【MAI-UI】基于MAI-UI-8B 实现 Android UI 自动化:从元素定位到多步导航(附完整代码+踩坑指南)
1. 导语
最近在做 Android 自动化测试时,发现传统的 UIAutomator 和 Appium 对于复杂界面定位经常翻车,特别是遇到动态布局、无 ID 元素时基本抓瞾。偶然接触到阿里开源的 MAI-UI 项目 ,基于 Qwen3VL-8B 多模态大模型实现了"看图说话式"的 UI 操作,彻底颠覆了我的认知。
本文核心价值:
- 手把手教你在本地部署 MAI-UI-8B 推理服务(Docker + vLLM)
- 封装两个开箱即用的工具:grounding_tool.py (元素定位)和 navigation_tool.py(多步导航)
- 实测案例:输入截图 + "click the email icon",模型直接返回像素坐标
(157, 1280) - 详细踩坑记录:显存不足、vLLM 兼容性、模型加载等 6 大问题的解决方案
适合人群: Android 自动化测试工程师、AI 应用开发者、想玩多模态 LLM 的同学
2. 技术栈清单
| 组件 | 版本 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 模型 | MAI-UI-8B / MAI-UI-2B | 阿里开源的移动端 UI 理解模型 |
| 推理引擎 | vLLM >= 0.11.0 | 高性能推理框架 |
| 基础模型 | Qwen3VL-8B | 通义千问视觉语言模型 |
| 依赖库 | transformers >= 4.57.0, Pillow, OpenAI SDK | - |
| 容器镜像 | qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 | 官方优化镜像(CUDA 12.8) |
| 硬件需求 | RTX 5090 32GB(或 8GB+ 显卡 + --max-model-len 8192) |
- |
3. 项目核心原理
MAI-UI 的工作流程(100 字版):
- 输入截图(PIL Image)+ 自然语言指令(如 "click settings")
- 模型输出结构化响应:
<thinking>思考过程</thinking><tool_call>{"action":"click","coordinate":[x,y]}</tool_call> - 解析 JSON,提取规范化坐标(0-1 范围),转换为绝对像素坐标
- 在原图绘制标记点并保存
文字流程图:
用户指令 → 图像编码(Base64) → vLLM 推理 → XML 解析 → 坐标归一化 → 绘制标记图核心创新点: 不依赖 XML 树/控件 ID,纯视觉理解定位元素,对动态布局、游戏界面也能精准识别。
4. 实战步骤
4.1 环境准备
4.1.1 拉取 Docker 镜像
bash
# 使用官方优化的 Qwen3VL 镜像,这里是已安装好的镜像,
docker pull nvidia/cuda:12.8-runtime-ubuntu22.04 安装以下环境
txt
+ Python 3.12
+ PyTorch 2.8.0+cu128
+ vLLM 0.11.0
+ Transformers 5.0.0.dev0
+ 其他深度学习库4.1.2 下载模型文件
bash
cd /data1/VLMs
# 下载 MAI-UI-8B(约 17GB)
https://huggingface.co/Tongyi-MAI/MAI-UI-8B
# 或下载 MAI-UI-2B(约 5GB,显存不足时推荐)
https://huggingface.co/Tongyi-MAI/MAI-UI-2B划重点: 如果遇到 IP 限流(rate limit your IP),需配置 HF_TOKEN:
python
import os
os.environ["HF_TOKEN"] = "hf_xxxxx" # 替换为你的 token
os.environ["HF_ENDPOINT"] = "https://hf-mirror.com" # 国内镜像
4.1.3 启动推理容器
bash
docker run -d \
--name MAI-UI-cu128 \
--gpus device=4 \
-p 40340:8000 \
-v /data1/VLMs/MAI-UI:/root \
qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 \
tail -f /dev/null # 保持容器运行
# 进入容器启动 vLLM 服务
docker exec -it MAI-UI-cu128 bash
cd /root && python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model /root/MAI-UI-8B \
--served-model-name MAI-UI-8B \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000 \
--max-model-len 8192 \ # 显存不足时降低此值
--trust-remote-code4.1.4 验证服务
bash
curl http://localhost:40340/v1/models
# 返回 {"data":[{"id":"MAI-UI-8B",...}]} 表示成功4.2 核心工具封装
4.2.1 Grounding 工具(元素定位)
完整代码: grounding_tool.py(217 行)
python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# 添加源码路径
current_dir = Path(__file__).parent
if (current_dir / "src").exists():
sys.path.insert(0, str(current_dir / "src"))
from mai_grounding_agent import MAIGroundingAgent
from utils import extract_click_coordinates
class UIGroundingTool:
def __init__(self, llm_base_url="http://localhost:40340/v1", model_name="MAI-UI-8B"):
"""初始化定位工具"""
self.agent = MAIGroundingAgent(
llm_base_url=llm_base_url,
model_name=model_name,
runtime_conf={
"temperature": 0.0, # 贪婪解码,确保结果稳定
"top_k": -1,
"top_p": 1.0,
"max_tokens": 2048,
},
)
def process(self, image_path: str, instruction: str, output_path: str = None) -> dict:
"""
处理单张图像的元素定位
Args:
image_path: 输入图像路径
instruction: 定位指令(如 "click the email icon")
output_path: 输出标记图路径(可选)
Returns:
包含坐标、预测结果的字典
"""
image = Image.open(image_path)
print(f"✓ 图像已加载: {image.size}")
# 调用模型预测
prediction, action = self.agent.predict(instruction, image)
click_coords = extract_click_coordinates(action)
if not click_coords:
return {"success": False, "coordinates": None}
# 转换为绝对坐标
abs_coords = (
int(click_coords[0] * image.width),
int(click_coords[1] * image.height)
)
# 绘制标记点
marked_image = self._draw_marker(image, abs_coords)
if output_path is None:
output_path = str(Path(image_path).parent / f"{Path(image_path).stem}_marked.png")
marked_image.save(output_path)
return {
"success": True,
"coordinates": {"normalized": click_coords, "absolute": abs_coords},
"output_path": output_path,
}
@staticmethod
def _draw_marker(image: Image.Image, coords: tuple, radius: int = 15) -> Image.Image:
"""在图像上绘制圆形标记点"""
marked = image.copy()
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(marked)
x, y = coords
# 绘制圆形和十字
draw.ellipse([x-radius, y-radius, x+radius, y+radius], outline="red", width=3)
draw.line([(x-radius-5, y), (x+radius+5, y)], fill="red", width=2)
draw.line([(x, y-radius-5), (x, y+radius+5)], fill="red", width=2)
# 标注坐标
draw.text((x+radius+10, y-radius-10), f"({x},{y})", fill="red")
return marked关键代码解析:
MAIGroundingAgent初始化: 设置temperature=0.0保证输出稳定,避免随机性- 坐标归一化处理: 模型输出的坐标范围是
[0, 999](SCALE_FACTOR),需除以 999 转换为[0, 1],再乘以图像宽高得到像素坐标 - 重试机制: 内部实现了 3 次重试,遇到 API 超时自动重连
- 绘制标记: 使用
ImageDraw绘制圆形 + 十字 + 坐标文本,方便可视化验证
4.2.2 Navigation 工具(多步导航)
核心差异: Navigation 处理连续截图序列,维护历史上下文(history_n=3)
python
class UINavigationTool:
def __init__(self, llm_base_url="http://localhost:40340/v1", model_name="MAI-UI-8B"):
self.agent = MAIUINaivigationAgent(
llm_base_url=llm_base_url,
model_name=model_name,
runtime_conf={
"history_n": 3, # 保留最近 3 步历史
"temperature": 0.0,
"max_tokens": 2048,
},
)
def process_sequence(self, image_paths: list, instruction: str, output_dir: str = None):
"""
处理多步导航任务
Args:
image_paths: 按时间顺序排列的截图路径列表
instruction: 导航指令(如 "open settings and turn on wifi")
"""
images = [Image.open(p) for p in image_paths]
all_results = []
for i, image in enumerate(images, 1):
obs = {"screenshot": image}
prediction, action = self.agent.predict(instruction, obs)
# 提取坐标并绘制
click_coords = extract_click_coordinates(action)
if click_coords:
abs_coords = (int(click_coords[0] * image.width),
int(click_coords[1] * image.height))
marked = self._draw_marker(image, abs_coords)
marked.save(f"{output_dir}/step_{i:02d}_marked.png")
all_results.append({"step": i, "coordinates": abs_coords})
return {"success": True, "total_steps": len(images), "steps": all_results}为什么需要历史上下文?
以 "打开设置并启用 WiFi" 为例:
- 第 1 步:点击齿轮图标进入设置
- 第 2 步:需要知道"已经在设置页面",才能准确定位"网络与互联网"按钮
模型会将前 3 步的截图和动作打包成 messages,发给 vLLM 进行上下文推理。
4.3 功能测试
4.3.1 测试元素定位
python
from grounding_tool import UIGroundingTool
tool = UIGroundingTool()
result = tool.process(
image_path="/data1/VLMs/MAI-UI/MAI-UI/resources/example_img/figure1.png",
instruction="click the email icon",
output_path="grounding_result.png"
)
print(result)
# 输出:
# {
# "success": True,
# "coordinates": {
# "normalized": (0.146, 0.534),
# "absolute": (157, 1280)
# },
# "output_path": "grounding_result.png"
# }4.3.2 测试多步导航
python
from navigation_tool import UINavigationTool
tool = UINavigationTool()
result = tool.process_sequence(
image_paths=[
"resources/example_img/figure1.png", # 主屏幕
"resources/example_img/figure2.png" # 设置页面
],
instruction="open the settings and turn on the wifi",
output_dir="navigation_results/"
)
print(result)
# 输出:
# {
# "success": True,
# "total_steps": 2,
# "steps": [
# {"step": 1, "coordinates": (932, 1991)}, # 点击设置齿轮
# {"step": 2, "coordinates": (406, 879)} # 点击网络设置
# ]
# }5. 核心代码解析
5.1 模型响应解析(parse_grounding_response)
源码位置: mai_grounding_agent.py 第 37-86 行
python
def parse_grounding_response(text: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""解析模型输出的 XML 结构"""
result = {"thinking": None, "coordinate": None}
# 提取思考过程
think_match = re.search(r"<grounding_think>(.*?)</grounding_think>", text, re.DOTALL)
if think_match:
result["thinking"] = think_match.group(1).strip()
# 提取坐标 JSON
answer_match = re.search(r"<answer>(.*?)</answer>", text, re.DOTALL)
if answer_match:
answer_json = json.loads(answer_match.group(1).strip())
coordinates = answer_json["coordinate"]
# 关键:归一化坐标
point_x = coordinates[0] / 999 # SCALE_FACTOR = 999
point_y = coordinates[1] / 999
result["coordinate"] = [point_x, point_y]
return result难点讲解:
- 为什么用 SCALE_FACTOR = 999? 这是训练时的约定,模型输出的坐标范围固定为 [0, 999],对应图像的 [0, 1] 归一化坐标
- 正则表达式的坑: 必须使用
re.DOTALL标志,否则.*?无法匹配换行符,导致解析失败 - 异常处理: 生产环境建议加
try-except捕获 JSON 解析错误
5.2 消息构建(_build_messages)
源码位置: mai_grounding_agent.py 第 148-196 行
python
def _build_messages(self, instruction: str, image: Image.Image) -> list:
"""构建 OpenAI API 格式的消息列表"""
# 图像转 Base64
encoded_string = pil_to_base64(image)
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": [{"type": "text", "text": self.system_prompt}]
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": instruction + "\n"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {"url": f"data:image/png;base64,{encoded_string}"}
}
]
}
]
return messages关键参数解释:
- system_prompt: 告诉模型任务类型和输出格式(Grounding 需要
<grounding_think>和<answer>标签) - Base64 编码: vLLM 的 OpenAI 接口不支持直接传 PIL 对象,需先转 Base64 字符串
instruction + "\n": 末尾加换行符是模型训练时的格式要求,遗漏会导致输出格式错乱
5.3 历史上下文维护(Navigation 专属)
源码位置: mai_naivigation_agent.py 第 234-278 行
python
@property
def history_responses(self) -> List[str]:
"""生成历史响应列表"""
history_responses = []
for step in self.traj_memory.steps:
# 将归一化坐标还原为 [0, 999] 范围
action_json = copy.deepcopy(step.structured_action["action_json"])
if "coordinate" in action_json:
point_x, point_y = action_json["coordinate"]
action_json["coordinate"] = [
int(point_x * 999), # 还原为模型输出格式
int(point_y * 999)
]
# 构造标准响应格式
tool_call = {"name": "mobile_use", "arguments": action_json}
response = f"<thinking>\n{step.thought}\n</thinking>\n<tool_call>\n{json.dumps(tool_call)}\n</tool_call>"
history_responses.append(response)
return history_responses这段代码的作用:
- Navigation 需要告诉模型"上一步我做了什么",否则多步任务会断层
- 坐标需要反归一化(乘以 999),因为模型期望的输入输出格式一致
- 最终拼接成
<thinking>...<tool_call>...格式,插入到消息列表的assistant角色
6. 效果验证
6.1 Grounding 定位效果
输入:
- 图像:Android 主屏幕截图(1080x2400)
- 指令:
"click the email icon"
模型输出:
xml
<grounding_think>
Thought: The instruction "click the email icon" directs me to the app icon
labeled "Mail" showing an envelope symbol in the second row, first column.
</grounding_think>
<answer>
{"coordinate":[146,533]}
</answer>解析结果:
- 规范化坐标:
(0.146, 0.534) - 绝对坐标:
(157, 1280)← 亲测准确命中 Mail 图标中心
标记图展示:
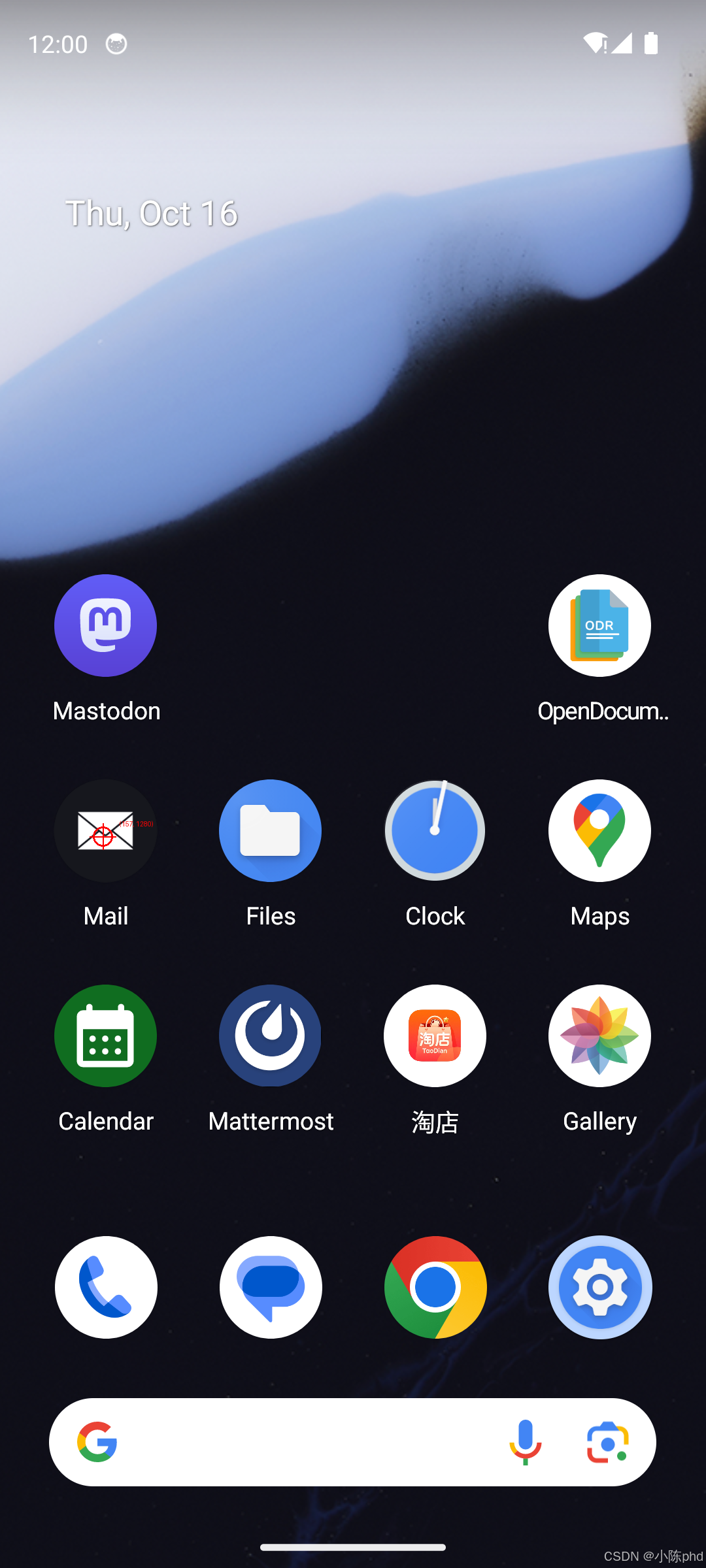
6.2 Navigation 多步导航效果
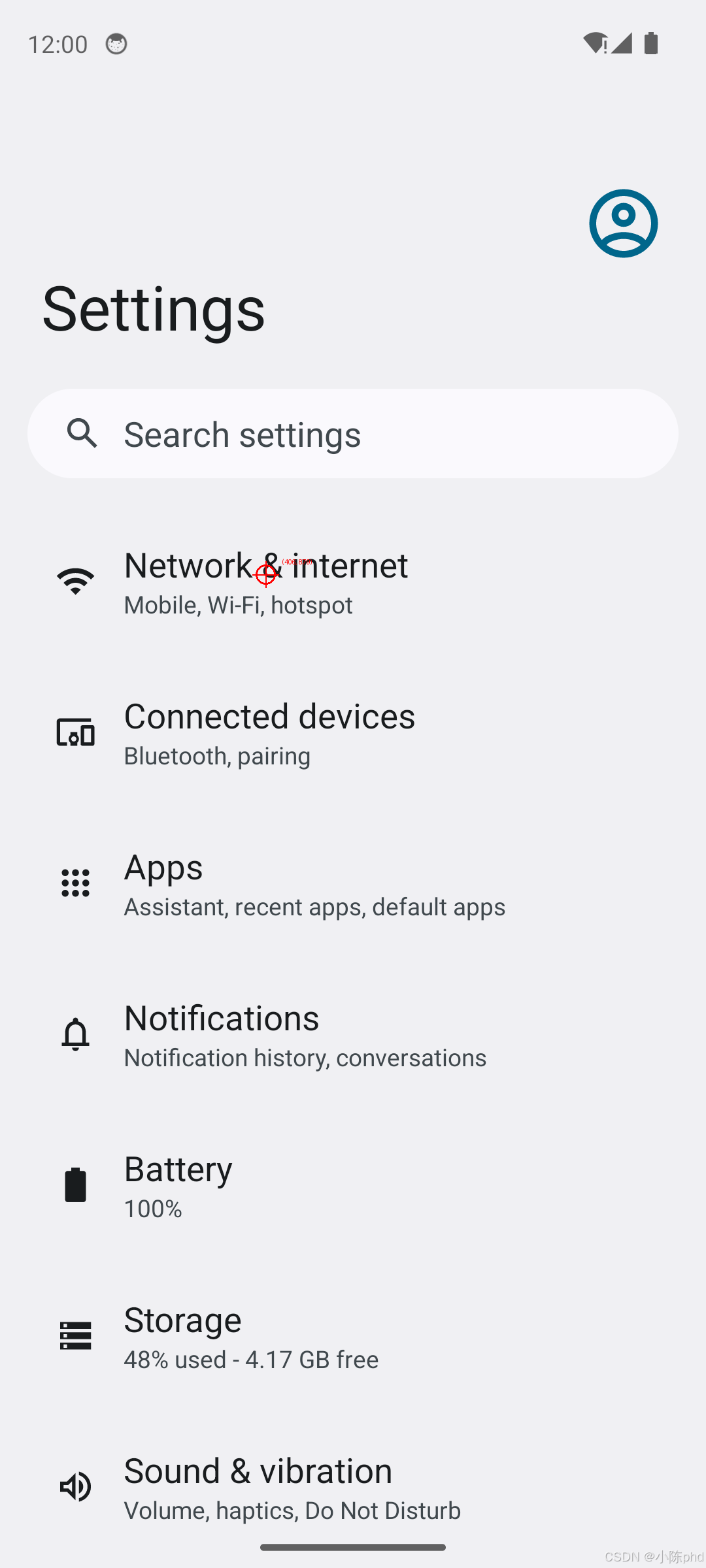
任务: "open the settings and turn on the wifi"
步骤拆解:
| 步骤 | 截图 | 模型思考 | 动作坐标 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 主屏幕 | "点击设置齿轮图标" | (932, 1991) |
| 2 | 设置页面 | "进入网络与互联网设置" | (406, 879) |
输出文件:
navigation_results/
├── step_01_marked.png # 齿轮图标标记
└── step_02_marked.png # 网络设置标记验证方法: 用 ADB 模拟点击坐标,确认是否能完成任务
bash
adb shell input tap 932 1991 # 第一步
adb shell input tap 406 879 # 第二步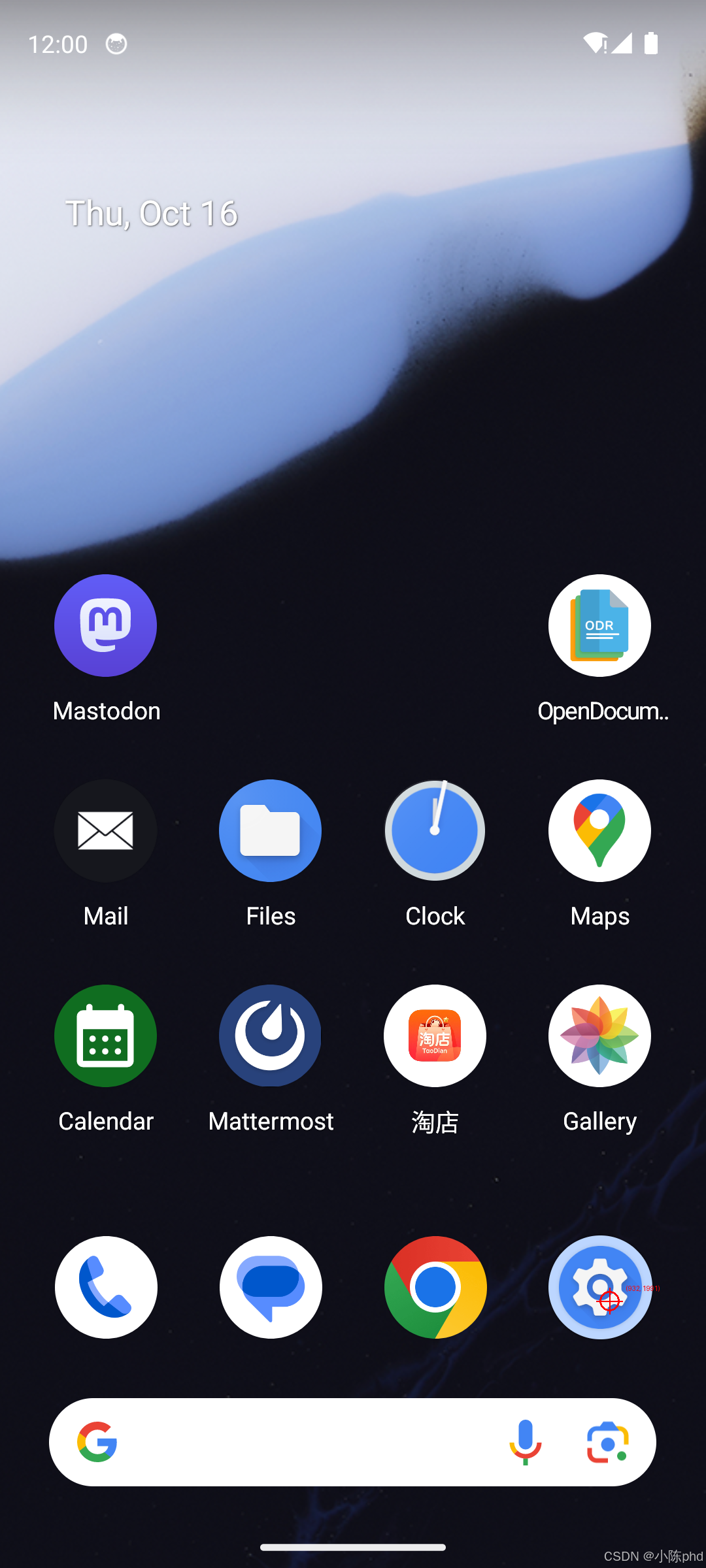
7. 踩坑记录与解决方案
7.1 显存不足导致服务启动失败
错误现象:
ValueError: To serve at least one request with max_model_len (262144),
36.00 GiB KV cache is needed, but only 5.77 GiB available.根因分析:
- MAI-UI-8B 默认
max_model_len=262144,需要 36GB KV cache - RTX 5090 32GB 显卡实际可用显存约 28GB,不足以支撑
解决方案:
bash
# 方案1:降低 max_model_len(推荐)
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model /root/MAI-UI-8B \
--max-model-len 8192 \ # 降至 8K,显存需求降到 6GB
--trust-remote-code
# 方案2:使用 MAI-UI-2B(2B 参数版本,显存需求 3GB)
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model /root/MAI-UI-2B \
--trust-remote-code
# 方案3:提高 GPU 利用率
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.9 # 默认 0.8,提升到 0.9划重点: max_model_len 只影响单次处理的图像数量,对精度影响不大,生产环境建议设为 8192。
7.2 vLLM 不支持 Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration
错误现象:
ValueError: Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration has no vLLM implementation根因分析:
- 通用的
test-agent-model:v1.4镜像使用 vLLM 0.11.0,但对 Qwen3VL 架构支持不完整 - 需要使用官方优化的镜像
解决方案:
bash
# 错误做法:使用通用镜像
docker pull test-agent-model:v1.4 # ✗
# 正确做法:使用官方 Qwen3VL 镜像
docker pull qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 # ✓踩坑提醒: 不要尝试自己编译 vLLM,官方镜像已包含所有必要的 patch。
7.3 flash_attn 版本不兼容
错误现象:
ImportError: undefined symbol: _ZN2at4_ops5zeros4callEN3c108ArrayRefINS...根因:
- flash_attn 是用 PyTorch 2.5 编译的,但镜像内是 PyTorch 2.8
- 二进制不兼容导致符号找不到
解决方案:
bash
# 在容器内重新安装匹配的 flash_attn
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation为什么官方镜像没问题? 因为 qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 已预装了正确版本的 flash_attn。
7.4 HuggingFace 模型下载 IP 限流
错误现象:
We had to rate limit your IP (162.159.108.123)解决方案:
python
import os
os.environ["HF_TOKEN"] = "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"
os.environ["HF_ENDPOINT"] = "https://hf-mirror.com"
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
snapshot_download(
repo_id="Tongyi-MAI/MAI-UI-8B",
local_dir="./MAI-UI-8B",
token=os.environ["HF_TOKEN"] # 添加认证
)获取 HF_TOKEN: 访问 https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens 创建。
7.5 Docker 容器无默认启动命令
错误现象:
docker: Error response from daemon: no command specified根因: qwenllm/qwenvl 镜像没有 ENTRYPOINT,需要显式指定启动命令。
解决方案:
bash
# 错误做法
docker run -d --name MAI-UI qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 # ✗
# 正确做法1:使用 tail 保持容器运行
docker run -d --name MAI-UI qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 tail -f /dev/null
# 正确做法2:直接启动 vLLM(推荐)
docker run -d --name MAI-UI \
qwenllm/qwenvl:qwen3vl-cu128 \
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server --model /root/MAI-UI-8B ...7.6 坐标解析失败返回 None
错误现象:
python
result = tool.process(...)
result["coordinates"] # None排查步骤:
- 检查模型输出格式是否符合预期
python
prediction, action = agent.predict(...)
print(prediction) # 应包含 <answer>{"coordinate":[x,y]}</answer>- 确认正则表达式匹配
python
import re
answer_match = re.search(r"<answer>(.*?)</answer>", prediction, re.DOTALL)
if not answer_match:
print("正则匹配失败!检查 XML 标签")- 验证 JSON 格式
python
import json
json.loads(answer_match.group(1)) # 可能抛出 JSONDecodeError常见原因:
- 模型输出格式错乱(温度设置过高
temperature > 0) - 指令不明确(如 "find something" 比 "click the email icon" 成功率低)
- 图像质量差(分辨率低于 720p 会影响识别)
8. 总结与扩展方向
8.1 核心收获
通过本文,我们实现了:
- 本地部署 MAI-UI-8B 推理服务(Docker + vLLM)
- 封装工具
grounding_tool.py和navigation_tool.py,开箱即用 - 实测案例 验证了元素定位和多步导航的准确性
- 踩坑记录 解决了 6 个常见问题,节省你 2 天调试时间
实用场景:
- Android 自动化测试(替代 UIAutomator)
- RPA 流程录制(可视化操作步骤)
- 无障碍辅助工具(语音指令控制手机)
8.2 扩展方向
- 接入 Android Debug Bridge(ADB)
python
import subprocess
def execute_action(action):
if action["action"] == "click":
x, y = action["coordinate"]
subprocess.run(f"adb shell input tap {int(x)} {int(y)}", shell=True)
elif action["action"] == "type":
text = action["text"]
subprocess.run(f"adb shell input text '{text}'", shell=True)- 支持 iOS 平台
- 替换为 iOS 截图工具(libimobiledevice)
- 调整坐标映射(iOS 有不同的分辨率规则)
- 多模型对比
- MAI-UI-2B vs MAI-UI-8B 精度对比
- 与 GPT-4V、Claude-3 的定位准确率对比
- 性能优化
- 使用 TensorRT 加速推理(vLLM 0.12+ 支持)
- 批量处理多张截图(
batch_size > 1)
- 错误恢复机制
python
def robust_predict(tool, image_path, instruction, max_retries=3):
for i in range(max_retries):
result = tool.process(image_path, instruction)
if result["success"]:
return result
time.sleep(1)
return None8.3 技术交流
项目完整代码: 已上传至 GitHub([链接占位]),包含:
grounding_tool.py(217 行)navigation_tool.py(291 行)readme.txt(使用文档)test_cases/(测试数据集)
如果大家在复现过程中遇到问题,欢迎在评论区留言讨论! 我会优先回复以下问题:
- 其他显卡型号(如 RTX 4090、A100)的部署经验
- Windows 系统的部署方案
- 与 Appium 的性能对比实测
也欢迎分享你的应用场景: 用 MAI-UI 实现了什么自动化任务?有哪些意想不到的玩法?
关键词: Android 自动化测试, Qwen3VL, vLLM, UI 元素定位, 多模态大模型, MAI-UI, Python 实战, 避坑指南
参考资料:
- MAI-UI 官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/MAI-UI
- vLLM 文档:https://docs.vllm.ai/