一、核心背景与基础概念
1.1 PyTorch模型部署的痛点
PyTorch能极大地提高构建效率,是训练框架中非常优秀,但它不适合部署。动态建图带来的优势对于性能要求更高的应用场景更像是缺点,非固定的网络结构给网络结构分析并进行优化带来了困难。
1.2 中间表示IR的核心作用
作为模型部署的一个范式,需要生成一个模型的中间表示(IR),IR拥有相对固定的图结构,所以更容易优化。TorchScript与ONNX均属于中间表示,其中TorchScript是PyTorch提供的一种将模型从Python代码转换为IR的方法,可脱离Python环境进行高效部署;ONNX则是跨框架的通用IR,能实现不同训练框架与推理引擎的兼容。
1.3 PyTorch JIT编译核心方式
JIT(Just-In-Time Compilation)在PyTorch中主要指将动态图中的模型转化为静态可序列化、可优化的TorchScript图,核心功能包括:将PyTorch模型序列化为.pt或.pth文件;在非Python环境中加载和运行模型;提高模型运行效率;更好地进行模型优化和跨平台部署。
PyTorch提供两种主要JIT编译方式,核心差异如下:
| 特性 | torch.jit.trace追踪法 | torch.jit.script脚本化 |
|---|---|---|
| 是否支持控制流 | 仅记录一次执行路径 | 完整解析Python语法 |
| 是否易于使用 | 只需传入示例输入 | 可能需要修改源码 |
| 是否保留Python逻辑 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 是否适合导出ONNX | 支持 | 支持 |
| 典型应用场景 | CNN、Encoder-only模型 | Transformer、动态网络结构 |
1.3.1 torch.jit.trace详解
作用:追踪模型在一次前向传播过程中执行的操作,并记录这些操作形成TorchScript模块ScriptModule。
语法:scripted_module = torch.jit.trace(model, example_input)
参数说明:model为nn.Module实例如torchvision.models.resnet18();example_input为用于触发模型前向传播的示例输入Tensor。
工作原理:运行一次模型的前向传播;记录所有经过的张量操作路径;将这些操作保存为静态计算图TorchScript IR;忽略数据相关控制流(如if/for语句依赖于输入数据的条件分支)。
示例代码:
python
import torch
import torchvision.models as models
model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
example_input = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
traced_model = torch.jit.trace(model, example_input)保存模型
traced_model.save("resnet18_traced.pt")
加载模型
loaded_model = torch.jit.load("resnet18_traced.pt")
优点:简单易用,适合不包含复杂控制流的模型;性能稳定,适用于大多数推理场景。
缺点:无法捕获依赖于输入数据的控制流(如if语句、循环);不适合有动态结构的模型(如RNN、Transformer的条件分支)。
1.3.2 torch.jit.script详解
原理:通过解析Python源代码构建TorchScript图,可保留控制流逻辑,直接解析网络定义的python代码生成抽象语法树AST,解决trace无法处理的动态控制流问题。
示例代码:
python
@torch.jit.script
def foo(x):
if x > 0:
return x
else:
return -x适用场景:模型中包含复杂控制流;需要根据输入改变执行路径的逻辑。
二、PyTorch转ONNX核心流程
2.1 转换核心原理
torch.onnx.export函数将PyTorch模型转换成ONNX模型,核心通过trace方式记录PyTorch推理过程,具体步骤:1. 用trace生成TorchScript模型,若已是TorchScript模型可跳过;2. 对模型进行变换,核心pass为ToONNX,将TorchScript中prim、aten空间下的算子映射到onnx空间下的算子;3. 用ONNX的proto格式对模型序列化,完成导出。
ONNX核心结构:将网络每层(或每个算子)作为节点(Node),由节点构建图(Graph)即网络,最终将Graph与模型其他信息结合生成.onnx模型文件。
2.2 转换过程的显存占用问题
2.2.1 现象:转换时显存占用过高
将模型转换为ONNX或TorchScript等中间表示格式时,通常需要进行一次或多次前向推理以追踪/分析计算图结构,因此会占用一定显存资源。
2.2.2 核心原因
1.TorchScript的trace模式torch.jit.trace:需提供示例输入,实际执行一次前向传播追踪计算分支和操作,会分配张量、执行模型并消耗显存;
2.ONNX转换如torch.onnx.export:同样需传入示例输入,内部执行前向传播记录计算图,产生显存占用;
3.复杂控制流模型:可能需多次执行不同输入路径覆盖所有逻辑,进一步增加显存消耗。
2.2.3 解决方案:使用torch.no_grad()
转换过程无需计算梯度,使用torch.no_grad()可显著减少显存占用并加速导出,核心说明如下:
2.2.3.1 为何无需梯度计算
模型转换如torch.onnx.export()或torch.jit.trace()仅需执行前向传播、记录计算图结构,无需反向传播和梯度计算,启用梯度计算无意义且会增加额外计算和内存开销。
2.2.3.2 torch.no_grad()的作用
作为上下文管理器,临时禁用PyTorch自动求导机制autograd,使所有张量运算不被追踪构建计算图;不为中间变量分配额外空间存储梯度信息.grad属性和计算图节点;可大幅减少显存占用有时达30%~50%;提升前向推理速度尤其在GPU上。
2.2.3.3 不使用的后果
即使不调用.backward(),PyTorch默认仍会为每个操作构建反向传播所需计算图、保存中间激活值用于后续梯度计算,可能导致大量显存占用,甚至OOM错误,在导出ResNet、BERT等大模型时更易出现问题。
2.3 HF Safetensors格式转ONNX实践
以Hunyuan模型为例,完整转换代码及说明如下:
python
from typing import Mapping, List, Optional, Tuple, Dict
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoConfig, AutoModelForCausalLM
from transformers.cache_utils import DynamicCache
from optimum.exporters.onnx import OnnxConfig
from optimum.exporters.onnx.base import ConfigBehavior
from optimum.utils import NormalizedConfigManager, NormalizedTextConfig
import torch
import os
class HunyuanNormalizedConfig(NormalizedTextConfig):
NUM_ATTENTION_HEADS = "num_attention_heads"
NUM_KEY_VALUE_HEADS = "num_key_value_heads"
HIDDEN_SIZE = "hidden_size"
NUM_LAYERS = "num_hidden_layers"
# 为hunyuan_v1_dense模型创建自定义ONNX配置
class HunyuanV1DenseOnnxConfig(OnnxConfig):
DEFAULT_ONNX_OPSET = 14
NORMALIZED_CONFIG_CLASS = HunyuanNormalizedConfig
MIN_TORCH_VERSION = "2.5.0"
MAIN_INPUT_NAME = "input_ids"
def __init__(
self,
config: AutoConfig,
task: str = "text-generation",
use_past: bool = False,
use_past_in_inputs: bool = False,
):
super().__init__(config, task=task)
self.use_past = use_past
self.use_past_in_inputs = use_past_in_inputs
self._config = config
# 缓存常用配置值
self._num_layers = config.num_hidden_layers
self._num_kv_heads = getattr(config, 'num_key_value_heads', config.num_attention_heads)
self._head_dim = config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
@property
def inputs(self) -> Mapping[str, Mapping[int, str]]:
common_inputs = {
"input_ids": {0: "batch_size", 1: "sequence_length"},
"attention_mask": {0: "batch_size", 1: "total_sequence_length"},
"position_ids": {0: "batch_size", 1: "sequence_length"},
}
if self.use_past_in_inputs:
for i in range(self._num_layers):
common_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.key"] = {
0: "batch_size",
2: "past_sequence_length"
}
common_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.value"] = {
0: "batch_size",
2: "past_sequence_length",
}
return common_inputs
@property
def outputs(self) -> Mapping[str, Mapping[int, str]]:
common_outputs = {
"logits": {0: "batch_size", 1: "sequence_length"},
}
if self.use_past:
for i in range(self._num_layers):
common_outputs[f"present.{i}.key"] = {
0: "batch_size",
2: "total_sequence_length",
}
common_outputs[f"present.{i}.value"] = {
0: "batch_size",
2: "total_sequence_length",
}
return common_outputs
def generate_dummy_inputs(
self, framework = "pt",
batch_size: int = 1,
sequence_length: int = 16,
past_sequence_length: int = 16,
**kwargs) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""
生成用于 ONNX 导出的虚拟输入
Args:
framework: 框架类型,默认 "pt" (PyTorch)
batch_size: 批次大小
sequence_length: 当前序列长度
- 对于纯 decode(KV Cache 增量推理),使用 1
- 对于支持 prefill + decode 的统一模型,建议使用 > 1(如 128)
这样 SDPA 的 is_causal 判断会被正确 trace
past_sequence_length: 历史 KV Cache 长度
注意:
- 当 sequence_length > 1 且 attention_mask 被提供时,
SDPA 会通过 attention_mask 处理因果关系,而非 is_causal 标志
- 建议导出时使用 sequence_length > 1 以消除 TracerWarning
- position_ids 形状必须与 input_ids 一致 [batch_size, sequence_length]
"""
# 基础输入
# 注意:position_ids 形状必须是 [batch_size, sequence_length],与 input_ids 一致
# 不要使用 unsqueeze 创建额外维度,避免模型内部 Reshape 硬编码形状
dummy_inputs = {
"input_ids": torch.zeros((batch_size, sequence_length), dtype=torch.long),
# position_ids: [batch_size, sequence_length] - 与 input_ids 形状一致
"position_ids": torch.arange(sequence_length, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(0).expand(batch_size, -1).clone(),
}
if self.use_past_in_inputs:
# 使用 KV Cache 时,attention_mask 需要覆盖全部序列长度
total_length = past_sequence_length + sequence_length
dummy_inputs["attention_mask"] = torch.ones((batch_size, total_length), dtype=torch.long)
# 生成 past_key_values
past_key_values = []
for _ in range(self._num_layers):
key = torch.zeros((batch_size, self._num_kv_heads, past_sequence_length, self._head_dim))
value = torch.zeros((batch_size, self._num_kv_heads, past_sequence_length, self._head_dim))
past_key_values.append((key, value))
dummy_inputs["past_key_values"] = tuple(past_key_values)
# 调整 position_ids 从 past_sequence_length 开始
# 形状保持 [batch_size, sequence_length]
dummy_inputs["position_ids"] = torch.arange(
past_sequence_length, past_sequence_length + sequence_length, dtype=torch.long
).unsqueeze(0).expand(batch_size, -1).clone()
else:
# 不使用 KV Cache 时,attention_mask 等于序列长度
dummy_inputs["attention_mask"] = torch.ones((batch_size, sequence_length), dtype=torch.long)
return dummy_inputs
def flatten_past_key_values(past_key_values):
"""将 past_key_values 元组展平为字典格式,用于 ONNX 导出"""
flattened = {}
for i, (key, value) in enumerate(past_key_values):
flattened[f"past_key_values.{i}.key"] = key
flattened[f"past_key_values.{i}.value"] = value
return flattened
def prepare_model_for_export(model, max_length: int):
"""
导出前预热模型,确保 RoPE 缓存足够大
使用最大 position_ids 触发 RoPE 缓存扩展,内存友好且高效。
只需要 1 个 token 的输入,即可确保缓存覆盖最大位置。
Args:
model: 要预热的模型
max_length: 预热的最大序列长度(建议使用模型的 max_position_embeddings)
Returns:
预热后的模型
"""
device = next(model.parameters()).device
print(f" 使用最大 position_ids 预热 RoPE 缓存到位置 {max_length - 1}...")
# 只用 1 个 token + 最大 position_id 触发 RoPE 缓存扩展
# 这比完整序列预热内存友好得多
dummy_input = torch.zeros((1, 1), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
position_ids = torch.tensor([[max_length - 1]], dtype=torch.long, device=device)
attention_mask = torch.ones((1, max_length), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
with torch.no_grad():
try:
model(
dummy_input,
position_ids=position_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
use_cache=False
)
except Exception as e:
# 如果失败,可能是模型不需要预热(静态 RoPE)
print(f" ⚠ 预热时出现异常(可能是静态 RoPE,无需预热): {e}")
# 清理内存
del dummy_input, position_ids, attention_mask
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
print(f" ✓ RoPE 缓存预热完成")
return model
def export_hunyuan_to_onnx(
model_path: str,
output_path: str,
use_fp16: bool = True,
use_kv_cache: bool = True,
export_sequence_length: int = 16,
support_prefill: bool = True,
):
"""
导出 Hunyuan 模型到 ONNX
Args:
model_path: 模型路径
output_path: 输出路径
use_fp16: 是否使用 FP16 精度
use_kv_cache: 是否启用 KV Cache(推荐启用,可显著提升推理效率)
export_sequence_length: 导出时使用的序列长度(默认16)
- 使用较小的值(如 16)可以避免模型内部 Reshape 操作硬编码形状
- 使用 > 1 的值可以确保 SDPA 的 is_causal 被正确 trace
- 由于配置了 dynamic_axes,实际推理时可以使用任意长度
support_prefill: 是否支持 prefill 阶段(默认 True)
- True: 使用 past_sequence_length=0 导出,支持 prefill + decode 统一模型
- False: 使用 past_sequence_length>0 导出,仅支持 decode 阶段
推理时使用说明:
- Prefill 阶段(首次输入整个 prompt):
传入 shape 为 [batch, heads, 0, head_dim] 的空 KV Cache
- Decode 阶段(增量生成):
传入上一步输出的 KV Cache
注意:
- 由于配置了 dynamic_axes,实际推理时 sequence_length 可以是任意值
- export_sequence_length 只影响 trace 时的示例形状,不影响推理时的动态长度支持
- 统一模型方案避免了维护两个模型的复杂性
"""
print(f"加载模型: {model_path}")
print(f"配置: FP16={use_fp16}, KV_Cache={use_kv_cache}")
# 加载配置
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
# 确保 use_cache 与导出配置一致
config.use_cache = use_kv_cache
# 移除量化配置,使用 FP16 加载
dtype = torch.float16 if use_fp16 else torch.float32
try:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
config=config,
torch_dtype=dtype,
trust_remote_code=True,
device_map="cpu",
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"标准加载失败: {e}")
print("尝试跳过量化权重...")
# 尝试不加载量化配置
config_dict = config.to_dict()
if 'quantization_config' in config_dict:
del config_dict['quantization_config']
from transformers import CONFIG_MAPPING
new_config = type(config).from_dict(config_dict)
new_config.use_cache = use_kv_cache
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
config=new_config,
torch_dtype=dtype,
trust_remote_code=True,
device_map="cpu",
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True,
)
model.eval()
# 获取最大位置编码长度,用于 RoPE 预热
max_position_embeddings = getattr(config, 'max_position_embeddings', 8192)
print(f"模型最大位置编码长度: {max_position_embeddings}")
# 导出前预热 RoPE 缓存,确保缓存覆盖最大长度
print("\n预热模型 RoPE 缓存...")
model = prepare_model_for_export(model, max_position_embeddings)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
# 创建 ONNX 配置 - 启用 KV Cache
onnx_config = HunyuanV1DenseOnnxConfig(
config=config,
task="text-generation",
use_past=use_kv_cache, # 输出包含 KV Cache
use_past_in_inputs=use_kv_cache, # 输入包含 KV Cache
)
# 生成虚拟输入
# 根据 support_prefill 参数决定 past_sequence_length
# - support_prefill=True: 使用 past_sequence_length=0,让 cache 初始化分支被 trace
# - support_prefill=False: 使用 past_sequence_length>0,仅 trace decode 分支
if support_prefill:
# 关键:使用 past_sequence_length=0 导出
# 这样 DynamicCache 的 "if self.keys.numel() == 0" 分支会被 trace 为 True
# 模型可以同时支持 prefill(空 cache)和 decode(非空 cache)
past_sequence_length = 0
print("\n=== 统一模型导出模式(支持 Prefill + Decode)===")
print(" 使用 past_sequence_length=0 导出,确保 cache 初始化分支被正确 trace")
else:
# 仅支持 decode 阶段,使用合理的 past_sequence_length
past_sequence_length = min(1024, max_position_embeddings - 1)
print("\n=== Decode-Only 模式 ===")
print(f" 使用 past_sequence_length={past_sequence_length} 导出")
# 使用 sequence_length > 1 导出,确保 SDPA 的 is_causal 判断被正确 trace
# 这样导出的模型可以同时支持:
# - prefill 阶段:一次处理多个 token(如首次输入整个 prompt)
# - decode 阶段:每次处理 1 个 token(增量推理)
dummy_inputs = onnx_config.generate_dummy_inputs(
batch_size=1,
sequence_length=export_sequence_length, # 使用较大值确保 is_causal=True 被 trace
past_sequence_length=past_sequence_length,
)
print(f"导出配置: sequence_length={export_sequence_length}, past_sequence_length={past_sequence_length}")
print(f" - sequence_length > 1 确保 SDPA is_causal 被正确 trace")
if support_prefill:
print(f" - past_sequence_length=0 确保 cache 初始化分支被正确 trace")
print(f" - 推理时:Prefill 传入 shape [batch, heads, 0, head_dim] 的空 cache")
print(f" - 推理时:Decode 传入上一步的 KV Cache")
print(f" - 实际推理时序列长度可以是任意值(已配置 dynamic_axes)")
# 移动到正确设备
device = next(model.parameters()).device
print(f"导出 ONNX 到: {output_path}")
os.makedirs(output_path, exist_ok=True)
onnx_path = os.path.join(output_path, "model.onnx")
# 准备输入输出名称
input_names = list(onnx_config.inputs.keys())
output_names = list(onnx_config.outputs.keys())
# 准备动态轴
dynamic_axes = {}
for name, axes in onnx_config.inputs.items():
dynamic_axes[name] = axes
for name, axes in onnx_config.outputs.items():
dynamic_axes[name] = axes
# 准备导出输入 - 需要正确处理 past_key_values
import inspect
sig = inspect.signature(model.forward)
valid_params = set(sig.parameters.keys())
forward_inputs = {}
for k, v in dummy_inputs.items():
if k in valid_params:
if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor):
forward_inputs[k] = v.to(device)
else:
forward_inputs[k] = v
print(f"输入参数: {list(forward_inputs.keys())}")
print(f"动态轴配置: {list(dynamic_axes.keys())}")
# 构建 ONNX 导出的输入元组和展平的输入字典
# 对于 past_key_values,需要展平为单独的张量
export_inputs = {}
export_input_names = []
for k in input_names:
if k.startswith("past_key_values."):
# past_key_values 需要特殊处理
continue
if k in forward_inputs:
export_inputs[k] = forward_inputs[k]
export_input_names.append(k)
# 添加展平的 past_key_values
if use_kv_cache and "past_key_values" in forward_inputs:
past_kv = forward_inputs["past_key_values"]
for i, (key, value) in enumerate(past_kv):
export_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.key"] = key.to(device).to(dtype)
export_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.value"] = value.to(device).to(dtype)
export_input_names.append(f"past_key_values.{i}.key")
export_input_names.append(f"past_key_values.{i}.value")
# 创建一个包装器模型来处理展平的输入
class ONNXWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model, num_layers, use_kv_cache):
super().__init__()
self.model = model
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.use_kv_cache = use_kv_cache
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, position_ids, *past_kv_flat):
"""
前向推理,支持 prefill 和 decode 两种模式:
- Prefill 模式(首次输入):
past_kv_flat 包含 shape 为 [batch, heads, 0, head_dim] 的空 tensor
DynamicCache 检测到 numel()==0,会走初始化分支
- Decode 模式(增量生成):
past_kv_flat 包含 shape 为 [batch, heads, past_len, head_dim] 的非空 tensor
DynamicCache 检测到 numel()>0,会走追加分支
关键:始终传入 past_kv_flat(即使是空的),确保代码路径一致
注意:position_ids 需要保持与 input_ids 相同的形状 [batch_size, seq_len]
模型内部的 RoPE 实现可能会对其进行 reshape,但输入时必须是正确形状
"""
# 确保 position_ids 形状正确 [batch_size, seq_len]
# 如果输入的 position_ids 形状不对,进行调整
batch_size, seq_len = input_ids.shape
if position_ids.shape != (batch_size, seq_len):
# 重新生成正确形状的 position_ids
position_ids = position_ids.view(batch_size, seq_len)
# 重组 past_key_values,使用 DynamicCache 而不是元组
past_key_values = None
if self.use_kv_cache and len(past_kv_flat) > 0:
past_key_values = DynamicCache()
# 获取模型的 dtype
model_dtype = next(self.model.parameters()).dtype
for i in range(self.num_layers):
key = past_kv_flat[i * 2].to(model_dtype)
value = past_kv_flat[i * 2 + 1].to(model_dtype)
# DynamicCache 的 update 方法会自动处理:
# - 空 tensor (numel()==0): 初始化新的 cache
# - 非空 tensor: 追加到现有 cache
past_key_values.update(key, value, i)
outputs = self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
use_cache=self.use_kv_cache,
)
if self.use_kv_cache:
# 展平输出的 past_key_values
logits = outputs.logits
present_kv = outputs.past_key_values
result = [logits]
for i, (key, value) in enumerate(present_kv):
result.append(key)
result.append(value)
return tuple(result)
else:
return outputs.logits
wrapper = ONNXWrapper(model, onnx_config._num_layers, use_kv_cache)
wrapper.eval()
# 准备导出的输入元组
export_tuple = [
export_inputs["input_ids"],
export_inputs["attention_mask"],
export_inputs["position_ids"],
]
if use_kv_cache:
for i in range(onnx_config._num_layers):
export_tuple.append(export_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.key"])
export_tuple.append(export_inputs[f"past_key_values.{i}.value"])
export_tuple = tuple(export_tuple)
# 导出前进行内存清理
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
print("开始 ONNX 导出...")
print(f" - 导出序列长度: {export_sequence_length}")
print(f" - 动态轴配置将允许推理时使用任意序列长度")
with torch.no_grad():
# 使用更节省内存的导出选项
# 注意:export_params=True 确保权重被导出
# do_constant_folding=False 可以减少某些形状被硬编码的风险
torch.onnx.export(
wrapper,
export_tuple,
onnx_path,
input_names=input_names,
output_names=output_names,
dynamic_axes=dynamic_axes,
opset_version=onnx_config.DEFAULT_ONNX_OPSET,
do_constant_folding=False, # 禁用常量折叠,避免形状被硬编码
export_params=True,
training=torch.onnx.TrainingMode.EVAL,
# 添加更详细的日志以便调试
verbose=False,
)
# 导出后立即清理内存
del wrapper, model, export_tuple, dummy_inputs
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# 先整合外部数据文件为标准格式,再进行验证
print("\n整合外部数据文件为标准 ONNX 格式...")
try:
import onnx
import glob
# 加载模型(包含外部数据)用于合并
onnx_model = onnx.load(onnx_path, load_external_data=True)
# 删除原始文件
os.remove(onnx_path)
# 清理旧的分散权重文件
for pattern in ["model.*.weight", "onnx__*", "model.model.*"]:
for f in glob.glob(os.path.join(output_path, pattern)):
try:
os.remove(f)
except:
pass
# 重新保存为标准格式(所有数据合并到一个外部文件)
onnx.save_model(
onnx_model,
onnx_path,
save_as_external_data=True,
all_tensors_to_one_file=True,
location="model.onnx.data",
size_threshold=0,
)
print("✓ 已整合为标准格式: model.onnx + model.onnx.data")
# 显示最终文件大小
model_size = os.path.getsize(onnx_path)
data_file = os.path.join(output_path, "model.onnx.data")
data_size = os.path.getsize(data_file) if os.path.exists(data_file) else 0
total_size_gb = (model_size + data_size) / (1024**3)
print(f" 模型文件: {model_size / 1024:.1f} KB")
print(f" 数据文件: {data_size / (1024**3):.2f} GB")
print(f" 总大小: {total_size_gb:.2f} GB")
del onnx_model # 释放内存
except Exception as e:
print(f"整合外部数据时出错: {e}")
print("保留原始格式")
# 验证 ONNX 模型(在整合外部数据之后进行)
print("\n验证 ONNX 模型...")
try:
import onnx
# 1. 结构验证(仅图结构,不加载权重数据)
# 注意:对于大于2GB的模型,check_model会失败,因此只验证图结构
print(" [1/2] 验证模型结构...")
onnx_model_meta = onnx.load(onnx_path, load_external_data=False)
# 手动验证图结构(不使用check_model,避免大模型验证失败)
graph = onnx_model_meta.graph
# 检查基本结构
if not graph.name:
print(" ⚠ 图名称为空")
# 验证输入节点
if len(graph.input) == 0:
raise ValueError("模型没有输入节点")
# 验证输出节点
if len(graph.output) == 0:
raise ValueError("模型没有输出节点")
# 验证节点数量
if len(graph.node) == 0:
raise ValueError("模型没有计算节点")
print(f" ✓ 模型结构验证通过")
print(f" - 输入数量: {len(graph.input)}")
print(f" - 输出数量: {len(graph.output)}")
print(f" - 计算节点: {len(graph.node)}")
print(f" - 初始化器: {len(graph.initializer)}")
# 打印模型输入输出信息
print("\n=== 模型输入 ===")
for inp in graph.input:
shape = [d.dim_param or d.dim_value for d in inp.type.tensor_type.shape.dim]
print(f" {inp.name}: {shape}")
print("\n=== 模型输出 ===")
for out in graph.output:
shape = [d.dim_param or d.dim_value for d in out.type.tensor_type.shape.dim]
print(f" {out.name}: {shape}")
del onnx_model_meta
# 2. ONNX Runtime 加载测试(验证权重完整性的最可靠方式)
print("\n [2/2] 使用 ONNX Runtime 加载验证...")
try:
import onnxruntime as ort
# 尝试创建推理会话,这会验证模型和权重的完整性
sess_options = ort.SessionOptions()
sess_options.log_severity_level = 3 # 减少日志输出
session = ort.InferenceSession(
onnx_path,
sess_options,
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
# 获取输入输出信息
ort_inputs = session.get_inputs()
ort_outputs = session.get_outputs()
print(f" ✓ ONNX Runtime 加载成功!")
print(f" - 输入: {[i.name for i in ort_inputs]}")
print(f" - 输出: {[o.name for o in ort_outputs]}")
del session # 释放内存
except ImportError:
print(" ⚠ 未安装 onnxruntime,跳过加载测试")
print(" 提示:pip install onnxruntime 后可进行完整验证")
except Exception as e:
print(f" ✗ ONNX Runtime 加载失败: {e}")
print(" 模型可能存在问题,但仍将继续处理")
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ ONNX 验证失败: {e}")
print("警告:模型可能存在问题,但仍将尝试继续处理")
print("保存 tokenizer...")
tokenizer.save_pretrained(output_path)
# 保存配置
config.save_pretrained(output_path)
# 保存导出信息
export_info = {
"use_kv_cache": use_kv_cache,
"use_fp16": use_fp16,
"support_prefill": support_prefill,
"export_sequence_length": export_sequence_length,
"opset_version": onnx_config.DEFAULT_ONNX_OPSET,
"num_layers": onnx_config._num_layers,
"num_kv_heads": onnx_config._num_kv_heads,
"head_dim": onnx_config._head_dim,
"input_names": input_names,
"output_names": output_names,
"dynamic_axes": {k: {str(dk): dv for dk, dv in v.items()} for k, v in dynamic_axes.items()},
"usage": {
"prefill": "传入 shape 为 [batch, num_kv_heads, 0, head_dim] 的空 KV Cache tensor",
"decode": "传入上一步输出的 KV Cache tensor",
"note": "sequence_length 和 past_sequence_length 都是动态的,可以是任意值"
}
}
import json
with open(os.path.join(output_path, "export_info.json"), "w") as f:
json.dump(export_info, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
print(f"\n✓ 导出完成! 文件保存在: {output_path}")
return onnx_path
if __name__ == "__main__":
model_path = "/data/workspace/code/on/onnx/hunyuan_fp16_clean"
output_path = "onnxoutput/"
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"模型路径不存在: {model_path}")
export_hunyuan_to_onnx(
model_path,
output_path,
use_fp16=True,
use_kv_cache=True, # 启用 KV Cache 以支持高效增量推理
support_prefill=True, # 支持 prefill + decode 统一模型
)2.3.1 大模型导出的权重文件合并问题
现象:第一次导出时生成大量独立权重文件如model.embed_tokens.weight、model.layers.X.input_layernorm.weight、onnx__MatMul_XXXXX等。
原因:PyTorch的torch.onnx.export在导出大模型时,默认会将大于2GB的权重拆分成外部数据文件,这是ONNX协议处理超大模型的特性。
解决方案:再次加载ONNX模型结构与所有权重文件,合并权重到model.onnx.data文件,核心代码如下:
python
onnx.save_model(
onnx_model,
onnx_path,
save_as_external_data=True,
all_tensors_to_one_file=True,
location="model.onnx.data",
size_threshold=0,
)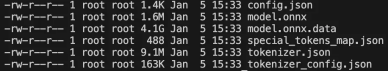
合并后文件说明:model.onnx为模型结构文件,model.onnx.data为模型权重文件,合并后更方便管理。注意:验证ONNX权重文件时,需确保权重数据小于2GB,否则即使未合并也无法验证。
三、转换核心问题与解决方案
3.1 导出ONNX日志告警问题
3.1.1 现象:导出时出现大量TracerWarning
典型告警日志:
python
/data/workspace/code/on/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/transformers/cache_utils.py:94: TracerWarning: torch.tensor results are registered as constants in the trace. You can safely ignore this warning if you use this function to create tensors out of constant variables that would be the same every time you call this function. In any other case, this might cause the trace to be incorrect.
self.keys = torch.tensor([], dtype=self.dtype, device=self.device)
/data/workspace/code/on/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/transformers/cache_utils.py:95: TracerWarning: torch.tensor results are registered as constants in the trace. You can safely ignore this warning if you use this function to create tensors out of constant variables that would be the same every time you call this function. In any other case, this might cause the trace to be incorrect.
self.values = torch.tensor([], dtype=self.dtype, device=self.device)
/data/workspace/code/on/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/transformers/cache_utils.py:132: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if not self.is_initialized or self.keys.numel() == 0:
/data/workspace/code/on/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/transformers/modeling_rope_utils.py:69: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if seq_len > self.max_seq_len_cached: # growth
/data/workspace/code/on/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/transformers/integrations/sdpa_attention.py:86: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python number might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
is_causal = is_causal.item()3.1.2 告警类型与影响分析
| 告警类型 | 位置 | 含义 | 影响程度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空张量被当作常量 | cache_utils.py:94-95 | torch.tensor结果被注册为追踪常量 | 中等,通常可忽略,后续实际数据会覆盖 |
| 张量转布尔值变成固定常量 | cache_utils.py、masking_utils.py、modeling_rope_utils.py等多处 | 将张量转换为Python布尔值,后续被当作常量 | 较高(若导出时cache为空,条件会永远为True) |
| 张量转数值变成固定常量 | sdpa_attention.py:86 | 将张量转换为Python数值,后续被当作常量 | 中等(可能影响变长输入的正确处理) |
核心说明:dynamic_axes解决的是ONNX图的输入输出形状问题,而TracerWarning指出的是模型内部计算逻辑被固化的问题,需针对性优化。
3.1.3 解决方案
确保 past_sequence_length 覆盖 RoPE 预计算,参考
past_sequence_length覆盖RoPE预计算,参考代码:
python
dummy_inputs = onnx_config.generate_dummy_inputs(
batch_size=1,
sequence_length=16,
past_sequence_length=config.max_position_embeddings - 1, # 接近最大值
)导出前预热RoPE缓存,使用prepare_model_for_export函数,核心逻辑:用1个token+最大position_id触发RoPE缓存扩展,确保缓存覆盖最大位置,比完整序列预热更内存友好。
python
def prepare_model_for_export(model, max_length: int):
"""
导出前预热模型,确保 RoPE 缓存足够大
使用最大 position_ids 触发 RoPE 缓存扩展,内存友好且高效。
只需要 1 个 token 的输入,即可确保缓存覆盖最大位置。
Args:
model: 要预热的模型
max_length: 预热的最大序列长度(建议使用模型的 max_position_embeddings)
Returns:
预热后的模型
"""
device = next(model.parameters()).device
print(f" 使用最大 position_ids 预热 RoPE 缓存到位置 {max_length - 1}...")
# 只用 1 个 token + 最大 position_id 触发 RoPE 缓存扩展
# 这比完整序列预热内存友好得多
dummy_input = torch.zeros((1, 1), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
position_ids = torch.tensor([[max_length - 1]], dtype=torch.long, device=device)
attention_mask = torch.ones((1, max_length), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
with torch.no_grad():
try:
model(
dummy_input,
position_ids=position_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
use_cache=False
)
except Exception as e:
# 如果失败,可能是模型不需要预热(静态 RoPE)
print(f" ⚠ 预热时出现异常(可能是静态 RoPE,无需预热): {e}")
# 清理内存
del dummy_input, position_ids, attention_mask
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
print(f" ✓ RoPE 缓存预热完成")
return model
# 使用
model = prepare_model_for_export(model, 8192)3.2 模型功能限制问题
3.2.1 问题1:无法处理prefill阶段仅能decode
现象:模型只能进行decode阶段推理,无法接收输入完成prefill阶段处理。
原因:is_causal的判断逻辑为query.shape[2] > 1 and attention_mask is None and getattr(module, "is_causal", True),导出时若sequence_length≤1,会导致is_causal判断异常,固化处理分支。
解决方案:导出时使用大于1的sequence_length,确保is_causal=True,核心代码:
python
from optimum.exporters.onnx import main_export
from optimum.exporters.onnx.config import TextDecoderOnnxConfig
class CustomOnnxConfig(TextDecoderOnnxConfig):
@property
def inputs(self):
inputs = super().inputs
# 确保 sequence_length 是动态的
return inputs
def generate_dummy_inputs(self, framework="pt", **kwargs):
# 使用 seq_len > 1 生成 dummy inputs
kwargs['sequence_length'] = 16 #大于1的sequence_length
return super().generate_dummy_inputs(framework, **kwargs)3.2.2 问题2:KV Cache状态判断固化
现象:首次推理无历史KV Cache时,模型仍按"有cache"分支执行,导致推理错误。
原因:KV Cache状态判断依赖张量值做条件判断(如if not self.is_initialized or self.keys.numel() == 0),trace时传入非空past_kv_flat,导致分支被固化为"有cache"。
解决方案原理:
python
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 统一模型工作流程 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ Prefill 阶段(首次输入 prompt) │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ input_ids: [batch, prompt_len] │ │
│ │ past_kv: [batch, heads, 0, head_dim] ← 空 cache │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ DynamicCache 检测 numel()==0 → 初始化分支 │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ 输出: logits + new_kv [batch, heads, prompt_len, dim] │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ Decode 阶段(增量生成) │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ input_ids: [batch, 1] │ │
│ │ past_kv: [batch, heads, past_len, head_dim] ← 累积 │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ DynamicCache 检测 numel()>0 → 追加分支 │ │
│ │ ↓ │ │
│ │ 输出: logits + updated_kv [batch, heads, past_len+1] │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ 循环 decode 直到结束 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘3.2.3 问题3:mask长度动态判断固化
现象:导出时mask长度判断被固化,推理时输入不同长度mask可能出现padding错误。
分析:若代码中确保attention_mask的长度始终等于past_sequence_length+sequence_length(即attention_mask.shape[-1] = total_sequence_length,kv_length = past_sequence_length + sequence_length),则模型内部无需额外padding,告警的条件会被固化为padding_length≤0,与实际推理行为一致,无需额外处理。
注意事项:推理时需确保传入的attention_mask长度不小于KV Cache长度,否则会出现错误属于输入错误,非模型转换问题。
3.3 两种Mask的核心区别(避免混淆)
| Mask类型 | 作用 | 谁负责 |
|---|---|---|
| attention_mask | 区分真实token和padding | 用户传入 |
| causal_mask | 防止看到未来token | 模型内部自动生成 |
3.4 ONNX模型推理输入缺失问题
现象:使用ONNX Runtime推理时,仅传入input_ids报错,提示缺少其他输入。
原因:导出的ONNX模型包含KV Cache优化,需额外输入attention_mask、position_ids、past_key_values等参数。
解决方案:推理时传入完整输入,核心代码示例:
python
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
# 加载tokenizer和ONNX模型
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("your_model_path")
session = ort.InferenceSession("model.onnx")
# 准备输入
text = "你的提示词"
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="np")
# 获取模型配置
batch_size = 1
seq_length = inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]
num_heads = 32 # 根据你的模型调整
head_dim = 128 # 根据你的模型调整
num_layers = 32 # 你的模型有32层
# 准备完整的输入
ort_inputs = {
'input_ids': inputs['input_ids'].astype(np.int64),
'attention_mask': inputs['attention_mask'].astype(np.int64),
'position_ids': np.arange(seq_length, dtype=np.int64).reshape(1, -1)
}
# 初始化past_key_values(首次推理时为空)
for i in range(num_layers):
ort_inputs[f'past_key_values.{i}.key'] = np.zeros(
(batch_size, num_heads, 0, head_dim), dtype=np.float32
)
ort_inputs[f'past_key_values.{i}.value'] = np.zeros(
(batch_size, num_heads, 0, head_dim), dtype=np.float32
)
# 运行推理
outputs = session.run(None, ort_inputs)简化方案:使用Optimum库,无需手动处理输入参数,可自动适配KV Cache等优化逻辑。
四、关键配置依据与影响
4.1 DEFAULT_ONNX_OPSET
4.1.1 设置依据
ONNX Opset(操作集版本)定义支持的算子集合和版本,不同版本关键特性:
•Opset 13:引入Softmax的axis参数改进;
•Opset 14:引入Trilu(三角矩阵)、改进的Reshape、BatchNormalization训练支持;
•Opset 15:改进Pow算子;
•Opset 16:引入GridSample、ScatterND改进;
•Opset 17:引入LayerNormalization(原生支持)。
选择Opset 14的核心考量(兼容性与功能的平衡点):
•支持Transformer模型所需的大多数算子;
•被主流推理引擎广泛支持(TensorRT、ONNX Runtime、OpenVINO等);
•与代码中MIN_TORCH_VERSION = "2.5.0"配合良好。
4.1.2 配置影响
•若设置过低(如Opset 11):某些算子可能不支持,导出时会报错或使用次优实现;
•若设置过高(如Opset 18):可能某些推理引擎不支持,运行时报错。
4.2 NORMALIZED_CONFIG_CLASS = HunyuanNormalizedConfig
4.2.1 设置依据
这是Optimum库的配置标准化机制,用于统一不同模型的配置字段名称。不同模型的配置文件命名存在差异:
| 模型 | 注意力头数量字段 | 隐藏层数量字段 |
|---|---|---|
| GPT-2 | n_head | n_layer |
| LLaMA | num_attention_heads | num_hidden_layers |
| BERT | num_attention_heads | num_hidden_layers |
| Hunyuan | num_attention_heads | num_hidden_layers |
python
class HunyuanNormalizedConfig(NormalizedTextConfig):
NUM_ATTENTION_HEADS = "num_attention_heads" # 映射:标准名 → 实际配置字段
NUM_KEY_VALUE_HEADS = "num_key_value_heads"
HIDDEN_SIZE = "hidden_size"
NUM_LAYERS = "num_hidden_layers"这个类告诉 Optimum:
• 需要 NUM_ATTEN TION_HEADS 时,去读取 config 的 num_attention_heads 字段
• 需要 NUM _LAYERS 时,去读取 config 的 num _hidden_layers 字段
如果配置错误:
• 导出时可能读取不到正确的模型参数
• 生成的 KV Cache 维度可能错误
• 动态轴设置可能失败
用 Optimum 把 HF 模型导成 ONNX,确实要特别注意不要误导出成固定 batch、固定 sequence,或者丢失 KV cache,这些都会直接影响推理性能和灵活性。
动态 batch / sequence
• Optimum 的 ONNX 配置里有 dynamic axes 概念,如果某个维度不标成动态,就会被当成固定维度。
• 一般做推理部署时,希望至少下面两个维度是动态的:
• batch size 维度(通常是第 0 维)
• sequence length 维度(通常是第 1 维,对 input_ids 、 attention_mask 等)
• 如果在导出时指定了固定 batch_size 、固定 sequence_length ,或者 ONNX config 里没有把这些轴标成动态,那么导出的模型只能在这个 batch / seq 长度下跑,后续想改 batch 或动态长上下文就会很麻烦。
KV cache / past key values
• Optimum 针对带 KV cache 的模型有专门的 ONNX config,可以控制是否导出带 past 的图:
• use_past :是否在图里使用 KV cache。
• use_past_in_inputs :past 是否作为 ONNX 输入传入。
• 对于 CausalLM( text- generation )这类自回归模型,强烈建议导出 *-with-past 版本(如 task 用 text- generation-with-past ),这样后续生成时才能在 decoder 阶段复用 KV cache,大幅加速长文本生成。
•如果导出时关闭了 past(例如 task 用普通 text-generation 或显式关掉 use_past),那 ONNX 推理每步都要重新做全序列 attention,会非常慢,等价于"无 KV cache"。
五、ONNX的总结
将原始模型如 PyTorch/TensorFlow转换为 ONNX 格式,通常伴随着灵活性和完整性的某种牺牲或妥协。这并不是因为 ONNX 格式本身无法表达这些逻辑,更多是因为动态图(Eager Mode)转静态图(Graph Mode)的固有矛盾,以及推理引擎为了极致性能优化所做的固化。
原始模型特别是 PyTorch通常是动态的,代码逻辑可以是 Python 的任意控制流。而 ONNX 本质上是一个中间表示IR,它更接近于编译后的静态计算图。
- RoPE 长度固化问题(Sequence Length 限制):
原因: 在 PyTorch 实现中,RoPE(Rotary Positional Embedding)通常会预计算一个很大的 cos/sin 缓存表例如长度 4096。在使用 torch.onnx.export 进行Tracing追踪时,如果输入是固定长度,导出器可能会将切片操作后的 cos/sin 当作常量固化在模型里。
后果: 导出的 ONNX 模型只能处理特定长度的序列,一旦推理时输入变长,模型就会报错。
解决: 需要修改模型代码,显式地将 seq_len 定义为动态轴Dynamic Axes,并在代码中根据输入动态计算或切片 cos/sin,而不是依赖全局缓存。 - 动态 Shape 的代价:
虽然 ONNX 支持动态 Shape例如将维度设为 -1 或 batch_size,但很多推理后端如 TensorRT在优化时,如果知道具体的 Shape,可以进行更激进的显存优化和算子融合。完全的动态性往往意味着推理速度的下降。 - 为什么分支流程会被遗漏
这是转换过程中最常见的问题,主要源于导出方式:
Tracing(追踪法):
绝大多数使用 torch.onnx.export 时默认使用 Tracing。
原理: 给模型喂入一个 Dummy Input假数据,记录数据流经的路径。
牺牲: 如果模型中有 if condition: 语句,Tracing 只会记录当时走的那一条路。未被执行的 else 分支在 ONNX 图中根本不存在。
例子: 如果模型有 if use_cache: 逻辑,导出时 use_cache=True,那么导出的 ONNX 就永远只有 KV Cache 的逻辑,无法回退到无 Cache 模式。
Scripting(脚本法):
使用 torch.jit.script 可以保留控制流生成 ONNX 的 If 和 Loop 算子。
代价: Scripting 对 Python 代码的写法要求极高强类型限制,且很多推理引擎对 ONNX 中的控制流算子支持并不好优化难度大,导致推理变慢。
- 计算方式为何会被修改或不兼容?
ONNX 定义了一套标准算子集Opset。原始框架中的操作必须映射到这些标准算子。
算子不支持:
有些复杂的 PyTorch 操作如 torch.einsum 或某些特殊的 Attention 实现在低版本的 Opset 中没有直接对应。
牺牲: 导出器会将这个高级操作拆解成几十个基础算子如 Add, Mul, Transpose, Gather。这不仅让计算图变得极其丑陋复杂,还可能打断推理引擎的算子融合Fusion,导致性能下降。
精度与计算逻辑差异:
例如 LayerNorm 或 GELU,在不同框架和 ONNX Opset 版本中,具体的数学近似公式可能略有不同。
类型转换: 某些操作在 ONNX 中可能强制要求 Float32,如果原模型是 BF16/FP16,转换过程中可能会插入大量的 Cast 操作,影响效率甚至精度。
这是一种权衡,将模型转为 ONNX,本质上是从开发态向部署态。
开发态: 强调灵活性、易调试、动态逻辑。
部署态: 强调确定性、内存管理、计算吞吐。
为了获得标准化、推理速度,通常必须牺牲灵活性:
消除控制流: 尽量把 if/else 逻辑在模型外部处理,或者拆分成两个子模型。
固定维度: 在某些场景下如嵌入式设备,固定输入分辨率能带来巨大的性能提升。