # 总 token 数(注意:未除 merge_size!) channel * temporal_patch_size * patch_size * patch_size, )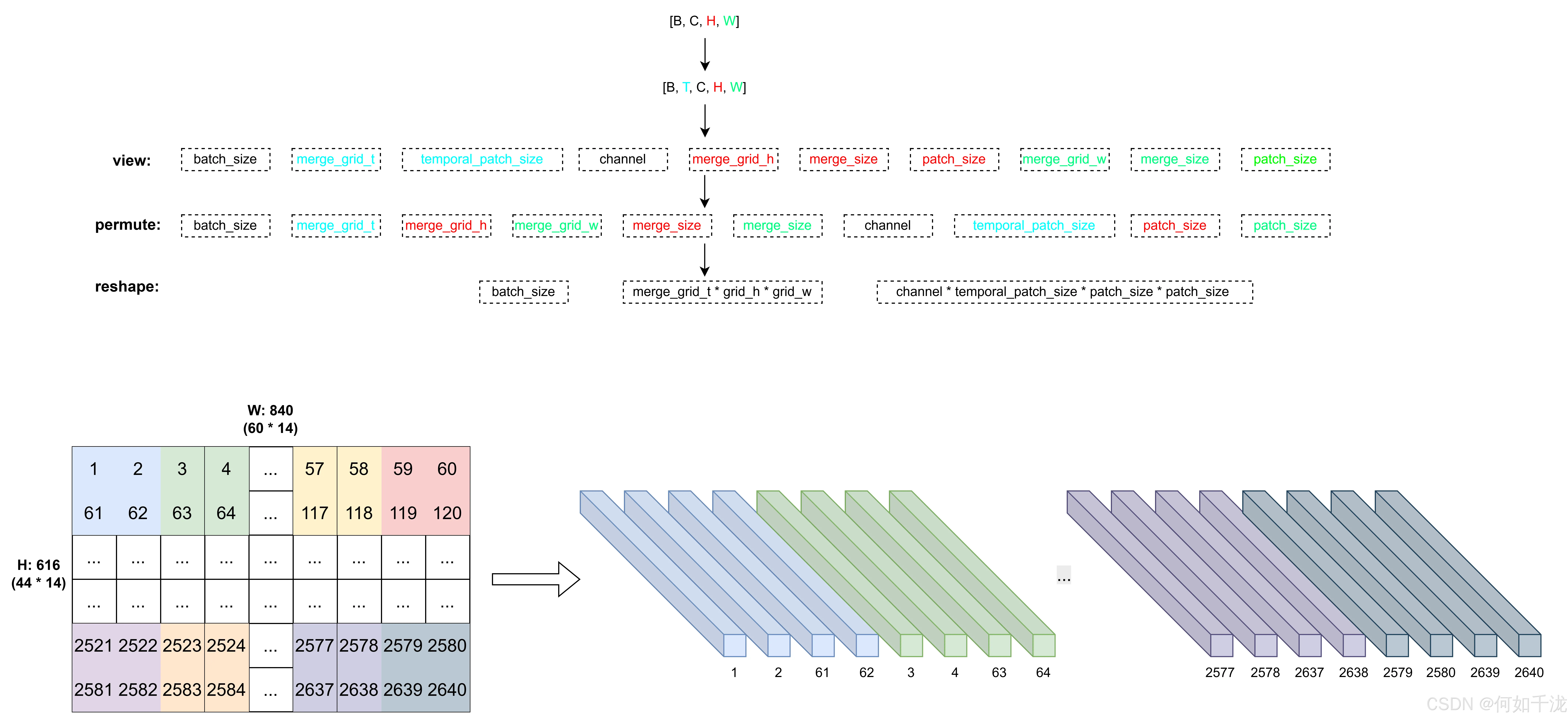
-
存储结果
pythonprocessed_images_grouped[shape] = flatten_patches # [B, num_tokens, embed_dim] processed_grids[shape] = [[grid_t, grid_h, grid_w]] * batch_size
-
-
还原顺序并拼接所有图像
pythonprocessed_images = reorder_images(...) processed_grids = reorder_images(...) pixel_values = torch.cat(processed_images, dim=0) # [total_num_images * num_tokens, embed_dim] image_grid_thw = torch.tensor(processed_grids) # [total_num_images, 3] -
返回
BatchFeaturepythonreturn BatchFeature(data={"pixel_values": ..., "image_grid_thw": ...})具体返回结果如下:
python{'pixel_values': tensor([[-0.9164, -0.7996, -0.9748, ..., -0.6555, -0.6555, -0.6555], [-0.9456, -0.9456, -0.9456, ..., -0.0724, 0.0982, 0.2546], [-0.9456, -0.9456, -0.9456, ..., -0.6555, -0.6555, -0.6555], ..., [-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802], [-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802], [-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802]]), 'image_grid_thw': tensor([[ 1, 44, 60], [ 1, 44, 60], [ 1, 44, 60], [ 1, 44, 60], [ 1, 44, 60], [ 1, 44, 60]])}pixel_values: 扁平化视觉 token(patches) ,shape为[num_images*grid_w*grid_h, channel * temporal_patch_size * patch_size * patch_size]image_grid_thw:每个图像在 token 空间中的 时空网格结构
Step 3:扩展媒体 token
找到所有媒体占位符的位置
python
idx_list = findall(input_ids, media_token)findall是一个辅助函数,返回input_ids中所有media_token的索引位置。
计算每个媒体应扩展为多少个 token
python
merge_length = processor.image_processor.merge_size**2- Qwen2.5-VL 引入了 token merge 机制:将
merge_size × merge_size个原始 patch 合并为 1 个 token; - 例如,原始图像被划分为 44×60 = 2640个 patch,而
merge_size=2,则merge_length=4,最终 token 数 = 2640 / 4 = 660。
定义 _get_new_tokens 函数
python
def _get_new_tokens(i):
token_len = (media_grid_thw[i].prod() // merge_length)
return [media_token] * token_len- 对第
i个媒体(图像或视频),计算其总 patch 数(prod()即 T×H×W),除以merge_length得到应保留的 token 数; - 返回一个长度为
token_len的列表,每个元素都是media_token(即用多个相同的 token 表示一个媒体)。 - 虽然 token ID 相同,但模型会通过位置编码和视觉特征区分它们。
调用 _extend_tokens 执行替换
python
input_ids, labels, loss_scale = self._extend_tokens(
input_ids, labels, loss_scale, idx_list, _get_new_tokens
)- 将原始
input_ids中的 单个<image>token 替换为 多个media_token; - 同时对
labels和loss_scale做相同长度的扩展(通常新插入的位置 label 为-100,不参与 loss); - 保持三者长度一致,供后续训练使用。
Step4:合并结果
python
encoded.update(media_inputs)
encoded['input_ids'] = input_ids
encoded['labels'] = labels
encoded['loss_scale'] = loss_scale具体如下所示:
python
{
'input_ids': [151652, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, 151655, ...],
'labels': [-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, ...],
'loss_scale': None,
'pixel_values': tensor([[-0.9164, -0.7996, -0.9748, ..., -0.6555, -0.6555, -0.6555],
[-0.9456, -0.9456, -0.9456, ..., -0.0724, 0.0982, 0.2546],
[-0.9456, -0.9456, -0.9456, ..., -0.6555, -0.6555, -0.6555],
...,
[-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802],
[-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802],
[-1.7923, -1.7923, -1.7923, ..., -1.4802, -1.4802, -1.4802]]),
'image_grid_thw': tensor([[ 1, 44, 60],
[ 1, 44, 60],
[ 1, 44, 60],
[ 1, 44, 60],
[ 1, 44, 60],
[ 1, 44, 60]]),
'length': 4024
}