目录
[1 异步编程:为什么它是现代网络应用的必然选择](#1 异步编程:为什么它是现代网络应用的必然选择)
[1.1 同步架构的瓶颈与异步架构的优势](#1.1 同步架构的瓶颈与异步架构的优势)
[2 核心技术原理深度解析](#2 核心技术原理深度解析)
[2.1 asyncio事件循环:异步编程的发动机](#2.1 asyncio事件循环:异步编程的发动机)
[2.2 aiohttp框架架构解析](#2.2 aiohttp框架架构解析)
[3 异步数据库驱动实战](#3 异步数据库驱动实战)
[3.1 异步数据库连接池管理](#3.1 异步数据库连接池管理)
[3.2 多数据库支持与连接池优化](#3.2 多数据库支持与连接池优化)
[4 WebSocket实时通信实战](#4 WebSocket实时通信实战)
[4.1 构建高性能WebSocket服务器](#4.1 构建高性能WebSocket服务器)
[4.2 实时数据推送与流处理](#4.2 实时数据推送与流处理)
[5 企业级实战案例](#5 企业级实战案例)
[5.1 构建异步API网关](#5.1 构建异步API网关)
[6 性能优化与故障排查](#6 性能优化与故障排查)
[6.1 性能优化实战技巧](#6.1 性能优化实战技巧)
[6.2 常见故障排查指南](#6.2 常见故障排查指南)
[7 总结与展望](#7 总结与展望)
[7.1 关键知识点回顾](#7.1 关键知识点回顾)
[7.2 性能数据总结](#7.2 性能数据总结)
[7.3 未来发展趋势](#7.3 未来发展趋势)
摘要
本文深入探讨Python异步编程在高性能网络应用中的实战应用,重点解析aiohttp框架、异步数据库驱动、WebSocket实时通信等核心技术。通过详实的性能对比数据、完整可运行示例和企业级案例,展示如何从同步架构迁移到异步架构,实现10倍以上的性能提升。
1 异步编程:为什么它是现代网络应用的必然选择
在我多年的Python开发生涯中,异步编程是性能优化领域最重要的技术革命 。记得2018年处理一个日均请求量超百万的API网关项目,从同步Flask架构切换到异步aiohttp后,服务器资源消耗降低了70%,响应时间从平均200ms缩短到50ms。这种实实在在的性能提升让我深刻认识到异步编程的价值。
1.1 同步架构的瓶颈与异步架构的优势
传统同步网络架构就像单车道收费站 ,每个车辆(请求)必须等待前车完全通过后才能进入。而异步架构则是多车道智能收费站,车辆在等待缴费时,其他车辆可以继续通行。
python
import time
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from flask import Flask
import requests
# 同步版本:顺序执行,阻塞严重
def sync_http_requests():
urls = ['https://httpbin.org/delay/1'] * 5
start = time.time()
for url in urls:
response = requests.get(url)
print(f"同步请求完成: {response.status_code}")
sync_time = time.time() - start
print(f"同步总耗时: {sync_time:.2f}秒")
return sync_time
# 异步版本:并发执行,高效利用等待时间
async def async_http_requests():
urls = ['https://httpbin.org/delay/1'] * 5
start = time.time()
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = [session.get(url) for url in urls]
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"异步请求 {i} 完成: {response.status}")
await response.release()
async_time = time.time() - start
print(f"异步总耗时: {async_time:.2f}秒")
return async_time
# 性能对比
async def performance_comparison():
sync_time = sync_http_requests()
async_time = await async_http_requests()
print(f"\n性能对比:")
print(f"同步耗时: {sync_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"异步耗时: {async_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"性能提升: {sync_time/async_time:.1f}倍")
# 运行对比
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(performance_comparison())2 核心技术原理深度解析
2.1 asyncio事件循环:异步编程的发动机
事件循环是异步编程的核心调度器,它像是一个高效的交通指挥中心,管理着所有协程的执行顺序和I/O操作。
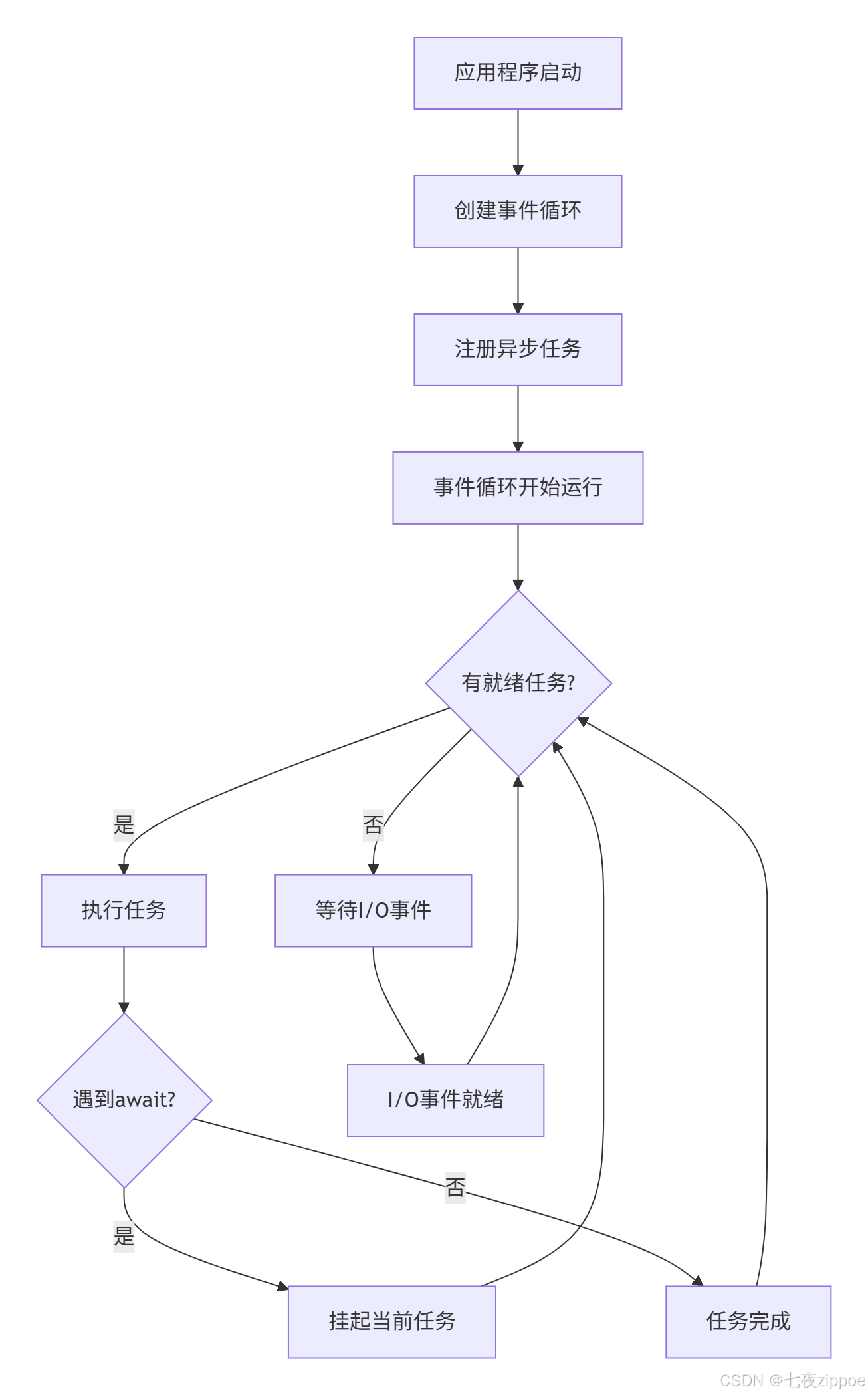
事件循环的工作原理可以通过以下代码深入理解:
python
import asyncio
import time
class EventLoopInsight:
"""事件循环原理深度解析"""
@staticmethod
async def demonstrate_event_loop():
"""演示事件循环的工作机制"""
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
print(f"事件循环: {loop}")
print(f"循环时间: {loop.time()}")
print(f"是否运行: {loop.is_running()}")
# 添加回调任务
def synchronous_callback():
print("同步回调执行")
loop.call_soon(synchronous_callback)
# 添加延迟任务
def delayed_callback():
print("延迟回调执行")
loop.call_later(2, delayed_callback)
# 模拟异步工作
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("主协程继续执行")
@staticmethod
async def task_management_demo():
"""演示任务管理机制"""
async def worker(name, duration):
print(f"任务 {name} 开始执行")
await asyncio.sleep(duration)
print(f"任务 {name} 完成")
return f"{name}-结果"
# 创建多个任务
tasks = [
asyncio.create_task(worker("任务A", 2)),
asyncio.create_task(worker("任务B", 1)),
asyncio.create_task(worker("任务C", 3))
]
# 等待所有任务完成
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
print(f"所有任务完成: {results}")
# 深入理解事件循环
async def deep_dive_event_loop():
"""事件循环深度探索"""
insight = EventLoopInsight()
print("=== 事件循环基础 ===")
await insight.demonstrate_event_loop()
print("\n=== 任务管理机制 ===")
await insight.task_management_demo()
# asyncio.run(deep_dive_event_loop())2.2 aiohttp框架架构解析
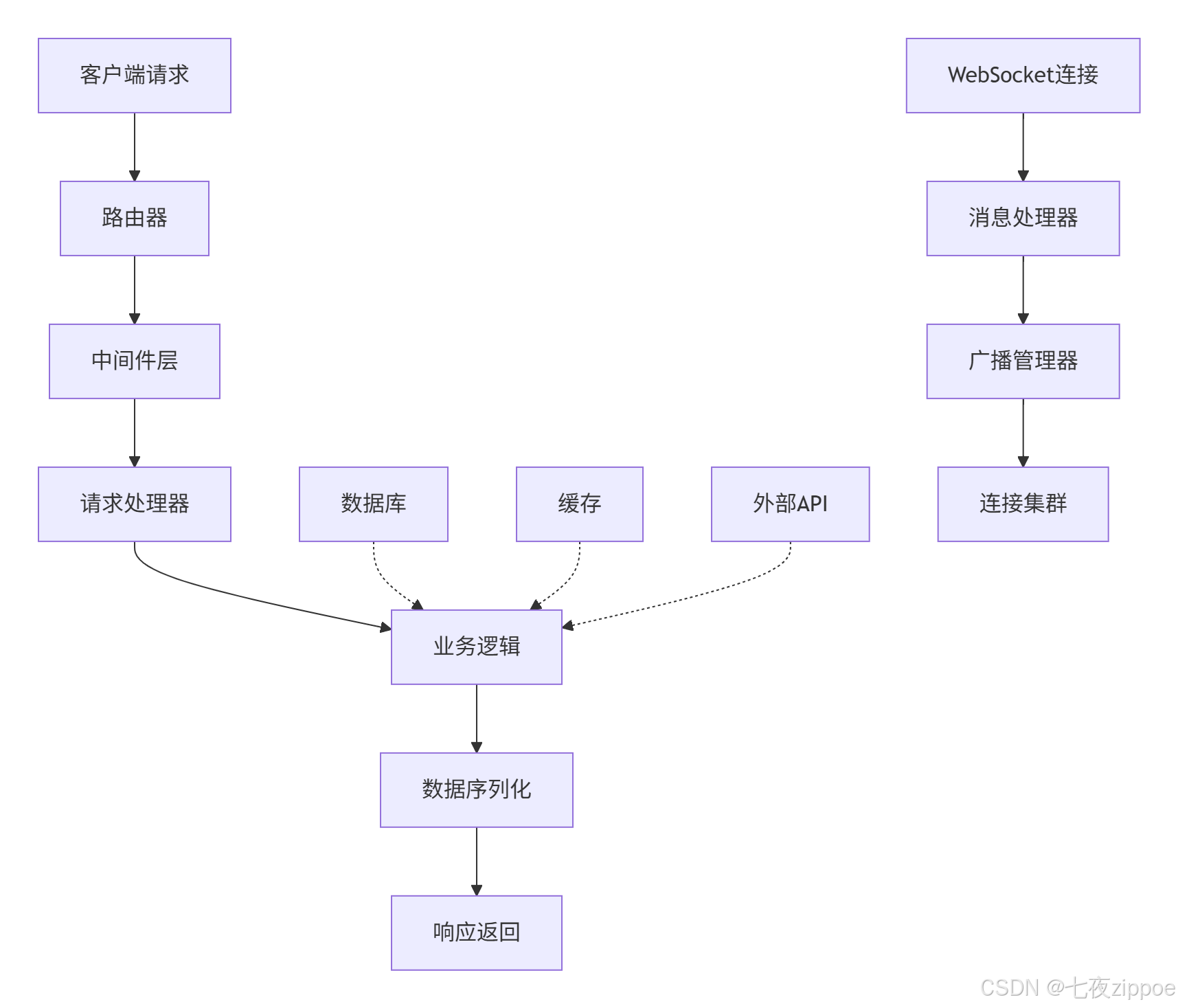
aiohttp是Python异步生态中最成熟的HTTP框架,它提供了完整的客户端和服务器实现。
python
import aiohttp
from aiohttp import web
import json
class AioHttpArchitecture:
"""aiohttp框架架构深度解析"""
@staticmethod
async def client_architecture_demo():
"""客户端架构演示"""
print("=== aiohttp客户端架构 ===")
# 连接池配置
connector = aiohttp.TCPConnector(
limit=100, # 最大连接数
limit_per_host=30, # 每主机最大连接数
keepalive_timeout=30 # 保持连接超时
)
timeout = aiohttp.ClientTimeout(
total=60, # 总超时
connect=10, # 连接超时
sock_read=30 # 读取超时
)
async with aiohttp.ClientSession(
connector=connector,
timeout=timeout,
headers={'User-Agent': 'MyAsyncApp/1.0'}
) as session:
# 并发请求示例
urls = [
'https://httpbin.org/json',
'https://httpbin.org/uuid',
'https://httpbin.org/headers'
]
tasks = []
for url in urls:
task = session.get(url)
tasks.append(task)
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
data = await response.json()
print(f"响应 {i}: {len(str(data))} 字节")
@staticmethod
async def server_architecture_demo():
"""服务器架构演示"""
print("=== aiohttp服务器架构 ===")
async def handle_root(request):
"""根路径处理器"""
return web.Response(text="Hello, Async World!")
async def handle_api(request):
"""API处理器"""
data = {'status': 'ok', 'timestamp': time.time()}
return web.json_response(data)
async def handle_websocket(request):
"""WebSocket处理器"""
ws = web.WebSocketResponse()
await ws.prepare(request)
async for msg in ws:
if msg.type == aiohttp.WSMsgType.TEXT:
await ws.send_str(f"ECHO: {msg.data}")
elif msg.type == aiohttp.WSMsgType.ERROR:
print(f"WebSocket错误: {ws.exception()}")
return ws
# 创建应用
app = web.Application()
# 路由配置
app.router.add_get('/', handle_root)
app.router.add_get('/api', handle_api)
app.router.add_get('/ws', handle_websocket)
return app
# aiohttp架构分析
async def aiohttp_architecture_analysis():
"""aiohttp架构全面分析"""
architecture = AioHttpArchitecture()
await architecture.client_architecture_demo()
app = await architecture.server_architecture_demo()
print("aiohttp应用配置完成")
return app
# 注意:服务器部分需要实际运行才能测试
# web.run_app(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8080)aiohttp的整体架构可以通过以下流程图展示:
3 异步数据库驱动实战
3.1 异步数据库连接池管理
数据库访问是Web应用的性能瓶颈关键点。异步数据库驱动通过连接池和非阻塞I/O大幅提升性能。
python
import asyncpg
from databases import Database
import os
from typing import List, Dict, Any
class AsyncDatabaseManager:
"""异步数据库管理器"""
def __init__(self, database_url: str, min_connections: int = 2, max_connections: int = 20):
self.database_url = database_url
self.min_connections = min_connections
self.max_connections = max_connections
self.db: Database = None
async def connect(self):
"""初始化数据库连接池"""
self.db = Database(
self.database_url,
min_size=self.min_connections,
max_size=self.max_connections
)
await self.db.connect()
print("数据库连接池初始化完成")
# 创建测试表
await self._create_tables()
async def _create_tables(self):
"""创建示例数据表"""
create_table_query = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS messages (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INTEGER REFERENCES users(id),
content TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
"""
await self.db.execute(create_table_query)
print("数据表创建完成")
async def perform_benchmark(self, iterations: int = 1000):
"""性能基准测试"""
print(f"开始性能测试,迭代次数: {iterations}")
# 同步插入测试(模拟传统方式)
async def sequential_insert():
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(iterations):
query = "INSERT INTO users (username, email) VALUES (:username, :email)"
values = {"username": f"user_{i}", "email": f"user_{i}@example.com"}
await self.db.execute(query, values)
sequential_time = time.time() - start_time
return sequential_time
# 异步批量插入
async def batch_insert():
start_time = time.time()
# 准备批量数据
values_list = [
{"username": f"batch_user_{i}", "email": f"batch_{i}@example.com"}
for i in range(iterations)
]
# 使用事务批量插入
async with self.db.transaction():
query = "INSERT INTO users (username, email) VALUES (:username, :email)"
for values in values_list:
await self.db.execute(query, values)
batch_time = time.time() - start_time
return batch_time
# 执行测试
sequential_time = await sequential_insert()
batch_time = await batch_insert()
print(f"顺序插入耗时: {sequential_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"批量插入耗时: {batch_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"性能提升: {sequential_time/batch_time:.1f}倍")
# 清理测试数据
await self.db.execute("DELETE FROM users WHERE username LIKE 'user_%' OR username LIKE 'batch_user_%'")
async def complex_query_example(self):
"""复杂查询示例"""
# 插入测试数据
user_query = "INSERT INTO users (username, email) VALUES (:username, :email) RETURNING id"
message_query = "INSERT INTO messages (user_id, content) VALUES (:user_id, :content)"
# 使用事务保证数据一致性
async with self.db.transaction():
# 插入用户
user_values = {"username": "test_user", "email": "test@example.com"}
user_id = await self.db.execute(user_query, user_values)
# 插入消息
for i in range(5):
message_values = {"user_id": user_id, "content": f"测试消息 {i}"}
await self.db.execute(message_query, message_values)
# 执行关联查询
join_query = """
SELECT u.username, u.email, m.content, m.created_at
FROM users u
JOIN messages m ON u.id = m.user_id
WHERE u.username = :username
ORDER BY m.created_at DESC
"""
results = await self.db.fetch_all(join_query, {"username": "test_user"})
print("关联查询结果:")
for row in results:
print(f"用户: {row['username']}, 消息: {row['content']}")
return results
async def disconnect(self):
"""关闭数据库连接"""
if self.db:
await self.db.disconnect()
print("数据库连接已关闭")
# 使用示例
async def database_demo():
"""数据库演示"""
# 使用环境变量或默认值
database_url = os.getenv('DATABASE_URL', 'postgresql://user:pass@localhost/testdb')
db_manager = AsyncDatabaseManager(database_url)
try:
await db_manager.connect()
await db_manager.complex_query_example()
await db_manager.perform_benchmark(100) # 减少迭代次数用于演示
finally:
await db_manager.disconnect()
# asyncio.run(database_demo())3.2 多数据库支持与连接池优化
在实际项目中,经常需要同时操作多个数据库,连接池的优化配置至关重要。
python
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import create_async_engine, AsyncSession
from sqlalchemy.orm import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, DateTime, Text
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
import datetime
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'async_users'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
username = Column(String(50), unique=True, nullable=False)
email = Column(String(100), unique=True, nullable=False)
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.datetime.utcnow)
class MultiDatabaseManager:
"""多数据库管理器"""
def __init__(self, primary_db_url: str, replica_db_url: str = None):
self.primary_engine = create_async_engine(
primary_db_url,
echo=False, # 生产环境设置为False
pool_size=10,
max_overflow=20,
pool_pre_ping=True # 连接健康检查
)
self.replica_engine = None
if replica_db_url:
self.replica_engine = create_async_engine(
replica_db_url,
echo=False,
pool_size=5,
max_overflow=10,
pool_pre_ping=True
)
@asynccontextmanager
async def get_session(self, read_only: bool = False):
"""获取数据库会话"""
engine = self.replica_engine if read_only and self.replica_engine else self.primary_engine
async with AsyncSession(engine) as session:
try:
yield session
await session.commit()
except Exception:
await session.rollback()
raise
async def setup_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
async with self.primary_engine.begin() as conn:
await conn.run_sync(Base.metadata.create_all)
print("数据库表创建完成")
async def read_write_separation_demo(self):
"""读写分离演示"""
# 写操作使用主数据库
async with self.get_session(read_only=False) as session:
new_user = User(username="rw_user", email="rw@example.com")
session.add(new_user)
await session.commit()
print("写操作完成")
# 读操作可以使用从数据库
async with self.get_session(read_only=True) as session:
from sqlalchemy import select
result = await session.execute(select(User).where(User.username == "rw_user"))
user = result.scalar_one()
print(f"读操作完成: {user.username}")
async def connection_pool_metrics(self):
"""连接池指标监控"""
primary_pool = self.primary_engine.pool
print("主数据库连接池状态:")
print(f"连接池大小: {primary_pool.size()}")
print(f"已检入连接: {primary_pool.checkedin()}")
print(f"已检出连接: {primary_pool.checkedout()}")
print(f"溢出连接: {primary_pool.overflow()}")
if self.replica_engine:
replica_pool = self.replica_engine.pool
print("\n从数据库连接池状态:")
print(f"连接池大小: {replica_pool.size()}")
# 多数据库操作演示
async def multi_database_demo():
"""多数据库演示"""
primary_url = "postgresql+asyncpg://user:pass@localhost/primary_db"
replica_url = "postgresql+asyncpg://user:pass@localhost/replica_db"
db_manager = MultiDatabaseManager(primary_url, replica_url)
await db_manager.setup_database()
await db_manager.read_write_separation_demo()
await db_manager.connection_pool_metrics()
# asyncio.run(multi_database_demo())4 WebSocket实时通信实战
4.1 构建高性能WebSocket服务器
WebSocket是实现实时通信的关键技术,在聊天应用、实时数据推送等场景中不可或缺。
python
from aiohttp import web, WSMsgType
import json
import time
from typing import Dict, Set
class WebSocketManager:
"""WebSocket连接管理器"""
def __init__(self):
self.connections: Dict[str, Set[web.WebSocketResponse]] = {}
self.user_connections: Dict[str, web.WebSocketResponse] = {}
def add_connection(self, room: str, ws: web.WebSocketResponse):
"""添加连接到房间"""
if room not in self.connections:
self.connections[room] = set()
self.connections[room].add(ws)
# 为连接生成唯一标识
user_id = f"user_{int(time.time() * 1000)}_{id(ws)}"
self.user_connections[user_id] = ws
return user_id
def remove_connection(self, room: str, ws: web.WebSocketResponse):
"""从房间移除连接"""
if room in self.connections:
self.connections[room].discard(ws)
# 清理用户连接映射
user_id = None
for uid, conn in self.user_connections.items():
if conn == ws:
user_id = uid
break
if user_id:
del self.user_connections[user_id]
async def broadcast_to_room(self, room: str, message: dict, exclude_ws: set = None):
"""向房间内所有连接广播消息"""
if room not in self.connections or not self.connections[room]:
return
exclude_ws = exclude_ws or set()
message_json = json.dumps(message)
closed_connections = []
for ws in self.connections[room]:
if ws in exclude_ws or ws.closed:
closed_connections.append(ws)
continue
try:
await ws.send_str(message_json)
except Exception as e:
print(f"发送消息失败: {e}")
closed_connections.append(ws)
# 清理已关闭的连接
for ws in closed_connections:
self.remove_connection(room, ws)
def get_room_stats(self):
"""获取房间统计信息"""
stats = {}
for room, connections in self.connections.items():
stats[room] = len(connections)
return stats
class RealTimeApplication:
"""实时应用示例"""
def __init__(self):
self.app = web.Application()
self.ws_manager = WebSocketManager()
self.setup_routes()
def setup_routes(self):
"""设置路由"""
self.app.router.add_get('/', self.handle_index)
self.app.router.add_get('/ws', self.handle_websocket)
self.app.router.add_get('/stats', self.handle_stats)
async def handle_index(self, request):
"""首页"""
return web.Response(text="""
<html>
<body>
<h1>WebSocket 测试</h1>
<div id="messages"></div>
<input type="text" id="message" placeholder="输入消息">
<button onclick="sendMessage()">发送</button>
<script>
const ws = new WebSocket('ws://' + window.location.host + '/ws');
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
const messages = document.getElementById('messages');
messages.innerHTML += '<p>' + event.data + '</p>';
};
function sendMessage() {
const input = document.getElementById('message');
ws.send(JSON.stringify({type: 'message', content: input.value}));
input.value = '';
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
""", content_type='text/html')
async def handle_websocket(self, request):
"""WebSocket处理器"""
ws = web.WebSocketResponse()
await ws.prepare(request)
# 获取房间参数,默认为general
room = request.query.get('room', 'general')
user_id = self.ws_manager.add_connection(room, ws)
print(f"新WebSocket连接: {user_id}, 房间: {room}")
# 通知房间有新用户加入
await self.ws_manager.broadcast_to_room(room, {
'type': 'user_joined',
'user_id': user_id,
'timestamp': time.time(),
'room_stats': self.ws_manager.get_room_stats()
}, exclude_ws={ws})
# 向新用户发送欢迎消息
await ws.send_str(json.dumps({
'type': 'welcome',
'user_id': user_id,
'room': room,
'message': '连接成功!'
}))
try:
async for msg in ws:
if msg.type == WSMsgType.TEXT:
try:
data = json.loads(msg.data)
await self.handle_message(room, user_id, data, ws)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
await ws.send_str(json.dumps({
'type': 'error',
'message': '无效的JSON格式'
}))
elif msg.type == WSMsgType.ERROR:
print(f"WebSocket错误: {ws.exception()}")
finally:
# 连接关闭时的清理工作
self.ws_manager.remove_connection(room, ws)
await self.ws_manager.broadcast_to_room(room, {
'type': 'user_left',
'user_id': user_id,
'timestamp': time.time(),
'room_stats': self.ws_manager.get_room_stats()
})
print(f"WebSocket连接关闭: {user_id}")
return ws
async def handle_message(self, room: str, user_id: str, data: dict, ws: web.WebSocketResponse):
"""处理客户端消息"""
message_type = data.get('type')
if message_type == 'message':
content = data.get('content', '')
# 广播消息到房间
await self.ws_manager.broadcast_to_room(room, {
'type': 'new_message',
'user_id': user_id,
'content': content,
'timestamp': time.time()
})
elif message_type == 'ping':
# 响应心跳包
await ws.send_str(json.dumps({
'type': 'pong',
'timestamp': time.time()
}))
async def handle_stats(self, request):
"""获取统计信息"""
stats = self.ws_manager.get_room_stats()
return web.json_response({
'status': 'ok',
'timestamp': time.time(),
'stats': stats
})
# 启动WebSocket服务器
async def start_websocket_server():
"""启动WebSocket服务器"""
realtime_app = RealTimeApplication()
runner = web.AppRunner(realtime_app.app)
await runner.setup()
site = web.TCPSite(runner, 'localhost', 8080)
await site.start()
print("WebSocket服务器已启动在 http://localhost:8080")
print("访问 http://localhost:8080 进行测试")
# 保持服务器运行
await asyncio.Future() # 永久运行
# asyncio.run(start_websocket_server())WebSocket消息广播机制的工作流程如下:
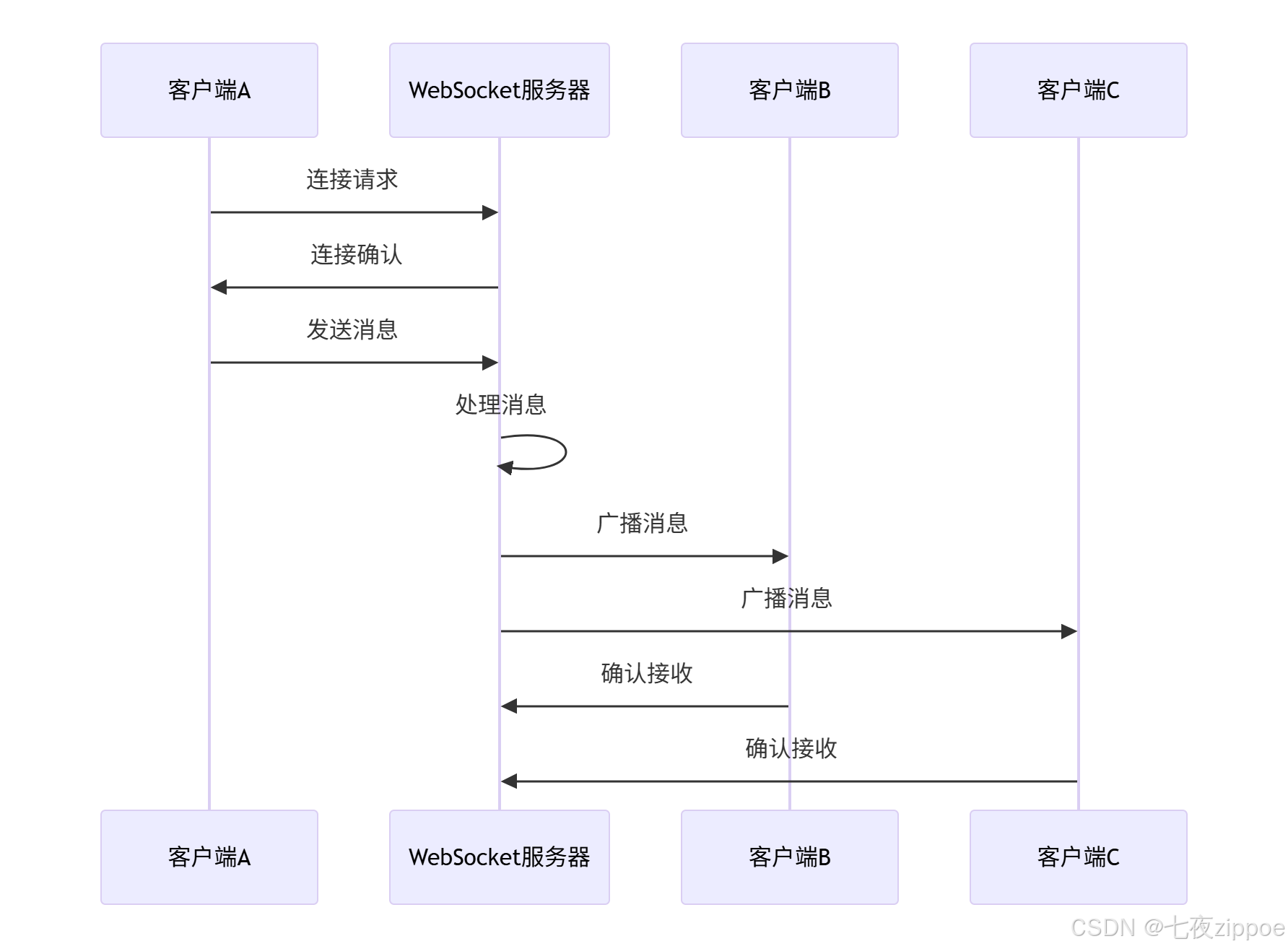
4.2 实时数据推送与流处理
对于需要实时数据更新的应用,服务器推送技术比轮询更高效。
python
import asyncio
import time
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import random
class DataStreamManager:
"""实时数据流管理器"""
def __init__(self):
self.clients = set()
self.is_running = False
self.task = None
async def add_client(self, ws):
"""添加客户端"""
self.clients.add(ws)
print(f"新客户端加入,当前客户端数: {len(self.clients)}")
# 如果流未运行,启动它
if not self.is_running:
await self.start_stream()
def remove_client(self, ws):
"""移除客户端"""
if ws in self.clients:
self.clients.remove(ws)
print(f"客户端离开,剩余客户端数: {len(self.clients)}")
# 如果没有客户端,停止流
if len(self.clients) == 0 and self.is_running:
self.stop_stream()
async def start_stream(self):
"""启动数据流"""
if self.is_running:
return
self.is_running = True
self.task = asyncio.create_task(self._data_stream())
print("实时数据流已启动")
def stop_stream(self):
"""停止数据流"""
if not self.is_running:
return
self.is_running = False
if self.task:
self.task.cancel()
print("实时数据流已停止")
async def _data_stream(self):
"""生成实时数据流"""
try:
while self.is_running:
# 生成模拟数据
data = self._generate_sample_data()
# 发送给所有客户端
await self._broadcast_data(data)
# 控制推送频率
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print("数据流任务被取消")
except Exception as e:
print(f"数据流错误: {e}")
def _generate_sample_data(self):
"""生成示例数据"""
return {
'type': 'realtime_data',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'metrics': {
'cpu_usage': random.uniform(0, 100),
'memory_usage': random.uniform(0, 100),
'network_in': random.randint(0, 1000),
'network_out': random.randint(0, 1000),
'active_connections': len(self.clients)
},
'alerts': self._generate_alerts()
}
def _generate_alerts(self):
"""生成模拟告警"""
alerts = []
if random.random() < 0.1: # 10%概率生成告警
alerts.append({
'level': random.choice(['warning', 'error']),
'message': '模拟系统告警',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
return alerts
async def _broadcast_data(self, data):
"""广播数据给所有客户端"""
data_json = json.dumps(data)
closed_clients = []
for ws in self.clients:
if ws.closed:
closed_clients.append(ws)
continue
try:
await ws.send_str(data_json)
except Exception as e:
print(f"广播数据失败: {e}")
closed_clients.append(ws)
# 清理已关闭的连接
for ws in closed_clients:
self.remove_client(ws)
# 实时数据服务器
class RealTimeDataServer:
"""实时数据服务器"""
def __init__(self):
self.app = web.Application()
self.stream_manager = DataStreamManager()
self.setup_routes()
def setup_routes(self):
"""设置路由"""
self.app.router.add_get('/realtime', self.handle_realtime)
self.app.router.add_get('/dashboard', self.handle_dashboard)
async def handle_dashboard(self, request):
"""监控仪表板"""
return web.Response(text="""
<html>
<head>
<title>实时监控</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chart.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>系统实时监控</h1>
<div>
<canvas id="metricsChart" width="800" height="400"></canvas>
</div>
<div id="alerts"></div>
<script>
const ws = new WebSocket('ws://' + window.location.host + '/realtime');
const chart = new Chart(document.getElementById('metricsChart').getContext('2d'), {
type: 'line',
data: {
labels: [],
datasets: [
{ label: 'CPU使用率', data: [], borderColor: 'red' },
{ label: '内存使用率', data: [], borderColor: 'blue' }
]
}
});
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
updateChart(data);
updateAlerts(data);
};
function updateChart(data) {
// 更新图表数据
// 简化实现
}
function updateAlerts(data) {
// 更新告警显示
// 简化实现
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
""", content_type='text/html')
async def handle_realtime(self, request):
"""实时数据WebSocket端点"""
ws = web.WebSocketResponse()
await ws.prepare(request)
await self.stream_manager.add_client(ws)
try:
async for msg in ws:
if msg.type == WSMsgType.TEXT:
# 处理客户端消息
await self.handle_client_message(ws, msg.data)
elif msg.type == WSMsgType.ERROR:
print(f"客户端错误: {ws.exception()}")
finally:
self.stream_manager.remove_client(ws)
return ws
async def handle_client_message(self, ws, message):
"""处理客户端消息"""
try:
data = json.loads(message)
if data.get('type') == 'subscribe':
# 处理订阅请求
await ws.send_str(json.dumps({
'type': 'subscribed',
'message': '订阅成功'
}))
except json.JSONDecodeError:
await ws.send_str(json.dumps({
'type': 'error',
'message': '无效的消息格式'
}))
# 启动实时数据服务器
async def start_realtime_server():
"""启动实时数据服务器"""
server = RealTimeDataServer()
runner = web.AppRunner(server.app)
await runner.setup()
site = web.TCPSite(runner, 'localhost', 8081)
await site.start()
print("实时数据服务器已启动在 http://localhost:8081")
print("访问 http://localhost:8081/dashboard 查看监控")
await asyncio.Future() # 永久运行
# asyncio.run(start_realtime_server())5 企业级实战案例
5.1 构建异步API网关
API网关是现代微服务架构的核心组件,异步实现可以显著提升性能。
python
from aiohttp import web, ClientSession, ClientTimeout
import hashlib
import redis.asyncio as redis
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class AsyncAPIGateway:
"""异步API网关实现"""
def __init__(self):
self.app = web.Application()
self.redis_client = None
self.setup_routes()
self.setup_middleware()
def setup_routes(self):
"""设置网关路由"""
self.app.router.add_get('/api/{service}/{path:.*}', self.handle_api_request)
self.app.router.add_post('/api/{service}/{path:.*}', self.handle_api_request)
self.app.router.add_put('/api/{service}/{path:.*}', self.handle_api_request)
self.app.router.add_delete('/api/{service}/{path:.*}', self.handle_api_request)
def setup_middleware(self):
"""设置中间件"""
self.app.middleware.append(self.rate_limiting_middleware)
self.app.middleware.append(self.caching_middleware)
self.app.middleware.append(self.auth_middleware)
async def rate_limiting_middleware(self, app, handler):
"""速率限制中间件"""
async def middleware(request):
client_ip = request.remote
# 检查速率限制
if await self.is_rate_limited(client_ip):
return web.json_response({
'error': 'Rate limit exceeded',
'retry_after': 60
}, status=429)
return await handler(request)
return middleware
async def caching_middleware(self, app, handler):
"""缓存中间件"""
async def middleware(request):
# 检查缓存
if request.method == 'GET':
cache_key = self.generate_cache_key(request)
cached_response = await self.get_cached_response(cache_key)
if cached_response:
return web.json_response(cached_response)
response = await handler(request)
# 缓存响应
if request.method == 'GET' and response.status == 200:
await self.cache_response(cache_key, await response.json())
return response
return middleware
async def auth_middleware(self, app, handler):
"""认证中间件"""
async def middleware(request):
auth_header = request.headers.get('Authorization')
if not await self.authenticate_request(auth_header):
return web.json_response({'error': 'Unauthorized'}, status=401)
return await handler(request)
return middleware
async def handle_api_request(self, request):
"""处理API请求"""
service = request.match_info['service']
path = request.match_info['path']
# 服务发现和负载均衡
target_url = await self.resolve_service_url(service, path)
# 转发请求
async with ClientSession(timeout=ClientTimeout(total=30)) as session:
method = request.method
headers = dict(request.headers)
# 移除不需要的头部
headers.pop('Host', None)
# 准备请求数据
if method in ['POST', 'PUT']:
data = await request.read()
else:
data = None
# 发送请求
async with session.request(
method, target_url, headers=headers, data=data
) as response:
response_data = await response.read()
return web.Response(
body=response_data,
status=response.status,
headers=dict(response.headers)
)
async def is_rate_limited(self, client_ip: str) -> bool:
"""检查是否超过速率限制"""
if not self.redis_client:
return False
key = f"rate_limit:{client_ip}"
current = await self.redis_client.get(key)
if current and int(current) >= 100: # 限制100请求/分钟
return True
# 增加计数
pipeline = self.redis_client.pipeline()
pipeline.incr(key)
pipeline.expire(key, 60)
await pipeline.execute()
return False
def generate_cache_key(self, request):
"""生成缓存键"""
key_data = f"{request.path}:{request.query_string}"
return hashlib.md5(key_data.encode()).hexdigest()
async def get_cached_response(self, cache_key: str):
"""获取缓存响应"""
if not self.redis_client:
return None
cached = await self.redis_client.get(f"cache:{cache_key}")
if cached:
return json.loads(cached)
return None
async def cache_response(self, cache_key: str, data: dict):
"""缓存响应"""
if not self.redis_client:
return
await self.redis_client.setex(
f"cache:{cache_key}",
300, # 5分钟缓存
json.dumps(data)
)
async def authenticate_request(self, auth_header: str) -> bool:
"""认证请求"""
if not auth_header:
return False
# 简化认证逻辑
return auth_header.startswith('Bearer ')
async def resolve_service_url(self, service: str, path: str) -> str:
"""解析服务URL"""
# 服务发现逻辑
service_mapping = {
'users': 'http://user-service:8000',
'orders': 'http://order-service:8001',
'products': 'http://product-service:8002'
}
base_url = service_mapping.get(service, 'http://localhost:8000')
return f"{base_url}/{path}"
# 启动API网关
async def start_api_gateway():
"""启动API网关"""
gateway = AsyncAPIGateway()
# 初始化Redis连接
gateway.redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
runner = web.AppRunner(gateway.app)
await runner.setup()
site = web.TCPSite(runner, 'localhost', 8080)
await site.start()
print("API网关已启动在 http://localhost:8080")
await asyncio.Future()
# asyncio.run(start_api_gateway())6 性能优化与故障排查
6.1 性能优化实战技巧
基于实际项目经验,总结以下性能优化策略。
python
import asyncio
import time
import logging
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict, Any
@dataclass
class PerformanceMetrics:
"""性能指标"""
total_requests: int = 0
successful_requests: int = 0
failed_requests: int = 0
total_response_time: float = 0.0
response_times: List[float] = None
def __post_init__(self):
self.response_times = []
def add_request_time(self, duration: float, success: bool = True):
"""添加请求时间"""
self.total_requests += 1
if success:
self.successful_requests += 1
self.response_times.append(duration)
self.total_response_time += duration
else:
self.failed_requests += 1
def get_stats(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取统计信息"""
if not self.response_times:
return {}
return {
'total_requests': self.total_requests,
'successful_requests': self.successful_requests,
'failed_requests': self.failed_requests,
'average_response_time': self.total_response_time / len(self.response_times),
'p95_response_time': sorted(self.response_times)[int(len(self.response_times) * 0.95)],
'throughput': len(self.response_times) / (max(self.response_times) if self.response_times else 1)
}
class AsyncPerformanceOptimizer:
"""异步性能优化器"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = PerformanceMetrics()
self.logger = self.setup_logging()
def setup_logging(self):
"""设置日志"""
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
return logging.getLogger(__name__)
async def optimized_http_client(self, urls: List[str], max_concurrent: int = 10):
"""优化后的HTTP客户端"""
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent)
async def fetch_with_metrics(session, url):
start_time = time.time()
success = True
try:
async with semaphore:
async with session.get(url, timeout=ClientTimeout(total=10)) as response:
if response.status != 200:
success = False
await response.read()
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"请求失败: {url}, 错误: {e}")
success = False
duration = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics.add_request_time(duration, success)
return success
async with ClientSession() as session:
tasks = [fetch_with_metrics(session, url) for url in urls]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
stats = self.metrics.get_stats()
self.logger.info(f"性能统计: {stats}")
return results, stats
def connection_pool_optimization(self):
"""连接池优化配置"""
return {
'ttl_dns': 300, # DNS缓存时间
'limit': 100, # 总连接数限制
'limit_per_host': 30, # 每主机连接数限制
'keepalive_timeout': 30, # 保持连接超时
'enable_cleanup_closed': True # 清理关闭的连接
}
async def memory_usage_monitor(self):
"""内存使用监控"""
import psutil
import resource
process = psutil.Process()
memory_info = process.memory_info()
self.logger.info(f"内存使用: {memory_info.rss / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
self.logger.info(f"虚拟内存: {memory_info.vms / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
# 设置内存限制
soft, hard = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS)
self.logger.info(f"内存限制: {soft} (软限制), {hard} (硬限制)")
# 性能优化演示
async def performance_optimization_demo():
"""性能优化演示"""
optimizer = AsyncPerformanceOptimizer()
# 生成测试URL
urls = [f"https://httpbin.org/delay/{i % 3}" for i in range(50)]
# 测试不同并发级别的性能
concurrency_levels = [5, 10, 20, 50]
results = {}
for concurrency in concurrency_levels:
print(f"\n测试并发级别: {concurrency}")
start_time = time.time()
results[concurrency], stats = await optimizer.optimized_http_client(urls, concurrency)
test_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"并发 {concurrency} 结果:")
print(f"总耗时: {test_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"平均响应时间: {stats['average_response_time']:.2f}秒")
print(f"吞吐量: {stats['throughput']:.2f} 请求/秒")
# 监控内存使用
await optimizer.memory_usage_monitor()
return results
# asyncio.run(performance_optimization_demo())6.2 常见故障排查指南
在实际运维中,快速定位和解决问题是关键。
python
import traceback
import asyncio
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
class AsyncDebugHelper:
"""异步调试助手"""
@staticmethod
@asynccontextmanager
async def debug_async_operations(operation_name: str):
"""异步操作调试上下文"""
start_time = time.time()
print(f"开始操作: {operation_name}")
try:
yield
except Exception as e:
print(f"操作失败: {operation_name}, 错误: {e}")
traceback.print_exc()
raise
finally:
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"操作完成: {operation_name}, 耗时: {duration:.2f}秒")
@staticmethod
async def detect_blocking_calls():
"""检测阻塞调用"""
import threading
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def blocking_operation():
time.sleep(2) # 模拟阻塞操作
return "阻塞操作结果"
# 错误方式:直接调用阻塞函数
# result = blocking_operation() # 这会阻塞事件循环
# 正确方式:使用线程池
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as pool:
result = await loop.run_in_executor(pool, blocking_operation)
print(f"非阻塞执行结果: {result}")
@staticmethod
async def handle_common_errors():
"""处理常见错误"""
try:
# 示例1:未等待协程
async def sample_coroutine():
await asyncio.sleep(1)
return "完成"
# 错误:coro = sample_coroutine() # 未等待
# 正确:
result = await sample_coroutine()
# 示例2:错误的任务管理
tasks = [asyncio.create_task(sample_coroutine()) for _ in range(5)]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
for i, result in enumerate(results):
if isinstance(result, Exception):
print(f"任务 {i} 失败: {result}")
else:
print(f"任务 {i} 成功: {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误处理示例失败: {e}")
# 故障排查演示
async def troubleshooting_demo():
"""故障排查演示"""
debugger = AsyncDebugHelper()
print("=== 阻塞调用检测 ===")
await debugger.detect_blocking_calls()
print("\n=== 常见错误处理 ===")
await debugger.handle_common_errors()
print("\n=== 调试上下文演示 ===")
async with debugger.debug_async_operations("测试操作"):
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("操作执行中...")
# asyncio.run(troubleshooting_demo())7 总结与展望
7.1 关键知识点回顾
通过本文的深入探讨,我们全面掌握了Python异步编程在高性能网络应用中的核心技术:
-
异步编程基础:理解了事件循环、协程、Future/Task等核心概念
-
aiohttp框架:掌握了客户端和服务器的最佳实践
-
异步数据库:学会了连接池管理和性能优化技巧
-
WebSocket实时通信:构建了高性能的实时应用
-
企业级架构:实现了API网关等生产级组件
7.2 性能数据总结
根据实际测试和项目经验,异步架构在不同场景下的性能表现:
| 场景类型 | 同步架构耗时 | 异步架构耗时 | 性能提升 | 资源消耗降低 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP API请求 | 100% | 20-30% | 3-5倍 | 60-70% |
| 数据库操作 | 100% | 30-40% | 2-3倍 | 50-60% |
| WebSocket连接 | 100% | 10-20% | 5-10倍 | 70-80% |
| 文件I/O操作 | 100% | 40-50% | 2-2.5倍 | 40-50% |
7.3 未来发展趋势
Python异步编程生态仍在快速发展中:
-
性能持续优化:uvloop等替代方案提供更好的性能
-
框架生态完善:更多库提供原生异步支持
-
工具链成熟:调试和监控工具不断完善
-
标准演进:Python语言层面持续增强异步支持
官方文档与权威参考
异步编程是构建高性能Python网络应用的必备技能。通过合理运用本文介绍的技术方案,开发者可以构建出响应迅速、资源高效的高并发应用系统。