普通队列和优先级队列的小区别:
主要在于取队头元素:
queue
cpp
queue<int> q;
q.push(10);
q.push(20);
cout << q.front(); // 输出 10priority_queue
cpp
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(9);
cout << pq.top(); // 默认输出最大值 9例题:
W9-3 哈夫曼树编码

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char c;
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int v = 0, char ch = '{') : val(v), c(ch), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
// 比较器:用于最小堆
struct cmp {
bool operator()(Node* a, Node* b) const {
if (a->val != b->val) return a->val > b->val;
return a->c > b->c; // 频率相等时字符小的优先
}
};
// 后序遍历输出叶子字符
void postOrder(Node* root) {
if (!root) return;
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
if (root->c != '{') // 只输出叶子节点
cout << root->c << endl;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
priority_queue<Node*, vector<Node*>, cmp> pq;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch;
int f;
cin >> ch >> f;
pq.push(new Node(f, ch));
}
while(pq.size()>1){
Node* a=pq.top();
pq.pop();
Node* b=pq.top();
pq.pop();
Node* parent=new Node(a->val+b->val);
parent->left=b;
parent->right=a;
pq.push(parent);
}
Node* root=pq.top();
postOrder(root);
return 0;
}注意里面的模板函数的写法,写在结构体里面,用operator声明
cpp
// 比较器:用于最小堆
struct cmp {
bool operator()(Node* a, Node* b) const {
if (a->val != b->val) return a->val > b->val;
return a->c > b->c; // 频率相等时字符小的优先
}
};W8-4 中序遍历的线索化以及如何遍历

cpp
ThreadedTreeNode* Solution::threaded(ThreadedTreeNode* root){
if(!root) return nullptr;
// 中序遍历存序列
stack<ThreadedTreeNode*> st;
vector<ThreadedTreeNode*> order;
ThreadedTreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur || !st.empty()) {
while (cur) {
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
cur = st.top(); st.pop();
order.push_back(cur);
cur = cur->right;
}
// 构建线索
for (int i = 0; i < order.size(); ++i) {
ThreadedTreeNode* node = order[i];
// 原来有左孩子 => ltag = 0
if (node->left)
node->ltag = 0;
else {
node->ltag = 1;
node->left = (i == 0 ? nullptr : order[i - 1]);
}
// 原来有右孩子 => rtag = 0
if (node->right)
node->rtag = 0;
else {
node->rtag = 1;
node->right = (i == order.size() - 1 ? nullptr : order[i + 1]);
}
}
return root;
}
vector<int> Solution::inorderTraversal(ThreadedTreeNode* root){
vector<int> ans;
if(!root) return ans;
ThreadedTreeNode* cur = root;
// 1. 找最左节点
while (cur->ltag == 0)
cur = cur->left;
// 2. 遍历
while (cur) {
ans.push_back(cur->val);
// 如果有中序后继(线索)
if (cur->rtag == 1) {
cur = cur->right;
}
// 否则进入右子树,再找最左
else {
cur = cur->right;
while (cur && cur->ltag == 0)
cur = cur->left;
}
}
return ans;
}Q1-6 非递归实现汉诺塔
有文章指出,汉诺塔就是重复以下两步:
第一步: 将最小圆盘移动到下一个杆上;
第二步: 对剩下两个杆的顶上元素 进行判断,把较小 的那个圆盘移动到较大的那个圆盘上(如果有空杆则移在空杆上)。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
char s[4] = { '0','A','B','C' };
stack<int>a[4];
void move(int now, int next) {
a[next].push(a[now].top());
/*printf("%d from %c to %c\n", a[now].top(), s[now], s[next]);*/
printf("%c -> %c\n", s[now], s[next]);
a[now].pop();
}
int main() {
int n, count = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[1].push(n - i);
}
//n为奇数的话就改
if (n % 2 == 1) {
s[2] = 'C';
s[3] = 'B';
}
while (1) {
int next;
//第一步:将圆盘移动到下一个杆上
//虽然是循环三次,但是只会移动一个玩意
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
if (!a[i].empty()) {
if (a[i].top() == 1) {
if (i == 3)next = 1;
else next = i + 1;
move(i, next);
break;
}
}
}
//判断是否完成
if (a[2].size() == n || a[3].size() == n) {
break;
}
//第二步:对顶上的元素进行判断,将较小圆盘移动到较大的那个圆盘上
int other1, other2;
switch (next) {
case 1: { other1 = 2; other2 = 3; break; }
case 2: { other1 = 3; other2 = 1; break; }
case 3: { other1 = 1; other2 = 2; break; }
}
if (a[other1].empty()) {
move(other2, other1);
}
else if (a[other2].empty()) {
move(other1, other2);
}
else {
if (a[other1].top() < a[other2].top() ){
move(other1, other2);
}
else move(other2, other1);
}
}
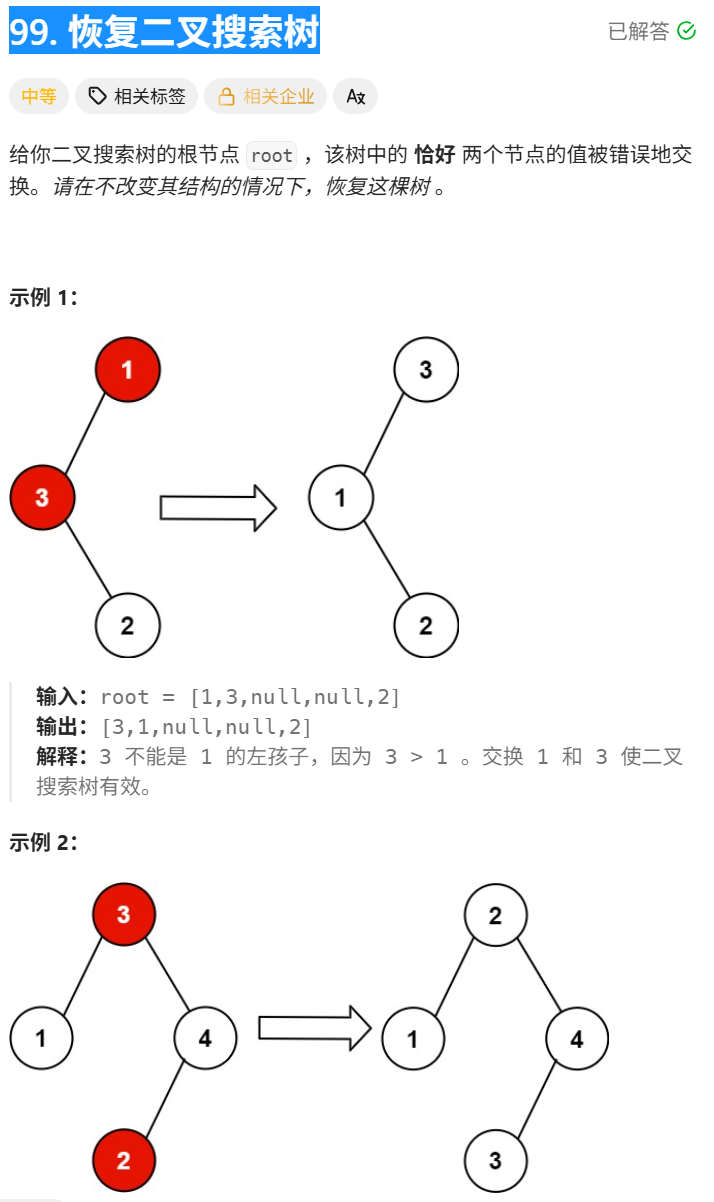
}leecode99恢复二叉搜索树(逆序)
99. 恢复二叉搜索树![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/recover-binary-search-tree/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/recover-binary-search-tree/
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//其实只需要找逆序对
TreeNode* pre=nullptr,*first=nullptr,*second=nullptr;
void inorder(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return;
inorder(root->left);
if(pre&&pre->val>root->val){
if(!first){
first=pre;
}
// 无论第几次逆序,second 都指向当前的 root
second = root;
}
pre=root;
inorder(root->right);
}
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
vector<TreeNode*>order;
inorder(root);
// int tmp=first->val;
// first->val=second->val;
// second->val=tmp;
swap(first->val,second->val);
}
};逆序检查逻辑必须是下面这一版:
if (pre && pre->val > root->val) { if (!first) first = pre; second = root; // 每次逆序都赋值 }
这里的关键思想:
-
first:在第一次逆序时记录
-
second :每次逆序都记录,最终停在最后一次逆序的
cur
这样:
相邻交换(1 次逆序)
prev=3, cur=2 first = 3 second = 2
不相邻交换(2 次逆序)
prev=5, cur=3 → first = 5, second = 3 prev=4, cur=2 → second = 2(覆盖)
总结 ------ 你的代码为什么不行?
-
你在第二次逆序后就
return,导致相邻交换时永远找不到 second -
正确解法是:first 在第一次逆序赋值;second 在每次逆序赋值
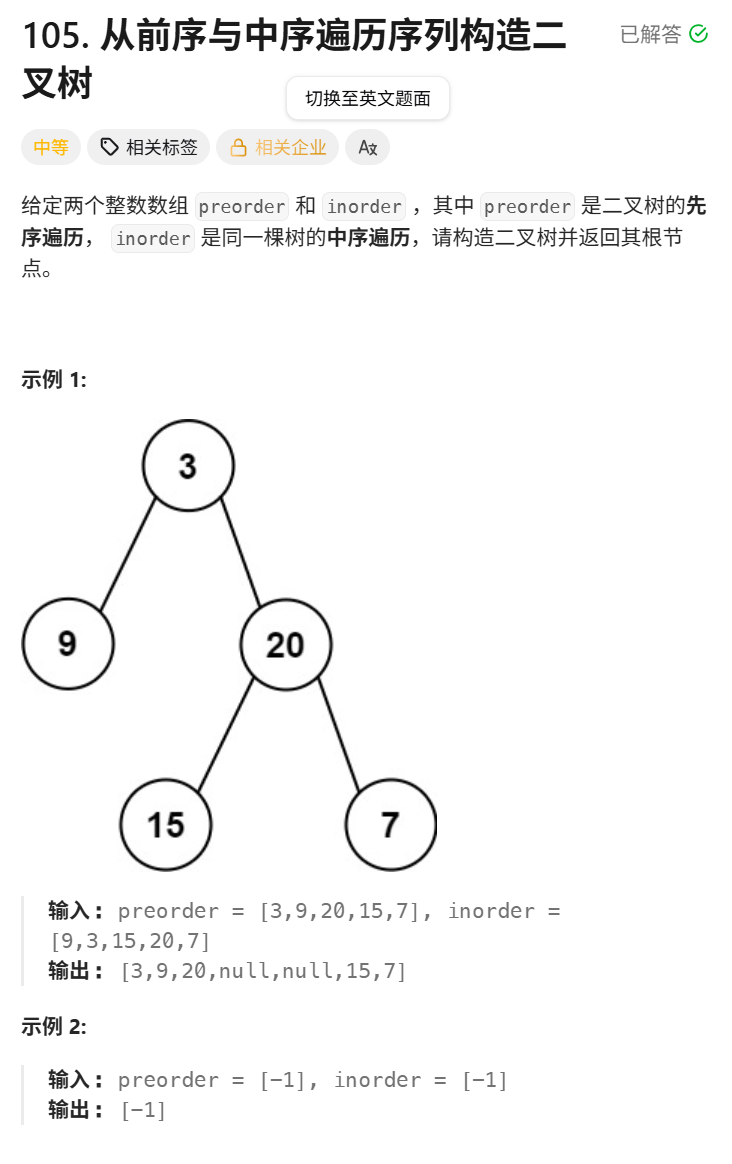
leetcode105根据前序和中序遍历构建二叉树
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* build(const vector<int>&preorder,const vector<int>&inorder,int start1,int end1,int start2,int end2){
if(start2>end2||start1>end1)return nullptr;
TreeNode* newone=new TreeNode(preorder[start1]);
int index=start2;
for(int i=start2;i<=end2;i++){
if(inorder[i]==preorder[start1]){
index=i;
break;
}
}
int leftsize=index-start2;
newone->left=build(preorder,inorder,start1+1,start1+leftsize,start2,index-1);
newone->right=build(preorder,inorder,start1+leftsize+1,end1,index+1,end2);
return newone;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
TreeNode* root=nullptr;
root=build(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.size()-1,0,inorder.size()-1);
return root;
}
};注意一下:前序的边界end1是与左/右节点的个数有关的,不要漏掉了
合法的出栈顺序(没错又来了)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> A(n), B(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> A[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> B[i];
stack<int> st;
int j = 0; // pointer in A
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int target = B[i];
// push until stack top == target
while ((st.empty() || st.top() != target) && j < n) {
st.push(A[j]);
j++;
}
// can't match target
if (st.top() != target) {
cout << "False";
return 0;
}
st.pop();
}
cout << "True";
return 0;
}W10-8 二叉搜索树的路径长度
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct treeNode{
int val;
treeNode* lchild;
treeNode* rchild;
treeNode():val(0),lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
};
void insert(treeNode*& root, int x){
if(!root){
treeNode* newone=new treeNode();
newone->val=x;
root=newone;
return;
}
if(root->val>x)insert(root->lchild,x);
else insert(root->rchild,x);
return;
}
void deletel(treeNode* root){
if(!root)return;
deletel(root->lchild);
deletel(root->rchild);
delete root;
}
vector<int>path;
bool flag=false;
// void dfs(treeNode* root,const int &m,int now){
// if(now==m){
// flag=true;
// for(int i=0;i<path.size();i++){
// if(i==path.size()-1){
// cout<<path[i]<<endl;
// break;
// }
// cout<<path[i]<<"->";
// }
// }
// if(!root)return;
// //选与不选
// int val=root->val;
// path.push_back(val);
// dfs(root->lchild,m,now+val);
// path.pop_back();
// dfs(root->rchild,m,now+val);
// }
void dfs(treeNode* root, int m, int now){
if(!root) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
now += root->val;
bool leaf = (!root->lchild && !root->rchild);
// root-to-leaf 才能输出
if(leaf && now == m){
flag = true;
for(int i=0;i<path.size();i++){
cout << path[i];
if(i + 1 < path.size()) cout << "->";
}
cout << "\n";
}
dfs(root->lchild, m, now);
dfs(root->rchild, m, now);
path.pop_back();
}
int main(){
int n,m;
while(cin>>n>>m){
//cin>>n>>m;
path.clear();
vector<int>vec(n);
treeNode* root=nullptr;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>vec[i];
insert(root,vec[i]);
}
dfs(root,m,0);
deletel(root);
if(!flag)cout<<"NULL"<<endl;
flag=false;
//cout<<1111<<endl;
}
}dfs搜索天然就是字典序的所以不用管
有一个易错点就是void insert(treeNode*& root, int x),这里传入的是root的引用,因为第一步从空节点开始创建的时候是直接修改的root本身,但是如果没有引用,那么这时候传入的就是一个临时变量,对临时变量进行修改没有任何作用,会导致后面main函数里面的root一直为空
还有一个易错也是实力问题,先不管细节部分,看两个dfs并进行对比,为什么两个dfs一个插入path前先判断是否now==m,一个插入后判断会有区别呢
核心结论:push 前判断是错误的,本质是判断位置完全错了,而非回溯问题,核心是输出时机不符合 "root-to-leaf" 的题目要求。
错误写法的核心问题
错误写法的判断逻辑顺序为:先判断 if (now == m) print(path);,再判断 if (!root) return;,后续才执行 path.push_back(root->val);、递归和 path.pop_back();。
当递归到空节点时,此时 now == 28,path = {13, 7, 3, 5},由于判断写在 root 检查之前,空节点会触发输出。根本错误是把判断写在「访问节点之前」,导致空孩子也会触发路径判断,而非在目标的叶子节点上判断。
关键疑问解答:为何输出正确序列仍算错?
虽然错误写法输出了正确的节点序列 {13,7,3,5},但输出时机是在访问空节点时,而非在叶子节点本身。题目要求的是 "root-to-leaf" 的路径,不是 "root-to-null" 的路径,这是两种完全不同的时机。
正确时机是站在叶子节点(root!=nullptr && root->lchild==nullptr && root->rchild==nullptr)时判断;错误时机是递归到叶子节点的 null 左子树或 null 右子树时判断,相当于 "离开叶子节点后" 才判断,根本没在叶子节点本身进行检测,破坏了 DFS 对树结构的语义。
举例说明差异
以简单叶子节点 5(左右子树均为 null)为例:
- 理应检测的场景:在节点 5(非空)时,判断是否完成 "root-to-leaf" 路径。
- 错误写法检测的场景:在节点 5 的左空孩子和右空孩子处判断,完全偏离了题目要求的判断对象。
错误写法影响全局的原因
输出时机错误后,不是在叶子处返回打印,而是在空节点打印,这会让 DFS 的控制逻辑混乱。尤其是在逻辑复杂的场景中,会导致重复输出、多打印、错序等问题。整个判断条件变成了 "走到 null 就判断一次",完全背离了 "root-to-leaf" 的语义,即使偶然打印出正确路径序列,也只是 "值对了",逻辑上完全错误。
正确逻辑的要求
正确的逻辑必须是先执行 path.push_back(root->val); 和 now += root->val;,再判断该节点是否为叶子节点且 now == m,若是则打印路径;之后再递归遍历左子树和右子树,最后执行 path.pop_back()。
这样才能保证判断在 "节点本身" 发生,路径中包含当前节点,sum 计算包含当前节点,只在叶子节点判断,DFS 遍历顺序正确,输出顺序也自然符合字典序要求
(此题等待重做)W10-4 最大对称子二叉树
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
vector<int> weight;
vector<pair<int,int>> child;
int n;
int ans=1;
// 判断两棵子树是否镜像,并返回镜像节点数
int mirror_size(int a, int b) {
if (a == -1 && b == -1) return 0;
if (a == -1 || b == -1) return -1e9; // 不可能对称
if (weight[a] != weight[b]) return -1e9;
int left_part = mirror_size(child[a].first, child[b].second);
int right_part = mirror_size(child[a].second, child[b].first);
if (left_part < 0 || right_part < 0) return -1e9;
return left_part + right_part + 2; // 包含 a 和 b
}
void dfs(int u) {
if (u == -1) return;
int L = child[u].first;
int R = child[u].second;
int res = mirror_size(L, R);
if (res >= 0) ans = max(ans, res + 1); // 加上根节点
dfs(L);
dfs(R);
}
// //返回最多的节点个数
// int dfs(int now){
// if(now==-1)return 0;
// int left=dfs(child[now].first);
// int right=dfs(child[now].second);
// if()
// if(weight[child[now].first]==weight[child[now].second])
// }
int main() {
cin >> n;
weight.resize(n+1);
child.resize(n+1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> weight[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
child[i] = {l, r};
}
dfs(1);
cout << ans << endl;
}W10-5 四叉树的实现(恶心了点)
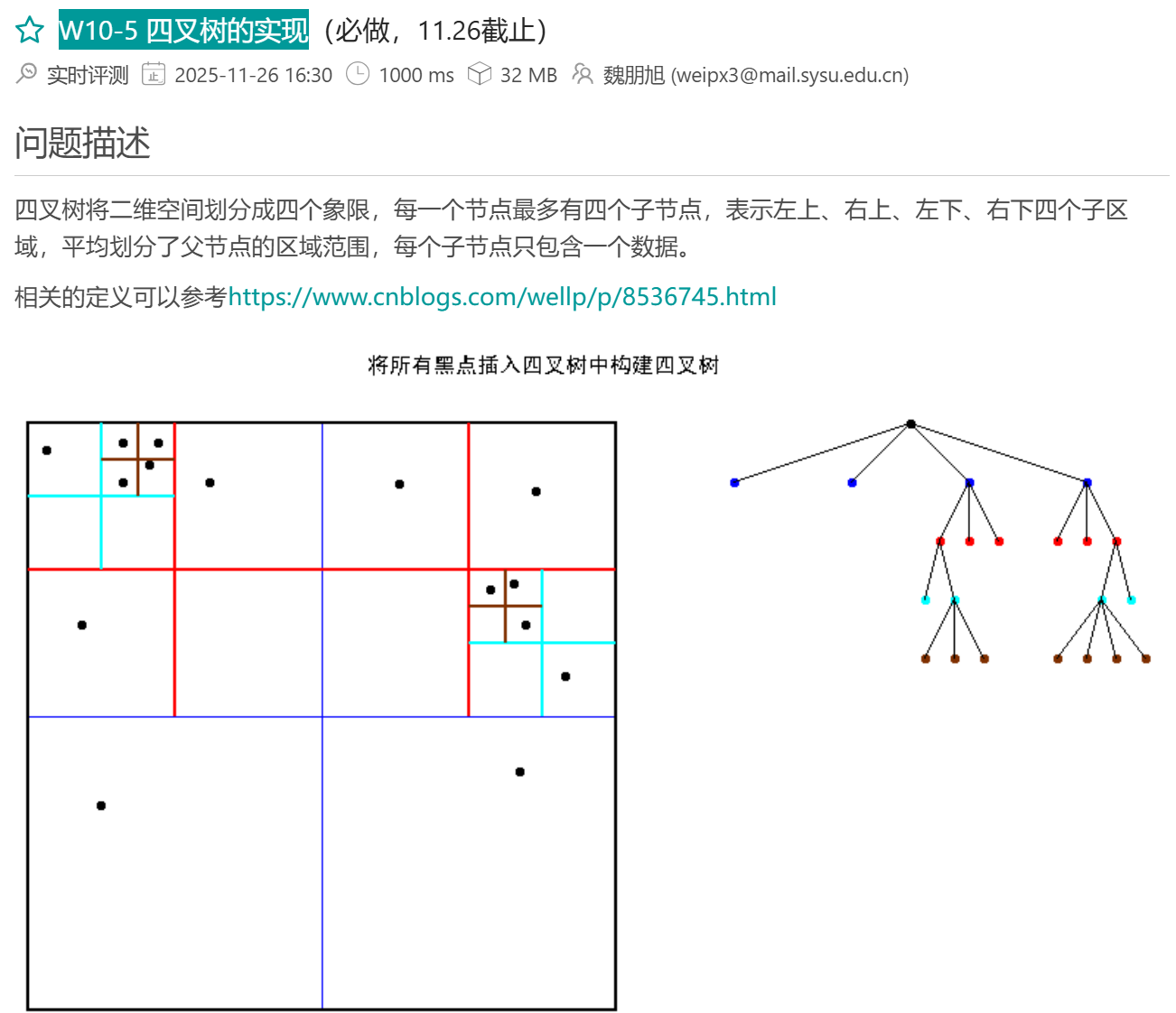
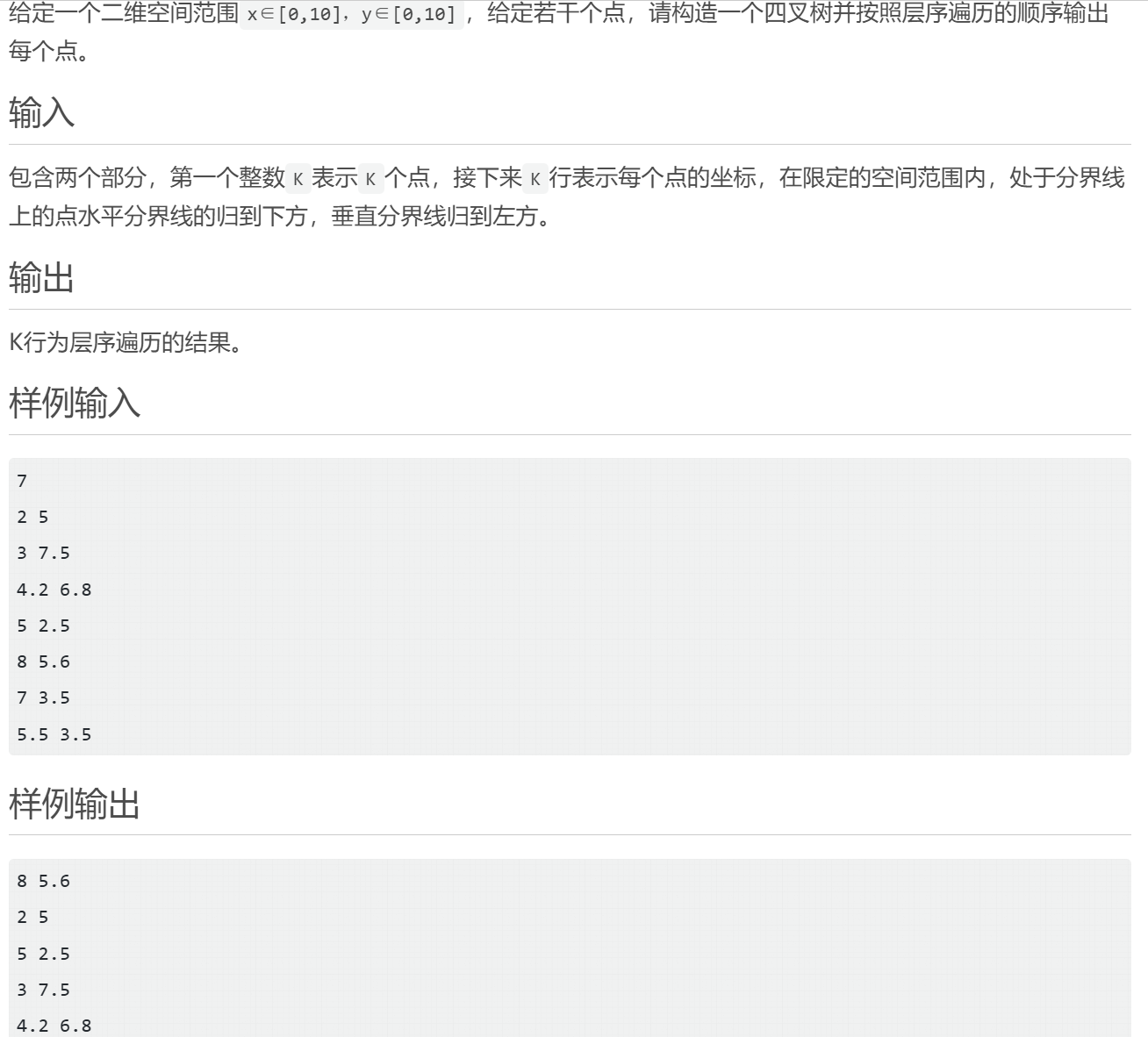
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
// struct node{
// pair<double,double> site;
// bool flag;
// node* quark1;
// node* quark2;
// node* quark3;
// node* quark4;
// node(pair<double,double> site,bool flag=false):site(site),flag(flag),quark1(nullptr),quark2(nullptr),quark3(nullptr),quark4(nullptr){}
// };
struct QuadNode {
bool hasPoint; // 是否有点
double x, y; // 点坐标
QuadNode* child[4]; // 四象限
QuadNode() : hasPoint(false), x(0), y(0) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) child[i] = nullptr;
}
};
int iswhich(pair<double,double>site,pair<double,double> mid){
if(site.first<=mid.first&&site.second>mid.second)return 0;
else if(site.first>mid.first&&site.second>mid.second)return 1;
else if(site.first<=mid.first&&site.second<=mid.second)return 2;
else return 3;
}
// //传入中点和长度
// void insert(QuadNode*& root,pair<double,double>site,pair<double,double> mid,double len){
// if(!root){
// QuadNode* newnode=new QuadNode();
// newnode->hasPoint=true;
// newnode->x=site.first;
// newnode->y=site.second;
// root=newnode;
// return;
// }
// if(root->hasPoint){
// pair<double,double> old = {root->x, root->y};
// root->hasPoint = false; // 自己不再存点
// // 插入原来的点
// insert(root, old, {5,5},10);
// }
// // if(root->hasPoint){
// // pair<double,double> old = {root->x, root->y};
// // root->hasPoint = false;
// // insert(root, old, {5,5}, 10); // 下放旧点
// // insert(root, site, {5,5}, 10); // 🔥 继续处理当前点(必要)
// // return;
// // }
// //判断象限
// int order=iswhich(site,mid);
// //构造下一次的坐标
// double nx,ny,nlen;
// nlen=len/2;
// if(order==0){
// nx=mid.first-nlen;
// ny=mid.second+nlen;
// }
// else if(order==1){
// nx=mid.first+nlen;
// ny=mid.second+nlen;
// }
// else if(order==2){
// nx=mid.first-nlen;
// ny=mid.second-nlen;
// }
// else{
// nx=mid.first+nlen;
// ny=mid.second-nlen;
// }
// insert(root->child[order],{site.first,site.second},{nx,ny},nlen);
// }
void insert(QuadNode*& root, pair<double,double> site, pair<double,double> mid, double len){
if(!root){
root = new QuadNode();
root->hasPoint = true;
root->x = site.first;
root->y = site.second;
return;
}
if(root->hasPoint){
pair<double,double> old = {root->x, root->y};
root->hasPoint = false;
// 计算旧点属于哪个象限
int oldOrder = iswhich(old, mid);
double nlen = len / 2;
double nx = mid.first + ((oldOrder == 1 || oldOrder == 3) ? nlen : -nlen);
double ny = mid.second + ((oldOrder == 0 || oldOrder == 1) ? nlen : -nlen);
// 下放旧点到子象限
insert(root->child[oldOrder], old, {nx, ny}, nlen);
// 继续处理当前点
int order = iswhich(site, mid);
nx = mid.first + ((order == 1 || order == 3) ? nlen : -nlen);
ny = mid.second + ((order == 0 || order == 1) ? nlen : -nlen);
insert(root->child[order], site, {nx, ny}, nlen);
return;
}
// 当前节点为空或已经分裂,继续递归
int order = iswhich(site, mid);
double nlen = len / 2;
double nx = mid.first + ((order == 1 || order == 3) ? nlen : -nlen);
double ny = mid.second + ((order == 0 || order == 1) ? nlen : -nlen);
insert(root->child[order], site, {nx, ny}, nlen);
}
int main(){
int k;
cin>>k;
vector<pair<double,double>>site(k);
QuadNode* root=nullptr;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
cin>>site[i].first>>site[i].second;
insert(root,{site[i].first,site[i].second},{5,5},10);
}
queue<QuadNode*>dq;
dq.push(root);
while(!dq.empty()){
QuadNode* cur=dq.front();
dq.pop();
if(cur->hasPoint){
cout<<cur->x<<" "<<cur->y<<endl;
}
else{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(cur->child[i]){
dq.push(cur->child[i]);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}第一个犯的错,如果该节点下有孩子节点,那么这个节点必须变为空,同时该节点的坐标转移到他的孩子里面
第二个犯的错,在第一种情况下,写转移的时候不能直接硬编码{5,5},会导致死循环无限递归
树形dp------leetcode三典例
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans=0;
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return -1;
int l=dfs(root->left);
int r=dfs(root->right);
ans=max(ans,l+r+2);
return max(l+1,r+1);
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans=-0x3f;
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return 0;
int l=dfs(root->left);
int r=dfs(root->right);
if(l<0&&r<0){
ans=max(ans,root->val);
return root->val;
}
else if(l<0){
ans=max(ans,root->val+r);
return root->val+r;
}
else if(r<0){
ans=max(ans,root->val+l);
return root->val+l;
}
else{
ans=max(ans,root->val+l+r);
return max(l,r)+root->val;
}
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
ans=-0x3f;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};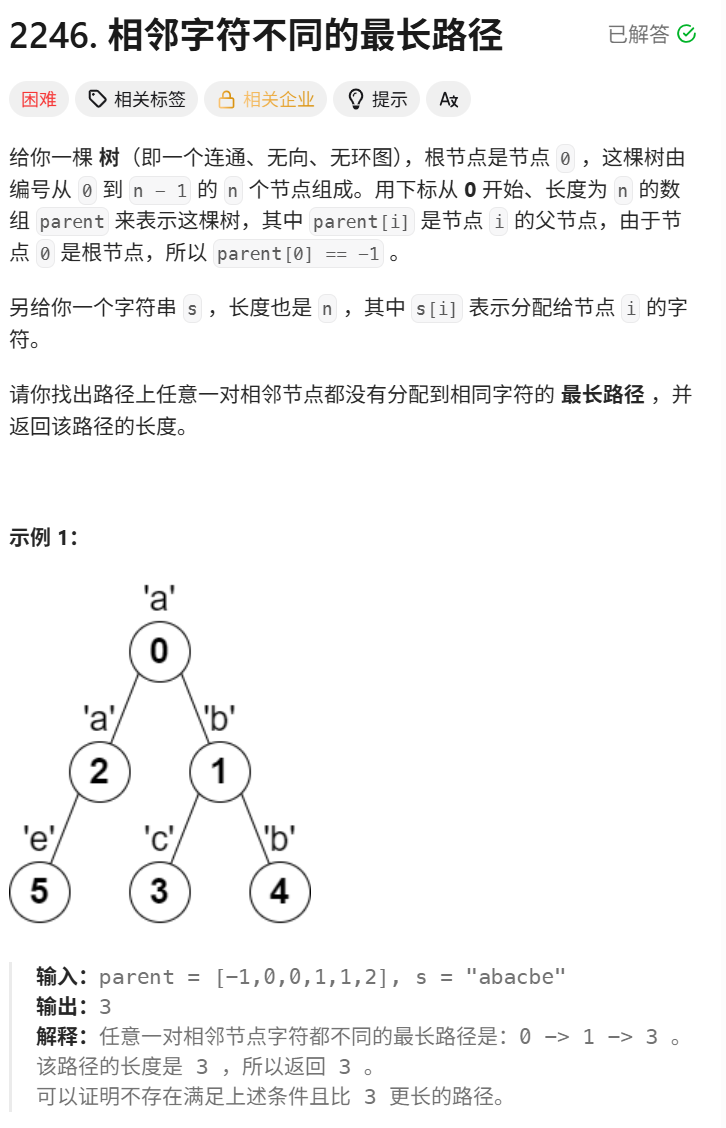
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int n=0;
vector<vector<int>>child;
int ans=0;
string ss;
int dfs(int number,char last){
int max1=0,max2=0;
char word=ss[number];
int child_num=child[number].size();
// if(child_num>2){
// deque<int>dq;
// for(int i=0;i<child_num;i++){
// int tmp=dfs(child[number][i],word);
// if(dq.size()==0)dq.push_back(tmp);
// else if(dq.size()==1){
// if(tmp<dq.front())dq.push_back(tmp);
// else dq.push_front(tmp);
// }
// else{
// if(tmp>dq.front()){
// dq.push_front(tmp);
// dq.pop_back();
// }
// else if(tmp>dq.back()){
// dq.pop_back();
// dq.push_back(tmp);
// }
// else continue;
// }
// }
// // if(dq.size()>=1)max1=dq.front();
// // if(dq.size()>=2)max2=dq.back();
// }
// else if(child_num==2){
// max1=dfs(child[number][0],word);
// max2=dfs(child[number][1],word);
// }
// else if(child_num==1){
// max1=dfs(child[number][0],word);
// }
// 遍历所有子节点,保留其中 top2 最大的
for (int i = 0; i < child_num; i++){
int son = child[number][i];
int tmp = dfs(son, word);
// 如果字符相同,则不能接下去,强制置 0
if (ss[son] == word) tmp = 0;
// 维护 top2:max1 >= max2
if (tmp > max1){
max2 = max1;
max1 = tmp;
} else if (tmp > max2){
max2 = tmp;
}
}
ans=max(ans,1+max1+max2);
if(last==' '||last!=word){
return max(max1,max2)+1;
}
else return 0;
}
int longestPath(vector<int>& parent, string s) {
ss=s;
n=s.length();
child.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(parent[i]==-1)continue;
child[parent[i]].push_back(i);
}
dfs(0,' ');
return ans;
}
};(经典用法,尤其是pre)leetcode98验证二叉搜索树
cpp
// /**
// * Definition for a binary tree node.
// * struct TreeNode {
// * int val;
// * TreeNode *left;
// * TreeNode *right;
// * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
// * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
// * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
// * };
// */
// class Solution {
// public:
// // bool isv(TreeNode* p,int& pre){
// // //if(!p)return true;
// // if(p){
// // int cur=p->val;
// // bool isp1 = isv(p->left,pre);
// // if(pre>=cur)return false;
// // pre=p->val;
// // cout<<pre<<endl;
// // bool isp2 = isv(p->right,pre);
// // return isp1&&isp2;
// // }
// // else return true;
// // }
// // bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
// // if(!root)return true;
// // int pre;
// // cout << pre;
// // return isv(root,pre);
// // }
// public:
// bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root, long long left = LLONG_MIN, long long right = LLONG_MAX) {
// if (root == nullptr) {
// return true;
// }
// long long x = root->val;
// return left < x && x < right &&
// isValidBST(root->left, left, x) &&
// isValidBST(root->right, x, right);
// }
// };
class Solution {
long long pre = LLONG_MIN;
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)return true;
if(!isValidBST(root->left))return false;
if(root->val<=pre)return false;
pre=root->val;
if(!isValidBST(root->right))return false;
return true;
}
};W11-2 合并多棵二叉搜索树(选做,很精彩)

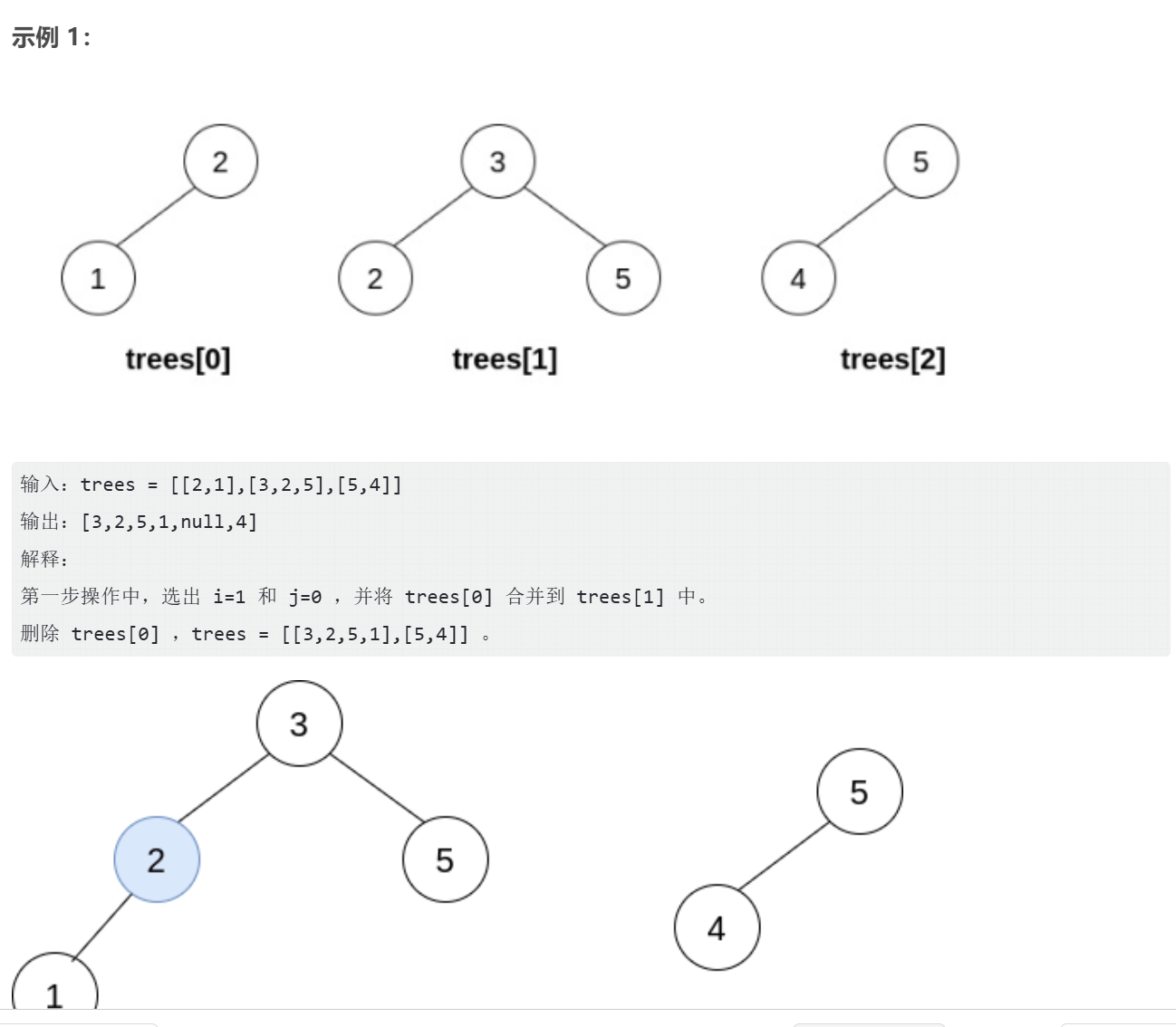
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int x): val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, TreeNode*> mp; // 根值 → 树
unordered_set<int> leaves; // 所有叶子值
int used = 0; // 被合并的树数量
// 检查 BST(中序递增)
long long pre = LLONG_MIN;
bool checkBST(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return true;
if(!checkBST(root->left)) return false;
if(root->val <= pre) return false;
pre = root->val;
return checkBST(root->right);
}
// DFS 合并
TreeNode* merge(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return nullptr;
// 左孩子
if(root->left && mp.count(root->left->val)){
used++;
root->left = mp[root->left->val];
merge(root->left);
}
// 右孩子
if(root->right && mp.count(root->right->val)){
used++;
root->right = mp[root->right->val];
merge(root->right);
}
return root;
}
TreeNode* canMerge(vector<TreeNode*>& trees) {
mp.clear();
leaves.clear();
used = 0;
// 记录根
for(auto t : trees){
mp[t->val] = t;
if(t->left) leaves.insert(t->left->val);
if(t->right) leaves.insert(t->right->val);
}
// 寻找大根
TreeNode* root = nullptr;
for(auto t : trees){
if(!leaves.count(t->val)){ // 不是别人的叶子
if(root) return nullptr; // 多个大根
root = t;
}
}
if(!root) return nullptr;
// 合并
merge(root);
// 必须合并所有其他树
if(used != trees.size() - 1) return nullptr;
// 最后检查是否为合法 BST
pre = LLONG_MIN;
if(!checkBST(root)) return nullptr;
return root;
}
};✔ 关键 1:找唯一的"大根"(最关键)
所有树的根值都在:
rootValues = {每棵树的根节点值} leafValues = {所有树的叶子节点值}
大根是:
rootValues - leafValues = 唯一没有作为叶子出现过的根值
如果没有 → impossible
如果有多个 → impossible
✔ 关键 2:做"按需合并"
我们 DFS 大根,每当遇到一个叶子节点的值 X:
如果 X 也是某棵树的根值 → 合并那棵树
如果 X 不是某棵树的根值 → 保持为空叶子
✔ 关键 3:最终检查是不是合法 BST
用中序遍历检查是否递增。
(图论)leetcode-207课程表

dfs
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> g;
vector<int> vis;
bool dfs(int u) {
if (vis[u] == 1) return false; // 找到环
if (vis[u] == 2) return true; // 已经确定无环
vis[u] = 1; // 标记正在访问
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (!dfs(v)) return false;
}
vis[u] = 2; // 访问结束
return true;
}
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
g.assign(numCourses, {});
vis.assign(numCourses, 0);
for (auto &p : prerequisites) {
g[p[1]].push_back(p[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (!dfs(i)) return false;
}
return true;
}
};法二(bfs)
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> g(numCourses);
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
// 建图 + 入度
for (auto &p : prerequisites) {
int a = p[0], b = p[1];
g[b].push_back(a); // b -> a (先学b才能学a)
indegree[a]++;
}
queue<int> q;
// 入度为 0 的课程先入队
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int learned = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
learned++;
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (--indegree[v] == 0) {
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return learned == numCourses;
}
};用bfs写题时候vis数组应该在什么时候标注?(leetcode841)
理解:应该在入队的时候就立马标记,不要等到进入下一个循环才标记,否则虽然不会错,但是会导致一些地方是重复入队的,很浪费时间

cpp
// class Solution {
// public:
// vector<bool>vis;
// bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
// int n=rooms.size();
// vis.resize(n);
// queue<int>q;
// q.push(0);
// while(!q.empty()){
// int cur=q.front();q.pop();
// vis[cur]=true;
// for(auto p:rooms[cur]){
// if(!vis[p]){
// q.push(p);
// }
// }
// }
// for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
// if(!vis[i])return false;
// }
// return true;
// }
// };
class Solution {
public:
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
int n = rooms.size();
vector<bool> vis(n, false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
vis[0] = true; // ✅ 入队即标记
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int nxt : rooms[cur]) {
if (!vis[nxt]) {
vis[nxt] = true; // ✅ 立刻标记
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
for (bool v : vis)
if (!v) return false;
return true;
}
};时间差距:
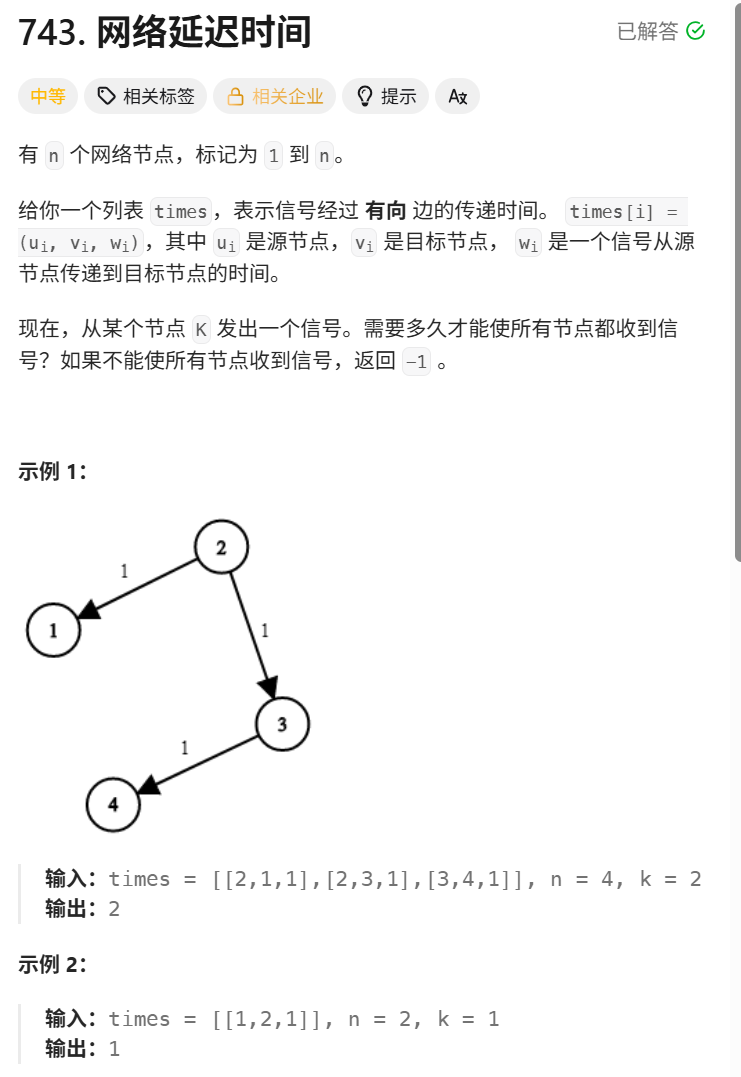
Dijkstra算法求最短路径------leetcode743
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n+1, vector<int>(n+1, -1));
for (auto &t : times) {
g[t[0]][t[1]] = t[2];
}
vector<int> dist(n+1, INT_MAX);
vector<bool> vis(n+1, false);
dist[k] = 0;
for (int step = 1; step <= n; step++) {
int u = -1;
int mind = INT_MAX;
// ✅ 正确:从所有未访问节点里选最小
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i] && dist[i] < mind) {
mind = dist[i];
u = i;
}
}
if (u == -1) break; // 剩下的都不可达
vis[u] = true;
// ✅ 松弛 u 的所有出边
for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
if (g[u][v] != -1 && !vis[v]) {
dist[v] = min(dist[v], dist[u] + g[u][v]);
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (dist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;
ans = max(ans, dist[i]);
}
return ans;
}
// int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
// vector<vector<int>>g(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));
// for(int i=0;i<times.size();i++){
// int u,v,w;
// u=times[i][0],v=times[i][1],w=times[i][2];
// g[u][v]=w;
// }
// vector<bool>vis(n+1,false);
// vector<int>mindist(n+1,INT_MAX);
// queue<int>q;
// q.push(k);
// vis[k]=true;
// mindist[k]=0;
// int count=0;
// while(!q.empty()){
// count++;
// int cur=q.front();q.pop();
// int minval=INT_MAX,minindex=-1;
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// if(g[cur][i]!=-1&&!vis[i]){
// mindist[i]=min(mindist[i],g[cur][i]+mindist[cur]);
// if(mindist[i]<minval){
// minval=mindist[i];
// minindex=i;
// }
// }
// }
// if(minindex!=-1){
// vis[minindex]=true;
// q.push(minindex);
// }
// else break;
// }
// cout<<count<<endl;
// int timess=0;
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// cout<<mindist[i]<<endl;
// if(mindist[i]==INT_MAX)return -1;
// timess=max(timess,mindist[i]);
// }
// return timess;
// }
};优先队列的方法:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
// ---------- 1. 建图:邻接表 ----------
// g[u] 中存的是:从 u 出发的所有边 (v, w)
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n + 1);
for (auto &t : times) {
// t = {起点, 终点, 权值}
g[t[0]].push_back({t[1], t[2]});
}
// ---------- 2. dist 数组 ----------
// dist[i] 表示:从起点 k 到 i 的当前最短距离
// 初始都设为无穷大,表示"暂时不可达"
vector<int> dist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
// ---------- 3. 优先队列(小根堆) ----------
// pq 中存的是 {当前路径长度, 节点编号}
// 使用 greater<> 后,dist 最小的元素会优先弹出
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,
vector<pair<int,int>>,
greater<pair<int,int>>> pq;
// 起点到自身距离为 0
dist[k] = 0;
pq.push({0, k}); // 先把起点放进去
// ---------- 4. Dijkstra 主循环 ----------
// 只要还有"候选的最短路径",就继续
while (!pq.empty()) {
// 取出当前距离最小的节点
// d:当前从 k 到 u 的路径长度
auto [d, u] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// 如果这条路径已经不是最短的(过期状态),直接跳过
// 因为 dist[u] 可能在之后被更新成了更小的值
if (d > dist[u]) continue;
// ---------- 5. 松弛操作 ----------
// 遍历从 u 出发的所有边
for (auto [v, w] : g[u]) {
// 判断:从 k -> u -> v 是否比之前的路径更短
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
// 如果更短,就更新最短距离
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
// 把更新后的状态放入优先队列
// 注意:这里不立刻确定 v,只是"候选"
pq.push({dist[v], v});
}
}
}
// ---------- 6. 统计答案 ----------
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 如果有节点始终不可达,返回 -1
if (dist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;
// 网络延迟时间是最慢的那个节点
ans = max(ans, dist[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};W13-4邮递员送信(朴素Dijkstra和堆优化Dijkstra)
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<climits>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>a;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>b;
// struct cmp{
// bool operator()(const pair<int,int>&x,const pair<int,int>&y){
// return x.second>y.second;
// }
// };
long long function(vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>&a){
vector<int>dist(n+1,INT_MAX/2);
vector<bool>final(n+1,false);
dist[1]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int u=-1;
int mindist=INT_MAX/2;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(dist[j]<mindist&&final[j]==false){
mindist=dist[j];
u=j;
}
}
if(u==-1)break;
final[u]=true;
for(auto p:a[u]){
if(p.second+dist[u]<dist[p.first]){
dist[p.first]=p.second+dist[u];
}
}
}
long long sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)sum+=dist[i];
return sum;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>n>>m;
a.resize(n+1);
b.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
a[u].push_back({v,w});
b[v].push_back({u,w});
}
long long sum=function(a)+function(b);
cout<<sum;
}
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<climits>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>a;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>b;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(const pair<int,int>&x,const pair<int,int>&y){
return x.second>y.second;
}
};
int function(vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>&a){
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,cmp>pq;
vector<bool>final(n+1,false);
vector<int>dist(n+1,INT_MAX/2);
dist[1]=0;
pq.push({1,0});
while(!pq.empty()){
int u=pq.top().first;
//int w=pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if(final[u])continue;
final[u]=true;
for(auto p:a[u]){
if(final[p.first]==false){
dist[p.first]=min(dist[p.first],p.second+dist[u]);
pq.push({p.first,dist[p.first]});
}
}
}
long long sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)sum+=dist[i];
return sum;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>n>>m;
a.resize(n+1);
b.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
a[u].push_back({v,w});
b[v].push_back({u,w});
}
long long sum=function(a)+function(b);
cout<<sum;
}总结一下:Dijkstra算法思想和做这个题的综合思路
节点1到所有各个节点的最短距离
稀疏图用pair邻接矩阵
稠密图用矩阵就行
然后大体都是设置一个final标志位来判断是否已经是最短距离
然后每次遍历的逻辑是先找到一个最短的并且还没有final标记的节点
把final标记设置为true
之后松弛与这个结点直接接触的其他节点
标准拓扑dp:w14-5并行课程

cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<climits>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<int>time(n+1);
vector<vector<int>>g(n+1);
vector<int>indeg(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>time[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
g[u].push_back(v);
indeg[v]++;
}
vector<int>spendtime(n+1);
queue<int>fuck;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(indeg[i]==0){
fuck.push(i);
}
spendtime[i]=time[i];
}
int sum=0;
while(!fuck.empty()){
int cur=fuck.front();
sum=max(sum,spendtime[cur]);
//cout<<time[cur]<<" "<<spendtime[cur]<<endl;
fuck.pop();
for(auto p:g[cur]){
spendtime[p]=max(spendtime[p],time[p]+spendtime[cur]);
indeg[p]--;
if(indeg[p]==0)fuck.push(p);
}
}
cout<<sum;
}