深度解析六大Java微服务框架
微服务架构已成为分布式系统开发的主流范式,而成熟的微服务框架是落地微服务的核心支撑。本文将深度剖析五款主流Java微服务框架------Spring Cloud(原生)、Spring Cloud Alibaba(SCA)、Apache Dubbo、Spring Cloud Huawei(SCH)、Spring Cloud Tencent(SCT)、Apache ServiceComb(ASC),从核心架构、核心组件功能与用途、实战代码三个维度展开,帮助开发者理解各框架的设计理念与落地方式。
一、Spring Cloud(原生):微服务生态的"标准"
1. 核心架构
Spring Cloud并非单一框架,而是基于Spring Boot的微服务生态集合,核心遵循"约定优于配置"原则,通过一系列组件实现服务治理全流程。其核心架构如下:
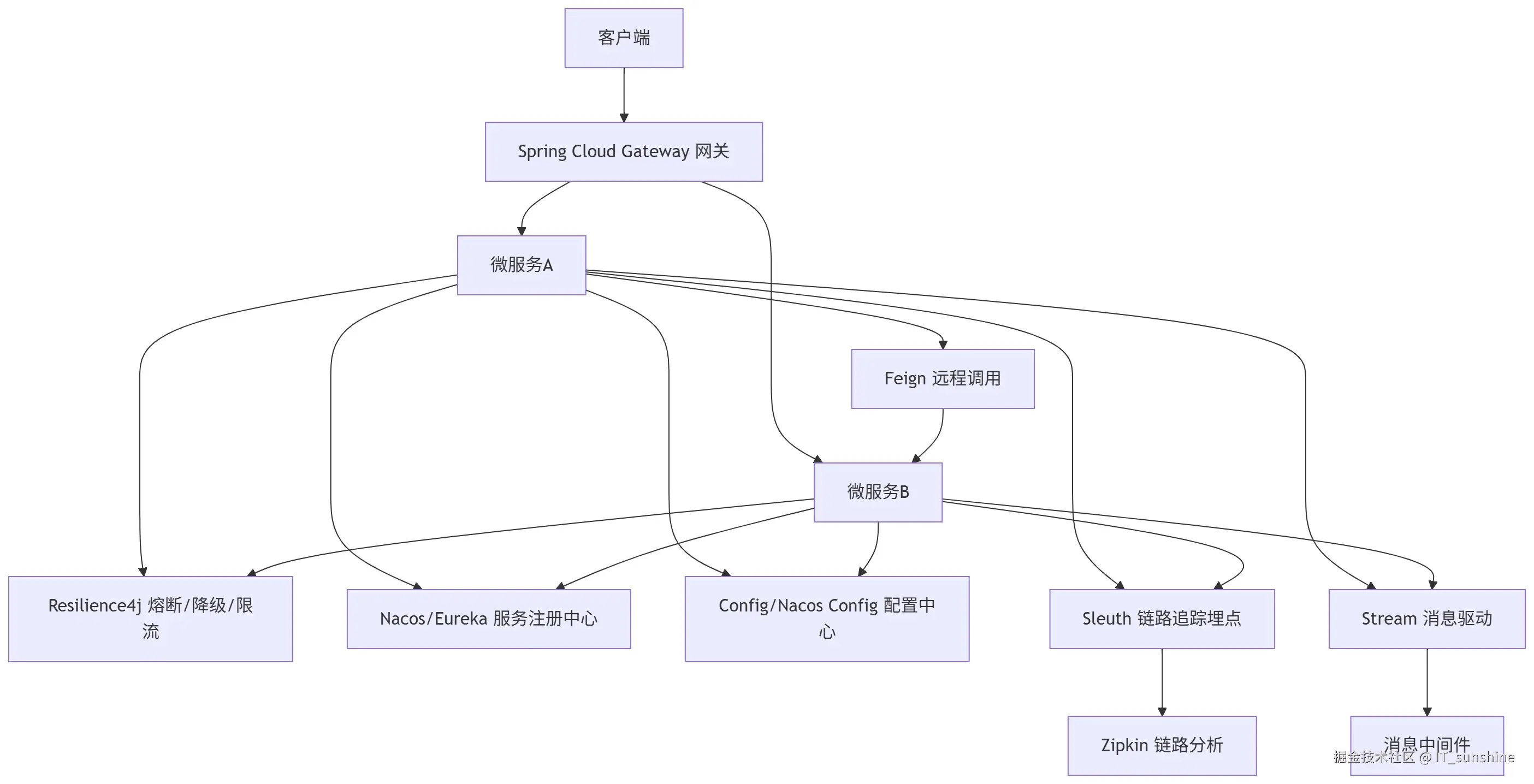
2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| Spring Cloud Gateway | 新一代网关,替代Zuul,实现路由转发、负载均衡、鉴权、限流等网关核心能力 |
| Eureka/Nacos | 服务注册中心,管理服务地址列表,支持服务注册、发现、健康检查 |
| Spring Cloud Config | 分布式配置中心,实现配置集中管理、动态刷新,避免配置文件分散在各服务节点 |
| Feign | 声明式HTTP远程调用组件,简化服务间调用(底层基于Ribbon实现负载均衡) |
| Resilience4j | 熔断/降级/限流组件(替代已停更的Hystrix),保障服务高可用 |
| Sleuth + Zipkin | 分布式链路追踪,定位微服务调用链中的性能瓶颈或故障点 |
| Spring Cloud Stream | 消息驱动组件,统一Kafka/RabbitMQ等消息中间件的使用方式 |
3. 实战代码示例
(1)服务注册(基于Eureka)
步骤1:引入依赖(pom.xml)
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件(application.yml)
yaml
spring:
application:
name: service-demo # 服务名称
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ # Eureka服务端地址
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true # 注册IP而非主机名步骤3:启动类
typescript
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 开启服务注册发现
public class ServiceDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}(2)Feign远程调用
步骤1:引入Feign依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>步骤2:声明式调用接口
kotlin
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
// 调用名为service-provider的服务
@FeignClient(name = "service-provider")
public interface ProviderClient {
// 映射服务提供者的接口
@GetMapping("/provider/hello/{name}")
String sayHello(@PathVariable("name") String name);
}步骤3:使用Feign调用
kotlin
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class ConsumerController {
@Resource
private ProviderClient providerClient;
@GetMapping("/consumer/hello/{name}")
public String hello(@PathVariable String name) {
// 远程调用service-provider的接口
return providerClient.sayHello(name);
}
}二、Spring Cloud Alibaba(SCA):国内微服务的"事实标准"
1. 核心架构
Spring Cloud Alibaba是阿里基于Spring Cloud原生生态的增强版,替换了原生框架中部分停更/功能薄弱的组件(如用Nacos替代Eureka/Config,Sentinel替代Hystrix),并新增分布式事务、消息队列等本土化组件,核心架构如下:

2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| Nacos | 一站式注册+配置中心,支持AP/CP模式切换,动态配置刷新、服务健康检查 |
| Sentinel | 流量治理组件,提供熔断、限流、降级、热点参数限流等能力,可视化控制台 |
| Seata | 分布式事务解决方案,支持AT/TCC/SAGA/XA四种事务模式,解决分布式数据一致性问题 |
| RocketMQ | 阿里开源消息队列,支持高吞吐、高可用,适配微服务异步通信、最终一致性 |
| Alibaba Cloud OSS | 对象存储服务,用于微服务中文件/图片等静态资源存储 |
| Alibaba Cloud SMS | 短信服务,适配微服务中的短信通知场景 |
3. 实战代码示例
(1)Nacos配置中心
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
<version>2023.0.1.0</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件(bootstrap.yml)
yaml
spring:
application:
name: service-demo
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848 # Nacos地址
file-extension: yaml # 配置文件格式
group: DEFAULT_GROUP # 配置分组步骤3:动态读取配置
kotlin
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RefreshScope // 开启配置动态刷新
public class ConfigController {
// 读取Nacos中的配置项
@Value("${demo.message:default}")
private String message;
@GetMapping("/config")
public String getConfig() {
return "配置内容:" + message;
}
}(2)Sentinel限流
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
<version>2023.0.1.0</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置限流规则
kotlin
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class SentinelController {
// 标记需要限流的资源
@SentinelResource(value = "hello", blockHandler = "helloBlockHandler")
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello Sentinel!";
}
// 限流降级方法
public String helloBlockHandler(BlockException e) {
return "请求过于频繁,请稍后再试!";
}
}三、Apache Dubbo:高性能RPC微服务框架
1. 核心架构
Dubbo是阿里开源的高性能RPC框架(后捐赠给Apache),核心聚焦"远程服务调用",相比Spring Cloud的HTTP调用,Dubbo的RPC调用性能更高,核心架构包含5个核心角色:
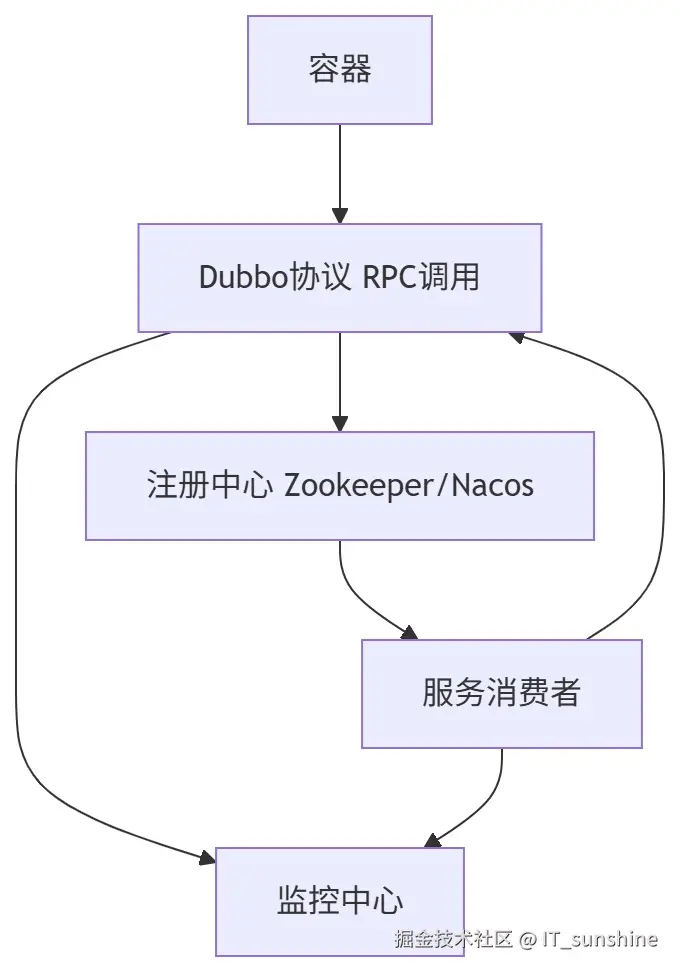
核心角色说明:
- Container:服务运行容器,负责启动、加载、运行服务提供者;
- Provider:服务提供者,暴露服务接口;
- Consumer:服务消费者,调用远程服务;
- Registry:注册中心,管理服务地址;
- Monitor:监控中心,统计服务调用次数、耗时等。
2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件/特性 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| 注册中心 | 支持Zookeeper/Nacos/Redis等,管理服务地址列表,实现服务注册发现 |
| Dubbo协议 | 默认高性能二进制协议,支持TCP传输,相比HTTP协议序列化效率更高 |
| 负载均衡 | 内置随机/轮询/最少活跃调用数/一致性哈希等策略,优化服务调用负载分布 |
| 容错机制 | 支持失败重试/失败快速返回/故障转移/熔断等,保障服务调用可靠性 |
| 服务监控 | 集成Prometheus/Grafana,监控服务调用QPS、耗时、失败率等指标 |
| 服务治理 | 支持服务降级、版本控制、配置动态调整等 |
3. 实战代码示例
(1)定义服务接口(公共模块)
arduino
// 公共接口,提供者和消费者共用
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}(2)服务提供者
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>步骤2:实现服务接口
typescript
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.DubboService;
// 暴露Dubbo服务
@DubboService(version = "1.0.0")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Dubbo Provider: Hello " + name;
}
}步骤3:配置文件
yaml
dubbo:
application:
name: dubbo-provider # 应用名称
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848 # Nacos注册中心地址
protocol:
name: dubbo # 协议类型
port: 20880 # 协议端口(3)服务消费者
步骤1:引入依赖(同提供者)
步骤2:调用远程服务
kotlin
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.DubboReference;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ConsumerController {
// 引用Dubbo服务
@DubboReference(version = "1.0.0")
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/dubbo/hello/{name}")
public String hello(@PathVariable String name) {
// 调用远程RPC服务
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}步骤3:配置文件
yaml
dubbo:
application:
name: dubbo-consumer
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848四、Spring Cloud Huawei(SCH):华为云原生微服务框架
1. 核心架构
Spring Cloud Huawei是华为基于Spring Cloud原生生态适配华为云的微服务框架,核心整合华为云中间件(CSE、ServiceStage等),支持混合云部署,架构如下:
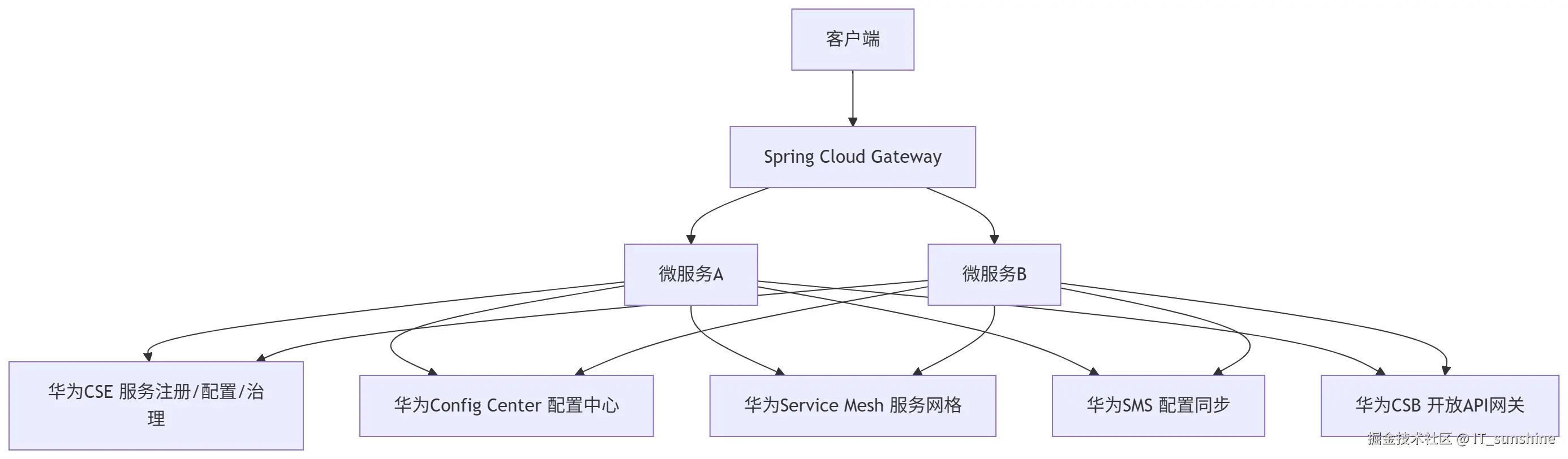
2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| 华为CSE | 云服务引擎,提供服务注册发现、配置管理、服务治理、流量控制等核心能力 |
| Config Center | 华为云配置中心,支持配置加密、多环境隔离、灰度发布 |
| Service Stage | 华为云应用托管平台,支持微服务的部署、运维、监控全生命周期管理 |
| Service Mesh | 基于Istio的服务网格,解耦服务治理与业务代码,支持流量治理、安全管控 |
| CSB | 云服务总线,提供API网关、服务开放、鉴权等能力,适配企业级服务开放场景 |
3. 实战代码示例
接入华为CSE服务注册
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.huaweicloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-huawei-service-engine</artifactId>
<version>3.1.8</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件
yaml
spring:
application:
name: service-huawei-demo
cloud:
huawei:
serviceengine:
address: https://cse.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com # CSE服务地址
access-key: your-access-key # 华为云AK
secret-key: your-secret-key # 华为云SK步骤3:启动类
typescript
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class HuaweiServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HuaweiServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}五、Spring Cloud Tencent(SCT):腾讯云原生微服务框架
1. 核心架构
Spring Cloud Tencent是腾讯基于Spring Cloud原生生态适配腾讯云的微服务框架,核心组件为Polaris(北极星),整合腾讯云中间件,支持私有化部署与公有云部署,架构如下:

2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| Polaris(北极星) | 一站式服务治理平台,集成注册中心、配置中心、限流、熔断、路由等能力 |
| Tencent Seata | 适配腾讯云的分布式事务组件,支持金融级分布式事务场景 |
| 腾讯CMQ/CKafka | 腾讯云消息队列,适配微服务异步通信、削峰填谷 |
| TSF | 腾讯微服务平台,提供微服务部署、运维、监控、链路追踪全生命周期管理 |
| Polaris Mesh | 基于Istio的服务网格,支持无侵入式服务治理 |
3. 实战代码示例
Polaris服务注册与配置
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-discovery</artifactId>
<version>1.11.0-2023.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-config</artifactId>
<version>1.11.0-2023.0</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件
yaml
spring:
application:
name: service-tencent-demo
cloud:
polaris:
address: grpc://localhost:8091 # Polaris服务地址
config:
groups:
- name: DEFAULT_GROUP # 配置分组
files:
- name: application.yaml # 配置文件名步骤3:读取Polaris配置
kotlin
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class PolarisController {
@Value("${tencent.demo.message:default}")
private String message;
@GetMapping("/polaris/config")
public String getConfig() {
return "Polaris配置:" + message;
}
}六、Apache ServiceComb:企业级开源微服务框架
1. 核心架构
Apache ServiceComb 是一款企业级开源微服务框架,基于"契约优先"理念设计,支持多语言开发,核心整合服务注册发现、配置管理、流量治理、分布式事务等全链路能力,架构如下:
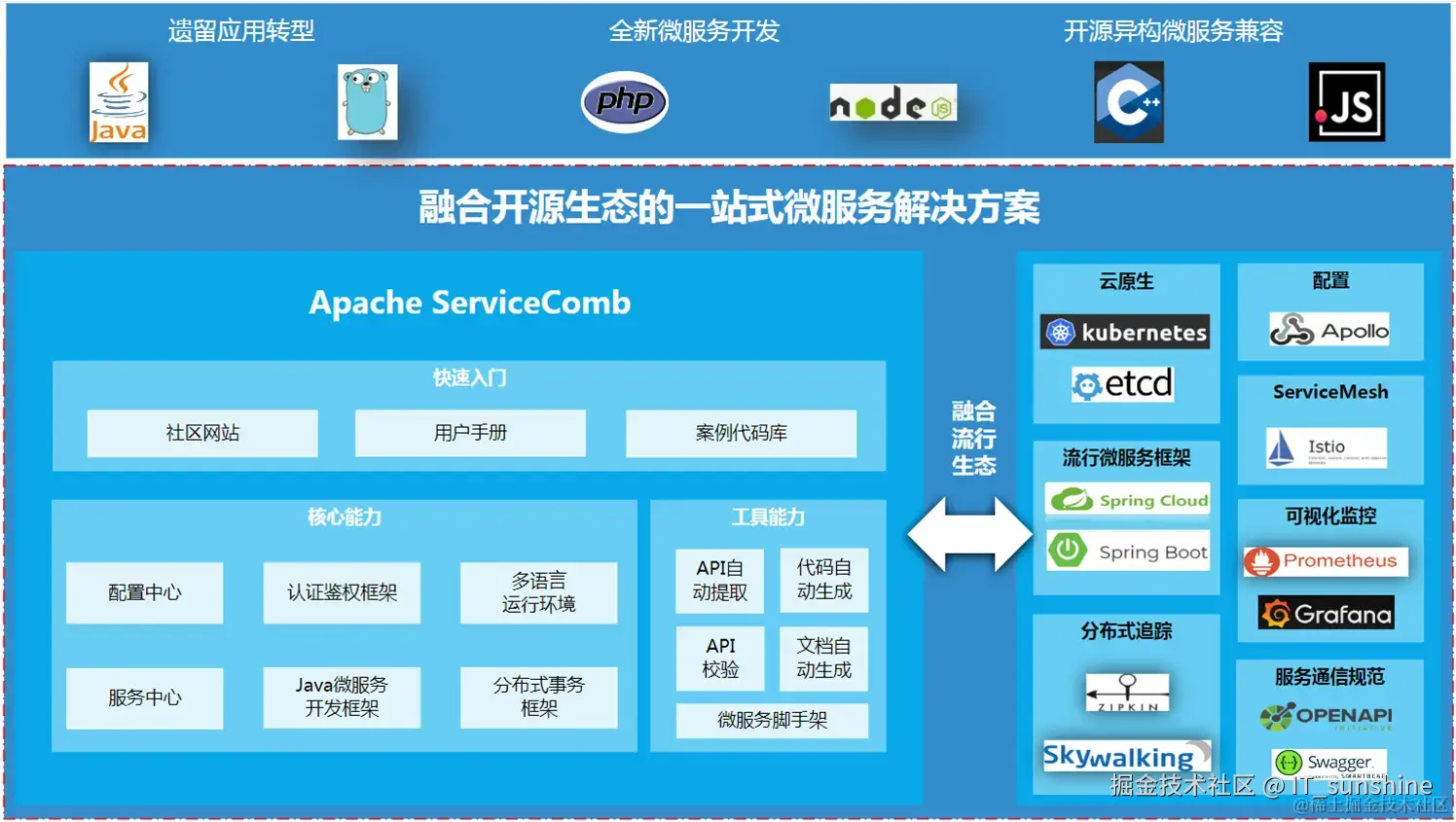
核心架构特点:采用分层设计,将服务治理能力与业务代码解耦,支持REST、RPC等多种通信协议,适配单体迁移、全新开发等多种微服务落地场景。
2. 核心组件功能与用途
| 组件 | 功能与用途 |
|---|---|
| ServiceCenter | 分布式服务注册发现中心,支持服务元数据管理、健康检查、服务订阅与发现,兼容多语言服务接入 |
| Config Center | 集中式配置管理组件,支持配置动态推送、多环境隔离、配置版本控制,保障配置一致性 |
| Edge Service | 微服务网关,提供路由转发、负载均衡、鉴权、限流、熔断等网关核心能力,适配内外网服务访问场景 |
| Saga | 分布式事务解决方案,基于补偿机制实现最终一致性,支持复杂业务场景下的事务协调 |
| Contract Manager | 契约管理组件,遵循"契约优先"开发模式,支持契约校验、版本管理,保障服务间接口一致性 |
3. 实战代码示例
(1)服务注册(基于ServiceCenter)
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.servicecomb</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-provider</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.servicecomb</groupId>
<artifactId>registry-service-center</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件(application.yml)
yaml
spring:
application:
name: servicecomb-provider
servicecomb:
service:
application: servicecomb-demo # 应用名称
name: provider-service # 服务名称
version: 1.0.0 # 服务版本
registry:
address: http://localhost:30100 # ServiceCenter地址
rest:
address: 0.0.0.0:8080 # 服务暴露端口步骤3:编写服务接口
kotlin
import org.apache.servicecomb.provider.rest.common.RestSchema;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@RestSchema(schemaId = "helloService") // 声明REST服务契约
public class HelloService {
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public String sayHello(@PathVariable String name) {
return "ServiceComb Provider: Hello " + name;
}
}步骤4:启动类
typescript
import org.apache.servicecomb.springboot.starter.EnableServiceComb;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableServiceComb // 开启ServiceComb微服务能力
public class ServiceCombProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceCombProviderApplication.class, args);
}
}(2)服务调用(消费者)
步骤1:引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.servicecomb</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-consumer</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.servicecomb</groupId>
<artifactId>registry-service-center</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>步骤2:配置文件(application.yml)
yaml
spring:
application:
name: servicecomb-consumer
servicecomb:
service:
application: servicecomb-demo
name: consumer-service
version: 1.0.0
registry:
address: http://localhost:30100
rest:
address: 0.0.0.0:8081步骤3:调用远程服务
kotlin
import org.apache.servicecomb.provider.springmvc.reference.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class ConsumerController {
// 构建ServiceComb专用RestTemplate
private final RestTemplate restTemplate = RestTemplateBuilder.create();
@GetMapping("/consumer/hello/{name}")
public String hello(@PathVariable String name) {
// 调用provider-service服务的接口
String url = "cse://provider-service/hello/" + name;
return restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
}
}七、框架对比与选型建议
| 框架 | 核心优势 | 适用场景 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Cloud | 生态完善、社区成熟、标准化 | 通用微服务场景,跨云/私有化部署 | 部分组件停更、HTTP调用性能一般 |
| Spring Cloud Alibaba | 本土化组件丰富、性能优、文档全 | 国内企业微服务场景,阿里生态适配 | 部分组件依赖阿里云 |
| Dubbo | RPC调用性能高、轻量、易扩展 | 高性能服务调用场景,中台/内部系统 | 服务治理生态不如Spring Cloud完善 |
| Spring Cloud Huawei | 深度适配华为云、混合云支持好 | 华为云用户,政企/国产化项目 | 生态封闭性较强,社区活跃度一般 |
| Spring Cloud Tencent | 深度适配腾讯云、Polaris功能全面 | 腾讯云用户,互联网/游戏行业 | 跨云适配性一般 |
| Apache ServiceComb | 契约优先、多语言支持、企业级特性完善 | 政企项目、多语言微服务场景、单体迁移改造 | 社区活跃度低于Spring Cloud生态,国内落地案例较少 |
选型建议:
- 通用场景:优先选择Spring Cloud Alibaba,本土化适配好,组件功能完善;
- 高性能RPC场景:选择Dubbo(可结合Spring Cloud Alibaba实现混合架构);
- 云厂商绑定场景:华为云用户选SCH,腾讯云用户选SCT;
- 国际化/跨云场景:选择Spring Cloud原生框架;
- 多语言/政企迁移场景:选择Apache ServiceComb,契约优先特性适配复杂企业级需求。
总结
本文详细解析了六款主流Java微服务框架的核心架构、组件功能与实战代码,各框架均有其定位与优势:Spring Cloud是基础标准,SCA是国内主流,Dubbo聚焦高性能RPC,SCH/SCT适配云厂商生态,Apache ServiceComb擅长企业级多语言场景与单体迁移。开发者应根据业务场景(性能、云厂商、本土化需求、多语言支持)选择合适的框架,也可结合多框架优势构建混合微服务架构,最大化发挥各框架的价值。
我是IT_sunshine👨🎓,我们下期见!!