前言
随着技术的发展和业务需求的变化,团队可能会面临从一种技术栈迁移到另一种技术栈的情况。本文档旨在帮助熟悉 Node.js + TypeScript 生态的开发者快速适应和掌握 Python 开发,特别是在本项目从 JavaScript/TypeScript 技术栈转向 Python 技术栈的过程中提供指导和参考。
通过本文档的阅读,您将收获:
- Node.js + TypeScript 与 Python 在语法和概念上的对应关系
- 异步编程在两种语言中的实现方式对比
- 模块导入和包管理机制的差异
- 面向对象编程的不同实现方式
- 类型系统和静态检查的差异
- 错误处理机制的对比
- 项目实践中需要注意的关键点
适用范围
本文档适用于:
- 熟悉 Node.js + TypeScript 开发,需要快速上手 Python 项目的开发人员
- 希望了解 Node.js + TypeScript 与 Python 差异的技术负责人和架构师
- 需要进行技术栈迁移评估的项目经理
具体方案
1. 语法基础对比
变量声明与类型系统
Node.js + TypeScript 是静态类型语言,而 Python 是动态类型语言。尽管 Python 3.5+ 支持类型提示,但它仍然在运行时进行类型检查。
const name: string = "张三";
const age: number = 25;
const isActive: boolean = true;
const hobbies: string[] = ["读书", "游泳"];
name: str = "张三"
age: int = 25
is_active: bool = True # 注意:Python 使用 snake_case 命名规范
hobbies: List[str] = ["读书", "游泳"] # 需要从 typing 导入 List注意:Python 推荐使用 snake_case 命名法,而 TypeScript 更常用 camelCase。
函数定义
function greet(name: string): string {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
// 箭头函数
const greet = (name: string): string => {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
};
def greet(name: str) -> str:
return f"Hello, {name}!"
# Lambda 函数
greet = lambda name: f"Hello, {name}!"2. 异步编程对比
这是 Node.js + TypeScript 和 Python 最重要的区别之一。Node.js 天生就是为异步 I/O 设计的,而 Python 通过 asyncio 模块提供了类似能力。
Node.js + TypeScript 异步编程
// Promise 方式
function fetchData(): Promise<string> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("数据获取成功");
}, 1000);
});
}
// Async/await 方式
async function getData(): Promise<void> {
try {
const result: string = await fetchData();
console.log(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}Python 异步编程
import asyncio
from typing import Awaitable
async def fetch_data() -> str:
await asyncio.sleep(1) # 模拟异步操作
return "数据获取成功"
async def get_data() -> None:
try:
result: str = await fetch_data()
print(result)
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
# 运行异步函数
asyncio.run(get_data())3. 模块导入机制对比
Node.js 使用 CommonJS 或 ES6 模块系统,而 Python 有自己的模块导入机制。
Node.js + TypeScript 模块导入
// CommonJS
const fs = require('fs');
const myModule = require('./myModule');
// ES6 模块
import fs from 'fs';
import { someFunction } from './myModule';
// TypeScript 中的类型导入
import type { SomeInterface } from './interfaces';Python 模块导入
# Python 标准库导入
import os
import json
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
# 自定义模块导入
from concat_model.service import default_concat_service
from concat_model.types import Node, Workflow在我们的项目中,可以看到复杂的导入路径(两层及以上),例如在 concat_model/core/llm_service.py 中:
import sys
import os
from typing import Dict, List, Any
# 添加项目根目录到Python路径,以便正确导入chat_model
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))))
# 直接导入chat_model中的llm_service
from search_rag_graph.chat_model.llm_service import llm_service as external_llm_service4. 面向对象编程对比
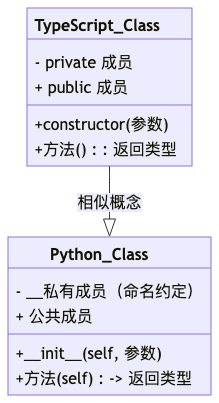
4. 类
Node.js + TypeScript 类定义
class Person {
private name: string;
private age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public greet(): string {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
}
}Python 类定义
class Node:
"""节点类"""
def __init__(self, node_id: str, tag_key: str, action_type: str, action_target: str, pre_snapshot: Optional[Any] = None, **kwargs):
self.node_id = node_id
self.tag_key = tag_key
self.action_type = action_type
self.action_target = action_target
self.pre_snapshot = pre_snapshot
self.__dict__.update(kwargs)
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""转换为字典"""
return self.__dict__.copy()Python 也支持通过类型注解实现类似 TypeScript 的类型安全,但检查是在编译时而不是运行时进行的(除非使用 mypy 等工具)。
OOP 特性对比:
|--------|--------------------------|---------------------|
| 特性 | Node.js + TypeScript | Python |
| 构造函数 | constructor() | __init__(self) |
| 私有成员 | private 关键字 | __成员名 (命名约定) |
| 方法参数 | 直接使用 | 必须包含 self 作为第一个参数 |
| 继承语法 | class A extends B | class A(B) |
5. 类型系统对比
TypeScript 类型系统
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email?: string; // 可选属性
}
// 泛型
interface ApiResponse<T> {
data: T;
status: number;
}
// 联合类型
type Status = "pending" | "approved" | "rejected";
// 类型别名
type UserId = string | number;Python 类型系统
# Python 类型提示
from typing import Optional, Union, Dict, List, TypeVar, Generic
# 类似接口的概念(使用 Protocol,Python 3.8+)
from typing_extensions import Protocol
class User(Protocol):
id: int
name: str
email: Optional[str]
# 泛型
T = TypeVar('T')
class ApiResponse(Generic[T]):
def __init__(self, data: T, status: int):
self.data = data
self.status = status
# 联合类型
from typing import Literal
Status = Literal["pending", "approved", "rejected"]
# 类型别名
UserId = Union[str, int]在我们的项目中,如 search_model/models.py 所示,广泛使用了 Pydantic 进行数据建模和验证:
class QueryFullFlowInput(BaseModel):
"""
查询全流程输入参数
"""
query_text: str = Field(..., description="查询语句,描述业务意图")
env_type: EnvironmentType = Field(..., description="环境类型,dev、test或prod")
form_params: Optional[List[str]] = Field(None, description="表单参数数组,可选")
version: Optional[str] = Field(None, description="版本约束,test、prod必填")这类似于 TypeScript 中使用接口定义数据结构的方式。
6. 错误处理机制对比
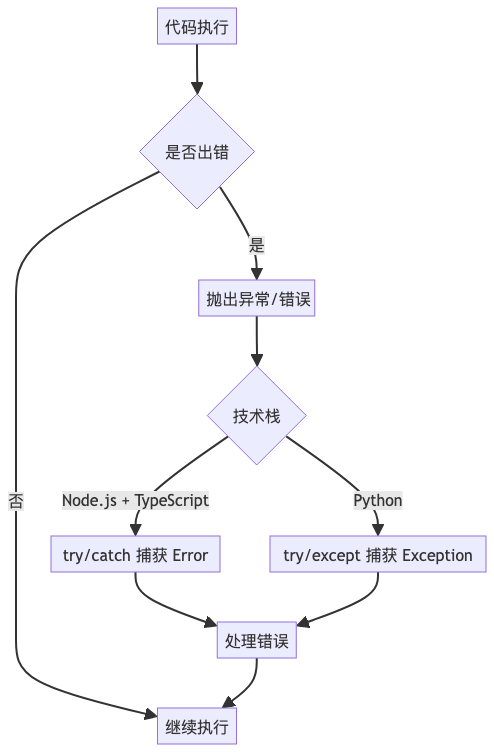
错误处理对比:
|--------|--------------------------|-------------------------|
| 特性 | Node.js + TypeScript | Python |
| 捕获关键字 | catch | except |
| 捕获所有错误 | catch (error) | except Exception as e |
| 自定义错误 | 继承 Error 类 | 继承 Exception 类 |
| 堆栈跟踪 | error.stack | traceback 模块 |
7. 包管理和依赖管理
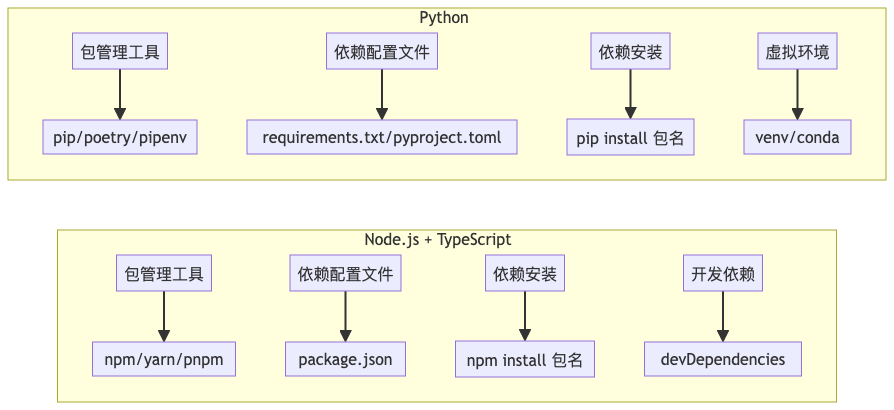
Node.js + TypeScript 包管理
Node.js 使用 npm 或 yarn 进行包管理,依赖定义在 package.json 中:
{
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.18.0",
"lodash": "^4.17.21"
},
"devDependencies": {
"typescript": "^4.9.0",
"ts-node": "^10.9.0"
}
}Python 包管理
Python 使用 pip 作为包管理工具,依赖通常定义在 requirements.txt 或 pyproject.toml 中。在我们的项目中,使用 pyproject.toml:
[project]
dependencies = [
"fastapi>=0.124.4",
"uvicorn>=0.38.0",
"requests>=2.31.0",
"chromadb>=0.4.24",
"jieba>=0.42.1",
"numpy>=1.26.4",
"pydantic>=2.5.3",
]
[build-system]
requires = ["setuptools>=42", "wheel"]
build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"成果展示
通过采用这些最佳实践,我们的项目实现了以下成果:
- 成功的技术栈迁移:从 JavaScript/TypeScript 生态顺利过渡到 Python 生态,保持了系统的稳定性和可维护性。
- 统一的代码风格:通过遵循 Python 的编码规范(如 PEP 8)和项目内部约定,保证了代码的一致性。
- 高效的异步处理:利用 Python 的 asyncio 特性,在处理大量 I/O 操作时仍能保持良好的性能表现。
- 清晰的模块结构:借鉴了 Node.js 的模块化思想,在 Python 中实现了清晰的包和模块组织结构。
- 完善的类型系统:通过使用 Python 的类型提示和 Pydantic 模型,提升了代码的可读性和可维护性。
- 完善的错误处理机制:建立了健壮的异常处理体系,提高了系统的稳定性。
- 强大的生态支持:充分利用 Python 在 AI、数据处理等领域的强大生态优势。
总结
从 Node.js + TypeScript 切换到 Python 并不仅仅是学习一门新语言,更是一种思维方式的转变。以下是几个关键要点:
- 拥抱差异而非抵触:两种语言各有优势,理解它们的设计哲学有助于更好地使用它们。TypeScript 提供了编译时类型检查,而 Python 提供了更灵活的运行时行为。
- 渐进式学习:不需要完全忘记 Node.js + TypeScript 的经验,而是要学会如何将其中的优秀思想(如模块化、异步编程、类型安全)应用到 Python 开发中。
- 重视工具链:Python 有着丰富的生态系统,学会使用合适的工具(如 black 代码格式化、mypy 类型检查、pytest 测试框架等)能够显著提升开发效率。
- 关注性能特征:Python 在某些方面与 Node.js 有不同的性能特征,了解这些差异有助于编写高性能的应用程序。
- 利用生态优势:Python 在数据科学、机器学习、AI 领域拥有强大的生态系统,这是从 Node.js 切换到 Python 的重要价值之一。
- 持续学习:技术在不断发展,保持对新技术和最佳实践的关注是每个开发者都应该具备的素质。
通过本文档提供的对比和实践建议,希望可以帮助您顺利完成从 Node.js + TypeScript 到 Python 的过渡,并在新的技术栈中发挥出色的表现。