异常处理-异常概述
7.1 异常概述与异常体系结构
在使用计算机语言进行项目开发的过程中,即使程序员把代码写得尽善尽美,在系统的运行过程中仍然会遇到一些问题,因为很多问题不是靠代码能够避免的。比如:客户输入数据的格式、读取的文件是否存在、网络是否始终保持通畅等等。
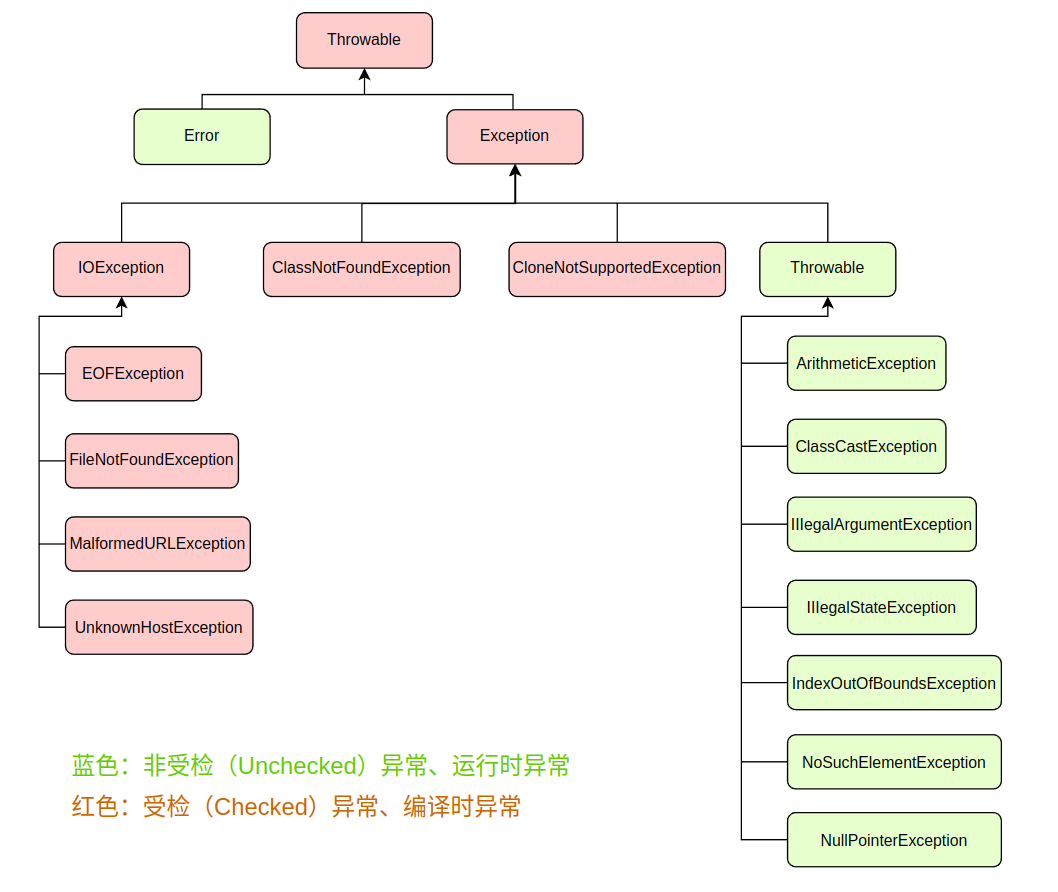
异常:在java语言中,将程序中发生的不正常的情况称为"异常"。(开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常),广义上分为Error和Exception,但是Error为无法解决的严重问题,一般不做处理。我们说的异常一般是狭义异常,即Exception。
-
Error
- java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。eg:StackOverFlowError和OOM。一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。
javapublic class ErrorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 运行报错:栈溢出 java.lang.StackOverflowError // main(args); // 在main中调用main,无限循环 // 运行报错:堆溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError // Integer[] arr1 = new Integer[Integer.MAX_VALUE]; // new的结构是在堆中的,堆中无法分配这么多控件 } } -
Exception
- 其他因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。eg:空指针访问、试图读取不存在的文件、网络连接中断、数组角标越界等。
异常处理-异常的分类
对于这些错误,一般有两种解决方法:一是遇到错误就终止程序的运行。另一种方法是由程序员在编写程序时,就考虑到错误的检测、错误消息的提示,以及错误的处理。
捕抓错误最理想的是在编译期间,但又得错误只有在运行时才会发生。比如:除数为0,数组下标越界等。
分类:编译时异常和运行时异常
异常处理-常见异常举例
java
public class ExceptionTest {
private int data;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionTest test = new ExceptionTest();
// 以下为编译时异常
// test.CheckedTest();
// 以下为运行时异常:
// test.NullPointerExceptionTest();
// test.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionTest();
// test.ClassCastExceptionTest();
// test.NumberFormatExceptionTest();
// test.InputMismatchExceptionTest();
// test.ArithmeticExceptionTest();
}
/********************************编译时异常*********************************/
void CheckedTest() {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
// Unhandled exception: java.io.FileNotFoundException
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// Unhandled exception: java.io.IOException
int data = fileInputStream.read();
while (data != -1) {
System.out.print((char)data);
// Unhandled exception: java.io.IOException
data = fileInputStream.read();
}
// Unhandled exception: java.io.IOException
fileInputStream.close();
}
/********************************运行时异常*********************************/
// 空指针异常:java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "String.toString()" because "a" is null
void NullPointerExceptionTest() {
String a = null;
a.toString();
}
// 数组角标越界:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 4 out of bounds for length 3
void ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionTest() {
int[] a = new int[]{0,1,2};
System.out.println(a[4]);
}
// 类型转换异常:java.lang.ClassCastException: class java.lang.String cannot be cast to class java.lang.Integer
void ClassCastExceptionTest() {
Object a = new String("a");
int b = (Integer)a;
}
// 数字格式异常:in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "a"
void NumberFormatExceptionTest() {
String a = new String("a");
Integer.parseInt(a);
}
// 输入不匹配异常:java.util.InputMismatchException
void InputMismatchExceptionTest() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入数值:");
int a = scanner.nextInt(); // 输入非int类型的值 "abc"
System.out.println(a);
scanner.close();
}
// 算术异常:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
void ArithmeticExceptionTest() {
int a = 1, b = 0;
System.out.println(a/b);
}
}异常处理-异常处理方式概述
异常的处理:抓抛模型
- 过程一
- "抛":程序在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象。并将此对象抛出。一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不再执行。
- 过程二
- "抓":可以理解为异常的处理方式:try-catch-finally; throws
7.3 异常的处理机制一
在编写程序时,经常要在可能出现错误的地方加上检测的代码,如进行x/y运算时,要检测分母为0,数据为空,输入的不是数据而是字符等。过多的if-else分支会导致程序的代码加长、臃肿、可读性差。因此采用异常处理机制。
java异常处理
java采用的异常处理机制,是将异常处理的程序代码集中在一起,与正常的程序代码分开,使得程序简洁、优雅、便于维护。