JS中的原型链
在理解原型链前,需先掌握 JS 中与原型相关的三个核心属性 / 方法。
定义
原型链是 JS 实现继承 的核心机制:当访问一个对象的属性 / 方法时,JS 引擎先在对象自身查找;若找不到,则通过 [[Prototype]] 向上查找其原型对象;若原型对象仍找不到,继续向上查找原型的原型,直到 Object.prototype;若最终仍未找到,返回 undefined(方法则报错 xxx is not a function)。这条由 [[Prototype]] 串联的链式结构,就是原型链。
核心逻辑
- 原型链的核心是 "委托" 而非 "复制":对象不拥有原型的属性 / 方法,仅在需要时委托原型查找。
- 所有对象最终都指向
Object.prototype,Object.prototype.__proto__ === null(原型链终点)。 - 函数既是函数也是对象 :函数的
[[Prototype]]指向Function.prototype,而Function.prototype的[[Prototype]]指向Object.prototype。
核心概念
prototype
描述 :**prototype**是仅函数(Function,箭头函数、绑定函数除外)拥有的原型对象,函数作为构造函数创建实例时,实例的隐式原型[[Prototype]](浏览器环境中通过实例的__proto__属性获取)也会指向这个原型对象。
默认特征:
- 原型对象默认包含
constructor属性,指向所属构造函数; - 原型对象继承自
Object.prototype。
js
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// Person函数的prototype是原型对象
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); // true
js
function User(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const user = new User('张三', 18);
console.log(user.__proto__===User.prototype); // true 实例的隐式原型为其构造函数的原型对象[[Prototype]]
描述 :所有对象(包括函数、普通对象、数组等)都拥有隐式原型。获取对象的__proto__属性是浏览器支持的获取隐式原型的方式,ES标准推荐使用``Object.getPrototypeOf()/Object.setPrototypeOf()` 获取/操作隐式原型。
- 以构造函数构造的对象,对象的原型指向构造函数的原型对象。
js
function User(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const user = new User('张三', 18);
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(user)===User.prototype); //true
/* user的原型链
user.__proto__ => User.prototype
User.prototype.__proto__ => Object.Prototype
*/function函数本身也是对象,它的隐式原型指向Function.prototype
js
function User(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(User) === Function.prototype); //true
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(Function.prototype) === Object.prototype); //true
/* User的原型链
User.__proto__ => Function.prototype
Function.prototype.__proto__ => Object.Prototype
*/- 直接键值对定义的对象,对象的原型指向
Object.prototype
js
const obj ={
name:'张三',
age:18,
}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)===Object.prototype); //true
/*obj的原型链
obj.__proto__ => Object.Prototype
*/- 数组的原型指向
Array.prototype
js
const users = ["张三", "李四"];
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(users) === Array.prototype); //true
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(Array.prototype) === Object.prototype); //true
/*users的原型链
users.__proto__ => Array.prototype
Array.prototype.__proto__ => Object.prototype
*/Object.prototype
描述 :Object.prototype是JS 中所有对象的 "根原型",其 [[Prototype]] 为 null(原型链的终点);Object.prototype包含 JS 内置的通用方法(如 toString()、valueOf()、hasOwnProperty()),所有对象均可通过原型链访问这些方法
原型继承
java
// 父类
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 子类
function Dog(name, breed) {
Animal.call(this, name); // 继承实例属性
this.breed = breed;
}
// 继承原型方法(连接原型链)
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog; // 恢复constructor
const dog = new Dog("旺财", "中华田园犬");
console.log(dog.__proto__ === Dog.prototype); // true
console.log(Dog.prototype.__proto__ === Animal.prototype); // true函数的prototype属性是可修改的,通过修改函数的原型可实现原型链的连接进而实现继承。
ES6及以上提供了class更语义化地定义类,提供extends更语义化地实现类继承(底层原理还是原型链的连接)。
js
class Person{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name, age, score){
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
}
const student = new Student('张三', 18, 100);
console.log(student.__proto__ === Student.prototype); //true
console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__ === Person.prototype); //true
console.log(Person.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); //true
/*student的原型链
student.__proto__ => Student.prototype
Student.prototype.__protot__ => Person.prototype
Person.prototype.__proto__ => Object.proto
*/常见误区
- 混淆
prototype和__proto__:prototype是函数的属性,__proto__是所有对象的属性,前者是函数对象的原型对象,后者是对象指向原型的链路。 - 认为原型链是 "复制" :原型链是 "委托查找",而非将原型属性复制到实例,修改原型会影响所有实例。
- 直接赋值
__proto__:__proto__性能差且易导致原型链混乱,优先使用Object.getPrototypeOf()/Object.setPrototypeOf()。 - 忽略
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null:所有原型链最终指向null,而非undefined。
总结
以User构造的user对象为例,分析原型链:
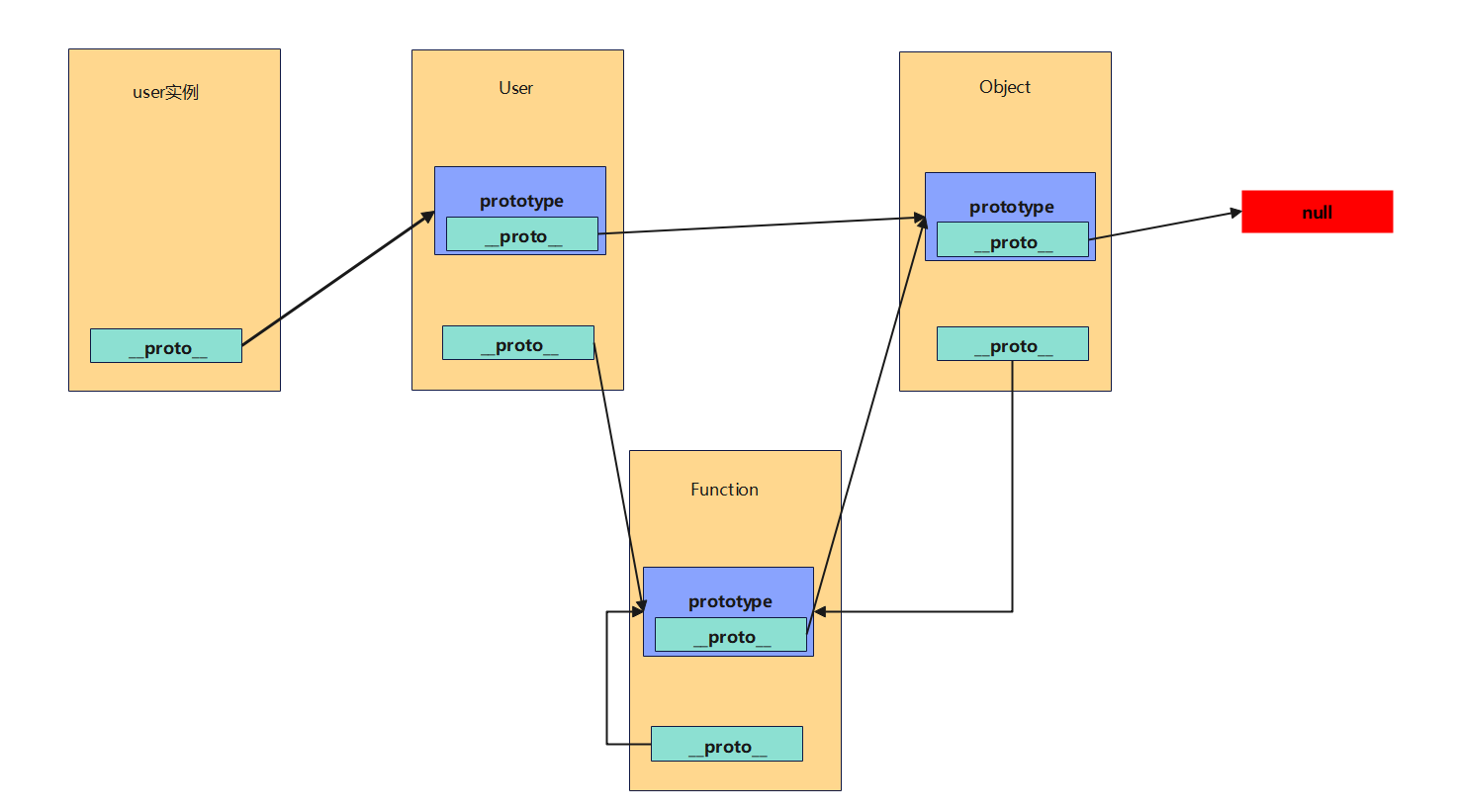
看似有点复杂,但可以总结以下特点:
-
所有普通对象 都有
__proto__属性,所有函数对象都有一个prototype属性,prototype属性是也一个普通对象。 -
所有函数对象的
__proto__属性指向FUnction.prototype,包括Function自身的__proto__也是如此。