作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo

学习如何使用 LangGraph 和 Elasticsearch 构建 人机交互 agents,在决策过程中引入人类,以填补上下文空白,并在执行之前审查 tool 调用。
Agent Builder 现在以技术预览形式提供。使用 Elastic Cloud Trial 开始,并在这里查看 Agent Builder 的文档。
在本文中,我们将探索如何结合 LangGraph 和 Elasticsearch 来构建 人机交互( HITL )应用。这种方法允许 AI 系统直接让用户参与决策过程,使交互更加可靠且具备上下文感知能力。我们将通过一个基于上下文的实际示例,演示 LangGraph 工作流如何与 Elasticsearch 集成,以检索数据、处理用户输入,并生成优化后的结果。
要求
- NodeJS 版本 18 或更新
- OpenAI API Key
- Elasticsearch 8.x+ 部署
为什么在生产级人机交互( HITL )系统中使用 LangGraph
在之前的一篇文章中,我们介绍了 LangGraph 以及它在使用 LLMs 和条件边(conditional edges )构建 RAG 系统方面的优势,从而可以自动做出决策并展示结果。有时,我们并不希望系统端到端地完全自主执行,而是希望用户在执行循环中选择选项并做出决策。这个概念被称为人机交互(**Human in the loop - ** HITL )。
人机交互( human-in-the-loop )或在循环中
这是一个 AI 概念,允许真实的人与 AI 系统进行交互,以提供更多上下文、评估响应、编辑响应、请求更多信息等。这在低容错场景中非常有用,例如合规、决策或内容生成,有助于提升 LLM 输出的可靠性。
一个常见的例子是,当你的编程助手在终端( terminal )中请求你授权执行某个命令,或者在开始编码之前向你展示逐步的思考过程,让你先进行确认。
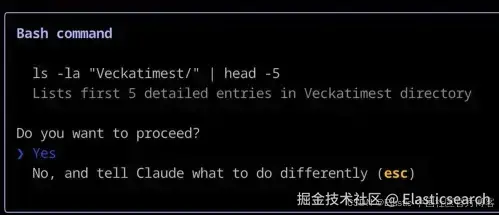 Claude Code 使用 人机交互( human-in-the-loop )在执行 Bash 命令之前向你请求确认
Claude Code 使用 人机交互( human-in-the-loop )在执行 Bash 命令之前向你请求确认
Elasticsearch + LangGraph:它们如何交互
LangChain 允许我们将 Elasticsearch 用作向量存储,并在 LangGraph 应用中执行查询,这对于执行全文或语义搜索非常有用,而 LangGraph 用于定义具体的工作流、工具和交互。它还将 HITL 作为与用户的额外交互层加入。
实际实现:人机交互
假设有一个律师对他最近处理的案件有疑问。如果没有合适的工具,他需要手动搜索法律文章和判例,完整阅读,然后解释它们如何适用于他的情况。然而,使用 LangGraph 和 Elasticsearch,我们可以构建一个系统,搜索法律判例数据库,并生成结合律师提供的具体细节和上下文的案件分析。
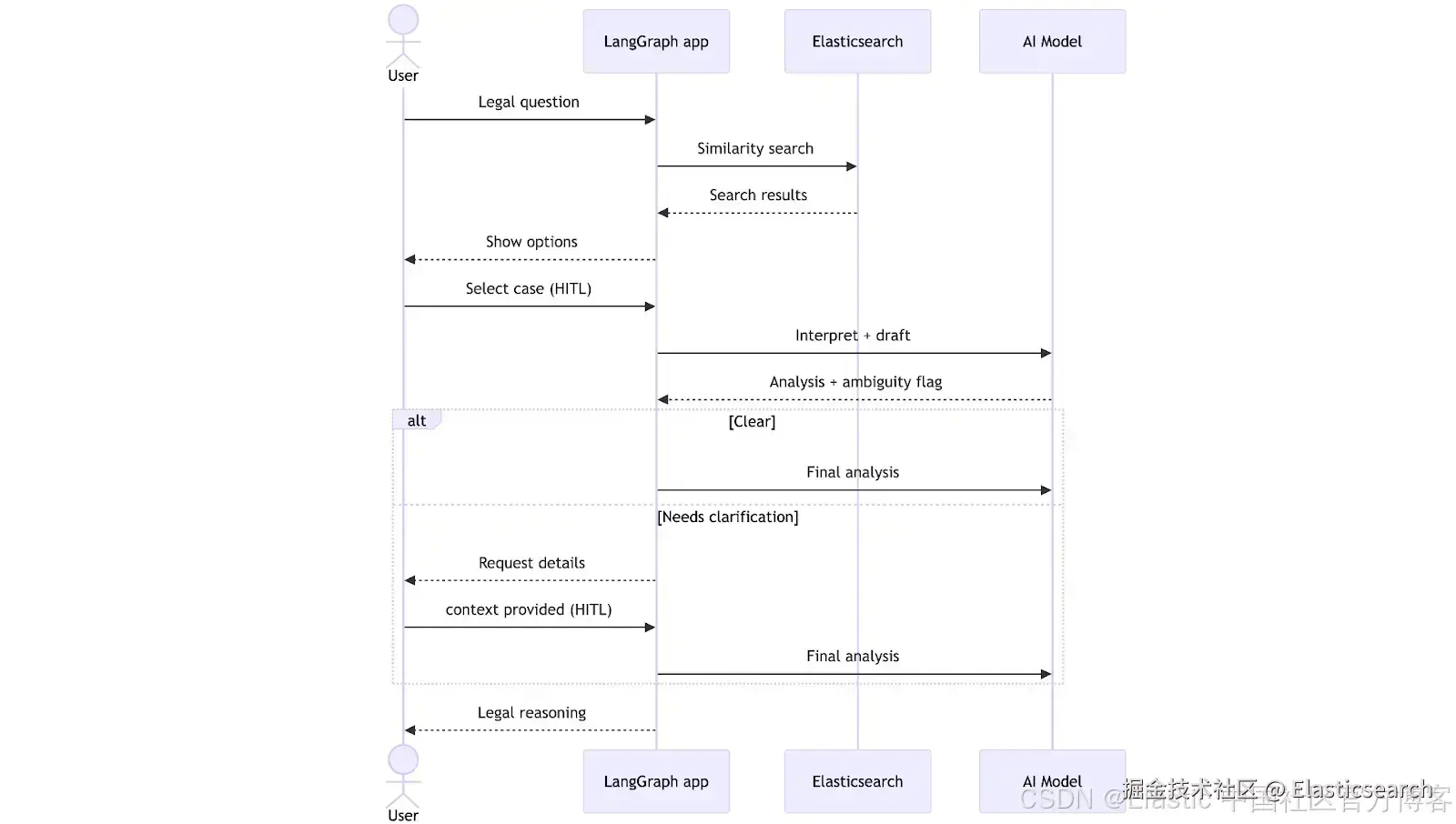
工作流从律师提交法律问题开始。系统在 Elasticsearch 中执行向量搜索,检索最相关的判例,并以自然语言呈现给律师选择。选择完成后,LLM 生成初步分析并检查信息是否完整。此时,工作流可以有两种路径:如果所有信息清晰,则直接生成最终分析;如果不清晰,则暂停以向律师请求澄清。一旦提供了缺失的上下文,系统完成分析并返回结果,同时考虑澄清内容。
下图是 LangGraph 绘制的图,显示应用开发完成后的结构。每个节点代表一个工具或功能:
数据集
这是本示例将使用的数据集。该数据集包含一系列法律判例,每个判例描述了涉及服务延迟的案件、法院的推理以及最终判决结果。
less
`
1. [2. {3. "pageContent": "Legal precedent: Case B - Service delay not considered breach. A consulting contract used term 'timely delivery' without specific dates. A three-week delay occurred but contract lacked explicit schedule. Court ruled no breach as parties had not defined concrete timeline and delay did not cause demonstrable harm.",4. "metadata": {5. "caseId": "CASE-B-2022",6. "contractType": "consulting agreement",7. "delayPeriod": "three weeks",8. "outcome": "no breach found",9. "reasoning": "no explicit deadline defined, no demonstrable harm",10. "keyTerms": "timely delivery, open terms, schedule definition",11. "title": "Case B: Delay Without Explicit Schedule"12. }13. },14. ...15. ]
`AI写代码数据摄取与索引设置
索引设置和数据摄取逻辑在 dataIngestion.ts文件中定义,我们在其中声明了用于处理索引创建的函数。此设置与 LangChain 的 Elasticsearch 向量存储接口兼容。
注意 :映射设置也包含在 dataIngestion.ts 文件中。
安装包并设置环境变量
让我们使用默认设置初始化一个 Node.js 项目:
- @elastic/elasticsearch:Node.js 的 Elasticsearch 客户端。用于连接、创建索引和运行查询。
- @langchain/community:提供对社区支持工具的集成,包括 ElasticVectorSearch 存储。
- @langchain/core:LangChain 的核心构建模块,如 chains、prompts 和工具函数。
- @langchain/langgraph:添加基于图的编排,允许使用节点、边和状态管理的工作流。
- @langchain/openai:通过 LangChain 访问 OpenAI 模型(LLMs 和 embeddings)。
- dotenv:将 .env 文件中的环境变量加载到 process.env 中。
- tsx:用于执行 TypeScript 代码的实用工具。
在控制台运行以下命令来安装所有依赖:
sql
`npm install @elastic/elasticsearch @langchain/community @langchain/core @langchain/langgraph @langchain/openai dotenv --legacy-peer-deps && npm install --save-dev tsx`AI写代码创建一个 .env 文件来设置环境变量:
ini
`
1. ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT=
2. ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY=
3. OPENAI_API_KEY=
`AI写代码我们将使用 TypeScript 编写代码,因为它提供类型安全层并改善开发者体验。创建一个名为 main.ts 的 TypeScript 文件,并插入下一节的代码。
包导入
在 main.ts 文件中,我们首先导入所需模块并初始化环境变量配置。这包括 LangGraph 的核心组件、OpenAI 模型集成以及 Elasticsearch 客户端。
我们还从 dataIngestion.ts 文件中导入以下内容:
- ingestData:用于创建索引并摄取数据的函数。
- Document 和 DocumentMetadata:定义数据集文档结构的接口。
Elasticsearch 向量存储客户端、embeddings 客户端和 OpenAI 客户端
这段代码将初始化向量存储、embeddings 客户端以及一个 OpenAI 客户端。
ini
`
1. const VECTOR_INDEX = "legal-precedents";
3. const llm = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-4o-mini" });
4. const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({
5. model: "text-embedding-3-small",
6. });
8. const esClient = new Client({
9. node: process.env.ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT,
10. auth: {
11. apiKey: process.env.ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY ?? "",
12. },
13. });
15. const vectorStore = new ElasticVectorSearch(embeddings, {
16. client: esClient,
17. indexName: VECTOR_INDEX,
18. });
`AI写代码应用工作流状态 schema 将有助于节点之间的通信:
markdown
`
1. const LegalResearchState = Annotation.Root({
2. query: Annotation<string>(),
3. analyzedConcepts: Annotation<string[]>(),
4. precedents: Annotation<Document[]>(),
5. selectedPrecedent: Annotation<Document | null>(),
6. draftAnalysis: Annotation<string>(),
7. ambiguityDetected: Annotation<boolean>(),
8. userClarification: Annotation<string>(),
9. finalAnalysis: Annotation<string>(),
10. });
`AI写代码在 state 对象中,我们将通过节点传递用户的查询、从中提取的概念、检索到的法律判例,以及检测到的任何歧义。state 还会跟踪用户选择的判例、过程中生成的分析草稿,以及在所有澄清完成后生成的最终分析。
节点
searchPrecedents:该节点根据用户输入在 Elasticsearch 向量存储中执行相似性搜索。它最多检索 5 个匹配文档并打印出来,以便用户进行审阅。
javascript
``
1. async function searchPrecedents(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. console.log(
3. "📚 Searching for relevant legal precedents with query:\n",
4. state.query
5. );
7. const results = await vectorStore.similaritySearch(state.query, 5);
8. const precedents = results.map((d) => d as Document);
10. console.log(`Found ${precedents.length} relevant precedents:\n`);
12. for (let i = 0; i < precedents.length; i++) {
13. const p = precedents[i];
14. const m = p.metadata;
15. console.log(
16. `${i + 1}. ${m.title} (${m.caseId})\n` +
17. ` Type: ${m.contractType}\n` +
18. ` Outcome: ${m.outcome}\n` +
19. ` Key reasoning: ${m.reasoning}\n` +
20. ` Delay period: ${m.delayPeriod}\n`
21. );
22. }
24. return { precedents };
25. }
``AI写代码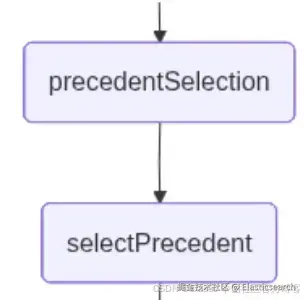
precedentSelection :该节点允许用户使用自然语言选择通过相似性搜索检索到的最符合问题的用例。在此阶段,应用会中断工作流并等待用户输入。
ini
`
1. function precedentSelection(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. console.log("\n⚖️ HITL #1: Human input needed\n");
3. const question = "👨⚖️ Which precedent is most similar to your case? ";
4. const userChoice = interrupt({ question });
6. return { userChoice };
7. }
`AI写代码selectPrecedent:该节点将用户输入以及检索到的文档发送出去进行解析,以便从中选择一个文档。LLM 执行此任务,通过返回一个数字表示它根据用户的自然语言输入推断出的文档。
javascript
``
1. async function selectPrecedent(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. const precedents = state.precedents || [];
3. const userInput = (state as any).userChoice || "";
5. const precedentsList = precedents
6. .map((p, i) => {
7. const m = p.metadata;
8. return `${i + 1}. ${m.caseId}: ${m.title} - ${m.outcome}`;
9. })
10. .join("\n");
12. const structuredLlm = llm.withStructuredOutput({
13. name: "precedent_selection",
14. schema: {
15. type: "object",
16. properties: {
17. selected_number: {
18. type: "number",
19. description:
20. "The precedent number selected by the lawyer (1-based index)",
21. minimum: 1,
22. maximum: precedents.length,
23. },
24. },
25. required: ["selected_number"],
26. },
27. });
29. const prompt = `
30. The lawyer said: "${userInput}"
32. Available precedents:
33. ${precedentsList}
35. Which precedent number (1-${precedents.length}) matches their selection?
36. `;
38. const response = await structuredLlm.invoke([
39. {
40. role: "system",
41. content:
42. "You are an assistant that interprets lawyer's selection and returns the corresponding precedent number.",
43. },
44. { role: "user", content: prompt },
45. ]);
47. const selectedIndex = response.selected_number - 1;
48. const selectedPrecedent = precedents[selectedIndex] || precedents[0];
50. console.log(`✅ Selected: ${selectedPrecedent.metadata.title}\n`);
51. return { selectedPrecedent };
52. }
``AI写代码收起代码块
createDraft:该节点根据用户选择的先例生成初步法律分析。它使用 LLM 评估所选先例如何适用于律师的问题,并判断系统是否拥有足够信息继续操作。
如果先例可以直接应用,该节点生成初稿分析,并沿正确路径跳转到最终节点。如果 LLM 检测到歧义,例如未定义的合同条款、缺失的时间线细节或不清晰的条件,它会返回一个标记,表示需要澄清,同时提供必须提供的具体信息列表。在这种情况下,歧义会触发图的左侧路径。
typescript
``
1. async function createDraft(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. console.log("📝 Drafting initial legal analysis...\n");
4. const precedent = state.selectedPrecedent;
5. if (!precedent) return { draftAnalysis: "" };
7. const m = precedent.metadata;
9. const structuredLlm = llm.withStructuredOutput({
10. name: "draft_analysis",
11. schema: {
12. type: "object",
13. properties: {
14. needs_clarification: {
15. type: "boolean",
16. description:
17. "Whether the analysis requires clarification about contract terms or context",
18. },
19. analysis_text: {
20. type: "string",
21. description: "The draft legal analysis or the ambiguity explanation",
22. },
23. missing_information: {
24. type: "array",
25. items: { type: "string" },
26. description:
27. "List of specific information needed if clarification is required (empty if no clarification needed)",
28. },
29. },
30. required: ["needs_clarification", "analysis_text", "missing_information"],
31. },
32. });
34. const prompt = `
35. Based on this precedent:
36. Case: ${m.title}
37. Outcome: ${m.outcome}
38. Reasoning: ${m.reasoning}
39. Key terms: ${m.keyTerms}
41. And the lawyer's question: "${state.query}"
43. Draft a legal analysis applying this precedent to the question.
45. If you need more context about the specific contract terms, timeline details,
46. or other critical information to provide accurate analysis, set needs_clarification
47. to true and list what information is missing.
49. Otherwise, provide the legal analysis directly.
50. `;
52. const response = await structuredLlm.invoke([
53. {
54. role: "system",
55. content:
56. "You are a legal research assistant that analyzes cases and identifies when additional context is needed.",
57. },
58. { role: "user", content: prompt },
59. ]);
61. let displayText: string;
62. if (response.needs_clarification) {
63. const missingInfoList = response.missing_information
64. .map((info: string, i: number) => `${i + 1}. ${info}`)
65. .join("\n");
66. displayText = `AMBIGUITY DETECTED:\n${response.analysis_text}\n\nMissing information:\n${missingInfoList}`;
67. } else {
68. displayText = `ANALYSIS:\n${response.analysis_text}`;
69. }
71. console.log(displayText + "\n");
73. return {
74. draftAnalysis: displayText,
75. ambiguityDetected: response.needs_clarification,
76. };
77. }
``AI写代码收起代码块图中可能走的两条路径如下所示:
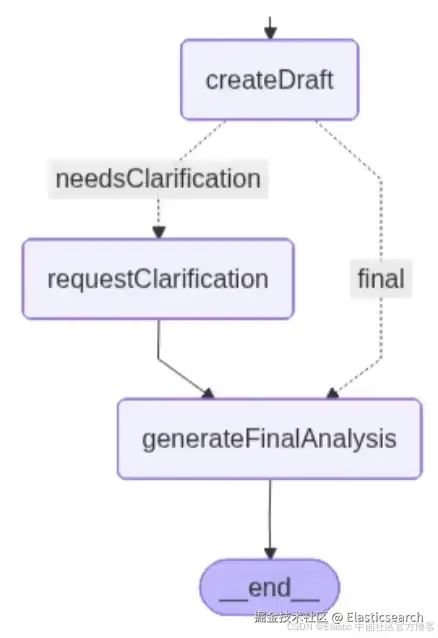
左侧路径包括一个额外的节点,用于处理澄清。
requestClarification:当系统发现初稿分析缺少关键上下文时,此节点触发第二个人机交互步骤。工作流会中断,并要求用户澄清前一个节点检测到的缺失合同细节。
markdown
`
1. function requestClarification(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. console.log("\n⚖️ HITL #2: Additional context needed\n");
3. const userClarification = interrupt({
4. question: "👨⚖️ Please provide clarification about your contract terms:",
5. });
6. return { userClarification };
7. }
`AI写代码generateFinalAnalysis:此节点生成最终的法律分析,通过将所选判例与用户提供的额外上下文(如需要)结合。利用前一步人机交互收集的澄清信息,LLM 综合判例推理、用户提供的合同细节,以及判断是否可能存在违约的条件。
该节点输出一个完整的分析,整合法律解读和实际建议。
markdown
``
1. async function generateFinalAnalysis(state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) {
2. console.log("📋 Generating final legal analysis...\n");
4. const precedent = state.selectedPrecedent;
5. if (!precedent) return { finalAnalysis: "" };
7. const m = precedent.metadata;
9. const prompt = `
10. Original question: "${state.query}"
12. Selected precedent: ${m.title}
13. Outcome: ${m.outcome}
14. Reasoning: ${m.reasoning}
16. Lawyer's clarification: "${state.userClarification}"
18. Provide a comprehensive legal analysis integrating:
19. 1. The selected precedent's reasoning
20. 2. The lawyer's specific contract context
21. 3. Conditions for breach vs. no breach
22. 4. Practical recommendations
23. `;
25. const response = await llm.invoke([
26. {
27. role: "system",
28. content:
29. "You are a legal research assistant providing comprehensive analysis.",
30. },
31. { role: "user", content: prompt },
32. ]);
34. const finalAnalysis = response.content as string;
36. console.log(
37. "\n" +
38. "=".repeat(80) +
39. "\n" +
40. "⚖️ FINAL LEGAL ANALYSIS\n" +
41. "=".repeat(80) +
42. "\n\n" +
43. finalAnalysis +
44. "\n\n" +
45. "=".repeat(80) +
46. "\n"
47. );
49. return { finalAnalysis };
50. }
``AI写代码收起代码块构建图:
kotlin
`
1. const workflow = new StateGraph(LegalResearchState)
2. .addNode("analyzeQuery", analyzeQuery)
3. .addNode("searchPrecedents", searchPrecedents)
4. .addNode("precedentSelection", precedentSelection)
5. .addNode("selectPrecedent", selectPrecedent)
6. .addNode("createDraft", createDraft)
7. .addNode("requestClarification", requestClarification)
8. .addNode("generateFinalAnalysis", generateFinalAnalysis)
9. .addEdge("__start__", "analyzeQuery")
10. .addEdge("analyzeQuery", "searchPrecedents")
11. .addEdge("searchPrecedents", "precedentSelection") // HITL #1
12. .addEdge("precedentSelection", "selectPrecedent")
13. .addEdge("selectPrecedent", "createDraft")
14. .addConditionalEdges(
15. "createDraft",
16. (state: typeof LegalResearchState.State) => {
17. // If ambiguity detected, request clarification (HITL #2)
18. if (state.ambiguityDetected) return "needsClarification";
19. // Otherwise, generate final analysis
20. return "final";
21. },
22. {
23. needsClarification: "requestClarification",
24. final: "generateFinalAnalysis",
25. }
26. )
27. .addEdge("requestClarification", "generateFinalAnalysis") // HITL #2
28. .addEdge("generateFinalAnalysis", "__end__");
`AI写代码在图中,我们可以看到条件边定义了选择"final"路径的条件。如图所示,决策现在取决于草稿分析是否检测到需要额外澄清的歧义。
将所有部分组合在一起以执行:
typescript
``
1. await ingestData();
3. // Compile workflow
4. const app = workflow.compile({ checkpointer: new MemorySaver() });
5. const config = { configurable: { thread_id: "hitl-circular-thread" } };
7. await saveGraphImage(app);
9. // Execute workflow
10. const legalQuestion =
11. "Does a pattern of repeated delays constitute breach even if each individual delay is minor?";
13. console.log(`⚖️ LEGAL QUESTION: "${legalQuestion}"\n`);
15. let currentState = await app.invoke({ query: legalQuestion }, config);
17. // Handle all interruptions in a loop
18. while ((currentState as any).__interrupt__?.length > 0) {
19. console.log("\n💭 APPLICATION PAUSED WAITING FOR USER INPUT...");
21. const interruptQuestion = (currentState as any).__interrupt__[0]?.value
22. ?.question;
23. const userChoice = await getUserInput(
24. interruptQuestion || "👤 YOUR CHOICE: "
25. );
27. currentState = await app.invoke(
28. new Command({ resume: userChoice }),
29. config
30. );
31. }
``AI写代码执行脚本:
在所有代码准备好之后,通过在终端中输入以下命令来执行 main.ts 文件:
css
`tsx main.ts`AI写代码一旦脚本执行,问题 "Does a pattern of repeated delays constitute breach even if each individual delay is minor?" 将被发送到 Elasticsearch 执行相似度搜索,并显示从索引中检索到的结果。应用程序检测到多个相关判例与查询匹配,因此暂停执行并请求用户帮助澄清哪一个法律判例最适用:
yaml
`1. 📚 Searching for relevant legal precedents with query:
2. Does a pattern of repeated delays constitute breach even if each individual delay is minor?
3. Found 5 relevant precedents:
5. 1. Case H: Pattern of Repeated Delays (CASE-H-2021)
6. Type: ongoing service agreement
7. Outcome: breach found
8. Key reasoning: pattern demonstrated failure to perform, cumulative effect
9. Delay period: multiple instances
11. 2. Case E: Minor Delay Quality Maintained (CASE-E-2022)
12. Type: service agreement
13. Outcome: minor breach only
14. Key reasoning: delay minimal, quality maintained, termination unjustified
15. Delay period: five days
17. 3. Case A: Delay Breach with Operational Impact (CASE-A-2023)
18. Type: service agreement
19. Outcome: breach found
20. Key reasoning: delay affected operations and caused financial harm
21. Delay period: two weeks
23. 4. Case B: Delay Without Explicit Schedule (CASE-B-2022)
24. Type: consulting agreement
25. Outcome: no breach found
26. Key reasoning: no explicit deadline defined, no demonstrable harm
27. Delay period: three weeks
29. 5. Case C: Justified Delay External Factors (CASE-C-2023)
30. Type: construction service
31. Outcome: no breach found
32. Key reasoning: external factors beyond control, force majeure applied
33. Delay period: one month
35. ⚖️ HITL #1: Human input needed
37. 💭 APPLICATION PAUSED WAITING FOR USER INPUT...
38. 👨⚖️ Which precedent is most similar to your case?` AI写代码这个应用程序有趣的地方在于,我们可以使用自然语言来选择一个选项,让 LLM 解释用户的输入以确定正确的选择。让我们看看如果输入文本:"Case H" 会发生什么。
vbnet
`
1. 💭 APPLICATION PAUSED WAITING FOR USER INPUT...
2. 👨⚖️ Which precedent is most similar to your case? Case H
4. ✅ Selected: Case H: Pattern of Repeated Delays
6. 📝 Drafting initial legal analysis...
8. AMBIGUITY DETECTED:
9. Based on Case H, a pattern of repeated delays can indeed constitute a breach of contract, even if each individual delay is minor. The outcome in Case H indicates that the cumulative effect of these minor delays led to a significant failure to perform the contractual obligations adequately. The reasoning emphasizes that consistent performance is critical in fulfilling the terms of a contract. Therefore, if the repeated delays create a situation where the overall performance is hindered, this pattern could be interpreted as a breach. However, the interpretation may depend on the specific terms of the contract at issue, as well as the expectations of performance set forth in that contract.
11. Missing information:
12. 1. Specific contract terms regarding performance timelines
13. 2. Details on the individual delays (duration, frequency)
14. 3. Context on consequences of delays stated in the contract
15. 4. Other parties' expectations or agreements related to performance
18. ⚖️ HITL #2: Additional context needed
21. 💭 APPLICATION PAUSED WAITING FOR USER INPUT...
22. 👨⚖️ Please provide clarification about your contract terms:
`AI写代码模型会接收用户的澄清并将其整合到工作流中,一旦提供了足够的上下文,就会继续进行最终分析。在此步骤中,系统还会利用先前检测到的歧义:初稿分析指出合同中缺失的细节可能会显著影响法律解释。这些"缺失信息"项引导模型确定在生成可靠最终意见之前,需要哪些澄清以消除不确定性。
用户必须在下一次输入中包含所请求的澄清。我们尝试输入:"Contract requires 'prompt delivery' without timelines. 8 delays of 2-4 days over 6 months. $50K in losses from 3 missed client deadlines. Vendor notified but pattern continued."
vbnet
`
1. 💭 APPLICATION PAUSED WAITING FOR USER INPUT...
2. 👨⚖️ Please provide clarification about your contract terms: Contract requires "prompt delivery" without timelines. 8 delays of 2-4 days over 6 months. $50K in losses from 3 missed client deadlines. Vendor notified but pattern continued.
4. 📋 Generating final legal analysis...
6. ================================================================================
7. ⚖️ FINAL LEGAL ANALYSIS
8. ================================================================================
10. To analyze the question of whether a pattern of repeated minor delays constitutes a breach of contract, we need to combine insights from the selected precedent, the specifics of the lawyer's contract situation, conditions that typically govern breach versus non-breach, and practical recommendations for the lawyer moving forward.
12. ### 1. Selected Precedent's Reasoning
14. The precedent case, referred to as Case H, found that a pattern of repeated delays amounted to a breach of contract. The court reasoned that even minor individual delays, when considered cumulatively, demonstrated a failure to perform as stipulated in the contract. The underlying rationale was that the cumulative effect of these minor delays could significantly undermine the purpose of the contract, which typically aims for timely performance and reliable delivery.
16. ### 2. Lawyer's Specific Contract Context
18. In the lawyer's situation, the contract specified "prompt delivery" but did not provide a strict timeline. The vendor experienced 8 delays ranging from 2 to 4 days over a period of 6 months. These delays culminated in $50,000 in losses due to three missed client deadlines. The vendor was notified regarding these delays; however, the pattern of delays persisted.
20. Key considerations include:
21. - **Nature of the Obligations**: While "prompt delivery" does not define a strict timeline, it does imply an expectation for timely performance.
22. - **Material Impact**: The missed client deadlines indicate that these delays had a material adverse effect on the lawyer's ability to fulfill contractual obligations to third parties, likely triggering damages.
24. ### 3. Conditions for Breach vs. No Breach
26. **Conditions for Breach**:
27. - **Pattern and Cumulative Effect**: Similar to the reasoning in Case H, evidence of a habitual pattern of delays can amount to a breach. Even if individual delays are minor, when combined, they may show a lack of diligence or reliability by the vendor.
28. - **Materiality**: The impact of these delays is crucial. If the cumulative delays adversely affect the contract's purpose or cause significant losses, this reinforces the case for a breach.
29. - **Notification and Opportunity to Cure**: The fact that the vendor was notified of the delays and failed to rectify the behavior can often be interpreted as a further indication of breach.
31. **Conditions for No Breach**:
32. - **Non-Material Delays**: If the delays did not affect the overall contractual performance or client obligations, this may lessen the likelihood of establishing a breach. However, given the risks and losses involved, this seems less relevant in this scenario.
33. - **Force Majeure or Justifiable Delays**: If the vendor could show that these delays were due to justify circumstances not within their control, it may potentially provide a defense against breach claims.
35. ### 4. Practical Recommendations
37. 1. **Assess Damages**: Document the exact nature of the financial losses incurred due to the missed deadlines to substantiate claims of damages.
39. 2. **Gather Evidence**: Collect all communication regarding the delays, including any notifications sent to the vendor about the issues.
41. 3. **Consider Breach of Contract Action**: Based on the precedent and accumulated delays, consider formalized communication to the vendor regarding a breach of contract claim, highlighting both the pattern and the impact of these repeated delays.
43. 4. **Evaluate Remedies**: Depending upon the contract specifics, the lawyer may wish to pursue several remedies, including:
44. - **Compensatory Damages**: For the financial losses due to missed deadlines.
45. - **Specific Performance**: If timely delivery is critical and can still be enforced.
46. - **Contract Termination**: Depending on the severity, terminating the contract and seeking replacements may be warranted.
48. 5. **Negotiate Terms**: If continuing to work with the current vendor is strategic, the lawyer should consider renegotiating terms for performance guarantees or penalties for further delays.
50. 6. **Future Contracts**: In future contracts, consider including explicit timelines and conditions for prompt delivery, as well as specified damages for delays to better safeguard against this issue.
52. By integrating the legal principles from the precedent with the specific context and conditions outlined, the lawyer can formulate a solid plan to address the repeated delays by the vendor effectively.
`AI写代码收起代码块此输出显示了工作流的最终阶段,模型将所选先例(Case H)和律师的澄清信息整合,生成完整的法律分析。系统解释了为何延迟模式很可能构成违约,概述支持这一解释的因素,并提供实际的建议。总体而言,输出展示了人机交互(HITL)澄清如何消除歧义,使模型能够生成有依据、具上下文的法律意见。
其他真实场景
这种结合 Elasticsearch、LangGraph 和人机交互的应用,可以在其他类型的应用中发挥作用,例如:
- 在工具执行前审查操作,例如在金融交易中,人工在下单前批准买/卖指令。
- 在需要时提供额外参数,例如在客户支持分流中,当 AI 对客户问题有多种可能解释时,人工 agent 选择正确的问题类别。
还有很多必须被发现的场景,人机交互将成为改变游戏规则的关键。
结论
通过 LangGraph 和 Elasticsearch,我们可以构建能够自行决策并作为线性工作流运行的 agents,或者根据条件选择不同路径。借助人机交互,agents 可以让真实用户参与决策过程,以填补上下文空白,并在关键容错系统中请求确认。
这种方法的一个优势是可以先使用 Elasticsearch 功能筛选大数据集,然后用 LLM 获取用户选择的单个文档。仅用 Elasticsearch 实现最后一步会更复杂,因为人类可以通过自然语言以多种方式指代结果。
这种方法保持系统运行快速且 token 高效,因为我们只将 LLM 所需信息发送以做最终决策,而不是整个数据集。同时,它也保持了对用户意图的高度精准识别,并可迭代直至选定所需选项。