目录
[二、从"点对点"到"闭环思考":Prompt Engineering 到 Agent Engineering](#二、从“点对点”到“闭环思考”:Prompt Engineering 到 Agent Engineering)
[三、ReAct Agent 的理论支柱](#三、ReAct Agent 的理论支柱)
[四、手把手:用 Python 从零构建 ReAct Agent](#四、手把手:用 Python 从零构建 ReAct Agent)
[五、为什么要用 ReAct Agent?](#五、为什么要用 ReAct Agent?)
刷了无数篇讲ReAct Agent的"深度好文",是不是感觉:
- 要么被天花乱坠的案例秀一脸? 仿佛明天AI就能接管世界;
- 要么被质疑的调调弄得更加迷惑? 这玩意儿到底行不行啊?
- 干货看了一大堆,代码一行没跑过? 原理似懂非懂,心里总不踏实?
你这状态我太懂了------缺的就是"上手玩透它"!不撸代码真的有点慌 ,可能程序员的思维刻在骨子里了。
看看现在这AI的浪潮:
①"聊天崽" --> ② 到能搬砖的"小助手"--> ③再到动脑子、做决策、搞执行的真Agent,
这步子迈得贼快!而"ReAct框架",就是让AI Agent"开窍"、能自主思考和行动的关键钥匙。
所以,这篇文章不谈虚的:咱今天就把ReAct Agent扒开,看看它到底是怎么"想事儿"和"干活儿"的, 顺便手把手带你把理论落地成实践。纸上谈兵?不存在的!准备好了就上车,一起把这"智能代理"的门道整明白!
一、大模型的三大落地形态
大模型的应用形态逐渐丰富,目前主要分为三类:聊天机器人、人工智能助手和人工智能代理。它们看似相似,但背后的技术逻辑和使用场景却大有不同。
1、聊天机器人:你的知识小助手
这是最基础、最常见的形态。用户提问,模型回答,靠的是大模型自带的"百科全书"能力。如果想让它了解公司内部流程或产品细节,通常会搭配 RAG(检索增强生成) 技术,从海量私有文档中精准提取信息并组织成对话。比如,你问"咱们公司去年的财报数据是啥",它就能迅速检索并给出答案。
2、人工智能助手(Assistant):任务执行小能手
你需要更多实际操作,比如下单、查询或调用内置功能,助手就派上用场了。它的核心技术是 Function Calling:在对话中,大模型判断需要调用哪个 API,向外部系统发起请求,再把结果反馈给你。例如,一个电商客服小助手可以接入"查商品""查优惠""下单"等工具,在对话中灵活执行。但如果任务复杂、涉及多步,单靠 Function Calling 就有点吼不住了。
3、人工智能代理(Agent):自主决策的"全能管家"
代理是目前最智能的形态,不仅能执行任务,还能自主规划步骤、根据环境调整策略。简单来说,助手是"单步执行",而代理则是能连续思考、行动的"机器人管家"。比如,你说"帮我打扫客厅",它会自己判断从哪开始、用什么工具。实现这种能力的钥匙,正是像 ReAct 这样的框架,让 AI 从"单线程"工作进化到像人类一样"思考--行动--再调整"。
二、从"点对点"到"闭环思考":Prompt Engineering 到 Agent Engineering
早期,我们用 Prompt Engineering(提示词工程) 给模型"下单"------告诉它做什么,它就照做。而 Agent Engineering 则更进一步,目标是让模型"自己想、自己做、自己看结果",形成闭环智能。
1、Prompt Engineering(提示工程)
我们告诉模型"做这件事",模型一次性完成。但对于多步骤任务,每个环节都要手动切换,效率低且难以复用。
2、Agent Engineering(代理工程)
则要求我们像设计"岗位流程"一样,明确:
- 职责(Job):AI 代理要干什么?
- 行动(Action):它拥有哪些工具?每个工具完成什么操作?
- 能力(Capability):内部推理需要哪些思考?
- 编排(Orchestration):如何将工具和思考串联成闭环?
举个例子:你想规划长沙三日游。Prompt Engineering 可能只给你一份攻略;而 Agent Engineering 能从小红书抓攻略、携程订机票、飞猪定酒店,最后整理成 PDF,全部自动完成。
三、ReAct Agent 的理论支柱
ReAct(Reason + Act) 框架诞生于 2022 年的一篇论文,其核心是将"推理"和"行动"结合,通过多轮循环解决问题。它的三大步骤是: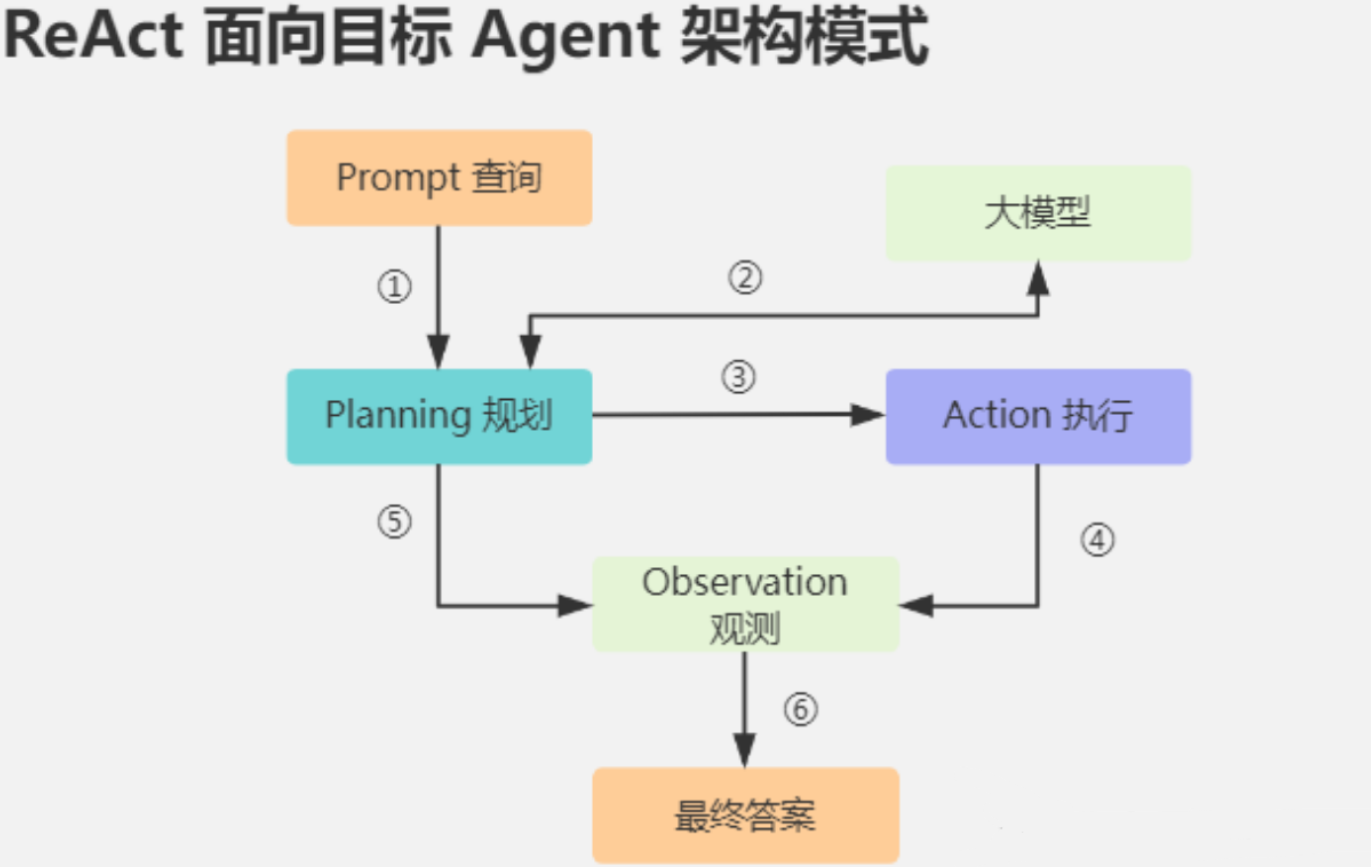
- Reason(推理):借鉴"Chain-of-Thought(思维链)",让模型先"自言自语"地分析问题。
- Act(行动):根据推理结果,调用工具执行操作(如 API、计算器、搜索)。
- Observation(观察):查看行动结果,进入下一轮推理或行动。
通过"思考--行动--观察"的循环,ReAct Agent 能在复杂场景中步步推进,碰到新问题也能灵活调整。
比如,你问"地球质量的两倍是多少":
- 思考:先查地球质量。
- 行动:搜索"地球质量"。
- 观察:得到 5.972×10²⁴ 千克。
- 思考:计算两倍。
- 行动:算 5.972×10²⁴ × 2。
- 观察:得出 1.1944×10²⁵ 千克。
- 回答:地球质量的两倍是 1.1944×10²⁵ 千克。
这过程是不是很像人类解题?这就是 ReAct 的独特魅力。
四、手把手:用 Python 从零构建 ReAct Agent
下面通过一个简单示例------支持实时搜索和数学运算的 Agent------带你实战搭建 ReAct Agent。虽然例子很简单,但是你真的跑通和只停在纸上的,差距不只是那么一点。
1、设计系统提示 Prompt
在 system 角色里,告诉模型循环步骤、可用工具、示例会话,确保它按"思考--行动--观察--回答"格式执行。
python
system_prompt = """
You run in a loop of Thought, Action, Observation, Answer.
At the end of the loop you output an Answer
Use Thought to describe your thoughts about the question you have been asked.
Use Action to run one of the actions available to you.
Observation will be the result of running those actions.
Answer will be the result of analysing the Observation.
Function calls MUST be used when calculating the current time.
Your available actions are:
get_current_time:
e.g. get_current_time: ''
Function: Retrieve the current time
Operation Principle: Get current time for subsequent logical judgments and operations
calculate:
e.g. calculate: 4 * 7 / 3
Runs a calculation and returns the number - uses Python so be sure to use floating point syntax if necessary
fetch_real_time_info:
e.g. fetch_real_time_info: 阿里
Returns a real info from searching SerperAPI
Always look things up on fetch_real_time_info if you have the opportunity to do so.
Example session:
Question: What is the capital of China?
Thought: I should look up on SerperAPI
Action: fetch_real_time_info: What is the capital of China?
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: China is a country. The capital is Beijing.
Thought: I think I have found the answer
Action: Beijing.
You should then call the appropriate action and determine the answer from the result
You then output:
Answer: The capital of China is Beijing
Example session
Question: What is the mass of Earth times 2?
Thought: I need to find the mass of Earth on fetch_real_time_info
Action: fetch_real_time_info : mass of earth
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: mass of earth is 1,1944×10e25
Thought: I need to multiply this by 2
Action: calculate: 5.972e24 * 2
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: 1,1944×10e25
If you have the answer, output it as the Answer.
Answer: The mass of Earth times 2 is 1,1944×10e25.
Example session
Question: Need to obtain current time for year calculation
Thought: Need current year
Action: get_current_time
Observation: Output 2025-12-01 09:01:01
Answer: 2025-12-01 09:01:01
Now it's your turn:
""".strip()2、定义工具函数
这些工具注册到一个字典,Agent 根据指令自动调用:
- fetch_real_time_info(query):调用 Serper API 获取实时信息。
- calculate(expr):用 Python eval 执行数学表达式。
- get_current_time():获取当前时间
python
def fetch_real_time_info(query):
"""
通过Serper API获取实时搜索信息
使用Serper的Google搜索API查询指定问题,并返回最相关结果的摘要片段。
参数:
query (str): 要搜索的查询字符串,表示用户提出的问题
返回:
str: 搜索结果摘要片段。若无结果则返回提示信息
"""
# API参数配置
params = {
'api_key': serper_key, # 使用您自己的API密钥
'q': query, # 查询参数,表示要搜索的问题。
'num': 1 # 返回结果的数量设为1,API将返回一个相关的搜索结果。
}
# 发起API请求
api_result = requests.get('https://google.serper.dev/search', params)
# 解析JSON响应数据
search_data = api_result.json()
# 提取并返回查询到的信息
if search_data["organic"]:
return search_data["organic"][0]["snippet"]
else:
return "没有找到相关结果。"
def calculate(operation: str) -> float:
"""
计算字符串数学表达式的值
使用内置eval()函数执行传入的数学表达式字符串,并返回浮点数结果。
注意:eval()会执行任何传入的Python代码,存在严重安全风险,
请确保仅传入可信来源的数学表达式。
Args:
operation: 包含数学表达式的字符串,例如 "2 * 3 + 4"
Returns:
表达式计算结果的浮点数值
Raises:
SyntaxError: 当传入字符串不是合法表达式时
TypeError: 当表达式结果无法转换为浮点数时
ZeroDivisionError: 当表达式中包含除以零操作时
"""
return eval(operation)
def get_current_time():
"""
获取当前系统时间并格式化为字符串
返回:
str: 格式为'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'的当前时间字符串
"""
return datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# 可用操作映射字典
# 该字典定义了系统支持的操作名称与对应处理函数的映射关系
# 键:操作名称字符串,用于标识具体操作
# 值:实际执行操作的函数对象
available_actions = {
# 实时信息获取操作:调用fetch_real_time_info函数处理
"fetch_real_time_info": fetch_real_time_info,
# 计算操作:调用calculate函数处理
"calculate": calculate,
# 获取当前时间操作:调用get_current_time函数处理
"get_current_time": get_current_time,
}3、搭建 ChatBot 框架
消息积累(系统提示 + 用户输入 + 历史对话)后,通过问 API 获取模型输出。
python
class ChatBot:
"""
聊天机器人实现类,用于处理用户消息并获取AI回复。
属性:
system (str): 系统级初始化指令,用于设定AI行为
messages (list): 存储所有对话消息的列表,包含角色和内容
"""
def __init__(self, system=""):
"""
初始化聊天机器人实例
参数:
system: 系统级初始化指令,用于设定AI行为(默认空字符串)
"""
self.system = system
self.messages = []
# 如果存在系统指令,添加到消息列表开头
if self.system:
self.messages.append({"role": "system", "content": system})
def __call__(self, message):
"""
使实例可调用,处理用户消息并返回AI回复
参数:
message: 用户输入的文本消息
返回:
str: AI生成的回复内容
"""
# 将用户消息添加到对话历史
self.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": message})
# 调用模型执行并获取回复
result = self.execute()
# 将AI回复添加到对话历史
self.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": result})
return result
def execute(self):
"""
调用AI模型API执行对话生成
返回:
str: 模型生成的文本回复内容
"""
# 创建API请求获取模型回复
completion = client.chat.completions.create(model="Qwen/Qwen3-32B", messages=self.messages , temperature=0.5)
# 提取模型返回的首选回复内容
return completion.choices[0].message.content4、实现 AgentExecutor 循环
Agent 在循环中解析输出,执行工具,直到得出最终答案。
python
def AgentExecutor(question, max_turns=5):
"""
执行多轮对话代理的核心逻辑
通过有限轮次的对话交互处理用户问题,当模型输出包含工具调用指令时,
自动执行相应工具并观察结果,否则返回完整对话记录
Args:
question (str): 用户输入的初始问题
max_turns (int, optional): 最大对话轮次数,默认5轮
Returns:
list: 当未触发工具调用时返回完整对话记录
str: 当触发工具调用时返回最后观察结果(循环中)
"""
i = 0
# 初始化对话机器人并加载系统预设
bot = ChatBot(system_prompt)
# 通过 next_prompt 标识每一个子任务的阶段性输入
next_prompt = question
# 解析AI返回结果中的动作指令
action_re = re.compile(r'^Action: (\w+)(?::\s*(.*))?$', re.MULTILINE)
# 限制最大交互轮次防止无限循环
while i < max_turns:
i += 1
# 调用ChatBot模型获取当前轮次响应
result = bot(next_prompt)
print(f"result:{result}")
actions = action_re.findall(result)
# 检测到工具调用指令时执行
if actions:
# 解析工具名称和调用参数
action, action_input = actions[0] # 取第一个动作指令
# 验证工具是否在允许列表中
if action not in available_actions:
raise Exception("Unknown action: {}: {}".format(action, action_input))
print(f"running: {action} {action_input}")
if action_input != "":
# 执行工具并获取返回结果
observation = available_actions[action](action_input)
else:
# 执行工具并获取返回结果
observation = available_actions[action]()
print(f"Observation: {observation}")
# 将工具结果作为下一轮输入
next_prompt = "Observation: {}".format(observation)
else:
# 未检测到工具指令则终止流程并返回对话记录
return bot.messages5、完整可运行代码
python
import json
import requests
import os
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
import sqlite3
import re
import datetime
api_url = os.getenv('GUIJI_API_URL')
token = os.getenv('GUIJI_API_KEY')
serper_key = os.getenv('SUPER_SER_KEY')
client = OpenAI(
api_key=token, # 从 https://cloud.siliconflow.cn/i/nRDJFg4z 获取
base_url="https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1"
)
def fetch_real_time_info(query):
"""
通过Serper API获取实时搜索信息
使用Serper的Google搜索API查询指定问题,并返回最相关结果的摘要片段。
参数:
query (str): 要搜索的查询字符串,表示用户提出的问题
返回:
str: 搜索结果摘要片段。若无结果则返回提示信息
"""
# API参数配置
params = {
'api_key': serper_key, # 使用您自己的API密钥
'q': query, # 查询参数,表示要搜索的问题。
'num': 1 # 返回结果的数量设为1,API将返回一个相关的搜索结果。
}
# 发起API请求
api_result = requests.get('https://google.serper.dev/search', params)
# 解析JSON响应数据
search_data = api_result.json()
# 提取并返回查询到的信息
if search_data["organic"]:
return search_data["organic"][0]["snippet"]
else:
return "没有找到相关结果。"
def calculate(operation: str) -> float:
"""
计算字符串数学表达式的值
使用内置eval()函数执行传入的数学表达式字符串,并返回浮点数结果。
注意:eval()会执行任何传入的Python代码,存在严重安全风险,
请确保仅传入可信来源的数学表达式。
Args:
operation: 包含数学表达式的字符串,例如 "2 * 3 + 4"
Returns:
表达式计算结果的浮点数值
Raises:
SyntaxError: 当传入字符串不是合法表达式时
TypeError: 当表达式结果无法转换为浮点数时
ZeroDivisionError: 当表达式中包含除以零操作时
"""
return eval(operation)
def get_current_time():
"""
获取当前系统时间并格式化为字符串
返回:
str: 格式为'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'的当前时间字符串
"""
return datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# 可用操作映射字典
# 该字典定义了系统支持的操作名称与对应处理函数的映射关系
# 键:操作名称字符串,用于标识具体操作
# 值:实际执行操作的函数对象
available_actions = {
# 实时信息获取操作:调用fetch_real_time_info函数处理
"fetch_real_time_info": fetch_real_time_info,
# 计算操作:调用calculate函数处理
"calculate": calculate,
# 获取当前时间操作:调用get_current_time函数处理
"get_current_time": get_current_time,
}
class ChatBot:
"""
聊天机器人实现类,用于处理用户消息并获取AI回复。
属性:
system (str): 系统级初始化指令,用于设定AI行为
messages (list): 存储所有对话消息的列表,包含角色和内容
"""
def __init__(self, system=""):
"""
初始化聊天机器人实例
参数:
system: 系统级初始化指令,用于设定AI行为(默认空字符串)
"""
self.system = system
self.messages = []
# 如果存在系统指令,添加到消息列表开头
if self.system:
self.messages.append({"role": "system", "content": system})
def __call__(self, message):
"""
使实例可调用,处理用户消息并返回AI回复
参数:
message: 用户输入的文本消息
返回:
str: AI生成的回复内容
"""
# 将用户消息添加到对话历史
self.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": message})
# 调用模型执行并获取回复
result = self.execute()
# 将AI回复添加到对话历史
self.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": result})
return result
def execute(self):
"""
调用AI模型API执行对话生成
返回:
str: 模型生成的文本回复内容
"""
# 创建API请求获取模型回复
completion = client.chat.completions.create(model="Qwen/Qwen3-32B", messages=self.messages , temperature=0.5)
# 提取模型返回的首选回复内容
return completion.choices[0].message.content
system_prompt = """
You run in a loop of Thought, Action, Observation, Answer.
At the end of the loop you output an Answer
Use Thought to describe your thoughts about the question you have been asked.
Use Action to run one of the actions available to you.
Observation will be the result of running those actions.
Answer will be the result of analysing the Observation.
Function calls MUST be used when calculating the current time.
Your available actions are:
get_current_time:
e.g. get_current_time: ''
Function: Retrieve the current time
Operation Principle: Get current time for subsequent logical judgments and operations
calculate:
e.g. calculate: 4 * 7 / 3
Runs a calculation and returns the number - uses Python so be sure to use floating point syntax if necessary
fetch_real_time_info:
e.g. fetch_real_time_info: 阿里
Returns a real info from searching SerperAPI
Always look things up on fetch_real_time_info if you have the opportunity to do so.
Example session:
Question: What is the capital of China?
Thought: I should look up on SerperAPI
Action: fetch_real_time_info: What is the capital of China?
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: China is a country. The capital is Beijing.
Thought: I think I have found the answer
Action: Beijing.
You should then call the appropriate action and determine the answer from the result
You then output:
Answer: The capital of China is Beijing
Example session
Question: What is the mass of Earth times 2?
Thought: I need to find the mass of Earth on fetch_real_time_info
Action: fetch_real_time_info : mass of earth
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: mass of earth is 1,1944×10e25
Thought: I need to multiply this by 2
Action: calculate: 5.972e24 * 2
PAUSE
You will be called again with this:
Observation: 1,1944×10e25
If you have the answer, output it as the Answer.
Answer: The mass of Earth times 2 is 1,1944×10e25.
Example session
Question: Need to obtain current time for year calculation
Thought: Need current year
Action: get_current_time
Observation: Output 2025-12-01 09:01:01
Answer: 2025-12-01 09:01:01
Now it's your turn:
""".strip()
def AgentExecutor(question, max_turns=5):
"""
执行多轮对话代理的核心逻辑
通过有限轮次的对话交互处理用户问题,当模型输出包含工具调用指令时,
自动执行相应工具并观察结果,否则返回完整对话记录
Args:
question (str): 用户输入的初始问题
max_turns (int, optional): 最大对话轮次数,默认5轮
Returns:
list: 当未触发工具调用时返回完整对话记录
str: 当触发工具调用时返回最后观察结果(循环中)
"""
i = 0
# 初始化对话机器人并加载系统预设
bot = ChatBot(system_prompt)
# 通过 next_prompt 标识每一个子任务的阶段性输入
next_prompt = question
# 解析AI返回结果中的动作指令
action_re = re.compile(r'^Action: (\w+)(?::\s*(.*))?$', re.MULTILINE)
# 限制最大交互轮次防止无限循环
while i < max_turns:
i += 1
# 调用ChatBot模型获取当前轮次响应
result = bot(next_prompt)
print(f"result:{result}")
actions = action_re.findall(result)
# 检测到工具调用指令时执行
if actions:
# 解析工具名称和调用参数
action, action_input = actions[0] # 取第一个动作指令
# 验证工具是否在允许列表中
if action not in available_actions:
raise Exception("Unknown action: {}: {}".format(action, action_input))
print(f"running: {action} {action_input}")
if action_input != "":
# 执行工具并获取返回结果
observation = available_actions[action](action_input)
else:
# 执行工具并获取返回结果
observation = available_actions[action]()
print(f"Observation: {observation}")
# 将工具结果作为下一轮输入
next_prompt = "Observation: {}".format(observation)
else:
# 未检测到工具指令则终止流程并返回对话记录
return bot.messages
if __name__ == "__main__":
#react_test_call()
#res = fetch_real_time_info("长沙岳麓山")
#print(res)
#print(get_current_time())
AgentExecutor("阿里成立多少年了?")
#test_split()
#test_split2()五、为什么要用 ReAct Agent?
通过查看执行过程发现,大模型的思考和人类还是非常像的。
代码流程执行完之后我想你应该能更好地理解为什么要用 ReAct Agent?主要在一下几个方面:
- 多步复杂任务:单步 Function Calling 难以胜任,ReAct 擅长多步串联。
- 自适应与可解释:每步都有"Thought"和"Observation"记录,便于优化和审计。
- 跨工具协作:搜索、计算、数据库操作、API 调用都能灵活整合。
当你需要一个"能思考、会行动、会反馈"的数字员工,ReAct Agent 是理想选择。
六、总结
从简单的聊天机器人到具备"闭环思考"的 AI 代理,这不仅是模型能力的提升,更是设计思路的飞跃。ReAct Agent 将推理与行动无缝融合,让我们从"孤立调用"迈向"智能协作"的新阶段。ReAct 框架让 AI 从"被动回答"进化到"主动解决问题",能在自动客服、旅行规划、复杂决策等场景大放异彩。如今,LangChain、LlamaIndex、CrewAI 等开源框架纷纷内置 ReAct 代理,助力开发者更快落地智能化工作流。希望这篇文章能帮你拨开迷雾,理解 ReAct 的原理,并在实战中快速上手,打造属于自己的智能应用。未来已来,一起动手,解锁 AI 的无限可能吧!