目录
- 前言
- [1 序列式容器和关联式容器](#1 序列式容器和关联式容器)
- [2 红黑树的修改](#2 红黑树的修改)
-
- [2.1 模板参数](#2.1 模板参数)
- [2.2 迭代器的实现](#2.2 迭代器的实现)
- [2.3 Insert 的修改](#2.3 Insert 的修改)
- [2.4 加入 Begin,End](#2.4 加入 Begin,End)
- [2.4 修改后的红黑树](#2.4 修改后的红黑树)
- [3 set 的模拟实现](#3 set 的模拟实现)
-
- [3.1 Begin,End,Insert](#3.1 Begin,End,Insert)
- [3.2 KeyofValue](#3.2 KeyofValue)
- [3.3 对值的限制](#3.3 对值的限制)
- [3.4 Set 的代码](#3.4 Set 的代码)
- [4 map 的模拟实现](#4 map 的模拟实现)
-
- [4.1 Begin,End,Insert](#4.1 Begin,End,Insert)
- [4.2 KeyofValue](#4.2 KeyofValue)
- [4.3 [] 重载](#4.3 [] 重载)
- [4.5 对值的限制](#4.5 对值的限制)
- [4.6 Map 的代码](#4.6 Map 的代码)
前言
STL 中,Map 和 Set 的底层实现使用到了红黑树,因此要模拟实现 Map 和 Set 的话,还需要模拟实现红黑树,关于红黑树的底层原理,可以参考这篇文章:
1 序列式容器和关联式容器
序列式容器 指逻辑结构 为线性结构 的容器,它内部存储的元素之间没有较强的关联性,互相进行交换以后不会破坏存储结构。在 STL 中,array(静态数组),vector(顺序表),forward_list(单链表),list(双向带头循环链表),deque(vector 和 list 的缝合) 都属于序列式容器
关联式容器 指逻辑结构 为非线性结构 的容器,它内部存储的元素之间有较强的关系,互相交换以后就会破坏原来的存储结构。在 STL 中,map/set(红黑树),unordered_map/unordered_set(哈希表)都属于关联式容器
2 红黑树的修改
2.1 模板参数
为了在 map 和 set 中封装红黑树,红黑树的模板参数中需要给定 K 和 T,其中 K 指用来比较的值的类型,也就是 Key 的类型,T 则指真正存储在结点中数据的类型,对于 set 来说,可能是 char,int 等类型,对于 map 来说则是 键值对 pair
在做值的比较时,set 存储的是值,所以 set 中的值可以直接用来比较 ,但是 map 存储的是键值对,需要取出 Key 对应的 Value 才可以进行比较,因此还需要给出模板参数 KeyofValue,它的作用是取出用作比较的值,是一个仿函数
cpp
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
{}
T _kv;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
COLOR _color;
};
//K -- 用于比较的值的类型
//T -- 真正存储的值的类型
//KeyofValue -- 取出用作比较的值的仿函数类型
template<class K, class T, class KeyofValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
//...
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};2.2 迭代器的实现
红黑树的迭代器是一个封装了指针的类,表面上是迭代器在进行着遍历,背地里实际上是指针在做遍历,在实现的时候,考虑到普通对象和 const 对象都需要进行调用,所以需要分普通迭代器 和 const 迭代器 ,为此迭代器类需要模板参数 Ref 和 Ptr,当普通对象调用时,Ref 就是普通的引用类型,Ptr 就是普通的指针类型,代表可以对结点中的 Value 进行修改,就是普通迭代器 ,当 const 对象调用时,Ref 就是 const 引用类型,Ptr 就是 const 指针,代表无法对结点中的 Value 进行修改,就是 const 迭代器
cpp
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class Iterator
{
typedef Iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; //代表迭代器自身
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
Iterator(Node* node, Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return (*_node)._kv;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
private:
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyofValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
KeyofValue kov;
public:
typedef Iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; //普通迭代器
typedef Iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; //const迭代器
//...
private:
//...
Node* _root = nullptr;
};迭代器的 ++ 操作在实现时的思路为:
由于红黑树也是一种二叉搜索树(BST),所以中序遍历序列是有序的,因此按照中序遍历来设计,中序遍历为左子树 -- 根节点 -- 右子树的顺序
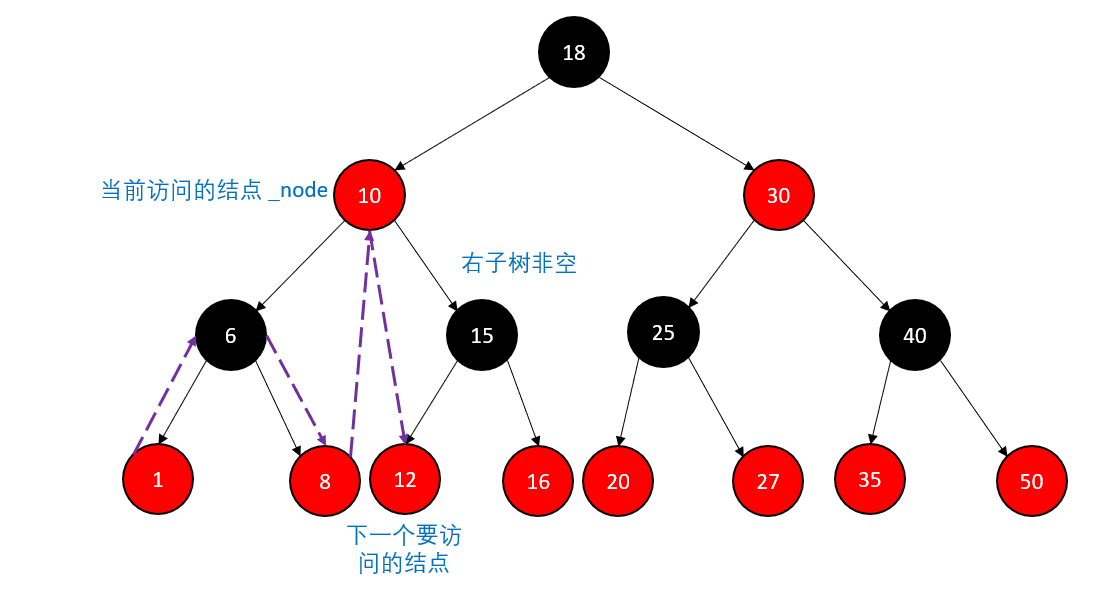
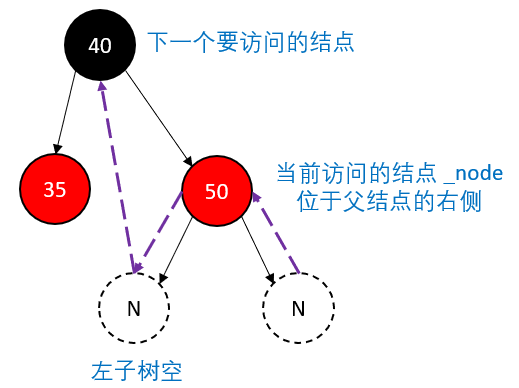
假设当前访问了根节点,那么接下来要访问的结点就是右子树了,对于右子树主要有两种情况:
右子树不为空,则接下来要访问的是右子树中最小的结点,也就是最左下角的结点
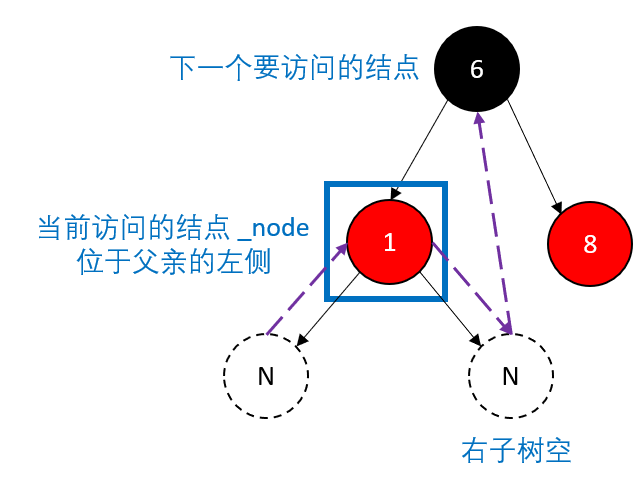
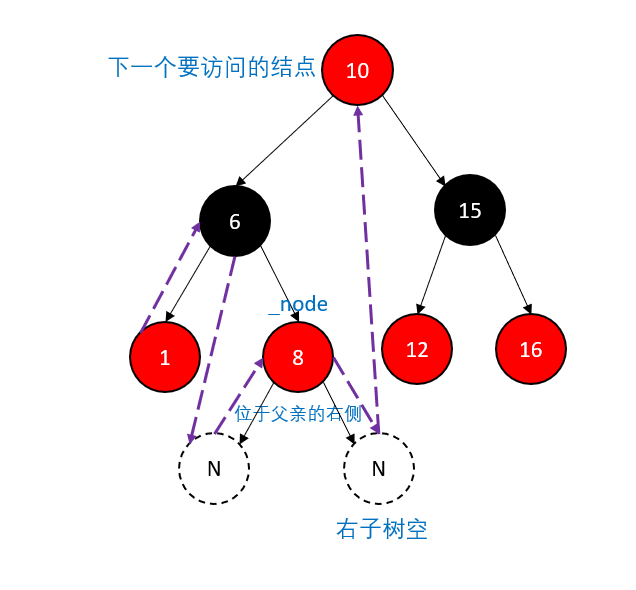
右子树为空,就说明当前这棵树访问完毕,则接下来访问的结点根据当前这棵树的位置有所不同:
如果当前这棵树是父结点的左孩子,那么根据 左 -- 根 -- 右,接下来要访问父结点
如果当前这棵树是父结点的右孩子,那么说明外层那一棵树访问完毕,接下来要访问祖父结点
迭代器的 - - 操作在实现时的思路为:
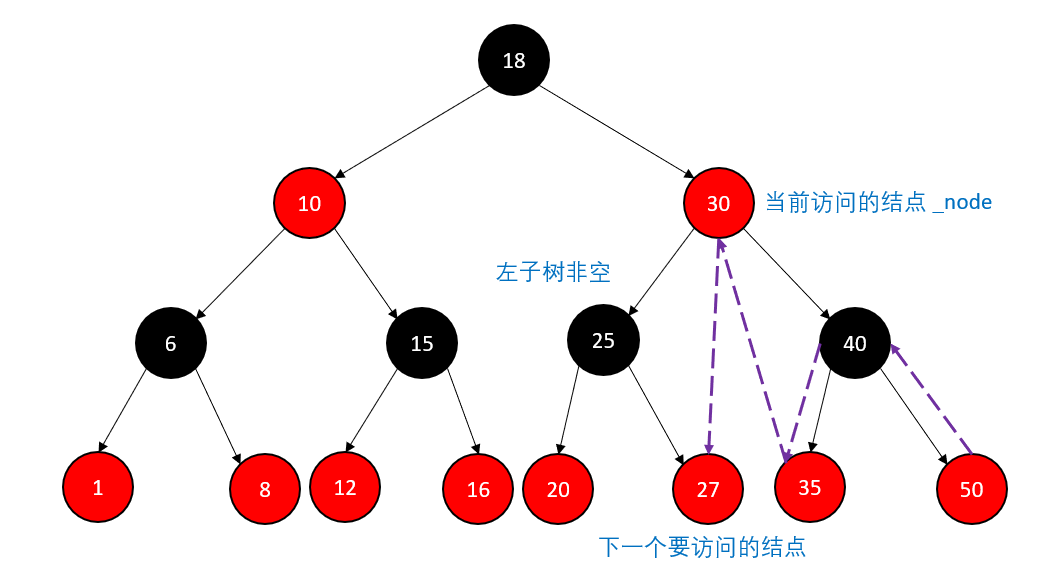
由于 -- 时进行反向遍历,因此需要按照反向的中序遍历设计,右子树 -- 根节点 -- 左子树
由于遍历红黑树到最后时,迭代器会指向空,所以 -- 在实现时,需要判断一下指针指向的是否为空结点
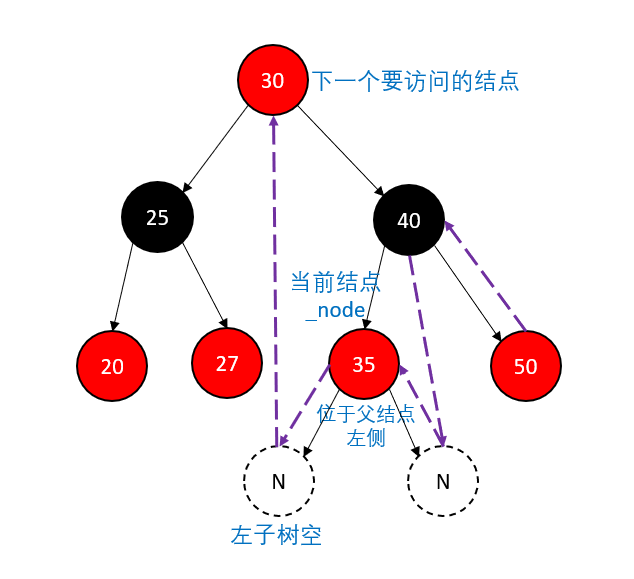
如果是空结点则需要先找到右子树中最大的结点,它是存在的最后一个结点,如果不是空结点,则假设当前访问的是根结点,接下来就要访问左子树了,对于左子树有两种情况:
左子树不为空,接下来要访问的是左子树中最大的结点,也就是左子树中最右下角的结点
左子树为空,就说明当前这棵树访问完了,接下来就要根据当前这棵树的位置来判断要访问的结点:当前这棵树是父结点的左孩子,则说明外层这棵树已经访问完,接下来要访问祖父结点
当前这棵树是父结点的右孩子,按照 右 -- 根 -- 左,接下来要访问根节点(父结点)
cpp
Self& operator++()
{
//左 根 右
if (_node->_right) //右子树存在,访问右子树最小结点
{
Node* cur = _node->_right;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
_node = cur;
}
else //右子树不存在,当前树访问完
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right) //当前的是右子树,要去访问祖先,是左子树访问父结点
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
//右 根 左
if (!_node) //End为空,所以需要先找到最右下角结点
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else if (_node->_left) //左子树不为空,要访问左子树最大节点
{
Node* cur = _node->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else //左子树为空
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}2.3 Insert 的修改
由于库中的 map 和 set 的 Insert 返回了带有迭代器和布尔值的键值对,所以在这里要将红黑树的 Insert 的返回值修改为一个键值对,键值对中,布尔值说明插入的值是否重复,迭代器为指向保存了要插入的值的结点的迭代器
cpp
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& kv)
{
//空树,插入为根节点,黑色
if (!_root)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_color = BLACK;
return { { _root, _root }, true };
}
//非空树
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
//查询插入的位置
while (cur)
{
if (kov(cur->_kv) < kov(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kov(cur->_kv) > kov(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return { { cur, _root }, false };
}
}
//插入结点
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_color = RED;
if (kov(cur->_kv) < kov(parent->_kv))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else if (kov(cur->_kv) > kov(parent->_kv))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
Node* newNode = cur;
while (parent && parent->_color == RED)
{
Node* grand = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = nullptr;
if (parent == grand->_left)
{
uncle = grand->_right;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right)
{
uncle = grand->_left;
}
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) //叔为红,叔父爷换色
{
grand->_color = RED;
parent->_color = BLACK;
uncle->_color = BLACK;
//继续向上更新
cur = grand;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else if (!uncle || uncle->_color == BLACK) //叔不存在或为黑
{
if (parent == grand->_left && cur == parent->_left) //parent为grand的左,cur插入在parent的左子树中,右单旋+换色
{
RotateToRight(parent);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right && cur == parent->_right) //parent为grand的右,cur插入在parent的右子树中,左单旋+换色
{
RotateToLeft(parent);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_left && cur == parent->_right) //左右双旋 + 换色
{
RotateToLeft(parent);
RotateToRight(grand);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right && cur == parent->_left) //右左双旋 + 换色
{
RotateToRight(parent);
RotateToLeft(grand);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
break;
}
}
_root->_color = BLACK;
return { { newNode, _root }, true };
}2.4 加入 Begin,End
Begin 中要返回的就是中序遍历的第一个结点,而中序遍历的第一个结点位于整棵树的最左下角,因此只需要使用指针一直向左下角遍历,直到左子树为空即可
cpp
iterator Begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return { cur, _root };
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return { cur, _root };
}End 中要返回的是中序遍历的最后一个结点的下一个结点,而这个结点就是空结点,因此直接返回空指针即可
cpp
iterator End()
{
return { nullptr, _root };
}
const_iterator End() const
{
return { nullptr, _root };
}2.4 修改后的红黑树
cpp
enum COLOR
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
{}
T _kv;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
COLOR _color;
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class Iterator
{
typedef Iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; //代表迭代器自身
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
Iterator(Node* node, Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return (*_node)._kv;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
Self& operator++()
{
//左 根 右
if (_node->_right) //右子树存在,访问右子树最小结点
{
Node* cur = _node->_right;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
_node = cur;
}
else //右子树不存在,当前树访问完
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right) //当前的是右子树,要去访问祖先,是左子树访问父结点
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
//右 根 左
if (!_node) //End为空,所以需要先找到最右下角结点
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else if (_node->_left) //左子树不为空,要访问左子树最大节点
{
Node* cur = _node->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else //左子树为空
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
private:
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyofValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
KeyofValue kov;
public:
typedef Iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; //普通迭代器
typedef Iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; //const迭代器
iterator Begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return { cur, _root };
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return { cur, _root };
}
iterator End()
{
return { nullptr, _root };
}
const_iterator End() const
{
return { nullptr, _root };
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& kv)
{
//空树,插入为根节点,黑色
if (!_root)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_color = BLACK;
return { { _root, _root }, true };
}
//非空树
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
//查询插入的位置
while (cur)
{
if (kov(cur->_kv) < kov(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kov(cur->_kv) > kov(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return { { cur, _root }, false };
}
}
//插入结点
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_color = RED;
if (kov(cur->_kv) < kov(parent->_kv))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else if (kov(cur->_kv) > kov(parent->_kv))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
Node* newNode = cur;
while (parent && parent->_color == RED)
{
Node* grand = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = nullptr;
if (parent == grand->_left)
{
uncle = grand->_right;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right)
{
uncle = grand->_left;
}
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) //叔为红,叔父爷换色
{
grand->_color = RED;
parent->_color = BLACK;
uncle->_color = BLACK;
//继续向上更新
cur = grand;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else if (!uncle || uncle->_color == BLACK) //叔不存在或为黑
{
if (parent == grand->_left && cur == parent->_left) //parent为grand的左,cur插入在parent的左子树中,右单旋+换色
{
RotateToRight(parent);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right && cur == parent->_right) //parent为grand的右,cur插入在parent的右子树中,左单旋+换色
{
RotateToLeft(parent);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_left && cur == parent->_right) //左右双旋 + 换色
{
RotateToLeft(parent);
RotateToRight(grand);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
else if (parent == grand->_right && cur == parent->_left) //右左双旋 + 换色
{
RotateToRight(parent);
RotateToLeft(grand);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grand->_color = RED;
}
break;
}
}
_root->_color = BLACK;
return { { newNode, _root }, true };
}
private:
//右单旋
void RotateToRight(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* grandParent = parent->_parent;
//更新子树
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
if (parent == _root) //父结点是根节点,更新根节点
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else //如果父结点不是根节点,那么要更新组父结点
{
subL->_parent = grandParent;
if (grandParent->_left == parent)
{
grandParent->_left = subL;
}
else if (grandParent->_right == parent)
{
grandParent->_right = subL;
}
}
}
//左单旋
void RotateToLeft(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* grandParent = parent->_parent;
//更新子树
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
if (parent == _root) //父结点是根节点,更新根节点
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else //如果父结点不是根节点,那么要更新组父结点
{
subR->_parent = grandParent;
if (grandParent->_left == parent)
{
grandParent->_left = subR;
}
else if (grandParent->_right == parent)
{
grandParent->_right = subR;
}
}
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};3 set 的模拟实现
set 通过封装红黑树的方式来进行实现
3.1 Begin,End,Insert
由于红黑树中已经实现了 Begin,End,Insert 这些函数,所以在实现 Set 时直接复用即可
cpp
iterator Begin()
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
const_iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& key)
{
return _tree.Insert(key);
}3.2 KeyofValue
对于 KeyofValue 仿函数,由于 set 中存储的值可以直接拿来作比较,所以在 KeyofValue 中直接返回传入的值即可
cpp
class KeyofValue
{
K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};3.3 对值的限制
由于 set 不支持对存储的值进行修改,一旦进行修改,则结构就会被破坏,所以要给 set 中封装的红黑树的第二个模板参数加上 const
cpp
RBTree<K, const K, KeyofValue> _tree;3.4 Set 的代码
cpp
template<class K>
class set
{
class KeyofValue
{
K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, KeyofValue>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, KeyofValue>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator Begin()
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
const_iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& key)
{
return _tree.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K, KeyofValue> _tree;
};4 map 的模拟实现
map 通过封装红黑树的方式来进行实现
4.1 Begin,End,Insert
map 在实现 End,Begin,Insert 时,直接复用红黑树的即可
cpp
iterator Begin()
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
const_iterator End() const
{
return _tree.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _tree.Insert(kv);
}4.2 KeyofValue
对于 KeyofValue 仿函数,由于 map 存储的是键值对 pair,所以要取出它的 key 来进行比较,KeyofValue 中需要返回 pair 中的 key 值
cpp
class KeyofValue
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};4.3 [] 重载
库中 map 的 [] 重载既可以根据给入的 Key 来进行插入,也可以进行更新、查找,为了实现这个功能,需要复用红黑树的 Insert 函数,在外部传入 Key 后,通过 Insert 先来做查找,如果找到了值与 Key 相同的结点,就意味着不需要进行插入,直接返回 pair,如果没有找到则需要进行插入,插入完后仍然返回一个 pair,pair 内是该结点的迭代器和一个布尔类型的值,布尔值为 false 代表插入失败,已经有相同的值了,为 true 则表示插入成功,接下来再通过 pair 内的迭代器,取出结点中的 Value 并返回它的引用,这样就可以做到对 Value 进行修改
cpp
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert({ key, V() });
//ret.first.operator->()->second
return ret.first->second;
}4.5 对值的限制
在 map 中,pair 内存储了 Key/Value 的键值对,其中 Key 是不允许修改的,修改后就会破坏结构,所以需要给 map 中封装的红黑树的第二个模板参数 pair 内的 Key 加上 const
4.6 Map 的代码
cpp
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
class KeyofValue
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyofValue>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyofValue>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator Begin()
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
return _tree.Begin();
}
iterator End()
{
return _tree.End();
}
const_iterator End() const
{
return _tree.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _tree.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert({ key, V() });
//ret.first.operator->()
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyofValue> _tree;
};