1 项目目标
前面一部分介绍了flash的驱动,但是有了flash驱动
2 fatfs 介绍
电脑的 windows 系统使用的就是 FAT 文件系统,大家都知道,一般我们新买的 SD 卡,如果没有使用过,插入电脑的时候都要先格式化,是因为 SD 卡里面没有建立 FAT 文件系统,所以格式化之后,建立了 FAT 文件系统,电脑才能识别 SD 卡上面的内存和文件。
要移植 FATFS 文件系统,首先需要下载 FATFS 文件系统的源码文件,可以到官网网站上下载。也可以从本博客绑定的网站上面下载ff12c。
2.1 文件介绍
diskio.c 文件是 FatFs 移植最关键的文件,它为文件系统提供了最底层的接口访问函数,这些函数在移植时都需要我们来编写。diskio.h 定义了 FatFs用到的宏,以及 diskio.c 文件内与底层硬件接口相关的函数声明。
integer.h 文件中包含了一些数值类型定义。
ff.c 是 FatFs 核心文件,文件管理的实现方法。该文件独立于底层介质操作文件的函数,通常用户无需修改,利用这些函数实现文件的读写。
ff.h 是它的头文件。
ffconf.h 这个头文件包含了对 FatFs 功能配置的宏定义,通过修改这些宏定义就可以裁剪 FatFs 的功能,已达到自己想要的标准。下面我们看下此文件内的几个重要选项配置。
- _FS_TINY
这个设置是配置是使用标准模式,还是微小模式。我们使用标准模式,这里
设置为:0。 - _FS_READONLY
是否使用只读模式,我们选择可读可写。设置为:0。 - _FS_MINIMIZE
这个设置是选择是否裁剪掉一些函数,具体裁剪那些,大家可以查看下面的
设置说明,我们这里使用的全功能模式。设置为:0。 - _USE_STRFUNC
这个用来设置是否支持字符串类操作,我们选择使用。设置为:1。 - _USE_MKFS
使用使用格式化,我们这里选择使用。设置为:1。 - _USE_FASTSEEK
使用使能快速定位,我们选择使用。设置为:1。 - _USE_LABEL
是否启用磁盘卷标功能。使用也可以,不使用也可以。我们这里使用。设置
为:1。 - _USE_FORWARD
这个是在 TINY 模式下的设置,我们这里使用标准模式,不理它。 - _CODE_PAGE
这个用于设置语言类型。我们使用的中文。设置为:936,需要将 cc936.c
文件添加到工程中。 - _USE_LFN
该选项用于设置是否支持长文件名(还需要_CODE_PAGE 支持),取值范围为 0 - 3。0,表示不支持长文件名,1~3 是支持长文件名,但是存储地方不一样。我们选择使用 3,通过 ff_memalloc 函数来动态分配长文件名的存储区域。 - _MAX_LFN
设置最大文件名长度,我们直接设置最大。设置为:255。 - _LFN_UNICODE
是否使用 FATFS 的字符编码。我们不使用。设置为:0 - _FS_RPATH
这里也是一些函数裁剪,我们这里设置为:0。 - _VOLUMES
这里设置的是支持的卷轴数量,这里我们挂载 SD 卡,有时候可以挂载下
FLASH 和外部 USB,所以这里我们设置为 3 个。 - _MAX_SS
这里是设置扇区缓冲的最大值,我们设置为:512。 - _MULTI_PARTITION
是否使用多重分区分配。我们这里设置为:0。 - _FS_EXFAT
用于定义是否支持 exFAT 文件系统,我们设置为 1,以支持 exFAT 文件系统。
2.2 文件移植
2.2.1 添加源文件
diskio.c - 磁盘I/O驱动接口 :FatFS与物理存储介质之间的硬件抽象层,需要用户根据实际硬件实现。
ff.c - FatFS核心引擎 -FatFS的核心实现,包含完整的文件系统逻辑。
cc936.c - 中文编码转换
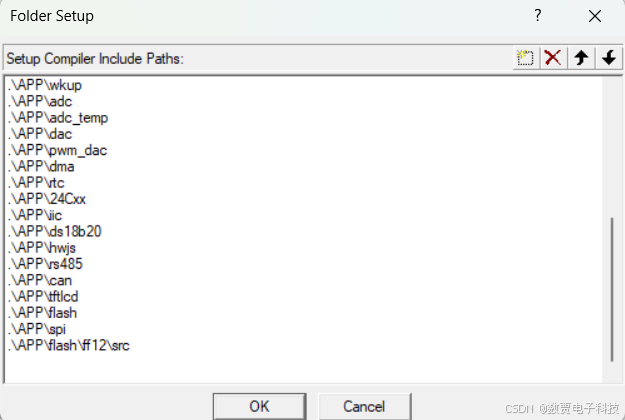
2.2.2 添加头文件地址
2.2.3 配置-ffconf.h 文件
1 . #define _FS_READONLY 0 支持读写
-
#define _USE_STRFUNC 1 支持字符串操作
-
#define _USE_MKFS 1 // 启用格式化功能
-
#define _USE_FASTSEEK 1 // 使用使能快速定位
-
#define _USE_LABEL 1 // 标签
-
#define _CODE_PAGE 936 // 支持中文系统
-
#define _USE_LFN 3
#define _USE_LFN 0 // 禁用长文件名(只支持8.3格式) #define _USE_LFN 1 // 启用长文件名(静态缓冲区) #define _USE_LFN 2 // 启用长文件名(栈上动态缓冲区) #define _USE_LFN 3 // 启用长文件名(堆上动态缓冲区) -
#define _VOLUMES 3 // 支持flash,sd 和 U盘
-
#define _FS_EXFAT 1 // 拓展文件名
2.3 接口函数
2.3.1 由于使用堆的问题,
需要在ffconf.h 文件中, 添加以下文件。如果有操作系统,可以使用操作系统的堆的分配。
c
#include "stdlib.h"
#define ff_memalloc malloc
#define ff_memfree free2.3.2 添加disk_status的状态
disk_status 是FatFS磁盘I/O层(diskio.c)中必须实现的磁盘状态查询函数。
返回值:
c
/* 正常状态(已初始化,有磁盘,可读写) */
return 0;
/* 常见状态组合 */
return STA_NOINIT; // 未初始化
return STA_NODISK; // 无磁盘
return STA_PROTECT; // 写保护
return STA_NOINIT | STA_NODISK; // 未初始化且无磁盘
return STA_NOINIT | STA_PROTECT; // 未初始化且写保护修改文件
c
#include "flash.h"
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case ATA :
{
// result = ATA_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
int initialized;
if (pdrv != 0) {
return STA_NOINIT | STA_NODISK;
}
initialized=EN25QXX_GetStatus();
// 如果未初始化
if (!initialized) {
return STA_NOINIT;
}
stat= 0; // 正常状态
return stat;
break;
}
case MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
return stat;
case USB :
// result = USB_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}2.3.3 修改disk_initialize 初始化函数
c
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case ATA :
// result = ATA_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
{
EN25QXX_Init(); // 初始化flash 文件
stat=0;
}
return stat;
case MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
return stat;
case USB :
// result = USB_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}2.3.4 修改 disk_read 函数
c
#define FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE 512 // 因为默认系统是 _MIN_SS 512
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case ATA :
// translate the arguments here
// result = ATA_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
{
for(;count>0;count--)
{
EN25QXX_Read(buff,sector*FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE,FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE);
sector++;
buff+=FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE;
}
return res;
}
case MMC :
// translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
return res;
case USB :
// translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}2.3.5 disk_ioctl 函数
c
#define FLASH_BLOCK_SIZE 8 //每个BLOCK有8个扇区
u16 FLASH_SECTOR_COUNT=2048*16; //W25Q1218,16M 字节
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case ATA :
// Process of the command for the ATA drive
{
switch(cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC:
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
*(WORD*)buff = FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
*(WORD*)buff = FLASH_BLOCK_SIZE;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = FLASH_SECTOR_COUNT;
res = RES_OK;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
return res;
}
case MMC :
// Process of the command for the MMC/SD card
return res;
case USB :
// Process of the command the USB drive
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}3 简单测试功能
3.1 创建文件
c
FRESULT res;
FATFS fs; /* 文件系统对象 */
res = f_mount(&fs, "0:", 1);
if (res != FR_OK) {
printf("文件系统挂载失败: %d\n\r", res);
/* 可能需要格式化,这里跳过 */
return 1;
}
printf("文件系统挂载成功\n");
FIL file;
UINT bw; /* 写入字节数 */
res = f_open(&file, "0:/hello.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if (res != FR_OK) {
printf("创建文件失败: %d\n\r", res);
res = f_mount(NULL, "0:", 0);
return 1;
}
/* 写入字符串 */
const char* text = "Hello, FatFS!\nThis is a simple example.\n";
res = f_write(&file, text, strlen(text), &bw);
if (res == FR_OK) {
printf("写入成功: %u 字节\n", bw);
}
else
{
printf("写入失败 %d \r\n",res);
}
/* 关闭文件 */
f_close(&file);
res = f_mount(NULL, "0:", 0);
if (res == FR_OK) {
printf("文件系统已卸载\n");
} else {
printf("卸载失败: %d\n", res);
}3.2 查看文件和文件夹
c
void list_directory(const char* path) {
FRESULT fr; // 操作结果
DIR dir; // 目录对象
FILINFO fno; // 文件信息对象[citation:2]
// 1. 打开目录
fr = f_opendir(&dir, path);
if (fr != FR_OK) {
printf("打开目录失败,错误码: %d\n", fr);
return;
}
printf("目录内容列表: %s\n", path);
printf("--------------------------\n");
// 2. 循环读取目录条目
for (;;) {
fr = f_readdir(&dir, &fno); // 读取一个条目[citation:2]
if (fr != FR_OK || fno.fname[0] == 0) {
break; // 发生错误或已无更多条目
}
// 3. 忽略当前目录(".")和上级目录("..")条目
if (fno.fname[0] == '.') continue;
// 4. 根据属性判断是文件还是目录,并打印信息
if (fno.fattrib & AM_DIR) {
// 是目录
printf("[DIR ] %s\n", fno.fname);
} else {
// 是文件
printf("[FILE] %-12s (大小: %lu 字节)\n", fno.fname, fno.fsize);
}
}
// 5. 关闭目录 (可选,但建议执行)
f_closedir(&dir);
}