Sentinel介绍
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 是面向分布式、多语言异构化服务架构的流量治理组件,主要以流量为切入点,从流量路由、流量控制、流量整形、熔断降级、系统自适应过载保护、热点流量防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 社区正在将流量治理相关标准抽出到 OpenSergo spec 中,Sentinel 作为流量治理标准实现

Sentinel规则类型
针对Sentinel的规则重新学习下,详细使用文档参见 官方文档
| 规则类型 | 核心作用维度 | 典型应用场景 | 触发后果 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流控规则 (Flow) | 限制流量 (QPS/线程数) | 秒杀限流、防止突发流量冲垮系统 | 请求被拒绝/排队等待 | 防刷、防过载 |
| 熔断规则 (Degrade) | 依赖稳定性 (响应时间/异常) | 调用第三方接口超时、数据库慢查询 | 暂停请求,快速失败(熔断) | 防雪崩、防依赖故障 |
| 热点规则 (Param) | 参数粒度 (特定参数值) | 某个热门商品被疯狂刷,其他商品正常访问 | 限制特定参数的访问频率 | 防热点数据击穿 |
| 系统规则 (System) | 整体负载 (CPU/Load/RT) | 大促期间防止机器过载,保护系统基线 | 拒绝部分请求,保护机器不挂 | 防机器挂掉 |
| 授权规则 (Auth) | 来源控制 (黑白名单) | 防止某个恶意 IP 或非法应用调用接口 | 允许或拒绝请求 | 防非法调用 |
流控规则(Flow Control)
最常用的规则,主要用于限流,有如下2种模式
- QPS 模式:每秒允许多少个请求通过。超过阈值则拦截。
- 线程数模式:限制同时处理该资源的线程数量。
除了简单的直接拒绝,它还有两种高级策略:
- Warm Up (预热):比如系统刚启动,像冷车一样,不能直接拉满油门。预热模式会在一定时间内逐渐将阈值从低升到高,防止瞬间流量把刚启动的服务打挂。
- 排队等待 (Queueing):不直接拒绝请求,而是让请求按照设定的时间间隔匀速通过(像检票口一样),用于处理突发的脉冲流量。
熔断规则 (Circuit Breaker)
关注服务的质量 。当它发现某个服务调用"不健康"时,会直接切断连接,防止连锁故障(雪崩)。
Sentinel 支持三种策略:
- 慢调用比例:如果一个接口的平均响应时间(RT)太长(比如超过 1 秒),且比例达到阈值,就熔断。适用于对响应速度敏感的场景。
- 异常比例:如果请求中出现的异常(如抛出 RuntimeException)比例过高,就熔断。
- 异常数:统计时间内出现的异常总数超过阈值,直接熔断。
熔断是"宁可错杀一百,不可放过一个"的保护机制。触发后,所有请求直接走"降级逻辑"(fallback),不再调用下游真实服务,直到经过一段"冷却时间"后尝试恢复
热点规则 (Hotspot Param)
流控规则的高级版 ,它能把限流的粒度细化到方法参数 级别。
通常情况下,流控是对整个接口(如 /getProduct)限流。但热点规则可以做到:当参数 id=1 的时候限流 100 QPS,而 id=2 的时候不限流
关注的是"不均匀"。在实际场景中,可能只有某个特定的"爆款"商品(热点 key)流量巨大,导致数据库压力大。如果对整个接口限流,会误伤其他正常的商品查询。热点规则就是为了解决这种"贫富不均"的问题
系统规则 (System Protection)
全局视角 的规则,它不针对某个具体的接口,而是针对整个应用实例 的系统指标。
它监控的指标包括:
- Load(仅 Linux/Unix):系统平均负载。
- CPU 使用率。
- 入口 QPS。
- 线程数。
- 平均 RT 。
"保底"机制。通常在单机的 QPS 或负载过高时触发,目的是让系统整体保持在一个稳定的水位,防止机器直接死机。它是一种兜底的保护,通常配置的阈值会比机器的极限处理能力稍微保守一点
授权规则 (Authority Rule)
黑白名单 机制,用于控制"谁可以调用"。
它通过 SentinelContext 中的 origin(来源标识)来判断。通常用来识别调用方的服务名、IP 地址等。 关注的是"身份",可以使用黑名单 或白名单限制
Spring boot 4如何集成Sentinel?
本次采用@SentinelResource + AOP 方式集成 Sentinel
添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-parameter-flow-control</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-annotation-aspectj</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>编写相关的测试代码
SentinelConfig类
java
@Configuration
public class SentinelConfig {
@PostConstruct
public void initFlowRules(){
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
rule.setResource("HelloWorld");
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// Set limit QPS to 20.
rule.setCount(10);
rules.add(rule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
@PostConstruct
public void initDegradeRules() {
List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();
rule.setResource("HelloWorld");
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT); // RT threshold degrade strategy
rule.setCount(200); // Max response time (ms)
rule.setTimeWindow(10); // Recovery timeout period in seconds
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
@Bean
public SentinelResourceAspect sentinelResourceAspect() {
return new SentinelResourceAspect();
}
}HelloWorldService
java
@Service
public class HelloWorldService {
@SentinelResource(value = "HelloWorld",
entryType = EntryType.IN,
exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalStateException.class},
blockHandler = "handleBlock",
fallback = "handleFallback")
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello, " + name;
}
public String handleBlock(String name, BlockException ex) {
return "Request blocked by Sentinel: " + ex.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
public String handleFallback(String name, Throwable t) {
return "Request failed and handled by fallback: " + t.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
}HelloWorldController
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
@Tag(name = "登录接口")
public class HelloWorldController {
@Autowired
private HelloWorldService helloWorldService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
@Operation(summary = "hello")
public String sayHello(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) {
return helloWorldService.sayHello(name);
}
}
java
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SentinelTest {
@Autowired
HelloWorldService helloWorldService;
private AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
private AtomicInteger blockCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
private AtomicInteger fallbackCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() throws Exception {
// Reset counters before each test
successCount.set(0);
blockCount.set(0);
fallbackCount.set(0);
}
@Test
public void testRateLimitingAndDegradation() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("准备测试...............");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
log.info("开始测试...............");
int numberOfThreads = 30; // Number of concurrent threads
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(numberOfThreads);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(numberOfThreads);
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfThreads; i++) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
try {
String result = helloWorldService.sayHello("TestUser");
if (result.contains("blocked")) {
blockCount.incrementAndGet();
} else if (result.contains("failed")) {
fallbackCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
successCount.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
fallbackCount.incrementAndGet();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await(); // Wait until all threads have completed
log.info("Success count: " + successCount.get());
log.info("Blocked count: " + blockCount.get());
log.info("Fallback count: " + fallbackCount.get());
// Assuming the flow rule is set to allow up to 20 requests per second
assert successCount.get() <= 20 : "Number of successful requests should not exceed 20";
assert blockCount.get() > 0 : "Some requests should be blocked due to rate limiting";
assert fallbackCount.get() == 0 : "No requests should go to fallback under normal conditions";
executorService.shutdown();
}
}启动程序
启动sentinel-dashboard
python
java -Dserver.port=8858 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8858 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -Dsentinel.dashboard.auth.username=sentinel -Dsentinel.dashboard.auth.password=123456 -Dserver.servlet.session.timeout=7200 -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.9.jar启动Springboot
注意在启动时需要添加VM参数
bash
-Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8858界面展示
- 通过界面可以针对规则进行修改,保存后可以立即生效
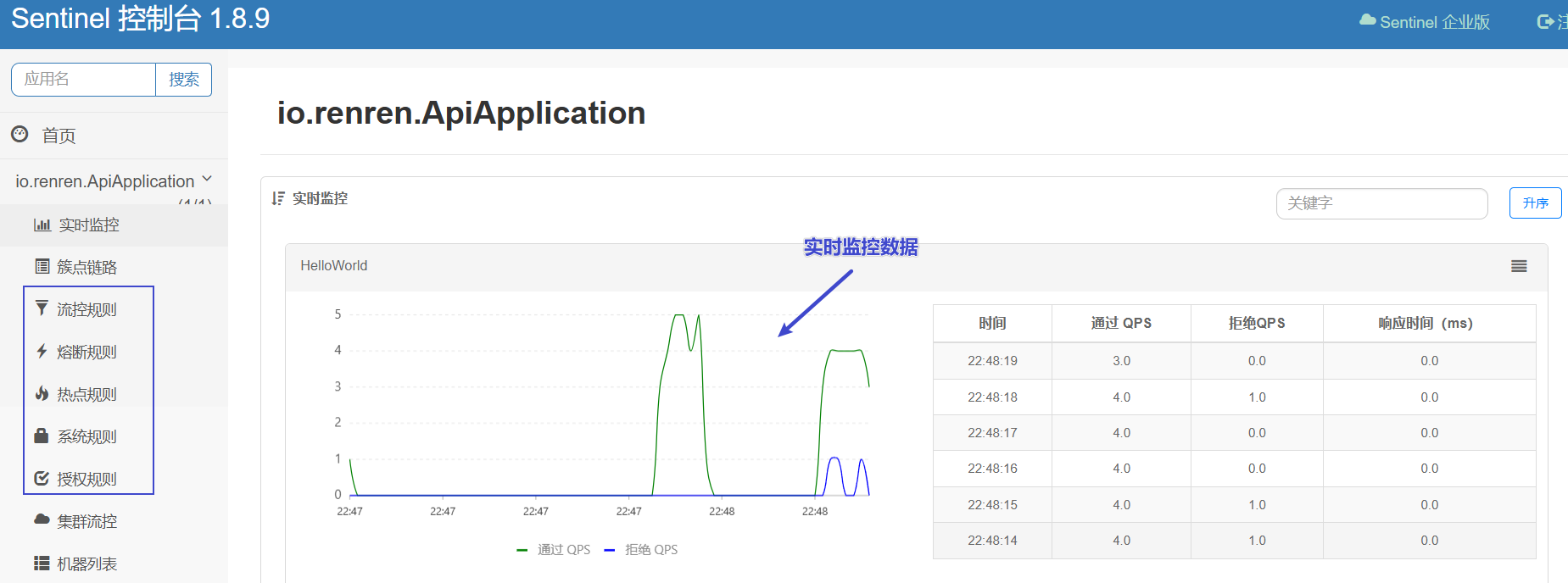
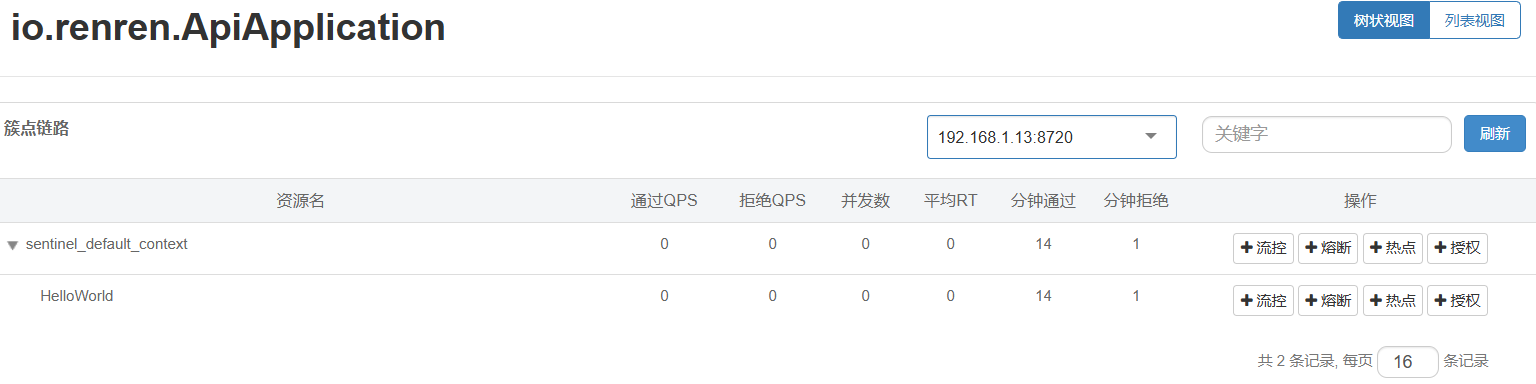

附录
限流常见配置参数速查表
| 概念 | 说明 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| QPS | 每秒查询率 | 大促抢购、防止刷单 |
| 线程数 | 并发占用线程数 | 保护慢接口不占用所有线程池 |
| 快速失败 | 超过阈值直接报错 | 默认策略,简单粗暴 |
| Warm Up | 预热模式,阈值缓慢升高 | 系统刚启动,防止瞬间高流量压垮 |
| 排队等待 | 请求匀速通过,处理不急的请求 | 订单创建等需要削峰填谷的场景 |
Token Server Cluster 部署方式对比
| 特性 | 嵌入模式 (Embedded) | 独立模式 (Alone) |
|---|---|---|
| 部署成本 | 低 (利用现有资源) | 高 (需要独立机器) |
| 隔离性 | 差 (与业务争抢资源) | 好 (完全隔离) |
| 适用场景 | 中小规模集群、对成本敏感 | 超大规模集群、核心中间件、全局限流 |
| 容灾能力 | 依赖应用集群的稳定性 | 强 (通常有主从热备) |
| 运维难度 | 简单 | 较复杂 (需维护 Server 集群) |
与springboot及springcloud版本对应关系
| Spring Boot 版本 | 对应的 Spring Cloud Alibaba (SCA) 版本 | 对应的 Sentinel 版本 | 状态 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.3.x | 2.2.x.RELEASE | 1.7.x / 1.8.0 | 旧版,已不再主推 |
| 2.4.x, 2.5.x, 2.6.x, 2.7.x | 2021.x (如 2021.0.5.0) | 1.8.5 / 1.8.6 | 目前最主流的生产环境组合 |
| 3.0.x, 3.1.x | 2022.0.0.0 (or 2022.0.0.0-RC2) | 1.8.6 (有限支持) | 注意:原生 Web 适配器不支持,需用 Gateway 或特定适配 |
- Sentinel(通过 Spring Cloud Alibaba)实际上支持 Spring Boot 2.x 的全系版本
- Spring Boot 3.0 的变化 :Spring Boot 3.0 强制要求 Java 17+,并且将底层的
javax.servlet(Java EE) 迁移为了jakarta.servlet(Jakarta EE)。 - Sentinel 对 Spring Boot 的支持在 3.0 上遇到了"断层",这才是目前版本选择的核心痛点
- Sentinel 的现状 :
- Sentinel-core / sentinel-web-servlet :目前的主流稳定版本(如 1.8.x)底层依然使用的是
javax.servlet.Filter。 - sentinel-spring-webmvc-adapter 目前使用的 springboot 2.5.x版本,servlet.api版本是3.1.0
- 不兼容 :这意味着,如果你直接使用原生的
sentinel-web-servlet依赖,它是无法运行在 Spring Boot 3.0 环境下的,会报ClassNotFoundException(找不到 javax 包)
- Sentinel-core / sentinel-web-servlet :目前的主流稳定版本(如 1.8.x)底层依然使用的是