Seata(AT模式)源码解析------全局事务的提交
- DefaultGlobalTransaction#commit()
- [DefaultTransactionManager#commit(String xid)](#commit(String xid))
- [DefaultCoordinator#doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, ...)](#doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, ...))
- DefaultCoordinator#init()
- AbstractRMHandler#handle(BranchCommitRequest)
- AsyncWorker
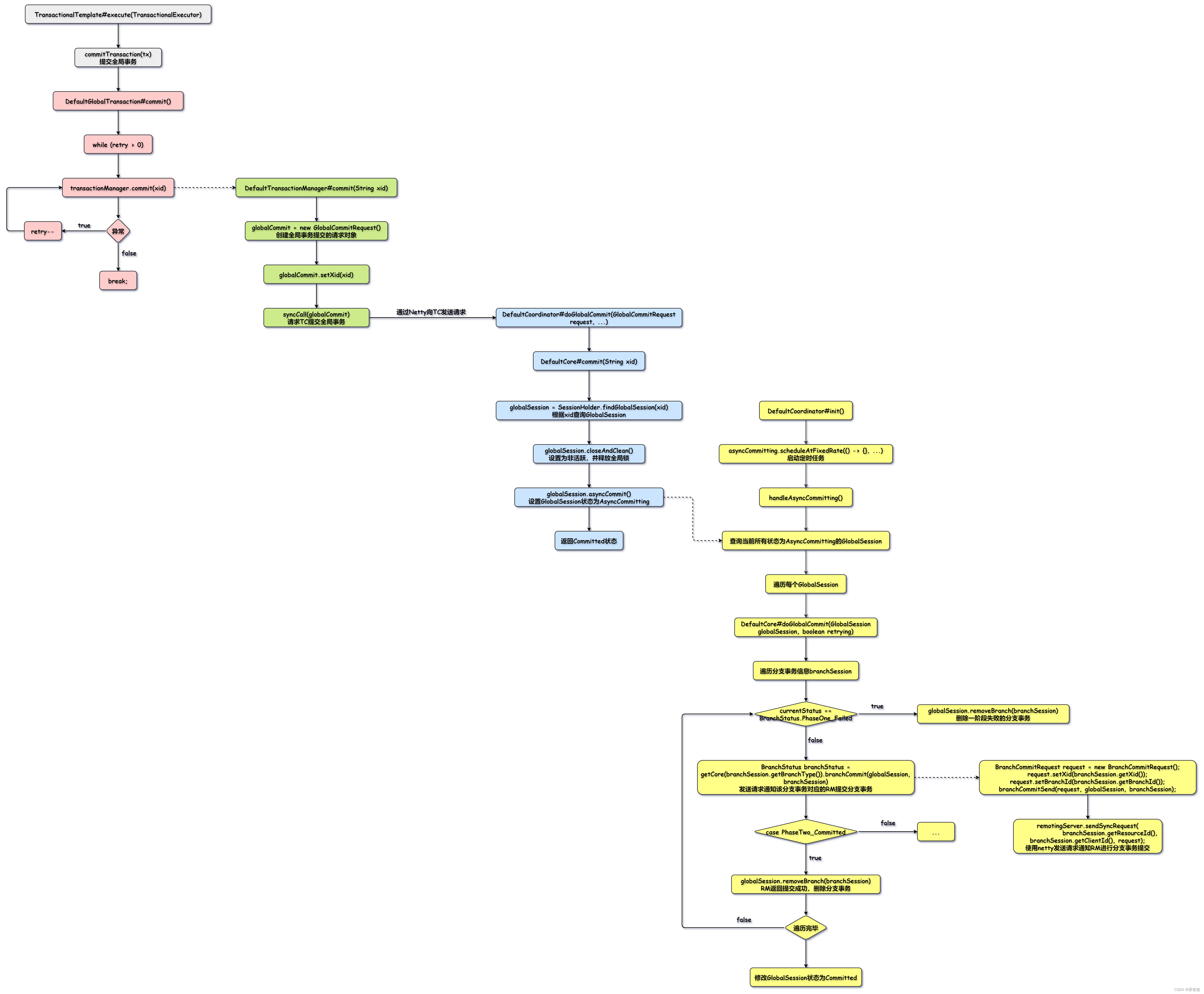
当调用链一切顺利,没有发生异常时,TM就会发起全局事务提交。
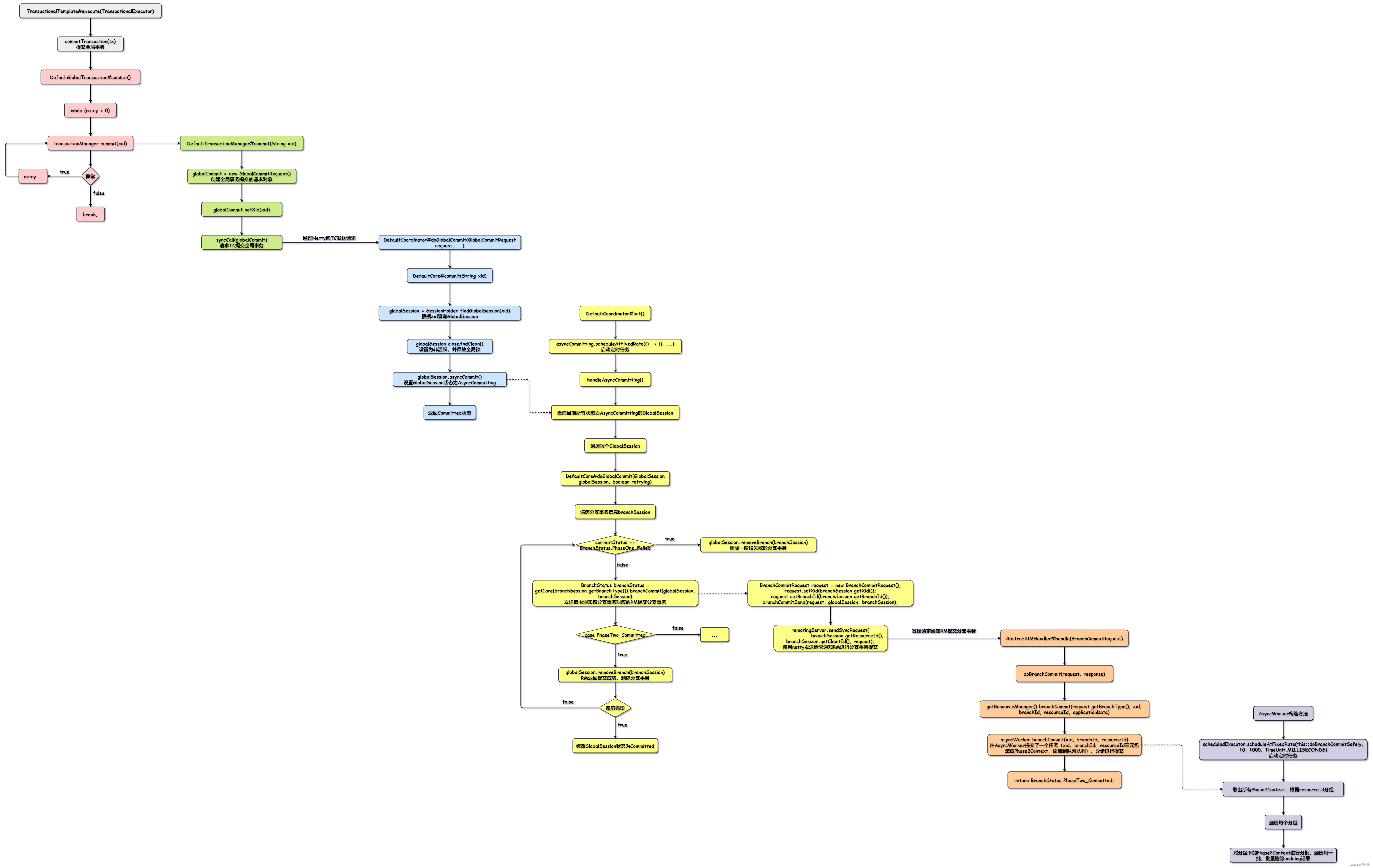
TransactionalTemplate#execute(TransactionalExecutor)
java
try {
// 开启全局事务
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// 执行业务逻辑
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 回滚全局事务
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 提交全局事务(本篇文章分析的重点)
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {}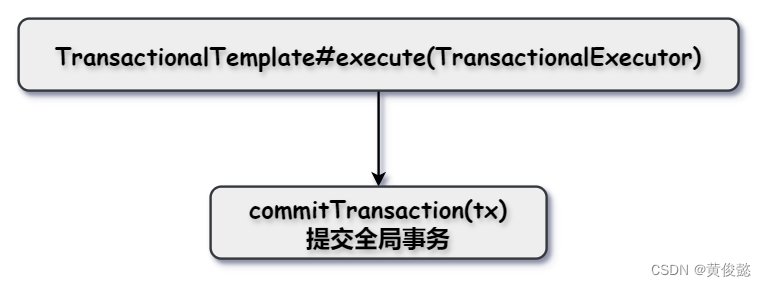
commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx)
java
private void commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
// 进入DefaultGlobalTransaction#commit()
tx.commit();
} catch () {}
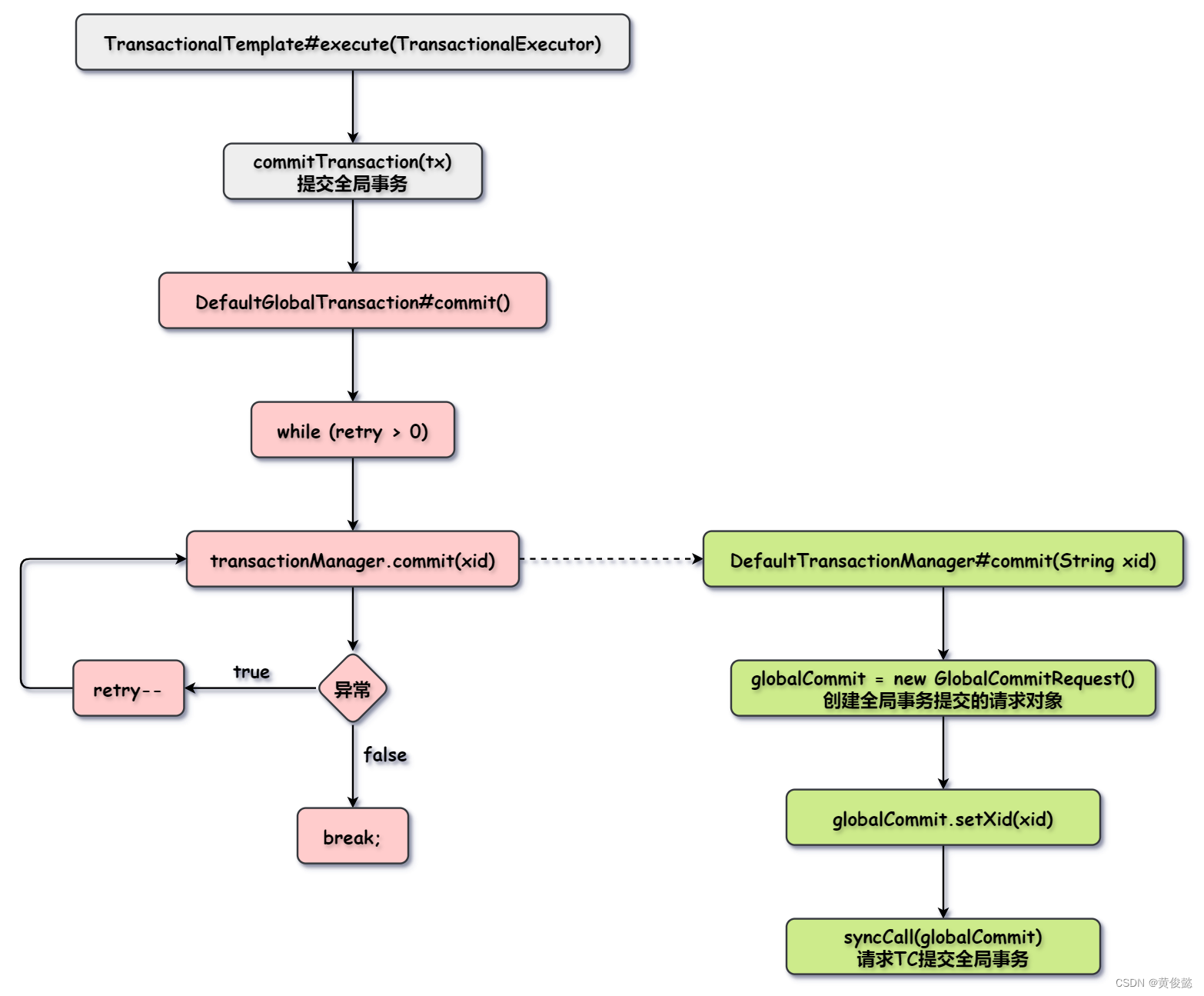
}commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx)会调用DefaultGlobalTransaction的commit()方法,里面会进行全局事务提交。
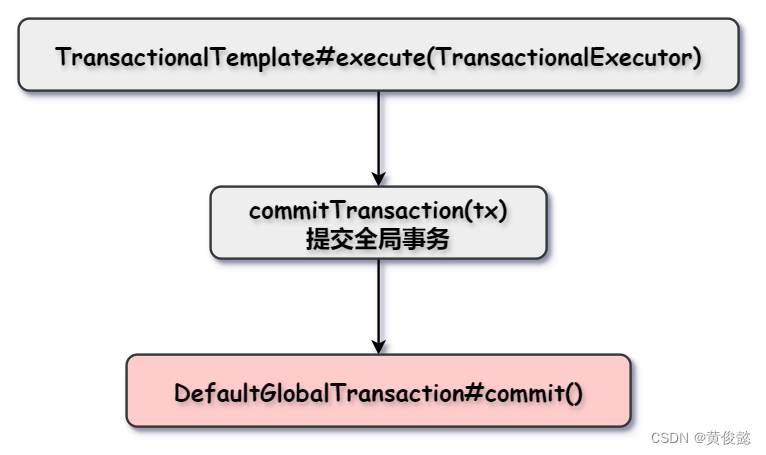
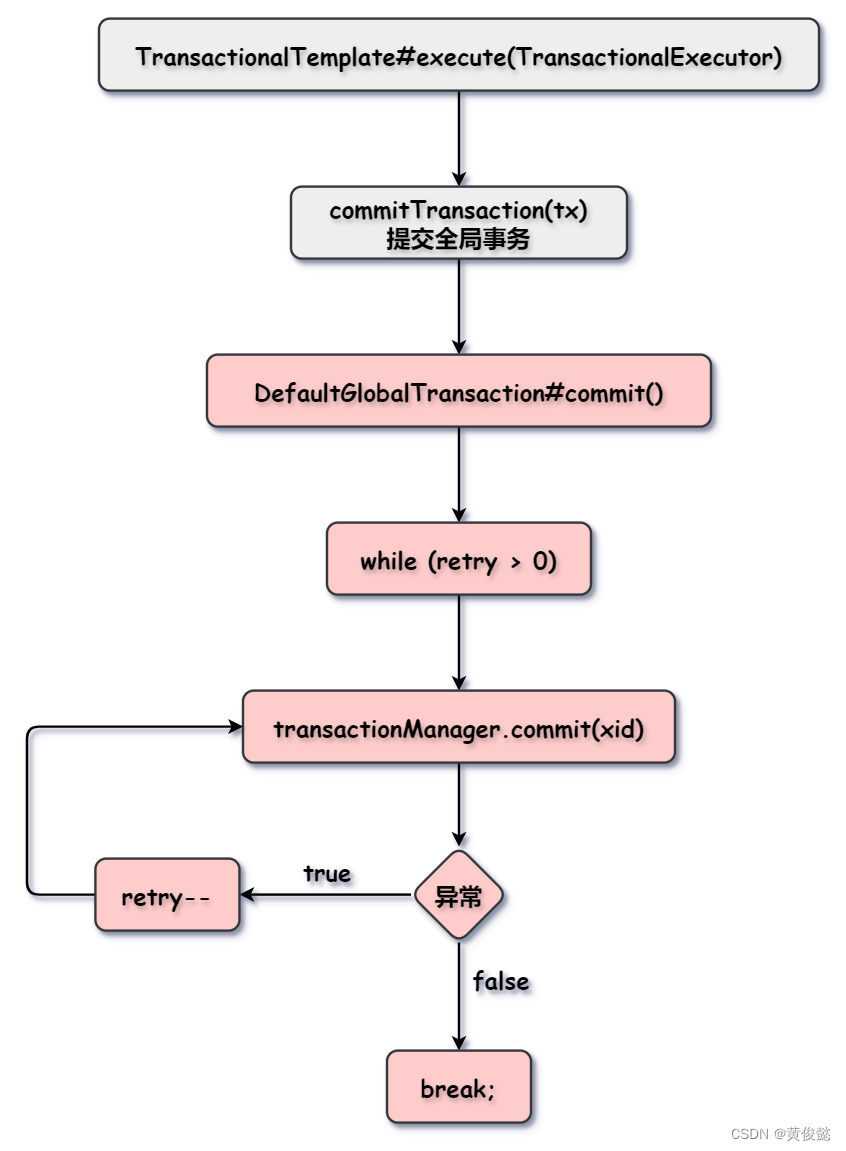
DefaultGlobalTransaction#commit()
java
@Override
public void commit() throws TransactionException {
try {
// 提交失败可以重试
while (retry > 0) {
try {
// 调用TransactionManager的commit方法提交全局事务
status = transactionManager.commit(xid);
break;
} catch () {
retry--;
}
}
} finally {}
}
DefaultTransactionManager#commit(String xid)
java
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
// 创建全局事务提交的请求对象
GlobalCommitRequest globalCommit = new GlobalCommitRequest();
globalCommit.setXid(xid);
// 请求TC提交全局事务
GlobalCommitResponse response = (GlobalCommitResponse) syncCall(globalCommit);
return response.getGlobalStatus();
}
java
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 使用Netty发起请求
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch () {}
}syncCall方法里面就是通过Netty向TC发起请求。
TC接收到请求后会调用DefaultCoordinator#doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, ...)方法处理请求。
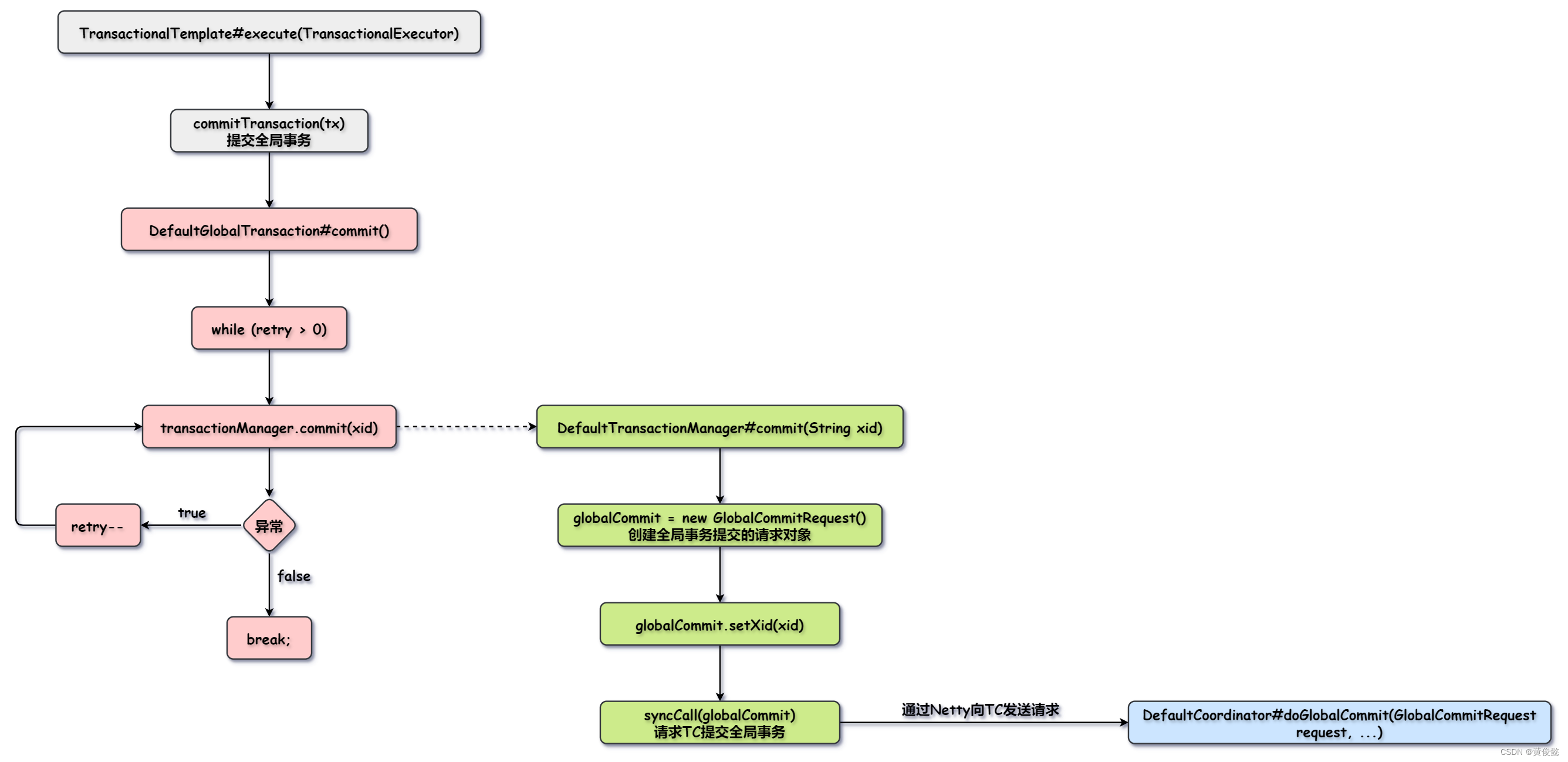
DefaultCoordinator#doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, ...)
java
@Override
protected void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
// 调用DefaultCode的commit方法处理全局事务提交请求
response.setGlobalStatus(core.commit(request.getXid()));
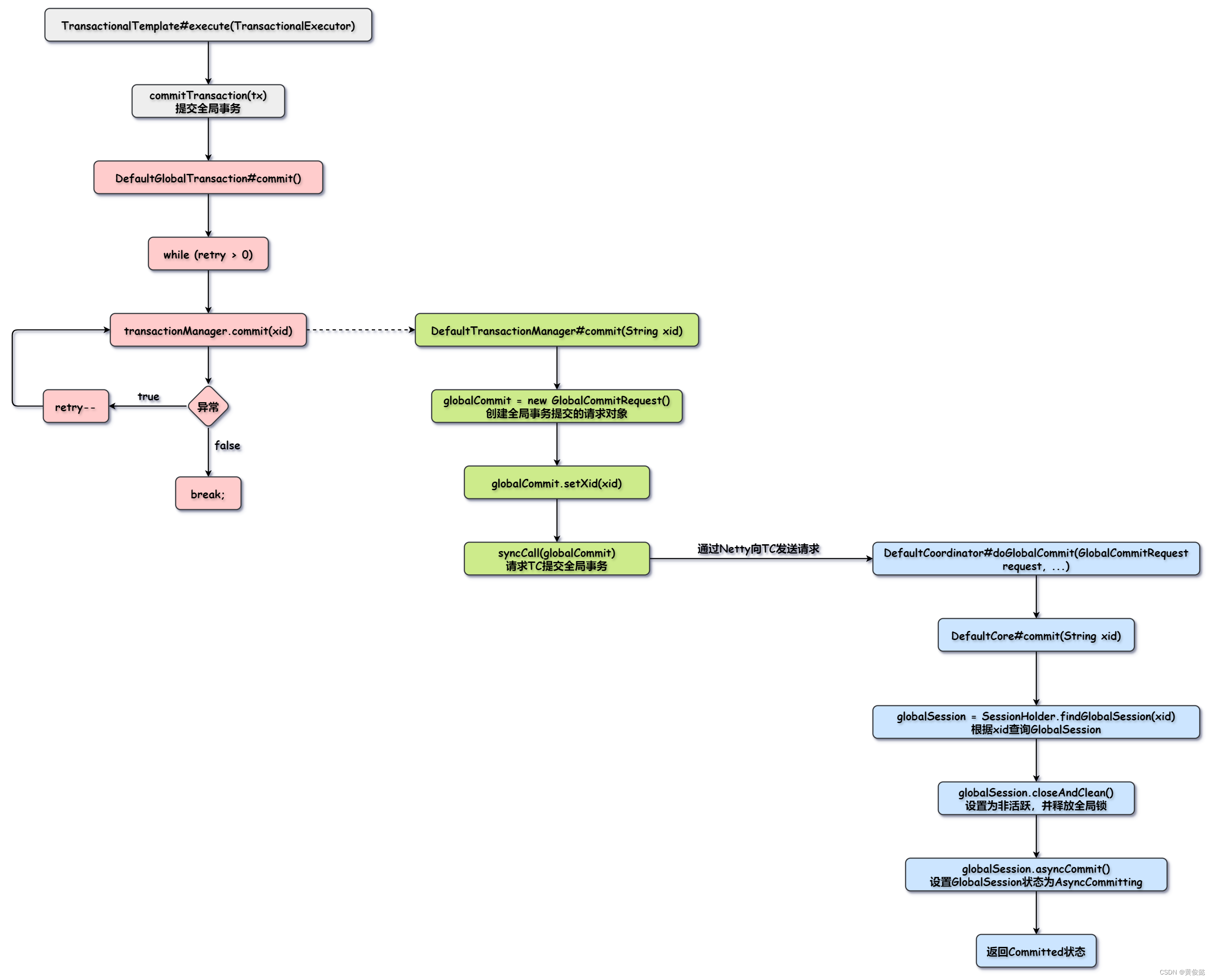
}DefaultCore#commit(String xid)
java
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
// 根据xid查询GlobalSession
GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
if (globalSession == null) {
// 如果GlobalSession为null,返回Finished状态
return GlobalStatus.Finished;
}
boolean shouldCommit = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// GlobalSession设置为非活跃,并释放全局锁
globalSession.closeAndClean();
if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
// 如果AT模式,会进入这个分支,设置GlobalSession状态为AsyncCommitting
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
globalSession.asyncCommit();
// shouldCommit为false
return false;
} else {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Committing);
return true;
}
}
return false;
});
if (shouldCommit) {
// 同步提交的逻辑,AT模式不会进这里,忽略...
} else {
// 返回Committed状态
return globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting ? GlobalStatus.Committed : globalSession.getStatus();
}
}AT模式下,不会进行同步提交。DefaultCore#commit(String xid)方法在AT模式下干的事情处理释放全局锁以外,仅仅就是把GlobalSession的状态改为AsyncCommitting也就没了。
GlobalSession被修改为AsyncCommitting状态后,会有定时任务对它们进行后续的处理。
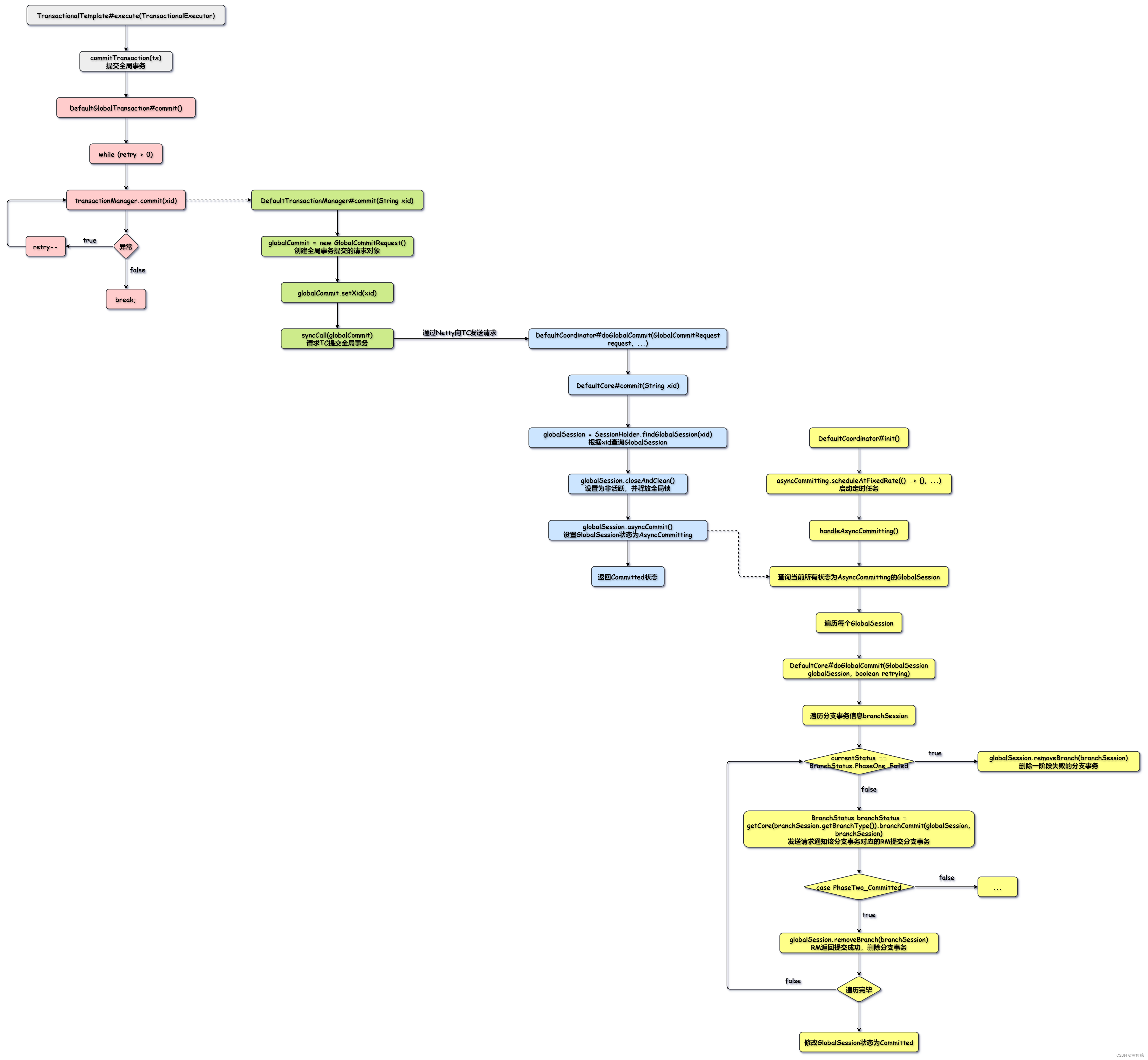
DefaultCoordinator#init()
java
public void init() {
asyncCommitting.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
boolean lock = SessionHolder.acquireDistributedLock(ASYNC_COMMITTING);
if (lock) {
try {
// 定时任务处理AsyncCommitting状态的GlobalSession
handleAsyncCommitting();
} catch () {} finally {
SessionHolder.releaseDistributedLock(ASYNC_COMMITTING);
}
}
}, 0, ASYNC_COMMITTING_RETRY_PERIOD, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}下面我们单独看看handleAsyncCommitting()方法。
handleAsyncCommitting()
java
protected void handleAsyncCommitting() {
// 查询当前所有状态为AsyncCommitting的GlobalSession
Collection<GlobalSession> asyncCommittingSessions = SessionHolder.getAsyncCommittingSessionManager()
.allSessions();
SessionHelper.forEach(asyncCommittingSessions, asyncCommittingSession -> {
try {
// 调用DefaultCore的doGlobalCommit方法
core.doGlobalCommit(asyncCommittingSession, true);
} catch () {}
});
}handleAsyncCommitting()方法会查询所有状态为AsyncCommitting的GlobalSession,然后遍历每一个GlobalSession,调用DefaultCore的doGlobalCommit方法进行处理。
DefaultCore#doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying)
java
@Override
public boolean doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
boolean success = true;
if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
// saga模式的处理逻辑,忽略
} else {
// 遍历分支事务信息branchSession 进行处理
Boolean result = SessionHelper.forEach(globalSession.getSortedBranches(), branchSession -> {
BranchStatus currentStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
if (currentStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
// 删除一阶段失败的分支事务
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
return CONTINUE;
}
try {
// 发送请求通知该分支事务对应的RM提交分支事务
BranchStatus branchStatus = getCore(branchSession.getBranchType()).branchCommit(globalSession, branchSession);
switch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Committed:
// RM返回提交成功,删除分支事务
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
return CONTINUE;
case PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable:
default:
}
} catch () {}
return CONTINUE;
});
}
if (success && globalSession.getBranchSessions().isEmpty() && retrying) {
// 修改GlobalSession状态为Committed
SessionHelper.endCommitted(globalSession);
}
return success;
}
getCore(branchSession.getBranchType()).branchCommit(globalSession, branchSession)里面会发送请求通知RM进行分支事务提交。
java
public BranchStatus branchCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 构建请求对象
BranchCommitRequest request = new BranchCommitRequest();
request.setXid(branchSession.getXid()); // 全局事务id
request.setBranchId(branchSession.getBranchId()); // 分支事务id
request.setResourceId(branchSession.getResourceId());
request.setApplicationData(branchSession.getApplicationData());
request.setBranchType(branchSession.getBranchType());
// 发送请求通知RM进行分支事务提交
return branchCommitSend(request, globalSession, branchSession);
} catch () {}
}
java
protected BranchStatus branchCommitSend(BranchCommitRequest request, GlobalSession globalSession,
BranchSession branchSession) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 使用netty发送请求通知RM进行分支事务提交
BranchCommitResponse response = (BranchCommitResponse) remotingServer.sendSyncRequest(
branchSession.getResourceId(), branchSession.getClientId(), request);
return response.getBranchStatus();
}最终通过netty发送请求。
AbstractRMHandler#handle(BranchCommitRequest)
RM接收到请求后,会进入AbstractRMHandler#handle(BranchCommitRequest)方法。
java
@Override
public BranchCommitResponse handle(BranchCommitRequest request) {
BranchCommitResponse response = new BranchCommitResponse();
exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<BranchCommitRequest, BranchCommitResponse>() {
@Override
public void execute(BranchCommitRequest request, BranchCommitResponse response)
throws TransactionException {
// RM进行分支事务提交的处理
doBranchCommit(request, response);
}
}, request, response);
return response;
}
java
protected void doBranchCommit(BranchCommitRequest request, BranchCommitResponse response)
throws TransactionException {
String xid = request.getXid();
long branchId = request.getBranchId();
String resourceId = request.getResourceId();
String applicationData = request.getApplicationData();
// 根据xid和branchId提交分支事务
BranchStatus status = getResourceManager().branchCommit(request.getBranchType(), xid, branchId, resourceId,
applicationData);
response.setXid(xid);
response.setBranchId(branchId);
response.setBranchStatus(status);
}
java
public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
// 往AsyncWorker提交了一个任务,异步进行提交
return asyncWorker.branchCommit(xid, branchId, resourceId);
}调用asyncWorker的branchCommit方法,里面就是提交一个任务到队列。
java
public BranchStatus branchCommit(String xid, long branchId, String resourceId) {
Phase2Context context = new Phase2Context(xid, branchId, resourceId);
// xid、branchId、resourceId三元包装成Phase2Context,添加到队列队列
addToCommitQueue(context);
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Committed;
}asyncWorker.branchCommit(xid, branchId, resourceId)方法添加任务到队列后,会返回PhaseTwo_Committed表示提交成功。
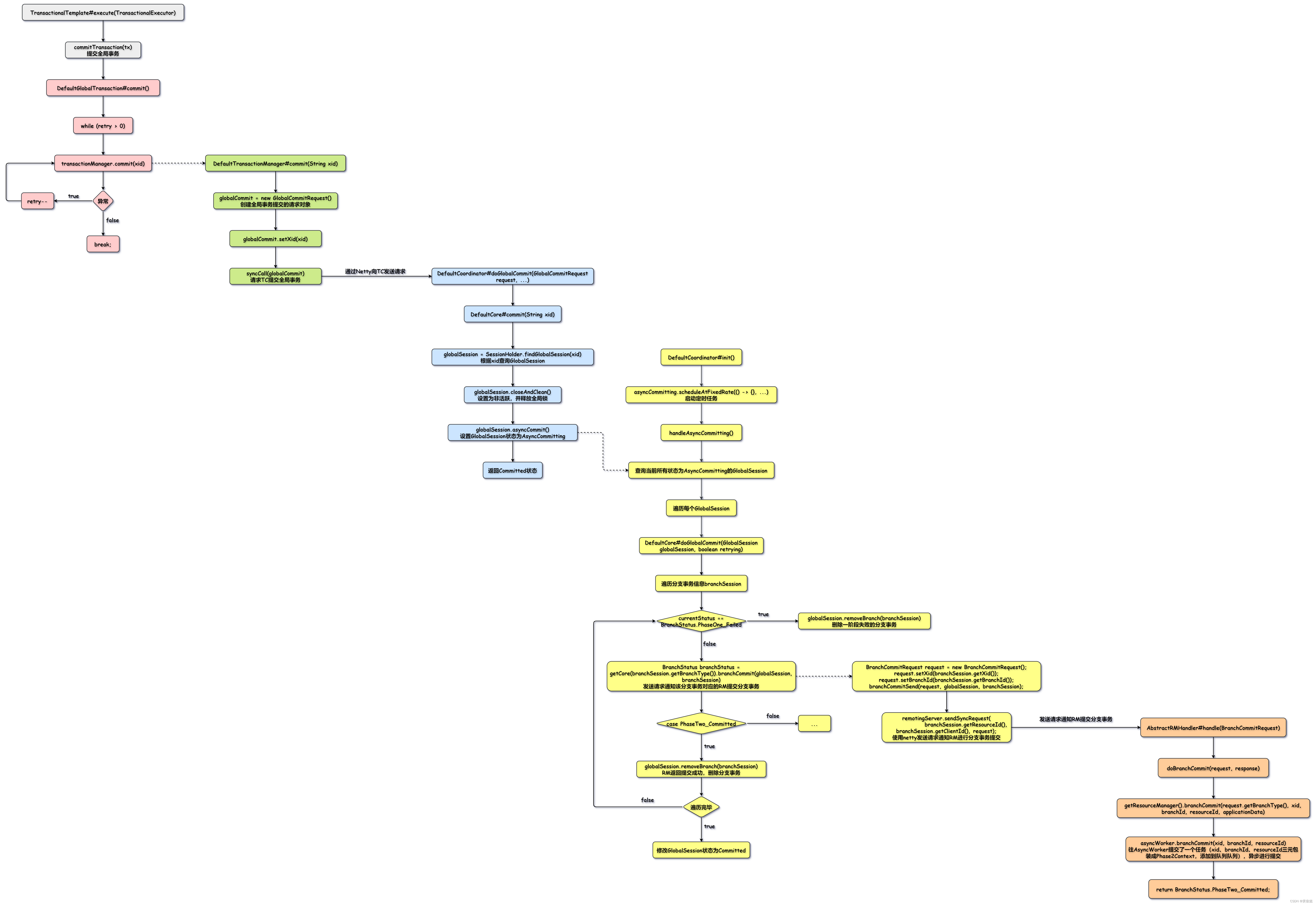
AsyncWorker
AsyncWorker的构造方法会启动定时任务,处理队列中的任务。
java
public AsyncWorker(DataSourceManager dataSourceManager) {
scheduledExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2, threadFactory);
// 启动定时任务
scheduledExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::doBranchCommitSafely, 10, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}定时任务调用doBranchCommitSafely方法。
java
void doBranchCommitSafely() {
try {
doBranchCommit();
} catch () {}
}
java
private void doBranchCommit() {
// 取出队列中所有的Phase2Context(也就是前面添加进去的任务)
List<Phase2Context> allContexts = new LinkedList<>();
commitQueue.drainTo(allContexts);
// 按resourceId分组
Map<String, List<Phase2Context>> groupedContexts = groupedByResourceId(allContexts);
// 遍历groupedContexts,调用dealWithGroupedContexts方法
groupedContexts.forEach(this::dealWithGroupedContexts);
}
java
private void dealWithGroupedContexts(String resourceId, List<Phase2Context> contexts) {
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = dataSourceManager.get(resourceId);
Connection conn;
try {
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
} catch () {}
UndoLogManager undoLogManager = UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType());
List<List<Phase2Context>> splitByLimit = Lists.partition(contexts, UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE);
// 对分组下的Phase2Context进行分批,遍历每一批,批量删除undolog记录
splitByLimit.forEach(partition -> deleteUndoLog(conn, undoLogManager, partition));
}所以异步操作只是做了一个删除undolog表记录的操作,其他啥也没干。