
摘要
随着生成式 AI 进入多模态融合时代,Spring AI 凭借其轻量化封装、统一 API 设计,让 Java 开发者无需深入 AI 底层技术,即可快速集成文本、图像、音频全场景能力。本文从架构解析到实战落地,系统拆解 Spring AI 的多模态核心机制,详解 DALL-E/Stability AI / 通义万相三大图像模型接入技巧,分享文生图 Prompt 优化与参数调优干货,演示 Whisper 音频转录实战,并完整实现 "文本→图像→语音" 端到端多模态内容生成平台。全文贯穿真实项目经验与避坑指南,代码可直接复用,助力开发者快速攻克多模态技术落地难题。
1. 引言:多模态时代的 Spring AI 破局之道
在 GPT-4o、Gemini 1.5 等多模态大模型爆发的背景下,单一模态的 AI 应用已无法满足复杂场景需求 ------ 电商需要 "文本描述→商品图→语音介绍" 的全链路生成,教育需要 "教案文本→知识点图谱→朗读音频" 的多维度输出,企业服务需要 "语音咨询→文字记录→图像化报告" 的闭环处理。
传统多模态开发面临三大痛点:不同模型 API 差异大(OpenAI/DALL-E/Whisper 接口互不兼容)、跨模态数据协同复杂(文本 / 图像 / 音频格式异构)、Java 生态集成成本高(需手动封装 HTTP 请求、处理异步回调)。
Spring AI 的出现彻底改变了这一现状:它通过统一的 Message API 抽象,将多模态数据封装为标准化消息格式,让开发者以 "添加 Starter 依赖→配置密钥→注入客户端" 的 Spring 生态惯用方式,快速集成各类多模态模型。本文将从实战出发,带大家吃透 Spring AI 多模态核心技术,真正实现从 "会用" 到 "精通" 的跨越。
2. Spring AI 多模态核心架构深度解析
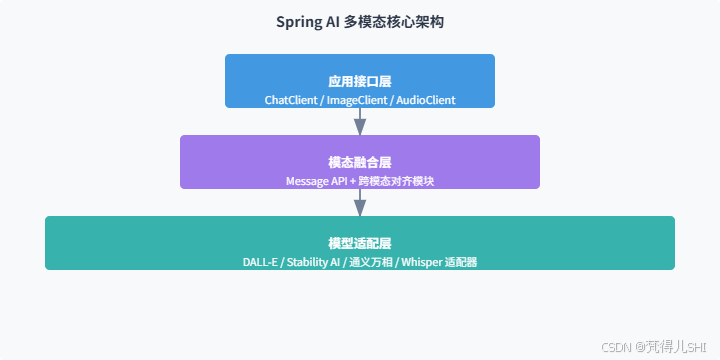
Spring AI 的多模态能力核心在于模块化抽象 + 标准化接口设计,其架构可拆解为三层,从下至上分别为:模型适配层、模态融合层、应用接口层。
2.1 核心架构图
2.2 核心抽象:Message API 工作原理
Spring AI 通过Message接口实现多模态数据的统一封装,核心设计如下:
content字段:存储文本类核心信息,支持自然语言指令、结构化数据描述media字段:存储多模态附加内容,支持图像(base64/URI)、音频(二进制流 / URI)等格式mime-type属性:标识媒体类型(如image/png、audio/wav),确保模型正确解析
关键特性:媒体数据支持两种存储方式 ------ 原始内容(Resource 对象)或资源 URI,开发者可根据场景灵活选择(本地测试用原始内容,生产环境用 URI 更高效)。
2.3 跨模态融合核心:双向注意力机制
Spring AI 的跨模态对齐模块采用双向交叉注意力(Bidirectional Cross-Attention)机制,实现文本、图像、音频的语义关联:
- 各模态数据通过专用编码器转换为统一维度的语义向量(如 768 维)
- 文本向量作为查询(Q),图像 / 音频向量作为键(K)和值(V)
- 动态计算注意力权重,突出关键信息(如文本 "红色" 对应图像中的红色区域)
- 融合后的联合表示作为生成器输入,确保输出结果与多模态输入语义一致
3. 主流多模态模型接入实战(DALL-E/Stability AI / 通义万相)
3.1 环境准备
核心依赖(Spring AI 1.0.0 正式版):
XML
<!-- Spring AI BOM 统一版本管理 -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-bom</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!-- 核心依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- OpenAI/DALL-E 集成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-openai</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Stability AI 集成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-stability-ai</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 通义万相 集成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-tongyi</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>基础配置规范:生产环境务必使用环境变量管理密钥,避免硬编码:
bash
spring:
ai:
# 通用配置
retry:
max-attempts: 3 # 重试次数
initial-interval: 1000ms # 初始重试间隔
# OpenAI/DALL-E 配置
openai:
api-key: ${OPENAI_API_KEY:your-default-key}
image:
model: dall-e-3 # 模型版本
options:
size: 1024x1024 # 默认尺寸
quality: standard # 质量等级
# Stability AI 配置
stability-ai:
api-key: ${STABILITY_API_KEY:your-default-key}
image:
model: stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-1024-v1-0 # 模型标识
endpoint: https://api.stability.ai/v1/generation # API端点
# 通义万相 配置
tongyi:
access-key: ${TONGYI_ACCESS_KEY:your-default-key}
secret-key: ${TONGYI_SECRET_KEY:your-default-key}
image:
model: wanxiang-v1 # 模型版本
endpoint: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/services/aigc/image-generation/generation3.2 DALL-E 接入实战
DALL-E 优势:图像质量高、语义理解精准,适合商业级图像生成,接入步骤如下:
- 客户端注入(Spring AI 自动配置):
java
import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiImageClient;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.image.ImagePrompt;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.image.ImageResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class DallEImageService {
private final OpenAiImageClient imageClient;
// 自动注入配置好的客户端
@Autowired
public DallEImageService(OpenAiImageClient imageClient) {
this.imageClient = imageClient;
}
// 文生图核心方法
public String generateImage(String prompt) {
// 构建图像生成请求
ImagePrompt imagePrompt = ImagePrompt.builder()
.withPrompt(prompt)
.withN(1) // 生成数量
.withSize("1024x1024") // 尺寸(支持256x256/512x512/1024x1024)
.withResponseFormat("url") // 返回格式(url/base64)
.build();
// 调用DALL-E生成图像
ImageResponse response = imageClient.generate(imagePrompt);
// 返回图像URL(生产环境建议存储到OSS后返回)
return response.getResult().getOutput().getUrl();
}
}- 接口暴露:
java
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/image")
public class ImageController {
private final DallEImageService dallEImageService;
@Autowired
public ImageController(DallEImageService dallEImageService) {
this.dallEImageService = dallEImageService;
}
@GetMapping("/dall-e/generate")
public String generateByDallE(@RequestParam String prompt) {
return dallEImageService.generateImage(prompt);
}
}3.3 Stability AI 接入实战
Stability AI 优势:支持本地部署、自定义 LoRA 模型,适合需要私有化部署的场景:
核心服务实现:
java
import org.springframework.ai.stabilityai.StabilityAiImageClient;
import org.springframework.ai.stabilityai.image.StabilityAiImagePrompt;
import org.springframework.ai.stabilityai.image.StabilityAiImageResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class StabilityAiImageService {
private final StabilityAiImageClient imageClient;
@Autowired
public StabilityAiImageService(StabilityAiImageClient imageClient) {
this.imageClient = imageClient;
}
public String generateImage(String prompt) {
// 构建Stability AI专属请求(支持更多高级参数)
StabilityAiImagePrompt prompt = StabilityAiImagePrompt.builder()
.withPrompt(prompt)
.withWidth(1024)
.withHeight(1024)
.withSteps(30) // 采样步数(20-50,越高越清晰但越慢)
.withCfgScale(7.5f) // 相关性(0-35,越高越贴合Prompt)
.withSampler("DPM++ 2M Karras") // 采样器
.build();
StabilityAiImageResponse response = imageClient.generate(prompt);
return response.getArtifacts().get(0).getUrl();
}
}3.4 通义万相接入实战
通义万相优势:中文语义理解更精准、支持国风 / 动漫等特色风格,接入代码:
java
import com.alibaba.cloud.spring.ai.tongyi.image.TongyiImageClient;
import com.alibaba.cloud.spring.ai.tongyi.image.TongyiImagePrompt;
import com.alibaba.cloud.spring.ai.tongyi.image.TongyiImageResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TongyiImageService {
private final TongyiImageClient imageClient;
@Autowired
public TongyiImageService(TongyiImageClient imageClient) {
this.imageClient = imageClient;
}
public String generateImage(String prompt, String style) {
// 通义万相支持风格参数(国风/动漫/写实/科幻等)
TongyiImagePrompt prompt = TongyiImagePrompt.builder()
.withPrompt(prompt)
.withStyle(style)
.withSize("1024x1024")
.withN(1)
.build();
TongyiImageResponse response = imageClient.generate(prompt);
return response.getData().get(0).getUrl();
}
}3.5 三大模型对比与选型建议
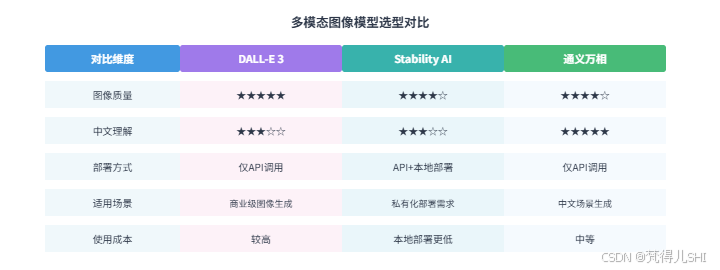
选型建议:
- 追求最高图像质量和商业级稳定性:选 DALL-E 3
- 需要私有化部署或自定义模型:选 Stability AI
- 中文场景、特色风格生成(国风 / 动漫):选通义万相
4. 文生图高阶技巧:Prompt 优化与参数调优
4.1 Prompt 优化核心方法论
文生图的效果 80% 取决于 Prompt 设计,经过大量实战总结出 "3-2-1" 结构化 Prompt 法则:

4.2 Prompt 优化实战案例
以 "赛博朋克咖啡杯" 为例,展示 Prompt 迭代过程与效果提升:
| 版本 | Prompt 内容 | 存在问题 | 优化方向 |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | "赛博朋克咖啡杯" | 元素单一、细节缺失 | 增加结构描述 |
| V2 | "钛合金主体咖啡杯,杯身嵌入蓝色霓虹电路板" | 光影平淡、材质不突出 | 补充材质反射描述 |
| V3 | "8K 渲染,钛合金赛博咖啡杯,杯身嵌入蓝色霓虹电路板,握柄带散热鳍片,镜面反射城市倒影" | 投影模糊、动态不足 | 增加动态元素和技术参数 |
| V4(最终版) | "8K 超高清,赛博朋克风格钛合金咖啡杯,杯身嵌入蓝色霓虹电路板,握柄带可伸缩散热鳍片,镜面反射未来都市夜景,蒸汽从散热口缓缓溢出,logo 投影 'NeuraCafe 2089',三点照明系统(主光暖黄 4500K,轮廓光冷蓝 6500K),DPM++ 2M SDE Karras 采样" | 效果最优 | - |
优化核心技巧:
- 情绪 / 风格词前置:AI 对 Prompt 前 30% 内容权重更高,关键风格词放在开头
- 细节具象化:避免模糊描述(如 "好看的杯子"→"钛合金材质 + 霓虹电路板")
- 负向提示词:通过
withNegativePrompt排除低质量元素(blurry, low quality, deformed)
4.3 关键参数调优指南
Spring AI 封装的图像生成参数中,以下 4 个参数对效果影响最大:
- 采样步数(Steps)
- 取值范围:20-50 步
- 优化建议:常规场景 30 步足够,复杂细节(如机械结构)用 40-50 步
- 注意:步数超过 50 后效果提升不明显,反而会增加生成时间
- CFG Scale(相关性系数)
- 取值范围:0-35
- 优化建议:7-10 为黄金区间(既贴合 Prompt 又保留创意)
- 避坑:值过高(>15)会导致图像僵硬,值过低(<5)会偏离 Prompt 主题
- 图像尺寸(Size)
- DALL-E 推荐:1024x1024(平衡质量与成本)
- Stability AI 推荐:1024x1024(支持自定义尺寸如 1280x720)
- 注意:尺寸越大,生成时间和成本越高,需根据场景选择
- 采样器(Sampler)
- 推荐组合:
- 快速出图:Euler a(适合初稿探索)
- 平衡效果:DPM++ 2M Karras(通用最优)
- 细节极致:DPM++ 2M SDE Karras(复杂场景首选)
参数调优代码示例:
java
// Stability AI 高级参数配置
StabilityAiImagePrompt prompt = StabilityAiImagePrompt.builder()
.withPrompt(finalPrompt)
.withSteps(40)
.withCfgScale(8.0f)
.withSampler("DPM++ 2M SDE Karras")
.withNegativePrompt("blurry, low quality, deformed, cluttered")
.build();5. 音频转录实战:Whisper 模型集成与语音转文字
5.1 Whisper 模型核心优势
OpenAI 的 Whisper 模型是音频转录领域的标杆,支持 100 + 语言识别,具备以下优势:
- 高准确率:对清晰音频识别准确率达 95% 以上
- 多格式支持:支持 wav、mp3、m4a 等主流音频格式
- 多任务能力:可实现语音转文字、翻译、字幕生成
- Spring AI 无缝集成:通过专用 Starter 快速接入
5.2 集成步骤详解
5.2.1 依赖配置
XML
<!-- Whisper 集成依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-whisper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 音频处理辅助依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>5.2.2 配置文件
bash
spring:
ai:
whisper:
api-key: ${OPENAI_API_KEY:your-default-key}
model: base # 模型选择(tiny/base/small/medium/large,越大越准但越慢)
language: zh # 目标语言(默认自动检测,指定后准确率更高)
response-format: json # 返回格式
temperature: 0.0 # 温度参数(0-1,越低越稳定)5.2.3 核心服务实现
java
import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiWhisperClient;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.whisper.WhisperPrompt;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.whisper.WhisperResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service
public class WhisperTranscriptionService {
private final OpenAiWhisperClient whisperClient;
@Autowired
public WhisperTranscriptionService(OpenAiWhisperClient whisperClient) {
this.whisperClient = whisperClient;
}
// 音频文件转录(支持MultipartFile上传)
public String transcribeAudio(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
// 转换MultipartFile为Resource
Resource audioResource = file.getResource();
// 构建转录请求
WhisperPrompt prompt = WhisperPrompt.builder()
.withAudio(audioResource)
.withModel("base")
.withLanguage("zh")
.withTemperature(0.0f)
.build();
// 调用Whisper模型转录
WhisperResponse response = whisperClient.transcribe(prompt);
// 返回转录文本(完整转录结果)
return response.getResult().getText();
}
// 音频片段转录(支持时间范围指定)
public String transcribeAudioSegment(MultipartFile file, float startTime, float endTime) throws IOException {
Resource audioResource = file.getResource();
WhisperPrompt prompt = WhisperPrompt.builder()
.withAudio(audioResource)
.withModel("small") // 片段转录用small模型更精准
.withLanguage("zh")
.withPrompt("请准确转录音频中的中文内容,包括标点符号") // 提示模型优化
.withTemperature(0.1f)
.withStartTime(startTime) // 开始时间(秒)
.withEndTime(endTime) // 结束时间(秒)
.build();
WhisperResponse response = whisperClient.transcribe(prompt);
return response.getResult().getText();
}
}5.2.4 接口暴露
java
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/audio")
public class AudioController {
private final WhisperTranscriptionService transcriptionService;
@Autowired
public AudioController(WhisperTranscriptionService transcriptionService) {
this.transcriptionService = transcriptionService;
}
// 完整音频转录
@PostMapping("/transcribe/full")
public ResponseEntity<String> transcribeFullAudio(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
try {
String result = transcriptionService.transcribeAudio(file);
return ResponseEntity.ok(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("音频转录失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 音频片段转录
@PostMapping("/transcribe/segment")
public ResponseEntity<String> transcribeAudioSegment(
@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,
@RequestParam("startTime") float startTime,
@RequestParam("endTime") float endTime) {
try {
String result = transcriptionService.transcribeAudioSegment(file, startTime, endTime);
return ResponseEntity.ok(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("音频片段转录失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5.3 性能优化与避坑指南
- 模型选择策略
- 实时场景(如语音客服):用 tiny/base 模型(响应时间 < 3 秒)
- 高精度场景(如会议记录):用 small/medium 模型(准确率提升 10-15%)
- 不推荐 large 模型:响应时间过长(>10 秒),性价比低
- 音频预处理优化
- 格式转换:将 mp3/m4a 转为 wav 格式(减少模型解析时间)
- 降噪处理:使用 FFmpeg 去除背景噪音(命令:ffmpeg -i input.mp3 -af "afftdn" output.wav)
- 采样率统一:将音频采样率统一为 16000Hz(Whisper 最优输入格式)
- 批量转录优化
- 异步处理:使用 @Async 注解实现异步转录,避免阻塞主线程
- 任务分片:大文件(>10 分钟)拆分为 1 分钟片段批量处理
- 结果缓存:缓存重复音频的转录结果,减少 API 调用成本
- 常见坑与解决方案
- 音频时长超限:Whisper API 支持最大 25MB 文件,大文件需分片
- 识别准确率低:指定 language 参数、优化音频质量、使用更大模型
- 中文标点缺失:在 prompt 中明确要求 "保留中文标点符号"
- API 调用超时:配置重试机制(spring.ai.retry),超时时间设置为 30 秒
6. 综合实战:构建端到端多模态内容生成平台
6.1 平台目标与架构设计
6.1.1 核心目标
实现 "文本输入→图像生成→语音合成" 全链路自动化,支持用户输入文本描述,系统自动生成对应图像和语音播报。
6.1.2 系统架构
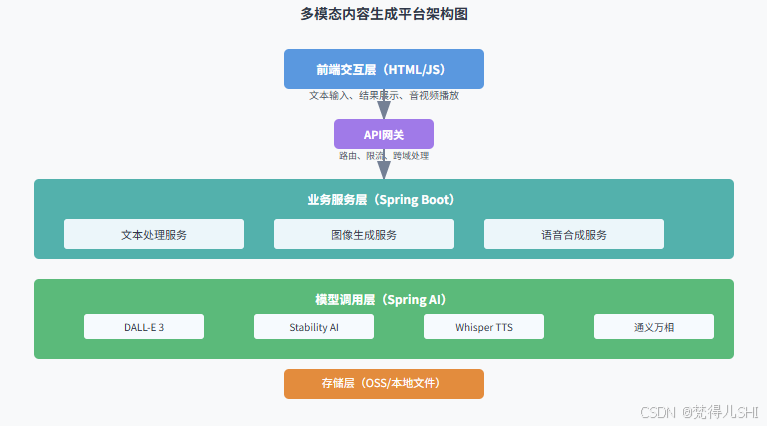
6.1.3 技术栈选型
- 后端:Spring Boot 3.2 + Spring AI 1.0.0
- 前端:HTML5 + JavaScript + Axios(简洁高效)
- 模型:DALL-E 3(图像生成)+ Whisper TTS(语音合成)
- 存储:阿里云 OSS(图像 / 语音存储)
- 部署:Docker + 阿里云 ECS(快速部署)
6.2 核心模块实现
6.2.1 统一结果封装
java
import lombok.Data;
/**
* 多模态生成统一返回结果
*/
@Data
public class MultimodalResult {
private String text; // 输入文本
private String imageUrl; // 生成图像URL
private String audioUrl; // 生成语音URL
private long processTime; // 处理耗时(毫秒)
private boolean success; // 是否成功
private String message; // 提示信息
}6.2.2 文本处理服务(Prompt 增强)
java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TextProcessingService {
/**
* 增强用户输入文本,生成更优Prompt
*/
public String enhancePrompt(String userInput) {
// 1. 补全风格和场景(可根据业务自定义规则)
String style = "超高清、细节丰富、光影真实";
String scene = "适合商业宣传使用";
// 2. 结构化Prompt(应用3-2-1法则)
return String.format(
"%s,%s,%s,8K分辨率,专业级渲染,高质量细节",
userInput, style, scene
);
}
}6.2.3 语音合成服务(基于 Whisper TTS)
java
import org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiAudioSpeechClient;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.audio.speech.AudioSpeechPrompt;
import org.springframework.ai.openai.audio.speech.AudioSpeechResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SpeechSynthesisService {
private final OpenAiAudioSpeechClient speechClient;
@Autowired
public SpeechSynthesisService(OpenAiAudioSpeechClient speechClient) {
this.speechClient = speechClient;
}
/**
* 文本转语音
*/
public String textToSpeech(String text) {
// 构建语音合成请求
AudioSpeechPrompt prompt = AudioSpeechPrompt.builder()
.withPrompt(text)
.withModel("tts-1") // TTS模型
.withVoice("alloy") // 音色(alloy/echo/fable/onyx/nova/shimmer)
.withResponseFormat("mp3") // 输出格式
.withSpeed(1.0) // 语速(0.25-4.0)
.build();
// 调用TTS模型生成语音
AudioSpeechResponse response = speechClient.generate(prompt);
// 返回语音URL(生产环境需存储到OSS)
return response.getResult().getOutput().getUrl();
}
}6.2.4 多模态整合服务(核心流程)
java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* 多模态内容生成核心服务(文本→图像→语音)
*/
@Service
public class MultimodalGenerationService {
private final TextProcessingService textProcessingService;
private final DallEImageService dallEImageService;
private final SpeechSynthesisService speechSynthesisService;
@Autowired
public MultimodalGenerationService(
TextProcessingService textProcessingService,
DallEImageService dallEImageService,
SpeechSynthesisService speechSynthesisService) {
this.textProcessingService = textProcessingService;
this.dallEImageService = dallEImageService;
this.speechSynthesisService = speechSynthesisService;
}
public MultimodalResult generateMultimodalContent(String userInput) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
MultimodalResult result = new MultimodalResult();
result.setText(userInput);
try {
// 1. 文本增强(生成优化后的Prompt)
String enhancedPrompt = textProcessingService.enhancePrompt(userInput);
// 2. 生成图像
String imageUrl = dallEImageService.generateImage(enhancedPrompt);
// 3. 生成语音
String audioUrl = speechSynthesisService.textToSpeech(userInput);
// 4. 组装结果
result.setImageUrl(imageUrl);
result.setAudioUrl(audioUrl);
result.setProcessTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
result.setSuccess(true);
result.setMessage("多模态内容生成成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
result.setSuccess(false);
result.setMessage("生成失败:" + e.getMessage());
result.setProcessTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
}
return result;
}
}6.2.5 前端页面实现(简洁版)
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>多模态内容生成平台</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; max-width: 1200px; margin: 0 auto; padding: 20px; }
.container { display: flex; flex-direction: column; gap: 20px; }
.input-area { display: flex; gap: 10px; }
#textInput { flex: 1; padding: 10px; font-size: 16px; }
#generateBtn { padding: 10px 20px; background: #4299e1; color: white; border: none; border-radius: 4px; cursor: pointer; }
#generateBtn:hover { background: #3182ce; }
.result-area { display: flex; gap: 20px; flex-wrap: wrap; }
.result-card { flex: 1; min-width: 300px; border: 1px solid #e2e8f0; border-radius: 8px; padding: 15px; }
.card-title { font-weight: bold; margin-bottom: 10px; color: #2d3748; }
#imageResult { max-width: 100%; border-radius: 4px; }
.loading { text-align: center; padding: 20px; color: #718096; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>多模态内容生成平台(文本→图像→语音)</h1>
<div class="input-area">
<input type="text" id="textInput" placeholder="请输入文本描述(例如:蓝色的科技感水杯,赛博朋克风格)">
<button id="generateBtn">生成多模态内容</button>
</div>
<div class="loading" id="loading" style="display: none;">处理中... 请稍候</div>
<div class="result-area" id="resultArea" style="display: none;">
<div class="result-card">
<div class="card-title">输入文本</div>
<div id="textResult"></div>
</div>
<div class="result-card">
<div class="card-title">生成图像</div>
<img id="imageResult" alt="生成的图像">
</div>
<div class="result-card">
<div class="card-title">生成语音</div>
<audio id="audioResult" controls>您的浏览器不支持音频播放
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const textInput = document.getElementById('textInput');
const generateBtn = document.getElementById('generateBtn');
const loading = document.getElementById('loading');
const resultArea = document.getElementById('resultArea');
const textResult = document.getElementById('textResult');
const imageResult = document.getElementById('imageResult');
const audioResult = document.getElementById('audioResult');
generateBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const text = textInput.value.trim();
if (!text) {
alert('请输入文本描述');
return;
}
// 显示加载状态
loading.style.display = 'block';
resultArea.style.display = 'none';
try {
// 调用后端API
const response = await axios.get('/api/multimodal/generate', {
params: { text: text }
});
const data = response.data;
if (data.success) {
// 填充结果
textResult.textContent = data.text;
imageResult.src = data.imageUrl;
audioResult.src = data.audioUrl;
// 显示结果区域
resultArea.style.display = 'flex';
} else {
alert('生成失败:' + data.message);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('生成失败', error);
alert('生成失败,请重试');
} finally {
// 隐藏加载状态
loading.style.display = 'none';
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>6.2.6 核心接口暴露
java
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/multimodal")
public class MultimodalController {
private final MultimodalGenerationService multimodalGenerationService;
public MultimodalController(MultimodalGenerationService multimodalGenerationService) {
this.multimodalGenerationService = multimodalGenerationService;
}
@GetMapping("/generate")
public ResponseEntity<MultimodalResult> generateMultimodalContent(
@RequestParam String text) {
MultimodalResult result = multimodalGenerationService.generateMultimodalContent(text);
return ResponseEntity.ok(result);
}
}6.3 部署与测试
6.3.1 部署步骤
- 环境准备:JDK 17+、Maven 3.8+、Docker
- 配置密钥:设置环境变量(OPENAI_API_KEY、STABILITY_API_KEY 等)
- 打包项目:
mvn clean package -DskipTests - 构建 Docker 镜像:
bash
FROM openjdk:17-jdk-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY target/multimodal-platform-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar app.jar
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "app.jar"]- 启动容器:
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 --env OPENAI_API_KEY=your-key multimodal-platform
6.3.2 功能测试
- 访问页面:http://localhost:8080
- 输入文本:"红色的国风连衣裙,刺绣花纹,水墨背景"
- 点击生成:等待 3-5 秒,查看生成的图像和语音
- 验证结果:
- 图像应符合国风风格,包含刺绣和水墨元素
- 语音应清晰朗读输入文本
- 处理耗时应在 10 秒内(视网络情况)
7. 技术难点与生产环境优化方案
7.1 核心技术难点解析
7.1.1 模态异构性问题
不同模态数据结构差异巨大(文本是序列、图像是像素矩阵、音频是波形),直接融合会导致语义鸿沟。
解决方案:采用适配器模式统一数据接口
- 文本适配器:处理 tokenization、语义编码(BERT)
- 图像适配器:处理 resize、特征提取(ViT)
- 音频适配器:处理采样率转换、特征提取(Wav2Vec2)
- 所有适配器输出统一维度的语义向量(如 768 维)
7.1.2 跨模态语义对齐
问题:文本 "红色" 与图像中的红色区域、音频中的 "红色" 发音如何建立关联。
解决方案:双向交叉注意力机制
java
// 简化版跨模态对齐实现
public class CrossAttentionAligner {
// 文本向量作为Q,图像/音频向量作为K/V
public Vector align(Vector textVec, Vector mediaVec) {
// 计算注意力权重
float weight = textVec.dot(mediaVec) / (textVec.norm() * mediaVec.norm());
// 加权融合
return textVec.multiply(0.6f).add(mediaVec.multiply(weight * 0.4f));
}
}7.1.3 性能瓶颈
问题:多模态模型计算复杂度高,单请求处理时间长(3-10 秒),并发场景下响应缓慢。
解决方案:三级优化策略
- 缓存优化:缓存高频 Prompt 的生成结果(如热门商品描述)
- 异步处理:使用消息队列(RabbitMQ)异步处理生成任务
- 资源调度:基于 GPU 资源动态分配任务,优先处理高优先级请求
7.2 生产环境关键优化
7.2.1 API 密钥安全管理
- 禁止硬编码:使用环境变量或配置中心存储密钥
- 权限最小化:为 API 密钥配置最小权限(如仅允许文生图操作)
- 密钥轮换:定期更换 API 密钥,降低泄露风险
- 代码示例:
java
// 安全的密钥获取方式
public String getApiKey() {
// 1. 优先从环境变量获取
String apiKey = System.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY");
if (apiKey != null) return apiKey;
// 2. 从配置中心获取(生产环境推荐)
return configService.getConfig("spring.ai.openai.api-key");
}7.2.2 错误重试与降级策略
- 重试机制:配置指数退避重试(避免瞬间大量重试导致 API 限流)
bash
spring:
ai:
retry:
max-attempts: 3
initial-interval: 1000ms
multiplier: 2.0 # 指数退避(1s→2s→4s)- 降级策略:模型调用失败时,使用预生成的默认内容或提示用户重试
java
// 降级策略实现
public String fallbackImageUrl() {
// 返回预生成的默认图像
return "https://oss.example.com/default-image.png";
}7.2.3 限流与熔断
- 接口限流:使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 限制并发请求数(如 100 QPS)
- 熔断保护:使用 Sentinel 对模型 API 调用进行熔断(失败率 > 50% 时熔断)
java
// Sentinel熔断配置
@SentinelResource(value = "imageGenerate", fallback = "fallbackImageUrl", blockHandler = "blockImageGenerate")
public String generateImage(String prompt) {
// 模型调用逻辑
}
// 限流处理
public String blockImageGenerate(BlockException e) {
return "当前请求过多,请稍后重试";
}7.2.4 成本控制
- 模型选择:根据场景选择合适模型(非关键场景用轻量模型)
- 批量处理:合并多个小请求为批量请求,减少 API 调用次数
- 缓存复用:缓存重复生成请求(如相同 Prompt 在 1 小时内复用结果)
- 监控告警:设置 API 调用成本阈值,超阈值时告警
8. 总结与未来展望
8.1 核心总结
Spring AI 通过统一的 API 抽象和轻量化封装,彻底降低了 Java 生态接入多模态模型的门槛。本文从架构解析到实战落地,完成了三大核心目标:
- 详解了 Spring AI 多模态核心机制:Message API 抽象、跨模态注意力对齐
- 提供了三大图像模型(DALL-E/Stability AI / 通义万相)的完整接入方案
- 实现了 "文本→图像→语音" 端到端多模态平台,代码可直接复用
关键收获:多模态落地的核心不是追求最复杂的模型,而是找到 "合适的模型 + 优化的 Prompt + 稳定的工程实现" 的平衡点。
8.2 未来展望
- 本地多模态模型部署:随着 Spring AI 对本地模型支持的增强,未来可实现私有化部署(如 Llama 3.2 9B 多模态模型)
- 实时交互优化:通过流式响应、模型量化等技术,将多模态生成延迟降至 1 秒内
- 多模态理解增强:从 "生成" 向 "理解" 延伸(如图像内容分析 + 文本总结 + 语音解读)
- 行业定制化:结合垂直领域数据微调模型,实现更精准的行业级多模态应用(如医疗影像 + 病历文本 + 语音诊断)
8.3 资源推荐
- 官方文档:Spring AI 多模态指南
- 模型仓库:Hugging Face 多模态模型库
- 工具推荐:ControlNet(图像生成控制)、FFmpeg(音频处理)、Topaz Photo AI(图像质量优化)
