文章目录
C语言笔记12:C语言内存函数
一、memcpy使用和模拟实现
函数声明:
cvoid *memcpy(void* destination ,const void* source ,size_t num);
与
strcpy不同的是,memcpy遇到\0不会停下来目标空间和源空间有重叠的情况是未定义的
使用:
c#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { int arr1[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; int arr2[10] = {0}; memcpy(arr2,arr1,20); for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) { printf("%d\n",arr2[i]); } return 0; }
输出:
c1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0
模拟实现:
cvoid* memcpy(void* destination ,const void* source ,size_t num) { void* ret = destination; assert(destination != NULL); assert(source != NULL); while(num--) { *(char*)destination = *(char*)source; destination = (char*)destination + 1;//这个写法?(char*)destination 是一个右值不能直接 += 1!!! source = (char*)source + 1; } return ret; }
二、memmove的使用和模拟实现
函数声明:
cvoid* memmove(void* destination ,const void* source ,size_t num);
memmove和memcpy的区别在于:
- memmove可以处理目的空间和源空间有重叠的情况。
使用:
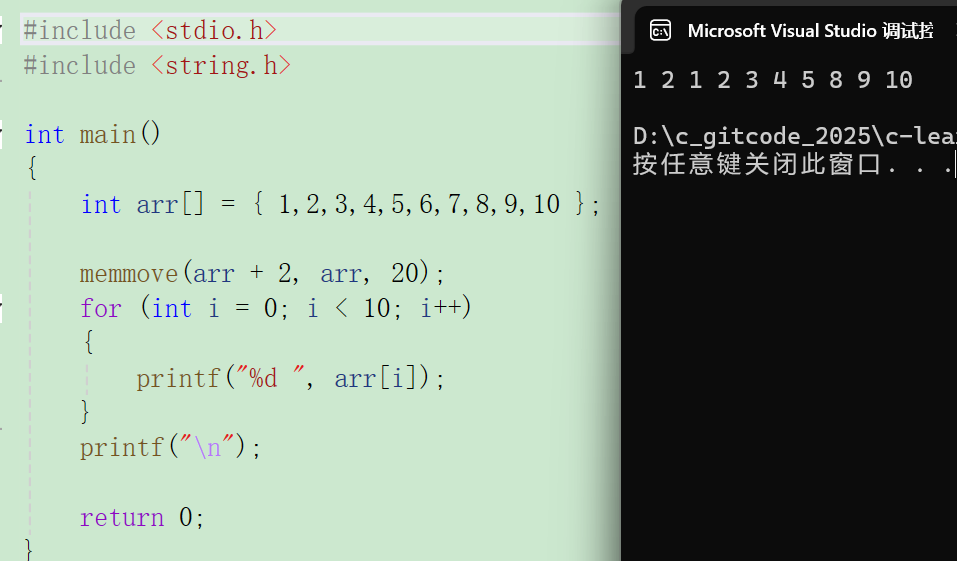
c#include <stdio.h> int main() { int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; memmove(arr+2,arr,20); for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) { printf("%d ",arr[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
结果:
模拟实现:
cvoid* memmove(void* dest ,const void* source ,size_t num) { void* ret = dest; //判断需不需要特殊处理 if(dest < source || dest >= source + num) { while(num--) { *(char*)dest = *(char*)source; dest = (char*)dest + 1; source = (char*)source + 1; } } else { dest = (char*)dest + num - 1; source = (char*)source + num - 1; while(num--) { *(char*)dest = *(char*)source; dest = (char*)dest - 1; source = (char*)source - 1; } } return ret; }
三、memset函数的使用
函数声明:
cvoid* memset(void* ptr ,int value ,size_t num);
函数使用:
c#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char str[] = "hello world"; memset(str,'x',5); printf("%s\n",str); return 0; }
四、memcmp函数的使用
函数声明:
cint memcmp(const void* ptr1, const void* ptr2, size_t num);
memcmp函数和strncmp的区别是,strncmp会遇到\0停止而memcmp不会
使用:
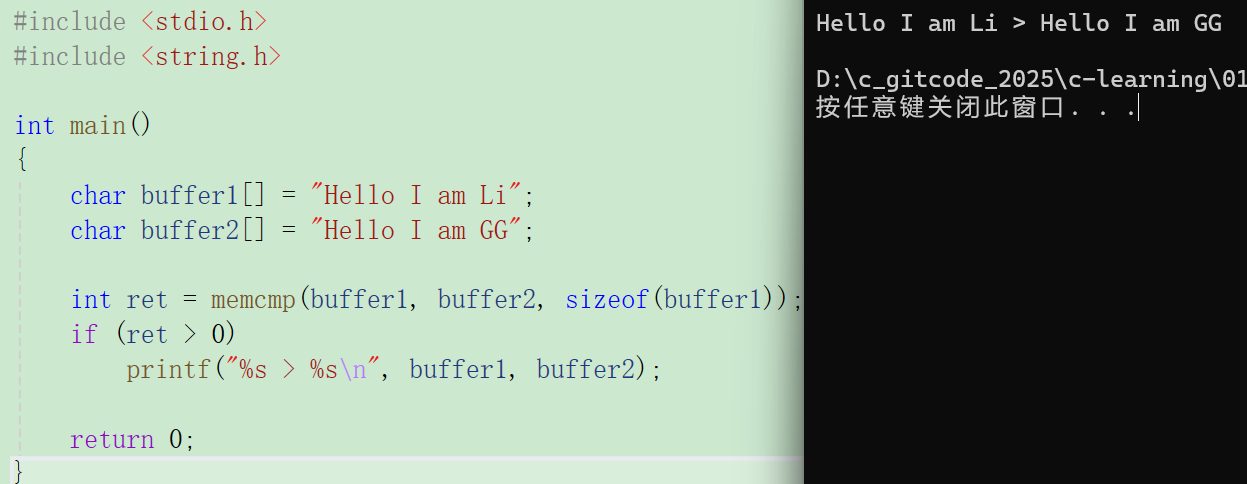
c#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char buffer1[] = "Hello I am Li"; char buffer2[] = "Hello I am GG"; int ret = memcmp(buffer1,buffer2,sizeof(buffer1));//这里使用sizeof,如果是strncmp就用strlen if(ret > 0) printf("%s > %s\n",buffer1,buffer2); return 0; }
结果:
内存函数和字符串函数的区别大致都在于\0,以及内存函数都带有size_t num这个参数,因为它不是对字符串操作,没有默认的终止位置。