注:该文用于个人学习记录和知识交流,如有不足,欢迎指点。
实现的接口:
- 构造函数
- 析构函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 拷贝赋值运算符
- 移动构造函数
- 移动赋值运算符
- 解引用 箭头运算符
- 引用计数、原始指针、重置指针
与原生shared_ptr对比
要求:
- 不考虑删除器和空间配置器
- 不考虑弱引用
- 考虑引用计数的线程安全
- 提出测试案例
关键点:引用计数的内存序选择!!!
手撕shared_ptr
1. 知识点:
std::atomic::fetch_sub(n)是原子减操作,它的核心行为是
- 获取当前值;
- 将当前值减去
n(原子性);- 返回操作前的原始值(而非操作后的值)。
- 有关内存序的选择:
add:relaxed。 原因:add可自行重排序,在x86中可见性是满足的。因此最终执行的结果是相同的,只是执行add的时机可能会变
sub:acquire and realse。获取其他线程sub后的最新值(好判断是否应该释放指针),然后-1,并刷新,让调用release的获取最新值。
(tips:sub以上的add操作无法重排序到sub下方,因此无论add怎么重排序,sub获得的 值肯定是add加过之后的最终值!!!)
- get_cout: acquire:获取sub后最新的结果,外部调用get_count 最多就是判断该指针是否被释放了,因此add的最新值获取不到没关系,只要确保不为0就行了(由sub决定)
注意赋值运算符要判断是否为自我赋值
带参构造 + explicit: 防止隐式转换,即不允许执行shared_ptr<int> p = new int(42);
cpp
#pragma once
#include <atomic>
// shared_ptr<int> p1(new int(42)); 带参构造
// shared_ptr<int> p2 = shared_ptr<int>(new int(42)); 拷贝构造
// shared_ptr<int> p3 = p1; 拷贝构造
// shared_ptr<int> p4; p4 = p1 赋值运算
class A {
public:
void func() {}
};
// shared_ptr<A> p1(new A());
// p1->func();
template <typename T>
class shared_ptr {
public:
shared_ptr() : ptr_(nullptr), ref_count_(nullptr) {}
explicit shared_ptr(T* ptr) : ptr_(ptr), ref_count_(ptr ? new std::atomic<std::size_t>(1) : nullptr) {} // 加explicit ,使程序不能执行shared_ptr<int> p2 = new int(42); (该语句默认会隐式转换成 shared_ptr<int> p2( new int(42) );)
~shared_ptr() {
release();
}
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& other) : ptr_(other.ptr_), ref_count_(other.ref_count_) {
if (ref_count_) {
ref_count_->fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
}
shared_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& other) {
if (this != &other) {
release();
ptr_ = other.ptr_;
ref_count_ = other.ref_count_;
if (ref_count_) {
ref_count_->fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
}
return *this;
}
// noexcept: the function will not throw exceptions
// 编译期会生成更高效的代码,不需要为异常处理生成额外的代码
// STL
shared_ptr<T>(shared_ptr<T>&& other) noexcept : ptr_(other.ptr_), ref_count_(other.ref_count_) {
other.ptr_ = nullptr;
other.ref_count_ = nullptr;
}
shared_ptr<T>& operator=(shared_ptr<T>&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
release();
ptr_ = other.ptr_;
ref_count_ = other.ref_count_;
other.ptr_ = nullptr;
other.ref_count_ = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
// *p1
T& operator*() const {
return *ptr_;
}
// p1->func()
T* operator->() const {
return ptr_;
}
std::size_t use_count() const {
return ref_count_ ? ref_count_->load(std::memory_order_acquire) : 0;
}
T* get() const {
return ptr_;
}
void reset(T * p = nullptr) {
release();
ptr_ = p;
ref_count_ = p ? new std::atomic<std::size_t>(1) : nullptr;
}
private:
void release() {
if (ref_count_ && ref_count_->fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_acq_rel) == 1) { // fetch_sub返回的是减操作前的值,所以这里取1而不是0
delete ptr_;
delete ref_count_;
}
}
T* ptr_;
std::atomic<std::size_t>* ref_count_;
};2. 测试用例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "shared_ptr.h"
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <memory>
void test_shared_ptr_thread_safety() {
shared_ptr<int> ptr(new int(42));
// 创建多个线程,每个线程都增加和减少引用计数
const int num_threads = 10;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
threads.emplace_back([&ptr]() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; ++j) {
shared_ptr<int> local_ptr(ptr);
// 短暂暂停,增加线程切换的可能性
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
}
});
}
// 等待所有线程完成
for (auto& thread : threads) {
thread.join();
}
// 检查引用计数是否正确
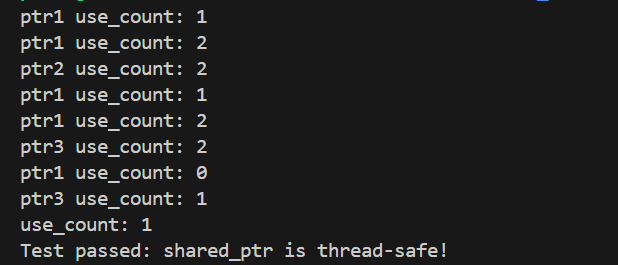
std::cout << "use_count: " << ptr.use_count() << std::endl;
if (ptr.use_count() == 1) {
std::cout << "Test passed: shared_ptr is thread-safe!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Test failed: shared_ptr is not thread-safe!" << std::endl;
}
}
// 测试代码
int main() {
shared_ptr<int> ptr1(new int(10));
std::cout << "ptr1 use_count: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 1
{
shared_ptr<int> ptr2 = ptr1;
std::cout << "ptr1 use_count: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 2
std::cout << "ptr2 use_count: " << ptr2.use_count() << std::endl; // 2
}
std::cout << "ptr1 use_count: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 1
shared_ptr<int> ptr3(new int(20));
ptr1 = ptr3;
std::cout << "ptr1 use_count: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 2
std::cout << "ptr3 use_count: " << ptr3.use_count() << std::endl; // 2
ptr1.reset();
std::cout << "ptr1 use_count: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 0
std::cout << "ptr3 use_count: " << ptr3.use_count() << std::endl; // 1
test_shared_ptr_thread_safety();
return 0;
}3. 测试结果: