1. 技术原理
PAST(Periodic Advertising Sync Transfer,周期性广播同步传输) 是蓝牙低功耗(BLE)协议中引入的一项功能,用于在两台已建立连接的设备之间传递周期性广播的同步信息。简单来说,一台设备(PAST 发送者)可以将它所掌握的某个周期性广播(Periodic Advertising)的同步细节,通过现有的单个 LE 连接发送给另一台设备(PAST 接收者)。这样,后者无需自己扫描就能获得同步参数,实现对该周期性广播的快速跟踪同步。
PAST 功能最初在蓝牙核心规范第 5.1 版中引入,旨在配合当时新推出的 LE Audio 等应用需求。在此之前,设备想要接收周期性广播(例如广播音频的数据)必须自行执行同步建立过程(扫描捕获广播的同步信息)。PAST 提供了一种替代途径,可以降低弱性能设备同步周期性广播的开销。通过让功耗或性能受限的设备将"扫描同步"的任务委托给另一台功能更强的设备来完成,再由后者把同步信息转交过来,PAST 极大减少了前者的扫描时间和能耗。这种机制对电池供电且不宜长时间扫描的设备(如助听器、传感节点等)特别有利。
技术原理(协议过程与数据结构)
周期性广播同步基础:
周期性广播是在 BLE 扩展广播基础上实现的一种广播方式,广播设备以固定的时间间隔发送数据,并在其扩展广播包中包含同步信息(如周期间隔、信道跳频序列等)供接收者使用。常规情况下,接收设备(扫描器)需要监听广播设备发出的扩展广告包(ADV_EXT_IND),从中获取名为 SyncInfo 的周期性广播同步信息,然后据此调整自己的扫描周期去同步接收后续的广播数据。这种扫描同步方法无需建立连接,但要求扫描器持续扫描,功耗较高。
PAST 同步过程:
PAST 提供了第二种同步方法:先由两设备建立一个普通的 LE 连接,再通过链路层的控制数据包传输同步信息。具体而言,PAST 使用一个专门的链路层控制 PDU ------ LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND 数据包来承载同步细节。当 PAST 过程启动时,发送方会在已建立的 ACL 连接上发送该 PDU,其中包含目标周期性广播同步所需的参数,例如广播设备的地址或 ID、周期广告间隔、窗口偏移、信道映射和跳频信息等。接收方拿到这些参数后,就能立即按照指定的时间表去收听相应的周期性广播,而无需自行完成完整的扫描同步过程。
整个 PAST 过程在同步信息成功发送并被接收后即可完成,所需开销非常小,通常只需一次控制数据包交换。
PAST 的两种拓扑模式:
根据设备扮演的角色不同,PAST 可有两种使用拓扑:
-
扫描器中继模式
涉及三台设备:
- 设备 A:周期性广播发送者
- 设备 B:扫描并同步了设备 A 的广播,同时与设备 C 建立连接
- 设备 C:最终接收同步信息的设备
在该模式中,设备 B 充当 PAST 发送者或发起设备,设备 C 为 PAST 接收者。
-
广播者直传模式
仅涉及两台设备:周期性广播发送者本身同时作为 PAST 发起者,通过与接收设备建立的连接,直接将自身广播的同步信息传输给对方。
协议层面,两种拓扑使用完全相同的链路层控制机制,仅角色不同。
需要注意,使用 PAST 需要 BLE 控制器和主机双方的支持。主机可以通过 HCI 命令配置或触发 PAST,例如用于设置当某连接上获取到周期性广播同步时,是否自动向对端发送同步信息,以及发送方式。应用层通常通过协议栈提供的 API 调用这一过程。一旦配置完成,当设备同步到目标周期性广播后,就会通过现有连接发送同步控制包,将同步信息交给对端。对端接收后,主机会收到相应事件通知,并向应用层提供周期性广播同步参数。
与 LE Audio 的集成方式或依赖关系
LE Audio 是蓝牙 5.2 及之后引入的新一代低功耗音频体系,允许 BLE 承载高质量音频流,包括多设备同步音频和广播音频等。PAST 在 LE Audio 中扮演了关键角色,特别是在广播音频(如 Auracast)场景中。
在广播音频应用中,通常由手机或遥控器等设备充当广播助手(Broadcast Assistant) ,负责扫描附近的广播音频源,并协助耳机、助听器等音频接收器接入用户选择的音频流。PAST 正是实现这一"扫描委托"和同步引导的核心机制:
- 扫描与发现:
广播助手扫描周围的扩展广播,发现可用的广播音频源并解析其元数据。 - PAST 传输同步:
当用户选择某个音频广播后,广播助手通过已有的 BLE 连接,将该广播源的周期性广告同步信息发送给接收设备,使其无需自行扫描即可快速加入广播。 - 助听器与省电:
对电池容量极小的助听器而言,PAST 极大减少了扫描时间和能耗,有效延长续航。
在 LE Audio 架构中,引入了广播音频扫描服务等机制,其中利用 PAST 实现"扫描委托"。广播助手不仅负责同步信息传递,还可配合上层协议将解密所需的信息下发给接收器,从而完成完整的广播音频接入过程。
与 PAwR 的协同或区分点
PAwR(Periodic Advertising with Responses,带响应的周期性广播) 是蓝牙 5.4 引入的新特性,在传统单向周期性广播基础上增加了受限的双向通信能力。PAST 与 PAwR 属于不同层面的功能,但可以协同使用,尤其在 PAwR 网络的同步建立阶段。
- 同步方式选择:
PAwR 节点可通过扫描扩展广播或通过 PAST 获取同步信息。对于电源受限的节点,PAST 更具优势。 - 信息范围与额外协商:
PAST 主要传递常规周期性广播的同步信息,而 PAwR 还需要额外的子事件、响应槽等参数,这通常由更高层协议或应用策略完成配置。 - 协同使用场景:
在 PAwR 网络中,PAST 常用于初始配网、低功耗重连等场景,使节点无需长时间扫描即可快速恢复同步。
来个完整实际具体参数解析

1. Opcode
LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_WR_IND- 说明这是 PAST + PAwR 扩展 的 LL 控制 PDU。
- 结构 =
LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND的 SyncInfo + PAwR timing(RspAA、numSubevents...)。
2. ID = 0x0000
ID shall be set to an identifier provided by the Host. This is for use by higher level protocols and its value is not specified or used by this specification. 默认给0吧
3. Sync Packet Offset = 50.07 ms
= 从**参考的 ACL 连接事件锚点(Connection Event Counter)**到 指定 periodic advertising 事件锚点 的时间差。
- 对应字段:
sync_info.offset+sync_info.offset_unit - 你抓包里:
Offset Units = 30 us,所以offset_us = offset * 30us ≈ 50.07 ms
4. Offset Units = 30 us
- 表示
offset的单位。 - 0 = 30 µs,1 = 300 µs(规范定义)。
- 你设置为 0:
offset_unit = 0; // 0 = 30us 单位
5. Offset Adjust = No
- 用在 offset 无法精确表示或者需要"后移/前移一个 event"时做补偿。
- 抓包显示 No,说明没有额外"偏半个 interval"之类的调整。
6. Interval = 60 ms
- Periodic Advertising Interval。
- 对应
sync_info.interval,单位 1.25 ms:实际间隔 us = interval * 1.25ms
- Ellisys已经帮你乘好了显示为 60 ms。
7. Channel Map = Used: 0--36 / Unused: none
- 对应
sync_info.chmapl/chmaph。 - 哪些 DATA channel 会用于 periodic advertising。
- 这里显示 "0--36 / none unused" 说明 37 个数据通道全用。
8. SCA (Clock Accuracy) = 251 ppm -- 501 ppm
- 注意这是 SyncInfo 里的 SCA ,指广播方的睡眠时钟精度等级(Advertiser Clock Accuracy)。
- 对应
sync_info.sca。 - 规范把 SCA 编码成一个 class(0...7),Ellisys帮你解成 ppm 范围。
9. Access Address = 0xA732D7C0
- 对应
sync_info.aa。 - 这是 Periodic Advertising train 的 AA ,也就是你在
periodic_adv_data.aa里配置的 AA。 - PAwR 里还会有一个 RspAA 给终端响应用,那是 WR_IND 扩展字段里的
rsp_aa,不同于这里的AA。
10. CRC Initial Seed = 0x1983AE
- 对应
sync_info.crcinit。 - Periodic advertising 的 CRC 初始值,接收端必须用这个解。
11. Event Counter = 31
-
对应
sync_info.event_counter。 -
这是发送端告诉你:
"本条 SyncInfo 是针对 第 31 次 periodic advertising event 的时间/频点信息"。
-
之后你按
interval推:event 32、33... 的时间都由这个基础 + n*interval 得出。
12. Connection Event Counter = 15 (-1) | 16:30:38.653 749 ...
-
对应
past.conn_event_count。 -
表示 参考的 ACL 连接事件号。规范里是:
offset 是"从某个 connection event 的 anchor 到某个 periodic event"。
-
Ellisys 显示成:
15 (-1):这个 15 是同步参考事件;括号里的-1是相对当前连接事件的差(工具自己的显示方式)。- 右边还有一个时间戳,是这个 connection event 的绝对时间。
相当于说:
"从 connection event #15 的 anchor 往后 50.07ms,会出现 periodic event #31"。
13. Last PA Event Counter = 31 (+15) | 16:30:39.613 ...
- 对应
past.last_pa_event_counter。 通常等于当前的 periodic event counter 或最近一次已广播的 event 计数。- 括号里的
+15是 Ellisys 自己算的"距 Connection Event Counter 的差",大概代表 15 个 periodic interval 之后/之前之类(取决于工具定义)。 - 右边同样给一个事件估算时间。
14. SID = 5
- 对应
past.sid,advertising SID。 - Host 用
SID + AdvA识别哪一组 periodic advertising。
15. AType = Public
- 对应
past.atype。 - 说明
AdvA是 Public Address 还是 Random Address。
16. SCA = 31 ppm -- 50 ppm
- 这个是 外层的 SCA 字段 (你结构体里的
past.sca),通常表示的是 本机/连接方的 SCA。 - 和 SyncInfo 里那个 SCA(Advertiser clock)是两个概念,但很多工具一起显示。
17. PHY = LE 2M
- 对应
past.phy。 - 说明 periodic advertising 使用的 PHY:1M / 2M / Coded。
- RspAA
- numSubevents
- subeventInterval (1.25 ms units)
- responseSlotDelay (1.25 ms units)
- responseSlotSpacing (0.125 ms units)
这些就是你 llcp_past_wr_trans_info_t 里新增的那几个字段,对应到
acad_pawr_timing_info_t 的 rspaa/num_subevents/subevent_interval/...,
用来描述 PAwR 里"从 PA event 锚点开始,subevent / 响应槽的具体时间布局"。
可以怎么理解整条 PAST / WR_IND 的含义?
把这些字段合起来,其实就是一句话:
在 连接事件 #15 的 anchor 之后 50.07ms ,
会有一个 Periodic Advertising event #31 ,
它的 间隔是 60ms 、
用 AA=0xA732D7C0、CRCInit=0x1983AE、Channel Map=0--36、PHY=2M ,广播者的时钟精度是 251--501 ppm ,
使用的广告身份是 SID=5 + AdvA(Public) ,
并且(因为是 WR_IND)还附带了一整套 PAwR 响应时序(RspAA + subevents + slot 布局)。
2. PAST说明规范文章
翻译自:
https://cloud2gnd.com/fundamentals-series-of-le-audio-periodic-advertising-sync-transfer/
Periodic Advertising Sync Transfer (PAST) is a Link Layer procedure [Vol 6, Part B, Section 5.1.13] that enables a device to share synchronization information about a periodic advertising train (PADV) with its connected peer.
周期性广告同步传输(PAST)是一种链路层协议[第 6 卷,第 B 部分,第 5.1.13 节],它使设备能够与其连接的配对设备共享关于周期性广告列车(PADV)的同步信息。
This article explains how PAST works and highlights its benefits for power-constrained and limited user-interface LE Audio Broadcast devices.
本文解释了 PAST 的工作原理,并强调了其对电源受限和用户界面有限的 LE 音频广播设备的好处。
How PAST Works PAST 的工作原理
The LE Periodic Advertising feature allows a device to share its advertising data at regular, predictable intervals. It also provides control information that a listening scanner device can use to align its scanning schedule with the advertiser's.
LE 周期性广播功能允许设备以定期、可预测的间隔共享其广播数据。它还提供控制信息,供监听扫描设备使用,以使其扫描计划与广播者保持一致。
This control information is called periodic advertising synchronization information. It details the interval timings and the frequency hopping sequence used by the periodic advertiser. To obtain this information, the listening device performs the periodic advertising synchronization establishment procedure.
这种控制信息称为周期性广播同步信息。它详细说明了周期性广播者使用的间隔时间和跳频序列。为了获取这些信息,监听设备执行周期性广播同步建立程序。
There are two ways to implement the periodic advertising synchronization establishment procedure. The first method involves the scanner device performing the scanning procedure, where it listens for non-connectable and non-scannable advertising packets containing the periodic advertising synchronization information.
实现周期性广告同步建立流程有两种方法。第一种方法涉及扫描器设备执行扫描流程,其中它监听包含周期性广告同步信息的非连接性且不可扫描的广告数据包。
The second method uses the PAST procedure. PAST was introduced in January 2021 as part of the Core Specification update v5.1. It allows a device to share synchronization details needed to receive periodic advertisements with another device through an ACL connection. This means a scanner can delegate the task of scanning for the periodic advertising synchronization information to another device. That device then relays this information back using PAST.
第二种方法使用 PAST 流程。PAST 于 2021 年 1 月作为核心规范更新 v5.1 的一部分被引入。它允许一个设备通过 ACL 连接与其他设备共享接收周期性广告所需的同步信息。这意味着扫描器可以将扫描周期性广告同步信息的任务委托给另一个设备。然后该设备使用 PAST 将此信息转发回来。
When the PAST procedure is initiated, a PAST sender, also known as the Initiating device, shares the periodic advertising synchronization information with a connected peer using a data packet called the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU. The procedure is complete when this packet has been sent or received.
当 PAST 流程被启动时,PAST 发送者(也称为发起设备)会通过一个名为 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 的数据包,将周期性广告同步信息与连接的配对设备共享。当该数据包被发送或接收时,流程即完成。

LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU
The LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU is a Link Layer Control PDU. It is used by a device to inform its connected peer about the synchronization details needed to synchronize with a specific PADV.
LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 是一种链路层控制 PDU。它被用于设备通知其连接的对端设备,以同步到特定 PADV 所需的同步细节。
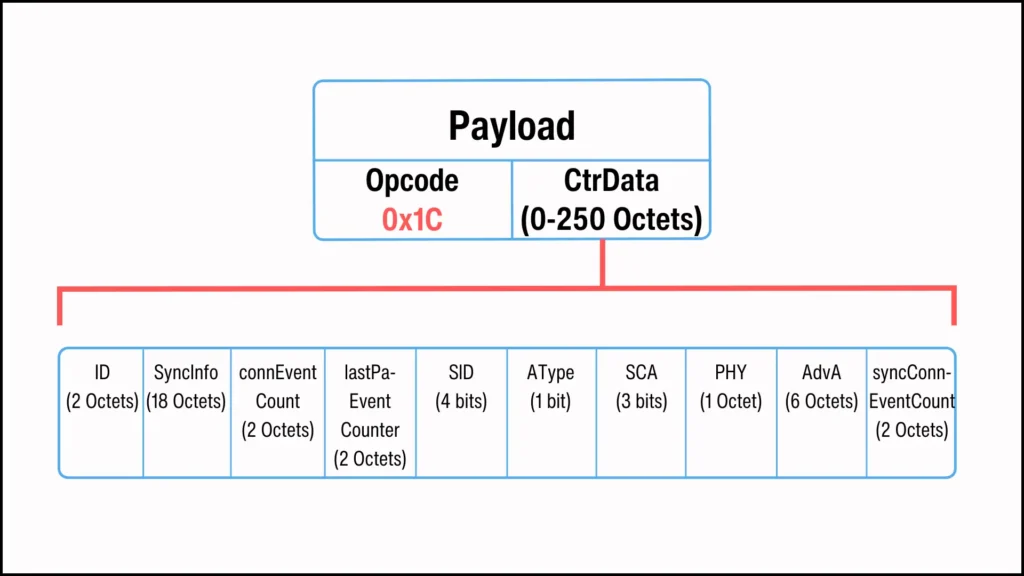 Figure 1. LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU format.
Figure 1. LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU format.
图 1. LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 格式。
PAST Topologies PAST 拓扑结构
In the PAST procedure, three devices are generally involved [Vol 6, Part B, Section 5.1.13.1]:
在 PAST 过程中,通常涉及三个设备[第 6 卷,第 B 部分,第 5.1.13.1 节]:
- Periodic Advertiser: This device advertises the PADV and its associated synchronization information.
周期性广告器:该设备广播 PADV 及其相关的同步信息。 - Initiating Device: This device relays the periodic advertising synchronization information to a connected peer device.
发起设备:该设备将周期性广告同步信息转发给一个已连接的同伴设备。 - Receiving Device: This device receives the synchronization information from a connected peer device.
接收设备:该设备从一个已连接的同伴设备接收同步信息。

PAST can be implemented in two topologies:
PAST 可以在两种拓扑中实现:
1. Transfer by Scanner: In this topology, the periodic advertiser, initiating device, and receiving device are three different devices. The initiating device scans for PADV from the periodic advertiser. It also has an ACL connection with the receiving device and sends it the synchronization information needed to synchronize with the periodic advertiser.
- 扫描器传输:在此拓扑中,周期性广告主、发起设备和接收设备是三个不同的设备。发起设备从周期性广告主处扫描 PADV。它还与接收设备有一个 ACL 连接,并向其发送与周期性广告主同步所需的同步信息。
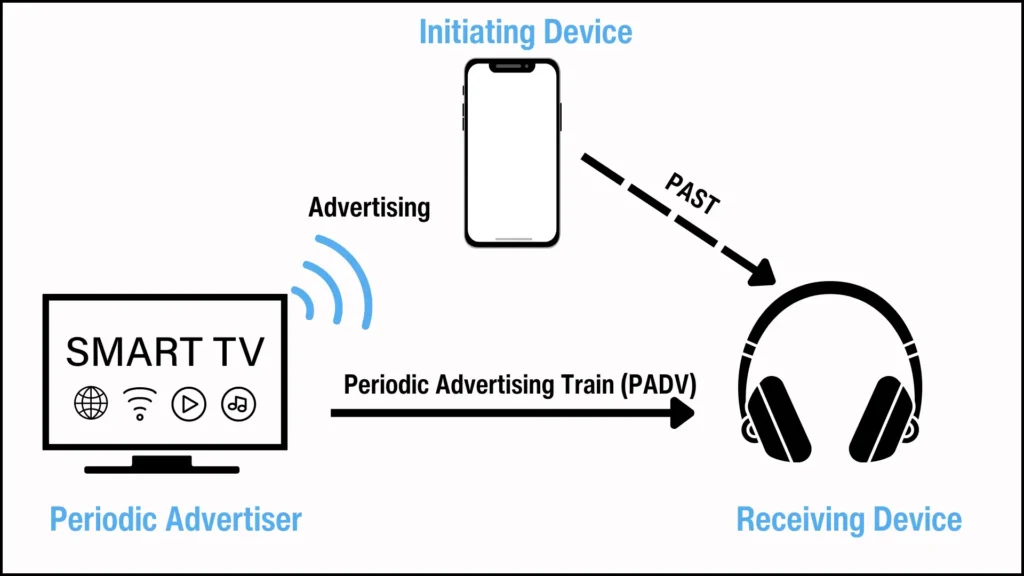 Figure 2. PAST performed by the initiating device.
Figure 2. PAST performed by the initiating device.
图 2. 由发起设备执行的 PAST。
2. Transfer by Advertiser: In this topology, the periodic advertiser and the initiating device are the same device. The periodic advertiser transfers the periodic advertising synchronization information about its periodic advertising set to the receiving device.
- 广告主传输:在此拓扑中,周期性广告主和发起设备是同一设备。周期性广告主将其周期性广告集的周期性广告同步信息传输给接收设备。
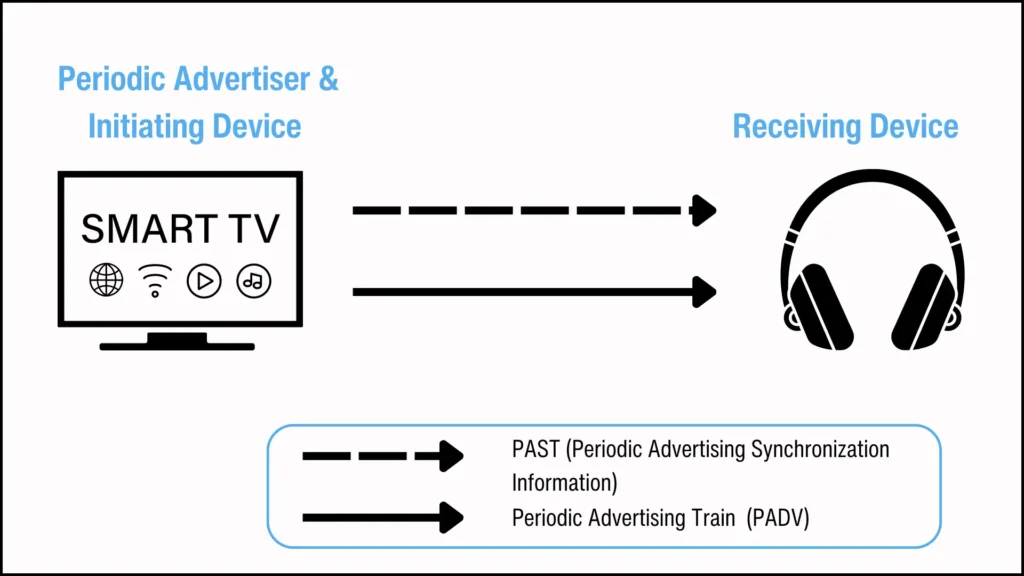 Figure 3. PAST performed by the periodic advertiser.
Figure 3. PAST performed by the periodic advertiser.
图 3. 周期性广告发布者执行的 PAST。
Generic Access Profile (GAP) Modes and Procedures for PAST 通用访问配置文件(GAP)模式与 PAST 的传输程序
The GAP layer defines the modes and access procedures that devices use when working with PAST.
GAP 层定义了设备在与 PAST 协同工作时使用的模式和访问程序。
Transfer by Scanner 扫描器传输
When implementing PAST with three devices, Device A is the periodic advertiser, Device B is the initiating device, and Device C is the receiving device. Here's how the GAP modes and procedures work:
在实现包含三台设备的 PAST 时,设备 A 是周期性广告者,设备 B 是启动设备,设备 C 是接收设备。以下是 GAP 模式与程序的工作方式:
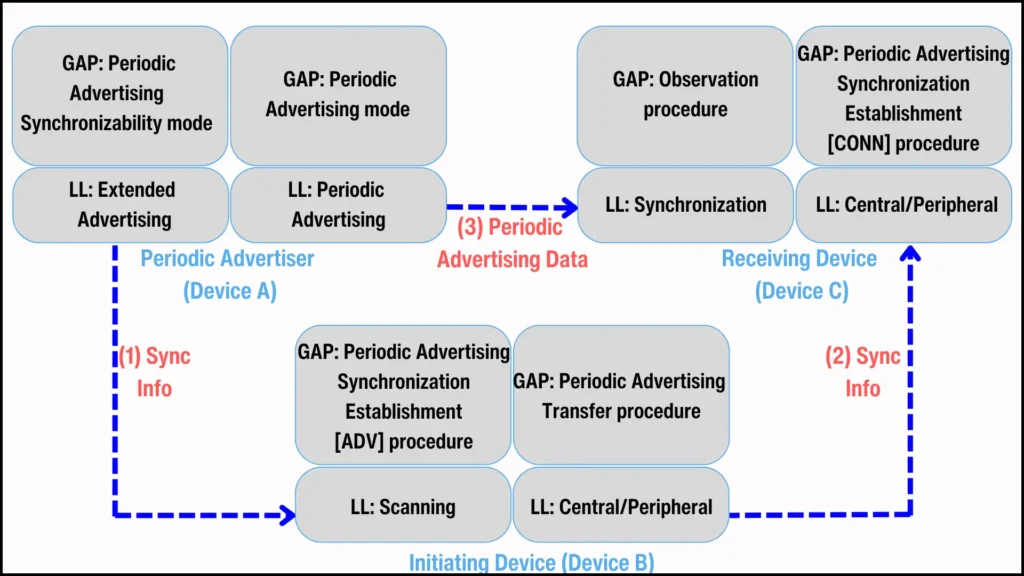 Figure 4. GAP modes and procedures for PAST implementation
Figure 4. GAP modes and procedures for PAST implementation
图 4. PAST 实现的 GAP 模式和流程
- Device A (Periodic Advertiser): It acts as the GAP Broadcaster. It sends out periodic advertising synchronization information through the GAP periodic advertising synchronizability mode and broadcasts periodic advertisements (PADV) using the GAP periodic advertising mode.
设备 A(周期性广播者):它充当 GAP 广播器。它通过 GAP 周期性广播同步模式发送周期性广播同步信息,并使用 GAP 周期性广播模式广播周期性广播(PADV)。 - Device B (Initiating Device): It scans for periodic advertising synchronization details as the GAP Observer. And then uses the GAP Central/Peripheral role to transfer this information to Device C using the GAP periodic advertising synchronization transfer procedure.
设备 B(发起设备):它作为 GAP 观察者扫描周期性广告同步详细信息,然后使用 GAP 中心/外围角色通过 GAP 周期性广告同步传输程序将此信息传输到设备 C。 - Device C (Receiving Device): It receives the periodic advertising synchronization information as the GAP Central/Peripheral. It also acts as a GAP Observer, using the information to sync with Device A and receive its periodic advertisements.
设备 C(接收设备):它作为 GAP 中心/外围接收周期性广告同步信息。它也充当 GAP 观察者,使用该信息与设备 A 同步并接收其周期性广告。
Transfer by Advertiser 广告发布者传输
When implementing PAST with two devices, Device A acts as both the periodic advertiser and the initiating device, while Device C is the receiving device.
在实现 PAST 时,如果使用两个设备,设备 A 既充当周期性广播者,也充当发起设备,而设备 C 是接收设备。
Device A sends periodic advertisements and maintains an ACL connection with the scanner device. Through this connection, Device A provides the necessary synchronization information to the scanner. In this case, the GAP modes and procedures are as follows:
设备 A 发送周期性广播,并与扫描设备保持 ACL 连接。通过这种连接,设备 A 向扫描设备提供必要的同步信息。在这种情况下,GAP 模式和流程如下:
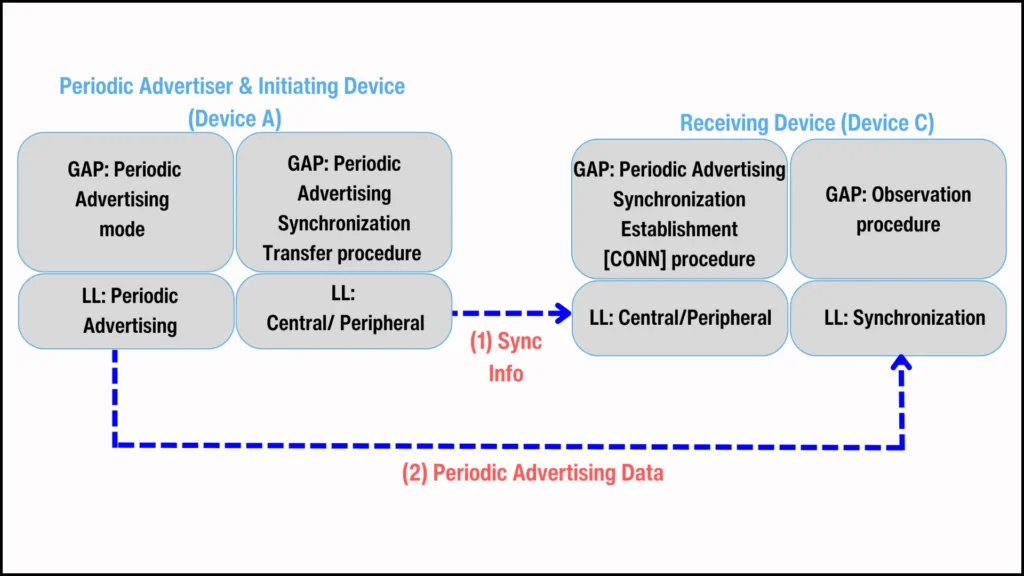 Figure 5. GAP modes and procedures for PAST implementation
Figure 5. GAP modes and procedures for PAST implementation
图 5. PAST 实现的 GAP 模式和流程
- Device A (Periodic Advertiser & Initiating Device): As the GAP Broadcaster, it sends out periodic advertisements. It also acts as the GAP Central/Peripheral, using the Periodic Advertising Synchronization Establishment procedure to send synchronization information to the connected scanner.
设备 A(周期性广播器 & 发起设备):作为 GAP 广播器,它发送周期性广播。它还作为 GAP 中心/外围设备,使用周期性广播同步建立程序向连接的扫描器发送同步信息。 - Device C (Receiving Device): Acts as the GAP Central/Peripheral, it receives periodic advertising synchronization details through the GAP periodic advertising synchronization establishment procedure. It also functions as the GAP Observer, using the received synchronization information to synchronize with the periodic advertiser and receive its periodic advertisements.
设备 C(接收设备):作为 GAP 中心/外围设备,它通过 GAP 周期性广播同步建立程序接收周期性广播同步详情。它还作为 GAP 观察者,使用接收到的同步信息与周期性广播器同步,并接收其周期性广播。
Host Controller Interface (HCI) Commands for PAST PAST 的 Host 控制器接口(HCI)命令
In both topologies, on the receiving device, the Host issues the 'HCI_LE_Set_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer_Parameters' command. This command tells the Controller what it should do when it receives the periodic advertising synchronization information ( LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU).
在两种拓扑结构中,在接收设备上,Host 发出"HCI_LE_Set_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer_Parameters"命令。该命令告诉控制器在收到周期性广播同步信息(LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU)时应该做什么。
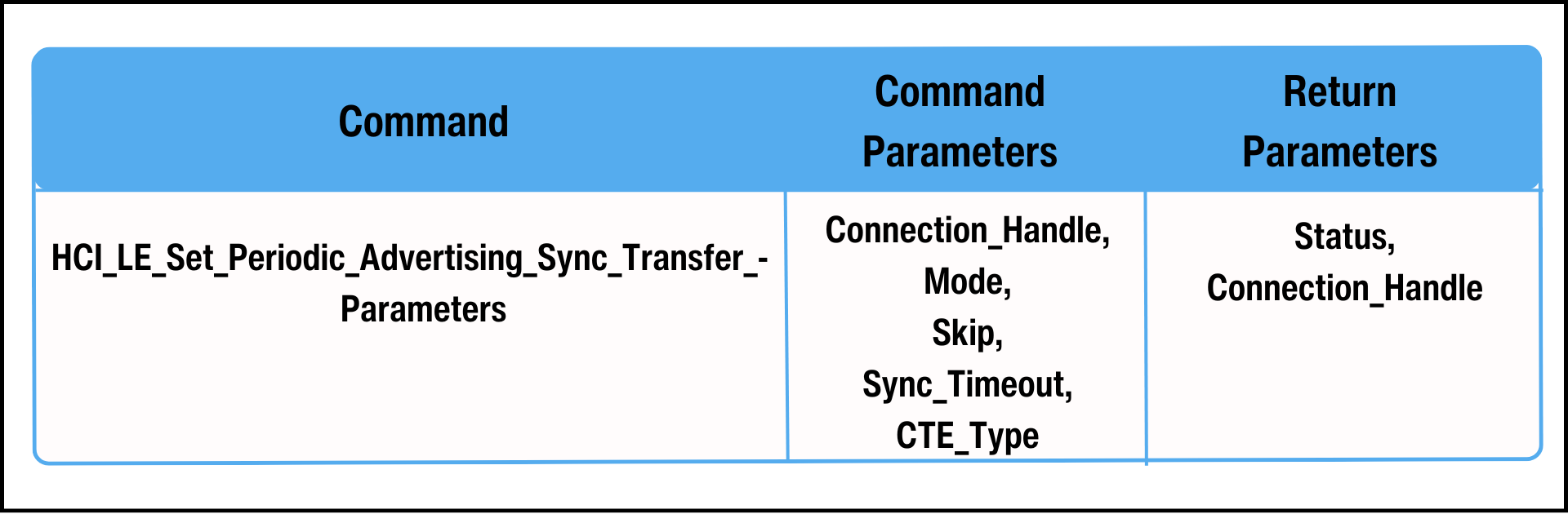 Figure 6. HCI_LE_Set_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer_Parameters
Figure 6. HCI_LE_Set_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer_Parameters
图 6. HCI_LE_Set_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer_Parameters
Transfer by Scanner 扫描器传输
In this PAST topology, three different devices are involved: Device A, Device B, and Device C. Device A is the periodic advertiser, Device B is the initiating device, and Device C is the receiving device.
在此 PAST 拓扑中,涉及三种不同的设备:设备 A、设备 B 和设备 C。设备 A 是周期性广播设备,设备 B 是发起设备,设备 C 是接收设备。
Device A sends out periodic advertisements. Device B and Device C are connected. Device C wants to receive PADV from Device A, and so solicits Device B to handle scanning for the needed periodic synchronization information.
设备 A 发送周期性广告。设备 B 和设备 C 已连接。设备 C 希望从设备 A 接收 PADV,因此请求设备 B 处理扫描所需的周期性同步信息。
Device B scans for Device A's PADV. Then, Device B's Host uses the HCI_LE_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer command to tell its Controller to transfer the PADV's periodic advertising synchronization information to Device C's Controller using the PAST procedure.
设备 B 扫描设备 A 的 PADV。然后,设备 B 的主机使用 HCI_LE_Periodic_Advertising_Sync_Transfer 命令告知其控制器,通过 PAST 程序将 PADV 的周期性广告同步信息传输到设备 C 的控制器。
The HCI commands and Link Layer messages between these three devices is shown in Figure 7 below:
这三台设备之间的 HCI 命令和链路层消息如图 7 所示:
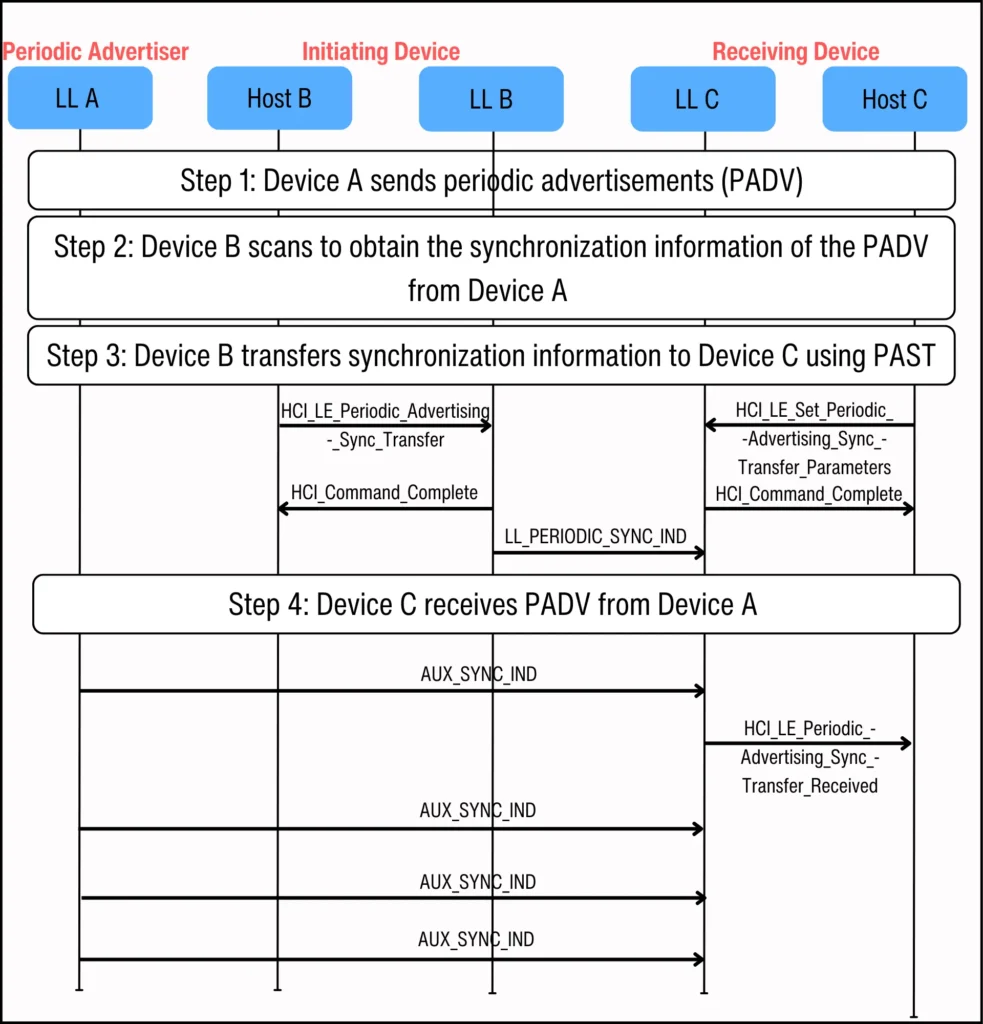 Figure 7. HCI commands and Link Layer messages for PAST implementation
Figure 7. HCI commands and Link Layer messages for PAST implementation
图 7. 用于 PAST 实现的 HCI 命令和链路层消息
Transfer by Advertiser 广告主传输
In this topology, two devices are involved: Device A and Device B. Device A acts as both the periodic advertiser and the initiating device.
在此拓扑中,涉及两个设备:设备 A 和设备 B。设备 A 既充当周期性广告主,也充当发起设备。
The Host of Device A sends the HCI_LE_Periodic_Advertising_Set_Info_Transfer_Parameters command. This command instructs Device A's Controller to transfer the synchronization information about a periodic advertisement (PADV) in one of its advertising sets to Device B, the receiving device.
设备 A 的主机发送 HCI_LE_Periodic_Advertising_Set_Info_Transfer_Parameters 命令。该命令指示设备 A 的控制器将其广告集中有关周期性广告(PADV)的同步信息传输给接收设备 B。
The HCI commands and Link Layer messages between the two devices is shown in Figure 8 below:
两台设备之间的 HCI 命令和链路层消息如图 8 所示:
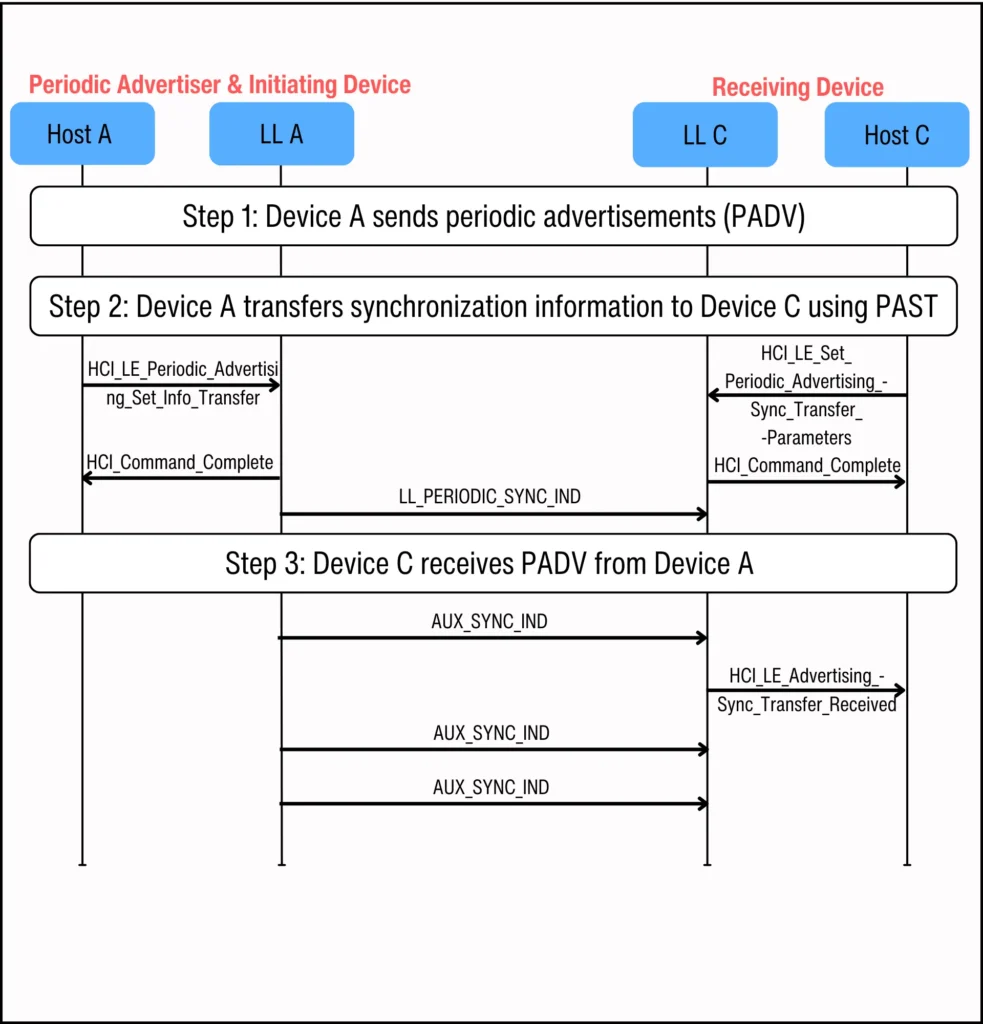 Figure 8. HCI commands and Link layer messages for PAST implementation
Figure 8. HCI commands and Link layer messages for PAST implementation
图 8. PAST 实现的 HCI 命令和链路层消息
PAST and LE Audio PAST 和 LE Audio
LE Audio uses the Basic Audio Profile (BAP) to define roles and procedures for Bluetooth LE devices involved in sending and receiving audio.
LE Audio 使用基本音频配置文件(BAP)来定义参与发送和接收音频的蓝牙 LE 设备所扮演的角色和流程。
For broadcasting Audio Streams, BAP specifies four device roles: Broadcast Source, Broadcast Sink, Scan Delegator, and Broadcast Assistant.
用于广播音频流,BAP 指定了四种设备角色:广播源、广播接收端、扫描委托者和广播助手。
A Broadcast Source device transmits broadcast Audio Streams to unconnected devices using one or more Broadcast Isochronous Streams (BISes) within a Broadcast Isochronous Group (BIG). A BIG is a group of a maximum of 31 time-related BISes.
广播源设备使用一个或多个广播等时流(BIS)在广播等时组(BIG)内将广播音频流传输给未连接的设备。BIG 是由最多 31 个与时间相关的 BIS 组成的组。
Additionally, a Broadcast Source also transmits extended advertising (EA) and periodic advertising (PADV) PDUs. EA PDU points to the PADV. The PADV PDU transmits the configuration parameters (BASE data) and synchronization information (BIGInfo data) for the broadcast Audio Streams.
此外,广播源设备还传输扩展广告(EA)和周期性广告(PADV)PDU。EA PDU 指向 PADV。PADV PDU 传输广播音频流的配置参数(BASE 数据)和同步信息(BIGInfo 数据)。
A Broadcast Sink device discovers and receives broadcast Audio Streams. It scans for EA that point to PADV that points to a BIG that contains one or more BISes used to transport the broadcast Audio Streams. However, scanning for EA PDUs can drain the power of small-battery devices quickly.
广播接收端设备发现并接收广播音频流。它扫描指向 PADV 的 EA,而 PADV 指向包含一个或多个用于传输广播音频流的 BIS 的 BIG。然而,扫描 EA PDU 会快速消耗小电池设备的电量。
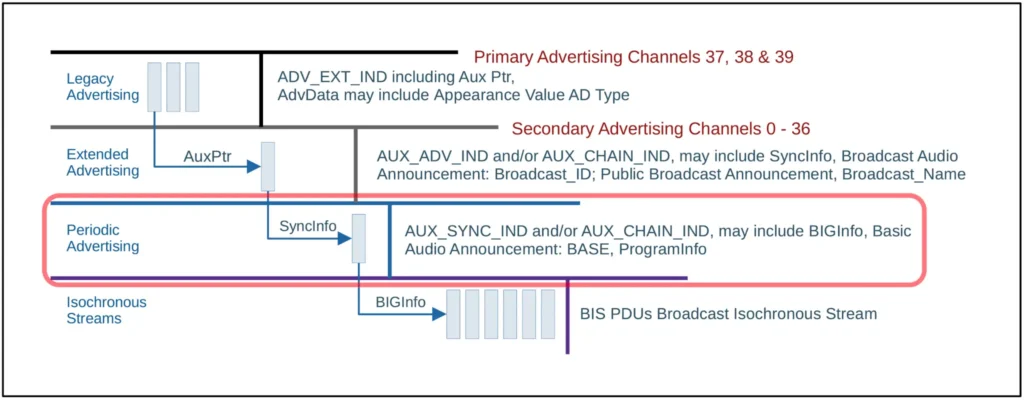 Figure 9. Multi-stage scanning required to synchronize to an on-going BIS
Figure 9. Multi-stage scanning required to synchronize to an on-going BIS
图 9. 同步到正在进行的 BIS 所需的多阶段扫描
Remote Broadcast Scanning and Scan Offloading 远程广播扫描和扫描卸载
A Scan Delegator delegates the task of scanning for SyncInfo from EA PDUs to another device, known as the Broadcast Assistant. This process is known as Remote Broadcast Scanning. It helps the Scan Delegator save power by reducing its scanning activities.
扫描委托者将扫描 SyncInfo 的任务从 EA PDU 委托给另一个设备,该设备称为广播助手。这个过程称为远程广播扫描。它通过减少扫描活动来帮助扫描委托者节省电量。
A Broadcast Assistant establishes a connection with the Scan Delegator. It then sends SyncInfo to the Scan Delegator through the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU, using the PAST procedure. This action is referred to as Scan Offloading or ScanInfo Transfer.
广播助手与扫描委托者建立连接。然后,它通过 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU,使用 PAST 程序将 SyncInfo 发送给扫描委托者。此操作称为扫描卸载或扫描信息传输。
Scan Delegators can use the SyncInfo data to synchronize to a PADV. This helps it find BASE configurations that describe the broadcast audio stream or BIGInfo data.
扫描委托者可以使用 SyncInfo 数据与一个 PADV 同步。这有助于它找到描述广播音频流或 BIGInfo 数据的 BASE 配置。

PAST allows an LE Audio Broadcast Sink to offload the scanning for SyncInfo needed to receive PADV to another more resourceful device. This is useful for Broadcast Sink devices with limited power. These devices save energy by relying on connected peers that do not have the same power limitations to find the PADV leading to the relevant BIS channel.
PAST 允许 LE 音频广播接收器将接收 PADV 所需的 SyncInfo 扫描任务卸载到另一个资源更丰富的设备。这对于电源有限的广播接收器设备很有用。这些设备通过依赖没有相同电源限制的连接对等设备来寻找通往相关 BIS 通道的 PADV,从而节省能源。
Additionally, PAST also reduces redundancy. A Central device can scan and distribute synchronization details to connected Peripheral devices, instead of multiple Peripherals scanning independently for the same synchronization information.
此外,PAST 还减少了冗余。一个中央设备可以扫描并向连接的周边设备分发同步详情,而不是多个周边设备独立地扫描相同的同步信息。
Broadcast Audio Scan Service Characteristics 广播音频扫描服务特性
The Broadcast Assistant and the Scan Delegator use the Broadcast Audio Scan Service (BASS) to communicate about broadcast Audio Streams. The Scan Delegator acts as the BASS server, while the Broadcast Assistant is the BASS client.
广播助手和扫描委托者使用广播音频扫描服务(BASS)来通信广播音频流。扫描委托者作为 BASS 服务器,而广播助手是 BASS 客户端。
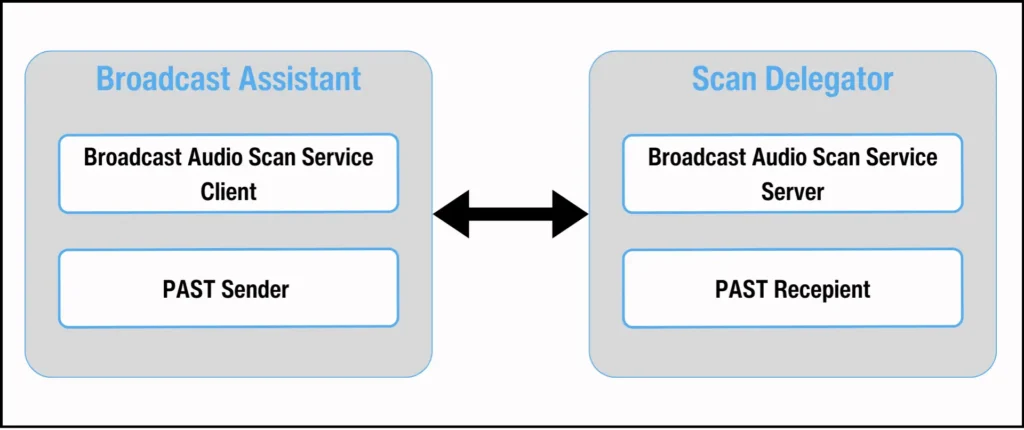 Figure 10. Broadcast Assistant relationship to Scan Delegator.
Figure 10. Broadcast Assistant relationship to Scan Delegator.
图 10. 广播助手与扫描委托者的关系。
The Scan Delegator solicits one or more Broadcast Assistants to scan on its behalf by advertising connectable EA PDUs with the BASS UUID. The Broadcast Assistant(s) in proximity scan for these solicitations from the Scan Delegator and reply by initiating a connection with the Scan Delegator.
扫描委托者通过广播可连接的 EA PDU 并使用 BASS UUID 来征集一个或多个广播助手为其扫描。邻近的广播助手会扫描来自扫描委托者的征集请求,并通过与扫描委托者建立连接来回复。
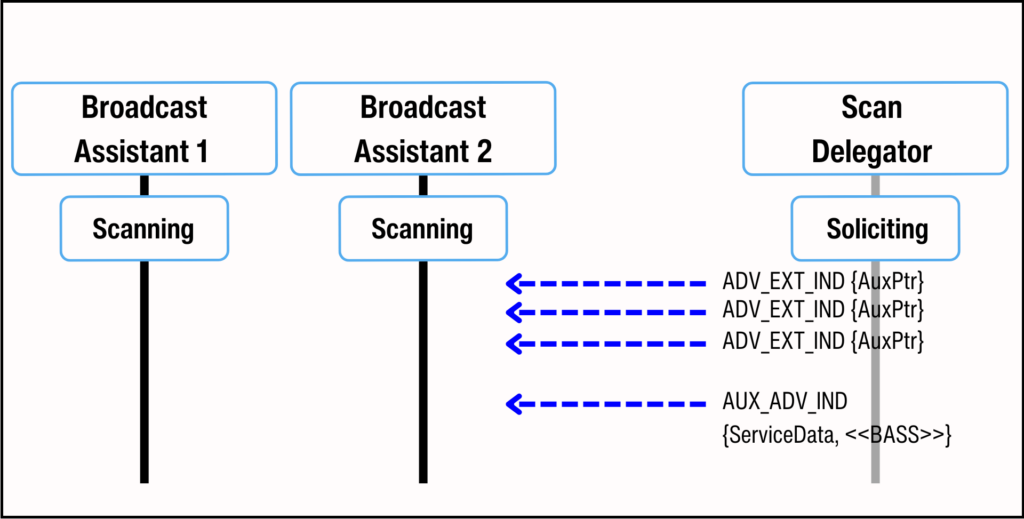 Figure 11. Scan Delegator soliciting for Broadcast Assistants.
Figure 11. Scan Delegator soliciting for Broadcast Assistants.
图 11. 扫描委托者征集广播助手。
BASS has two characteristics: Broadcast Audio Scan Control Point characteristic and the Broadcast Receive State characteristic.
BASS 具有两个特性:广播音频扫描控制点特性和广播接收状态特性。
The Broadcast Assistant updates the Scan Delegator on its Remote Broadcast Scanning status by writing values to the Broadcast Audio Scan Control Point characteristic. An opcode value of 0x01 signifies that Remote Broadcast Scanning has started, while 0x00 indicates that it has stopped and so the Broadcast Assistant is no longer scanning on behalf of the Scan Delegator.
广播助手通过向广播音频扫描控制点特征写入值来更新扫描委托方的远程广播扫描状态。操作码值 0x01 表示远程广播扫描已开始,而 0x00 表示它已停止,因此广播助手不再代表扫描委托方进行扫描。
The Scan Delegator may change its scanning behavior based on the Remote Broadcast Scanning status of the Broadcast Assistant. It can either stop scanning if the Broadcast Assistant is scanning on its behalf or start scanning when the Broadcast Assistant stops. The specific behavior is determined by the implementation.
扫描委托方可以根据广播助手的远程广播扫描状态改变其扫描行为。如果广播助手正在代表它扫描,它可以停止扫描;如果广播助手停止扫描,它可以开始扫描。具体行为由实现决定。
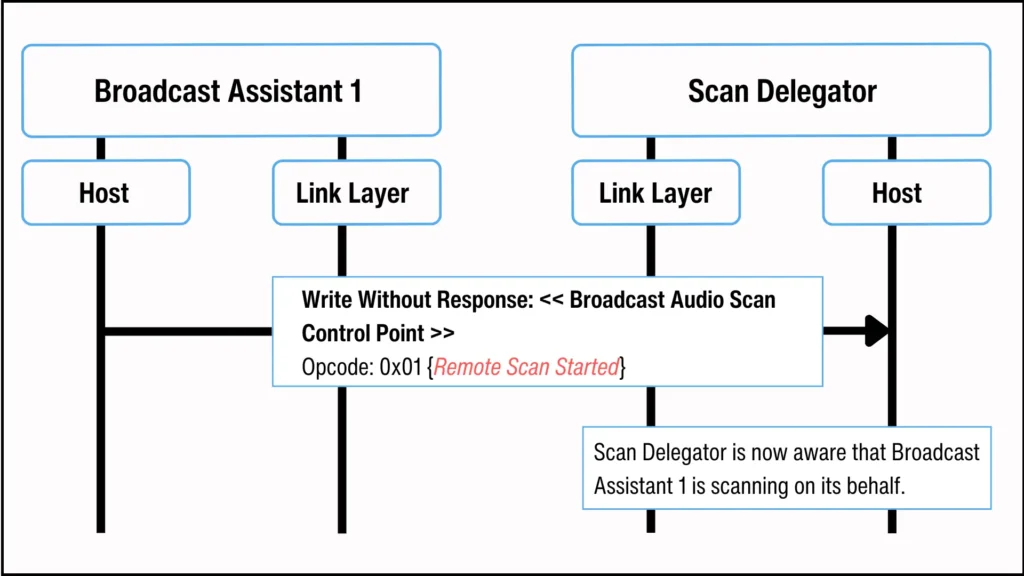 Figure 12. Broadcast Assistant in remote scanning informs Scan Delegator.
Figure 12. Broadcast Assistant in remote scanning informs Scan Delegator.
图 12. 远程扫描中的广播助手通知扫描委托方。
The Broadcast Assistant uses the Broadcast Receive State characteristic, either by reading it or receiving a notification, to check if the Scan Delegator requests SyncInfo data. It looks for a value of 0x01 (SyncInfo Request) in the PA_Sync_State field of this characteristic. The Broadcast Assistant should not transfer SyncInfo data to the Scan Delegator until it detects this 0x01 value in the PA_Sync_State field.
广播助手通过读取或接收通知来使用广播接收状态特性,以检查扫描委托者是否请求 SyncInfo 数据。它在该特性的 PA_Sync_State 字段中查找 0x01(SyncInfo 请求)的值。广播助手在检测到 PA_Sync_State 字段中的 0x01 值之前,不应将 SyncInfo 数据传输给扫描委托者。
Once the Broadcast Assistant confirms that the Scan Delegator is requesting SyncInfo data, it will transfer the data using the PAST procedure. This procedure is completed when the Broadcast Assistant sends an LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU to the Scan Delegator.
一旦广播助手确认扫描委托方正在请求同步信息数据,它将使用 PAST 程序传输数据。当广播助手向扫描委托方发送 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 时,此程序完成。
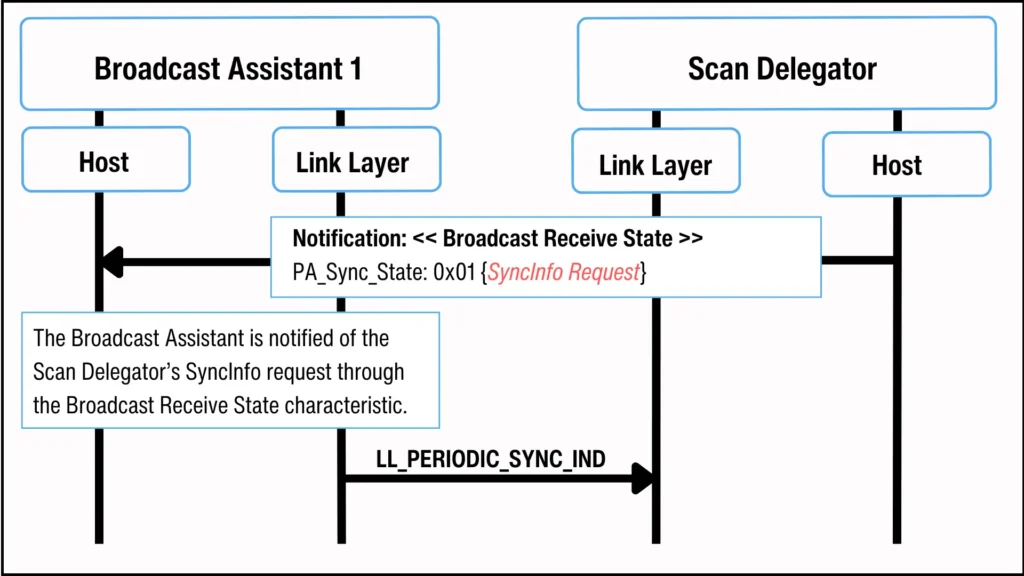 Figure 13. Broadcast Assistant receives SyncInfo request and then performs Scan Offloading.
Figure 13. Broadcast Assistant receives SyncInfo request and then performs Scan Offloading.
图 13. 广播助手接收 SyncInfo 请求,然后执行扫描卸载。
LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU: AdvA and ID fields LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU:AdvA 和 ID 字段
When initiating PAST, the default behavior of the Broadcast Assistant is to match the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU AdvA parameter and the AdvA field of the ADV_EXT_IND PDUs from the Broadcast Source identified by the Broadcast Receive State characteristic requesting for the SyncInfo.
在启动 PAST 时,广播助手的默认行为是匹配 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 的 AdvA 参数以及由请求 SyncInfo 的广播接收状态特性标识的广播源发送的 ADV_EXT_IND PDU 中的 AdvA 字段。
The Broadcast Assistant should only use a different AdvA parameter if:
广播助手只有在以下情况下才应该使用不同的 AdvA 参数:
- It is aware that the Broadcast Source has updated the AdvA parameter for that advertising set.
已知广播源已更新该广告集的 AdvA 参数。 - The new AdvA value is derived from the same Identity Resolving Key (IRK) used to generate both the Resolvable Private Address for the original AdvA parameter and the Source_Address field in the Broadcast Receive State characteristic.
新的 AdvA 值是由用于生成原始 AdvA 参数的可解析私有地址以及广播接收状态特性的 Source_Address 字段的同一身份解析密钥(IRK)派生而来。
The Broadcast Assistant writes the ID field in the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU using the table below:
广播助手使用下表将 ID 字段写入 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU:
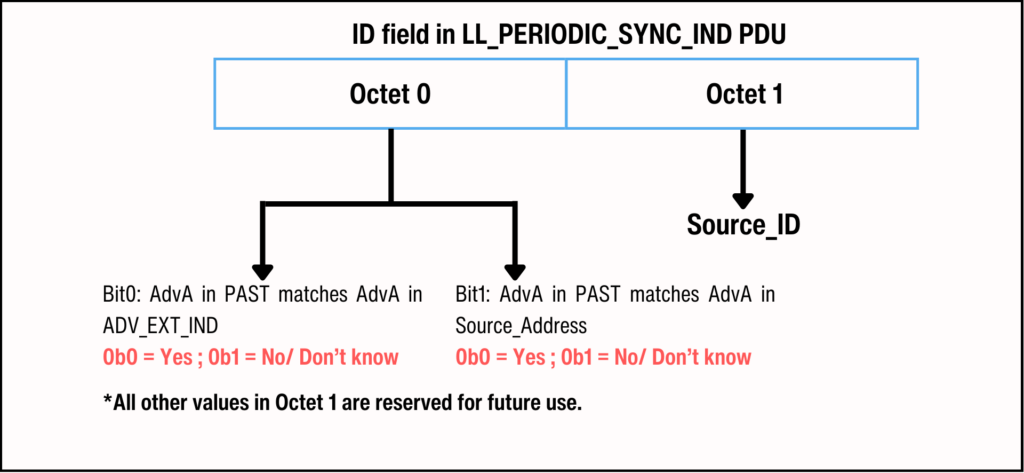 Figure 14. Contents of ID field in the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU during PAST.
Figure 14. Contents of ID field in the LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU during PAST.
图 14. PAST 期间 LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND PDU 中 ID 字段的 contents。
Concluding Remarks 结论性评述
This article explains what PAST is and how the Core Specification enables it at the Link Layer, GAP, and HCI layers. PAST is useful when a Broadcast Sink, limited by battery life, cannot continuously search for SyncInfo that leads to a PADV and then to a BIS.
本文解释了 PAST 是什么,以及核心规范如何在链路层、GAP 层和 HCI 层实现它。当广播接收端受限于电池寿命,无法持续搜索导致 PADV 并最终到达 BIS 的 SyncInfo 时,PAST 非常有用。
In such cases, the Broadcast Sink may use a collocated Scan Delegator to assign the task of scanning for SyncInfo to another device, the Broadcast Assistant. The SyncInfo data is then received from the Broadcast Assistant using the PAST procedure.
在这种情况下,广播接收器可能会使用一个同位的扫描委托者来将扫描 SyncInfo 的任务分配给另一个设备,即广播助手。然后,SyncInfo 数据通过 PAST 程序从广播助手接收。