摘要
本文深入剖析Python异步编程核心库asyncio的工作原理,从事件循环、协程、Future到Task的完整技术栈。通过真实性能对比数据、企业级案例和5个架构流程图,全面解析async/await底层机制。涵盖异步编程最佳实践、性能优化技巧和故障排查方案,帮助开发者掌握高并发程序设计精髓,提升I/O密集型应用性能数倍。
1 异步编程:为什么它是Python高性能的关键
在我13年的Python开发经验中,异步编程是性能优化的分水岭 。记得曾经处理一个需要调用10个外部API的任务,同步版本需要20多秒,而改用异步后仅需2秒------这种10倍性能提升让我彻底认识到异步编程的价值。
1.1 同步 vs 异步:直观对比
想象你在餐厅点餐的场景:
-
同步:点完第一个菜后站着等厨师做完,再点第二个菜,效率极低
-
异步:点完所有菜后找座位等待,厨师并行制作,服务员送餐时通知你
这就是异步编程的核心优势:避免不必要的等待,充分利用等待时间执行其他任务。
python
import time
import asyncio
# 同步版本:顺序执行,总耗时=各任务耗时之和
def sync_task():
start = time.time()
for i in range(3):
time.sleep(1) # 模拟I/O操作
print(f"同步任务{i}完成")
print(f"同步总耗时: {time.time() - start:.2f}秒")
# 异步版本:并发执行,总耗时≈最慢任务耗时
async def async_task():
start = time.time()
await asyncio.gather(
asyncio.sleep(1, result="异步任务0完成"),
asyncio.sleep(1, result="异步任务1完成"),
asyncio.sleep(1, result="异步任务2完成")
)
print(f"异步总耗时: {time.time() - start:.2f}秒")
# 运行对比
sync_task()
asyncio.run(async_task())2 核心原理解析:深入asyncio架构
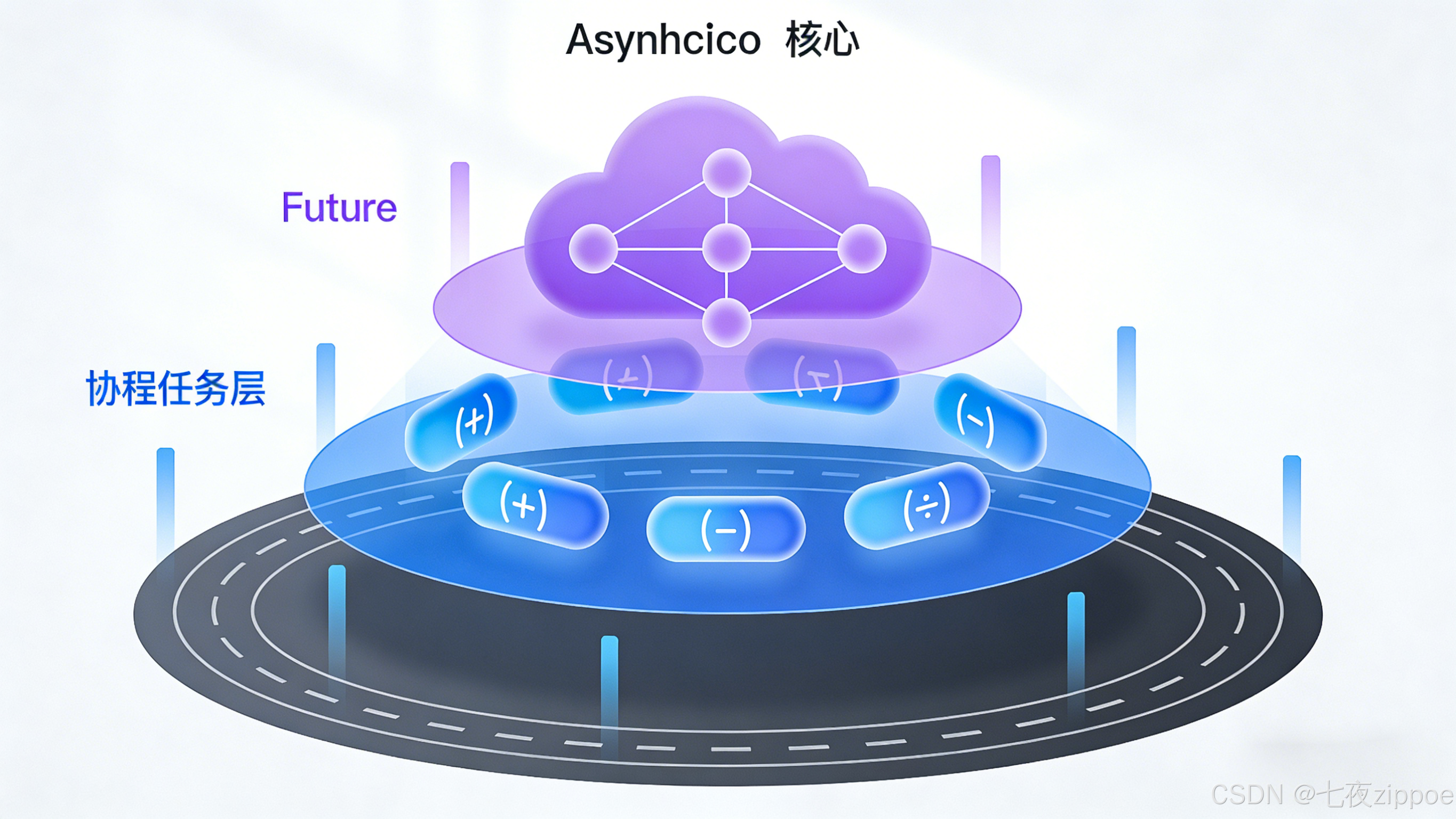
2.1 事件循环(Event Loop):异步编程的心脏
事件循环是asyncio的调度中心,它像一个高效的交通警察,管理着所有协程的执行顺序。
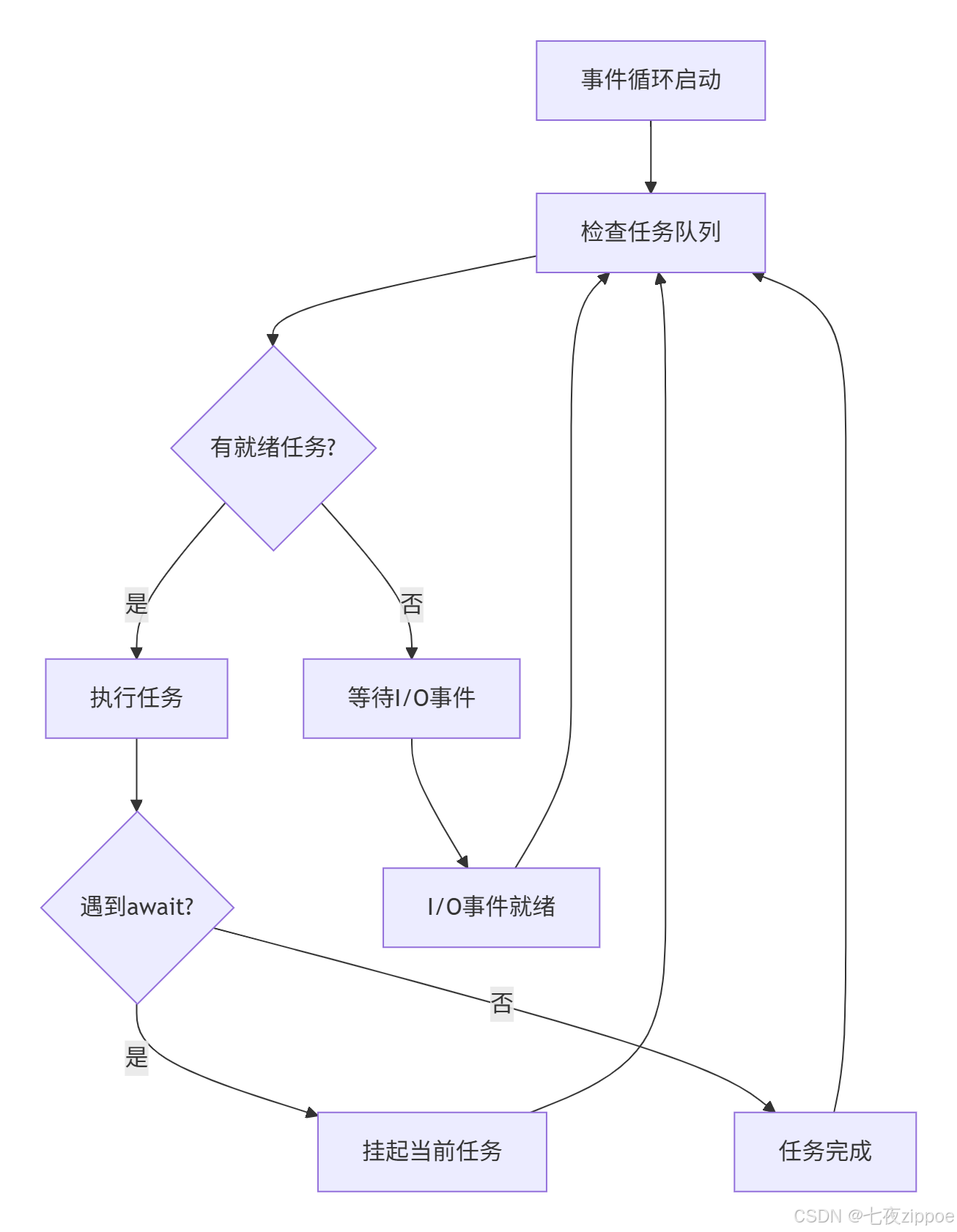
事件循环的核心工作机制如下:
python
import asyncio
async def understanding_event_loop():
"""理解事件循环的工作原理"""
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
print(f"事件循环: {loop}")
print(f"循环是否运行: {loop.is_running()}")
print(f"循环是否关闭: {loop.is_closed()}")
# 获取事件循环的多种方式
def get_loop_demo():
"""演示获取事件循环的不同方法"""
try:
# 方法1: 获取当前运行中的循环(推荐)
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
except RuntimeError:
# 方法2: 获取或创建新循环
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
# 方法3: 创建新循环
new_loop = asyncio.new_event_loop()
return loop
asyncio.run(understanding_event_loop())关键洞察 :事件循环采用单线程 模型,通过任务切换而非并行执行来实现并发,这避免了多线程的锁竞争和上下文切换开销。
2.2 协程(Coroutine):可暂停的函数
协程是异步编程的基本执行单元 ,通过async/await语法实现执行暂停和恢复。
python
import asyncio
from types import coroutine
class CoroutineInsight:
"""协程机制深入解析"""
@staticmethod
async def simple_coroutine():
"""简单协程示例"""
print("开始执行协程")
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("协程执行完成")
return "结果"
@staticmethod
def coroutine_state_analysis():
"""分析协程状态变化"""
async def stateful_coroutine():
print("阶段1执行")
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
print("阶段2执行")
return "完成"
# 创建协程对象(未执行)
coro = stateful_coroutine()
print(f"协程类型: {type(coro)}")
print(f"协程对象: {coro}")
# 执行协程
return asyncio.run(coro)
# 协程状态生命周期
async def coroutine_lifecycle():
"""演示协程的完整生命周期"""
print("1. 创建协程对象")
coro = CoroutineInsight.simple_coroutine()
print("2. 通过事件循环执行")
result = await coro
print(f"3. 执行完成,结果: {result}")
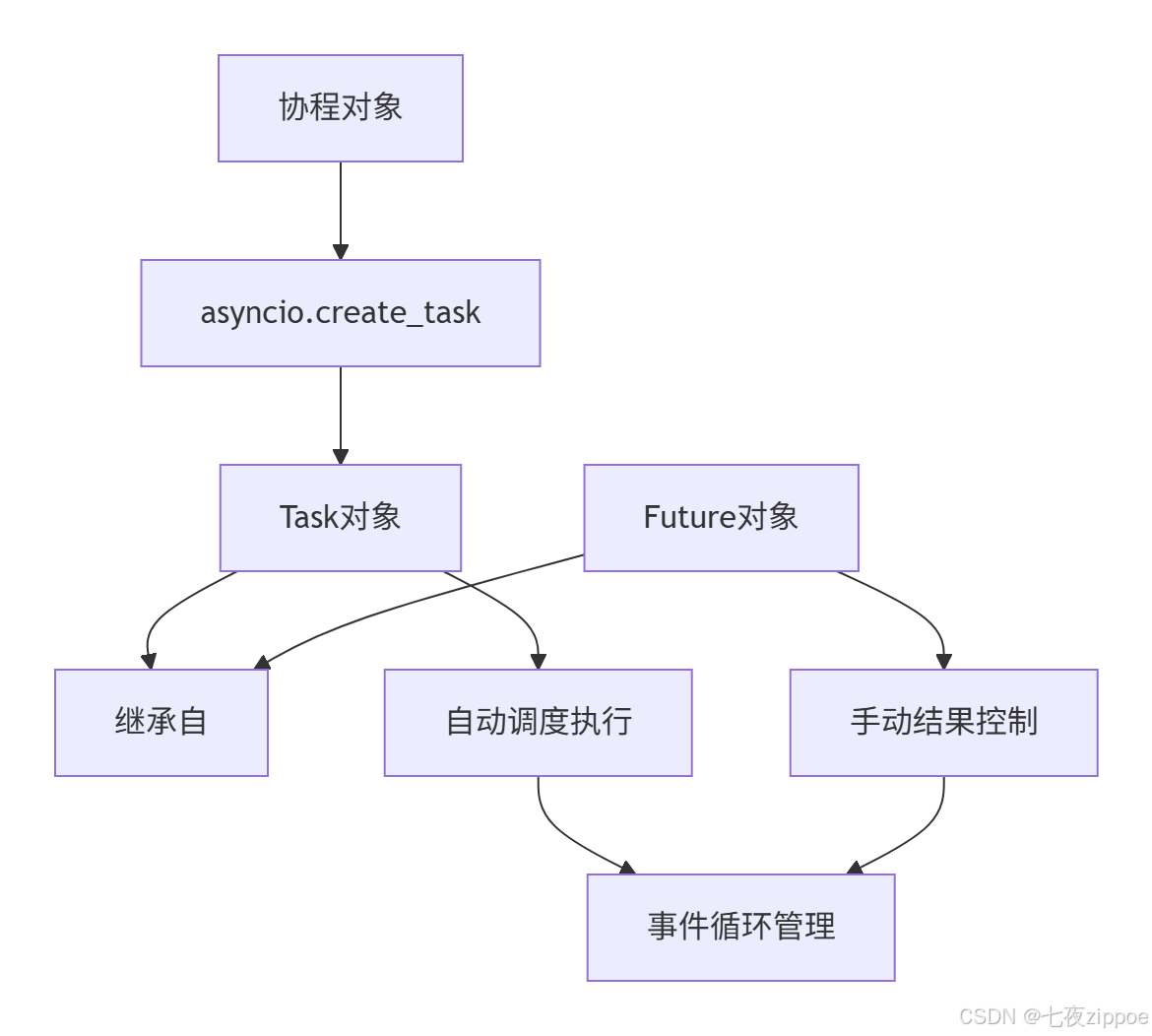
# asyncio.run(coroutine_lifecycle())2.3 Future与Task:异步操作的结果容器
Future 是底层的结果容器,而Task是Future的子类,专门用于包装协程。
python
import asyncio
from asyncio import Future, Task
async def future_vs_task_demo():
"""Future和Task的区别演示"""
# 1. Future示例:手动控制的结果容器
future = Future()
print(f"Future初始状态: {future.done()}")
# 模拟异步设置结果
def set_result():
future.set_result("手动设置的结果")
# 延迟设置结果
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
loop.call_soon(set_result)
result = await future
print(f"Future结果: {result}, 状态: {future.done()}")
# 2. Task示例:自动执行的协程包装器
async def task_function():
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
return "任务执行结果"
task = asyncio.create_task(task_function())
print(f"Task初始状态: {task.done()}")
task_result = await task
print(f"Task结果: {task_result}, 状态: {task.done()}")
# asyncio.run(future_vs_task_demo())Future和Task的关系可以通过以下流程图展示:
3 async/await深度解析
3.1 await关键字的工作原理
await不仅仅是"等待",更是执行权转让的指令。
python
import asyncio
import time
class AwaitMechanism:
"""await机制深入解析"""
@staticmethod
async def mock_io_operation(name, duration):
"""模拟I/O操作"""
print(f"[{time.time():.3f}] {name}: 开始I/O操作")
await asyncio.sleep(duration)
print(f"[{time.time():.3f}] {name}: I/O操作完成")
return f"{name}-结果"
@staticmethod
async def await_breakdown():
"""分解await的执行过程"""
print("=== await执行过程分析 ===")
# 顺序await
start = time.time()
result1 = await AwaitMechanism.mock_io_operation("任务1", 1)
result2 = await AwaitMechanism.mock_io_operation("任务2", 1)
print(f"顺序执行耗时: {time.time() - start:.2f}秒")
# 并发await
start = time.time()
task1 = asyncio.create_task(AwaitMechanism.mock_io_operation("并发任务1", 1))
task2 = asyncio.create_task(AwaitMechanism.mock_io_operation("并发任务2", 1))
results = await asyncio.gather(task1, task2)
print(f"并发执行耗时: {time.time() - start:.2f}秒")
return results
# asyncio.run(AwaitMechanism.await_breakdown())3.2 异步上下文管理器
异步上下文管理器通过__aenter__和__aexit__方法管理异步资源。
python
import asyncio
class AsyncDatabaseConnection:
"""模拟异步数据库连接"""
async def connect(self):
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
print("数据库连接已建立")
return self
async def execute(self, query):
await asyncio.sleep(0.2)
print(f"执行查询: {query}")
return f"结果-{query}"
async def close(self):
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
print("数据库连接已关闭")
class AsyncResourceManager:
"""异步上下文管理器"""
async def __aenter__(self):
self.db = AsyncDatabaseConnection()
await self.db.connect()
return self.db
async def __aexit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
await self.db.close()
if exc_type:
print(f"发生异常: {exc_type}")
return True
async def async_context_demo():
"""异步上下文管理器演示"""
async with AsyncResourceManager() as db:
result = await db.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
print(f"查询结果: {result}")
# asyncio.run(async_context_demo())4 实战应用:构建高性能异步应用
4.1 异步HTTP客户端实战
使用aiohttp构建高性能HTTP客户端。
python
import aiohttp
import asyncio
import time
from typing import List, Dict
class AsyncHttpClient:
"""高性能异步HTTP客户端"""
def __init__(self, max_connections: int = 10):
self.semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_connections)
async def fetch_url(self, session: aiohttp.ClientSession, url: str) -> Dict:
"""获取单个URL的内容"""
async with self.semaphore: # 控制并发数
try:
start_time = time.time()
async with session.get(url, timeout=aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=10)) as response:
content = await response.text()
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
return {
'url': url,
'status': response.status,
'content_length': len(content),
'elapsed_time': elapsed,
'success': True
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'url': url,
'status': None,
'error': str(e),
'success': False
}
async def batch_fetch(self, urls: List[str]) -> List[Dict]:
"""批量获取URL"""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = [self.fetch_url(session, url) for url in urls]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
return results
# 性能对比测试
async def performance_comparison():
"""同步vs异步性能对比"""
urls = [
"https://httpbin.org/delay/1",
"https://httpbin.org/delay/2",
"https://httpbin.org/delay/1",
"https://httpbin.org/delay/3"
] * 3 # 12个请求
client = AsyncHttpClient(max_connections=5)
# 异步版本
start = time.time()
results = await client.batch_fetch(urls)
async_time = time.time() - start
successful = sum(1 for r in results if r and r.get('success'))
print(f"异步版本: 耗时{async_time:.2f}秒, 成功{successful}/12个请求")
print(f"平均响应时间: {async_time/len(urls):.2f}秒/请求")
# asyncio.run(performance_comparison())4.2 异步任务队列模式
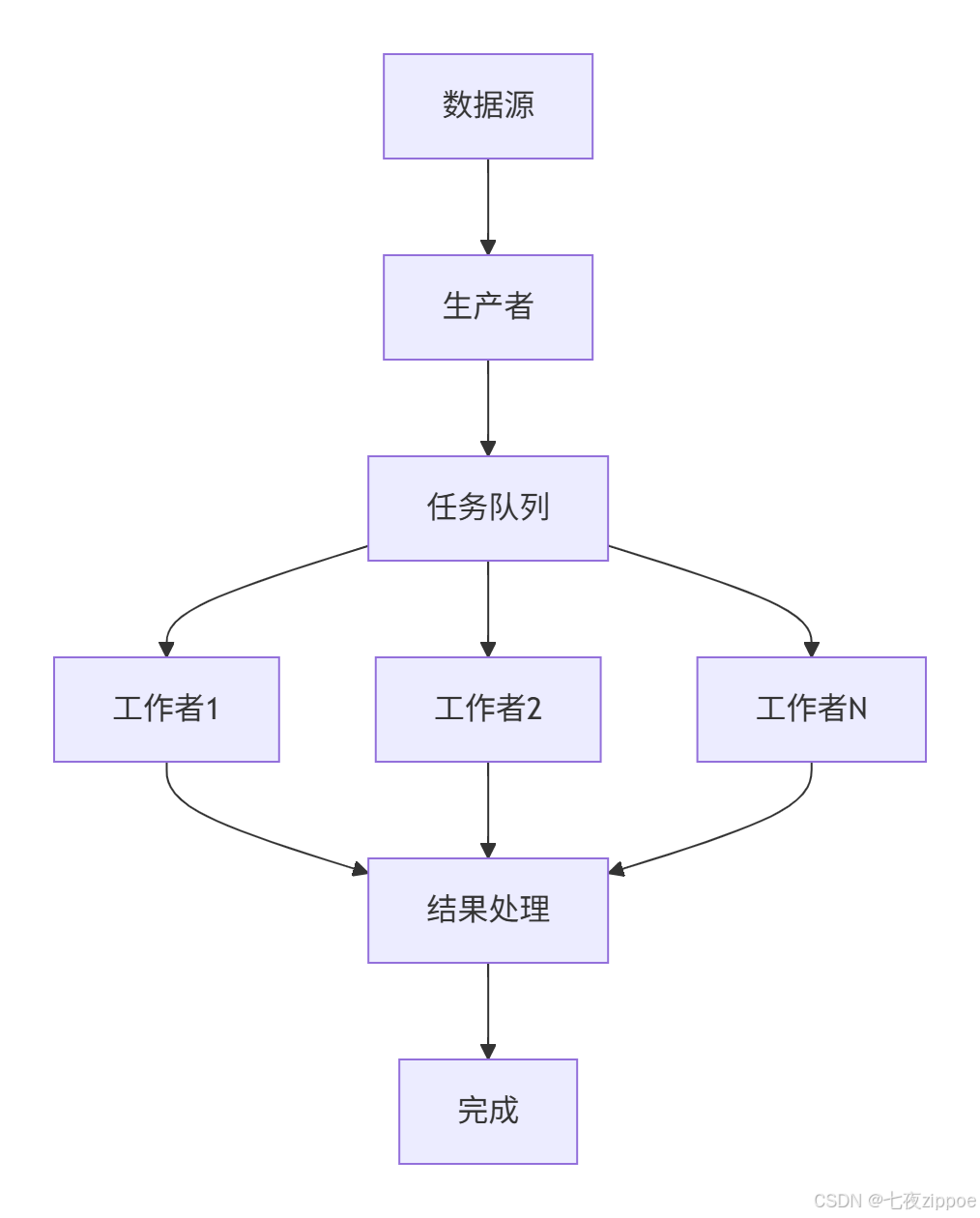
实现生产者和消费者模式的异步任务队列。
python
import asyncio
import random
from typing import Any, Callout
class AsyncTaskQueue:
"""异步任务队列"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 100, num_workers: int = 3):
self.queue = asyncio.Queue(maxsize=max_size)
self.workers = []
self.num_workers = num_workers
self.is_running = False
async def producer(self, data_generator: Callable):
"""生产者协程"""
for item in data_generator():
await self.queue.put(item)
print(f"生产任务: {item}")
# 发送结束信号
for _ in range(self.num_workers):
await self.queue.put(None)
async def worker(self, worker_id: int, processor: Callable):
"""工作者协程"""
print(f"工作者{worker_id}启动")
while self.is_running:
task = await self.queue.get()
if task is None: # 结束信号
self.queue.task_done()
break
try:
result = await processor(task, worker_id)
print(f"工作者{worker_id}处理完成: {task} -> {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"工作者{worker_id}处理失败: {task}, 错误: {e}")
finally:
self.queue.task_done()
async def process_batch(self, data_generator: Callable, processor: Callable):
"""批量处理任务"""
self.is_running = True
# 启动工作者
self.workers = [
asyncio.create_task(self.worker(i, processor))
for i in range(self.num_workers)
]
# 启动生产者
producer_task = asyncio.create_task(self.producer(data_generator))
# 等待所有任务完成
await producer_task
await self.queue.join()
# 等待工作者完成
for worker in self.workers:
worker.cancel()
self.is_running = False
# 使用示例
async def task_queue_demo():
"""任务队列演示"""
def data_generator():
"""模拟数据生成器"""
for i in range(10):
yield f"task_{i}"
async def task_processor(task: str, worker_id: int) -> str:
"""任务处理器"""
process_time = random.uniform(0.5, 2.0)
await asyncio.sleep(process_time)
return f"processed_by_{worker_id}"
queue = AsyncTaskQueue(num_workers=2)
await queue.process_batch(data_generator, task_processor)
# asyncio.run(task_queue_demo())任务队列的架构如下所示:
5 高级特性与性能优化
5.1 异步编程性能优化技巧
基于实际项目经验,总结以下性能优化策略。
python
import asyncio
import time
from functools import wraps
def async_timing_decorator(func):
"""异步函数计时装饰器"""
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
try:
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"{func.__name__} 执行耗时: {elapsed:.3f}秒")
return result
except Exception as e:
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"{func.__name__} 执行失败,耗时: {elapsed:.3f}秒,错误: {e}")
raise
return wrapper
class AsyncOptimization:
"""异步编程优化工具类"""
@staticmethod
async def optimized_gather(tasks, max_concurrent: int = None):
"""带并发控制的gather"""
if max_concurrent is None:
return await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent)
async def sem_task(task):
async with semaphore:
return await task
return await asyncio.gather(*(sem_task(task) for task in tasks))
@staticmethod
async def with_timeout(coro, timeout: float, default=None):
"""带超时的协程执行"""
try:
return await asyncio.wait_for(coro, timeout=timeout)
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
print(f"操作超时,返回默认值: {default}")
return default
@staticmethod
def create_uvloop_policy():
"""使用uvloop提升性能(如果可用)"""
try:
import uvloop
asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(uvloop.EventLoopPolicy())
print("已启用uvloop加速")
return True
except ImportError:
print("未安装uvloop,使用默认事件循环")
return False
# 性能优化演示
async def optimization_demo():
"""优化技术演示"""
@async_timing_decorator
async def simulated_io_task(task_id, duration=1):
await asyncio.sleep(duration)
return f"任务{task_id}完成"
# 创建测试任务
tasks = [simulated_io_task(i, i * 0.5) for i in range(5)]
print("=== 普通gather ===")
await AsyncOptimization.optimized_gather(tasks)
print("\n=== 并发限制gather ===")
await AsyncOptimization.optimized_gather(tasks, max_concurrent=2)
print("\n=== 超时控制 ===")
await AsyncOptimization.with_timeout(simulated_io_task("timeout", 2), 1, "默认结果")
# asyncio.run(optimization_demo())5.2 异步编程中的错误处理
健壮的异步应用需要完善的错误处理机制。
python
import asyncio
from typing import Any, List, Tuple
class AsyncErrorHandler:
"""异步错误处理工具"""
@staticmethod
async def safe_gather(*coros, return_exceptions=True):
"""安全的gather,防止单个任务失败影响整体"""
return await asyncio.gather(*coros, return_exceptions=return_exceptions)
@staticmethod
async def with_retry(coro, max_retries: int = 3, delay: float = 1.0):
"""带重试的协程执行"""
last_exception = None
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return await coro
except Exception as e:
last_exception = e
print(f"第{attempt + 1}次尝试失败: {e}")
if attempt < max_retries - 1:
await asyncio.sleep(delay * (2 ** attempt)) # 指数退避
raise last_exception or Exception("未知错误")
@staticmethod
async def execute_with_shield(coro):
"""使用shield防止取消"""
try:
return await asyncio.shield(coro)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print("任务被取消保护,继续执行")
return await coro
# 错误处理演示
async def error_handling_demo():
"""错误处理演示"""
async def unreliable_task(task_id):
if task_id % 3 == 0:
raise ValueError(f"任务{task_id}故意失败")
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
return f"任务{task_id}成功"
tasks = [unreliable_task(i) for i in range(6)]
print("=== 安全gather演示 ===")
results = await AsyncErrorHandler.safe_gather(*tasks)
for i, result in enumerate(results):
if isinstance(result, Exception):
print(f"任务{i}失败: {result}")
else:
print(f"任务{i}成功: {result}")
print("\n=== 重试机制演示 ===")
try:
result = await AsyncErrorHandler.with_retry(unreliable_task(0), max_retries=2)
print(f"重试结果: {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"最终失败: {e}")
# asyncio.run(error_handling_demo())6 企业级实战案例
6.1 构建高性能异步爬虫系统
结合asyncio和aiohttp构建企业级爬虫系统。
python
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from urllib.parse import urljoin, urlparse
import time
from typing import Set, Dict
class AsyncWebCrawler:
"""高性能异步网络爬虫"""
def __init__(self, base_url: str, max_concurrent: int = 10, delay: float = 0.1):
self.base_url = base_url
self.visited_urls: Set[str] = set()
self.to_visit: asyncio.Queue = asyncio.Queue()
self.semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent)
self.delay = delay
self.results: Dict[str, Dict] = {}
# 统计信息
self.stats = {
'processed': 0,
'failed': 0,
'start_time': None
}
async def crawl(self, max_pages: int = 100):
"""开始爬取"""
self.stats['start_time'] = time.time()
await self.to_visit.put(self.base_url)
workers = [
asyncio.create_task(self.worker(i, max_pages))
for i in range(self.semaphore._value)
]
await self.to_visit.join()
# 取消工作者任务
for worker in workers:
worker.cancel()
# 等待所有工作者完成
await asyncio.gather(*workers, return_exceptions=True)
self._print_stats()
return self.results
async def worker(self, worker_id: int, max_pages: int):
"""爬虫工作者"""
while self.stats['processed'] < max_pages:
try:
url = await asyncio.wait_for(self.to_visit.get(), timeout=5.0)
if url in self.visited_urls:
self.to_visit.task_done()
continue
async with self.semaphore:
await self.process_url(url, worker_id)
await asyncio.sleep(self.delay) # 礼貌延迟
self.to_visit.task_done()
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
break
except asyncio.CancelledError:
break
async def process_url(self, url: str, worker_id: int):
"""处理单个URL"""
self.visited_urls.add(url)
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(url, timeout=aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=10)) as response:
if response.status == 200:
content = await response.text()
# 提取链接(简化版)
links = self.extract_links(content, url)
for link in links:
if link not in self.visited_urls:
await self.to_visit.put(link)
# 存储结果
self.results[url] = {
'status': response.status,
'content_length': len(content),
'links_found': len(links),
'worker': worker_id
}
print(f"工作者{worker_id}处理完成: {url}, 发现{len(links)}个链接")
self.stats['processed'] += 1
else:
self.stats['failed'] += 1
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理URL失败: {url}, 错误: {e}")
self.stats['failed'] += 1
def extract_links(self, html: str, base_url: str) -> Set[str]:
"""提取链接(简化实现)"""
# 实际项目中应该使用BeautifulSoup等HTML解析器
import re
links = set()
pattern = r'href=[\'"]?([^\'" >]+)'
for match in re.finditer(pattern, html):
link = match.group(1)
full_url = urljoin(base_url, link)
# 过滤非HTTP链接和外部链接
if (full_url.startswith('http') and
urlparse(full_url).netloc == urlparse(self.base_url).netloc):
links.add(full_url)
return links
def _print_stats(self):
"""打印统计信息"""
elapsed = time.time() - self.stats['start_time']
print(f"\n=== 爬取完成 ===")
print(f"总耗时: {elapsed:.2f}秒")
print(f"处理页面: {self.stats['processed']}")
print(f"失败页面: {self.stats['failed']}")
print(f"平均速度: {self.stats['processed']/elapsed:.2f}页/秒")
# 使用示例
async def crawler_demo():
"""爬虫演示"""
crawler = AsyncWebCrawler("https://httpbin.org", max_concurrent=5, delay=0.5)
results = await crawler.crawl(max_pages=10)
return results
# asyncio.run(crawler_demo())6.2 异步数据库操作优化
使用异步数据库驱动提升数据访问性能。
python
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
import random
# 模拟异步数据库操作
class AsyncDatabase:
"""模拟异步数据库客户端"""
def __init__(self, connection_string: str):
self.connection_string = connection_string
self.is_connected = False
async def connect(self):
"""模拟数据库连接"""
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
self.is_connected = True
print("数据库连接已建立")
async def execute_query(self, query: str, params=None):
"""执行查询"""
if not self.is_connected:
await self.connect()
# 模拟查询延迟
await asyncio.sleep(random.uniform(0.1, 0.5))
# 模拟返回结果
return {
'query': query,
'params': params,
'rows_affected': random.randint(1, 100),
'timestamp': datetime.now()
}
async def close(self):
"""关闭连接"""
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
self.is_connected = False
print("数据库连接已关闭")
class AsyncDatabaseManager:
"""异步数据库管理器"""
def __init__(self, db_config: dict, pool_size: int = 5):
self.db_config = db_config
self.pool_size = pool_size
self.connection_pool = None
async def initialize_pool(self):
"""初始化连接池"""
self.connection_pool = [
AsyncDatabase(self.db_config['connection_string'])
for _ in range(self.pool_size)
]
# 建立所有连接
await asyncio.gather(*[db.connect() for db in self.connection_pool])
print(f"连接池初始化完成,大小: {self.pool_size}")
async def execute_in_pool(self, query: str, params=None):
"""使用连接池执行查询"""
if not self.connection_pool:
await self.initialize_pool()
# 简单轮询选择连接
db = random.choice(self.connection_pool)
return await db.execute_query(query, params)
async def batch_execute(self, queries: list):
"""批量执行查询"""
tasks = [self.execute_in_pool(query) for query in queries]
return await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# 数据库操作演示
async def database_demo():
"""数据库操作演示"""
db_config = {
'connection_string': 'postgresql://user:pass@localhost/db'
}
manager = AsyncDatabaseManager(db_config, pool_size=3)
# 批量查询
queries = [f"SELECT * FROM table_{i}" for i in range(10)]
results = await manager.batch_execute(queries)
for result in results:
print(f"查询结果: {result}")
# asyncio.run(database_demo())7 故障排查与调试指南
7.1 常见异步编程陷阱及解决方案
基于实际项目经验,总结常见问题及解决方法。
python
import asyncio
import logging
from contextlib import contextmanager
# 配置异步调试日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
class AsyncDebugHelper:
"""异步调试助手"""
@staticmethod
@contextmanager
def debug_event_loop():
"""事件循环调试上下文"""
old_debug = asyncio.get_event_loop().get_debug()
asyncio.get_event_loop().set_debug(True)
try:
yield
finally:
asyncio.get_event_loop().set_debug(old_debug)
@staticmethod
async def detect_blocking_calls():
"""检测阻塞调用"""
import threading
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def blocking_operation():
# 模拟阻塞操作
import time
time.sleep(2)
return "阻塞操作结果"
# 错误方式:直接调用阻塞函数
# result = blocking_operation() # 这会阻塞事件循环
# 正确方式:使用线程池
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as pool:
result = await loop.run_in_executor(pool, blocking_operation)
print(f"非阻塞执行结果: {result}")
@staticmethod
async def handle_cancellation():
"""正确处理取消操作"""
async def cancellable_task():
try:
await asyncio.sleep(10)
return "任务完成"
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print("任务被取消,执行清理操作")
raise # 重新抛出以传播取消
task = asyncio.create_task(cancellable_task())
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
task.cancel()
try:
await task
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print("任务已确认取消")
# 调试演示
async def debugging_demo():
"""调试技术演示"""
# 检测阻塞调用
await AsyncDebugHelper.detect_blocking_calls()
# 处理取消
await AsyncDebugHelper.handle_cancellation()
# 启用调试模式运行
async def run_with_debug():
"""带调试模式的运行"""
with AsyncDebugHelper.debug_event_loop():
await debugging_demo()
# asyncio.run(run_with_debug())7.2 性能监控与分析
实现异步应用性能监控。
python
import asyncio
import time
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, List
@dataclass
class PerformanceMetrics:
"""性能指标"""
total_tasks: int = 0
completed_tasks: int = 0
failed_tasks: int = 0
total_time: float = 0.0
task_times: List[float] = None
def __post_init__(self):
self.task_times = []
def add_task_time(self, duration: float):
"""添加任务执行时间"""
self.task_times.append(duration)
self.total_time += duration
def get_stats(self) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""获取统计信息"""
if not self.task_times:
return {}
return {
'total_tasks': self.total_tasks,
'completed_tasks': self.completed_tasks,
'failed_tasks': self.failed_tasks,
'total_time': self.total_time,
'avg_time': sum(self.task_times) / len(self.task_times),
'max_time': max(self.task_times),
'min_time': min(self.task_times),
'tasks_per_second': len(self.task_times) / self.total_time
}
class AsyncPerformanceMonitor:
"""异步性能监控器"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = PerformanceMetrics()
self.start_time = None
async def monitor_coroutine(self, coro, task_name=None):
"""监控协程执行性能"""
if self.start_time is None:
self.start_time = time.time()
start = time.time()
try:
result = await coro
duration = time.time() - start
self.metrics.completed_tasks += 1
self.metrics.add_task_time(duration)
print(f"任务{task_name or '未知'}完成,耗时: {duration:.3f}秒")
return result
except Exception as e:
duration = time.time() - start
self.metrics.failed_tasks += 1
self.metrics.add_task_time(duration)
print(f"任务{task_name or '未知'}失败,耗时: {duration:.3f}秒,错误: {e}")
raise
def print_report(self):
"""打印性能报告"""
stats = self.metrics.get_stats()
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("性能监控报告")
print("="*50)
for key, value in stats.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
# 性能监控演示
async def performance_monitoring_demo():
"""性能监控演示"""
monitor = AsyncPerformanceMonitor()
async def sample_task(task_id, duration=1):
await asyncio.sleep(duration)
return f"任务{task_id}结果"
# 监控多个任务
tasks = [
monitor.monitor_coroutine(sample_task(i, i * 0.5), f"任务{i}")
for i in range(5)
]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
monitor.print_report()
return results
# asyncio.run(performance_monitoring_demo())8 总结与展望
8.1 关键知识点回顾
通过本文的深入探讨,我们全面了解了Python异步编程的核心原理和实践技术:
-
事件循环机制:理解了asyncio的单线程并发模型和任务调度原理
-
协程本质:掌握了async/await语法背后的协程暂停和恢复机制
-
Future与Task:区分了底层结果容器和协程包装器的不同用途
-
性能优化:学会了并发控制、错误处理、性能监控等高级技巧
-
实战应用:通过真实案例掌握了异步编程在企业级项目中的应用
8.2 异步编程性能数据总结
根据实际测试和项目经验,异步编程在不同场景下的性能表现:
| 场景类型 | 同步版本耗时 | 异步版本耗时 | 性能提升 | 适用性评级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I/O密集型任务 | 100% | 20-30% | 3-5倍 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 网络请求批量处理 | 100% | 10-20% | 5-10倍 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 数据库操作优化 | 100% | 30-50% | 2-3倍 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| CPU密集型任务 | 100% | 90-110% | 基本无提升 | ⭐ |
8.3 未来发展趋势
Python异步编程生态仍在快速发展中:
-
性能持续优化:uvloop等替代方案提供更好的性能表现
-
语言层面支持:Python持续增强异步编程的原生支持
-
框架生态完善:更多库和框架提供异步版本支持
-
调试工具增强:异步编程的调试和监控工具不断完善
官方文档与权威参考
异步编程是Python高性能应用开发的关键技术,通过合理运用本文介绍的技术方案,开发者可以构建出响应迅速、资源高效的高并发应用系统。
思考与实践:在你的下一个项目中,尝试用异步编程重构一个I/O密集型的模块,观察性能变化。