HTTP协议概括
应用层的实现需要制定协议,但我们也不必每次从零开始,我们可以借鉴和使用前辈制定好的优良协议,其中包括http协议。
在互联网世界中,HTTP(HyperTextTransfer Protocol,超文本传输协议)是一个至关重要的协议。它定义了客户端(如浏览器)与服务器之间如何通信,以交换或传输超文本(如HTML文档)。
HTTP协议是客户端与服务器之间通信的基础。客户端通过HTTP协议向服务器发送请求,服务器收到请求后处理并返回响应。HTTP协议是一个无连接、无状态的协议,即每次请求都需要建立新的连接,且服务器不会保存客户端的状态信息。
相信各位对http协议再熟悉不过了,我们现在浏览的网站大多都是https开头,在十几年前还是http占优。https相较http更加安全,我们暂时将其看作一致,后续再探讨https协议。
URL
我们平时所说的网址就是Uniform Resource Locator(统一资源定位符)。
具体格式为:[协议]: //[主机名]:[端口]/[路径]?[查询参数]#[片段标识符]
如:
http://www.baidu.com:443/s?wd=QT\&tn=68018901_65_oem_dg#content
这明显就是我们所用过的网址,不过还有一些细节需要注意。
首先www.baidu.com就是域名他会经过DNS(Domain Name System,域名系统)转化成ip地址。
我们可以在cmd中用ping指令调出域名和ip地址的转换:
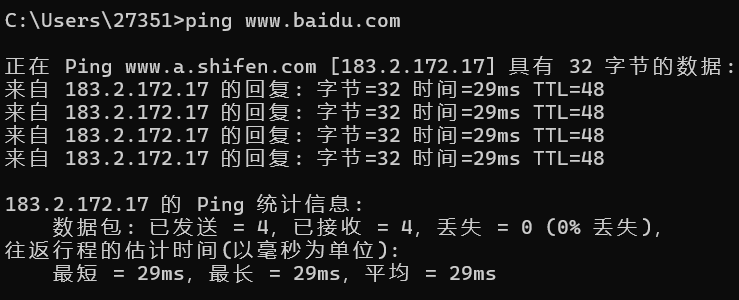
细心的读者依旧注意到了,我们平时访问的网址根本就没有端口号。这时因为http会默认和80端口号绑定,如果不显示输入就是接入80端口。
那么现在我们就知道http://baidu.com:80就可以标记互联网上唯一一台主机。
后面的/s就是该主机上的资源路径,也代表客户端要访问的资源路径。
但是'/'不是根目录,它可以在服务器的任一目录下,称为web根目录。
?后面跟的就是查询参数,查询参数以&相连。
片段标识符
页面内的锚点(可选),用于定位到网页的具体位置(比如跳转到文章的某一节),该部分不会发送到服务器,仅由浏览器解析。
Encode
URL 只能包含 ASCII 字符,特殊字符(如中文、空格、&、=)需要URL 编码(比如空格编码为 %20,中文 QT 编码为 %E5%8D%8E%E4%B8%BA);
示例:https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=中文 → 编码后 https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=中文。
HTTP协议请求和响应格式
我们可以先写一份代码打印一下http应答的报文。
先修改一下TcpServer的逻辑:

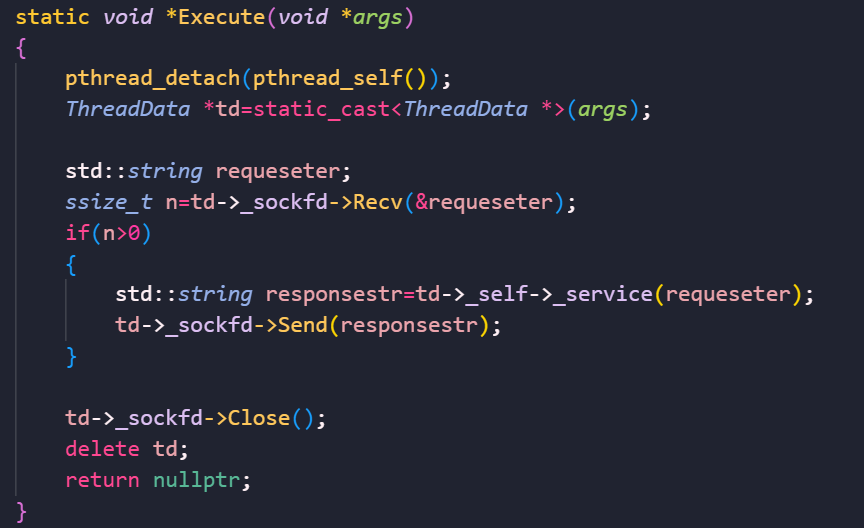
我们这里将消息读取交给http.hpp模块处理

改一下Main函数逻辑:
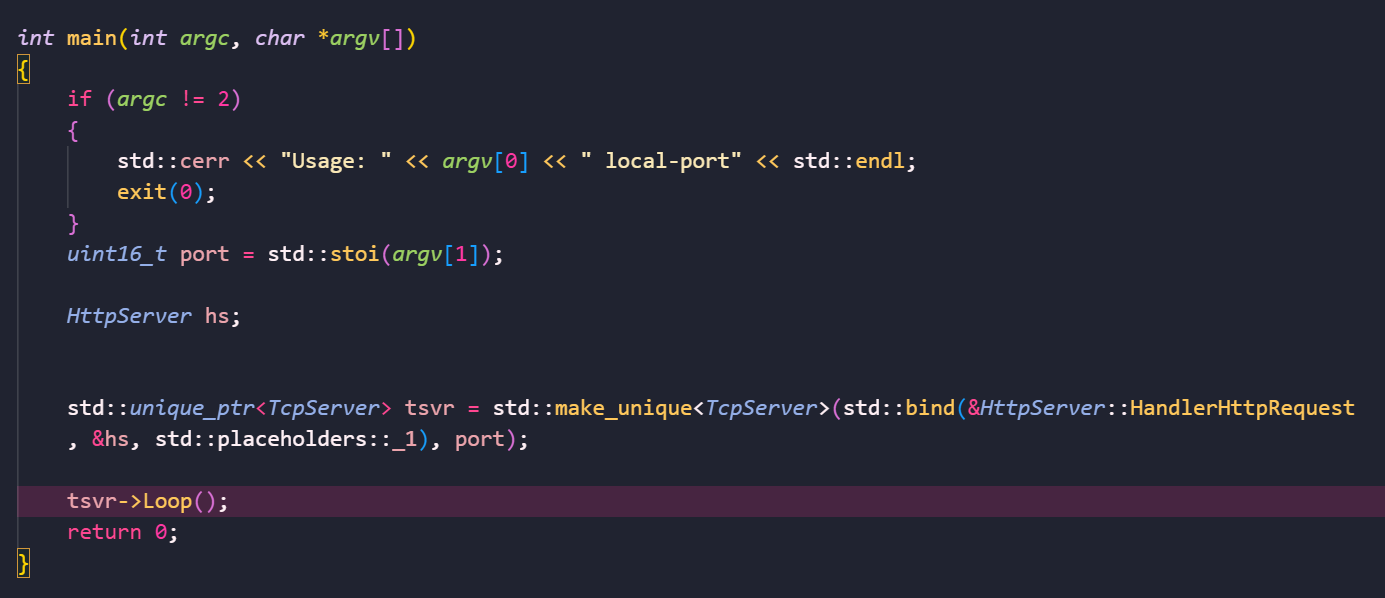
那么我们就来试试会有什么结果吧:
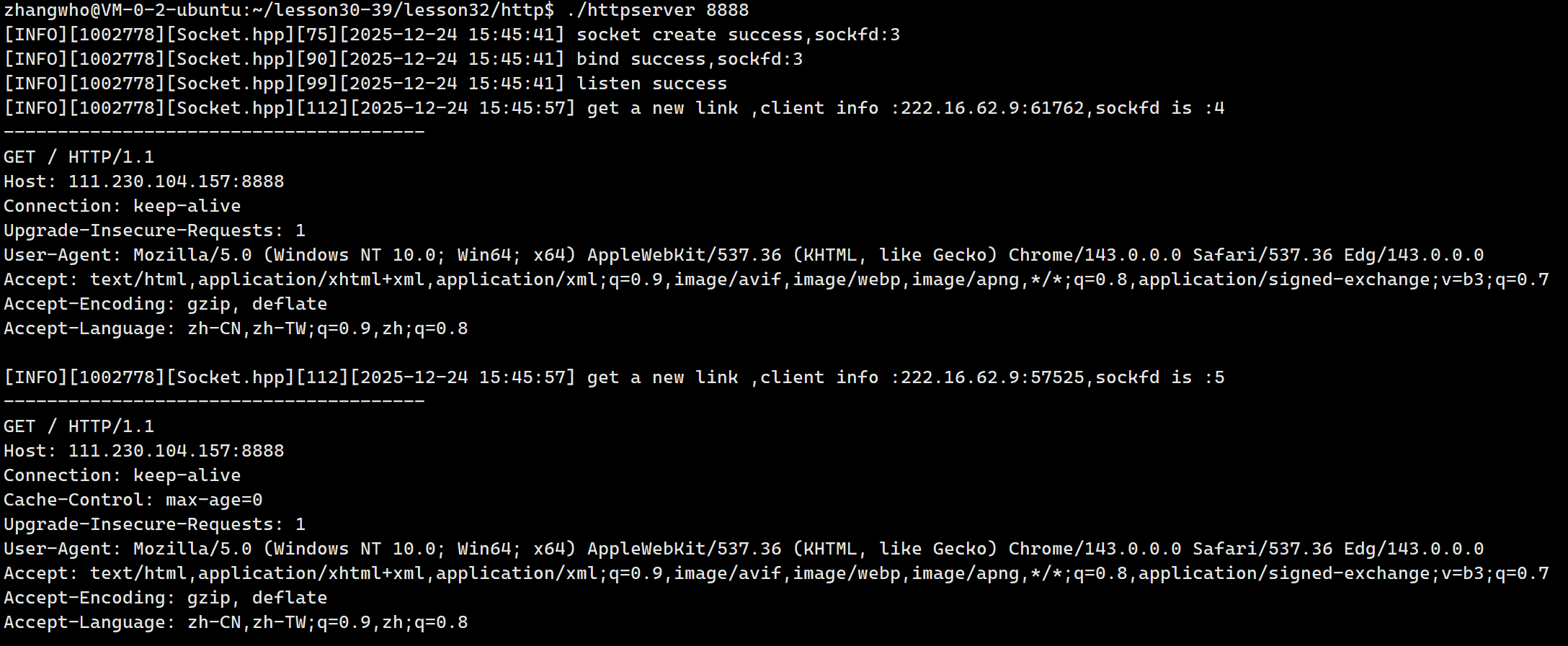
在浏览器上访问了我的云服务器主机后就收到了上述请求。
可以看到请求会发起多次,并且每次请求建立一次连接,还允许建立多个连接。
当然因为我的响应是空的,所以页面什么都看不到,我们可以写一些简单的回应:
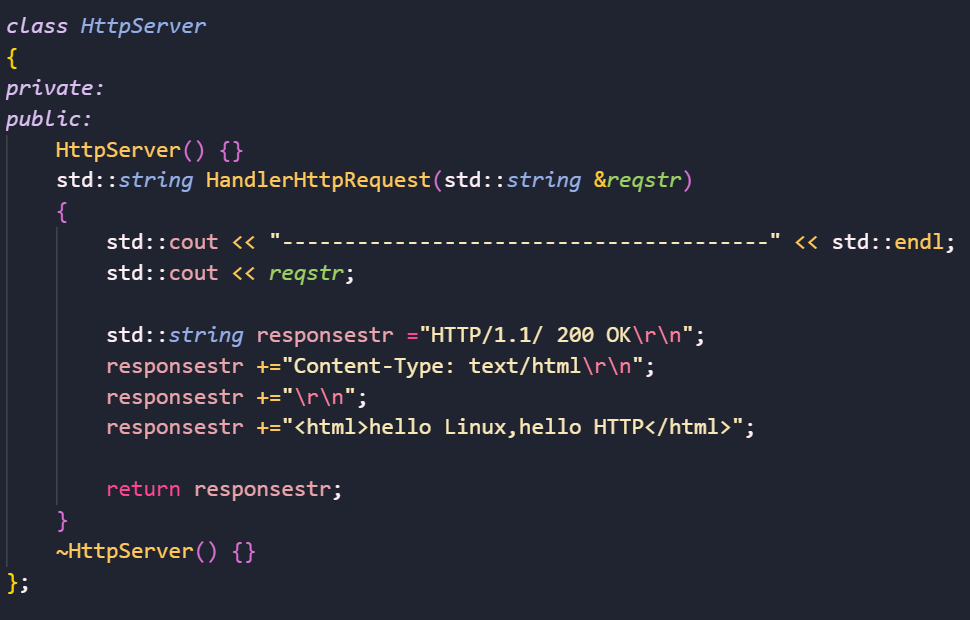
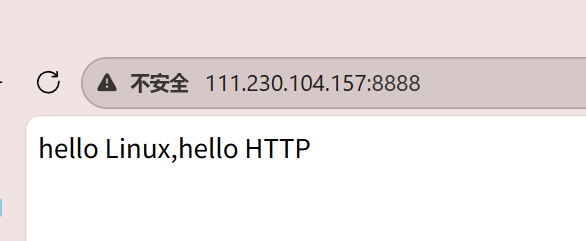
可以看到,我们就收到了应答。
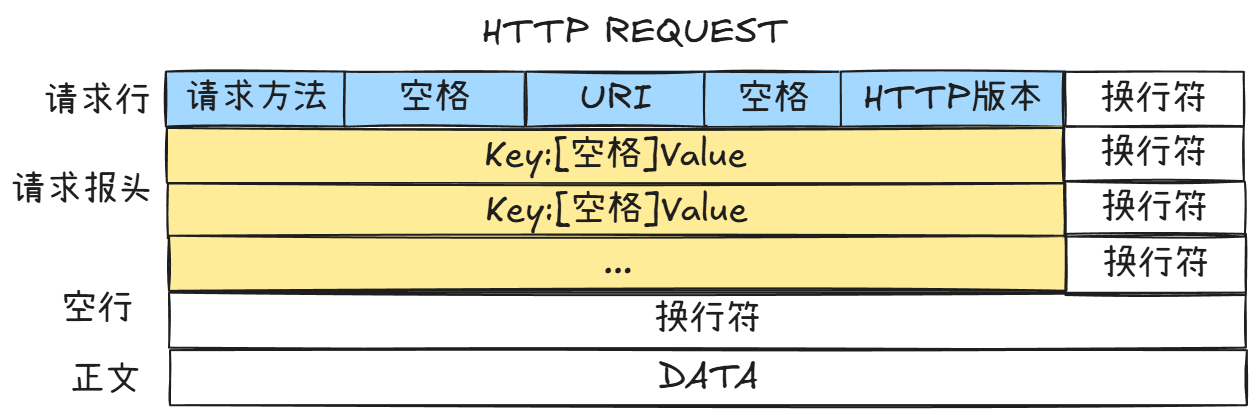
- 请求报文格式:
请求行:[请求方法] [URI] [HTTP版本]
请求报头:Key: Value \r\n
请求报头:Key: Value \r\n
...(更多请求报头)
(空行,仅换行符\r\n)
请求正文:DATA
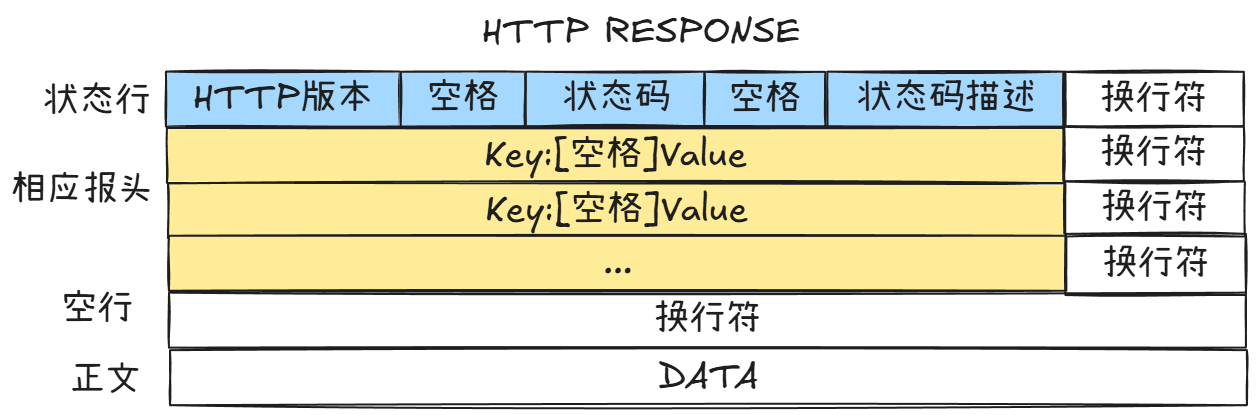
- 响应报文格式:
状态行:[HTTP版本] [状态码] [状态码描述]
响应报头:Key: Value \r\n
响应报头:Key: Value \r\n
...(更多响应报头)
(空行,仅换行符\r\n)
响应正文:DATA
可以看到响应正文以上都是报头,我们等会对报文做序列化和反序列化。
HTTP方法
GET和POST
请求报文的第一个数据就是请求方法:
| 方法 | 说明 | 支持的HTTP协议版本 |
|---|---|---|
| GET | 获取资源 | 1.0、1.1 |
| POST | 传输实体主体 | 1.0、1.1 |
| PUT | 传输文件 | 1.0、1.1 |
| HEAD | 获得报文首部 | 1.0、1.1 |
| DELETE | 删除文件 | 1.0、1.1 |
| OPTIONS | 询问支持的方法 | 1.1 |
| TRACE | 追踪路径 | 1.1 |
| CONNECT | 要求用隧道协议连接代理 | 1.1 |
| LINK | 建立和资源之间的联系 | 1.0 |
| UNLINE | 断开连接关系 | 1.0 |
其中最常用的就是GET方法和POST方法。
这两个方法通常是基于form表单实现的。
HTML表单通过标签创建,用于收集用户输入。基本结构包含action(提交目标URL)、method(GET/POST请求方式)和表单控件(如输入框、按钮)。
示例:
html
<form action="/submit" method="POST">
<label for="username">用户名:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>表单的方法如果不写的话就是默认GET。
get和post都可以向服务器提交数据,不同的是:
- GET提交的数据放在查询参数部分,也就是URL里和url用'?'分隔的后半部分如:
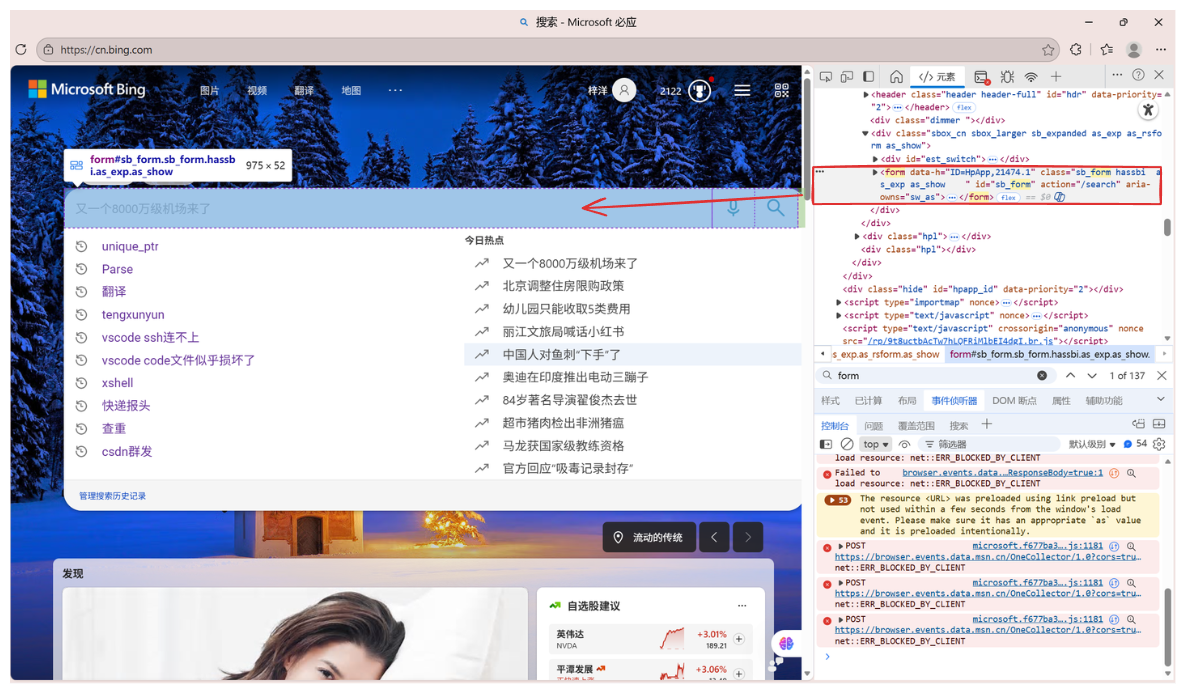
可以看到我们常见的搜索框就是一个表单,这里没写方法也说明默认调用的是GET。那么我们尝试搜索:
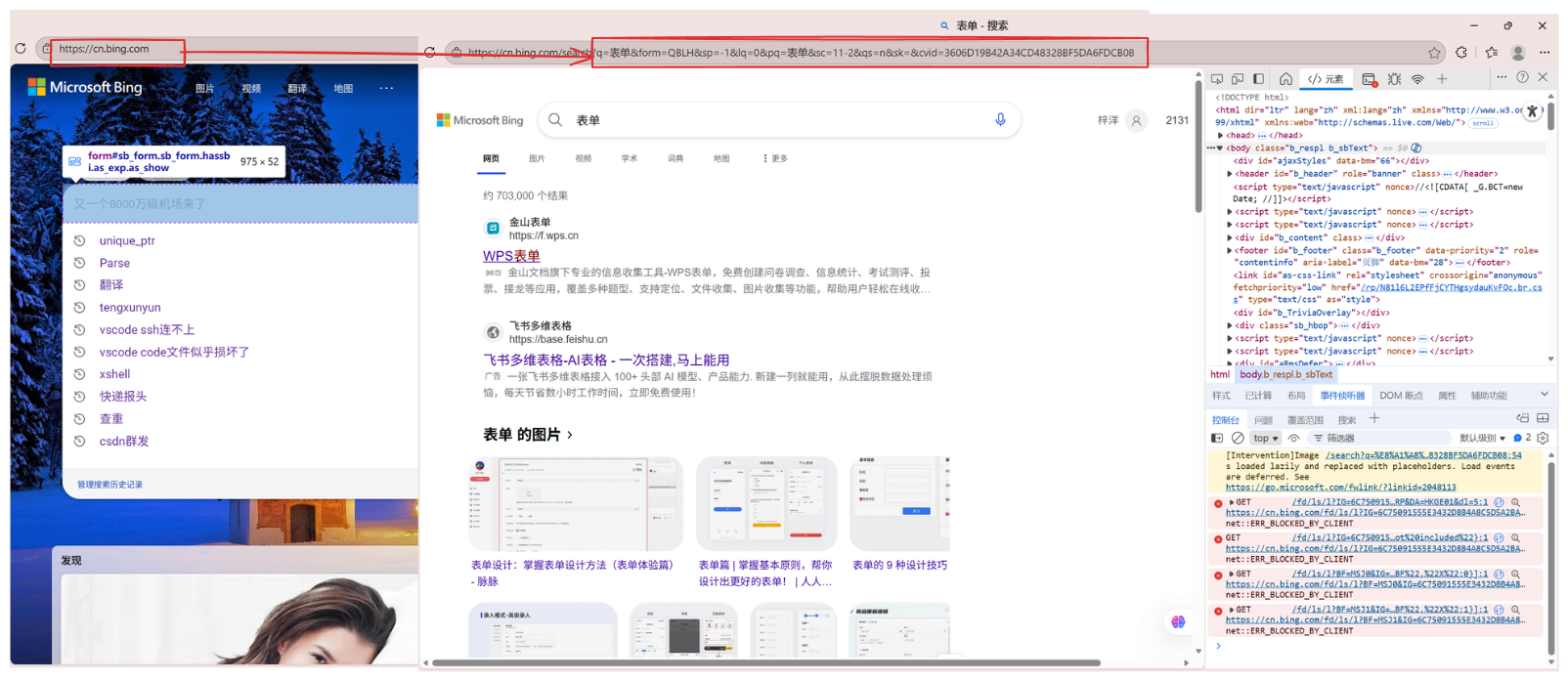
可以看到我们的参数就放在了URL。 - POST方法传递的参数则放到请求报文的正文:
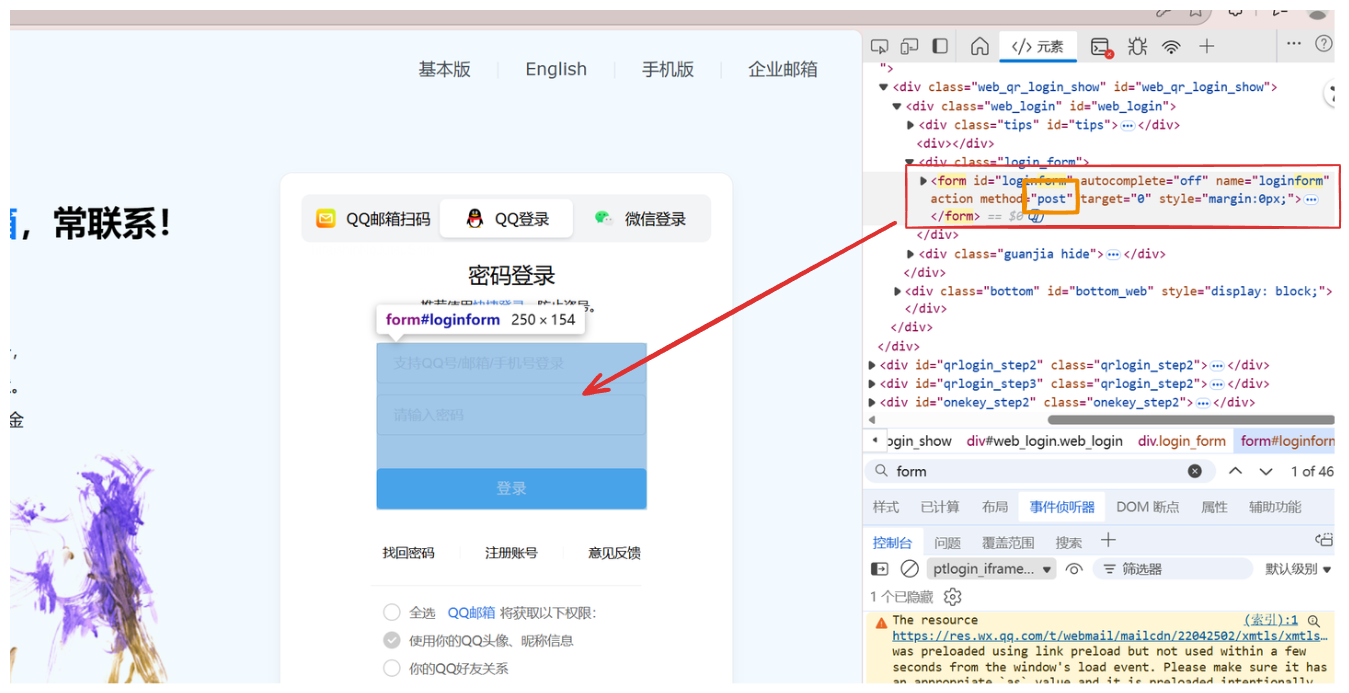
可以看到像登陆界面这些表单一般用的就是post方法,这避免了将你的密码直接暴露在URL上。当然HTTP的GET和POST方法都是不安全的,需要HTTPS的加密才能安全传输数据。
事实上请求的正文部分主要是由请求方法决定的。而我们大多数情况用的都是GET方法,这样意味着我们大多数情况下请求报文的正文都是空的。
其他方法
- PUT方法(不常用)
用途:用于传输文件,将请求报文主体中的文件保存到请求URL指定的位置。
示例:PUT /example.html HTTP/1.1
特性:不太常用,但在某些情况下,如RESTfulAPI中,用于更新资源。 - HEAD方法
用途:与GET方法类似,但不返回报文主体部分,仅返回响应头。
示例:HEAD /index.html HTTP/1.1
特性:用于确认URL的有效性及资源更新的日期时间等。 - DELETE方法(不常用)
用途:用于删除文件,是PUT的相反方法。
示例:DELETE/example.htmlHTTP/1.1
特性:按请求URL删除指定的资源。 - OPTIONS方法
用途:用于查询针对请求URL指定的资源支持的方法。
示例:OPTIONS*HTTP/1.1
特性:返回允许的方法,如GET、POST等。
HTTP状态码
| 类别 | 原因短语 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1XX | Informational(信息性状态码) | 接收的请求正在处理 |
| 2XX | Success(成功状态码) | 请求正常处理完毕 |
| 3XX | Redirection(重定向状态码) | 需要进行附加操作以完成请求 |
| 4XX | Client Error(客户端错误状态码) | 服务器无法处理请求 |
| 5XX | Server Error(服务器错误状态码) | 服务器处理请求出错 |
最常见的状态码,比如200(OK),404(NotFound), 403(Forbidden), 302(Redirect, 重定向), 504(Bad Gateway)
部分状态码:
| 状态码 | 含义 | 应用样例 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Continue | 上传大文件时,服务器告诉客户端可以继续上传 |
| 200 | OK | 访问网站首页,服务器返回网页内容 |
| 201 | Created | 发布新文章,服务器返回文章创建成功的信息 |
| 204 | No Content | 删除文章后,服务器返回"无内容"表示操作成功 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | 网站换域名后,自动跳转到新域名;搜索引擎更新网站链接时使用 |
| 302 | Found / See Other | 用户登录成功后,重定向到用户首页 |
| 304 | Not Modified | 浏览器缓存机制,对未修改的资源返回304状态码 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 填写表单时,格式不正确导致提交失败 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 访问需要登录的页面时,未登录或认证失败 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 尝试访问你没有权限查看的页面 |
| 404 | Not Found | 访问不存在的网页链接 |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务器崩溃或数据库错误导致页面无法加载 |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | 使用代理服务器时,代理服务器无法从上游服务器获取有效响应 |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | 服务器维护或过载,暂时无法处理请求 |
需要注意HTTP状态码301(永久重定向)和302(临时重定向)都依赖Location选项。
HTTP常见Header
- Content-Type: 数据类型(text/html等)
内容类型(Content-Type)是HTTP协议中的一个头部字段,用于标识请求或响应中传输的数据的媒体类型(MIME类型)。它帮助客户端和服务器正确解析和处理数据。

- Content-Length: Body的长度
这部分报头我们在实现网络计算器的时候也写了,能帮助我们完整提取有效载荷。 - Host:客户端告知服务器,所请求的资源是在哪个主机的哪个端口上;
- User-Agent: 声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息;
我们可以根据用户的操作系统,优先推送对应资源。 - referer: 当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的;
- Location: 搭配3xx状态码使用,告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问;
- Cookie: 用于在客户端存储少量信息.通常用于实现会话(session)的功能;
Cookie最常见在一些有登录界面的网页。譬如bilibili,正常第一次进入之后都是无登录状态。然后我们登录之后,再次进入该页面也是默认登录状态,这就是因为我们将登录信息通过Cookie报头传递给了服务器,服务器每次和客户端建立连接时,就预先处理这个数据:
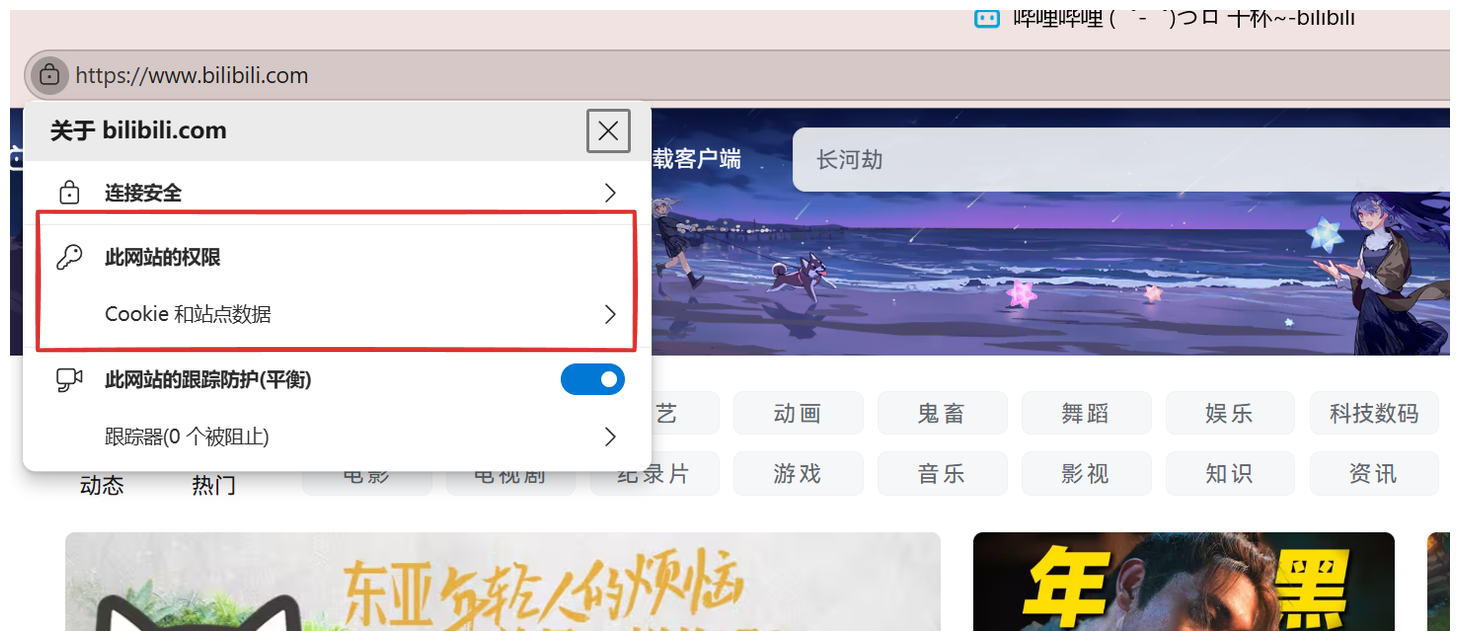
如果我们将这些Cookie删除掉,那么下次进入该界面就是无登陆状态了。
后续我们还会详谈Cookie的应用场景。
还有一个报头是Connection:
HTTP中的Connection 字段是HTTP报文头的一部分,它主要用于控制和管理客户端与服务器之间的连接状态
作用:
管理持久连接:Connection字段还用于管理持久连接(也称为长连接)。持久连接允许客户端和服务器在请求/响应完成后不立即关闭TCP连接,以便在同一个连接上发送多个请求和接收多个响应。
- HTTP/1.1:在HTTP/1.1协议中,默认使用持久连接。当客户端和服务器都不明确指定关闭连接时,连接将保持打开状态,以便后续的请求和响应可以复用同一个连接。
- HTTP/1.0:在HTTP/1.0协议中,默认连接是非持久的。如果希望在HTTP/1.0上实现持久连接,需要在请求头中显式设置Connection: keep-alive。
序列化和反序列化
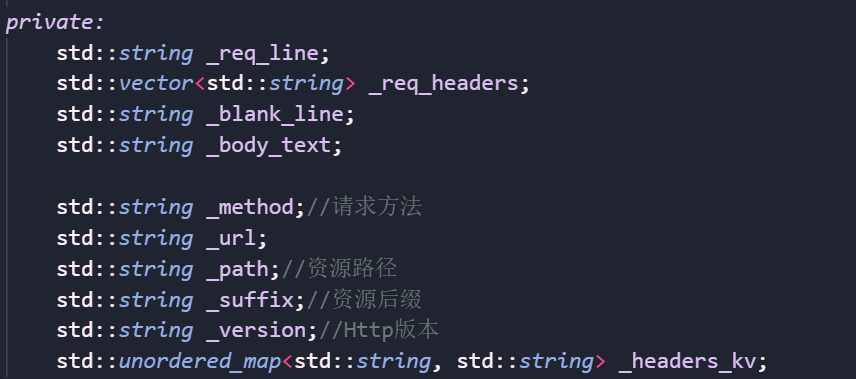
首先根据上面报文的格式,我们先封装基本的成员变量:

请求报文
更详细的成员变量:
初始化:
cpp
HttpRequest() : _blank_line(base_sep), _path(prefixpath)
{
}prefixpath就是web根目录的路径
获取行:
cpp
std::string GetLine(std::string &reqstr)
{
auto pos = reqstr.find(base_sep);
if (pos == std::string::npos)
return std::string();
std::string line = reqstr.substr(0, pos);
reqstr.erase(0, line.size() + base_sep.size());
return line.empty() ? base_sep : line;
}有了这些我们就可以初步反序列化了:
cpp
void Deserialize(std::string &reqstr)
{
_req_line = GetLine(reqstr);
std::string header;
do
{
header=GetLine(reqstr);
if(header.empty())
break;
else if(header==base_sep)
break;
_req_headers.push_back(header);
} while (true);
if(!reqstr.empty())
_body_text=reqstr;
//进一步反序列化
ParseReqLine();
ParseReqHeader();
}那么我们还可以将请求行里的数据载入_method...
将请求报头的数据载入map中。
解析请求行:
cpp
void ParseReqLine()
{
std::stringstream ss(_req_line);
ss >> _method >> _url >> _version;
if (strcasecmp(_method.c_str(), "GET") == 0)
{
auto pos = _url.find(arg_sep);
if (pos != std::string::npos)
{
_body_text = _url.substr(pos + arg_sep.size());
_url.resize(pos);
}
}
_path += _url;
if (_path[_path.size() - 1] == '/')
_path += homepage;
auto pos = _path.find(suffixsep);
if (pos != std::string ::npos)
{
_suffix = _path.substr(pos);
}
else
{
_suffix = ".default";
}
}解析请求报头:
cpp
void ParseReqHeader()
{
for (auto &header : _req_headers)
{
auto pos = header.find(line_sep);
if (pos == std::string ::npos)
continue;
std::string k = header.substr(0, pos);
std::string v = header.substr(pos + line_sep.size());
if (k.empty() || v.empty())
continue;
_headers_kv.insert({k, v});
}
}最后实现一个打印报文:
cpp
void Print()
{
std::cout << "----------------------------" << std::endl;
std::cout << "###" << _req_line << std::endl;
for (auto &header : _req_headers)
{
std::cout << "@@@" << header << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "***" << _blank_line;
std::cout << ">>>" << _body_text << std::endl;
std::cout << "Method: " << _method << std::endl;
std::cout << "Url: " << _url << std::endl;
std::cout << "Version: " << _version << std::endl;
for (auto &header_kv : _headers_kv)
{
std::cout << ")))" << header_kv.first << "->" << header_kv.second << std::endl;
}
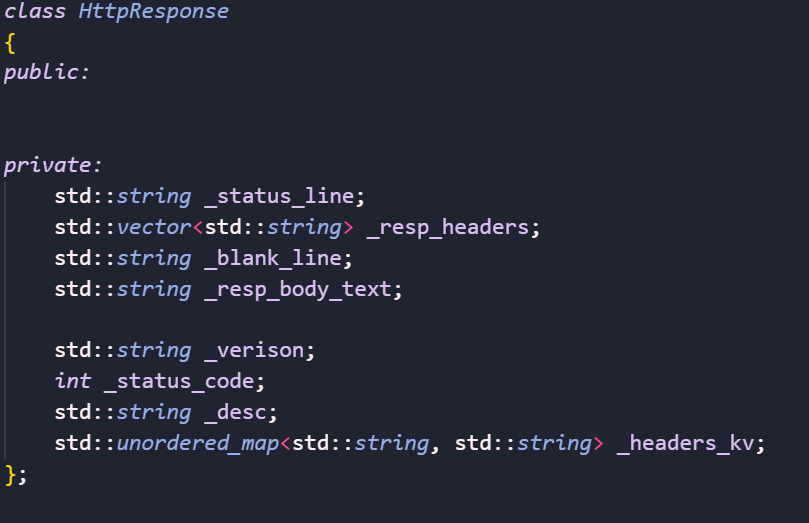
}应答报文
一样我们需要更多的成员变量:
首先实现一些基本的设置函数:
cpp
void AddCode(int code ,const std::string &desc)
{
_status_code=code;
_desc=desc;
}
void AddHeader(const std::string &k, const std::string &v)
{
_headers_kv[k] = v;
}
void AddBodyText(const std::string &body_text)
{
_resp_body_text = body_text;
}序列化
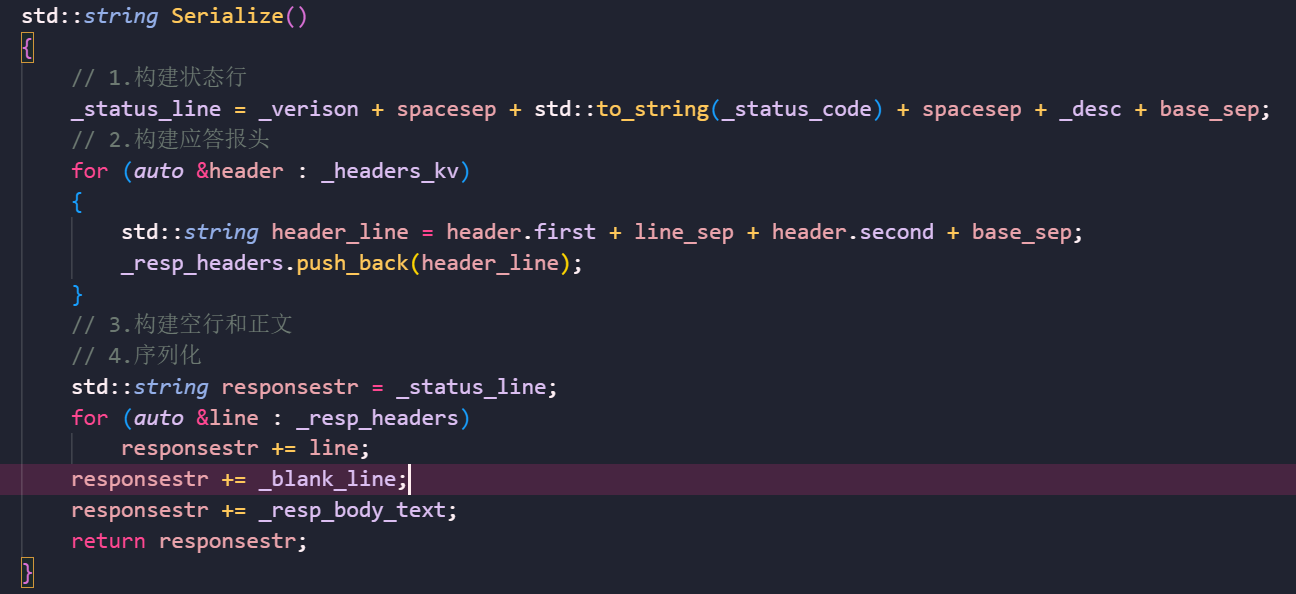
可以看到我们只需要实现请求报文的反序列化和应答报文的序列化。
剩下的都交给客户端实现了,这还是非常舒服的。
简单服务器
我们实现一个简单的服务功能,首先要以二进制文件流形式打开文件:

初始化一些状态码和类型:
完整代码
cpp
#pragma once
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "TcpServer.hpp"
using fun_c = std::function<std::string(std::string &requeststr)>;
class HttpRequest;class HttpResponse;
using func_t = std::function<HttpResponse(HttpRequest &)>;
const static std::string base_sep = "\r\n";
const static std::string prefixpath = "wwwroot";
const static std::string homepage = "index.html";
const static std::string httpversion = "HTTP/1.0";
const static std::string suffixsep = ".";
const static std::string spacesep = " ";
const static std::string line_sep = ": ";
const static std::string arg_sep = "?";
class HttpRequest
{
private:
std::string GetLine(std::string &reqstr)
{
auto pos = reqstr.find(base_sep);
if (pos == std::string::npos)
return std::string();
std::string line = reqstr.substr(0, pos);
reqstr.erase(0, line.size() + base_sep.size());
return line.empty() ? base_sep : line;
}
void ParseReqLine()
{
std::stringstream ss(_req_line);
ss >> _method >> _url >> _version;
if (strcasecmp(_method.c_str(), "GET") == 0)
{
auto pos = _url.find(arg_sep);
if (pos != std::string::npos)
{
_body_text = _url.substr(pos + arg_sep.size());
_url.resize(pos);
}
}
_path += _url;
if (_path[_path.size() - 1] == '/')
_path += homepage;
auto pos = _path.find(suffixsep);
if (pos != std::string ::npos)
{
_suffix = _path.substr(pos);
}
else
{
_suffix = ".default";
}
}
void ParseReqHeader()
{
for (auto &header : _req_headers)
{
auto pos = header.find(line_sep);
if (pos == std::string ::npos)
continue;
std::string k = header.substr(0, pos);
std::string v = header.substr(pos + line_sep.size());
if (k.empty() || v.empty())
continue;
_headers_kv.insert({k, v});
}
}
public:
HttpRequest() : _blank_line(base_sep), _path(prefixpath)
{
}
// 反序列化
void Deserialize(std::string &reqstr)
{
_req_line = GetLine(reqstr);
std::string header;
do
{
header = GetLine(reqstr);
if (header.empty())
break;
else if (header == base_sep)
break;
_req_headers.push_back(header);
} while (true);
if (!reqstr.empty())
_body_text = reqstr;
// 进一步反序列化
ParseReqLine();
ParseReqHeader();
}
std::string Url()
{
LOG(DEBUG, "Client want url %s\n", _url.c_str());
return _url;
}
std::string Path()
{
LOG(DEBUG, "Client want path %s\n", _url.c_str());
return _path;
}
std::string Suffix()
{
return _suffix;
}
std::string Method()
{
LOG(DEBUG, "Client request method is %s\n", _method.c_str());
return _method;
}
std::string GetResuestBody()
{
LOG(DEBUG, "Client request method is %s, args: %s, request path: %s\n",
_method.c_str(), _body_text.c_str(), _path.c_str());
return _body_text;
}
void Print()
{
std::cout << "----------------------------" << std::endl;
std::cout << "###" << _req_line << std::endl;
for (auto &header : _req_headers)
{
std::cout << "@@@" << header << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "***" << _blank_line;
std::cout << ">>>" << _body_text << std::endl;
std::cout << "Method: " << _method << std::endl;
std::cout << "Url: " << _url << std::endl;
std::cout << "Version: " << _version << std::endl;
for (auto &header_kv : _headers_kv)
{
std::cout << ")))" << header_kv.first << "->" << header_kv.second << std::endl;
}
}
~HttpRequest() {}
private:
std::string _req_line;
std::vector<std::string> _req_headers;
std::string _blank_line;
std::string _body_text;
std::string _method; // 请求方法
std::string _url;
std::string _path; // 资源路径
std::string _suffix; // 资源后缀
std::string _version; // Http版本
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers_kv;
};
class HttpResponse
{
public:
HttpResponse() : _verison(httpversion), _blank_line(base_sep)
{
}
void AddCode(int code, const std::string &desc)
{
_status_code = code;
_desc = desc;
}
void AddHeader(const std::string &k, const std::string &v)
{
_headers_kv[k] = v;
}
void AddBodyText(const std::string &body_text)
{
_resp_body_text = body_text;
}
std::string Serialize()
{
// 1.构建状态行
_status_line = _verison + spacesep + std::to_string(_status_code) + spacesep + _desc + base_sep;
// 2.构建应答报头
for (auto &header : _headers_kv)
{
std::string header_line = header.first + line_sep + header.second + base_sep;
_resp_headers.push_back(header_line);
}
// 3.构建空行和正文
// 4.序列化
std::string responsestr = _status_line;
for (auto &line : _resp_headers)
responsestr += line;
responsestr += _blank_line;
responsestr += _resp_body_text;
return responsestr;
}
private:
std::string _status_line;
std::vector<std::string> _resp_headers;
std::string _blank_line;
std::string _resp_body_text;
std::string _verison;
int _status_code;
std::string _desc;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers_kv;
};
class HttpServer
{
private:
std::string GetFileContent(const std::string &path)
{
std::ifstream in(path, std::ios::binary); // 二进制形式打开
if (!in.is_open())
return std::string();
// 获取文件大小
in.seekg(0, in.end);
int filesize = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0, in.beg);
std::string content;
content.resize(filesize);
in.read((char *)content.c_str(), filesize);
in.close();
return content;
}
public:
HttpServer()
{
_mime_type.insert(std::make_pair(".html", "text/html"));
_mime_type.insert(std::make_pair(".jpg", "image/jpeg"));
_mime_type.insert(std::make_pair(".png", "image/png"));
_mime_type.insert(std::make_pair(".default", "text/html"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(100, "Continue"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(200, "OK"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(201, "Created"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(301, "Moved Permanently"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(302, "Found"));
_code_to_desc.insert(std::make_pair(404, "Not Found"));
}
std::string HandlerHttpRequest(std::string &reqstr)
{
std::cout << "---------------------------------------" << std::endl;
std::cout << reqstr;
std::cout << "---------------------------------------" << std::endl;
HttpRequest req;
HttpResponse resp;
req.Deserialize(reqstr);
if (req.Path() == "wwwroot/redir")
{
// 处理重定向
std::string redir_path = "https://www.qq.com";
resp.AddCode(301, _code_to_desc[301]);
resp.AddHeader("Location", redir_path);
}
else if(!req.GetResuestBody().empty())
{
//处理动态资源
if(IsServiceExists(req.Path()))
{
resp = _service_list[req.Path()](req);
}
}
else
{
// 最基本的上层处理,处理静态资源
std::string content = GetFileContent(req.Path());
if (content.empty())
{
content = GetFileContent("wwwroot/404.html");
resp.AddCode(404, _code_to_desc[404]);
resp.AddHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(content.size()));
resp.AddHeader("Content-Type", _mime_type[".html"]);
resp.AddBodyText(content);
}
else
{
resp.AddCode(200, _code_to_desc[200]);
resp.AddHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(content.size()));
resp.AddHeader("Content-Type", _mime_type[req.Suffix()]);
resp.AddHeader("Set-Cookie", "username=zhangwho");
resp.AddBodyText(content);
}
}
return resp.Serialize();
}
void InsertService(const std::string &servicename,func_t f)
{
std::string s = prefixpath + servicename;
_service_list[s] = f;
}
bool IsServiceExists(const std::string &servicename)
{
auto iter = _service_list.find(servicename);
if(iter == _service_list.end()) return false;
else return true;
}
~HttpServer() {}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _mime_type;
std::unordered_map<int, std::string> _code_to_desc;
std::unordered_map<std::string, func_t> _service_list;
};