目录
- 六、Redisson:
-
- 1.基础配置:
- 2.Redisson解决一人一单问题:
- 3.Redisson可重入锁源码:
-
- 1)获取锁
- [3.1 获取锁 tryLockInnerAsync()](#3.1 获取锁 tryLockInnerAsync())
- [3.2 定时刷新锁的过期时间逻辑 scheduleExpirationRenewal()](#3.2 定时刷新锁的过期时间逻辑 scheduleExpirationRenewal())
- [3.3 获取锁的剩余有效期(调用3.1和3.2,被3.4调用) tryAcquireAsync()](#3.3 获取锁的剩余有效期(调用3.1和3.2,被3.4调用) tryAcquireAsync())
- [3.4 获取锁失败时尝试获取锁的逻辑tryLock()](#3.4 获取锁失败时尝试获取锁的逻辑tryLock())
- 2)释放锁
- [3.5 释放锁 unlockInnerAsync()](#3.5 释放锁 unlockInnerAsync())
- 4.红锁
六、Redisson:
Redisson提供了用redis实现的分布式Java对象,有一系列的分布式服务,包括分布式锁。实际开发中其实不用手写分布式锁,直接调用框架就行。

1.基础配置:
1.引入依赖:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>2.编写配置类配置redisson:
java
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean //将方法的返回值放到IOC容器中交给Spring管理
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
// 对redis的配置
Config config = new Config();
// useSingleServer单结点,config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.50.128:6379");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}2.Redisson解决一人一单问题:
原理和我们自己写的可重入锁其实差不多,就是封装了一下,底层用的是lua保证原子操作。
java
@Service
public class VoucherOrderServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<VoucherOrderMapper, VoucherOrder> implements IVoucherOrderService {
@Autowired
private SeckillVoucherServiceImpl seckillVoucherService;
@Autowired
private RedisIdWorker idWorker;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Override
public Result seckillVoucher(Long voucherId) {
// 查询优惠券
SeckillVoucher seckillVoucher = seckillVoucherService.getById(voucherId);
// 判断秒杀是否开始
LocalDateTime beginTime = seckillVoucher.getBeginTime();
LocalDateTime endTime = seckillVoucher.getEndTime();
if(LocalDateTime.now().isAfter(beginTime) && endTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){
if (seckillVoucher.getStock() > 0){
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();//Thread Local
IVoucherOrderService proxy = (IVoucherOrderService) AopContext.currentProxy();// 获取代理对象
// 获取锁对象
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("order:" + userId);
// 尝试获取锁,
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock(10, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (isLock){ // 分布式锁解决一人一单问题,且先提交事务后释放锁
try {
return proxy.createVoucherOrder(voucherId, seckillVoucher.getStock(), userId);// 代理对象调用方法才能进行AOP
}finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
} else{
Result.fail("一人只能下一单");
}
}
return Result.fail("无库存");
}
return Result.fail("不在秒杀时间内");
}
@Transactional //业务逻辑层事务
@Override
public Result createVoucherOrder(Long voucherId, Integer stock, Long userId){
// 一人一单
int count = query().eq("user_id", userId).eq("voucher_id", voucherId).count();
if (count > 0){
return Result.fail("无法重复下单");
}
// 库存-1,解决超卖问题
boolean success = seckillVoucherService.update().setSql("stock = stock - 1").eq("voucher_id", voucherId).
eq("stock", stock).update();// where voucherId=#{voucherId} and stock=#{seckillVoucher.getStock()}
if (success==false){
IVoucherOrderService proxy = (IVoucherOrderService) AopContext.currentProxy();// 获取代理对象
// 失败重试
return proxy.seckillVoucher(voucherId);
}
// 创建订单
VoucherOrder voucherOrder = new VoucherOrder();
long orderId = idWorker.nextId("order");// 自己编写的唯一ID生成器
voucherOrder.setId(orderId);
voucherOrder.setUserId(userId);
voucherOrder.setVoucherId(voucherId);
save(voucherOrder);
return Result.ok(voucherOrder);
}
}3.Redisson可重入锁源码:
redisson的可重入锁中,可重入机制和我们在第四、五章中写的差不多,通过计数的方式实现可重入,但是Redisson更高级的地方在于它的不可重试和超时释放的解决思路。
- 不可重入:同一个线程无法多次获取同一把锁(失败时递归重试)
- 不可重试:获取锁只尝试一次,失败就返回false,没有重试机制
- 超时释放:锁超时释放虽然可以避免死锁,但如果是业务执行耗时较长,锁提前释放会导致其他线程提前获取锁,有线程安全问题
Redisson获取锁和释放锁的流程图如下,下面来看Redisson是如何解决不可重试和超时释放的:
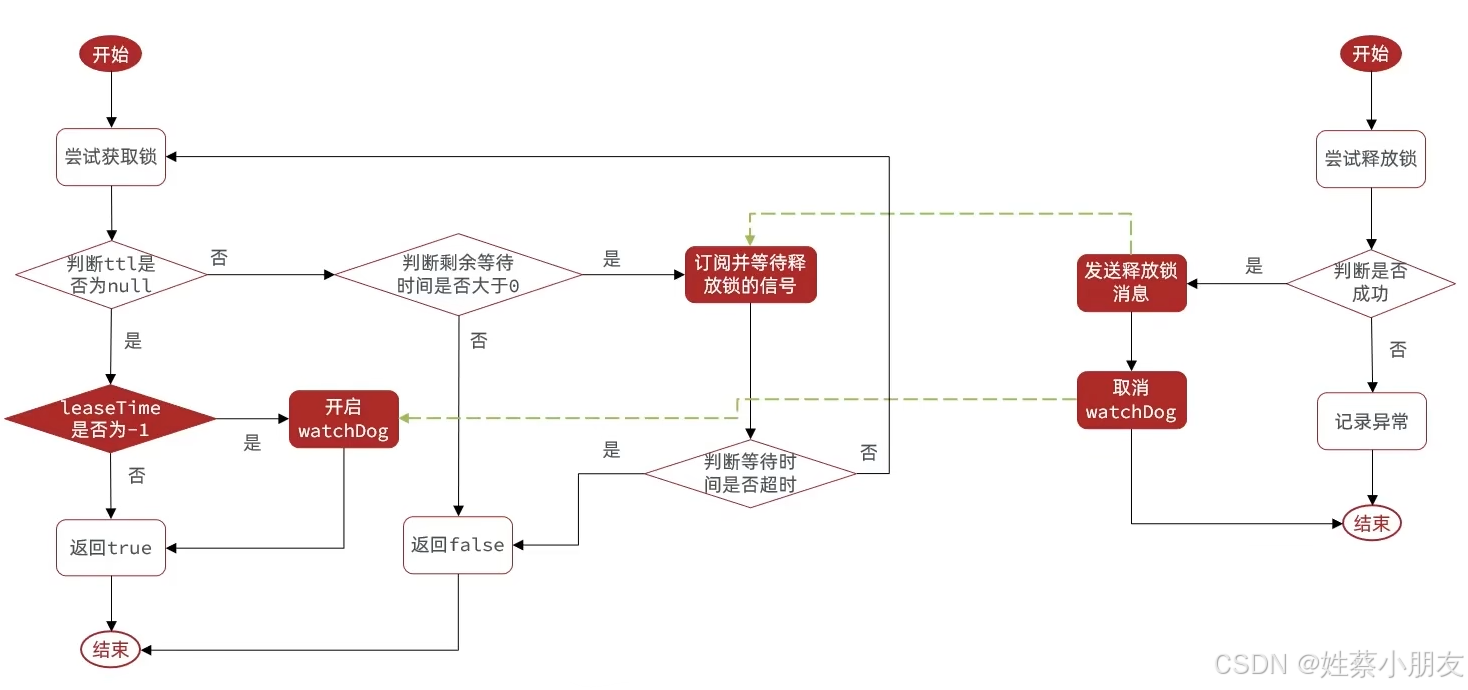
1)获取锁
3.1 获取锁 tryLockInnerAsync()
该方法用于执行lua脚本获取锁:
- 若锁不存在,新建锁(获取锁),key=getName()用户id,field=threadId线程id,value=1,并设置超时释放时间leaseTime
- 若锁存在,如果锁持有者是当前线程,那么重入次数value++,重置超时释放时间,返回空nil
- 若锁持有者不是当前线程,那么会返回锁的剩余有效期
java
// waitTime表示当前线程可以等待的最长时间,leaseTime表示锁的超时释放时间
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
// 记录锁释放时间
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
// 执行lua脚本
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}3.2 定时刷新锁的过期时间逻辑 scheduleExpirationRenewal()
该方法用于刷新锁的剩余有效期,防止拿到锁的线程在业务执行完释放锁前,锁的有效期到期而提前释放锁,引起线程安全问题。
调用关系:scheduleExpirationRenewal()->renewExpiration()->renewExpirationAsync()
java
// 该方法用于判断当前锁是否是新的,调用renewExpiration()方法为新的锁设置定时任务
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();
/** 根据锁的key从EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP中获取对应的ExpirationEntry对象
*getEntryName()当前锁的key
*EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP的作用:在MAP中每个锁会有唯一的ExpirationEntry对象,从而保证锁和ExpirationEntry对象是一对一关系
**/
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {// 当前锁不是第一次创建
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {// 当前锁是第一次创建
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
// 为新锁设置定时任务
renewExpiration();
}
}
// 该方法用于设置定时任务,定时任务调用renewExpirationAsync()方法,每过leaseTime/3秒执行一次,并将定时任务存储到ExpirationEntry对象中
private void renewExpiration() {
// 获取当前锁对应的ExpirationEntry对象
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
// 定时任务,设锁的超时释放时间初始传入为leaseTime,则该任务在leaseTime/3后执行
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
// 获取当前锁对应的ExpirationEntry对象
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
// 获取当前线程的id
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
// 刷新锁的超时释放时间,也就是说如果锁没有释放,那么每过leaseTime/3秒重置锁的超时释放时间为leaseTime
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
if (res) {
// 递归当前方法,每过leaseTime/3秒执行定时任务,重置锁的超时释放时间为leaseTime
renewExpiration();
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 将当前的定时任务存储到当前锁对应的ExpirationEntry对象中
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
// 该方法使用lua脚本来重置锁的超时释放时间
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
// 这里if判断多余了,因为只有当前线程拿到锁后才能执行该方法
// 使用pexpire重置锁的超时释放时间
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(getName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}总结一下关键点感觉就是:
java
// 从MAP中根据锁的key获取对应的ExpirationEntry对象(一对一关系,ExpirationEntry对象中保存了2个内容,一个是占用锁的线程id,一个是定时任务)
ExpirationEntry oldentry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(key, entry);
// 当前锁是第一次在redis中创建,还没有ExpirationEntry对象
if(EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(key, entry) == null){
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry(); // 为该锁实例化一个ExpirationEntry对象
// 创建一个定时任务
task = renewExpiration();
entry.setTimeout(task); //将定时任务添加到entry对象中,定时任务每过一段时间自动执行,直到锁被删除定时任务停止执行
}
entry.addThreadId(threadId);// 修改或写入线程id(确保一致性,因为可能上一个线程已经释放锁了,现在是另一个线程持有锁)
// 定时任务。leaseTime是初始给定超时释放时间
renewExpiration(){
wait(leaseTime/3); //等待leaseTime/3秒
redis.call('pexpire', key, leaseTime);// 重置锁key的超时释放时间为初始值:leaseTime*2/3->leaseTime
// 递归调用自己
renewExpiration()
}3.3 获取锁的剩余有效期(调用3.1和3.2,被3.4调用) tryAcquireAsync()
-
该方法调用tryLockInnerAsync()尝试获取锁,如果获取锁成功那么返回null,如果获取锁失败那么返回锁的剩余有效期。
-
该方法调用scheduleExpirationRenewal()刷新锁的剩余有效期,防止拿到锁的线程在业务执行完释放锁前,锁的有效期到期而提前释放锁,引起线程安全问题。
java
// waitTime表示当前线程可以等待的最长时间,leaseTime表示锁的超时释放时间
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 判断是否传入锁超时释放时间(我们没有传)
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
// 两个方法是一样的,区别在于是否指定锁的超时释放时间
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
// 给定默认锁超时释放时间为this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout()=30s
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 回调函数,ttlRemaining就是tryLockInnerAsync()的返回值
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
// tryLockInnerAsync()返回null表示获取锁成功
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
//renew更新Expiration超时释放时间
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}3.4 获取锁失败时尝试获取锁的逻辑tryLock()
Redisson获取锁失败时不会一直尝试获取锁,这样会浪费计算资源,且频繁的尝试没有意义,所以Redisson采用了一种发布订阅模式来判断何时重新尝试获取锁。
java
1.首先执行获取锁的代码
// 给定当前线程可以等待的最长时间,等待时间内可以多次尝试尝试获取锁
isLock = lock.tryLock(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
↓
// waitTime表示当前线程可以等待的最长时间,leaseTime表示锁的超时释放时间
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 将等待时间换转成毫秒
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
// 获取当前时间
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取线程ID
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 调用tryAcquireAsync尝试获取锁,返回剩余锁的有效期或null(tryAcquire就是简单的return了tryAcquireAsync)
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {// 表示获取锁成功
return true;
} else {// 表示获取锁失败
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;// 计算当前线程剩余可以等待的时间(waitTime-获取锁消耗的时间)
if (time <= 0L) {// 若获取锁消耗的时间大于最长等待时间
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;// 获取锁失败
} else {// 若等待时间还有剩余
current = System.currentTimeMillis();// 更新当前时间
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);// 重点:订阅其他线程释放锁的信号,等待获得释放锁的信号,而不是盲目的重试占用CPU资源(这里如果有多个线程等待的话感觉可以设置一个队列,先到先得)
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {// 若等待信号的时间超过剩余时间
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);// 取消订阅
}
});
}
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;// 获取锁失败
} else {// 若剩余等待时间内接收到其他线程释放锁的信号
boolean var14;
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;// 计算当前线程剩余可以等待的时间(waitTime-获取锁消耗的时间-等待接收信号的时间)
if (time > 0L) {// 若等待时间还有剩余
boolean var16;
do {// 循环开始
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//更新当前时间
ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);//同该方法的第四条语句,调用tryAcquireAsync重新尝试获取锁,返回剩余锁的有效期或null(因为此时接收到其他线程释放锁的信号了)
if (ttl == null) {// 获取锁成功
var16 = true;
return var16;
}
// 获取锁又失败了(啰嗦了,用个队列就好很多)
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0L) {// 该线程的剩余等待时间不够了
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;// 获取锁失败
}
// 若该线程还有等待时间,即剩余等待时间大于0
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 更新当前时间
// 再次订阅其他线程释放锁的信号并等待,直到接收到信号
if (ttl >= 0L && ttl < time) {
((RedissonLockEntry)subscribeFuture.getNow()).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
((RedissonLockEntry)subscribeFuture.getNow()).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 此时接收到其他线程释放锁的信号了
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;// 计算当前线程剩余可以等待的时间
} while(time > 0L);// 循环这个过程,直到当前线程的剩余等待时间小于0
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;// 当前线程剩余等待时间不足(<0),获取锁失败
}
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var14 = false;
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);// 获取锁失败都要取消订阅
}
return var14;// 当前线程剩余等待时间不足(<0),获取锁失败
}
}
}
}感觉这里的while又一次判断获取锁成功和失败有点麻烦,直接设置一个队列,每次只有队首的线程能获得订阅的信号从而获取锁,非队首的一直等待到达队首才能等待获取订阅的信号不就行了。
总结一下关键点感觉就是:
java
waitTime // 当前线程可以等待的最长时间,等待时间内可以多次尝试尝试获取锁,假设可以实时更新
do{
ttl = tryAcquireAsync() // 获取锁
// 获取锁成功
if(ttl == null)
return true;
// 获取锁失败
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);// 订阅其他线程释放锁的信号,等待获得释放锁的信号,等到信号才会执行下一步操作
}while(waitTime>0);2)释放锁
3.5 释放锁 unlockInnerAsync()
释放锁的源码没什么重要的地方就不介绍了,这里只注意一点:发布释放锁信号的代码为redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); ,其他获取锁失败的线程在3.4节通过订subscribe阅来监听这个信号。
java
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}4.红锁
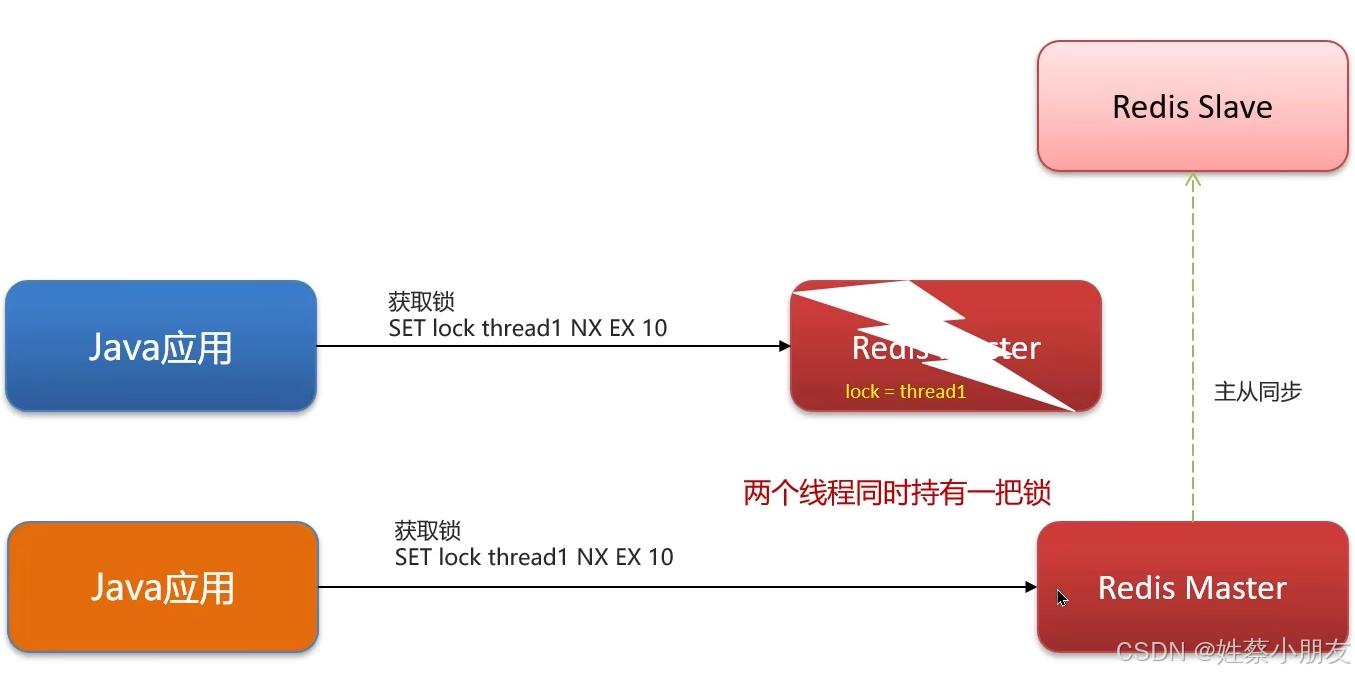
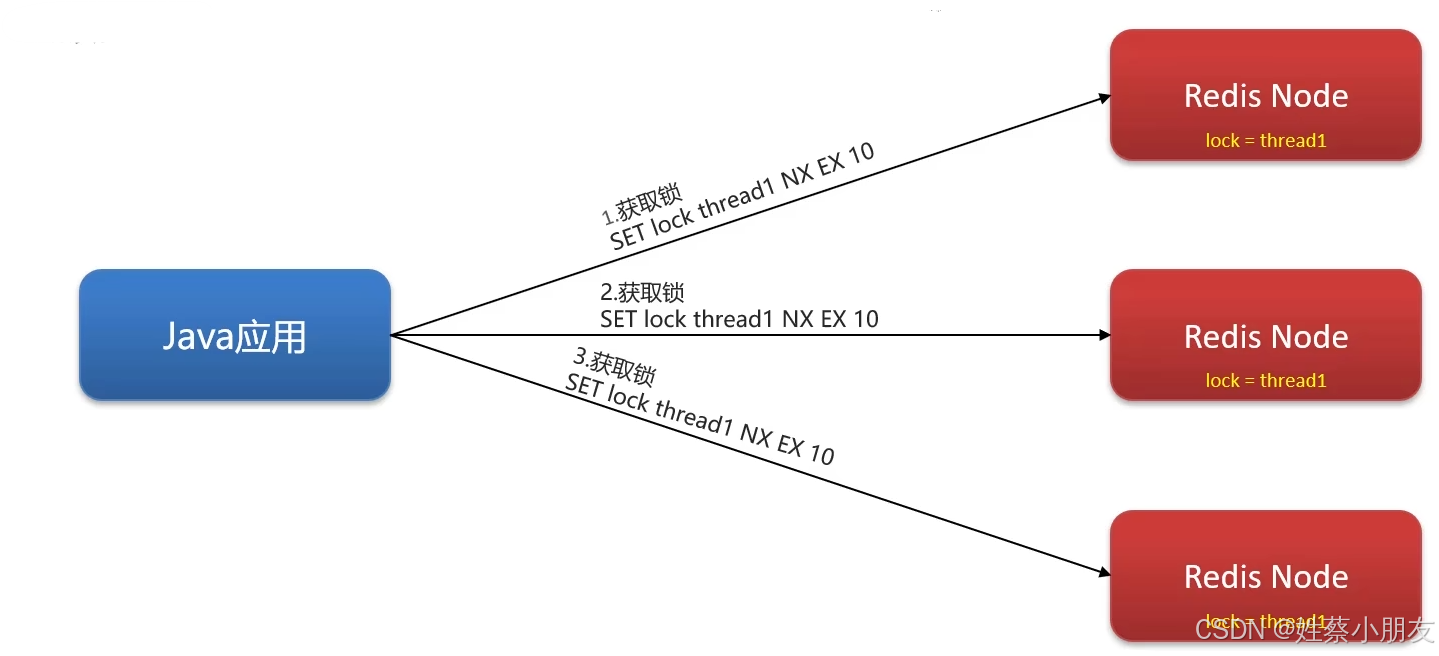
可重入锁只在redis集群的主节点(写操作)上加锁,当主从同步前主节点就宕机了,哨兵会将某一从节点提升为主节点,此时新的主节点上没有锁,就会出现主从不一致问题,而红锁就是为了解决主从不一致问题。
红锁的思路是不能只在主节点上创建锁,而应在(n/2 + 1)个节点上创建锁 ,其中n是主从集群中节点数量。避免主节点数据同步前宕机导致的锁丢失问题。