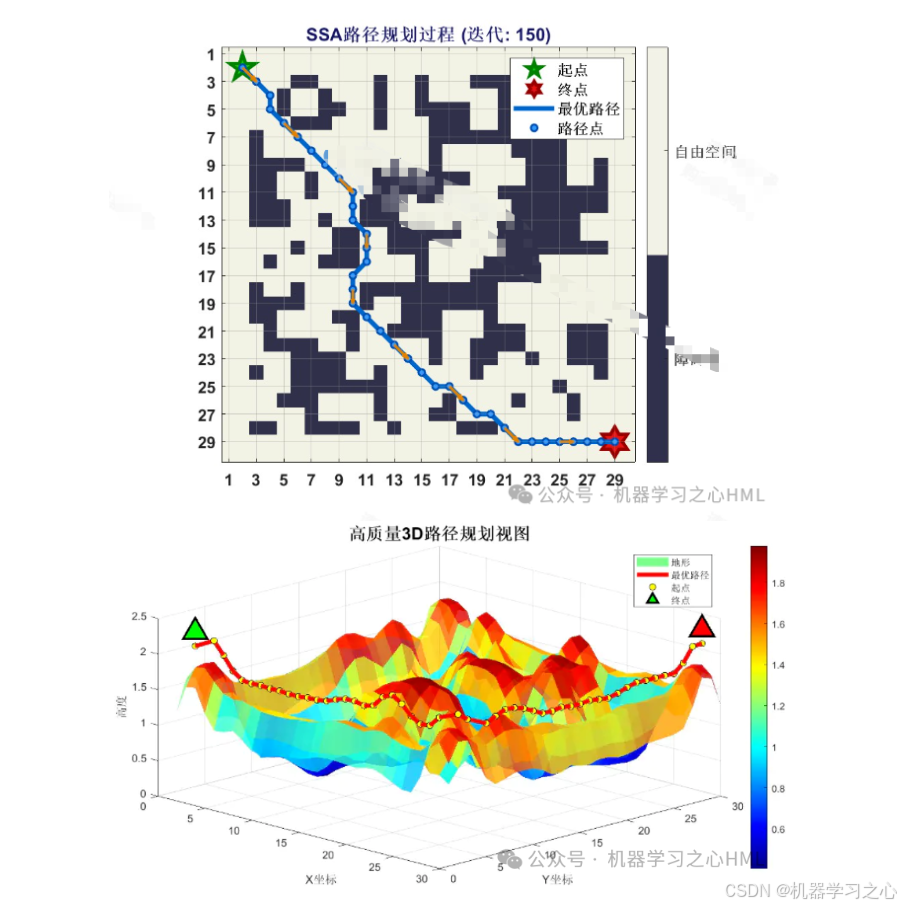
1. 算法原理
麻雀搜索算法是一种新型的群智能优化算法,模拟麻雀的觅食和反捕食行为:
- 发现者:引领群体寻找食物源
- 加入者:跟随发现者寻找食物
- 警戒者:侦查危险并发出警报
2. MATLAB实现代码
主程序 SSA_PathPlanning.m
matlab
% 基于麻雀搜索算法的栅格地图路径规划
clear; clc; close all;
%% 参数设置
numSparrows = 30; % 麻雀数量
maxIter = 100; % 最大迭代次数
dim = 2; % 每个路径点的维度(x,y)
numPoints = 10; % 路径点数量(不含起点终点)
PD = 0.7; % 发现者比例
SD = 0.2; % 警戒者比例
ST = 0.8; % 安全阈值
%% 创建栅格地图
mapSize = 20; % 地图大小
map = createMap(mapSize); % 创建随机栅格地图
% 或者使用固定地图
% map = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
% 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0;
% 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0;
% 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0;
% 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0;
% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0];
%% 设置起点和终点
startPos = [1, 1]; % 起点坐标
goalPos = [mapSize, mapSize]; % 终点坐标
%% 显示地图
figure(1);
hold on;
imagesc(1:mapSize, 1:mapSize, map);
colormap([1 1 1; 0 0 0]); % 0=白色(可行), 1=黑色(障碍)
plot(startPos(1), startPos(2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
plot(goalPos(1), goalPos(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
xlabel('X'); ylabel('Y');
title('栅格地图路径规划');
grid on;
axis equal;
%% 初始化麻雀种群
sparrows = zeros(numSparrows, numPoints*dim);
fitness = zeros(numSparrows, 1);
% 随机初始化路径点
for i = 1:numSparrows
path = initializePath(startPos, goalPos, numPoints, mapSize, map);
sparrows(i, :) = path(:)';
fitness(i) = calculateFitness(path, startPos, goalPos, map);
end
%% SSA主循环
bestFitness = inf;
bestPath = [];
convergenceCurve = zeros(maxIter, 1);
for iter = 1:maxIter
% 排序,找到最佳和最差适应度
[sortedFitness, sortedIdx] = sort(fitness);
bestIdx = sortedIdx(1);
worstIdx = sortedIdx(end);
% 更新全局最优
if sortedFitness(1) < bestFitness
bestFitness = sortedFitness(1);
bestPath = reshape(sparrows(bestIdx, :), numPoints, dim);
end
% 计算发现者、加入者、警戒者的数量
numDiscoverers = round(numSparrows * PD);
numWatchers = round(numSparrows * SD);
numFollowers = numSparrows - numDiscoverers - numWatchers;
%% 更新发现者位置
for i = 1:numDiscoverers
R2 = rand(); % 预警值
if R2 < ST
% 安全,正常搜索
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) .* ...
exp(-i / (rand() * maxIter));
else
% 危险,飞向安全区域
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) + ...
randn(1, numPoints*dim) .* ones(1, numPoints*dim);
end
end
%% 更新加入者位置
for i = numDiscoverers+1:numDiscoverers+numFollowers
if i > numSparrows/2
% 饥饿的加入者
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = randn(1, numPoints*dim) .* ...
exp((sparrows(worstIdx, :) - sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :)) / i^2);
else
% 跟随发现者
A = floor(rand(1, numPoints*dim) * 2) * 2 - 1;
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = sparrows(bestIdx, :) + ...
abs(sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) - sparrows(bestIdx, :)) * ...
A' * (A * A')^(-1);
end
end
%% 更新警戒者位置
for i = numSparrows-numWatchers+1:numSparrows
f_i = fitness(sortedIdx(i));
f_g = bestFitness;
f_w = fitness(worstIdx);
if f_i > f_g
% 靠近最佳位置
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = sparrows(bestIdx, :) + ...
randn(1, numPoints*dim) .* abs(sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) - ...
sparrows(bestIdx, :));
elseif f_i == f_g
% 保持当前位置
c = randn(1, numPoints*dim);
sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) = sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) + ...
c .* (abs(sparrows(sortedIdx(i), :) - sparrows(worstIdx, :)) / ...
(f_i - f_w + eps));
end
end
%% 边界处理
for i = 1:numSparrows
% 确保路径点在范围内
path = reshape(sparrows(i, :), numPoints, dim);
for j = 1:numPoints
path(j, 1) = max(min(path(j, 1), mapSize), 1);
path(j, 2) = max(min(path(j, 2), mapSize), 1);
end
sparrows(i, :) = path(:)';
% 重新计算适应度
fitness(i) = calculateFitness(path, startPos, goalPos, map);
end
convergenceCurve(iter) = bestFitness;
%% 显示当前最优路径
if mod(iter, 10) == 0
fprintf('迭代 %d, 最佳适应度: %.4f\n', iter, bestFitness);
figure(1);
hold on;
plotPath(bestPath, startPos, goalPos, 'b-');
title(sprintf('迭代 %d, 适应度: %.4f', iter, bestFitness));
drawnow;
end
end
%% 显示最终结果
figure(1);
hold on;
finalPath = [startPos; bestPath; goalPos];
plot(finalPath(:,1), finalPath(:,2), 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2);
plot(bestPath(:,1), bestPath(:,2), 'b*');
title(sprintf('最终路径 (适应度: %.4f)', bestFitness));
figure(2);
plot(convergenceCurve, 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('最佳适应度');
title('收敛曲线');
grid on;
%% 平滑路径
smoothedPath = smoothPath(finalPath, map);
figure(3);
imagesc(1:mapSize, 1:mapSize, map);
colormap([1 1 1; 0 0 0]);
hold on;
plot(startPos(1), startPos(2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
plot(goalPos(1), goalPos(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
plot(smoothedPath(:,1), smoothedPath(:,2), 'm-', 'LineWidth', 2);
title('平滑后路径');
grid on; axis equal;辅助函数 createMap.m
matlab
function map = createMap(mapSize)
% 创建随机栅格地图
% mapSize: 地图尺寸
% 返回值: 二值地图 (0=可行, 1=障碍)
map = zeros(mapSize);
% 随机生成障碍物
obstacleRatio = 0.2; % 障碍物比例
numObstacles = round(mapSize * mapSize * obstacleRatio);
for i = 1:numObstacles
x = randi([1, mapSize]);
y = randi([1, mapSize]);
% 避免起点和终点被设为障碍
if ~((x == 1 && y == 1) || (x == mapSize && y == mapSize))
map(y, x) = 1;
end
end
% 添加一些连续的障碍物
for i = 1:mapSize
if rand() < 0.3
startX = randi([1, mapSize-5]);
length = randi([3, 6]);
for j = 0:length
if startX + j <= mapSize
map(i, startX+j) = 1;
end
end
end
end
end路径初始化函数 initializePath.m
matlab
function path = initializePath(startPos, goalPos, numPoints, mapSize, map)
% 初始化路径
% numPoints: 中间路径点数量
path = zeros(numPoints, 2);
for i = 1:numPoints
% 在起点和终点之间均匀分布路径点
ratio = i / (numPoints + 1);
x = startPos(1) + ratio * (goalPos(1) - startPos(1));
y = startPos(2) + ratio * (goalPos(2) - startPos(2));
% 添加随机扰动
x = x + randn() * 2;
y = y + randn() * 2;
% 确保在边界内
x = max(min(x, mapSize), 1);
y = max(min(y, mapSize), 1);
% 避开障碍物
while map(round(y), round(x)) == 1
x = x + randn();
y = y + randn();
x = max(min(x, mapSize), 1);
y = max(min(y, mapSize), 1);
end
path(i, :) = [x, y];
end
end适应度计算函数 calculateFitness.m
matlab
function fitness = calculateFitness(path, startPos, goalPos, map)
% 计算路径适应度
% 适应度 = 路径长度 + 障碍物惩罚
% 完整路径
fullPath = [startPos; path; goalPos];
% 计算路径长度
pathLength = 0;
for i = 1:size(fullPath, 1)-1
dist = norm(fullPath(i, :) - fullPath(i+1, :));
pathLength = pathLength + dist;
end
% 检查碰撞惩罚
collisionPenalty = 0;
collisionWeight = 100; % 碰撞惩罚权重
for i = 1:size(fullPath, 1)
x = round(fullPath(i, 1));
y = round(fullPath(i, 2));
% 边界检查
if x < 1 || x > size(map, 2) || y < 1 || y > size(map, 1)
collisionPenalty = collisionPenalty + collisionWeight;
continue;
end
% 障碍物检查
if map(y, x) == 1
collisionPenalty = collisionPenalty + collisionWeight;
end
end
% 检查路径段是否穿过障碍物
segmentPenalty = 0;
for i = 1:size(fullPath, 1)-1
p1 = fullPath(i, :);
p2 = fullPath(i+1, :);
% 采样路径段上的点
numSamples = 10;
for t = 0:1/numSamples:1
p = p1 + t * (p2 - p1);
x = round(p(1));
y = round(p(2));
if x >= 1 && x <= size(map, 2) && y >= 1 && y <= size(map, 1)
if map(y, x) == 1
segmentPenalty = segmentPenalty + collisionWeight/numSamples;
end
end
end
end
% 总适应度
fitness = pathLength + collisionPenalty + segmentPenalty;
end路径平滑函数 smoothPath.m
matlab
function smoothedPath = smoothPath(path, map)
% 平滑路径
% 使用简单的B样条平滑
n = size(path, 1);
if n < 3
smoothedPath = path;
return;
end
% B样条平滑
t = linspace(0, 1, n);
tt = linspace(0, 1, n*3);
% 使用三次样条插值
smoothedPath(:,1) = spline(t, path(:,1), tt);
smoothedPath(:,2) = spline(t, path(:,2), tt);
% 确保路径避开障碍物
for i = 1:size(smoothedPath, 1)
x = round(smoothedPath(i, 1));
y = round(smoothedPath(i, 2));
if x >= 1 && x <= size(map, 2) && y >= 1 && y <= size(map, 1)
if map(y, x) == 1
% 如果碰到障碍物,调整点
% 寻找最近的可行点
found = false;
for r = 1:5
for angle = 0:pi/8:2*pi
newX = round(x + r * cos(angle));
newY = round(y + r * sin(angle));
if newX >= 1 && newX <= size(map, 2) && ...
newY >= 1 && newY <= size(map, 1) && ...
map(newY, newX) == 0
smoothedPath(i, :) = [newX, newY];
found = true;
break;
end
end
if found, break; end
end
end
end
end
end路径绘制函数 plotPath.m
matlab
function plotPath(path, startPos, goalPos, style)
% 绘制路径
fullPath = [startPos; path; goalPos];
plot(fullPath(:,1), fullPath(:,2), style, 'LineWidth', 1.5);
plot(path(:,1), path(:,2), 'b*');
plot(startPos(1), startPos(2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
plot(goalPos(1), goalPos(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 3);
end3. 算法特点
- 快速收敛:SSA算法具有较快的收敛速度
- 全局搜索:通过发现者机制进行全局探索
- 局部优化:加入者和警戒者机制进行局部优化
- 避障能力:适应度函数包含障碍物惩罚项
4. 参数调优建议
matlab
% 关键参数调优建议
% 1. 麻雀数量:20-50,复杂环境可以适当增加
% 2. PD(发现者比例):0.6-0.8
% 3. ST(安全阈值):0.6-0.9
% 4. 迭代次数:50-200,根据地图复杂度调整